Performance Degradation of Nanofilament Switching Due to Joule Heat Dissipation
Abstract
1. Introduction
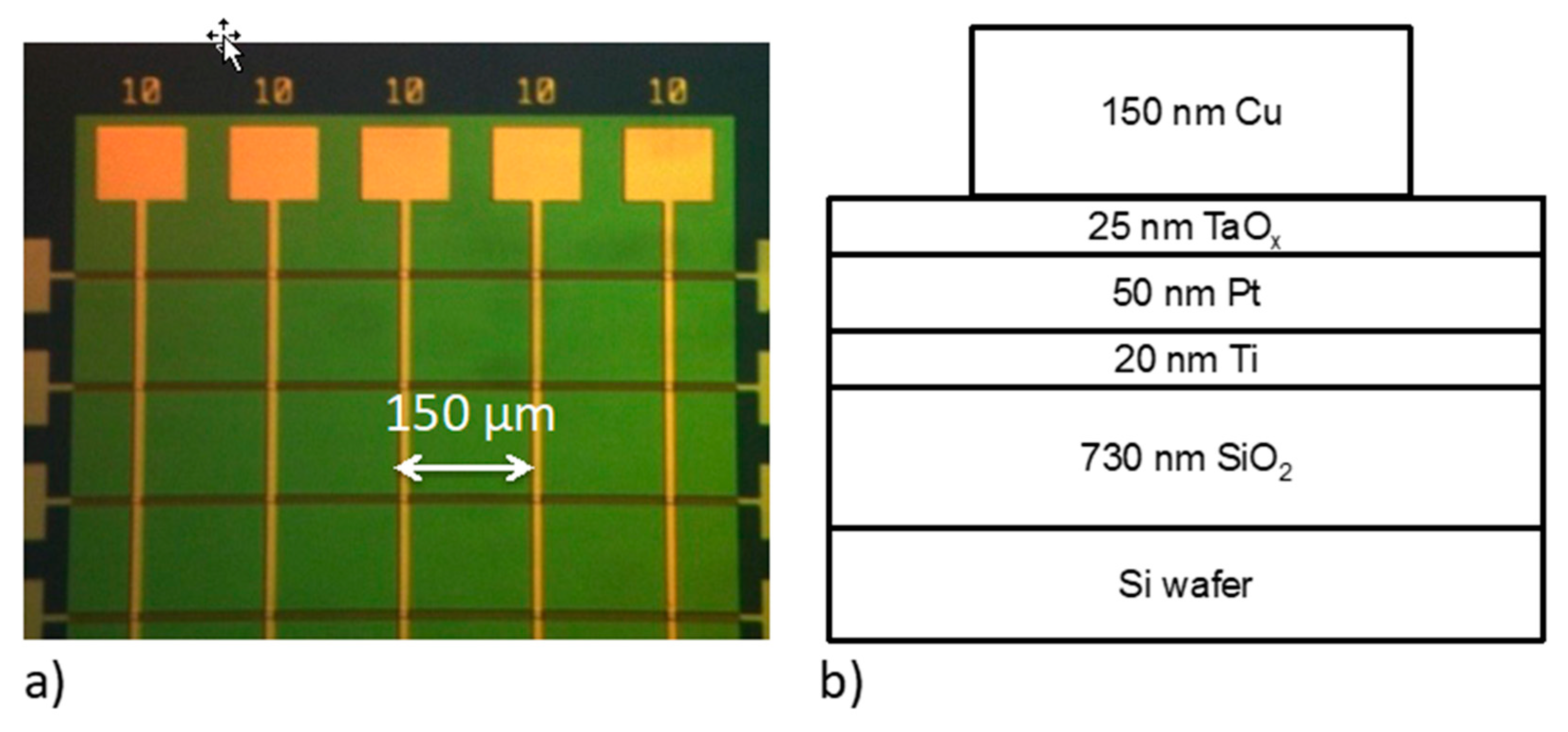
2. Device Fabrication and Electrical Characterization Methodology
3. Thermal Cell-to-Cell Cross-Talk Effects in ReRAM Array
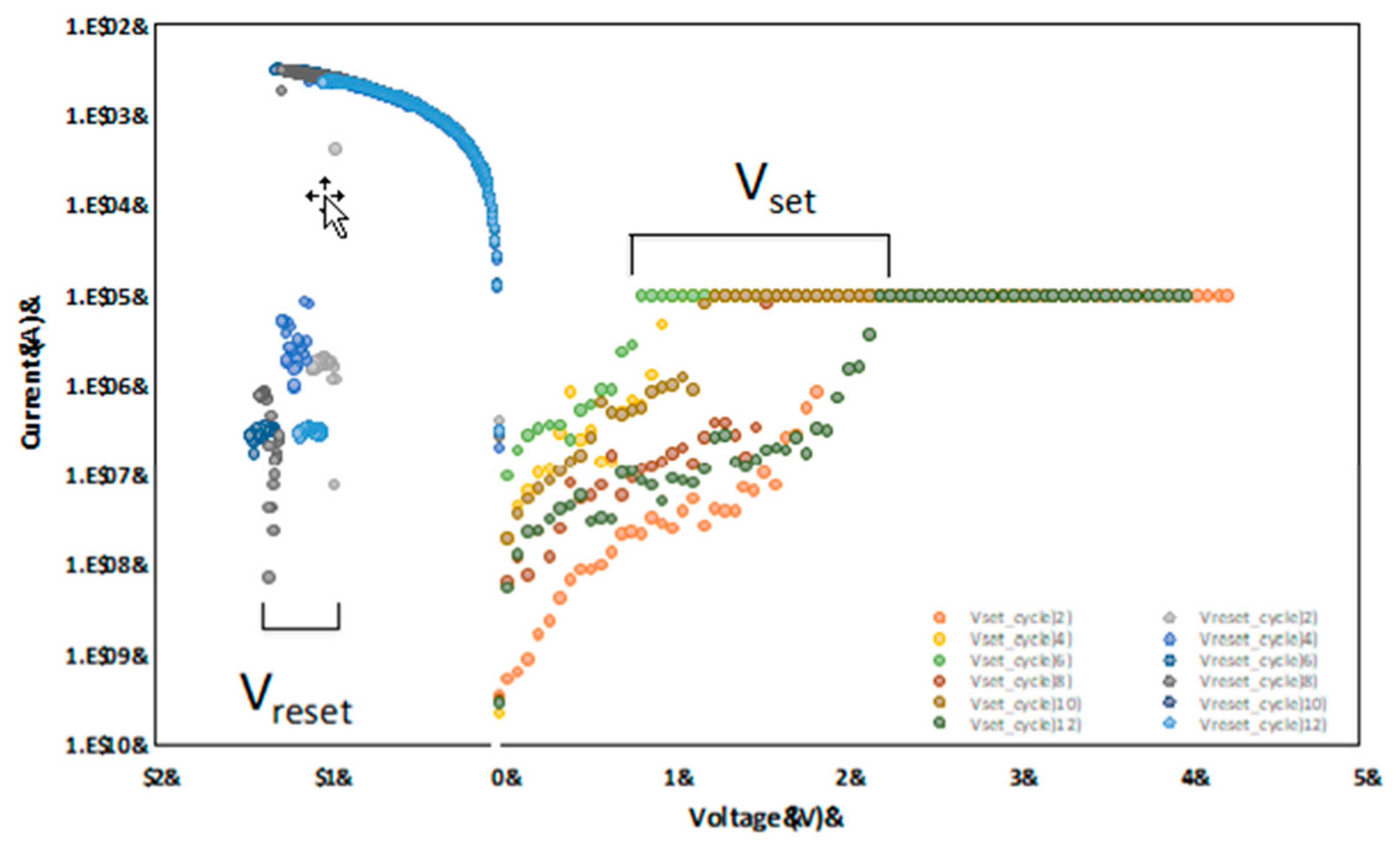
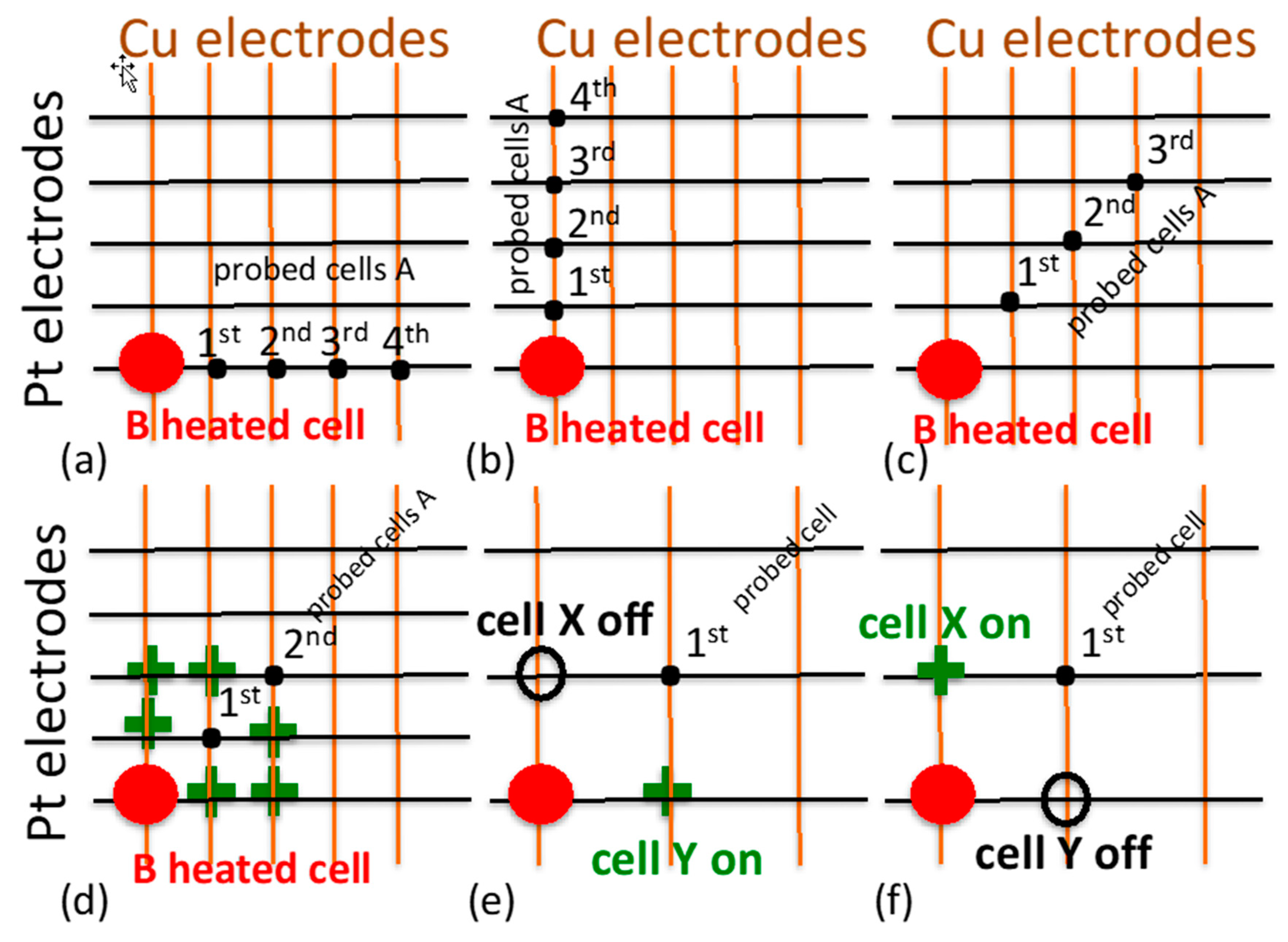
3.1. Definition of a “Marginal” Device as a Probe into Cross-Talk Effects
3.2. Dissipation and Transport of Joule Heat in ReRAM Arrays
3.3. Degradation of Electric Performance of Cells Sharing the Pt Electrode
3.4. Degradation of Electric Performance of Cells Sharing the Cu Electrode
3.5. Degradation of Electric Performance of Cells with No Common Electrodes with the Heated Cell
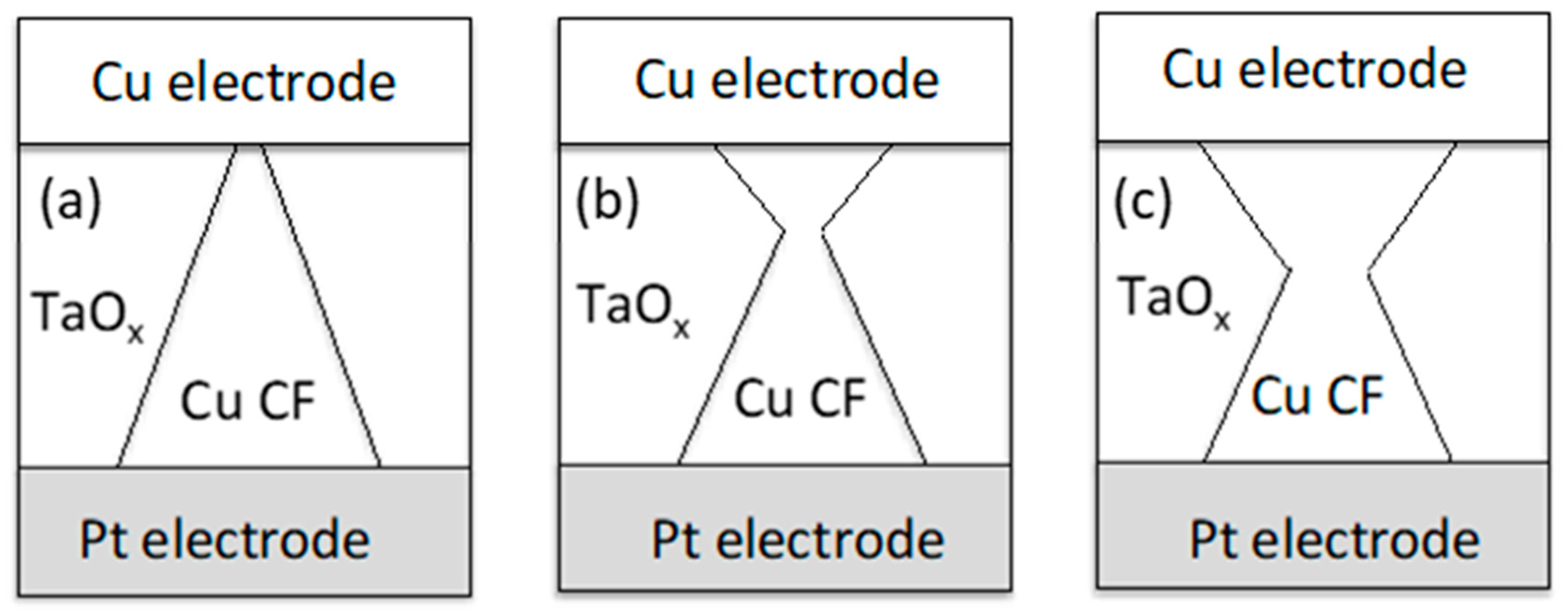
3.6. Inference of the Nanofilament Shape
4. Analysis and Implications for High-Pitch Nanometer-Sized Commercial Arrays
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Valov, I.; Waser, R.; Jameson, J.R.; Kozicki, M.N. Electrochemical metallization memories—fundamentals, applications, prospects. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 254003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, D.S.; Thomas, R.; Katiyar, R.S.; Scott, J.F.; Kohlstedt, H.; Petraru, A.; Hwang, C.S. Emerging memories: Resistive switching mechanisms and current status. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2012, 75, 076502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.J.; Lee, C.B.; Lee, D.; Lee, S.R.; Chang, M.; Hur, J.H.; Kim, Y.B.; Kim, C.J.; Seo, D.H.; Seo, S.; et al. A fast, high-endurance and scalable non-volatile memory device made from asymmetric Ta2O5−x/TaO2−x bilayer structures. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, H.; Al-Mamun, M.S.; Orlowski, M.K.; Yi, Y. Learning Accuracy Analysis of Memristor-based Nonlinear Computing Module on Long Short-term Memory. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neuromorphic Systems, Knoxville, Tennessee, 23–26 July 2018; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2018. ISBN 978-1-4503-6544-4/18/07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beigi, M.V.; Memik, G. Thermal-Aware Optimizations of Reram-Based Neuromorphic Computing Systems. In Proceedings of the 55th Annual Design Automation Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 24–28 June 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Verma, M.; Kang, Y.; Orlowski, M. Volatile resistive switching in Cu/TaOx/δ-Cu/Pt devices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 073510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozicki, M.N.; Yun, M.; Hilt, L.; Singh, A. Applications of programmable resistance changes in metal-doped chalcogenides. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1999, 99, 298–309. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, P.; Lu, N.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Lv, H.; Liu, Q.; Long, S.; Liu, S.; Liu, M. Thermal crosstalk in 3-dimensional RRAM crossbar array. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickel, P.R.; Lohn, A.J.; James, C.D.; Marinella, M.J. Isothermal switching and detailed filament evolution in memristive systems. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 4486–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, U.; Ielmini, D.; Cagli, C.; Lacaita, A.L. Self-accelerated thermal dissolution model for reset programming in unipolar resistive-switching memory (RRAM) devices. IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 2009, 56, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ielmini, D. Modeling the universal set/reset characteristics of bipolar RRAM by field-and temperature-driven filament growth. IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 2011, 58, 4309–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.H.; Chae, S.C.; Lee, S.B.; Liu, C.; Noh, T.W.; Lee, J.S.; Kahng, B.; Jang, J.H.; Kim, M.Y.; Kim, D.W.; et al. Effects of heat dissipation on unipolar resistance switching in Pt/NiO/Pt capacitors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 183507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczyk, C.; Walczyk, D.; Schroeder, T.; Bertaud, T.; Sowinska, M.; Lukosius, M.; Fraschke, M.; Wolansky, D.; Tillack, B.; Miranda, E.; et al. Impact of Temperature on the Resistive Switching Behavior of Embedded HfO2-Based RRAM Devices. IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 2011, 58, 3124–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terai, M.; Saitoh, M.; Nagumo, T.; Sakotsubo, Y.; Yabe, Y.; Takeda, K.; Hase, T. High Thermal Robust ReRAM with a New Method for Suppressing Read Disturb. In Proceedings of the 2011 Symposium on VLSI Technology-Digest of Technical Papers, Honolulu, HI, USA, 14–16 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Mamun, M.; Orlowski, M. Performance Degradation Due to Nonlocal Heating Effects in Resistive ReRAM Memory Arrays. MRS Adv. 2019, 4, 2593–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, G.; Kang, Y.; King, S.W.; Orlowski, M. Role of CMOS Back-End Metals as Active Electrodes for Resistive Switching in ReRAM Cells. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2017, 6, N1–N9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Liu, T.; Potnis, T.; Orlowski, M.K. Composite Cu/VO and VO/Cu Nanofilaments in Cu/Ta2O5/Pt Devices. ECS Solid State Lett. 2013, 2, Q54–Q57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Verma, M.; Kang, Y.; Orlowski, M.K. I-V characteristics of antiparallel resistive switching observed in a single Cu/TaOx/Pt cell. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2012, 34, 108–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linn, E.; Rosezin, R.; Kügeler, C.; Waser, R. Complementary resistive switches for passive nanocrossbar memories. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, G.; Orlowski, M. Write and Erase Threshold Voltage Interdependence in Resistive Switching Memory Cells. IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 2015, 62, 2850–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, G.; Orlowski, M.K. Correlation between set and reset voltages in resistive RAM cells. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2015, 15, 1124–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Kang, Y.; El-Helw, S.; Potnis, T.; Orlowski, M. Physics of the voltage constant in multilevel switching of conductive bridge resistive memory. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 52, 084202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landon, C.D.; Wilke, R.H.; Brumbach, M.T.; Brennecka, G.L.; Blea-Kirby, M.; Ihlefeld, J.F.; Marinella, M.J.; Beechem, T.E. Thermal transport in tantalum oxide films for memristive applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 023108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickel, P.R.; Lohn, A.J.; Marinella, M.J. Detection and characterization of multi-filament evolution during resistive switching. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 053503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickel, P.R.; Lohn, A.J.; Marinella, M.J. Memristive switching: Physical mechanisms and applications. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2014, 28, 1430003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Li, L.; Lu, N.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Xie, H.; Liu, S.; Liu, M. Physical model of dynamic Joule heating effect for reset process in conductive-bridge random access memory. J. Comp. Electron. 2014, 13, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X. Demonstration of Ultra-Fast Switching in Nanometallic Resistive Switching Memory Devices. J. Nanosci. 2016, 8132701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, M. A Review on Resistive Switching in High-k Dielectrics: A Nanoscale Point of View Using Conductive Atomic Force Microscope. Materials 2014, 7, 2155–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mamun, M.S.; Orlowski, M. Quick heat dissipation in ReRAM with graphene engineered electrodes. In preparation.
- Lohn, A.J.; Mickel, P.R.; Marinella, M.J. Analytical estimations for thermal crosstalk, retention, and scaling limits in filamentary resistive memory. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 234507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niraula, D.; Karpov, V.G. Heat transfer in filamentary RRAM devices. IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 2017, 64, 4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Neighbor Cell to the Heated Cell Along Pt Metal Line | Neighbor Cell to the Heated Cell Along Cu Metal Line | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #neighbor | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th |
| D [%] | 67 | 53 | 40 | 13 | 80 | 75 | 70 | 67 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Mamun, M.S.; Orlowski, M.K. Performance Degradation of Nanofilament Switching Due to Joule Heat Dissipation. Electronics 2020, 9, 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9010127
Al-Mamun MS, Orlowski MK. Performance Degradation of Nanofilament Switching Due to Joule Heat Dissipation. Electronics. 2020; 9(1):127. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9010127
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Mamun, Mohammad Shah, and Marius K. Orlowski. 2020. "Performance Degradation of Nanofilament Switching Due to Joule Heat Dissipation" Electronics 9, no. 1: 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9010127
APA StyleAl-Mamun, M. S., & Orlowski, M. K. (2020). Performance Degradation of Nanofilament Switching Due to Joule Heat Dissipation. Electronics, 9(1), 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9010127




