Noncoding RNA Profile in Reovirus Treated KRAS-Mutated Colorectal Cancer Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Ethical Considerations
2.3. Institutional Review Board/Ethics Committee Approval and Informed Consent
2.4. Sample Harvesting and Processing
2.5. Data Sharing
2.6. Reovirus Administration
2.7. Transcriptome Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
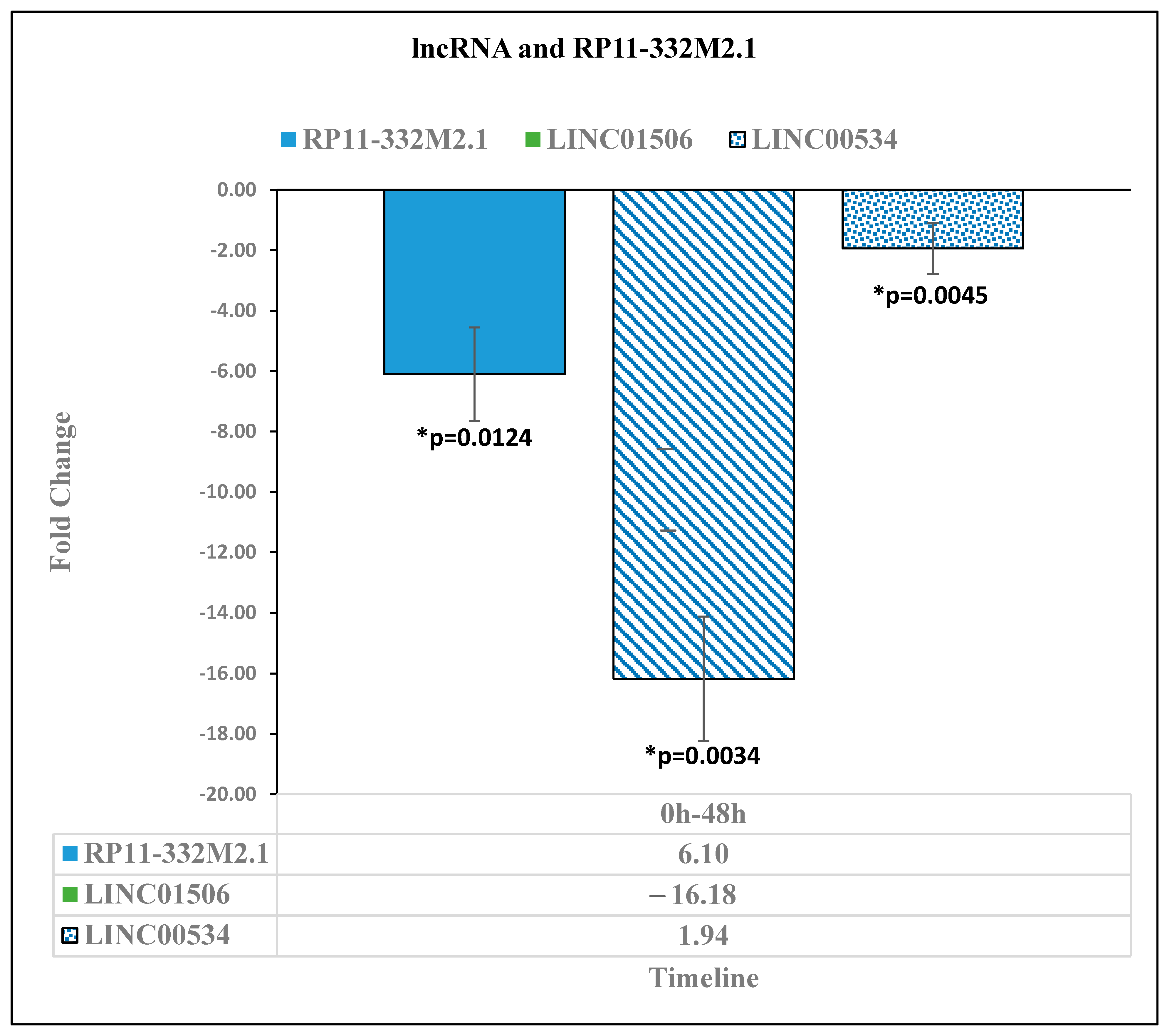
3.1. Downregulation in the Expression of Long Noncoding RNAs after Reovirus Administration
3.2. Upregulation in the Expression of RNA EPB41L4A-AS1 on Day 8
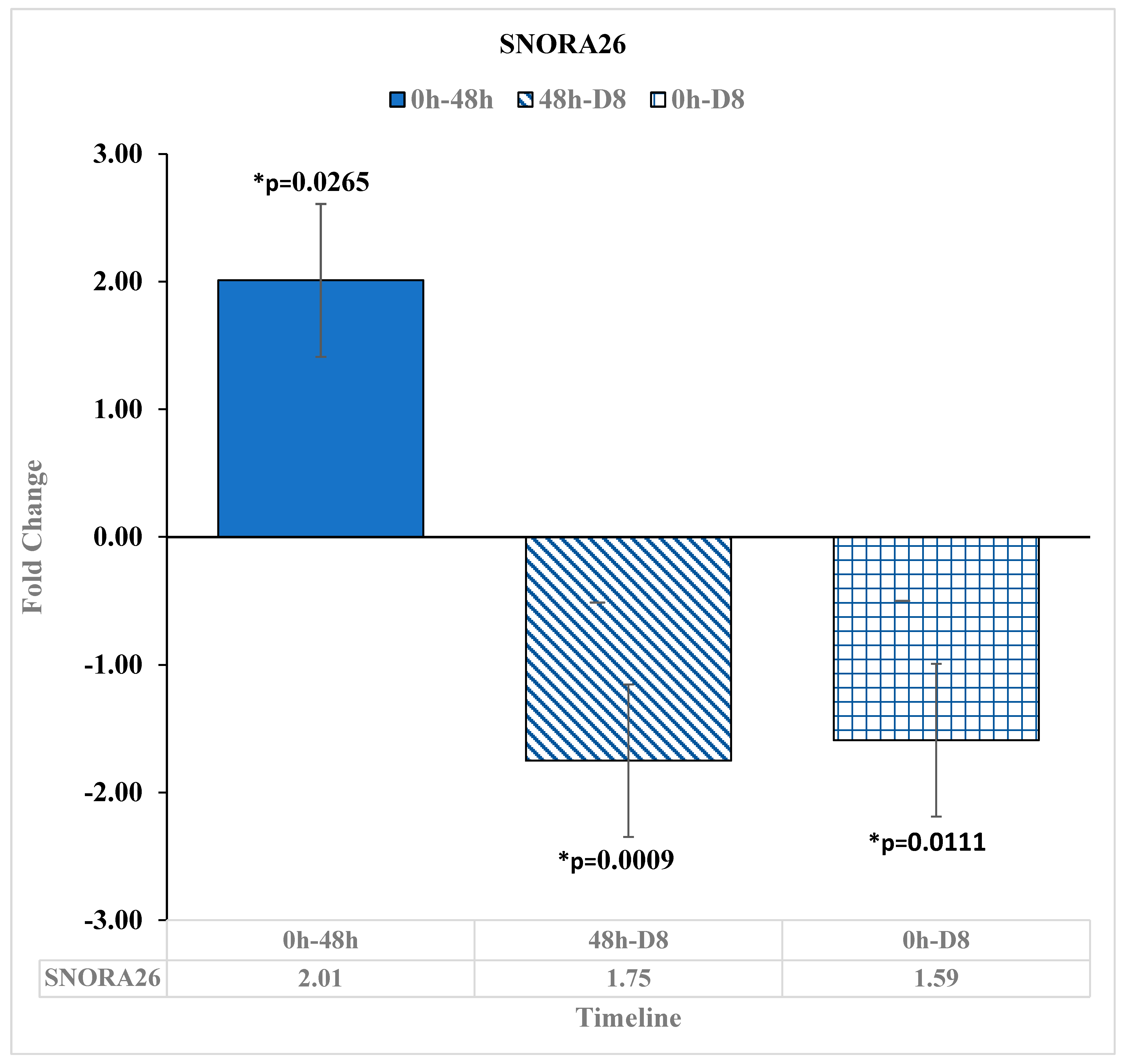
3.3. Downregulation of Small Noncoding RNA SNORA26 after Reovirus Administration
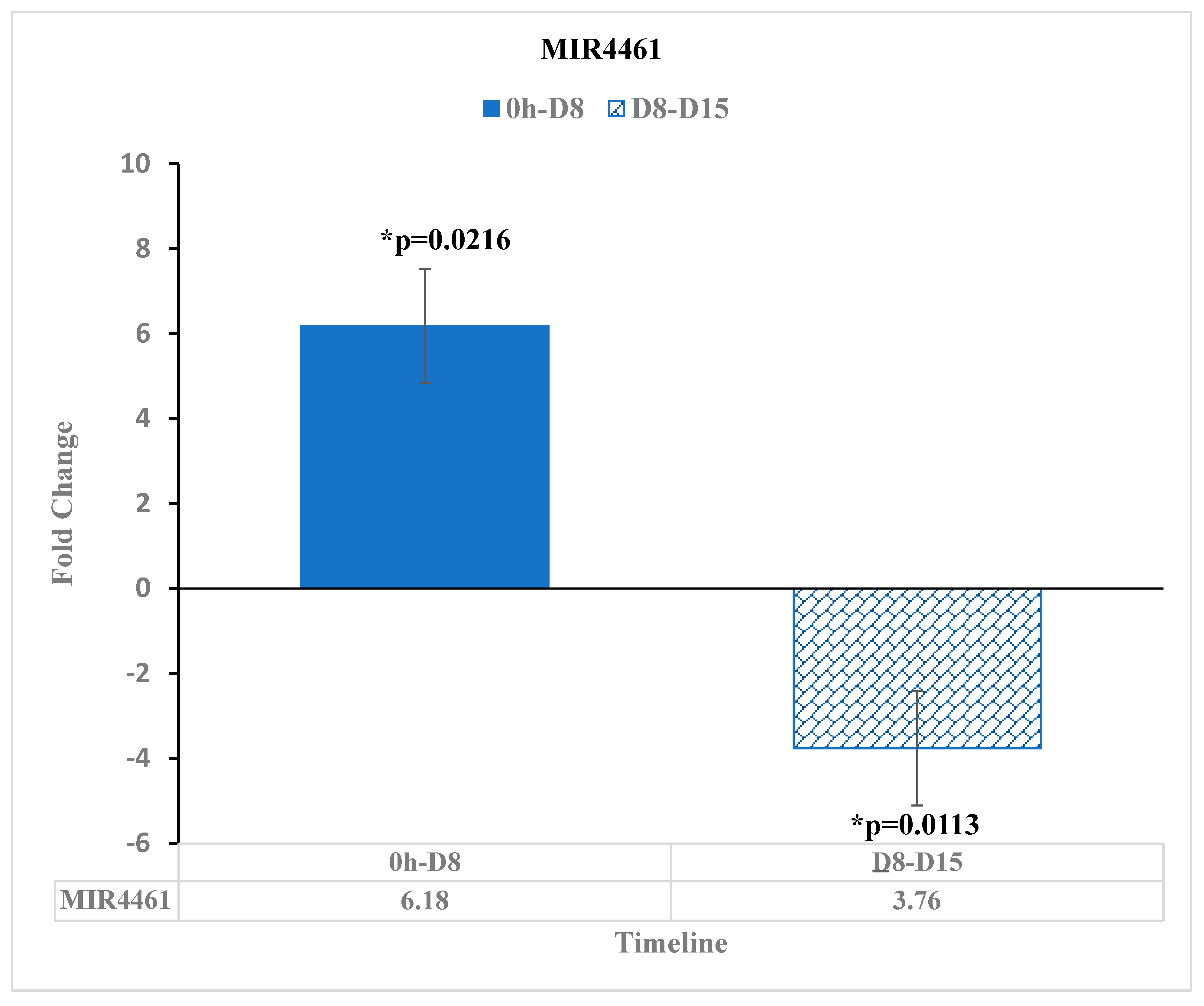
3.4. Micro RNA MIR-4461 Shows an Upward Trend in Expression after Reovirus Treatment
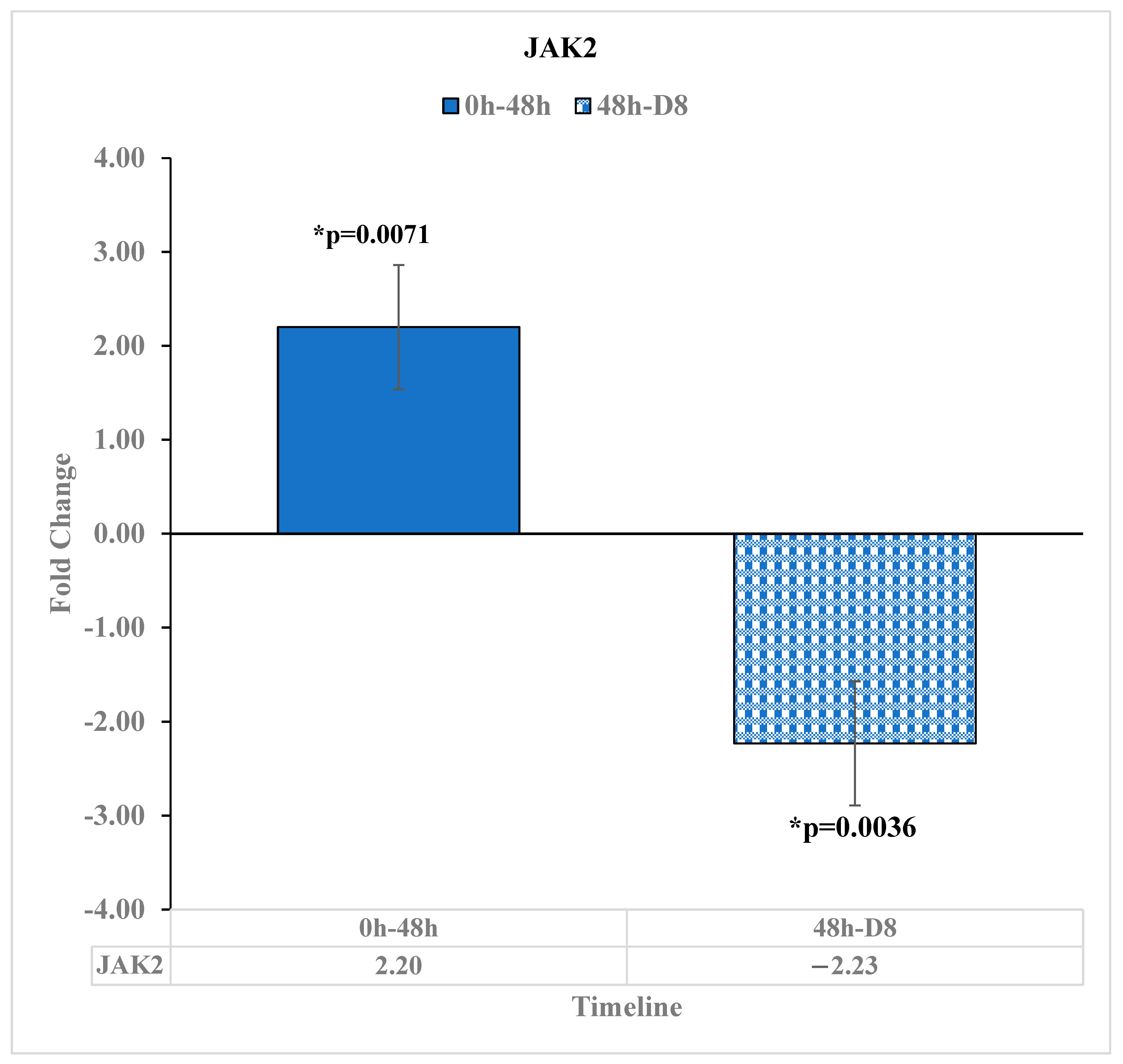
3.5. Expression of JAK2 Is Upregulated Immediately after Reovirus Administration
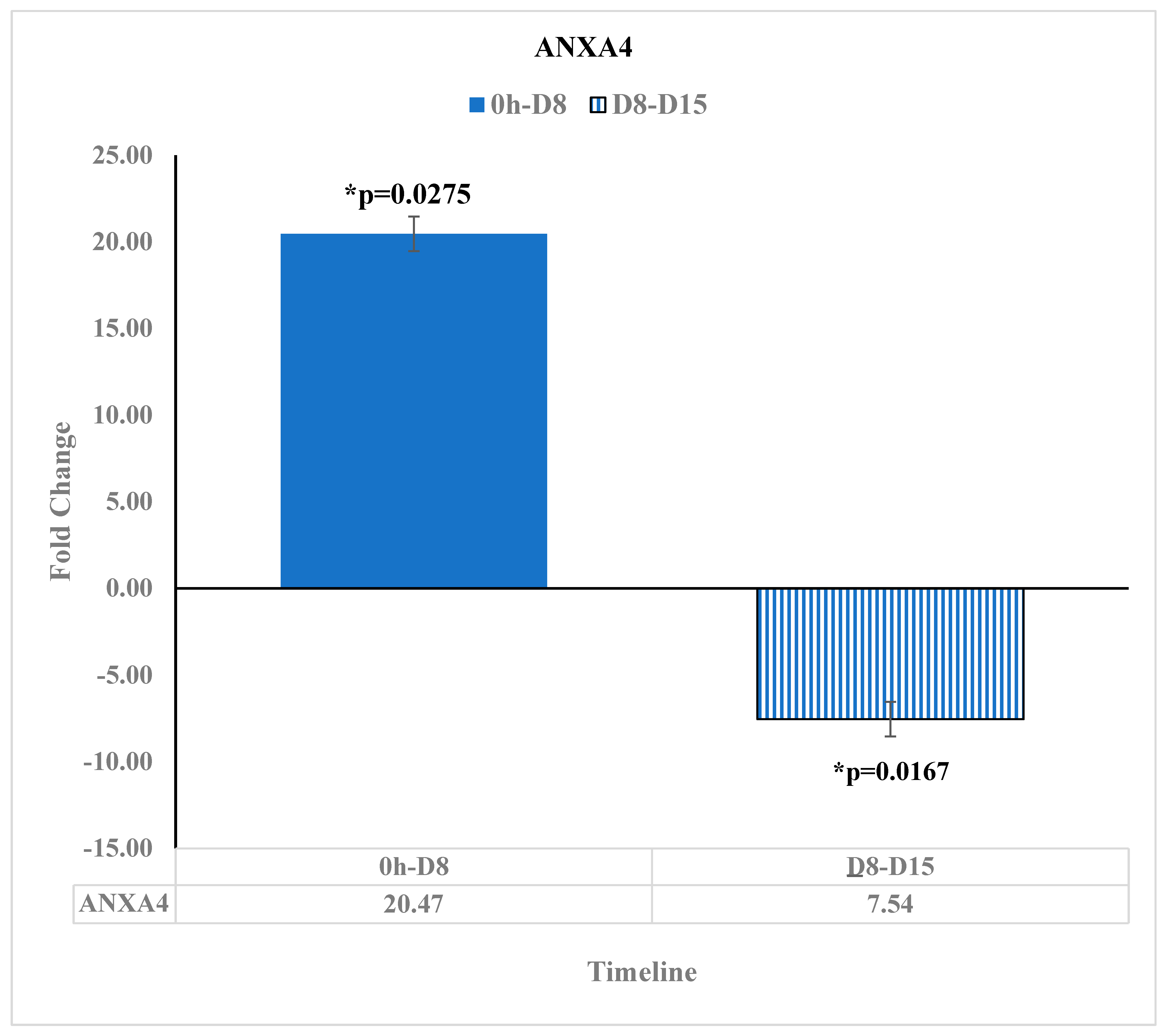
3.6. ANXA4 Is Downregulated at Day 15 after the Reovirus Administration
3.7. Tumor Suppressor Protocadherin 9 (PCDH9) Transcript Was Upregulated at Day 15 after Reovirus Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mattick, J.S.; IMakunin, V. Non-coding RNA. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, R17–R29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattick, J.S. Challenging the dogma: The hidden layer of non-protein-coding RNAs in complex organisms. Bioessays 2003, 25, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Yang, S.; Hong, F. Role of noncoding RNAs and untranslated regions in cancer: A review. Medicine 2022, 101, e30045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfarlane, L.A.; Murphy, P.R. MicroRNA: Biogenesis, Function and Role in Cancer. Curr. Genom. 2010, 11, 537–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Croce, C.M. The role of MicroRNAs in human cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2016, 1, 15004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinu, D.; Dobre, M.; Panaitescu, E.; Bîrlă, R.; Iosif, C.; Hoara, P.; Caragui, A.; Boeriu, M.; Constantinoiu, S.; Ardeleanu, C. Prognostic significance of KRAS gene mutations in colorectal cancer—Preliminary study. J. Med. Life 2014, 7, 581–587. [Google Scholar]
- Maitra, R.; Seetharam, R.; Tesfa, L.; Augustine, T.A.; Klampfer, L.; Coffey, M.C.; Mariadason, J.M.; Goel, S. Oncolytic reovirus preferentially induces apoptosis in KRAS mutant colorectal cancer cells, and synergizes with irinotecan. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 2807–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogel, E.J.; Samouha, A.; Goel, S.; Maitra, R. Transcriptome Signature of Immune Cells Post Reovirus Treatment in KRAS Mutated Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 6743–6754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, D.; Helson, E.; Gujar, S.A.; Lee, P.W. Reovirus in cancer therapy: An evidence-based review. Oncolytic Virother. 2014, 3, 69–82. [Google Scholar]
- Jiffry, J.; Thavornwatanayong, T.; Rao, D.; Fogel, E.J.; Saytoo, D.; Nahata, R.; Guzik, H.; Chaudhary, I.; Augustine, T.; Goel, S.; et al. Oncolytic Reovirus (pelareorep) Induces Autophagy in KRAS-mutated Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 865–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parakrama, R.; Fogel, E.; Chandy, C.; Augustine, T.; Coffey, M.; Tesfa, L.; Goel, S.; Maitra, R. Immune characterization of metastatic colorectal cancer patients post reovirus administration. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, S.; Ocean, A.J.; Parakrama, R.Y.; Ghalib, M.H.; Chaudhary, I.; Shah, U.; Viswanathan, S.; Kharkwal, H.; Coffey, M.; Maitra, R. Elucidation of Pelareorep Pharmacodynamics in A Phase I Trial in Patients with KRAS-Mutated Colorectal Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2020, 19, 1148–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berti, F.C.B.; Mathias, C.; Garcia, L.E.; Gradia, D.F.; de Araújo-Souza, P.S.; Cipolla, G.A.; de Oliveira, J.C.; Malheiros, D. Comprehensive analysis of ceRNA networks in HPV16- and HPV18-mediated cervical cancers reveals XIST as a pivotal competing endogenous RNA. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2021, 1867, 166172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Z.; Mehrpour, M.; Hamaï, A.; Gong, C. Non-coding RNAs as new autophagy regulators in cancer progression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2022, 1868, 166293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, Z.; Tian, L.; Jiang, G.; Chen, F.; Li, J.; An, P.; Lu, L.; Luo, N.; et al. m(6)A-induced lncRNA RP11 triggers the dissemination of colorectal cancer cells via upregulation of Zeb1. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Wang, X.; Han, D.; Lu, E.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, L.; Yang, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Wu, J.; et al. A Six-lncRNA Signature for Immunophenotype Prediction of Glioblastoma Multiforme. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 604655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, B.; Li, F.; Chen, M.; Weng, Y.; Qi, C.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, H.; Zhang, J.; Gao, X. A panel of platelet-associated circulating long non-coding RNAs as potential biomarkers for colorectal cancer. Genomics 2022, 114, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Liao, W.; Xu, N.; Li, B.; Liu, F.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, D.; et al. LncRNA EPB41L4A-AS1 regulates glycolysis and glutaminolysis by mediating nucleolar translocation of HDAC2. EBioMedicine 2019, 41, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Venneti, S.; Nagrath, D. Glutaminolysis: A Hallmark of Cancer Metabolism. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 19, 163–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Song, X.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, S. Long non-coding small nucleolar RNA host genes in digestive cancers. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 7693–7704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, L.; Zhang, Y. miR-4461 Regulates the Proliferation and Metastasis of Ovarian Cancer Cells and Cisplatin Resistance. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 614035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consortium, A.P.G. AACR Project GENIE: Powering Precision Medicine through an International Consortium. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 818–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Ai, B.; Kong, X.; Wang, X.; Qi, Y.; Wang, Z.; Fang, Y.; Wang, J. JAK2 expression is correlated with the molecular and clinical features of breast cancer as a favorable prognostic factor. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 90, 107186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, B.; Guo, C.; Liu, S.; Sun, M.-Z. Annexin A4 and cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 447, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Zhu, P.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Lu, F.; Yu, Z.; Liu, S. PCDH9 acts as a tumor suppressor inducing tumor cell arrest at G0/G1 phase and is frequently methylated in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 4475–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Noncoding RNA, Small RNA, and microRNA That May Impact Colorectal Cancer Progression—p-Values Shown | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RNA Type | Fold Change | ||||||||
| ncRNA | 0 h/48 h | p-Value | 0 h/D8 | p-Value | 48 h/D8 | p-Value | D8/D15 | p-Value | |
| RP11-332M2.1 | −6.1 | * 0.0124 | -- | -- | 6.7 | * 0.0013 | -- | -- | |
| EPB41L4A-AS1 | −6.43 | * 0.036 | -- | -- | 11.99 | * 0.0439 | -- | -- | |
| JAK2 | 2.2 | * 0.0071 | -- | -- | −2.23 | * 0.0036 | -- | -- | |
| LINC01506 | −16.18 | * 0.0034 | -- | -- | 7.49 | * 0.0254 | -- | -- | |
| LINC00534 | −1.94 | * 0.0045 | -- | -- | 3.39 | * 0.0003 | -- | -- | |
| ANXA4 | -- | -- | 20.47 | * 0.0275 | -- | -- | −7.54 | * 0.0167 | |
| PCDH9 | -- | -- | −2.09 | * 0.0469 | -- | -- | 1.82 | * 0.038 | |
| snRNA | |||||||||
| SNORA26 | 2.01 | * 0.0265 | −1.59 | * 0.0111 | −1.75 | * 0.0009 | -- | -- | |
| miRNA | |||||||||
| MIR-4461 | -- | -- | 6.18 | * 0.0216 | -- | -- | −3.76 | * 0.0113 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saperstein, R.; Goel, S.; Maitra, R. Noncoding RNA Profile in Reovirus Treated KRAS-Mutated Colorectal Cancer Patients. Diseases 2023, 11, 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases11040142
Saperstein R, Goel S, Maitra R. Noncoding RNA Profile in Reovirus Treated KRAS-Mutated Colorectal Cancer Patients. Diseases. 2023; 11(4):142. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases11040142
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaperstein, Rafael, Sanjay Goel, and Radhashree Maitra. 2023. "Noncoding RNA Profile in Reovirus Treated KRAS-Mutated Colorectal Cancer Patients" Diseases 11, no. 4: 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases11040142
APA StyleSaperstein, R., Goel, S., & Maitra, R. (2023). Noncoding RNA Profile in Reovirus Treated KRAS-Mutated Colorectal Cancer Patients. Diseases, 11(4), 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases11040142







