Single Inductor Multiple Output Auto-Buck-Boost DC–DC Converter with Error-Driven Randomized Control
Abstract
:1. Introduction
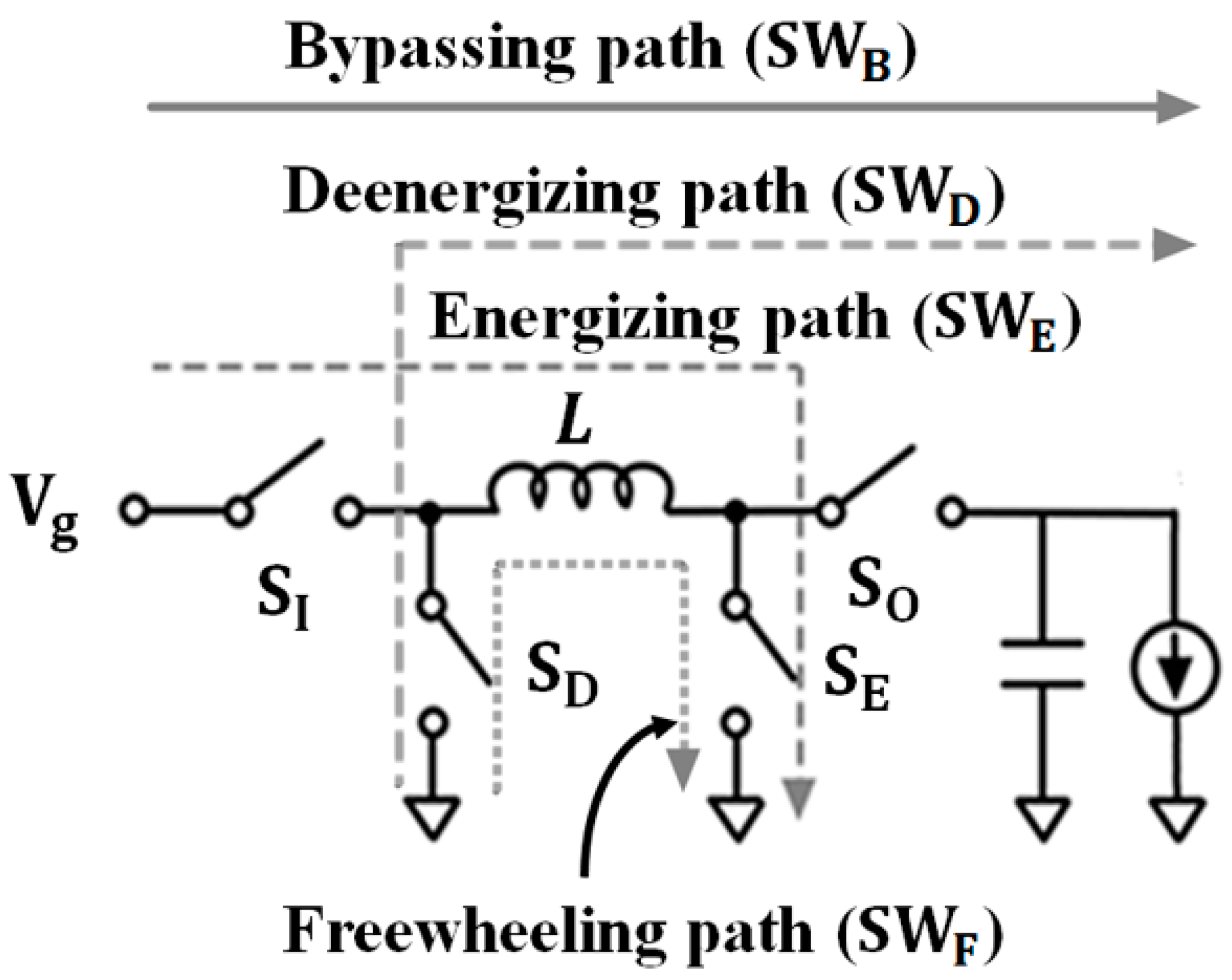
2. Proposed SIMO Architecture and Control Scheme
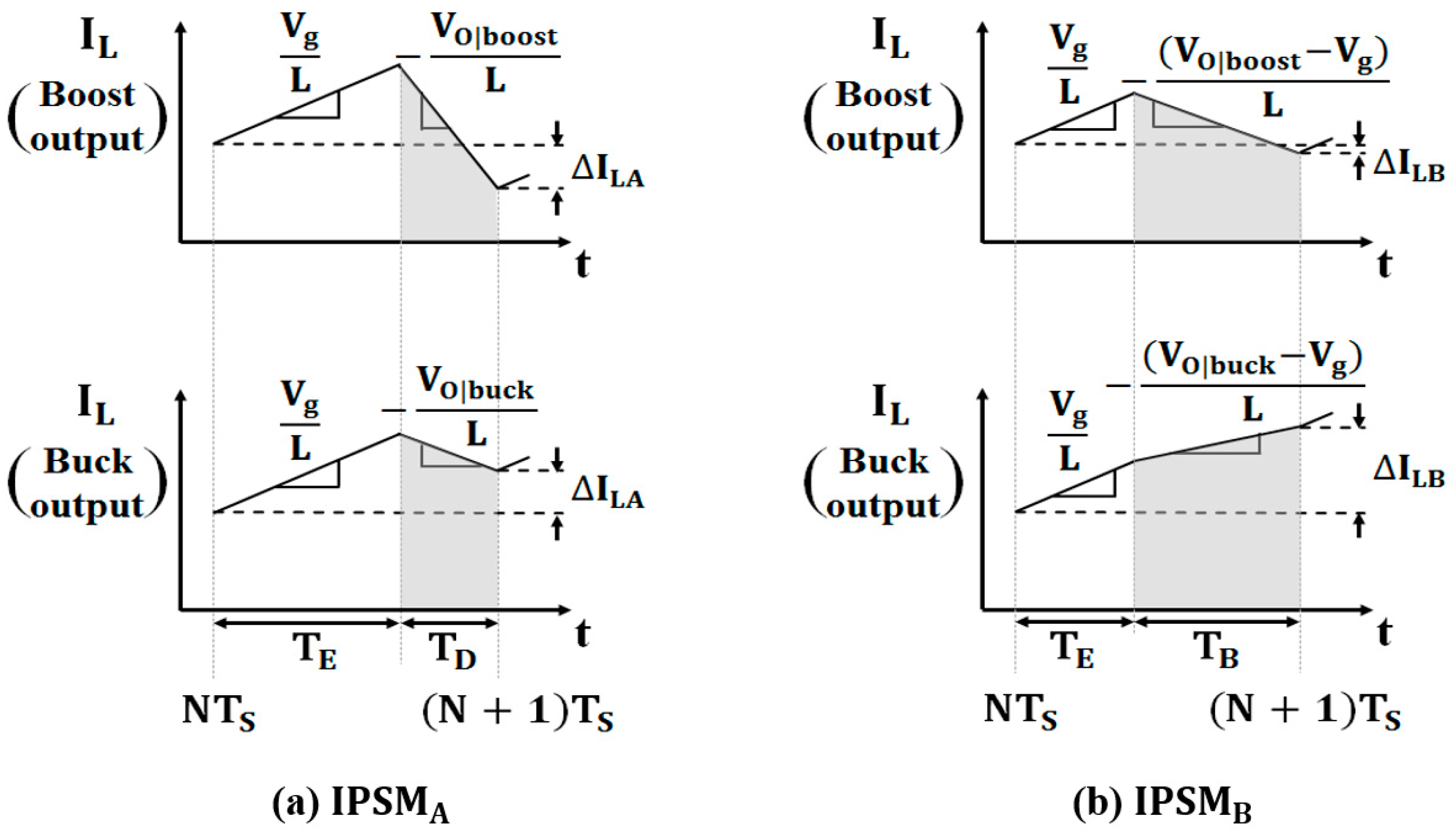
2.1. Error-driven Randomized Control (EDRC) for Auto Buck-Boost SIMO Converter
2.2. Condition Setting of Deep Boost
2.3. Architecture of the Proposed EDRC
3. Simulation Results
4. Experimental Results
5. Discussions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Ma, D.; Ki, W.H.; Tsui, C.Y.; Mok, P.K. Single-inductor multiple-output switching converters with time-multiplexing control in discontinuous conduction mode. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2003, 38, 89–100. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, D.; Ki, W.H.; Tsui, C.Y. A pseudo-CCM/DCM SIMO switching converter with freewheel switching. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2003, 38, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar]
- Koon, S.-C.; Lam, Y.-H.; Ki, W.-H. Integrated charge–control single-inductor dual-output step-up/step-down converter. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Kobe, Japan, 23–26 May 2005; pp. 3071–3074. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, J.; Leung, K.N. Digital-control single-inductor triple-output dc-dc converter with pre-sub-period inductor-current control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 2028–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, P.; Patra, A.; Misra, N. A single-inductor multiple-output switcher with simultaneous buck, boost, and inverted outputs. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 1936–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, H.-P.; Chae, C.-S.; Lee, K.-C.; Wang, S.-W.; Cho, G.-H.; Cho, G.-H. A single-inductor switching dc-dc converter with five outputs and ordered power-distributive control. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2007, 42, 2706–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, Y.; Le, H.-P.; Cho, G.-H.; Cho, G.-H. Load-independent control of switching DC-DC converters with freewheeling current feedback. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2008, 43, 2798–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, C.-S.; Le, H.-P.; Lee, K.-C.; Cho, G.-H.; Cho, G.-H. A single-inductor step-up DC-DC switching converter with bipolar outputs for active matrix OLED mobile display panels. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2009, 44, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.-H.; Huang, T.-C.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Chou, W.-S.; Chen, K.-H.; Huang, C.-C.; Lin, Y.-H. Minimized transient and steady-state cross regulation in 55-nm CMOS single-inductor dual-output (SIDO) step-down dc-dc converter. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2011, 46, 2488–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, D. Adaptive pseudo-continuous conduction mode operation schemes and circuit designs for single inductor multiple output switching converters. J. Analog Integr. Circ. Signal Process. 2012, 72, 419–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Chang, X.; Wang, W.; Tan, X.; Yan, N.; Min, H. Predictive digital current control of single-inductor multiple-output converters in CCM with low cross regulation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 1917–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, P.; Ghosh, J.; Patra, A. Control scheme for reduced cross regulation in single-inductor multiple-output dc-dc converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 5095–5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Qian, Y.; Hong, Z. An 87%-peak-efficiency DVS-capable single-inductor 4-output DC-DC buck converter with ripple-based adaptive off-time control. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference Digest of Technical Papers (ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 9–13 February 2014; pp. 82–84. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, M.Y.; Park, S.H.; Bang, J.S.; Cho, G.H. An error-based controlled single-inductor 10-output dc-dc buck converter with high efficiency under light load using adaptive pulse modulation. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2015, 50, 2825–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Li, Y.; Hong, Z.; Killat, D. A 90% peak efficiency single-inductor dual-output buck-boost converter with extended-PWM control. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 20–24 February 2011; pp. 394–396. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.; Zhou, G.; Liu, G.; Mao, G. Small-signal Modeling and Cross-regulation Suppressing for Current-mode Controlled Single-inductor Dual-output DC-DC Converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Yin, G. Cross-Regulation Suppression and Stability Analysis of Capacitor Current Ripple Controlled SIDO CCM Buck Converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 1770–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Ho, M.; Guo, J.; Leung, K.N. A single-inductor multiple-output auto-buck-boost dc-dc converter with tail-current control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 31, 7857–7875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Ho, M.; Guo, J.; Mak, K.-L.; Leung, K.N. A single-inductor multiple output auto-buck-boost dc-dc converter with autophase allocation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron 2015, 31, 2296–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Guo, J.; Leung, K.N. A Single-Inductor Multiple-Output Buck/Boost DC–DC Converter with Duty-Cycle and Control-Current Predictor. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 12022–12039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.L.; Chen, C.H.; Wu, K.C.; Ko, I.T. Design of an average-current mode noninverting buck-boost DC-DC converter with reduced switching and conduction losses. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 4934–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Ruan, X.; Cao, W.; Chen, P. A two-mode control scheme with input voltage feed-forward for the two-switch buck-boost DC-DC converter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 2037–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Khaligh, A.; Emadi, A. A compensation technique for smooth transitions in a noninverting buck-boost converter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2009, 24, 1002–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Erickson, R.W.; Maksimovic, D. AC equivalent circuit modeling. In Fundamentals of Power Electronics, 2nd ed.; Kluwer Academics: Secaucus, NJ, USA, 2001; pp. 187–263. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, X.; Mok, P.K.T.; Lee, M.C. A wide-load-range constant-charge-auto-hopping control single-inductor-dual-output boost regulator with minimized cross-regulation. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2011, 46, 2350–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ki, W.-H. Signal flow graph in loop gain analysis of DC-DC PWM CCM switching converters. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Fundam. Theory Appl. 1998, 45, 644–655. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.-C.; Bass, R.M. Eliminating the effects of the right-half plane zero in fixed frequency boost converters. In Proceedings of the PESC 98 Record. 29th Annual IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference, Fukuoka, Japan, 22 May 1998; pp. 362–366. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.J. Analysis of a Small-Signal Model of a PWM DC-DC Buck-Boost Converter in CCM. Master’s Thesis, Wright State University, Dayton, OH, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Linear Technology, LTC3536 Datasheet. Available online: https://www.analog.com/en/products/ltc3536.html (accessed on 18 August 2020).
- Sahu, B.; Rincon-Mora, G.A. A low voltage, dynamic, noninverting synchronous buck-boost converter for portable applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron 2004, 19, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Conditions Based on Comparison of Magnitude of Inputs | Output | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 () | ||
| 1 () | ||
| - | 1 () | |
| - | 0 () | |
| Number of Channels | 3 |
|---|---|
| Vg | 1~3.5 V (2 V nominal) |
| Vout1, Vout2, and Vout3 | 1.5 V, 2.5 V, 3.3 V |
| Switching frequency | 195 kHz |
| L(DCR) | 5.8 (5 m) |
| Cout1, Cout2, and Cout3(ESR) | 39 F (15 m) |
| 0.7 | |
| 19% |
| Ref [14] | Ref [18] | Ref [19] | Ref [20] | Present Work | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Published Year | 2015 | 2016 | 2016 | 2020 | - |
| Implementation | Discrete component | 0.35m CMOS | 0.35m CMOS | 0.35m CMOS | Discrete component |
| Input voltage (V) | 4.8 | 5 | 1.85–2.9 | 2.5 | 1.7– 3.4 |
| Number of outputs | 2 | 10 | 4 | 4 | 3 |
| Output voltages (V) | 3.3, 1.2 | 3.3 (3), 2.8 (2), 2.5 (2), 1.8 (3) | 3.3, 3, 2.5, 1.8 | 3.4, 3, 2.5, 1.8 | 3.3, 2.5, 1.5 |
| Switching frequency (MHz) | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.25 | 0.75~1 | 0.195 |
| Peak efficiency (%) | 78 | 88.7 | 89 | 89.5 | 91.2 |
| Light-load efficiency | 77%@0.11 W | 83.5%@0.14 W | 7%@0.2 W | 83%@0.15W | 85.5%@0.1 W |
| Auto-buck-boost | No | No | Yes | YES | Yes |
| Output driving capability (mA) | 100 | 185 | 110 | 300 | 277 |
| Load-regulation (mV/mA) | 1 | 0.17 | 2 | 0.56 | 0.27 |
| Cross-regulation (mV/mA) | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.67 | 0.05 | 0.042 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, H.; Kim, S. Single Inductor Multiple Output Auto-Buck-Boost DC–DC Converter with Error-Driven Randomized Control. Electronics 2020, 9, 1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9091335
Park H, Kim S. Single Inductor Multiple Output Auto-Buck-Boost DC–DC Converter with Error-Driven Randomized Control. Electronics. 2020; 9(9):1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9091335
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Hyunbin, and Shiho Kim. 2020. "Single Inductor Multiple Output Auto-Buck-Boost DC–DC Converter with Error-Driven Randomized Control" Electronics 9, no. 9: 1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9091335
APA StylePark, H., & Kim, S. (2020). Single Inductor Multiple Output Auto-Buck-Boost DC–DC Converter with Error-Driven Randomized Control. Electronics, 9(9), 1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9091335






