1. Introduction
Operability, maintainability, and network addressing issues in the legacy IPv4 networks are being investigated with the emergence of next-generation networking paradigms like software-defined networking (SDN) and Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) [
1]. The network addressing and routing issues are being undertaken by IPv6-enabled networking, while the operational complexities of the vertically integrated legacy network can be minimized by the implementation of SDN. IPv6 and the SDN are not backward-compatible, leading to complexities and challenges in the real-time migration of the legacy IPv4 networking system, which is currently operating world-wide. Network migration is inevitable for service providers, though there have been several challenges with migration from the technical, financial, as well as business perspectives [
2]. The higher costs of network migration to replace or upgrade network devices, transformations in software systems and related services, along with a lack of skilled human resources to operate and maintain the newer networking systems are becoming the major hurdles of technology migration in service provider networks.
Internet service provider (ISP) networks consist of multiple autonomous systems, and are generally heterogeneous in nature. Hence, multi-domain heterogeneous network migration planning is a challenge. The solution of IPv4 address depletion was devised more than three decades ago in the 1990s with the introduction of IPv6 addressing, also termed as “IP next generation (IPng)” [
3]. However, the global IPv6 adoption rate is not satisfactory [
4]; it has just crossed 25% adoption worldwide, while the adoption rate in developing countries is still below 1% [
5]. The early stage of IPv6 network migration and the premature stage of SDN migration [
2,
5] in telecommunications (Telcos) and ISP networks indicate that sufficient efforts in the research and development of SDN and IPv6 network migration are needed. IPv6 and SDN are interrelated, because IPv6 deals with routing and addressing in the IP layer, while SDN deals with the controlling of the operations of the networking management layer. IPv6 avoids the IPv4 routing and addressing issues, while SDN avoids the management and controlling issues of legacy networks. These two networking paradigms, which are recognized in the network operation layer, are operated by service providers. Hence, in our previous works, we introduced a joint SDN and IPv6 network as an SDN-enabled IPv6 network called the software-defined IPv6 (SoDIP6) network, with its benefits and challenges for efficient migration planning [
1,
2,
6]. Combining the features of IPv6 and SDN creates more robust networks. Those combined features [
2] are more attractive for service providers for the timely migration of their legacy networks. For migration cost reduction with optimization of the capital and operational expenditures (CapEX and OpEX), the joint migration planning of SDN and the IPv6 network is beneficial for service providers [
7].
Well-defined migration methods, progressive migration scenarios, sufficient applications, and protocol standards are supportive for ISPs to take decisions for IPv6 migration, but there is still a lack of standards and applications towards bringing SDN implementation in ISP networks close to reality. However different transition techniques have been defined; dual-stack IPv6 and hybrid SDN approach [
8,
9] are the more appropriate solutions for smooth and gradual transition to IPv6 and SDN. The evaluation of production standards under Hybrid SDN require deep investigation.
With the implementation of multi-domain SoDIP6 networks for service providers, the controller placement problem during and after the migration is a major concern. Increasing the number of SDN switches during migration affects the controller capacity. To address the problem of increasing control traffic with the increase of SDN switches, a suitable approach is needed to locate the controller and add other controllers in the network for load balancing. In this article, we implement the incremental transition of a legacy network into a SoDIP6 network by performing experimental tests and simulations to measure the viability of the real production of an SDN-enabled IPv6 network in service provider networks by implementing Open Network Operating System (ONOS) and SDN-IP, the recently emerging robust networking platform for SDN migration. SDN-IP is an application developed and implemented over ONOS to integrate SDN and legacy networks in terms of routing and interoperability so that service providers can have a gradual migration by smoothly integrating SDN with the legacy networks. SDN-IP implements border gateway protocol (BGP) for communications among multiple autonomous systems (ASes), as with BGP implemented in legacy routing. BGP speakers help to establish the peering with external gateway routers by obtaining route information from the ONOS SDN controller. We propose a heuristic for the best ONOS controller location and routers migration in real time considering optimal path routing and optimal control path latency. Following are the major contributions of this work.
A study on the viable implementation of multi-domain SoDIP6 networks is carried out.
The incremental deployment of an SDN-enabled IPv6 network using ONOS/SDN-IP is implemented.
A solution for controller placement based on control path latency is presented using a breadth-first router replacement (BFR) approach for router migration planning during the migration of carrier-grade service provider networks.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows.
Section 2 presents the related work in hybrid-SDN migration methods and practices.
Section 3 briefly presents the concepts of ONOS and SDN-IP.
Section 4 proposes methodology for multi-domain SoDIP6 network implementation. We present a network use-case for SoDIP6 network implementation, simulations and experimental tests/analysis, and evaluations in
Section 5.
Section 6 provides a summative discussion and future work, while the paper is concluded in
Section 7.
2. Related Work
The higher costs of CapEX and OpEX investments with technical human resources (HR) development are the major hindrance for ISPs trying to implement technology migration. There are also certain implementation challenges with respect to management, availability of technological standards, and user interface provision while providing new technology-based services to customers during and after the network migration [
1,
10]. The replacement of existing networking devices or their hardware/firmware upgrades are the only options for network migration. For the optimization of migration cost, the upgrade of network devices is economically feasible compared to replacement. We presented an approach for network migration planning with migration cost optimization via simulations and empirical analysis in our previous works [
2,
7,
11], where we focused on skilled HR management, technical issues like hardware/software standards and protocols, and managerial issues like proper scheduling and migration planning for network upgrades.
SDN migration in Telcos/ISP networks is a central research focus; however, there are few contributory works attempting to provide the paths for the real-time transition of legacy networks into SDN. The article [
10], however, is not concerned with the legacy network migration to SDN; an example use case is well-discussed regarding cost-effective virtual private network service provisioning over an SDN-based federated network with challenges and solutions in providing services over an SDN environment.
HARMLESS [
8] is an approach that simply patches the OpenFlow soft-switch over the conventional Ethernet switching devices. It is encouraged for the cost-effective deployment of SDN in an enterprise network. For the fairly sustained service providers, those legacy switches that are identified as capable based on their performance for high-speed communication can be upgraded to SDN switches using the HARMLESS concept. This supports incremental deployment towards an SDN mixed network as a part of hybrid/SDN deployment. However, from the overall network operation perspective during migration, the interoperability between legacy IP routing devices and upgraded SDN switches has not been ensured.
OSHI [
12] is a prototype developed to integrate legacy IP routers with SDN switches in ISP backbone networks. This concept emerged with the operation of dual-stack SDN devices like those of dual-stack IPv6 networking, in which the hybrid IP/SDN node performs legacy routing as well as data plane forwarding.
Panopticon [
13] is an another proposed approach for the incremental deployment of SDN in the legacy networks. It makes it possible to have logical SDN control ports in the legacy switch. Conceptually, the SDN switch residing in the legacy networks can act as a VLAN gateway to bridge communication between legacy devices or create tunnels between legacy switches through the SDN switches in the path. This appears to have a separate protocol that the author has conceptually realized in order to manage this implementation in data plane devices. The implementation of this approach in carrier-grade ISP networks is fairly complex, and its real implementation in production networks is not known.
RouteFlow [
14] is a concept that simply mimics the legacy routing operations to ease the gradual migration of legacy ISP networks into SDN by implementing a RouteFlow (RF) server above the SDN controller. A mapping of an SDN network is done in the virtual environment and emulates legacy routing. The RF server provides the routing information to the SDN controller to install flow rules in the SDN network for proper routing. RouteFlow is still not close to a real-life implementation, which needs additional measures to fix the issues related to performance and operational complexities.
Fibbing [
15] is an approach that attempts to abstract the distributed routing into centralized control in order to implement the features defined by SDN. The legacy networks running legacy routing protocols like OSPF, IS-IS, and BGP are fully distributed. Fibbing extracts the forwarding information base of the legacy routing engine and transforms it to centralized control so that the scalability and programmability features of the centralized controller can be achieved. While Fibbing is claimed to have programmability features and to be easy to deploy, to our best knowledge, its implementation in production networks is not known. Different hybrid SDN implementation approaches are summarized in
Table 1.
3. SDN-IP Overview
SDN-IP is an application developed to implement routing between SDN and legacy networks [
22]. It enables communication over a multi-autonomous system (multi-AS) within the SDN and legacy networks.
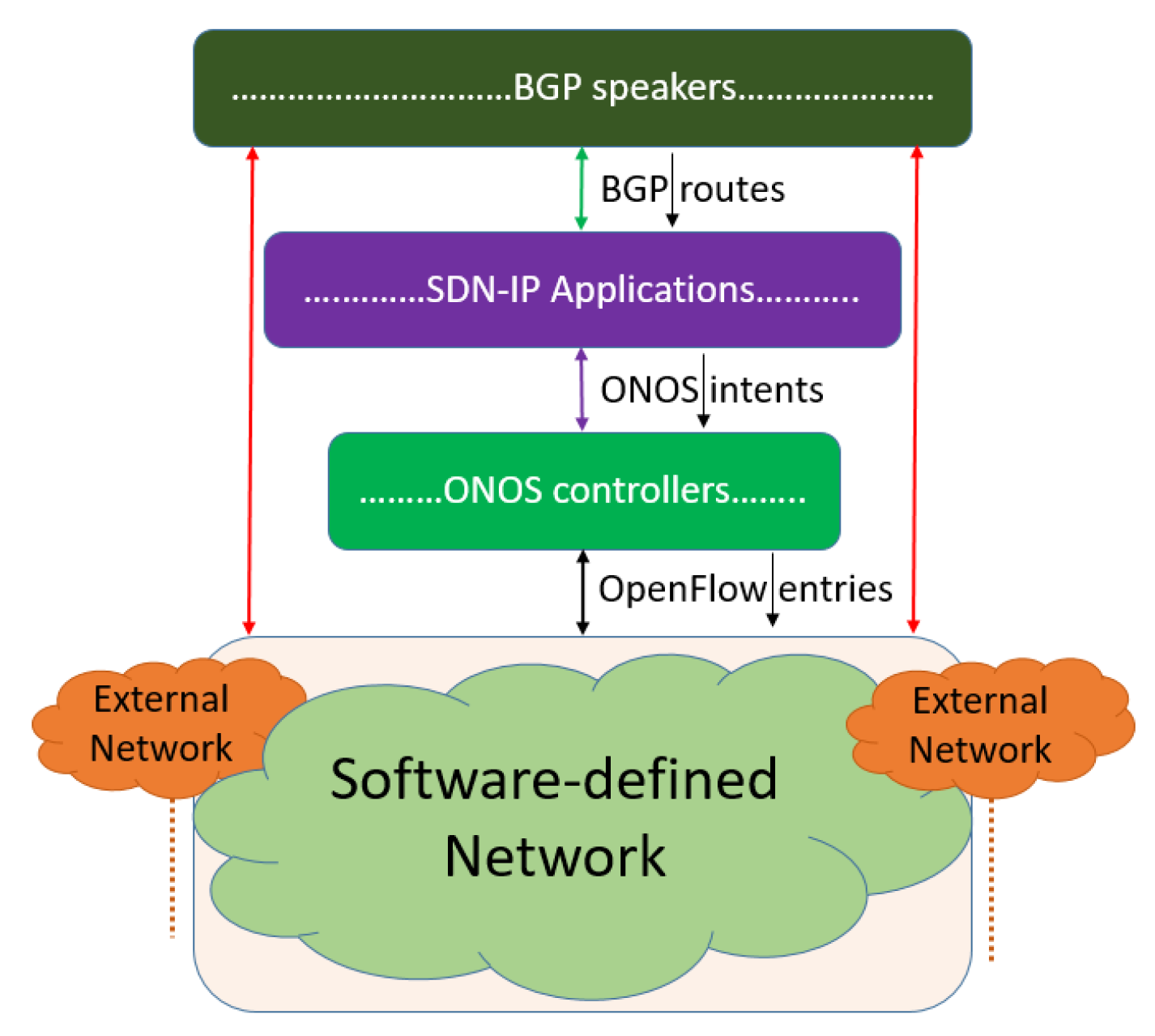
Figure 1 depicts the overall architecture of ONOS/SDN-IP implementation [
23]. The architecture supports the multiple instances in the distributed cluster of BGP speakers, SDN-IPs, and ONOS for robust operation and load balancing. SDN-IP is implemented as an API over ONOS, a robust and distributed network control plane operating system developed for carrier-grade SDN implementation in the ISP/Telcos networks. SDN-IP transforms BGP peering sessions between BGP speaker and external gateway routers into intents to establish point-to-point and multi-point-to-multi/single-point communications. Single-point-to-single-point intents are used to establish peering between BGP speaker and external gateway routers via two attachment points containing details about attached switch ports, data-path identification (DPID), and MAC addresses of the attached BGP speaker and external gateway routers [
24]. ONOS then translates those intents into a forwarding rule to be deployed over SDN switches [
25]. Operational flexibility, compatibility, scalability, high availability, and vendor neutrality are the major features of SDN-IP [
23].
SDN-IP enables service providers to conduct the greenfield deployment of SDN in an AS, and communicates with legacy networks. Additionally, it treats the SDN network as an autonomous transit network so that multiple legacy networks attached to the SDN network can communicate with each other by translating BGP routes into ONOS application intent requests, while ONOS translates those intent requests into forwarding rules to deploy to the data plane devices to establish communication with external networks. The fair communication mechanisms developed between SDN switches and the legacy routers in the hybrid network enables the gradual migration of the legacy network into SDN. The network under migration as a whole becomes a hybrid network so that normal traffic and control traffic load balancing as well as failure handling during the migration have to be carefully designed. ONOS considers multiple instances, having its flexibility and scalability features in the distributed clustered environment, allowing multiple instances of SDN-IP and BGP speakers to consider efficient traffic load management. Increasing the number of SDN data plane devices during incremental deployment increases the control traffic between the controller and the SDN switches. Additionally, when attached with SDN switches, the legacy BGP routers reroute the BGP routing traffic to the SDN BGP speaker. During the migration, at some points, increasing SDN switches will increase internal BGP (iBGP) peers, leading to higher control traffic to the BGP speaker, which ultimately increases the intent calculation and flow-rule processing load of ONOS.
From
Table 1, it seems that ONOS/SDN-IP implementation in ISP network migration comes to reality. So, we can plan for smooth migration of legacy networks into SoDIP6 networks with the consideration of controller placement and traffic engineering. Hence, in this article, we consider shortest-path routers migration and identify the best location for controller placement with its instance creation for control traffic load balancing through the selection of median point router by implementing the ONOS/SDN-IP platform for network migration.
The controller is the heart of the SDN, in which propagation delay, controller and switch latency, resiliency, and quality of service are the major and most sensitive parameters to be considered to have minimum flow setup time in SDN. The number of controllers required to be assigned to switches and their proper placement in SDN play an important role in achieving considerable flow setup time with better fault handling and effective controller load balancing [
26]. Sufficient studies [
26,
27,
28,
29,
30] using different techniques are available regarding the controller placement in pure SDN [
26,
27]. One of our concerns in this study was to find a proper location for a master controller during carrier-grade service provider network migration. Das T. et al. [
31] presented resilient controllers placement in a hybrid SDN/legacy network, and achieved a better result by comparing with existing controller placement strategies in the pure SDN. For the controller fault handling and resiliency in SoDIP6 networks, this approach can be applied to add other controllers after locating the master controller in the SoDIP6 networks during and after migration.
4. Proposed Method and Problem Formulations
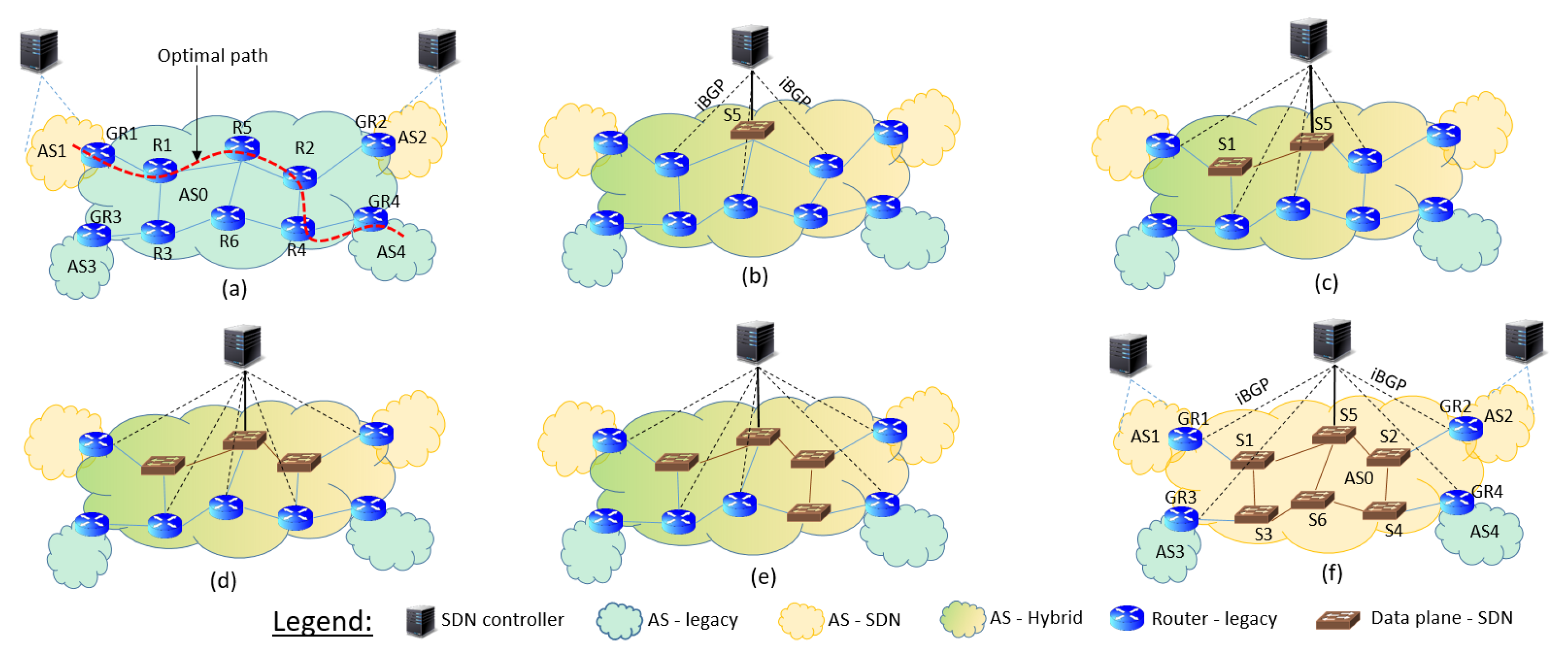
Figure 2 presents the glimpses of the migration of a starting network (
Figure 2a) to the target network (
Figure 2f). We assume that the ISP network initially consists of multiple autonomous domains, in which few ASes (e.g., AS1 and AS2) are already SoDIP6 capable and other ASes (AS0, AS2, and AS3) are still running with legacy IPv4. AS0 is considered as a transit AS running the legacy IPv4 network. It is interconnected with other ASes. The purpose of this study is that the transit AS has to be smoothly migrated to the SoDIP6 network and run the multi-domain SoDIP6 networks with its legacy network integration. We consider that gateway router 4 (GR4) in
Figure 2a is the foreign transit gateway. Following our previous work [
7], we consider the choice of shortest path (SP) from the customer endpoint router to a foreign gateway for router replacement. In the beginning, it looks like a transit network migration, and we consider AS0 as a transit AS; however, this approach is applicable to any other ASes having multiple customer gateways (CGs) attached to it. For example, AS3 in
Figure 2a is a legacy IPv4 network, where we suppose that services are provided to customers via multiple CGs attached with AS3, and then gateway router GR3 can be considered as the FG. We start the longest span shortest path (LSSP) between CG and FG for the migration.
- LSSP:
The shortest path consisting of the highest number of nodes between source and destination among the set of other shortest paths obtained from different CGs to a FG is defined as the longest span shortest path (LSSP).
The gateway routers GR1, GR2, and GR3 are treated as CG routers, while GR4 is the FG router. During migration, AS0 becomes a hybrid SDN with dual-stack IPv6 operation. We consider minimum control path latency (MCPL) between switch–controller communications. MCPL provides the propagation latency in terms of control communication between the switch and the controller.
- MCPL:
The shortest path from switch to controller with minimum propagation delay for control communication is termed as the minimum control path, and the propagation latency over the minimum control path is termed as minimum control path latency (MCPL).
The propagation latency and the controller processing capacity [
32] are the two major driving parameters that need to be considered for the suitable placement of controllers to achieve better control communications in the SDN. To achieve this, a median router in the LSSP is selected for controller attachment. The migration sequence of other routers in the shortest path is generated using breadth-first traversal (BFT) after finding the median router as a starting point for traversal.
Figure 2f is an example of a multi-domain SoDIP6 network, in which AS0, AS1, and AS2 are SoDIP6-capable but AS3 and AS4 are still operating as legacy networks. Our proposed approach is domain specific for migration and controller placement. Hence, the remaining legacy ASes can be migrated following the same proposed approach.
Problem Formulations
This subsection presents the mathematical formulation of our proposed approach for migration modeling and controller placement. The fundamental requirement is that ONOS/SDN-IP should be directly connected with any one SDN switch for its operation. The first migrated switch is supposed to be the root source switch (RSS) that has a direct connection to the ONOS controller with a BGP speaker. The first router selected in the optimal path during migration is the RSS. The RSS is determined by the median router amongst the routers in the LSSP. The list of parameters used in the problem formulation of our proposed approach is defined in
Table 2.
The least cost path routers from source to destination are identified by Equation (
1). The shortest path is calculated using the well-known Dijkstra algorithm [
33].
The median router that is best suited to directly connect to the controller for control path latency optimization is determined by Equation (
2).
where “
n” is the number of routers in the shortest path. The sequence of routers to be migrated in the shortest path is identified using BFT, then only the routers which are not already migrated to switches are set into migration. The median router is migrated first, and then other routers are either upgraded or replaced using the BFT approach. Router replacement planning using the BFT approach is termed as the breadth-first router replacement (BFR) mechanism. Equation (
3) defines the median router replacement, while Equation (
4) defines the BFT on other router replacements in the shortest path. If we define a timestamp (
) of 6 months to be considered to migrate routers in the shortest paths, then the total time period for whole network migration depends on the size of the network.
The functions “
” in Equations (
3) and (
4) transform the legacy router into a SoDIP6-capable switch. Router migration means either upgrading the device hardware/firmware to make it compatible with SDN/IPv6 or replacing the device with a newer one that is already SoDIP6-capable. The details on router migration considering technical and budgetary constraints are discussed in our previous work [
7].
If customer endpoint router is originated from AS1, then the shortest path routers from GR1 to GR4 are (R1, R5, R2). To replace these routers into SoDIP6-capable switches, we drill the network in the sequence (GR1, R1, R2, GR4). However, whenever a router is replaced by an SDN switch, the network turns into hybrid SDN, and a controller should directly be attached with that switch to establish the communication as shown in
Figure 2b. In this drilling, router R5 is selected as the median router for migration. After router R5 is replaced to switch S5, it is now called the root source switch (RSS). All the traffic to be routed through the RSS is to be managed by the controller where iBGP peering sessions are to be established between switch gateway routers (R1, R6, R2) that are directly connected with switch S5. Multiple sessions with multiple paths as BGP multi-homing can be established between the BGP speaker and switch gateway routers (iBGP routers) of AS0, which ensures better failure handling.
The first established controller is the master controller, while other controllers will be established based on control traffic load in the future during the migration of other routers. Increasing the number of SDN switches increases the control path traffic, while iBGP peering traffic varies based on the number of routers attached with the switches. Hence, we consider two latencies: the control path latency (or propagation latency) due to SDN switches, and the gateway latency by iBGP peering gateway routers. We also consider that after finding the RSS, breadth-first routers are to be replaced/upgraded to SoDIP6-enabled switches in the hierarchy through BFT. In the shortest path, after finding the RSS, the routers are replaced in the sequence provided by BFT. Considering one branch migration via random or depth-first order creates control traffic imbalance in the network. Hence, our choice of BFT with median point router for migration help maintains the equilibrium in the control path traffic between switch–controller communications. BFT gives the best choice of control traffic load balancing if we slice or cluster the network into different segments for controller placement. The details about the choice of first shortest path, their router migration, and the situation of the network after the first SP routers’ migration are depicted in
Figure 3. We consider the selection of LSSP from the customer endpoint router to the foreign gateway router having the higher number of routers in its path as the first shortest path for migration. The steps to identify the LSSP are presented in Algorithm 1. The shortest paths are put into order from longest span to shortest span in terms of router numbers, and follow migration in the consequent next phases. Hence, among the available alternate shortest paths, SP2 is selected as the LSSP. In the subsequent migration phases, there might have the chances of some routers which were already migrated to switches in a previous migration. Hence, fewer routers in the path are set to be migrated in the subsequent migration phases. The stub routers or backup path routers, if not migrated in the all shortest paths migrations, will be migrated in the last phase.
The binding of the number of switches to the corresponding SDN controller depends on the traffic volume that a controller can process, and the requirement of minimum latency. One controller is generally sufficient to handle one AS in a multi-domain ISP network. However, the distance between the controller and switches matters such that the minimum round-trip latency is to be considered between controllers and switches [
34]. For fail-safe operation and controller load balancing, additional controllers can be attached to the east and west bounds of the master controller, with at least one backup controller. Finding the approach to locate additional controllers in a large network is not within the scope of this paper.
| Algorithm 1: Identify LSSP in the AS from network (V,E) |
![Electronics 09 01454 i001]() |
The average control path latency (
) [
34] due to “
n” number of switches between switch “
s” to controller “
c” is defined by Equation (
5):
Equation (
5) considers the minimum path cost (
) for the latency calculation. This average value can be considered a generalized value with respect to the number of switches in the network. Instead of averaging, we consider the actual propagation latency in the shortest path from the switch to the controller by considering the sum of hop-to-hop path cost as a control path latency. In an AS, legacy routing runs interior gateway routing protocols (e.g., Routing Information Protocol - RIP, Open Shortest Path First - OSPF). Based on the ONOS/SDN-IP implementation, any router when replaced with an SDN switch needs to configure directly attached routers with BGP, and establish an iBGP peering session with the BGP speaker. An automatic Python script enables BGP on those routers attached with the SDN switch; these are identified by Equation (
6).
The average iBGP peering traffic latency due to “
k” number of switch gateways is defined by Equation (
7).
Constraints to trigger controller addition is defined by Equation (
8).
Algorithm 1 identifies the LSSP in an AS of the network, while we implement the network migration and identify the controller location based on Algorithm 2. The simulation consists of several Python functions. The functions and their major tasks are summarized in the comments of the algorithm.
| Algorithm 2: Network migration implementation and controller placement with breadth-first router replacement (BFR) |
Data: Network topology , Customer gateway records
/* Load standard network data (net_data) as an AS (e.g., “Abilene”) having the number of vertexes “V” and edges “E” for network graph and also attached customer gateways (CGs). CG data-sets are available in Appendix A */
![Electronics 09 01454 i002]() |
5. Experimental Setup, Analysis and Evaluations
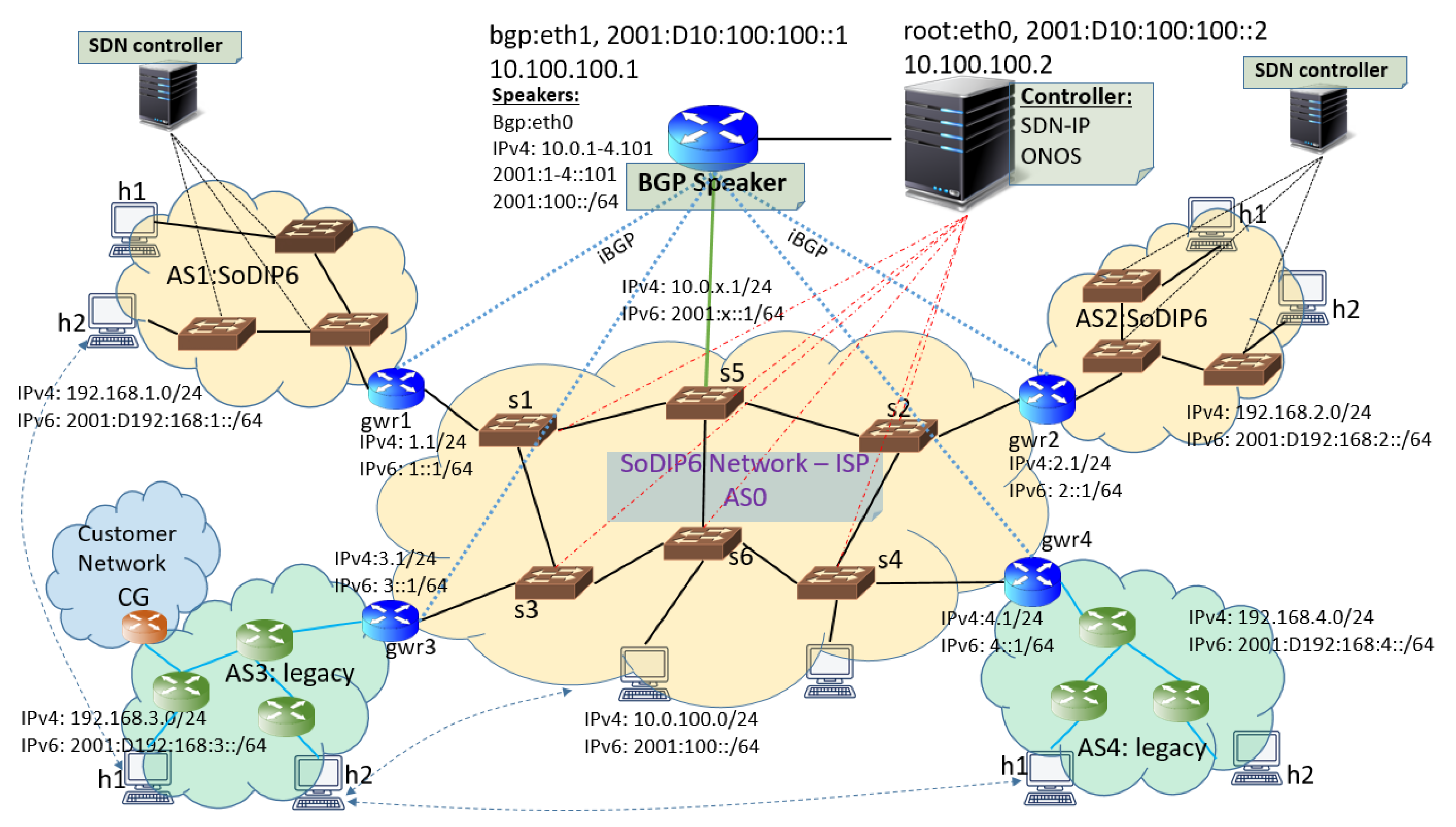
A complete multi-domain SoDIP6 network environment after following the migration was established as shown in
Figure 4. We considered AS0 migration in this work, while the proposed approach is also applicable for other ASes. For example, during AS0 migration, gwr1, gwr2, and gwr3 are considered as CGs, and gwr4 is the FG. Similarly, for AS3 migration, routers attached to customer endpoints are CGs, and gateway router “gr3” can be considered as the FG. Due to resource limits, for this particular experiment, we supposed that AS1, AS2, AS3, and AS4 had hosts h1, h2, h3, and h4 respectively and tested the communications among those hosts over a SoDIP6 network environment.
Figure 4 shows a complete dual-stack hybrid SoDIP6 network. Because every host and gateway is configured with dual-stack IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, it was implemented in the Mininet emulator running Ubuntu 14.04 virtual machine with ONOS/SDN-IP. The Quagga routing engine with Zebra daemon was enabled in the virtual machine, in which a separate instance of Zebra daemon was executed for each gateway to run the BGP daemon and follow the configuration details provided in ONOS/SDN-IP tutorial [
23] regarding importing network, host, and BGP configuration details. The link to access the simulation program code and network/BGP configuration details is provided in the
Supplementary Materials section of this article. The SDN-enabled dual-stack IPv6 network was implemented. The IPv6 address for a machine was generated using the mapping of the corresponding IPv4 address. For the six SDN switches in AS0, we ran a single instance of SDN-IP in the controller with a BGP speaker. All the gateway routers established iBGP peering sessions with the BGP speaker attached with the controller. The connectivity among the ASes, and hosts within the ASes, was successfully implemented. Similarly, reactive routing features enabled in the SDN-IP allowed for the communication among hosts from AS0 to hosts in the external ASes.
The successful implementation of this SoDIP6 network with the legacy network integration shows that bigger enterprise networks like ISPs and Telcos networks can be smoothly transitioned into operable SoDIP6 networks. Taking the reference of this use-case, we performed extensive simulations for migration implementation, and controller placement with standard network topology following the set of constraints formulated in
Section 4 with the Python NetworkX module as a network graph analysis. The proposed approach was implemented with Random, Abilene, Xeex and GEANT2009 networks downloaded from “Internet Topology Zoo” (
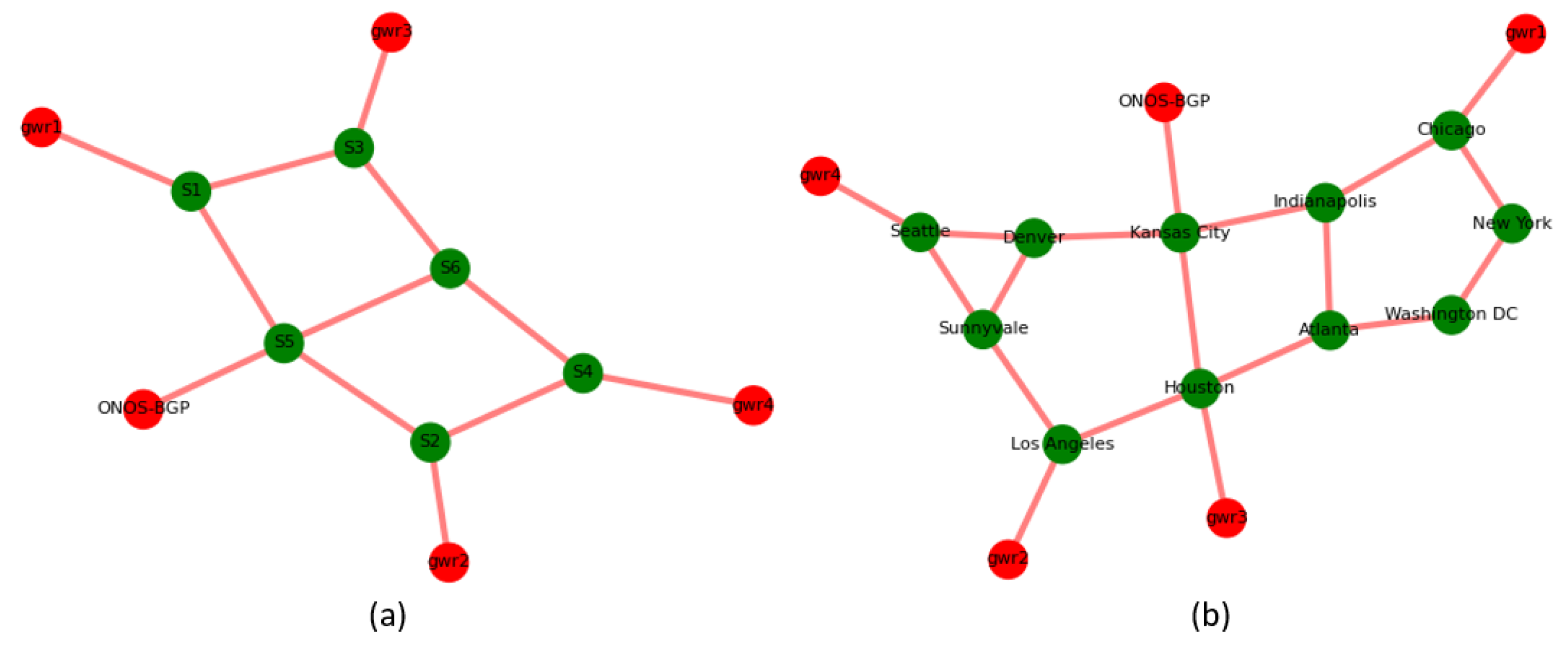
www.topology-zoo.org), while the output of Random and Abilene networks are presented in
Figure 5. For all networks, we ran simulations in two phases: (a) sequential replacement of routers from CG to FG with different RSS sets in the LSSP, (b) BFT to replace routers called BFR with different RSS sets in the LSSP. CG and FG routers were added after importing the network for simulations. For all networks, gwr4 was considered as the foreign gateway, while other gateways (gwr1–3) were considered as the AS gateways attached to the customer endpoints, recognized as CGs. Controller placement was defined based on the control path traffic latency by switches and the BGP-peers formed during migration. The green nodes in the figures are migrated, while red nodes are the gateway routers acting as iBGP peers with the ONOS-BGP speaker after migration. In
Figure 5a, the routers in the LSSP are identified as (S1, S5, S6, S4). Similarly, in
Figure 5b, the LSSP routers are [Chicago, Indianapolis, Kansas City, Denver, Seattle]. Hence, we simulated the network by setting those shortest path routers as RSSes and evaluated the switch and gateway latency to properly locate the controller.
The latency graphs depicted in
Figure 6a,b shows the latency status of switches and iBGP-peers in the random network without applying the BFR technique. Routers were migrated in a sequence ordering the shortest paths from the highest to lowest number of routers. Both graphs in
Figure 6 show that the controller connected to either S5 or S6 gave the MCPL value. During the switch migration, iBGP-peers automatically appear and disappear. After the complete migration of transit routers, only AS gateways acted as iBGP-peers. This can be seen from the control path latency by gateway routers, in which latency increased, reached the peak value, and then reduced to zero after complete migration. We avoided the control traffic due to AS gateways during migration since AS gateways are fixed and generate regular iBGP peering traffic after complete migration of all routers in the AS.
Figure 7 presents the latency by switches, and gateways after applying the BFR approach. From
Figure 7a, based on switch latency traffic, attaching the controller with S6 gave minimum latency, while gateway latency shows that setting S5 as RSS gave a slightly better result. The number of iBGP peers changes dynamically during the router migration. Hence, we considered the minimum latency generated by switches to take the decision for controller placement.
Figure 8 shows that application of the BFR technique yielded a better result than sequential replacement to attach the controller with S6. This is also clarified by the curve of the difference in latency value with and without BFR for switch S6, which shows the overall difference in the positive distribution during migration.
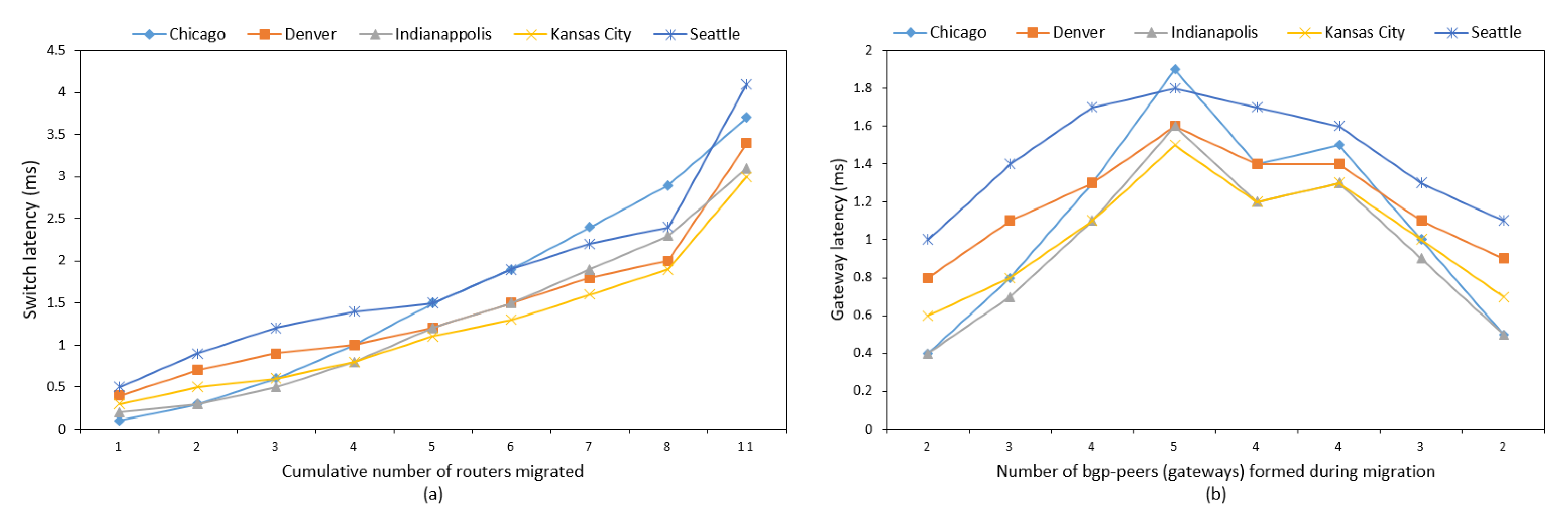
We ran another experiment with the standard Abilene network depicted in
Figure 5b. gwr4 was considered as the foreign gateway connected via “Seattle”. The LSSP was found to be from gwr1 to gwr4 via (Chicago, Indianapolis, Kansas City, Denver, Seattle).
Figure 9a,b shows the graphs of control path latency by SDN switches and gateways without using BFR, while
Figure 10a,b shows the same after using BFR. The latency plots in both figures indicate that attaching the controller with median router “Kansas City” gave the best result.
Choosing the optimal path for router replacement sometimes left the stub or backup link routers unmigrated. Those routers left unmigrated were set into migration in the final stage. For example, in
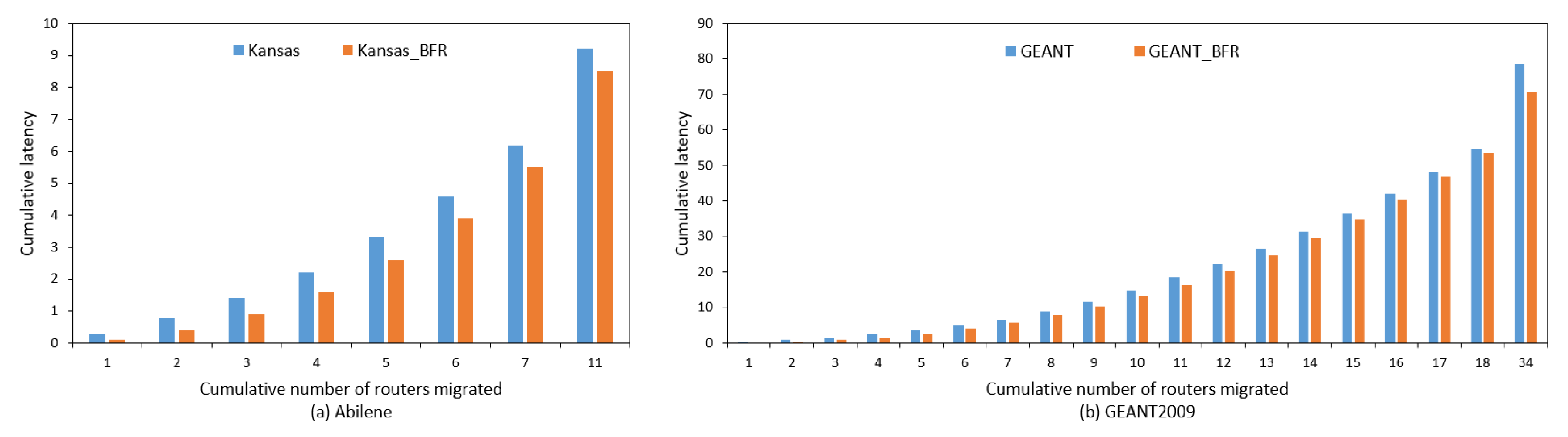
Figure 11, there are seven routers identified in the shortest path and four routers left unmigrated. Hence, these four routers were migrated in the final stage, making the cumulative number of migrated routers eleven.
Figure 11 presents the comparative chart of the latency plot with and without using BFR in the router migration of the Abilene network. Additionally, it shows the difference of latency value without and with using BFR for “Kansas City”, as the RSS has positive distribution. This shows that implementation of BFR approach gave the better result in attaching the controller with “Kansas City”. Based on our assumption of a hop-to-hop propagation latency of 0.1 ms, the maximum latency reported at the migration by switches was 3 ms and gateways was 1.5 ms for controller attachment with “Kansas City” using the BFR approach. However, our concern is the latency difference with and without using BFR to properly locate the master controller in the network. Details on latency evaluation with the ONOS controller are available at [
35].
Figure 12a,b presents the bar graphs of cumulative latency values for Abilene and GEANT2009 networks. Node “ESS” is identified as the RSS for the GEANT2009 network. This graph shows the lower cumulative latency value with BFR as compared with the cumulative latency without BFR for both Abilene and GEANT2009 networks.
Triggering Controller Addition during Network Migration
Once the location of the master controller was identified during the network migration, overloading of the master controller, while increasing the number of SDN switches in the network was continuously monitored.
Figure 13 presents the traffic load on the master controllers. Taking the reference from [
31], we assumed a number of OpenFlow requests (
) in the range of 0.05–0.105 million per second by an SDN switch, the request-handling capacity of controller (
) as 1.1 million requests per second, and 0.01–0.02 million iBGP peering session requests per second by iBGP (gateways) routers formed during migration.
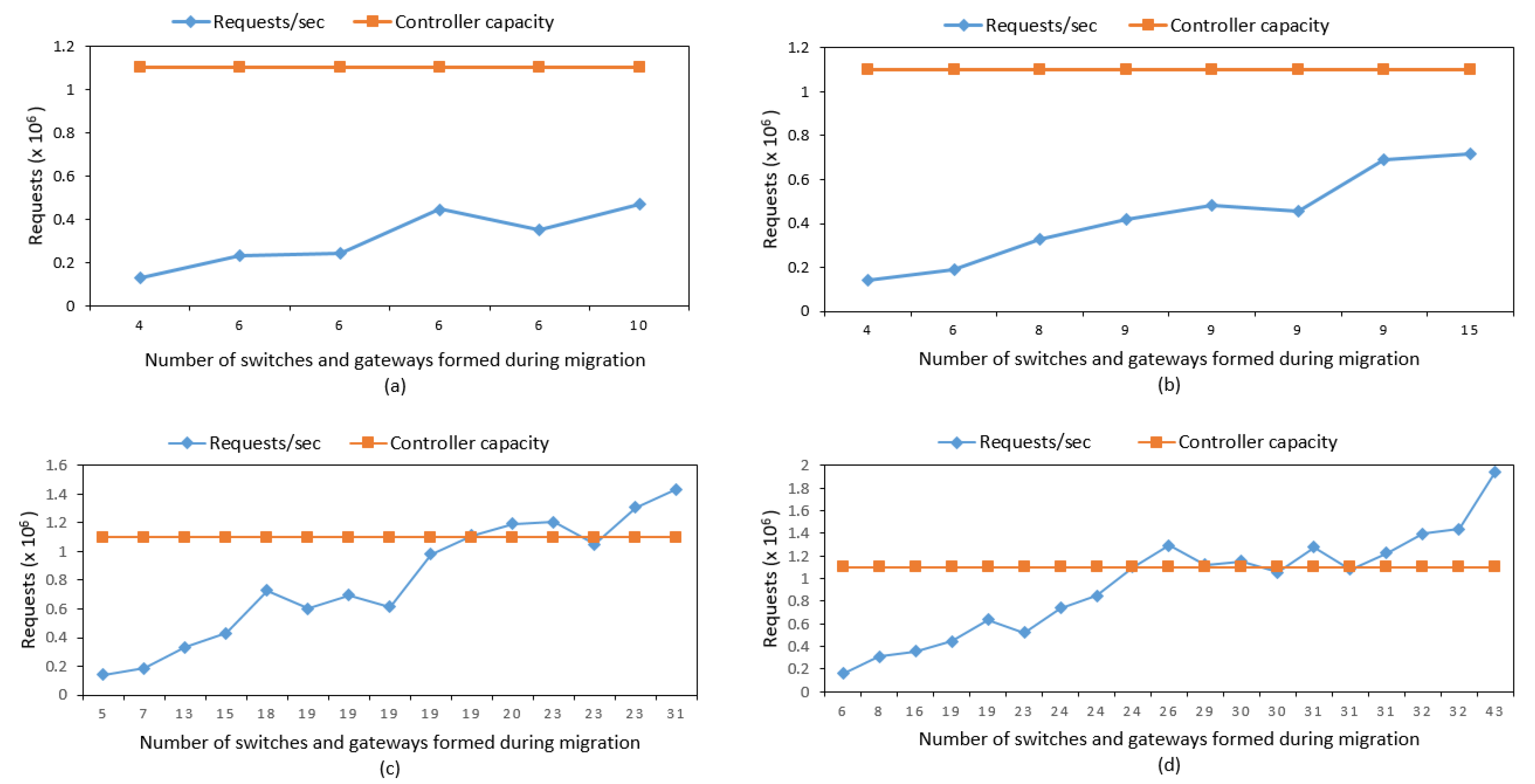
Figure 13a–d shows the number of requests made by switches and iBGP-peers (gateways) formed during migration in Random, Abilene, Xeex, and GEANT2009 networks, respectively. The horizontal axis of
Figure 13 shows the sum of the number of switches migrated and iBGP gateways formed during migration. Switches were set for incremental migration by one, while the number of gateways formed during migration increased or decreased based on the switch migration. Hence, in some steps of the migration, the same number of nodes migrated due to dynamically changing iBPG peers. We ran the experiment with two other networks (viz. Xeex and GEANT2009) to measure the controller overloading situation during migration. The Random network has six switches and four gateways. After migration, in total, 10 nodes generated control/iBGP traffic to the controller. Similarly, the Abilene network has 11 nodes and 4 gateways, and hence a total of 15 nodes generate control/iBGP traffic to the controller at the end of migration. Similarly, the same applies to Xeex and GEANT2009 networks. The decision to add a new controller is taken only if the number of requests by switches and gateways exceeds the controller capacity. For example, in
Figure 13c,d, the number of requests made by switches and gateways to the controller exceeded the controller capacity after a certain number of routers were migrated.
6. Discussion and Future Work
The paradigm shift in network operation and management using SDN creates concerns regarding the proper placement of the network control plane to optimize the control of communications between data plane devices and the controller. ONOS is a dedicated distributed network operating system developed to focus the implementation of SDN in carrier-grade service provider networks. Considering the smooth and incremental deployment of SDN, SDN-IP is an application which runs on top of ONOS to enable communications between SDN and legacy networks. Similarly, the future of smart networking is considered to lie with IPv6 addressing after the depletion of IPv4 addressing. In this paper, we implemented an SDN-enabled IPv6 network using ONOS/SDN-IP to enable communications among multiple ASes in the SoDIP6 network environment, and proposed a heuristic to identify the proper location of the master ONOS controller by considering optimal path routing and the minimum control path latency.
The southbound communication protocols in SDN (e.g., OpenFlow version 1.3 and beyond) support IPv6. With the migration of SDN, IPv6 addressing and routing implementations are preferable for the development of smart future networks so that all the issues of legacy networks can be avoided. Although the controller placement problem is the concern of SDN only, we considered IPv6 addressing and routing in order to encourage service providers to engage in effective joint migration planning and implementations to achieve the benefits of SoDIP6 networks.
There are certain limitations to our experiment. ONOS/SDN-IP still lacks dynamic and automatic network configurations for IPv6 addressing implementation in SDN. We first implemented the use case scenario presented in
Figure 4 in Mininet to verify the operation of multi-domain SoDIP6 networks with ONOS/SDN-IP implementation. Larger-size network migration implementation was not viable due to resource limits. Looking to
Figure 4, all the external gateways established peering with the BGP speaker, which acted as a passive speaker. A neighbor advertisement interval of 5 s was set per peer to avoid the BGP updates flooding. However, the BGP convergence time in this scenario was negligible, because external gateways had direct peering with the BGP speaker and hence, BGP updates were not propagated through the number of hops. However, for large networks with increasing BGP broadcast traffic, the BGP speaker will be a performance bottleneck. Similarly, intent calculation takes time for SDN-IP to translate intentions into flow rules and disseminate to the data plane devices. Hence, we considered proper location for controller placement with MCPL among the BGP speaker, external gateways, and switches. Fault and failure handling with the placement of other controller/BGP-speakers are not within the scope of this paper. We performed the simulation of routers migration and controller placement using Python programming with a NetworkX module for migration modeling and controller placement. The gateway routers as AS gateways or CGs were randomly attached to the network nodes. In reality, the changes of number of AS gateways affects the migration time, and the controller location might be changed.
The suitable placement of the SDN control plane is identified by considering the minimum control path latency using optimal path routing and BFR technique during the real-time migration of an existing legacy network into a SoDIP6 network. Our simulation results show that the BFR approach for controller placement and router migrations gave a better result than sequential router migrations in the optimal path. With the increasing number of routers migrated to SDN switches, the number of controllers required and their placement in SDN have major concerns. Several studies related to controller placement are related to pure SDN. We considered master controller placement in the incremental deployment of SoDIP6 networks over hybrid SDN/legacy networks. Defining the controller count during network migration depends upon the size of networks, consisting of the number of routers to be migrated. During the network migration, a (3+1) controller (three master/slave controllers and one backup controller) placement strategy is the reasonable starting point [
34], since latency is an important parameter in SDN for better quality of service. Because the controller provides the operational life to the data plane, in which the flow setup time is dependent on switch–controller communication latency, we considered latency in the optimal path (i.e., shortest path) as the optimal latency to take the decision regarding controller placement using BFR. Finding the optimal placement of other controllers is not within the scope of this paper. The placement of other master/slave ONOS controllers for proper load balancing and resiliency in large carrier-grade networks during migration using other optimization approaches will be considered as future works.