Smooth 3D Path Planning by Means of Multiobjective Optimization for Fixed-Wing UAVs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. MultiObjetive Optimization
2.2. 3D Curves for UAVs
3. Problem Definition
4. Methodology
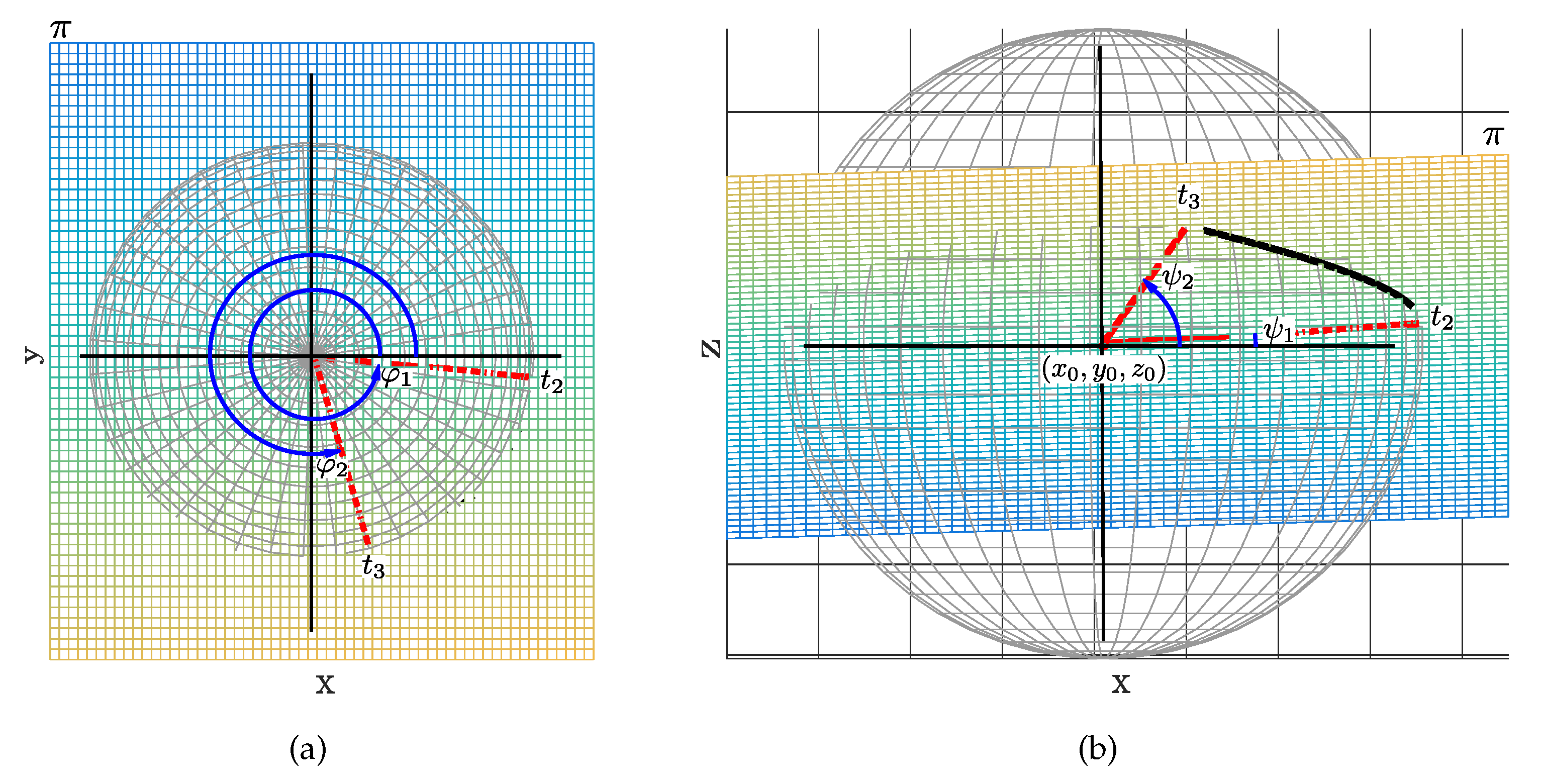
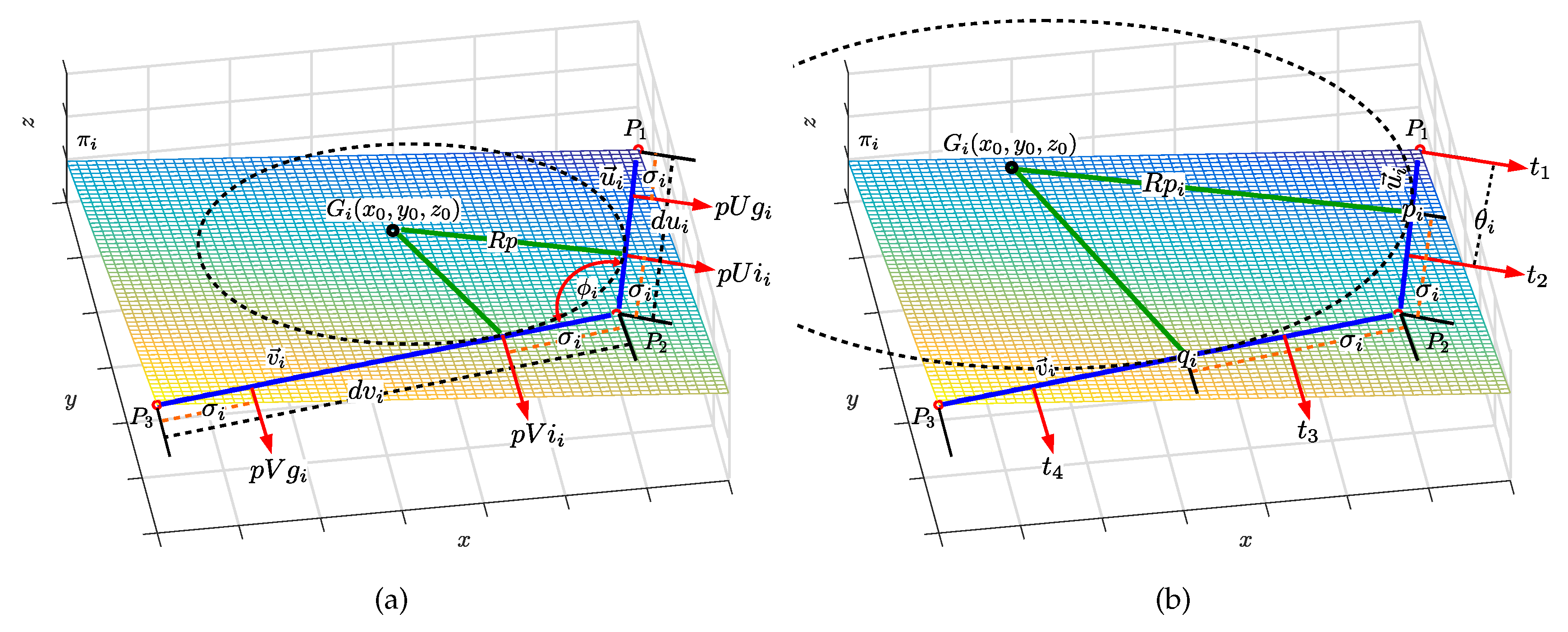
4.1. Definition of Spherical Segment
| Algorithm 1 First set of |
|
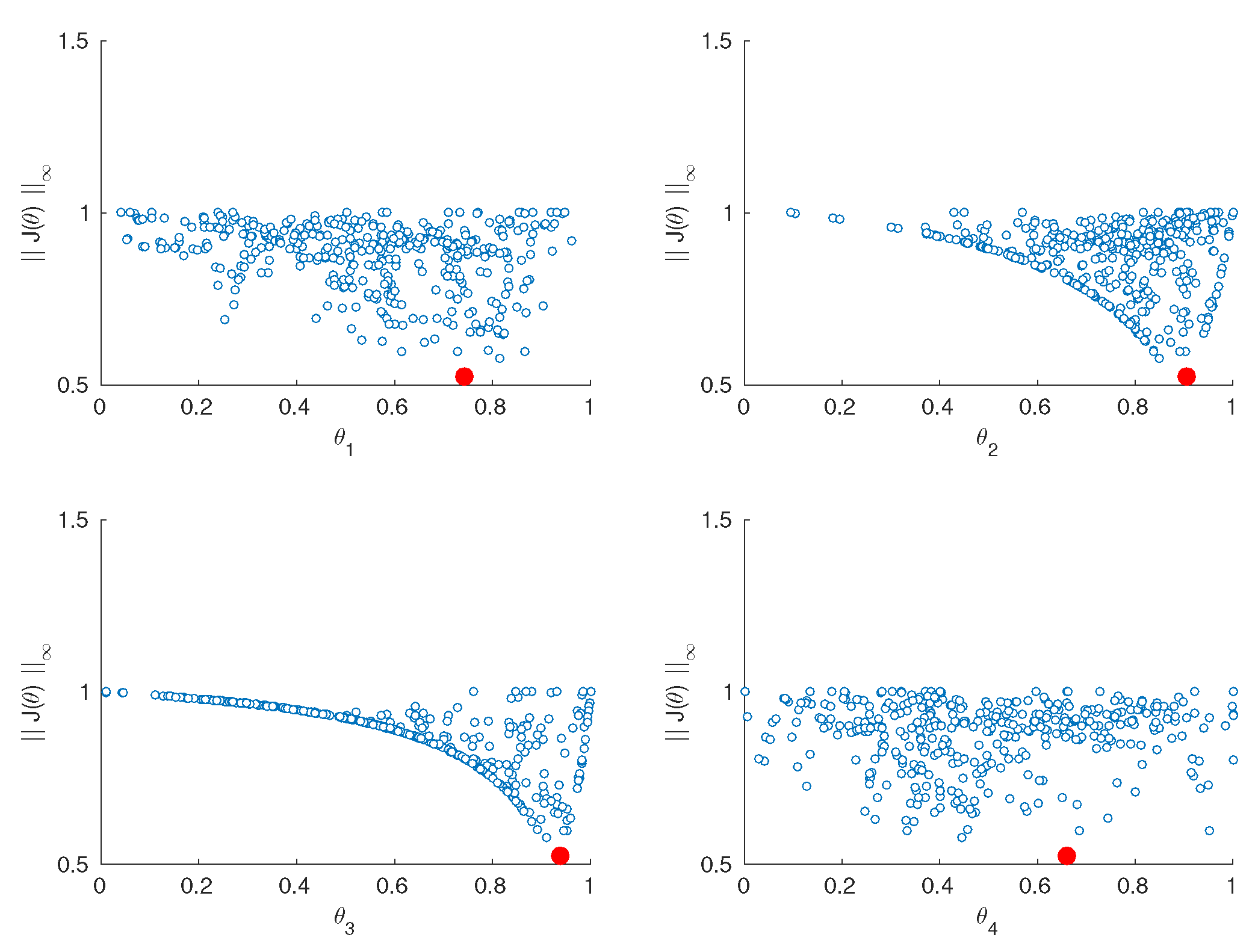
Multiobjective Problem Definition (MOP)
4.2. Definition of Straight-Line Segment
5. Experiments and Results
5.1. Bézier
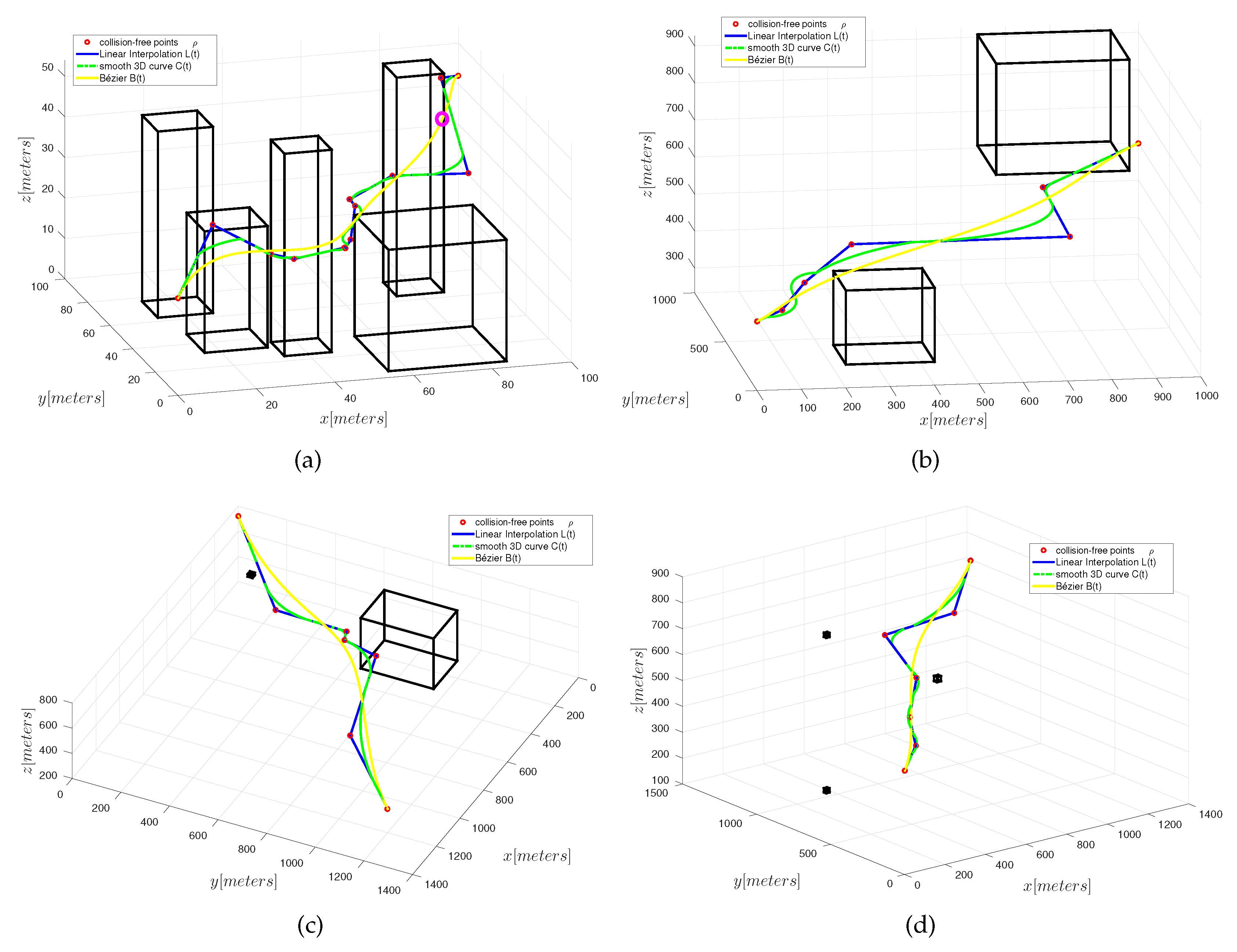
5.2. Application Example
6. Conclusions and Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fagnant, D.J.; Kockelman, K. Preparing a nation for autonomous vehicles: Opportunities, barriers and policy recommendations. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2015, 77, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakidis, M.; Happee, R.; de Winter, J.C. Public opinion on automated driving: Results of an international questionnaire among 5000 respondents. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2015, 32, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münzer, S.; Zimmer, H.D.; Schwalm, M.; Baus, J.; Aslan, I. Computer-assisted navigation and the acquisition of route and survey knowledge. J. Environ. Psychol. 2006, 26, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, Y.; Kallakuri, N.; Shinozawa, K.; Miyashita, T.; Hagita, N. Human-comfortable navigation for an autonomous robotic wheelchair. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Tokyo, Japan, 3–7 November 2013; pp. 2737–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krotkov, E.; Hebert, M. Mapping and positioning for a prototype lunar rover. In Proceedings of the 1995 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Nagoya, Japan, 21–27 May 1995; Volume 3, pp. 2913–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Seda, E.J. Decentralized trajectory tracking with collision avoidance control for teams of unmanned vehicles with constant speed. In Proceedings of the 2014 American Control Conference, Portland, OR, USA, 4–6 June 2014; pp. 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Cai, Z. Kinematics model of unmanned driving vehicle. In Proceedings of the 2010 8th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation, Jinan, China, 7–9 July 2010; pp. 5910–5914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, C.; Frew, E.W. Decentralized extremum-seeking control of nonholonomic vehicles to form a communication chain. In Advances in Cooperative Control and Optimization; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, J.Y.; Saut, J.P.; Benamar, F. Pose estimation-based path planning for a tracked mobile robot traversing uneven terrains. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2016, 75, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ding, L.; Liu, G. Attitude-based dynamic and kinematic models for wheels of mobile robot on deformable slope. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2016, 75, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, G.; Kumar, S.; Pathak, P. Wireless hybrid visual servoing of omnidirectional wheeled mobile robots. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2016, 75, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, M.; Qiao, L. Dynamical sliding mode control for the trajectory tracking of underactuated unmanned underwater vehicles. Ocean Eng. 2015, 105, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gafurov, S.A.; Klochkov, E.V. Autonomous unmanned underwater vehicles development tendencies. Procedia Eng. 2015, 106, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Cai, Z.j. Three-dimensional formation control based on nonlinear small gain method for multiple underactuated underwater vehicles. Ocean Eng. 2018, 151, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, S.; Sabatini, R.; Gardi, A.; Liu, J. LIDAR obstacle warning and avoidance system for unmanned aerial vehicle sense-and-avoid. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2016, 55, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Cheng, X.; Yuan, F.G. A 3D collision avoidance strategy for UAV with physical constraints. Measurement 2016, 77, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee, K.; Zhong, Z. Control, navigation and collision avoidance for an unmanned aerial vehicle. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2013, 190, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courbon, J.; Mezouar, Y.; Guénard, N.; Martinet, P. Vision-based navigation of unmanned aerial vehicles. Control Eng. Pract. 2010, 18, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, D.G. Fundamentals of Airplane Flight Mechanics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Available online: https://scholar.google.co.uk/scholar?q=fundamental+of+airplane+flight+mechanics+david+hull&btnG=&hl=en&as_sdt=0,5#0 (accessed on 1 September 2019).
- Abbadi, A.; Matousek, R.; Jancik, S.; Roupec, J. Rapidly-exploring random trees: 3D planning. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Soft Computing MENDEL, Brno, Czech Republic, 27–29 June 2012; pp. 594–599. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar, W.; Morales, S. 3D environment mapping using the Kinect V2 and path planning based on RRT algorithms. Electronics 2016, 5, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, W.G.; Morales, S.; Ruiz, H.; Abad, V. RRT* GL based optimal path planning for real-time navigation of UAVs. In Proceedings of the International Work-Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, Cadiz, Spain, 14–16 June 2017; pp. 585–595. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, P.; Wang, H.; Su, Z. Hybrid UAV path planning based on interfered fluid dynamical system and improved RRT. In Proceedings of the IECON 2015—41st Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics, Yokohama, Japan, 9–12 November 2015; pp. 000829–000834. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, F.; Liu, Y.S.; Xiao, J.Z. Path planning in complex 3D environments using a probabilistic roadmap method. Int. J. Autom. Comput. 2013, 10, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, H.Y.; Thomas, S.; Eppstein, D.; Amato, N.M. UOBPRM: A uniformly distributed obstacle-based PRM. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Vilamoura, Portugal, 7–12 October 2012; pp. 2655–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denny, J.; Amatoo, N.M. Toggle PRM: A coordinated mapping of C-free and C-obstacle in arbitrary dimension. In Algorithmic Foundations of Robotics X; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wei, C.; Wu, J.; Zhu, X. Improved PRM method of low altitude penetration trajectory planning for UAVs. In Proceedings of the IEEE Chinese Guidance, Navigation and Control Conference, Yantai, China, 8–10 August 2014; pp. 2651–2656. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz-Arroyo, D. A hybrid 3D path planning method for UAVs. In Proceedings of the 2015 Workshop on Research, Education and Development of Unmanned Aerial Systems (RED-UAS), Cancun, Mexico, 23–25 November 2015; pp. 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Yang, C. Robot path planning based on adaptive isolation niche genetic algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2008 Second International Symposium on Intelligent Information Technology Application, Shanghai, China, 20–22 December 2008; Volume 2, pp. 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Xu, L. Global path planning for mobile robot based genetic algorithm and modified simulated annealing algorithm. In Proceedings of the first ACM/SIGEVO Summit on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation, Shanghai, China, 12–14 June 2009; pp. 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, H.; Tian, X.; Gao, M. An improved ant colony algorithm for robot path planning. Soft Comput. 2017, 21, 5829–5839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Sun, S.; Zhang, K.; Tang, Z. Visualized trajectory planning of flexible redundant robotic arm using a novel hybrid algorithm. Optik 2016, 127, 9974–9983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Qiao, P. Pigeon-inspired optimization: A new swarm intelligence optimizer for air robot path planning. Int. J. Intell. Comput. Cybern. 2014, 7, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhanjouri, M.A.; Alfarra, B. Ant colony versus genetic algorithm based on travelling salesman problem. Int. J. Comput. Technol. Appl. 2011, 2, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakdi, A.; Hentout, A.; Boutami, H.; Maoudj, A.; Hachour, O.; Bouzouia, B. Optimal path planning and execution for mobile robots using genetic algorithm and adaptive fuzzy-logic control. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2017, 89, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Parhi, D.R. Optimum path planning of mobile robot in unknown static and dynamic environments using Fuzzy-Wind Driven Optimization algorithm. Def. Technol. 2017, 13, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanou, M.; Tzes, A. Distributed visibility-based coverage using a swarm of UAVs in known 3D-terrains. In Proceedings of the 2014 6th International Symposium on Communications, Control and Signal Processing (ISCCSP), Athens, Greece, 21–23 May 2014; pp. 425–428. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Optimal flight path planning for UAVs in 3-D threat environment. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS), Orlando, FL, USA, 27–30 May 2014; pp. 149–155. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Z.; Luan, C.; Sun, Z. A 2d voronoi-based random tree for path planning in complicated 3d environments. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Autonomous Systems, Shanghai, China, 3–7 July 2016; pp. 433–445. [Google Scholar]
- Khuswendi, T.; Hindersah, H.; Adiprawita, W. Uav path planning using potential field and modified receding horizon a* 3d algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Informatics, Bandung, Indonesia, 17–19 July 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, J. The three-dimension path planning of UAV based on improved artificial potential field in dynamic environment. In Proceedings of the 2013 5th International Conference on Intelligent Human-Machine Systems and Cybernetics, Hangzhou, China, 26–27 August 2013; Volume 2, pp. 144–147. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera, D.M.; Prieto, F.A.; Ramírez, R. Trajectory planning for uavs in 3d environments using a moving band in potential sigmoid fields. In Proceedings of the 2012 Brazilian Robotics Symposium and Latin American Robotics Symposium, Fortaleza, Brazil, 16–19 October 2012; pp. 115–119. [Google Scholar]
- Lifen, L.; Ruoxin, S.; Shuandao, L.; Jiang, W. Path planning for UAVS based on improved artificial potential field method through changing the repulsive potential function. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Chinese Guidance, Navigation and Control Conference (CGNCC), Nanjing, China, 12–14 August 2016; pp. 2011–2015. [Google Scholar]
- Samaniego, F.; Sanchis, J.; García-Nieto, S.; Simarro, R. Recursive Rewarding Modified Adaptive Cell Decomposition (RR-MACD): A Dynamic Path Planning Algorithm for UAVs. Electronics 2019, 8, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubins, L.E. On curves of minimal length with a constraint on average curvature, and with prescribed initial and terminal positions and tangents. Am. J. Math. 1957, 79, 497–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, R.W.; McLain, T.W. Small Unmanned Aircraft: Theory and Practice; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fleury, S.; Soueres, P.; Laumond, J.P.; Chatila, R. Primitives for smoothing mobile robot trajectories. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1995, 11, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanegas, G.; Samaniego, F.; Girbes, V.; Armesto, L.; Garcia-Nieto, S. Smooth 3D path planning for non-holonomic UAVs. In Proceedings of the 2018 7th International Conference on Systems and Control (ICSC), Valencia, Spain, 24–26 October 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezak, M.; Petrović, I. Real-time approximation of clothoids with bounded error for path planning applications. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2013, 30, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsky, B.; DeRose, T. Geometric continuity of parametric curves: Three equivalent characterizations. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 1989, 9, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, D.; Shin, J.U.; Kim, H.; Myung, H. Angular rate-constrained path planning algorithm for unmanned surface vehicles. Ocean Eng. 2014, 84, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacs, J.; Hespanha, J. Dubins Traveling Salesman Problem with Neighborhoods: A Graph-Based Approach. Algorithms 2013, 6, 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masehian, E.; Kakahaji, H. NRR: A nonholonomic random replanner for navigation of car-like robots in unknown environments. Robotica 2014, 32, 1101–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraichard, T.; Scheuer, A. From Reeds and Shepp’s to continuous-curvature paths. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2004, 20, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepy, R.; Lambert, A.; Mounier, H. Path Planning using a Dynamic Vehicle Model. In Proceedings of the 2006 2nd International Conference on Information & Communication Technologies, Damascus, Syria, 24–28 April 2006; Volume 1, pp. 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girbés, V.; Vanegas, G.; Armesto, L. Clothoid-Based Three-Dimensional Curve for Attitude Planning. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2019, 42, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lorenzis, L.; Wriggers, P.; Hughes, T.J. Isogeometric contact: A review. GAMM-Mitteilungen 2014, 37, 85–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pigounakis, K.G.; Sapidis, N.S.; D, K.P. Fairing spatial B-spline curves. J. Ship Res. 1996, 40, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez, L.H.; Aguilar, M.C.M.; Sánchez, N.M.; Montesinos, A.F. Path Planning Based on Parametric Curves. In Advanced Path Planning for Mobile Entities; InTech: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, U.Y.; Chang, S.R. A G2 continuous path-smoothing algorithm using modified quadratic polynomial interpolation. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2014, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.R.; Huh, U.Y. A Collision-Free G2 Continuous Path-Smoothing Algorithm Using Quadratic Polynomial Interpolation. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2014, 11, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, J.M.; Martínez, M.; Sanchis, J.; Blasco, X. Well-Distributed Pareto Front by Using the -MOGA Evolutionary Algorithm. In Computational and Ambient Intelligence; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Sendhoff, B. Pareto-Based Multiobjective Machine Learning: An Overview and Case Studies. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. Part C Appl. Rev. 2008, 38, 397–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farin, G. Curves and Surfaces for Computer-Aided Geometric Design: A Practical Guide; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Velasco-Carrau, J.; García-Nieto, S.; Salcedo, J.V.; Bishop, R.H. Multi-Objective Optimization for Wind Estimation and Aircraft Model Identification. J. Guid. Control. Dyn. 2016, 39, 372–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honig, E.; Schucking, E.L.; Vishveshwara, C.V. Motion of charged particles in homogeneous electromagnetic fields. J. Math. Phys. 1974, 15, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, B.R.; Vishveshwara, C.V. The Frenet-Serret formalism and black holes in higher dimensions. Class. Quantum Gravity 1988, 5, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbena, E.; Salamon, S.; Gray, A. Modern Differential Geometry of Curves and Surfaces with Mathematica; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lazard, S.; Reif, J.; Wang, H. The Complexity of the Two Dimensional Curvature-Constrained Shortest-Path Problem. In Proceedings of the Third International Workshop on the Algorithmic Foundations of Robotics, Houston, TX, USA, 5–7 March 1998; pp. 49–57. [Google Scholar]
- Coello Coello, C.A.; Pulido, G.T.; Montes, E.M. Current and Future Research Trends in Evolutionary Multiobjective Optimization. In Information Processing with Evolutionary Algorithms; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 213–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laumanns, M.; Thiele, L.; Deb, K.; Zitzler, E. Combining Convergence and Diversity in Evolutionary Multiobjective Optimization. Evol. Comput. 2002, 10, 263–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco, X.; Herrero, J.; Sanchis, J.; Martínez, M. A new graphical visualization of n-dimensional Pareto front for decision-making in multiobjective optimization. Inf. Sci. 2008, 178, 3908–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mclnnes, C. Satellite attitude slew manoeuvres using inverse control. Aeronaut. J. 1998, 102, 259–266. [Google Scholar]






| Env. | RR-MACD 4 Constraints | RR-MACD 10 Constraints | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | # | # | # | |
| # 1 | 115 | 18 | 202 | 27 |
| # 2 | 27 | 8 | 35 | 10 |
| # 3 | 19 | 6 | 16 | 7 |
| # 4 | 11 | 6 | 51 | 10 |
| # 5 | 19 | 7 | 35 | 10 |
| Env. | Flight Distance [Meters] | EAA Error [Meters] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L(t) | C(t) | B(t) | L(t) vs C(t) | L(t) vs B(t) | |
| #1 | 182.929355 | 174.002834 | 148.911388 | 0.622684 | 3.248545 |
| #2 | 1728.757868 | 1610.781941 | 1453.060601 | 17.234613 | 41.453691 |
| #3 | 1863.391222 | 1721.505017 | 1526.055284 | 14.600159 | 56.678212 |
| #4 | 1936.078758 | 1860.263202 | 1772.944453 | 9.871725 | 36.617234 |
| #5 | 1873.814514 | 1839.965587 | 1743.723244 | 9.891240 | 36.614752 |
| Env. | Curve | Collision | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | C(t) | 0.157961 | 0.185973 | o |
| B(t) | 0.019513 | 0.092539 | x | |
| #2 | C(t) | 0.007138 | 0.159732 | o |
| B(t) | 0.001082 | 0.006652 | o | |
| #3 | C(t) | 0.004556 | 0.185806 | o |
| B(t) | 0.001068 | 0.004442 | o | |
| #4 | C(t) | 0.003445 | 0.574121 | o |
| B(t) | 0.000812 | 0.003332 | o | |
| #5 | C(t) | 0.004515 | 0.135183 | o |
| B(t) | 0.000643 | 0.004253 | o |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samaniego, F.; Sanchis, J.; Garcia-Nieto, S.; Simarro, R. Smooth 3D Path Planning by Means of Multiobjective Optimization for Fixed-Wing UAVs. Electronics 2020, 9, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9010051
Samaniego F, Sanchis J, Garcia-Nieto S, Simarro R. Smooth 3D Path Planning by Means of Multiobjective Optimization for Fixed-Wing UAVs. Electronics. 2020; 9(1):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9010051
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamaniego, Franklin, Javier Sanchis, Sergio Garcia-Nieto, and Raul Simarro. 2020. "Smooth 3D Path Planning by Means of Multiobjective Optimization for Fixed-Wing UAVs" Electronics 9, no. 1: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9010051
APA StyleSamaniego, F., Sanchis, J., Garcia-Nieto, S., & Simarro, R. (2020). Smooth 3D Path Planning by Means of Multiobjective Optimization for Fixed-Wing UAVs. Electronics, 9(1), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9010051







