Impact of Comorbidity on the Duration from Symptom Onset to Death in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Retrospective Study of 104,753 Cases in Pakistan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
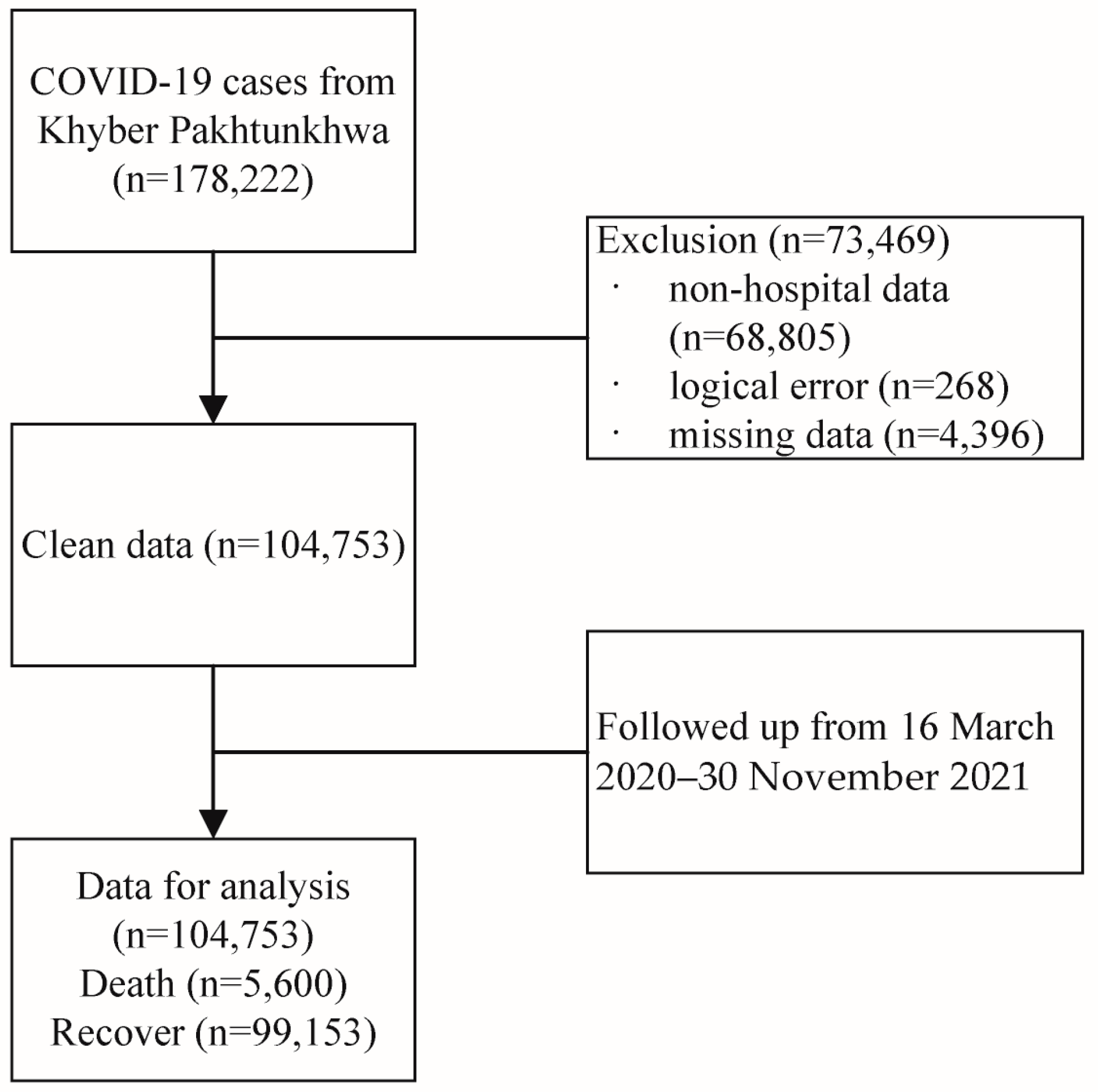
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Data Extraction
2.2. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Study Participants by Death
3.2. Characteristics of Study Participants by Comorbidities
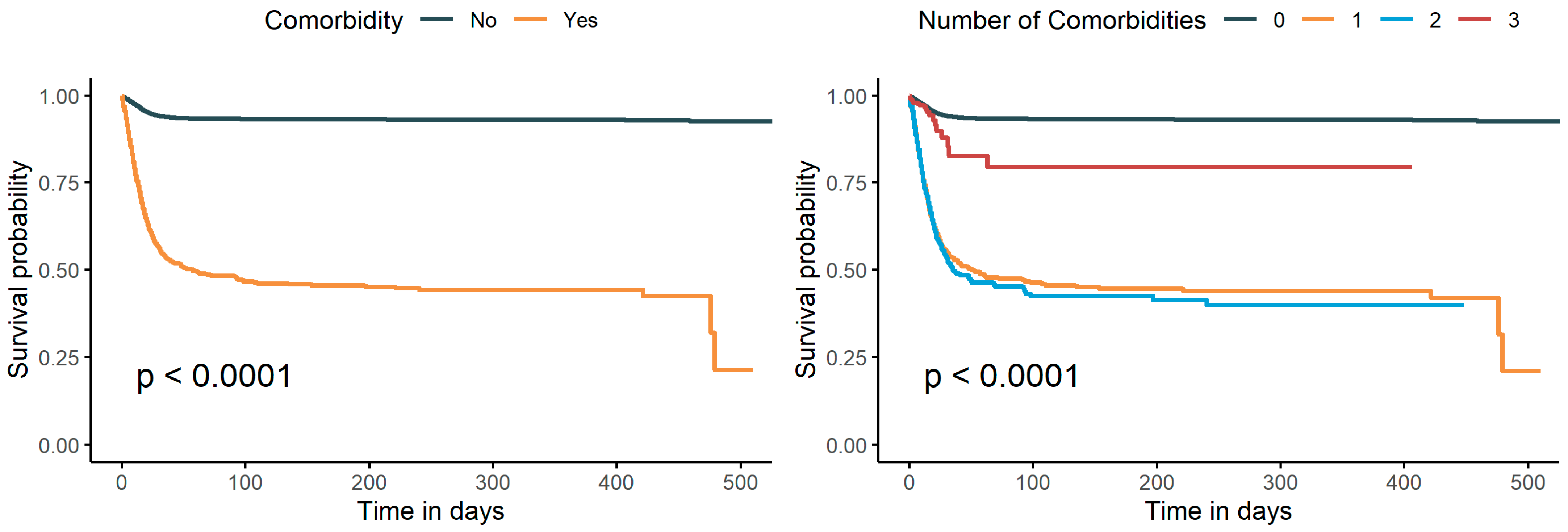
3.3. Impact of Comorbidity on Length of the SOD
3.4. Stratified Analyses
3.5. Sensitivity Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/?gclid=CjwKCAiA57D_BRAZEiwAZcfCxWQWth4sNqEZ1J34KInDRNOjiLuwzkFwpDNCU7V2CPqCPGDU2jLYfhoCb6UQAvD_BwE (accessed on 18 August 2023).
- Thakur, B.; Dubey, P.; Benitez, J.; Torres, J.P.; Reddy, S.; Shokar, N.; Aung, K.; Mukherjee, D.; Dwivedi, A.K. A systematic review and meta-analysis of geographic differences in comorbidities and associated severity and mortality among individuals with COVID-19. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ul Haq, Z.; Shahzad, M.; Khattak, M.I.; Fazid, S.; Ullah, N.; Shireen, A.; Ulhaq, N.; Izhar, A.; Farooq, U.; Darwesh, N.M.; et al. Clinical Characteristics, Mortality and Associated risk factors in COVID-19 patients reported in ten major hospitals of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. J. Ayub Med. Coll. Abbottabad 2020, 32 (Suppl. S1), S633–S639. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.; Fu, M.; Li, Y.; Hu, S.; Luo, J.; Chen, Z.; Yu, J.; Li, W.; Dong, R.; Yang, Y.; et al. The potential association between common comorbidities and severity and mortality of coronavirus disease 2019: A pooled analysis. Clin. Cardiol. 2020, 43, 1478–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ssentongo, P.; Ssentongo, A.E.; Heilbrunn, E.S.; Ba, D.M.; Chinchilli, V.M. Association of cardiovascular disease and 10 other pre-existing comorbidities with COVID-19 mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Ramirez, D.C.; Mackey, D. Underlying respiratory diseases, specifically COPD, and smoking are associated with severe COVID-19 outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Respir. Med. 2020, 171, 106096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalbandian, A.; Desai, A.D.; Wan, E.Y. Post-COVID-19 Condition. Annu. Rev. Med. 2023, 74, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsampasian, V.; Elghazaly, H.; Chattopadhyay, R.; Debski, M.; Naing, T.K.P.; Garg, P.; Clark, A.; Ntatsaki, E.; Vassiliou, V.S. Risk Factors Associated With Post-COVID-19 Condition A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Intern. Med. 2023, 183, 566–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adab, P.; Haroon, S.; O’Hara, M.E.; Jordan, R.E. Comorbidities and COVID-19. BMJ 2022, 377, o1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Asghar, N.; Ullah, A.; Liang, B.; Long, M.; Hu, T.; Zhou, X. Two-Dose Vaccination Significantly Prolongs the Duration from Symptom Onset to Death: A Retrospective Study Based on 173,894 SARS-CoV-2 Cases in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 11531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boger, B.; Fachi, M.M.; Vilhena, R.O.; Cobre, A.F.; Tonin, F.S.; Pontarolo, R. Systematic review with meta-analysis of the accuracy of diagnostic tests for COVID-19. Am. J. Infect. Control 2021, 49, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basheer, A.; Zahoor, I. Genomic Epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 Divulge B.1, B.1.36, and B.1.1.7 as the Most Dominant Lineages in First, Second, and Third Wave of SARS-CoV-2 Infections in Pakistan. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad Khanal, S.; Sreenivas, V.; Acharya, S.K. Accelerated Failure Time Models: An Application in the Survival of Acute Liver Failure Patients in India. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2014, 3, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Atkins, J.L.; Masoli, J.A.H.; Delgado, J.; Pilling, L.C.; Kuo, C.L.; Kuchel, G.A.; Melzer, D. Preexisting Comorbidities Predicting COVID-19 and Mortality in the UK Biobank Community Cohort. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2020, 75, 2224–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpin, D.M.G.; Faner, R.; Sibila, O.; Badia, J.R.; Agusti, A. Do chronic respiratory diseases or their treatment affect the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection? Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 436–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Hu, B.; Hu, C.; Zhu, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Xiang, H.; Cheng, Z.; Xiong, Y.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients with 2019 Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA 2020, 323, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahamat-Saleh, Y.; Fiolet, T.; Rebeaud, M.E.; Mulot, M.; Guihur, A.; El Fatouhi, D.; Laouali, N.; Peiffer-Smadja, N.; Aune, D.; Severi, G. Diabetes, hypertension, body mass index, smoking and COVID-19-related mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e052777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halbreich, U. Allostasis, homeostasis and the cost of physiological adaptation. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2005, 17, 821–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwen, B.S. Sex, stress and the hippocampus: Allostasis, allostatic load and the aging process. Neurobiol. Aging 2002, 23, 921–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawi, A.; Ryoo, S.G. Prevalence of comorbidities in the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 49, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yu, Y.; Xu, J. Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A single-centred, retrospective, observational study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, E26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenblock, C.; Schwarz, P.E.H.; Ludwig, B.; Linkermann, A.; Zimmet, P.; Kulebyakin, K.; Tkachuk, V.A.; Markov, A.G.; Lehnert, H.; de Angelis, M.H.; et al. COVID-19 and metabolic disease: Mechanisms and clinical management. Lancet Diabetes Endo. 2021, 9, 786–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasmi, A.; Peana, M.; Pivina, L.; Srinath, S.; Benahmed, A.G.; Semenova, Y.; Menzel, A.; Dadar, M.; Bjorklund, G. Interrelations between COVID-19 and other disorders. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 224, 108651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Huang, Z.; Lin, L.; Lv, J. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) and Cardiovascular Disease: A Viewpoint on the Potential Influence of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors/Angiotensin Receptor Blockers on Onset and Severity of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e016219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceriello, A. Hyperglycemia and the worse prognosis of COVID-19. Why a fast blood glucose control should be mandatory. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 163, 108186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajpal, A.; Rahimi, L.; Ismail-Beigi, F. Factors leading to high morbidity and mortality of COVID-19 in patients with type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes 2020, 12, 895–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Kruger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Qiao, S.; Zhang, G. Analysis of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) from different species sheds some light on cross-species receptor usage of a novel coronavirus 2019-nCoV. J. Infect. 2020, 80, 469–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.Y.; Ma, Y.T.; Zhang, J.Y.; Xie, X. COVID-19 and the cardiovascular system. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 259–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou-Suckow, Z.; Duerr, J.; Hagner, M.; Agrawal, R.; Mall, M.A. Airway mucus, inflammation and remodeling: Emerging links in the pathogenesis of chronic lung diseases. Cell Tissue Res. 2017, 367, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aveyard, P.; Gao, M.; Lindson, N.; Hartmann-Boyce, J.; Watkinson, P.; Young, D.; Coupland, C.A.C.; San Tan, P.; Clift, A.K.; Harrison, D.; et al. Association between pre-existing respiratory disease and its treatment, and severe COVID-19: A population cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 909–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, E.J.; Walker, A.J.; Bhaskaran, K.; Bacon, S.; Bates, C.; Morton, C.E.; Curtis, H.J.; Mehrkar, A.; Evans, D.; Inglesby, P.; et al. Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY. Nature 2020, 584, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Jehan, I.; de Silva, H.A.; Naheed, A.; Farazdaq, H.; Hirani, S.; Kasturiratne, A.; Ranasinha, C.D.; Islam, M.T.; Siddiquee, A.T.; et al. Prevalence and correlates of cardiometabolic multimorbidity among hypertensive individuals: A cross-sectional study in rural South Asia-Bangladesh, Pakistan and Sri Lanka. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e030584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, W.J.; Liang, W.H.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, H.R.; Chen, Z.S.; Li, Y.M.; Liu, X.Q.; Chen, R.C.; Tang, C.L.; Wang, T.; et al. Comorbidity and its impact on 1590 patients with COVID-19 in China: A nationwide analysis. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 2000547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Docherty, A.B.; Harrison, E.M.; Green, C.A.; Hardwick, H.E.; Pius, R.; Norman, L.; Holden, K.A.; Read, J.M.; Dondelinger, F.; Carson, G.; et al. Features of 20 133 UK patients in hospital with COVID-19 using the ISARIC WHO Clinical Characterisation Protocol: Prospective observational cohort study. BMJ 2020, 369, m1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Wang, F.Z.; Rodewald, L.E.; Wang, X.Y.; Liu, S.Y.; Liu, Q.Q.; Wang, X.Q.; Wu, D.; Li, M.S.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Real-world effectiveness of primary series and booster doses of inactivated COVID-19 vaccine against Omicron BA.2 variant infection in China: A retrospective cohort study. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, 228, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twohig, K.A.; Nyberg, T.; Zaidi, A.; Thelwall, S.; Sinnathamby, M.A.; Aliabadi, S.; Seaman, S.R.; Harris, R.J.; Hope, R.; Lopez-Bernal, J.; et al. Hospital admission and emergency care attendance risk for SARS-CoV-2 delta (B.1.617.2) compared with alpha (B.1.1.7) variants of concern: A cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristic | Overall, n (%) | Death, n (%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | |||
| N | 104,753 | 99,153 | 5600 | |
| Age (year) | 42.7 ± 18.0 | 41.6 ± 17.6 | 62.0 ± 13.7 | <0.001 |
| Gender | <0.001 | |||
| Male | 64,667 (61.7) | 61,415 (61.9) | 3252 (58.1) | |
| Female | 40,086 (38.3) | 37,738 (38.1) | 2348 (41.9) | |
| Symptoms | <0.001 | |||
| No | 74,675 (71.3) | 73,046 (73.7) | 1629 (29.1) | |
| Yes | 30,078 (28.7) | 26,107 (26.3) | 3971 (70.9) | |
| Type of symptom | ||||
| Fever | 26,268 (25.1) | 22,877 (23.1) | 3391 (60.6) | <0.001 |
| Sore throat | 10,207 (9.7) | 9304 (9.4) | 903 (16.1) | <0.001 |
| Cough | 22,435 (21.4) | 19,198 (19.4) | 3237 (57.8) | <0.001 |
| Diarrhea | 1521 (1.5) | 1365 (1.4) | 156 (2.8) | <0.001 |
| Respiratory issues | 12,073 (11.5) | 8787 (8.9) | 3286 (58.7) | <0.001 |
| Headache | 3889 (3.7) | 3474 (3.5) | 415 (7.4) | <0.001 |
| Comorbidity | <0.001 | |||
| No | 100,149 (95.6) | 96,144 (97.0) | 4005 (71.5) | |
| Yes | 4604 (4.4) | 3009 (3.0) | 1595 (28.5) | |
| Type of comorbidity | ||||
| Hypertension | 3551 (3.4) | 2325 (2.3) | 1226 (21.9) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes | 2728 (2.6) | 1850 (1.9) | 878 (15.7) | <0.001 |
| Chronic lung disease | 574 (0.5) | 446 (0.4) | 128 (2.3) | <0.001 |
| Number of comorbidities | <0.001 | |||
| 0 | 100,149 (95.6) | 96,144 (97.0) | 4005 (71.5) | |
| 1 | 2673 (2.6) | 1695 (1.7) | 978 (17.5) | |
| 2 | 1613 (1.5) | 1016 (1.0) | 597 (10.7) | |
| 3 | 318 (0.3) | 298 (0.3) | 20 (0.4) | |
| Epidemic wave | <0.001 | |||
| 1st wave | 22,372 (21.4) | 21,219 (21.4) | 1153 (20.6) | |
| 2nd wave | 16,236 (15.5) | 15,462 (15.6) | 774 (13.8) | |
| 3rd wave | 39,218 (37.4) | 36,972 (37.3) | 2246 (40.1) | |
| 4th wave | 26,927 (25.7) | 25,500 (25.7) | 1427 (25.5) | |
| Type of virus | <0.001 | |||
| Alpha | 32,325 (30.9) | 30,470 (30.7) | 1855 (33.1) | |
| Delta | 26,719 (25.5) | 25,306 (25.5) | 1413 (25.2) | |
| Characteristic | Number of Comorbidities | HTN Only | DM Only | CLD Only | HTN and DM | HTN and CLD | DM and CLD | HTN, DM, and CLD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ≥2 | ||||||||
| Gender | |||||||||
| Male | 1655 (61.9) | 1025 (53.1) * | 1031 (62.4) | 536 (60.2) | 88 (67.2) | 762 (51.2) * | 59 (62.8) | 19 (61.3) | 185 (58.2) |
| Female | 1018 (38.1) | 906 (46.9) | 620 (37.6) | 355 (39.8) | 43 (32.8) | 726 (48.8) | 35 (37.2) | 12 (38.7) | 133 (41.8) |
| Age group | |||||||||
| <18 | 5 (0.2) | 9 (0.5) * | 2 (0.1) * | 2 (0.2) * | 1 (0.8) * | 1 (0.1) * | 0 (0.0) * | 1 (3.2) * | 7 (2.2) * |
| 18–59 | 1223 (45.8) | 823 (42.6) | 672 (40.7) | 473 (53.1) | 78 (59.5) | 562 (37.8) | 24 (25.5) | 11 (35.5) | 226 (71.1) |
| ≥60 | 1445 (54.1) | 1099 (56.9) | 977 (59.2) | 416 (46.7) | 52 (39.7) | 925 (62.2) | 70 (74.5) | 19 (61.3) | 85 (26.7) |
| Epidemic wave | |||||||||
| 1st wave | 1030 (38.5) | 558 (28.9) * | 615 (37.3) * | 330 (37.0) * | 85 (64.9) * | 459 (30.8) * | 54 (57.4) * | 23 (74.2) * | 22 (6.9) * |
| 2nd wave | 501 (18.7) | 371 (19.2) | 312 (18.9) | 172 (19.3) | 17 (13.0) | 348 (23.4) | 14 (14.9) | 1 (3.2) | 8 (2.5) |
| 3rd wave | 787 (29.4) | 470 (24.3) | 491 (29.7) | 273 (30.6) | 23 (17.6) | 445 (29.9) | 16 (17.0) | 3 (9.7) | 6 (1.9) |
| 4th wave | 355 (13.3) | 532 (27.6) | 233 (14.1) | 116 (13.0) | 6 (4.6) | 236 (15.9) | 10 (10.6) | 4 (12.9) | 282 (88.7) |
| Type of virus | |||||||||
| Alpha | 648 (24.2) | 410 (21.2) * | 415 (25.1) * | 215 (24.1) * | 18 (13.7) * | 389 (26.1) * | 15 (16.0) * | 3 (9.7) * | 3 (0.9) * |
| Delta | 349 (13.1) | 528 (27.3) | 228 (13.8) | 115 (12.9) | 6 (4.6) | 232 (15.6) | 10 (10.6) | 4 (12.9) | 282 (88.7) |
| Length of SOD, median (95% CI) | 13.9 (13, 14.9) | 13.7 (12.9, 14.6) | 13.7 (12.8, 14.6) * | 14.5 (13.6, 15.5) * | 13.7 (12.8, 14.7) | 13.7 (12.9, 14.5) * | 14.0 (13.1, 15.0) | 17.0 (15.9, 18.1) | 13.8 (13.2, 14.4) * |
| Death, n | Case Fatality Rate | OR (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Comorbidity | 1595 | 0.346 | 0.16 [0.14–0.17] |
| Number of comorbidities | |||
| 1 | 978 | 0.366 | 0.14 [0.12–0.16] |
| ≥2 | 617 | 0.320 | 0.18 [0.16–0.21] |
| Type of comorbidity | |||
| HTN only | 618 | 0.374 | 0.15 [0.13–0.18] |
| DM only | 300 | 0.337 | 0.15 [0.12–0.18] |
| CLD only | 60 | 0.458 | 0.06 [0.03–0.09] |
| HTN and DM | 549 | 0.369 | 0.17 [0.14–0.20] |
| HTN and CLD | 39 | 0.415 | 0.19 [0.10–0.34] |
| DM and CLD | 9 | 0.290 | 0.33 [0.10–1.09] |
| HTN, DM, and CLD | 20 | 0.063 | 0.53 [0.26–1.08] |
| Characteristic | OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Comorbidity | ||
| 0 | Reference | Reference |
| 1 | 4.8 [4.4–5.3] | <0.001 |
| ≥2 | 3.9 [3.5–4.3] | <0.001 |
| Death, n | Case Fatality Rate | OR (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Comorbidity | 1595 | 0.346 | 0.15 [0.14–0.17] |
| Number of comorbidities | |||
| 1 | 978 | 0.366 | 0.13 [0.12–0.16] |
| ≥2 | 617 | 0.320 | 0.16 [0.13–0.19] |
| Type of comorbidity | |||
| HTN only | 618 | 0.374 | 0.12 [0.10–0.14] |
| DM only | 300 | 0.337 | 0.14 [0.11–0.18] |
| CLD only | 60 | 0.458 | 0.08 [0.05–0.13] |
| HTN and DM | 549 | 0.369 | 0.12 [0.10–0.15] |
| HTN and CLD | 39 | 0.415 | 0.09 [0.05–0.16] |
| DM and CLD | 9 | 0.290 | 0.20 [0.06–0.68] |
| HTN, DM, and CLD | 20 | 0.063 | 2.17 [1.06–4.43] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, H.; Wang, J.; Asghar, N.; Liang, B.; Song, Q.; Zhou, X. Impact of Comorbidity on the Duration from Symptom Onset to Death in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Retrospective Study of 104,753 Cases in Pakistan. Diseases 2023, 11, 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases11040176
Zhou H, Wang J, Asghar N, Liang B, Song Q, Zhou X. Impact of Comorbidity on the Duration from Symptom Onset to Death in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Retrospective Study of 104,753 Cases in Pakistan. Diseases. 2023; 11(4):176. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases11040176
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Haoqi, Jingyuan Wang, Naseem Asghar, Baosheng Liang, Qianqian Song, and Xiaohua Zhou. 2023. "Impact of Comorbidity on the Duration from Symptom Onset to Death in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Retrospective Study of 104,753 Cases in Pakistan" Diseases 11, no. 4: 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases11040176
APA StyleZhou, H., Wang, J., Asghar, N., Liang, B., Song, Q., & Zhou, X. (2023). Impact of Comorbidity on the Duration from Symptom Onset to Death in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Retrospective Study of 104,753 Cases in Pakistan. Diseases, 11(4), 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases11040176






