Abstract
Pancreatic (PC), colorectal (CRC), hepatocellular (HCC), and gallbladder (GC) cancers together account for nearly 20% of all cancer cases. However, specific biomarkers and therapeutic targets for these cancers are lacking. Diagnosing these cancers early and providing timely, appropriate treatment to improve patient outcomes is crucial. In this context, previous studies, including ours, have highlighted the potential of non-coding RNAs, particularly long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), in diagnosing and prognosis of various cancers. This review focuses on the mechanistic role of the recently identified lncRNA LINC00261 in PC, CRC, HCC, and GC. Our comprehensive literature analysis revealed that LINC00261 functions as a tumor suppressor, and its reduced expression is associated with larger tumor size, advanced tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) stages, lymphatic metastasis, and poorer overall survival rates. Additionally, we discovered that LINC00261 acts as a molecular sponge for miRNAs, such as miR-550a-3p, miR-23a-3p, miR-148a, miR-324-3p, and miR-105-5p, regulating critical cancer-related signaling pathways, including PI3K/Akt/mTOR, Protein kinase B, and Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). Further bioinformatic analysis revealed that LINC00261 regulates key cellular processes, such as protein-DNA complex formation, ribonuclease complex activity, histone deacetylase complexes, and nuclear matrix interactions. Overall, we believe that LINC00261 holds significant promise as a future biomarker and, when combined with existing treatment strategies, may enhance cancer patient care and survival.
1. Introduction
Cancer is one of the most significant global health challenges, impacting individuals and families both emotionally and financially. The gravity of this global issue is highlighted by the latest GLOBOCAN (Global Cancer Observatory) 2022 data, which indicate that cancer incidence reached 196.9 cases per 100,000 individuals [1]. Notably, the global age-standardized rate (ASR) for hepatocellular, pancreatic, colorectal, and gallbladder cancer mortality rates are 7.8% (liver), and 4.8%, 9.3%, and 0.9% for both sexes, respectively [2]. This alarming statistic underscores the urgent need for intensified research and improved treatment options. The high mortality rates associated with hepatocellular, gallbladder, and pancreatic cancers can be attributed mainly to their multifactorial nature, often characterized by uncontrolled cell growth, invasion, and metastasis to distant tissues. Factors such as a poor diet, smoking, pollution, and an aging population significantly contribute to the rising global incidence and mortality rates of cancer [3]. Limited access to early detection and treatment, particularly in low and middle-income countries, also results in higher mortality. Furthermore, projections indicate that over the next 20 years, the death rate may rise substantially due to the absence of early symptoms, late-stage diagnoses, and resistance to current regimen treatments [4].
Recent evidence indicates that long non-coding RNAs having a size of more than 200 nucleotides modulate several biological activities such as epigenetics, immune response regulation, transcription, splicing, translation, cell integrity, migration, cell cycle, and cell proliferation [5,6,7]. Additionally, it has been shown that lncRNAs have a role in the regulation of the critical hallmarks of cancer, including persistent proliferative signaling, evasion of growth suppressors, anti-apoptotic behavior, immune escape, oncogenic inflammation, disruptions in cellular metabolism, and genomic instability [5,8,9]. Recently, we and other researchers have shown the critical role that non-coding RNAs like miRNAs and lncRNAs play in the pathophysiology of many types of cancer [10,11,12,13,14]. Hence, due to their excellent association with the tumorigenesis process, they are suggested as diagnostic/prognostic biomarkers and targets for therapeutic intervention in cancer [15]. Moreover, lncRNA expression was also found to be affected by various clinicopathological features, including Ki-67 levels (Antigen Kiel 67), age, gender, tumor-node metastatic stage, histological grade, and lymph node metastasis age [16].
The long intergenic non-protein coding RNA LINC00261 has been newly identified as having diverse functions in cancers. LINC00261 is located at chromosome 20p11.21 (GRCh38/hg38), having Size ≈ 44,299 bases [17,18]. There are some other aliases for the LINC00261, such as TCONS_00027846 (Transcript consensus number), DEANR1 (Definitive endoderm-associated lncRNA1), Onco-lncRNA-17, ALIEN (A Long Intergenic Non-coding RNA enhancing Neuroblastoma), and FALCOR (Folate associated long non-coding RNA) [19]. It functions as a tumor suppressor in thyroid cancer by negatively regulating EBF1 (Early B cell factor 1), which has a partial role in the inhibition of tumor growth and metastasis, and its downregulation is associated with advanced disease and poor prognosis [20]. Moreover, it suppresses viability, migration, and invasion of breast cancer stem cells (BCSC) by sponging the miR-550a-3p to upregulate (SDPR) serum deprivation response protein [21]. LINC00261 is suppressed by hypermethylation, which causes platinum resistance and a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) through the miR-545-3p/MT1M (metallothionein1M) axis [22]. Moreover, it acts as a tumor suppressor that modulates certain cellular functions such as proliferative activity, programmed cell death, motility, chemoresistance, and tumorigenesis across multiple human oncological conditions [23,24,25].
Although the role of LINC00261 is explored in various cancers, comprehensive knowledge of its clinical potential has yet to be studied in hepatocellular, pancreatic, colorectal, and gallbladder cancers. Therefore, this review focused on how LINC00261 mechanistically regulates the oncogenesis process in the cancers mentioned above and how it can be utilized as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers of PC, CRC, HCC, and GBC. Furthermore, we give insight into how LINC00261 can sponge multiple miRNAs to its target and regulate various cancer-associated signaling pathways.
2. Literature Search Methodology
The clinical and functional importance of LINC00261, a long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) linked to cancer biology, is examined in a recent study. The broad term “cancer” was combined with the key term “LINC00261” in a literature search on PubMed, Web of Science, Science Direct, DOAJ (Directory of Open Access Journals), and Google Scholar to find relevant articles. The review emphasizes important elements, such as lncRNA LINC00261 expression dysregulation in various cancers, tissue samples, cell lines, and in vivo mice models, experimental procedures employed, target genes/proteins, and clinicopathological associations. Through in-depth analysis, we sorted 18 papers dated January 2025 that directly showed pertinence with LINC00261 expression in various cancers, including pancreatic cancer (2020–2024), colorectal cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, and gallbladder cancer. Two authors (S.D. and S.B.), under the direction of senior author A.J., improved the review’s depth even further. Through discussions and comprehensive analysis, the team confirmed the possible function of LINC00261 among the functional characteristics of these cancers, including invasion, cell viability, and apoptotic activity.
3. Role of LINC00261 in Various Cancers
The LINC00261 is found to be aberrantly expressed in various cancers such pancreatic, gastric, colorectal, lung, hepatocellular, breast, laryngeal, endometrial, esophageal, prostate, choriocarcinoma, thyroid, and bile duct cancers [23]. Given the fact that there are specific biological characteristics of LINC00261, we have discussed the effects of the LINC00261 and mechanisms governed by it in the tumorigenesis of pancreatic, colorectal, hepatocellular, and gallbladder cancers.
3.1. LINC00261 and Pancreatic Cancer
Multiple studies have indicated the critical involvement of diverse lncRNAs in the progression and treatment of pancreatic cancer (PC). For example, HOTAIR (HOX transcript antisense intergenic RNA), MALAT1 (Metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1), HOTTIP (HOXA transcript at the distal tip), and PVT1 (Plasmacytoma Variant Translocation 1) have recently been found to be essential regulators linked to the progression of PC and have diagnostic and prognostic implications [26,27,28].
In one of the recent studies, LINC00261 was investigated as an important regulator of PC, where authors have demonstrated that it is abnormally expressed in PC patients and cell lines compared to corresponding control samples. Most of these studies reported lower expression of LINC00261 in PC, which is associated with its tumorigenesis [29,30].
LINC00261 expression is significantly downregulated in pancreatic cancer (PC) cell lines, including AsPC-1 (Ascites Pancreatic Cancer-1), BxPC-3 (Biopsy xenograft of Pancreatic Carcinoma line-3), PANC-1 (Pancreatic Cancer-1), and CFAC-1 (cystic fibrosis pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell line), compared to normal pancreatic ductal epithelial cells (HPDE6-C7). The observed reduction, with a fold change of (~1.20), suggests a potential tumor-suppressive role in PC [31]. Moreover, through the TCGA (The Cancer Genome Atlas) database, the authors found low expression of LINC00261 in PC patients compared to healthy individuals, which also correlates with poor patient survival [31]. This dysregulation may contribute to PC pathogenesis, indicating the need for further investigation into its functional and mechanistic implications.
To know how LINC00261 affects the cell’s viability, invasion, and apoptotic activity in PC cells, the authors transfected the LINC00261 overexpression vector into two PC cell lines named CFPAC-1 and BxPC-3 (Biopsy xenograft of Pancreatic Carcinoma line-3). Through the Western blot analysis, they found suppression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), as evidenced by decreased expression of mesenchymal markers (N-cadherin, vimentin, MMP2) and a concurrent increase in epithelial marker E-cadherin, reinforcing cell-cell adhesion and limiting metastatic potential. These data suggest that an increase in the expression of LINC00261 leads to less aggressive tumor phenotypes, better clinical outcomes, and improved prognosis [31]. These features of LINC00261 suggest that it plays an important role as a tumor suppressor and can be utilized for future cancer-targeting strategies in PC. Moreover, through flow cytometry and transwell assays, it was found that LINC00261 also plays a crucial role in inhibiting metastasis and increasing apoptosis. To further know how this LINC00261 mechanistically suppresses (PC), LINC00261-targeted miRNA analysis was performed. For this, authors selected five miRNAs, namely miR-23a-3p, miR-21, miR-222, miR-193b, and miR-221, from the LinkedOmics TCGA database. Following an in-depth analysis using starBase v2.0 (https://rnasysu.com/encori/index.php), accessed on 4 December 2024 (an online bioinformatics tool), they found that miR-23a-3p exhibited stronger and more effective binding sequences with LINC00261. TCGA database analysis demonstrated a statistically significant inverse correlation (p < 0.0001) between LINC00261 and miR-23a-3p, suggesting a functional axis that may contribute to PC progression. This highlights the emerging concept of lncRNA-miRNA interactions as critical regulatory networks in oncogenesis, providing a novel avenue for targeted therapy [31]. RNA Immunoprecipitation assays and dual-luciferase reporters further validate the direct interaction between LINC00261 and miR-23a-3p [31]. Besides identifying in the plasma of patients with PC, Humeau et al. (2015) discovered that miR-23a acts as oncogenic and overexpressed in the saliva of PC patients with precursor lesions [32]. To further check the viability, PC cells BxPC-3 and CFPAC-1 were given a transfection containing several vectors, specifically with a vector + miR-con (control), a LINC00261 overexpression vector + miR-con, or a LINC00261 overexpression vector + miR-23a-3p and were assessed using the MTT (3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay) test and found that miR-23a-3p partially reversed cell viability of these effects by lowering viability reduction and invasion reduction. Thus, LINC00261 may inhibit PC progression by regulating miR-23a-3p and can be considered a possible target for PC therapy. These findings indicate that the LINC00261/miR-23a-3p axis could be explored as a potential therapeutic target, highlighting the importance of RNA-based interventions in cancer treatment. However, further research is still needed to better understand its role as a tumor suppressor molecule. Further mechanistic analysis revealed that LINC00261 exerts its effects through post-transcriptional regulation via miRNA interactions. Bioinformatic screening using the LinkedOmics TCGA database and starBase identified miR-23a-3p as the most likely downstream target of LINC00261, with a statistically significant inverse correlation (p < 0.0001). Functional assays, including RNA immunoprecipitation and dual-luciferase reporter assays, confirmed direct LINC00261-miR-23a-3p binding, supporting a regulatory axis in PC pathogenesis. Given that miR-23a-3p has been previously implicated in oncogenic processes and detected in the plasma and saliva of PC patients, its interaction with LINC00261 provides a compelling avenue for further therapeutic exploration.
Functional rescue experiments using MTT assays demonstrated that miR-23a-3p overexpression partially reversed the tumor-suppressive effects of LINC00261, restoring cell viability and invasion potential. This suggests that LINC00261 inhibits PC progression by acting as a miRNA sponge, sequestering oncogenic miR-23a-3p to prevent downstream pro-tumorigenic effects. These findings highlight the LINC00261/miR-23a-3p axis as a promising therapeutic target; further in vivo validation and mechanistic insights are required to characterize its clinical relevance fully. Understanding the broader implications of LINC00261–miRNA interactions in pancreatic tumorigenesis could open new frontiers in RNA-based interventions for PC management.
In another study, the authors investigated the expression levels of LINC00261 in 54 PCs and 54 neighboring non-cancerous tissues and found considerable downregulation (fold change = 2.3) [33]. This was confirmed by using GEPIA (Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis) bioinformatics analysis, which also showed reduced LINC00261 expression in PC tissues (n = 179) against normal tissues (n = 171) [33]. The authors used Kaplan–Meier survival curves to learn more about its clinical relevance, revealing that decreased LINC00261 expression is associated with poor prognosis and adverse clinical features, such as greater tumor size, advanced TNM (Tumor, Node, Metastasis) stage, and higher metastatic rates [31,33].
Furthermore, it showed that the levels of LINC00261 expression were significantly decreased in the PC cell lines MIA-PaCa2 (Mouse Insulinoma-Associated Pancreatic Cancer-2), Capan-2 (Carcinoma of the Pancreas-2), BXPC-3, PANC-1, CFPAC-1, and AsPC-1 in comparison with the human pancreatic epithelial cells. To further understand its function in vivo, it was discovered that mice injected with PC cells overexpressing LINC00261 had greater survival rates and fewer metastatic foci than mice treated with control cells. In PC cells, LINC00261 mainly targets the molecular level of miR-552-5p. These results from their study highlight the function of LINC00261 in lowering PC metastasis [33]. Additionally, through TargetScan, the authors demonstrated that miR-552-5p has binding sites for LINC00261, which have been further validated using dual luciferase reporter assays. It was observed that the luciferase activity of LINC00261 diminished in PANC-1 and MIA-PaCa2 cells co-transfected with the miR-552-5p and LINC00261-WT plasmid compared to miR-552-5p negative control in pancreatic epithelial cell lines [33]. Also, miR-552-5p was shown to target FOXO3 (Forkhead box O3). FOXO3 is a tumor suppressor and crucial regulator of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. It has been identified as a direct target of miR-552-5p [33]. Since it has been demonstrated that FOXO3 regulates the Wnt signaling pathway, the expression of β-catenin and transcription factor 4 (TCF4) was assessed. LINC00261, by sponging miR-552-5p, restores FOXO3 expression and suppresses the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, as evidenced by reduced levels of β-catenin and transcription factor 4 (TCF4). This suppression effectively inhibits epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) and metastasis—key processes driving pancreatic cancer (PC) progression via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Conversely, reactivation of Wnt signaling leads to increased β-catenin and TCF4 expression, enhancing EMT markers and underscoring the critical role of the LINC00261/miR-552-5p/FOXO3 axis in PC metastasis (Figure 1). However, these effects are reversed when miR-552-5p is reintroduced into LINC00261 overexpressing PC cells [33]. Given the pivotal role of Wnt signaling activation in PC metastasis, LINC00261’s ability to restore FOXO3 expression and suppress this pathway highlights its broader tumor-suppressive potential. This aligns with existing research emphasizing FOXO3 as a key target in inhibiting pancreatic tumor progression. The LINC00261/FOXO3 axis effectively disrupts EMT and metastasis, reinforcing its therapeutic significance [33].
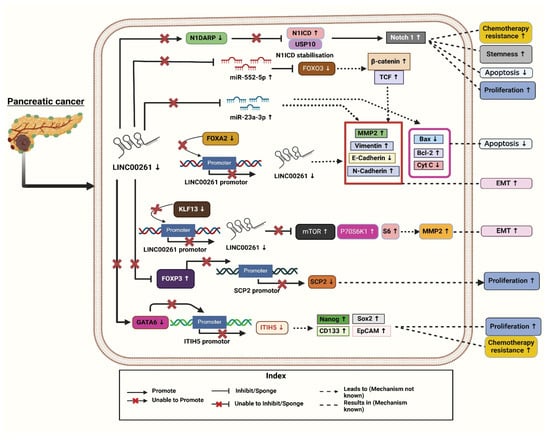
Figure 1.
Molecular mechanisms associated with downregulation of LINC00261 leading to the clinical progression and pathogenesis of pancreatic cancer. [Note: ↑—Upregulated, ↓—downregulated]. Created with BioRender.com.
Four molecular subtypes of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) were reported using the International Cancer Genome Consortium’s (ICGC) PDAC dataset: aberrantly differentiated endocrine exocrine (ADEX), immunogenic, pancreatic progenitor, and squamous. In this study, LINC00261 was identified as the most significantly differentially expressed lncRNAs, with a substantial downregulation reported in the squamous subtype compared to the other three [4]. Further, to investigate the pathways linked to deregulated LINC00261 expression in PDAC samples, the authors used gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA). They identified Forkhead box A2 (FOXA2), a chromosomal neighbor of LINC00261, as a direct regulator, with a strong association of (r = 0.72–0.91) across datasets and found a strong positive correlation between LINC00261 and FOXA2, an epithelial marker and EMT inhibitor. Both FOXA2 and LINC00261 showed similar expression patterns across PDAC subtypes. To investigate the regulatory relationship, the authors altered FOXA2 levels in PANC-1 cells [4]. FOXA2 knockdown reduced LINC00261 transcript levels, while overexpression increased RNA expression and promoter activity (Figure 1). FOXA2 binding to the LINC00261 promoter was confirmed by ChIP-qPCR (Chromatin Immunoprecipitation followed by quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction). Further, the authors analyzed datasets, such as CCLE (Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia), PDAC samples (Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma), and lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD), demonstrating that LINC00261 expression correlated positively with epithelial markers (e.g., CDH1, KRT19, CLDN7 (cadherin 1, cytokeratin 19, claudin 7) and negatively with mesenchymal markers, highlighting its role in regulating differentiation and EMT processes [4].
Additionally, the researchers further studied the effect of LINC00261 for checking cell migration and invasion in PC cells (PANC-1) and by correlating its expression with CDH1 (Cadherin1) encoding E-cadherin, which is a key epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) marker. Mechanistically, the depletion of LINC00261 was linked to reduced expression of CDH1 (E-cadherin), a crucial protein for maintaining cell–cell adhesion. This suggests that the loss of LINC00261 compromises E-cadherin-mediated adhesion, thereby enhancing cell motility and invasiveness. These results are consistent with clinical data showing that low LINC00261 expression is associated with more aggressive pancreatic cancer (PDAC) phenotypes and worse patient outcomes, underscoring its potential as both a biomarker and a therapeutic target in pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PDAC) [4].
Based on GSE16515 (Gene Expression Series number 16515) and GSE32676 dataset analyses, Li Zou et al. (2021) reported that LINC00261 expression is markedly reduced in PC tissues compared to normal controls. Their study identified a positive association between LINC00261 and Inter-Alpha-Trypsin Inhibitor Heavy Chain 5 (ITIH5) expression using ChIPBase (Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Database). Additionally, predictions from lncMAP indicated that LINC00261 might have ITIH5 expression through the transcription factor GATA6 (GATA Binding Protein 6), suggesting an important regulatory function of LINC00261 in the progression of PC (Figure 1) [34]. The authors further examined the fact that LINC00261 upregulates ITIH5 expression in PANC-1 cells and stem cells by recruiting the transcription factor GATA6 to a specific binding site (site two) on the ITIH5 promoter. Through a dual-luciferase assay, the authors confirmed that the overexpression of LINC00261 enhances ITIH5 promoter activity while its silencing decreases it. Bioinformatics analyses identified two potential GATA6 binding sites on the promoter, and experimental validation confirmed site two as the functional site for GATA6 binding. ChIP-qPCR assays demonstrated that GATA6 binds effectively to site 2 in a LINC00261-dependent manner, and RIP assays (RNA Immunoprecipitation Assays) established a direct interaction between LINC00261 and GATA6. Silencing GATA6 in LINC00261-overexpressing cells abrogated ITIH5 upregulation, indicating that the effect of LINC00261 is mediated through GATA6 [34]. These findings suggest that LINC00261 facilitates ITIH5 expression by acting as a scaffold for GATA6 recruitment, highlighting a potential regulatory axis that could be explored for therapeutic interventions in PC. Functional assays demonstrated that increased LINC00261 expression leads to the suppression of key stem cell markers (Nanog, Oct4 (Octamer-binding Transcription Factor 4), Sox2 (SRY-Box Transcription Factor 2), CD133 (Cluster of Differentiation 133), and EpCAM (Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule) and reduced cell viability, self-renewal capacity, invasive ability, and tumorigenicity. Additionally, it was observed that PANC-1 stem cells, which had restored LINC00261 expression, exhibited reduced resistance to gemcitabine, the standard chemotherapy drug for PC. The overexpression of LINC00261 in PANC-1 stem cells suggested its potential role as a tumor suppressor in PC. Various assays including sphere formation assays, transwell invasion tests, cytotoxicity assays, and tumor xenograft studies confirmed these effects. This indicates that upregulating LINC00261 could help suppress the aggressive and drug-resistant characteristics of pancreatic cancer stem cells, providing a novel therapeutic approach to combat PC progression and improve drug sensitivity [34]. Moreover, flow cytometry analysis was conducted to check how it regulates the cell cycle, which revealed that overexpression of LINC00261 increased the proportion of cells in the G0/G1 phase, suggesting an interruption in the cell cycle.
To gain more in-depth knowledge, researchers uncovered that LINC00261 regulates PC progression through its interaction with FOXP3 (Forkhead Box Protein P3). FISH (Fluorescence in situ hybridization) assays revealed nuclear localization of LINC00261 and FOXP3 in PC cells, while RIP and ChIP assays confirmed that LINC00261 binds FOXP3, which in turn binds the SCP2 (Sterol Carrier Protein 2) promoter. Overexpression of LINC00261 increased SCP2 expression while reducing FOXP3 levels, disrupting FOXP3-mediated suppression of SCP2. These findings suggest that the LINC00261/FOXP3/SCP2 axis influences PC development, presenting a novel regulatory mechanism and therapeutic target (Figure 1) [29].
Through GEO (Gene Expression Omnibus) datasets (GSE15471, GSE16515, and GSE32676), LINC00261 was identified as significantly downregulated in PC tissues, with this reduction correlating to poor patient prognosis (p = 0.014). Survival analysis confirmed that patients with low LINC00261 expression had decreased survival rates [15]. Functional assays in human PC cell lines revealed lower LINC00261 levels in AsPC-1, Patu8988, MIAPaCa-2, and SW1990 cells than in normal pancreatic cells (HPDE6-C7). Additionally, RNA FISH showed that LINC00261 was localized to both the nucleus and cytoplasm in PANC-1 cells, with a primary concentration in the nucleus. The authors further conclude that low LINC00261 expression is a potential prognostic biomarker in PC, suggesting its tumor-suppressive role [15].
The authors investigated the potential of LINC00261 as a prognostic biomarker for pancreatic cancer (PC). Initially, they transfected SW1990 cells with the pcDNA3.1-H-LINC00261 plasmid. This process resulted in a significant increase in the levels of LINC00261. Additionally, to silence LINC00261 in PANC-1 cells, the authors utilized the pLV3ltr-Puro-U6-LINC00261-i plasmid. This approach led to a reduction in LINC00261 expression by up to 64.2%. It revealed that through transwell assays, LINC00261 expression had no significant effect on cell growth, proliferation, or overall apoptosis rates; overexpression markedly suppressed PC cells’ migratory and invasive capabilities. These findings highlight LINC00261’s critical role in limiting tumor aggressiveness in PC [15]. The regulatory role of LINC00261 in EMT and its downstream effects were thoroughly investigated. To demonstrate how LINC00261 regulates PC progression, the authors used qRT-PCR and Western blotting to validate changes in the expression of key EMT markers and transcription factors [15].
Additionally, the analysis of the GEPIA database revealed that the Twist1 (Twist-related protein1) transcription factor is highly expressed in PC tissues. This Twist1 is known to play a critical role in promoting EMT by activating key target genes such as MMP2 (Matrix Metalloproteinase 2) in cancers. It was observed that the downregulation of LINC00261 resulted in increased Twist1 transcription, thereby enhancing EMT processes. The findings reveal LINC00261 as a pivotal regulator in mitigating PC aggressiveness, making it a potential therapeutic target for inhibiting EMT and tumor metastasis in PC. Also, their study discovered that the KLF13 transcription factor upregulates LINC00261 transcription by binding to its promoter. Bioinformatic analyses identified KLF13 as a potential regulator and experimental validation showed that KLF13 co-localized with LINC00261 in the nucleus of PANC-1 cells. Overexpression of KLF13 increased LINC00261 expression significantly, and luciferase assays confirmed that KLF13 directly binds to the LINC00261 promoter, enhancing its activity [15]. Further, LINC00261 interacts through specific RNA sequences by acting as a decoy molecule to prevent transcription factors from binding to their target DNA, thus either inhibiting or activating gene expression. LINC00261 interacts through specific RNA sequences by acting as a decoy molecule to prevent transcription factors from binding to their target DNA, thus either inhibiting or activating gene expression. Moreover, the study shows that LINC00261 suppresses mTOR-P70S6K1-S6 (mechanistic Target of Rapamycin-p70 S6 Kinase 1-S6 ribosomal proteins), a signaling pathway activation through KLF13 regulation, which is critical in suppressing PC metastasis. The PI3K/Akt/mTOR (Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase/Protein Kinase B/mechanistic Target of Rapamycin) pathway is known to promote cell migration and metastasis by phosphorylating P70S6K1, leading to actin filament rearrangement and upregulating MMP2 expression. Overexpression of KLF13 suppressed the pathway and decreased metastasis by preventing the activation of mTOR, P70S6K1-S6. However, when LINC00261 was silenced, this inhibitory effect of KLF13 was reversed, highlighting that LINC00261 plays a pivotal role in modulating this pathway to prevent PC metastasis (Figure 1) [15]. By suppressing mTOR and its downstream effectors, LINC00261 appears to inhibit metastatic spread, offering a potential molecular target for therapeutic intervention. With the increasing focus on PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibitors in cancer therapy, further exploring LINC00261-mediated regulation in this pathway could provide novel treatment strategies.
Zhai et al. (2023) identified the highest differential expression of LINC00261 between PC and normal cancer through the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. Additionally, the authors found that the LINC00261 had more potential for coding probability than other proven translatable lncRNAs evaluated by the online tool CPC2 (Coding Potential Calculator 2). Further, the results obtained by ORF Finder (Open Reading Frames) showed that ORF2, ORF7, and ORF12 could be translated. Additionally, the CCK8 (Cell Counting Kit-8) experiment revealed that only ORF12 overexpression prevented the growth of PC cells, implying that these ORFs may have biological roles. Moreover, the authors found LINC00261 as a key regulator of Notch1 (Notch homolog 1) signaling in PC by encoding the microprotein Notch1 degradation-associated regulatory polypeptide (N1DARP). In normal conditions, Notch1 signaling controls crucial cellular processes like differentiation and apoptosis by promoting the degradation of the Notch1 intracellular domain (N1ICD) [30].
Moreover, in PC, hyperactivation of this pathway occurs due to the stabilization of N1ICD, driving uncontrolled cell proliferation, stemness, and chemoresistance (Figure 1). N1DARP, encoded by LINC00261, acts as a tumor suppressor by disrupting the interaction between N1ICD and the deubiquitinase USP10 (Ubiquitin-Specific Protease 10), leading to polyubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of N1ICD confirmed by the Western blotting analysis in CAPAN1 transfected with a vector or varying concentrations of FLAG-tagged (Fluorescent Antigen) N1DARP plasmid, where overexpressed N1DARP inhibited Notch activation. This results in reduced Notch1 activity, thereby inhibiting tumor growth, stemness traits, and chemoresistance [30]. The authors also highlighted the therapeutic potential of targeting this disrupted interaction, with the stapled peptide SAH-mAH2-5 derived from N1DARP offering a promising strategy for treating Notch1-activated PC. The authors validated their findings using both preclinical and clinical samples. Preclinical models included pancreatic cancer organoids (PDAC-1, PDAC-2, PDAC-R) derived from patient samples and genetically engineered KPC (Kras/p53/Cre) and KPNC (Kras/p53/Notch/Cre) mice [30].
Overall, the results above show that LINC00261 has a tumor-suppressive effect in PC, influencing key pathways such as EMT, mTOR, and Notch signaling as illustrated in Figure 1. LINC00261’s downregulation is associated with poor prognosis and aggressive tumor phenotypes. However, further research is needed to investigate it as a viable biomarker for early PC detection and/or treatment. Despite its potential as a biomarker and therapeutic target, further research is needed to fully understand its mechanisms and validate its clinical application in combating pancreatic cancer progression and improving treatment outcomes.
3.2. LINC00261 and Colorectal Cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is recognized as one of the most prevalent and aggressive malignancies affecting the digestive system, characterized by/known for high morbidity and mortality rates. It continues to pose a significant global challenge [35,36,37]. Despite recent improvements in therapy, patients with metastatic CRC still have a poor 5-year survival rate, which is critically low globally (~10%) despite recent developments in treatment [36]. Studies have demonstrated that numerous long non-coding RNAs play crucial roles in regulating CRC-related pathways [38]. Moreover, a poor clinical prognosis and the onset of metastasis in CRC patients are strongly associated with increased expression levels of MALAT1 (Metastasis-Associated Lung Adenocarcinoma Transcript 1), HOTAIR (HOX transcript antisense intergenic RNA), and H19 (H19 Imprinted Maternally Expressed Transcript) [39]. According to a recent study, the lncRNAs KCNQ1OT1 (KCNQ1 overlapping transcript 1) and WT1-AS (Wilms tumor 1 antisense RNA) have substantial interactions with most miRNAs in the ceRNA network (competing endogenous RNA), indicating that they play important roles in the development of CRC [39].
In one of the recent studies, Liu et al. (2020) evaluated the clinical and mechanistic role of LINC00261 in CRC. They used RNA expression profiling from the TCGA dataset, which included 459 non-metastatic colorectal CRC samples and 87 metastatic CRC samples, to examine metastasis-specific mRNAs, miRNAs, and lncRNAs in CRC tissue. By comparing non-metastatic and metastatic tissues, the results confirmed 628 differentially expressed (DE) mRNAs, of which 354 were upregulated and 274 were downregulated, along with 25 aberrantly expressed miRNAs and 144 dysregulated lncRNAs. Out of 144 dysregulated, 3-lncRNA, such as LINC00114 (long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 114), LINC00261, and HOTAIR, were found to be highly significant in CRC patients compared to normal tissue samples. Additionally, analysis of lncRNA expression and clinical features in CRC showed LINC00261 had a positive correlation with overall survival (OS) (p = 0.044 and p = 0.0006, respectively), but HOTAIR had a negative correlation with OS (p = 0.012). Moreover, the authors observed that LINC00261 expression varies throughout the different stages of colorectal cancer. They noted significant reductions in the expression of lncRNA in stages III and IV of CRC in comparison to stages I and II CRC. Furthermore, the authors did not identify any significant differences when comparing combined CRC tissues to normal colorectal tissues. Their findings emphasize the importance of these lncRNAs as biomarkers in improving CRC prognosis and informing treatment decisions [39].
In terms of LINC00261, it is found that it exhibits positive coexpression with mRNAs involved in important biological processes such as “GO:0042158~lipoprotein biosynthetic process”, (Gene Ontology (GO), “GO:0008152~metabolic process”, “Drug metabolism cytochrome P450 (pigment 450)”, and “Chemical carcinogenesis” [39]. The expression of individual P450 variants has been associated with colorectal cancer, where some of these P450s show increased levels. Notably, P450 components showed high expression of CYP51 or CYP2S1 (Cytochrome P450 2S1), which has been correlated with a poor prognosis, with CYP51 (cytochrome P450 14α-sterol demethylase) serving as an independent prognostic indicator (15897573). The findings indicate that LINC00261 is downregulated in colorectal cancer (CRC) and actively influences tumorigenesis and key cancer pathways.
Xi et al. (2023) investigated whether LINC00261 plays a role in CRC through the miRNAs-mRNA axis. For this, they took the LINC00261-miRNA-148a/WNT10b axis. They established that targeting the LINC00261-miRNA-148a/WNT10b axis could significantly affect CRC cell proliferation and apoptosis, highlighting its importance in tumor growth and programmed cell death. Further, they found that by regulating the miRNA-148a/WNT10b axis, LINC00261 may impact the proliferation of SW480 CRC cells. Further studies reported that transfection of LINC00261-specific siRNAs in CRC cells significantly increased miR-148a and decreased WNT10b (wingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 10B) and β-catenin proteins. The WNT10b is a key molecule of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, while miR-148a is reported as an oncogenic miRNA in CRC. According to the above findings, LINC00261 may influence the advancement of colon cancer by interfering with the miR-148a/WNT10b axis and disrupting Wnt/β-catenin signaling [37].
Moreover, the reduced expression of LINC00261 significantly decreased cell viability, increased the apoptosis rate, and caused G1-phase cell cycle arrest in CRC cells. These effects also underscore LINC00261’s potential in CRC cancer treatment [37]. It was also observed that higher expression levels of LINC00261 tend to improve overall survival compared to CRC patients with lower expression levels. LINC00261 is a tumor suppressor in colon cancer, showing that its overexpression inhibits cell growth and migration, and deactivates the Wnt signaling pathway. Both in vitro and xenograft models confirmed LINC00261’s role in slowing tumor progression, suggesting it could be a promising therapeutic target for colon cancer. From the data above, we can conclude that LINC00261 could be linked to CRC patients’ prognoses, indicating that it could be a useful biomarker for patients with colon cancer [37].
Wang et al. (2018) demonstrated that LINC00261 levels markedly down-regulated in tissues and cell lines of colon cancer, with the lowest expression observed in Stage III compared to Stages I and II [35], which also suggests its prognostic value. Furthermore, the authors observed that LINC00261 significantly decreased cisplatin resistance in colon cancer in vivo while enhancing the drug’s efficacy by reducing tumor volume and weight. Their research also utilized the SW480 colon cancer cell line to investigate the relationship between LINC00261 and cisplatin resistance and revealed that the cisplatin-resistant SW480 cell line exhibited markedly lower LINC00261 expression than drug-sensitive cells [35]. It was observed that when LINC00261 expression was increased in CRC cells through expression vector-based methods, the expression of pro-apoptotic proteins such as BAX (BCL2-associated X protein), FAS (FS-7-associated surface antigen, Fas receptor), Bim (Bcl-2-interacting mediator of cell death), and cleaved caspase-3 increases, which in turn reduced cell viability and migration of CRC cells by increasing E-cadherin and reducing EMT proteins such as MMP2 and MMP9 (Matrix Metalloproteinase-9) [35]. Further, it also blocked β-catenin nuclear translocation, which suppressed Wnt/β-catenin signaling and its target genes such as Myc (Myelocytomatosis oncogene) and CCND1 (Cyclin D1). The in vivo studies further indicated that the overexpression of LINC00261 effectively inhibited both the initiation and progression of colon cancer [35]. LINC00261 also synergized with cisplatin in the reduction of tumor growth in mice, indicating its potential therapeutic value in overcoming drug resistance and tumor progression. This research underscores that LINC00261 plays an essential role in cell proliferation, migration, and apoptosis and mediated drug resistance in colon cancer cells. Other studies have indicated that overexpressing LINC00261 could reverse drug resistance, inhibit CRC cell migration and invasion, and identify it as a promising molecule for CRC diagnosis and prognosis. These data provide a solid foundation for LINC00261-based innovative treatment strategies for CRC [35].
Tang et al. (2022) identified an 8-lncRNA prognostic signature, including SNHG7 (small nucleolar RNA host gene 7), ZEB1-AS1 (zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1 antisense 1), U47924.27, NIFK-AS1 (NIFK Antisense RNA 1), RP1-170O19.17, LINC00261, LINC00925, and CAPN10-AS1 (Calpain 10 Antisense RNA 1), as a potential independent prognostic factor for CRC patients based on the TCGA dataset. The predictive ability of this signature was validated using additional datasets (GSE39582, GSE29621 Gene Expression Omnibus Series) and effectively predicted chemotherapy responses [36]. Among these lncRNAs, SNHG7, ZEB1-AS1, NIFK-AS1, and others were positively associated with survival risk, whereas LINC00261 was negatively correlated. In a recent study, LINC00261 was significantly downregulated in CRC tissues and linked to lymph node metastasis and clinical stage (Figure 2) [40]. The signature identified high-risk patients with poor survival outcomes, as shown by Kaplan–Meier and ROC analyses (Receiver-operating characteristic curve), where the risk score became an independent prognostic factor. Immune profiling revealed differences in immune cell infiltration and mutational landscapes between risk groups, while IC50 analyses (Half-maximal inhibitory concentration) indicated varying sensitivities to chemotherapy drugs. Functional studies showed that lncRNAs, like ZEB1-AS1 and SNHG7, inhibited CRC cells’ growth, migration, and EMT through PI3K/AKT signaling (phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase /protein kinase B), supported by Gene Ontology enrichment and pathway analyses. This indicates that LINC00261 is a prognostic and therapeutic tool for CRC [40].
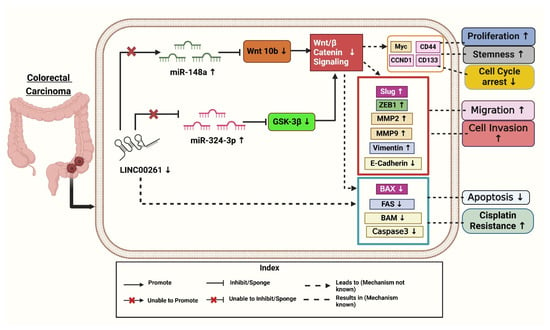
Figure 2.
Downregulation of LINC00261 and its effective targets leads to the progression of colorectal cancer. Created with BioRender.com [Note: ↑—Upregulated, ↓—downregulated].
It was found that LINC00261 expression was significantly reduced in (SW620, HT-29, DLD-1, HCT-116, and SW480) colon cancer cells compared to HCEPIC and normal colon cells [40]. In contrast, miR-324-3p levels were notably elevated in colon cancer cells. Further analysis showed overexpression of LINC00261, using a lentiviral vector (LV-LINC00261) in colon cancer cell lines HCT-116 and DLD-1, inhibits tumor progression by sponging the oncogenic miR-324-3p to activate GSK-3β (glycogen synthase kinase 3β), thus degrading β-catenin and inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and resulting in decreased proliferation, migration, invasion, apoptosis enhancement, and decreased tumor growth both in vitro and in vivo. Overexpression of LINC00261 reduced miR-324-3p levels and suppressed colon cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, as demonstrated in HCT-116 and DLD-1 cell lines. Additionally, experiments confirmed that LINC00261 upregulation inhibited cell proliferation [17].
Mechanistically, LINC00261 repressed colon cancer progression by inactivating the Wnt signaling pathway by modulating miR-324-3p (Figure 2). These findings suggest that LINC00261 reduces colon cancer by competitively binding itself to miR-324-3p and interfering with oncogenic signaling pathways [17]. As demonstrated in Figure 2, LINC00261 is significantly downregulated in colon cancer, while miR-324-3p is upregulated. By inactivating the Wnt pathway and negatively regulating miR-324-3p, overexpression of LINC00261 inhibits the spread of colon cancer and could serve as a target for therapeutic intervention [17].
3.3. Role of LINC00261 in Hepatocellular Cancer
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a significant global health issue and is the fourth most prevalent cause of cancer-related deaths globally, ranking sixth in terms of incidence [8,19,41]. Numerous investigations have demonstrated that fatty acid metabolism is a vital metabolic process that supplies energy and signaling molecules, and encourages HCC [8].
Chen et al. (2022) investigated the role of fatty acid (FA) metabolism-related lncRNAs in HCC. The authors aimed to identify key lncRNAs linked to FA metabolism and assess their prognostic and therapeutic potential. Using datasets from TCGA and Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO), they identified LINC00261, along with SNHG1 (Small Nucleolar RNA Host Gene 1) and SNHG7 (Small Nucleolar RNA Host Gene 7), as pivotal lncRNAs associated with FA metabolism [8]. To explore these associations, the study employed advanced bioinformatics techniques, such as single-sample gene set enrichment analysis (ssGSEA), to derive FA metabolism scores and correlate them with lncRNA expression. Experimental approaches, including qRT-PCR, FA metabolism PCR arrays, and Western blotting, were utilized to validate their findings and assess the downstream effects of these lncRNAs. Their results demonstrated that LINC00261, a key part of the FA metabolism-related lncRNA signature, plays a critical role in regulating FA metabolism, contributing to immune infiltration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), processes linked to HCC progression and immune evasion. Patients with higher LINC00261 expression exhibited better survival outcomes, underscoring its potential as a prognostic biomarker. Additionally, the study highlighted the significant molecular differences between patient subgroups based on FA metabolism-related lncRNA profiles, such as immune cell heterogeneity, genomic mutations, and EMT activity. These findings suggest that LINC00261 holds promise as a therapeutic target and a predictor of immunotherapy response in HCC [8]. To get into clinical insights, the authors treated HCC cell lines Huh7 and HepG2 with Transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1) to induce higher expression of EMT-associated proteins and observed reduced LINC00261 expression [19]. To gain further insight, the authors investigated the clinical relevance of LINC00261 in HCC and performed immunohistochemistry (IHC) on patient samples to correlate LINC00261 expression and found that low levels of LINC00261 were associated with high levels of p-SMAD3 (phospho-small mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3), a molecule activated during TGF-β1 signaling, which promotes EMT (epithelial-mesenchymal transition), stemness, and metastasis (Figure 3). Moreover, it is observed that HCC patients having lower expression of LINC00261 and a higher level of p-SMAD3 have overall poorer recurrence-free survival [19]. The above data suggest the combined potential of LINC00261 and p-SMAD3 as useful biomarkers for predicting prognosis outcomes in HCC patients. To better understand LINC00261, the authors constructed LINC00261 knockdown models using MHCC-LM3 (Hepatocellular Carcinoma cell line—Liver Metastatic Cell line 3) and SNU-449 (Seoul National University cell line 449) HCC cell lines. Through these models, they observed that migration and invasion were significantly promoted after LINC00261 knockdown but were suppressed with LINC00261 overexpression of the EMT-associated protein levels. The knockdown of LINC00261 increased ZEB1 (Zinc-finger E-box binding homeobox 1) and vimentin levels while reducing E-cadherin expression, which indicated EMT promotion (Figure 3). Conversely, overexpression of LINC00261 reversed these effects, decreasing ZEB1, Slug, and vimentin, while restoring E-cadherin levels. These findings highlighted that LINC00261 suppressed EMT and limited cancer cell viability, suggesting its therapeutic potential in treating cancer by regulating molecular pathways involved in metastasis [19].
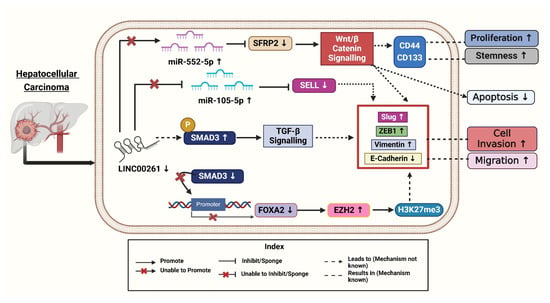
Figure 3.
LINC00261 and its downregulation affect various signalings ultimately leading to development of Hepatocellular cancers. Created with BioRender.com [Note: ↑—Upregulated, ↓—downregulated].
To uncover the mechanisms underlying LINC00261’s role in HCC, Chen et al. (2021) performed gain- and loss-of-function studies demonstrating that LINC00261 suppresses migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in HCC cells [41]. Following this, the researchers investigated the molecular mechanisms involved, using advanced techniques like RNA pull-down assays to identify proteins interacting with LINC00261. The authors revealed that LINC00261 recruits SMAD3 to the promoter region of FOXA2 (Forkhead Box A2), a neighboring tumor suppressor gene, thereby activating its expression [41]. Further bioinformatics analyses and rescue experiments confirmed that FOXA2 mediates the tumor-suppressive effects of LINC00261 while restoring FOXA2 levels reversed the effects of LINC00261 loss. To explore the silencing of LINC00261, the authors treated HCC cells with GSK126, an inhibitor of Enhancer of Zeste Homolog 2 (EZH2) [41]. This treatment reduced the trimethylation of histone H3 at lysine 27 (H3K27me3) levels and restored LINC00261 expression. Combining these findings with immunohistochemical staining of patient tissues, they linked high levels of EZH2 and H3K27me3 to low expression of LINC00261 and poorer patient outcomes (Figure 3). Overall, these experiments provided compelling evidence for the EZH2/LINC00261/FOXA2 axis as a critical regulator of HCC metastasis [41].
Ma et al. (2021) revealed that fucoidan is a natural polysaccharide derived from brown algae, exhibiting various biological activities, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antitumor properties. This compound has been shown to inhibit cell growth in vitro and in vivo, decrease invasion and motility, and trigger apoptosis and cell cycle arrest [42]. The antitumor efficacy of fucoidan has been validated in various cancers, including pancreatic, bladder, and ovarian cancers. Fucoidan inhibits tumor occurrence and development by modulating tumor immunity, obstructing angiogenesis, and disrupting cell cycle processes and apoptosis, indicating its significant potential in tumor therapy [42]. Fucoidan was found to upregulate LINC00261, which interacted with miR-522-3p and increased the expression of SFRP2 in HCC. Conversely, the down-regulation of LINC00261 increases the expression of miR-522-3p and down-regulated SFRP2 expression and supports cell proliferation (Figure 3) [42]. This pathway is crucial in inducing dose-dependent arrest of the cell cycle and induction of apoptosis. It has been previously established that LINC00261 acts as a tumor suppressor in terms of regulating the expression of miRNA. LINC00261 could also be associated with reduced tumorigenicity of MHCC97H cells through miR-522-3p regulation in HCC. SFRP2 was significantly enhanced in the fucoidan treatment group, suggesting the interaction of LINC00261, miR-522-3p, and SFRP2 in HCC cells [42].
Song et al. (2022) investigated the role of the LINC00261/miR105-5p/SELL axis in HCC, particularly its connection to immune cell dysfunction and patient survival. This study highlighted LINC00261 as a critical component of the LINC00261/miR105-5p/SELL axis, which influences immune cell function and patient survival in HCC [7], and explored how post-transcriptional regulatory mechanisms involving the LINC00261/miR105-5p/SELL axis influence immune dysfunction and overall survival in HCC patients. They utilized TCGA (The Cancer Genome Atlas) dataset samples (379 HCC out of these 337 tumor samples and 42 adjacent tissues) to perform comprehensive immune cell profiling and gene expression analysis with CIERSORT (Cell-type Identification by Estimating Relative Subsets of RNA Transcripts). Most of the patients were males with a median age of 61 and were diagnosed at an early stage of HCC as per the TNM staging system. In contrast to the surrounding tissues, tumor tissues exhibited considerably lower expression levels of SELL (L-selectin) (Log2 fold-change = −1.14) and LINC00261 (Log2 fold-change = −0.90) [7].
In HCC tissues, the researchers found 201 differentially expressed miRNAs (DEMs), 216 differentially expressed lncRNAs (179 upregulated and 37 downregulated), and 3705 differentially expressed genes (1628 upregulated and 2077 downregulated). When compared to nearby normal tissues, tumor tissues showed downregulation of SELL (Selectin L). Selectin L is an important immunological regulator with adhesive properties, and its reduced expression contributes to cancer progression by promoting cell proliferation and metastasis [43]. Further, miR-105-5p plays a role in liver cancer (HCC) by influencing immune cells, especially B cells, through the LINC00261/miR-105-5p/SELL pathway. The presence of this miRNA has a direct association with the survival status of patients. Better overall survival (OS) was positively connected with its expression. When LINC00261 attaches itself to miR-105-5p, it functions as a “molecular sponge”. Through this interaction, SELL expression is maintained by preventing miR105-5p from binding to the 3′ untranslated region (UTR) of the SELL mRNA. In tumor tissues, decreased LINC00261 levels increase miR105-5p activation. Higher levels of LINC00261 therapeutic target in HCC [7]. A more immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME) results from improved immune cell homing and function caused by increased miR-105-5p suppressing SELL. By sponging miR105-5p, LINC00261 functions as a competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA), stopping miR105-5p from down-regulating SELL. In HCC samples, decreased LINC00261 levels were accompanied by elevated miR105-5p levels, which inhibited SELL (Figure 3). Survival analysis showed higher SELL and LINC00261 levels were linked to better results, whereas higher miR-105-5p predicted worse overall survival. Kaplan–Meier survival analyses confirmed SELL’s positive association with overall survival, further reinforcing its potential as a prognostic marker [7].
The above analysis reveals significant expression differences between tumor and normal tissues, identifying 3705 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) vital for cancer research. Upregulated DEGs are linked to cell division and DNA replication, emphasizing their role in tumor growth [7]. In contrast, downregulated DEGs are associated with immune responses, inflammation, and cell adhesion, suggesting potential therapeutic targets. The study found 201 differentially expressed miRNAs (DEMs) and 216 expressed long non-coding RNAs (DELs), enhancing our understanding of tumor biology and offering new research opportunities. LINC00261 is significantly downregulated in HCC tissues, interfering with its function as a ceRNA (competing endogenous RNA) that protects SELL from miR-105-5p repression, which in turn leads to impairment of immunological functions and metastasis of HCC [7].
Furthermore, they established a ceRNA network identifying critical interactions influencing survival outcomes. Eleven immune cell types showed alterations in HCC tissues compared to non-cancerous tissues. The LINC00261/miR105-5p/SELL pathway emerged as a key marker, with decreased Selectin L, a molecule essential for immune cell homing and function, and was positively correlated with patient survival and markedly downregulated in HCC tissues [7]. This ceRNA axis implies restoring SELL levels may enhance immune function and outcomes in HCC. SELL expression correlates with improved overall survival. This underscores SELL’s importance in immune function and its connection to immunotherapy gene signatures, indicating potential for novel therapeutic approaches. The LINC00261/miR105-5p/SELL axis is a crucial prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target for HCC, substantially improving immunotherapy effectiveness. Further research is necessary to validate these findings and advance targeted treatments [7].
The above findings indicate that LINC00261 plays a critical role as a tumor suppressor in HCC, and regulates various cancer-associated pathways, including the EZH2/FOXA2 and miRNA axes as shown in (Figure 3). The LINC00261 also affects fatty acid metabolism, immune cell function, and the epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Targeting the mechanisms associated with LINC00261 presents promising opportunities for enhancing immunotherapy and improving clinical outcomes in HCC patients. However, further research is needed to translate these findings into effective treatment
3.4. LINC00261 in Gallbladder Cancer
Although gallbladder cancer (GBC) is considered highly dangerous, only one study to date has examined the role of LINC00261 in GBC. In that study, the researchers analyzed LINC00261 expression in 100 paired clinical samples of GBC tissues and adjacent normal tissues using quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). Their findings revealed that patients with low LINC00261 expression had significantly bad overall survival (OS, p = 0.0188) and progression-free survival (PFS, p = 0.0029) [44].
To elucidate the potential role of LINC00261 in GBC, Niu et al. (2020) analyzed the relationship between LINC00261 expression levels and the clinicopathological factors in GBC patients. Their findings indicated that lower levels of LINC00261 expression were linked to a higher degree of differentiation (p = 0.017), an absence of liver metastases (p = 0.027), an advanced TNM stage (p = 0.008), and a bigger tumor size (p < 0.0001). The authors performed a Kaplan–Meier survival analysis to assess how LINC00261 affects the prognosis of GBC patients. This analysis revealed that patients with low LINC00261 expression had significantly poorer outcomes regarding overall survival (OS, p = 0.0188) and progression-free survival (PFS, p = 0.0029) [44]. Assessing LINC00261 levels in tissue samples or serum could serve as a vital prognostic indicator for GBC, and incorporating this biomarker into clinical practice may improve patient outcomes and facilitate timely intervention strategies for GBC management [44]. Since the research on LINC00261 in GC cancer is very scanty, the mechanistic role of LINC00261 is still missing. Thus, more research is needed on these aspects.
4. Biological and Cellular Pathways Associated with LINC00261
The targets of LINC00261 play critical roles in various biological and cellular pathways. We conducted a Gene Set Enrichment Analysis of the targets to understand the contributions of LINC00261 within different KEGG pathways and Gene Ontology (GO) biological, cellular, and molecular processes. As depicted in Figure 4A the results indicate that the target genes of LINC00261 are primarily involved in significant biological processes, such as the regulation of miRNA and mRNA transcription, mRNA processing (including splicing), regulation of gene expression, and transcription by RNA polymerase II. This reinforces the antitumorigenic functions of LINC00261 which were demonstrated through wet lab experiments of LINC00261 binding to various miRNAs such as miR-550a-3p, miR-23a-3p, miR-148a, mir-324-3p, and miR105-5p [7,17,21,31,37].
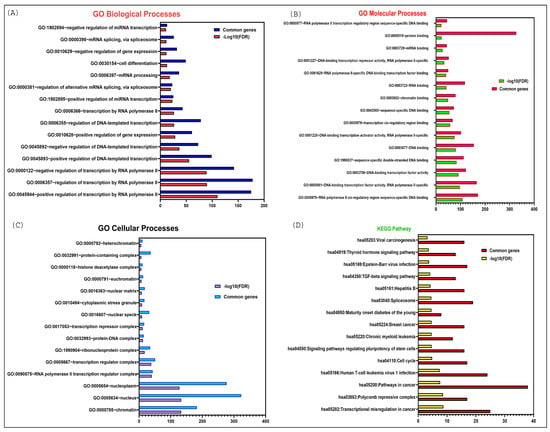
Figure 4.
DAVID functional enrichment analysis of LINC00261 target genes in various biological processes and signaling pathways. (A) Significantly enriched GO biological terms; (B) Significantly enriched GO molecular processes; (C) Significantly enriched GO cellular processes; (D) Significantly enriched KEGG pathway.
In addition, these targets are actively engaged in various molecular functions, including protein binding, RNA binding (especially mRNA binding), DNA binding (such as chromatin binding and transcription cis-regulatory sequences), and other forms of sequence-specific DNA binding as demonstrated in Figure 4B. Moreover, they are involved in numerous cellular processes, including protein-DNA complex formation, ribonuclease complexes, histone deacetylase complexes, and the nuclear matrix, most of which are localized in the nucleus as elucidated in Figure 4C.
Finally, the KEGG pathway enrichment analysis revealed a significant association of LINC00261 targets with cancer-related pathways, such as transcriptional misregulation in cancer, viral carcinogenesis, the TGF-beta signaling pathway, pathways regulating the pluripotency of stem cells, and the cell cycle Figure 4D.
5. Conclusions and Future Aspects
Cancer is an enormous health issue, impacting individuals and communities alike. This review highlights the essential role of LINC00261 in influencing several biological functions, such as invasion, metastasis, apoptosis, angiogenesis, and proliferation. It has been identified as a tumor suppressor in gallbladder, hepatic, colorectal, and pancreatic cancers. According to the literature reviewed, the expression of LINC00261 is found to be downregulated in PC, CRC, HCC, and GBC cancer tissues, as well as in cell lines (Table 1). This reduced expression is associated with worse outcomes, which correlates with poor prognosis and increased tumor growth. Lower levels of LINC00261 lead to a decrease in results in epithelial markers, such as E-cadherin, while simultaneously increasing mesenchymal markers like vimentin and N-cadherin (Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3). This shift from epithelium to mesenchymal tissue promotes tumor invasion and metastasis. Additionally, LINC00261 interacts with specific miRNAs; for instance, it binds with miR-23a-3p and miR-552-5p in PC, miR-148a, and miR-324-3p in colorectal cancer, miR-522-3p and miR105-5p in hepatocellular carcinoma, to downregulate oncogenic pathways in these cancers [7,17,32,33,37,42].

Table 1.
Clinical characteristics and properties of LINC00261 in various cancers.
This review discusses how LINC00261 modulates oncogenic pathways in various cancers. Specifically, LINC00261 suppresses the PI3K/Akt/mTOR (Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K), Protein kinase B (AKT), and Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway by interacting with KLF13 (Krüppel-like factor 13) in pancreatic cancer, thereby reducing metastasis and invasive characteristics. Additionally, the miR-148a/WNT10b axis inhibits tumor growth and enhances sensitivity to cisplatin when the expression levels of LINC00261 are elevated through its interaction with WNT10b (wingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 10B) [37]. Furthermore, knocking down LINC00261 results in increased cell proliferation due to the elevated levels of miR-522-3p in HCC. This increase in miR-522-3P subsequently reduces the expression of its downstream target, SFRP2 (Secreted Frizzled-Related Protein 2) (Figure 3), which is critical for various cellular processes, including development, differentiation, and tumorigenesis [42].
It has been found that LINC00261 contributes to transcriptional regulation by modulating transcription factors such as GATA6 (GATA binding protein 6), influencing the expression of ITIH5 (Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain 5), and encoding the microprotein N1DARP (Notch1 degradation-associated regulatory polypeptide). This microprotein disrupts hyperactive Notch1 signaling (Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1), which is a hallmark of PC progression, stemness, and chemoresistance. Overexpression of LINC00261 has been shown to reduce cell motility, invasion, and chemical resistance, making it a promising option for targeted therapies. The multifaceted roles of LINC00261 highlight its potential as a biomarker (diagnostic and prognostic) and in clinical treatment.
The prospects of LINC00261 indicate great potential for transforming the clinical relevance of cancer diagnosis and treatment. The tumor-suppressive properties of LINC00261 could serve as a foundation for future RNA-based therapies or microprotein-based approaches that aim to inhibit cancer development. Combining strategies targeting LINC00261 with existing treatments could improve therapeutic outcomes by reducing metastasis, drug resistance, and tumor progression. Although its potential remains largely untapped, dysregulation of LINC00261 has consistently been associated with poor patient outcomes, making it a reliable biomarker for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic approaches. Large-scale clinical studies will be essential to validate its effectiveness as both a biomarker and a therapeutic target. Additionally, a deeper exploration of the regulatory networks surrounding LINC00261 will facilitate its integration into precision medicine. By addressing critical factors driving cancer progression, LINC00261 holds the promise to revolutionize the management of cancers such as pancreatic, colorectal, gallbladder, and hepatocellular carcinoma. However, despite the promising role of lncRNAs in cancer therapeutics, several limitations hinder their clinical application. One major challenge is the cellular penetration of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), which requires improved stabilization against rapid degradation in the biological environment. To enhance their therapeutic potential, the development of optimized chemical structures is necessary to improve their stability and bioavailability [45].
Additionally, while lncRNAs are relatively easy to manufacture and can be chemically modified for enhanced protection against nucleotide degradation, their efficient delivery remains a significant hurdle. Liposomal delivery systems, which have been widely explored for lncRNA transport, face challenges such as scalability, reproducibility, chemical instability, and the risk of denaturation. Overcoming these barriers is crucial to harnessing the full therapeutic potential of lncRNAs, ensuring their safe and effective integration into precision oncology [45]
Overall, LINC00261 represents a significant advancement in treating pancreatic, colorectal, hepatocellular, and gallbladder cancers. It provides a way for novel therapeutic and diagnostic approaches by altering important carcinogenic pathways. Further research is needed to validate the reported LINC00261 findings in larger cohorts, explore its integration with existing therapies, and clarify its regulatory networks for therapeutic applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.J.; methodology S.B. and S.D.; investigation, S.B. and S.D.; data curation, S.B., S.D., A.D., A.K.T., K.M., S.M., V.U., M.R.A., V.Y., H.S.T. and A.J.; writing—original draft preparation, S.B., S.D., A.D., A.K.T., K.M., S.M., V.U., M.R.A., V.Y., H.S.T. and A.J.; writing—review and editing, S.B., S.D., A.D., A.K.T., K.M., S.M., V.U., M.R.A., V.Y., H.S.T. and A.J.; visualization, S.B., S.D., A.D., A.K.T., K.M., S.M., V.U., M.R.A., V.Y., H.S.T. and A.J.; supervision, A.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This review received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
Aklank Jain, Department of Zoology, is thankful to the Central University of Punjab, DST-FIST, and the DST-PURSE Scheme.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest to report.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| PC | Pancreatic Cancer |
| CRC | Colorectal Cancer |
| HCC | Hepatocellular Cancer |
| GBC | Gallbladder Cancer |
| lncRNAs | Long non-coding RNAs |
| miRNAs | microRNA |
| GLOBOCAN | Global Cancer Observatory |
| ASR | Age-Standardized Rate |
| Ki-67 | Antigen Kiel 67 |
| TCONS_00027846 | Transcript consensus number |
| DEANR1 | Definitive Endoderm-Associated lncRNA1 |
| ALIEN | A Long Intergenic Non-coding RNA enhancing Neuroblastoma |
| FALCOR | Folate Associated Long non-coding RNA |
| EBF1 | Early B cell factor 1 |
| BCSC | Breast Cancer Stem Cells |
| SDPR | Serum Deprivation Response Protein |
| EOC | Epithelial Ovarian Cancer |
| MT1M | Metallothionein1M |
| HOTAIR | HOX transcript antisense intergenic RNA |
| MALAT1 | Metastasis-Associated Lung Adenocarcinoma Transcript 1 |
| HOTTIP | HOXA transcript at the distal tip |
| PVT1 | Plasmacytoma Variant Translocation 1 |
| AsPC-1 | Ascites Pancreatic Cancer-1 |
| BxPC-3 | Biopsy xenograft of Pancreatic Carcinoma line-3 |
| PANC-1 | Pancreatic Cancer-1 |
| CFPAC-1 | Cystic Fibrosis Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Cell line |
| HPDE6-C7 | Human Pancreatic Duct Epithelial cell line clone7 |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas |
| MMP2 | Matrix Metalloproteinase 2 |
| E-cadherin | Epithelial Cadherin |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| GEPIA | Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis |
| TNM | Tumor, Node, Metastasis |
| MIA-PaCa2 | Mouse Insulinoma-Associated Pancreatic Cancer-2 |
| Capan-2 | Carcinoma of the Pancreas-2 |
| FOXO3 | Forkhead box O3 |
| TCF4 | Transcription Factor 4 |
| EMT | Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition |
| PDAC | Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma |
| ICGC | International Cancer Genome Consortium’s |
| ADEX | Aberrantly Differentiated Endocrine exocrine |
| FOXA2 | Forkhead box A2 |
| GSEA | Gene Set Enrichment Analysis |
| ChIP-qPCR | Chromatin Immunoprecipitation followed by quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| CCLE | Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia |
| LUAD | Lung Adenocarcinoma |
| CLDN7 | cadherin 1, cytokeratin 19, claudin 7 |
| CDH1 | Cadherin1 |
| EMT | Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition |
| GSE16515 | Gene Expression Series number 16515 |
| ITIH5 | Inter-Alpha-Trypsin Inhibitor Heavy Chain 5 |
| ChIPBase | Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Database |
| GATA6 | GATA Binding Protein 6 |
| Oct4 | Octamer-binding Transcription Factor 4 |
| Sox2 | SRY-Box Transcription Factor 2 |
| CD133 | Cluster of Differentiation 133 |
| EpCAM | Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule |
| FOXP3 | Forkhead Box Protein P3 |
| FISH | Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization |
| SCP2 | Sterol Carrier Protein 2 |
| GEO | Gene Expression Omnibus |
| Twist1 | Twist-related protein1 |
| mTOR-P70S6K1-S6 | Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin-p70 S6 Kinase 1-S6 ribosomal proteins |
| PI3K/Akt/mTOR | Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase/Protein Kinase B/mechanistic Target of Rapamycin |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas |
| CPC2 | Coding Potential Calculator 2 |
| ORF | Open Reading Frames |
| CCK8 | Cell Counting Kit-8 |
| Notch1 | Notch homolog 1 |
| N1ICD | Notch1 intracellular domain |
| USP10 | Ubiquitin-Specific Protease 10 |
| FLAG | Fluorescent Antigen |
| KPC | Kras/p53/Cre |
| KPNC | Kras/p53/Notch/Cre |
| KCNQ1OT1 | KCNQ1 overlapping transcript 1 |
| H19 | H19 Imprinted Maternally Expressed Transcript |
| WT1-AS | Wilms tumor 1 antisense RNA |
| ceRNA | Competing Endogenous RNA |
| DE | Differentially Expressed |
| LINC00114 | Long Intergenic Non-Protein Coding RNA 114 |
| OS | Overall Survival |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| P450 | Pigment 450 |
| CYP2S1 | Cytochrome P450 2S1 |
| CYP51 | Cytochrome P450 14α-sterol Demethylase |
| WNT10b | Wingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 10B |
| BAX | BCL2-associated X protein |
| FAS | FS-7-associated surface antigen, Fas receptor |
| Bim | Bcl-2-interacting mediator of cell death |
| MMP9 | Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 |
| Myc | Myelocytomatosis oncogene |
| CCND1 | Cyclin D1 |
| SNHG7 | Small Nucleolar RNA Host Gene 7 |
| ZEB1-AS1 | Zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1 antisense 1 |
| NIFK-AS1 | NIFK Antisense RNA 1 |
| CAPN10-AS1 | Calpain 10 Antisense RNA 1 |
| GSE39582 | Gene Expression Omnibus Series |
| ROC | Receiver-operating characteristic curve |
| IC50 | Half-maximal inhibitory concentration |
| PI3K/AKT | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase /Protein Kinase B |
| LV-LINC00261 | Lentiviral Vector |
| GSK-3β | Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3β |
| SNHG1 | Small Nucleolar RNA Host Gene 1 |
| SNHG7 | Small Nucleolar RNA Host Gene 7 |
| ssGSEA | Single-Sample Gene Set Enrichment Analysis |
| TGF-β1 | Transforming Growth Factor-Beta 1 |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| p-SMAD3 | Phospho-Small Mothers Against Decapentaplegic homolog 3 |
| MHCC-LM3 | Hepatocellular Carcinoma cell line—Liver Metastatic Cell line 3 |
| SNU-449 | Seoul National University cell line 449 |
| ZEB1 | Zinc-finger E-box binding homeobox 1 |
| EZH2 | Enhancer of Zeste Homolog 2 |
| H3K27me3 | Trimethylation of Histone H3 at lysine 27 |
| CIERSORT | Cell-type Identification by Estimating Relative Subsets of RNA Transcripts |
| SELL | Selectin L |
| UTR | 3′ Untranslated Region |
| TME | Tumor Microenvironment |
| ceRNA | Competitive Endogenous RNA |
| DEGs | Differentially Expressed Genes |
| DEMs | Differentially Expressed miRNAs |
| DELs | DNA Encoded Libraries |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative Real-Time PCR |
| PFS | Progression-Free Survival |
| KLF13 | Krüppel-like factor 13 |
| SFRP2 | Secreted Frizzled-Related Protein 2 |
| N1DARP | Notch1 Degradation-Associated Regulatory Polypeptide |
References
- Cao, W.; Qin, K.; Li, F.; Chen, W. Comparative study of cancer profiles between 2020 and 2022 using global cancer statistics (GLOBOCAN). J. Natl. Cancer Cent. 2024, 4, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koya, A.I.; Ibrahim, S.A. Carcinogenesis. In StatPearls; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Dorn, A.; Glass, M.; Neu, C.T.; Heydel, B.; Huttelmaier, S.; Gutschner, T.; Haemmerle, M. LINC00261 Is Differentially Expressed in Pancreatic Cancer Subtypes and Regulates a Pro-Epithelial Cell Identity. Cancers 2020, 12, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, U.; Barwal, T.S.; Acharya, V.; Tamang, S.; Vasquez, K.M.; Jain, A. Cancer Susceptibility Candidate 9 (CASC9): A Novel Targetable Long Noncoding RNA in Cancer Treatment. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 13, 100774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiu, B.; Chi, Y.; Liu, L.; Chi, W.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.; Guo, R.; Si, J.; Li, L.; Xue, J.; et al. LINC02273 drives breast cancer metastasis by epigenetically increasing AGR2 transcription. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Huang, X.F.; Hu, S.Y.; Lu, L.L.; Yang, X.Y. The LINC00261/MiR105-5p/SELL axis is involved in dysfunction of B cell and is associated with overall survival in hepatocellular carcinoma. PeerJ 2022, 10, e12588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.; Yi, J.; Jiang, J.; Zou, Z.; Mo, Y.; Ren, Q.; Lin, Z.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J. Identification and validation of a fatty acid metabolism-related lncRNA signature as a predictor for prognosis and immunotherapy in patients with liver cancer. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutschner, T.; Diederichs, S. The hallmarks of cancer: A long non-coding RNA point of view. RNA Biol. 2012, 9, 703–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, U.; Kaur Rana, M.; Singh, K.; Jain, A. LINC00324 promotes cell proliferation and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through sponging miR-493-5p via MAPK signaling pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2023, 207, 115372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F.; Liang, B.; Chen, C.; Zeng, D.X.; Zhao, Y.X.; Su, N.; Ning, W.W.; Yang, W.; Huang, J.A.; Gu, N.; et al. Long Intergenic Non-protein Coding RNA 511 in Cancers. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, U.; Barwal, T.S.; Murmu, M.; Acharya, V.; Pant, N.; Dey, D.; Vivek; Gautam, A.; Bazala, S.; Singh, I.; et al. Clinical potential of long non-coding RNA LINC01133 as a promising biomarker and therapeutic target in cancers. Biomark. Med. 2022, 16, 349–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Kumawat, R.K.; Uttam, V.; Behera, A.; Rani, M.; Singh, N.; Barwal, T.S.; Sharma, U.; Jain, A. The imminent role of microRNAs in salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma. Transl. Oncol. 2023, 27, 101573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, A.; Malhotra, A.; Jain, M.; Vasquez, K.M.; Jain, A. The emerging role of long non-coding RNA in gallbladder cancer pathogenesis. Biochimie 2017, 132, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Pang, S.; Dou, J.; Zhou, C.; Shen, B.; Zhou, Y. The inhibitory effect of LINC00261 upregulation on the pancreatic cancer EMT process is mediated by KLF13 via the mTOR signaling pathway. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 24, 1059–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, U.; Murmu, M.; Barwal, T.S.; Tuli, H.S.; Jain, M.; Prakash, H.; Kaceli, T.; Jain, A.; Bishayee, A. A Pleiotropic Role of Long Non-Coding RNAs in the Modulation of Wnt/beta-Catenin and PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathways in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Implication in Chemotherapeutic Drug Response. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 2326–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Luo, M. LINC00261 suppresses human colon cancer progression via sponging miR-324-3p and inactivating the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 22648–22656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, L.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, S.; Chen, E.; Hu, Y. Long non-coding RNA linc00261 suppresses gastric cancer progression via promoting Slug degradation. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 955–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Xiang, L.; Li, L.; Ou, H.; Fang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Hu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Li, X.; et al. TGF-beta1 induced deficiency of linc00261 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal-transition and stemness of hepatocellular carcinoma via modulating SMAD3. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.D.; Liu, C.Y.; Liu, Y.L.; Su, D.W.; Chi, N.N.; Zhang, J.L.; Wei, W.W. LINC00261 regulates EBF1 to suppress malignant progression of thyroid cancer. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 7626–7634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, C. LINC00261/microRNA-550a-3p/SDPR axis affects the biological characteristics of breast cancer stem cells. IUBMB Life 2021, 73, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.L.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Fan, H.W.; Du, N.Y.; Kang, S. LncRNA LINC00261 associates with chemoresistance and clinical prognosis in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2024, 50, 2271–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Gao, F.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, Z.; He, Y.; Guo, W. LINC00261: A burgeoning long noncoding RNA related to cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, G.; Dai, S.; Chen, Q. Long Noncoding RNA LINC00261 Reduces Proliferation and Migration of Breast Cancer Cells via the NME1-EMT Pathway. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 3081–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xue, K.; Guan, Y.; Jin, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Han, L. Long Noncoding RNA LINC00261 Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Invasion and Promotes Cell Apoptosis in Human Choriocarcinoma. Oncol. Res. 2017, 25, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barwal, T.S.; Sharma, U.; Rana, M.K.; Bazala, S.; Singh, I.; Murmu, M.; Kapoor, H.S.; Thakur, S.; Jain, M.; Jain, A. A diagnostic and prognostic value of blood-based circulating long non-coding RNAs in thyroid, pancreatic and ovarian cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2022, 171, 103598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.J.; Shi, S.B.; Tian, J.; Xu, J.; Niu, Z.X. lncRNA MALAT1, HOTTIP and PVT1 as predictors for predicting the efficacy of GEM based chemotherapy in first-line treatment of pancreatic cancer patients. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 95108–95115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Oropeza, R.; Melendez-Zajgla, J.; Maldonado, V.; Vazquez-Santillan, K. The emerging role of lncRNAs in the regulation of cancer stem cells. Cell. Oncol. 2018, 41, 585–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Pei, X.; Xing, D.; Wu, X.; Chen, S. LINC00261 elevation inhibits angiogenesis and cell cycle progression of pancreatic cancer cells by upregulating SCP2 via targeting FOXP3. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 9826–9836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, S.; Lin, J.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tang, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, P.; et al. A microprotein N1DARP encoded by LINC00261 promotes Notch1 intracellular domain (N1ICD) degradation via disrupting USP10-N1ICD interaction to inhibit chemoresistance in Notch1-hyperactivated pancreatic cancer. Cell Discov. 2023, 9, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gao, X.; Tian, J.; Zhang, R.; Qiao, Y.; Hua, X.; Shi, G. LINC00261 inhibits progression of pancreatic cancer by down-regulating miR-23a-3p. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 689, 108469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humeau, M.; Vignolle-Vidoni, A.; Sicard, F.; Martins, F.; Bournet, B.; Buscail, L.; Torrisani, J.; Cordelier, P. Salivary MicroRNA in Pancreatic Cancer Patients. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Lei, S.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xue, Y.; Sun, Y.; Lan, J.; Xu, S.; Mao, D.; Guo, B. Linc00261 inhibits metastasis and the WNT signaling pathway of pancreatic cancer by regulating a miR-552-5p/FOXO3 axis. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 43, 930–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; He, H.; Li, Z.; Chen, O.; Jia, X.; Zhang, H. Long noncoding RNA LINC00261 upregulates ITIH5 to impair tumorigenic ability of pancreatic cancer stem cells. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.K.; Yang, L.; Wu, L.L.; Mao, H.; Zhou, Y.H.; Zhang, P.F.; Dai, G.H. Long non-coding RNA LINC00261 sensitizes human colon cancer cells to cisplatin therapy. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2017, 51, e6793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Hu, X.; Guo, Q.; Shi, Y.; Liu, L.; Ying, G. Discovery and Validation of a Novel Metastasis-Related lncRNA Prognostic Signature for Colorectal Cancer. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 704988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, J.; Shi, L.; Zhou, D.; Cao, D.; Peng, B. Effects of LINC00261 targeting miR-148a/WNT10b axis on the proliferation and apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells. Heliyon 2023, 9, e22094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, U.; Barwal, T.S.; Malhotra, A.; Pant, N.; Vivek; Dey, D.; Gautam, A.; Tuli, H.S.; Vasquez, K.M.; Jain, A. Long non-coding RNA TINCR as potential biomarker and therapeutic target for cancer. Life Sci. 2020, 257, 118035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Cao, Q.; An, G.; Yan, B.; Lei, L. Identification of the 3-lncRNA Signature as a Prognostic Biomarker for Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Ma, J. Expression and Clinical Significance of Long-chain Noncoding RNA LINC00261 in Colon Cancer. Clin. Lab. 2019, 65, 2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xiang, L.; Hu, Z.; Ou, H.; Liu, X.; Yu, L.; Chen, W.; Jiang, L.; Yu, Q.; Fang, Y.; et al. Epigenetically silenced linc00261 contributes to the metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma via inducing the deficiency of FOXA2 transcription. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 277–296. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, D.; Wei, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Ning, L.; Luo, S.H.; Liu, C.L.; Song, G.; Yao, Q. Fucoidan Inhibits the Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Causing lncRNA LINC00261 Overexpression. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 653902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsig, L. Selectins in cancer immunity. Glycobiology 2018, 28, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, J.Z.; Liang, X.C.; Xu, Z.W.; Li, Z.H.; Li, J.; Meng, Y.; Sun, Z.W. Long non-coding RNA Linc00261 as a novel potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for gallbladder cancer. Transl. Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 6078–6085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barwal, T.S.; Sharma, U.; Bazala, S.; Singh, I.; Jain, M.; Prakash, H.; Shekhar, S.; Sandberg, E.N.; Bishayee, A.; Jain, A. MicroRNAs and Long Noncoding RNAs as Novel Therapeutic Targets in Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast and Ovarian Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).