Analysis of Steady-State Characteristics for a Newly Designed High Voltage Gain Switched Inductor Z-Source Inverter
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The detailed analytical model has been developed along with the analysis of the ripples in the inductor currents and capacitor voltages.
- This work includes more analyses associated with the switching device power and efficiency calculation.
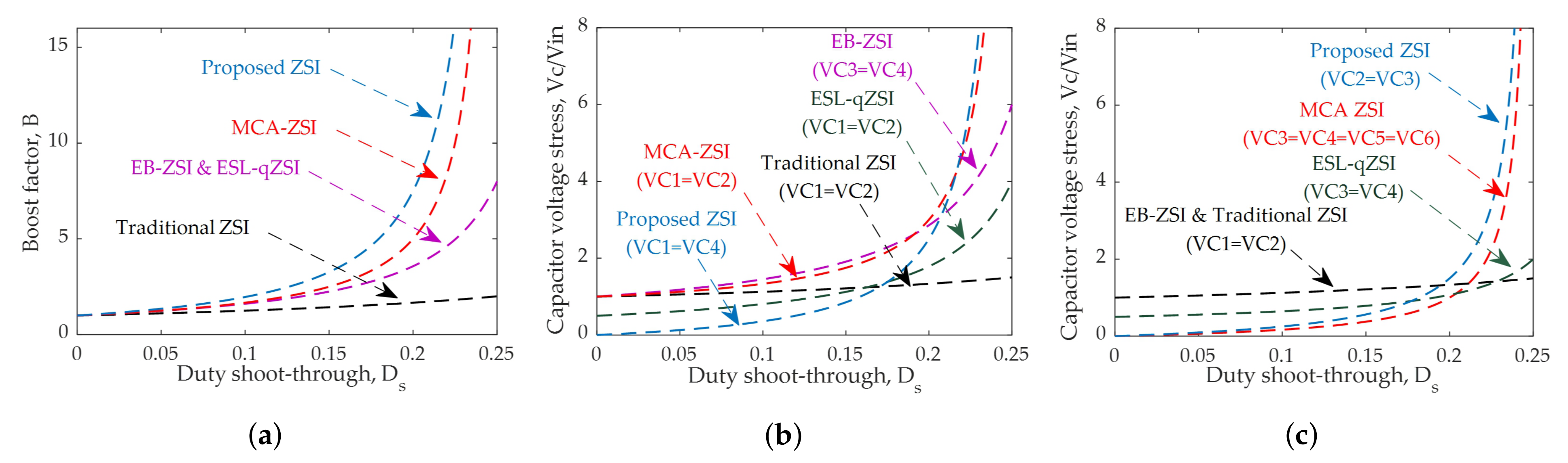
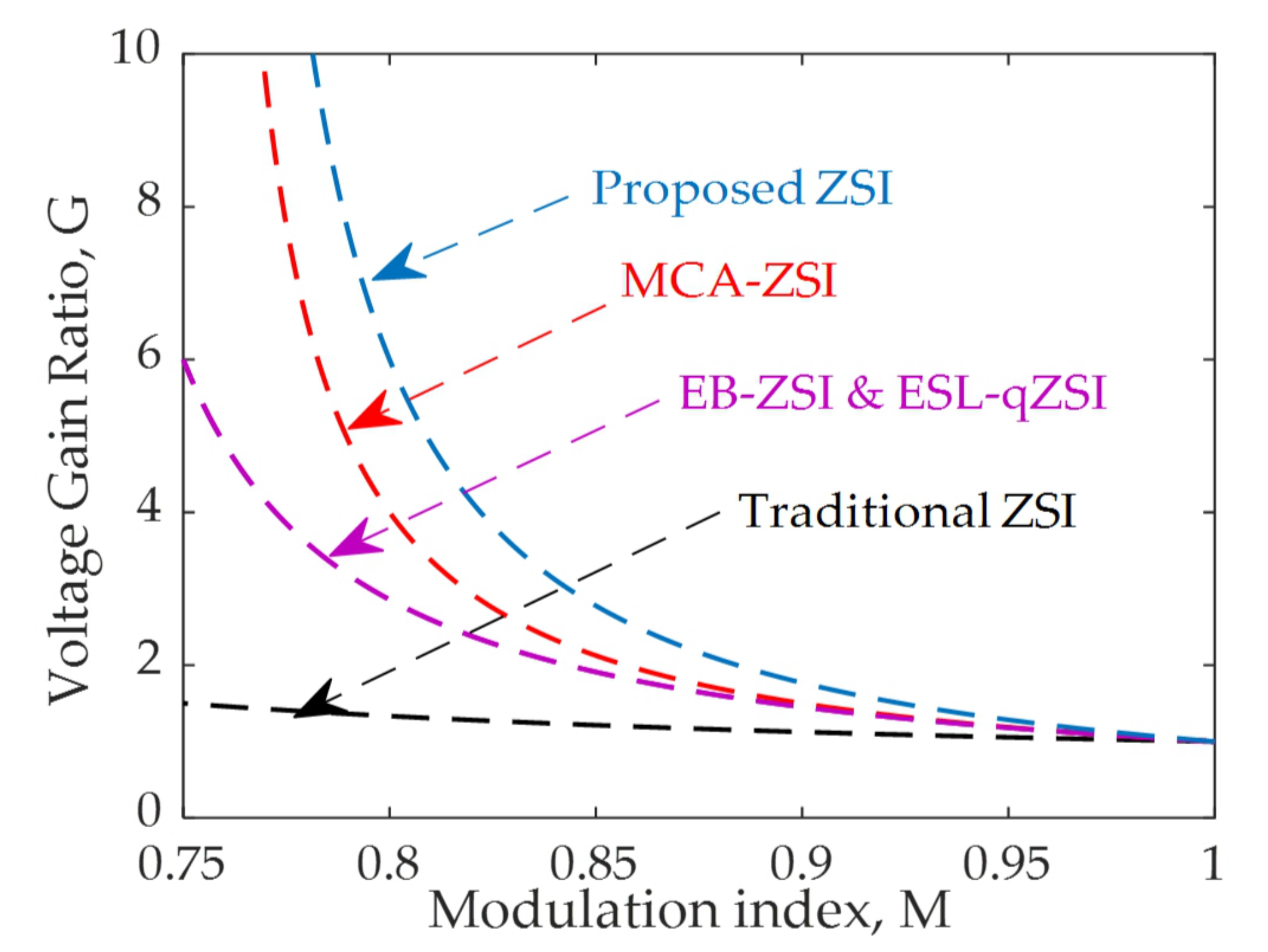
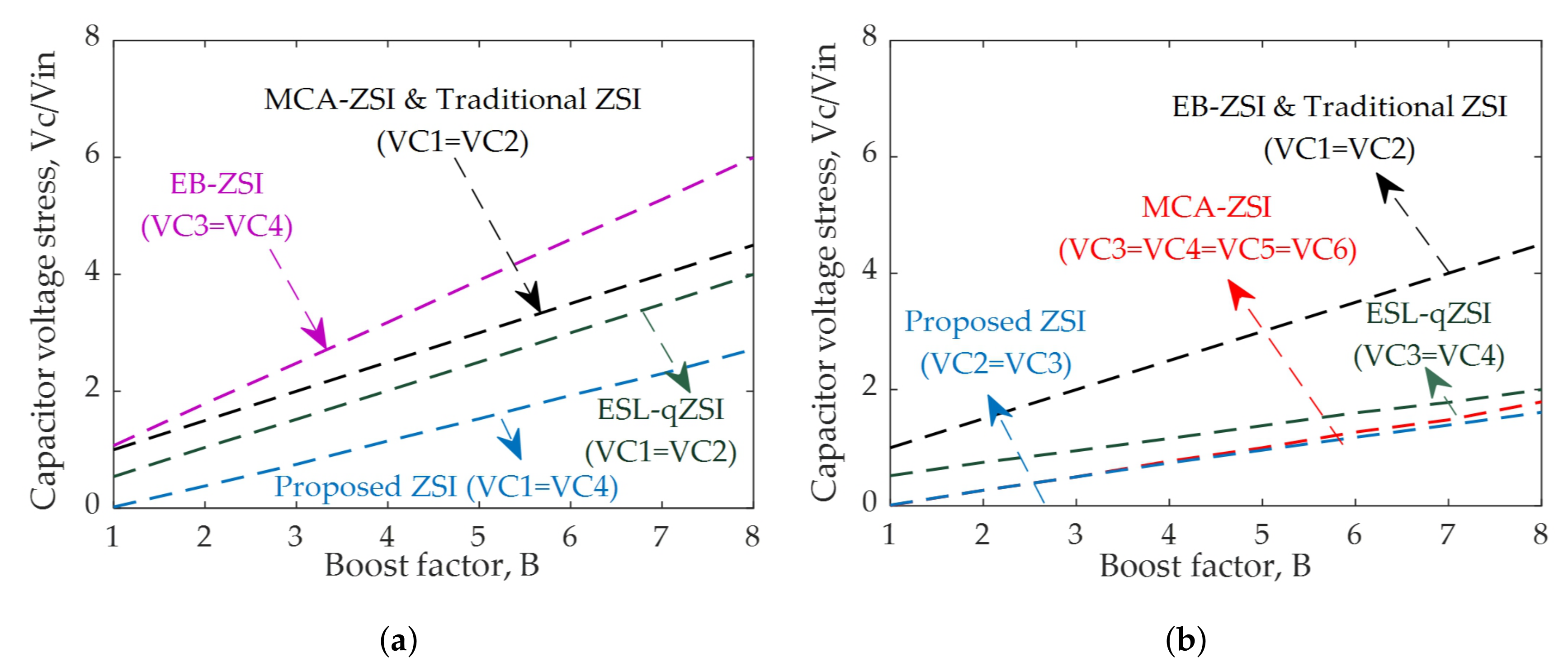
- The analytical models reveal several advanced features of the proposed topologies such as the reduced capacitor voltage stress for the same boost factor; improved boosting capability for the same input voltage and shoot-through duty ratio, improved efficiency, reduced inrush current, and significantly improved dynamic voltage compensation capability as compared to all existing topologies.
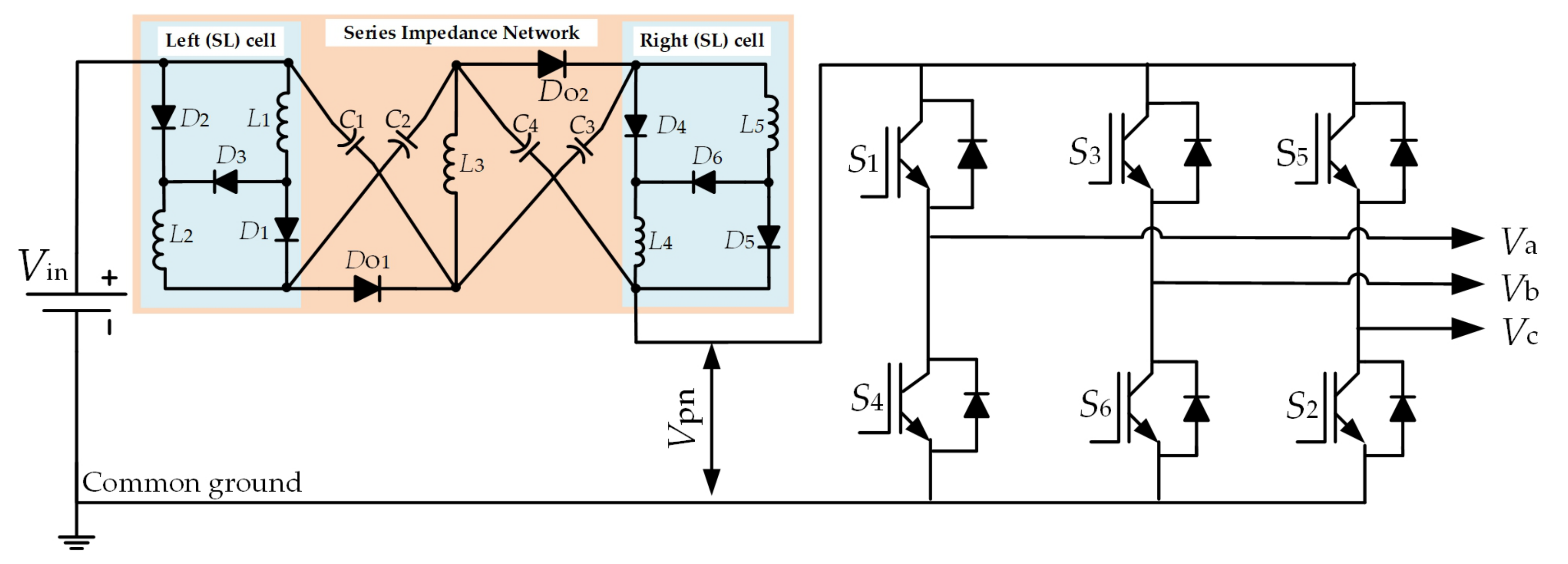
2. Operating Characteristics of the Proposed SL-SBZSI Topology
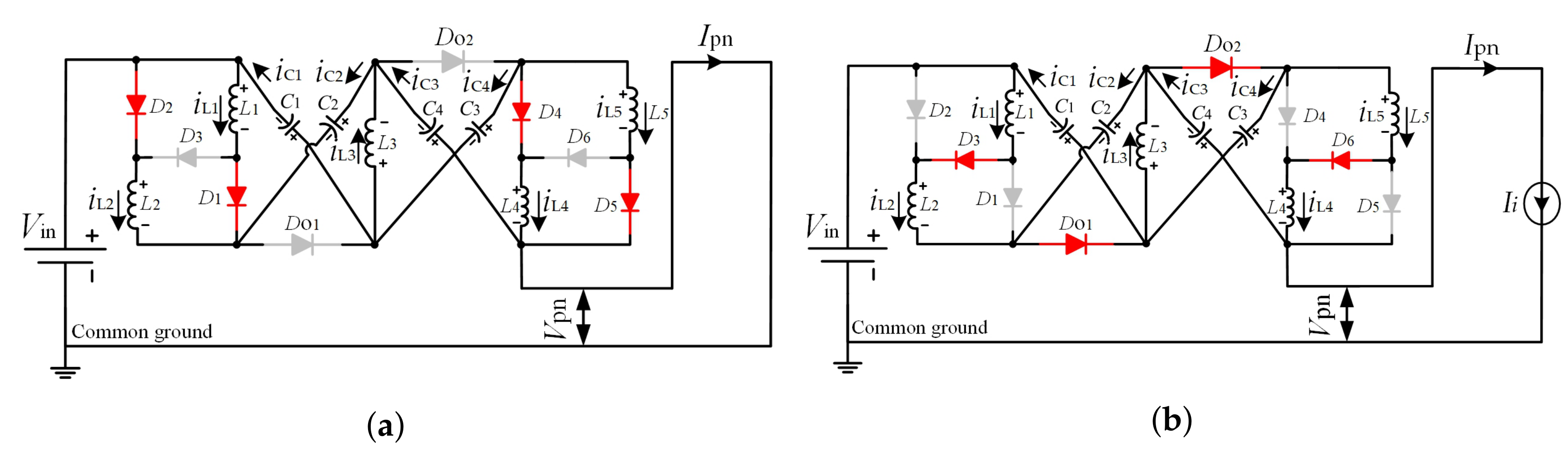
2.1. Shoot-Through Operating Mode
2.2. Non-Shoot-Through Operating Mode
3. Performance Characteristics of Proposed SL-SBZSI
3.1. Mathematical Modeling of Proposed SL-SBZSI
3.2. Analysis of Ripples in the Inductor Current for the Proposed SL-SBZSI
3.3. Analysis of Ripples in the Capacitor Voltage for the Proposed SL-SBZSI
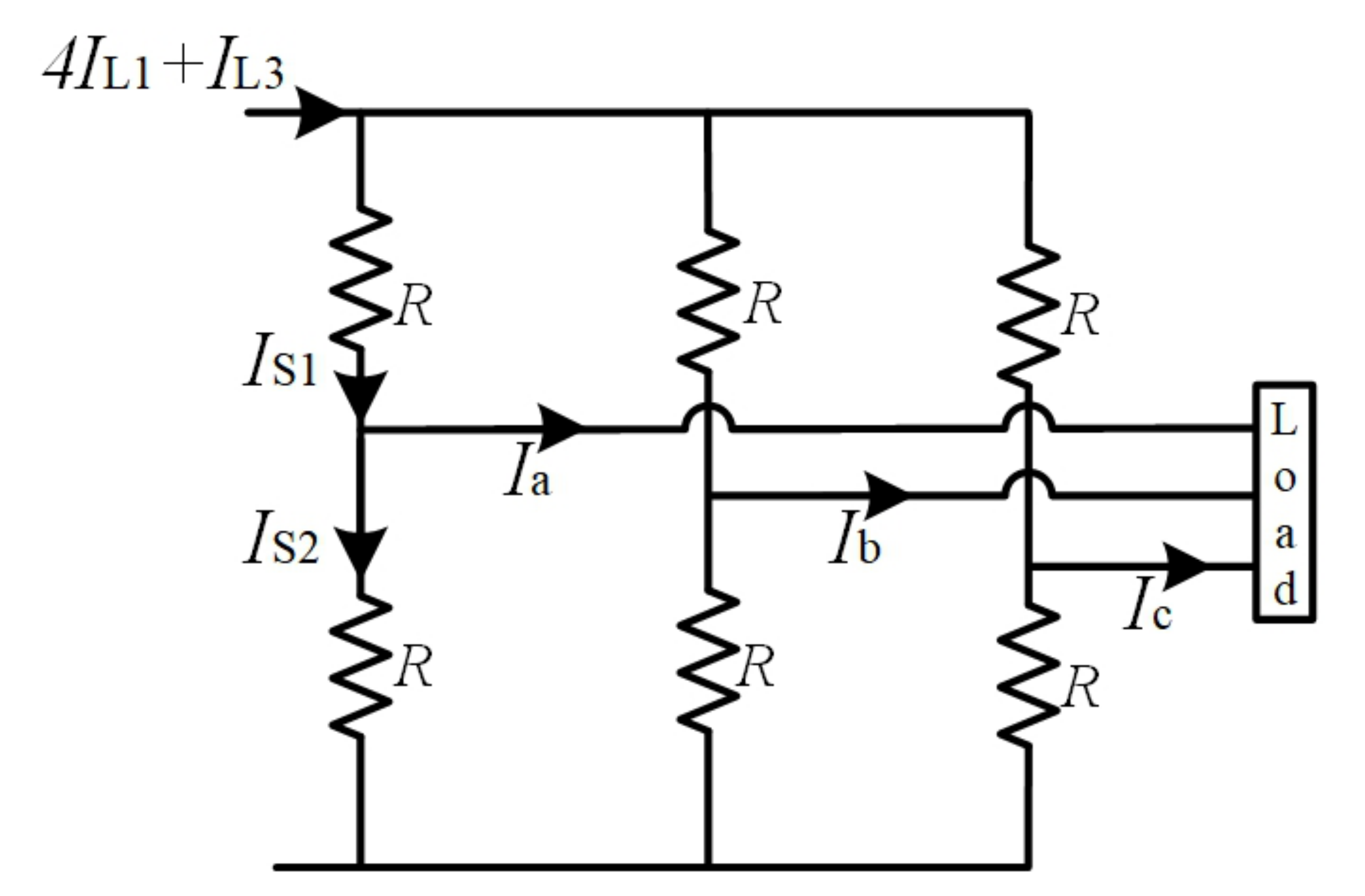
3.4. Inverter Switching Device Power
- Current to load during the non-shoot-through mode and
- Current through switches during the shoot-through mode.
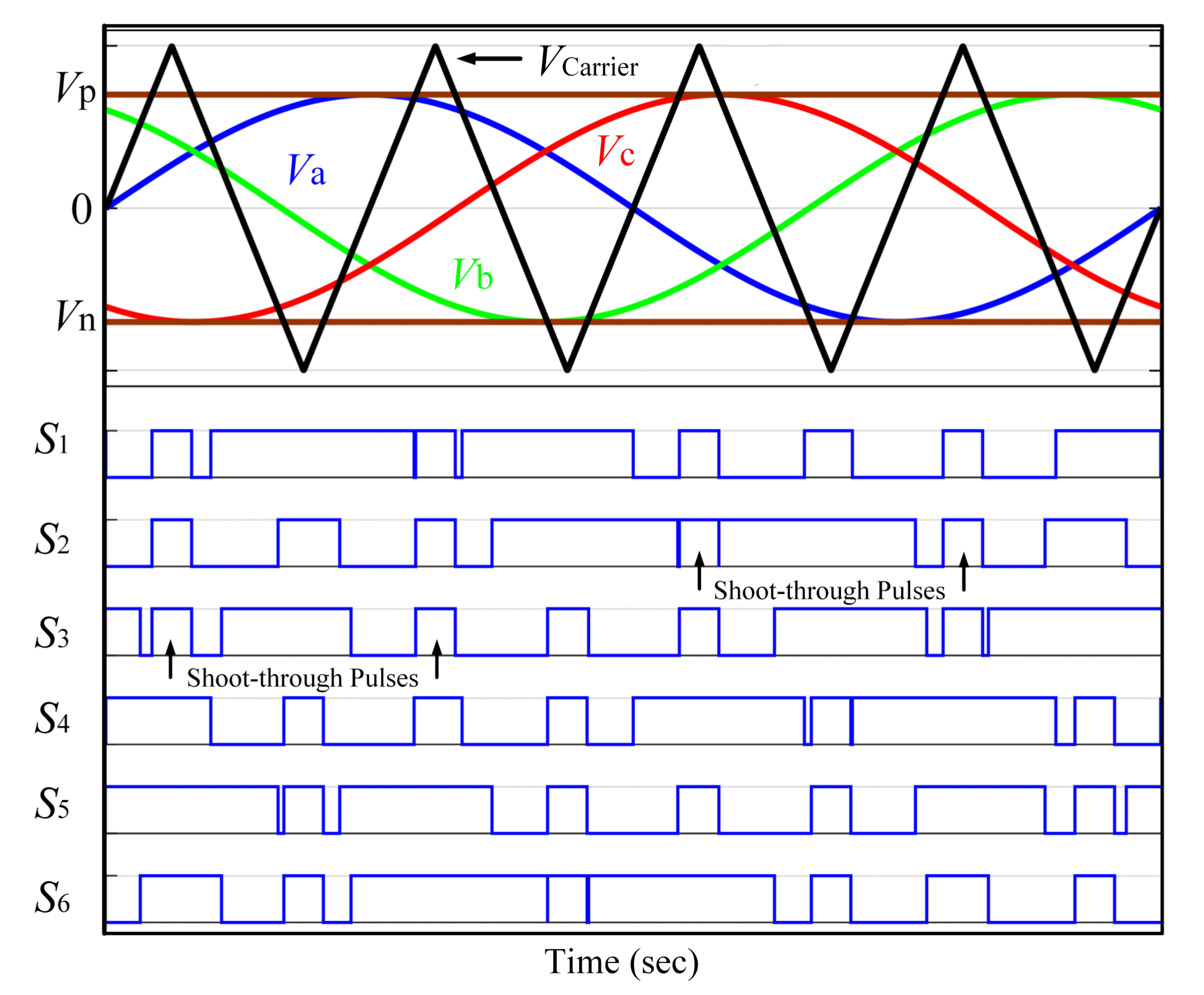
4. Inverter Switching Control Method
5. Comparative Analysis for the Capacitor Voltage Stress
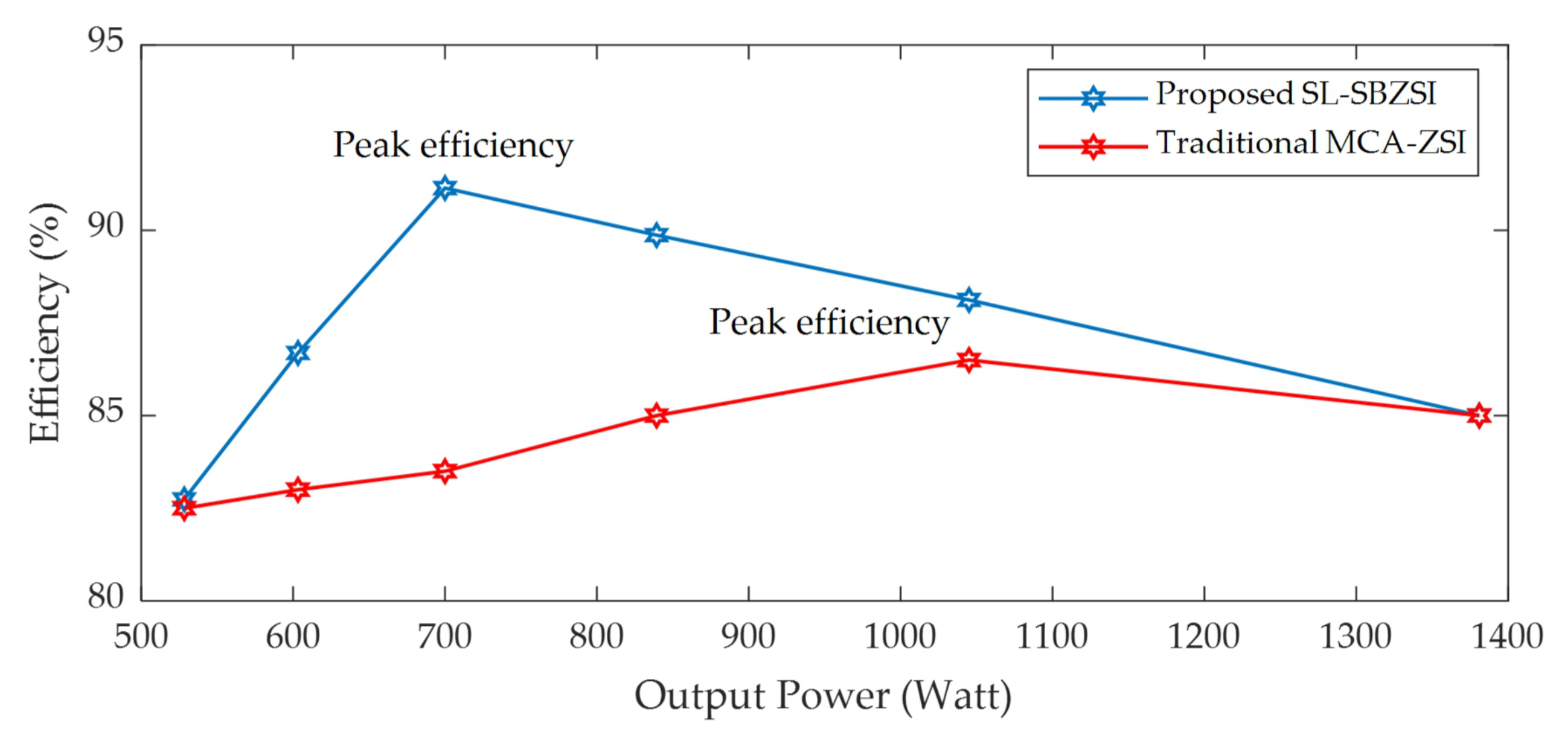
6. Calculation of Power Loss and Efficiency of the Proposed SL-SBZSI
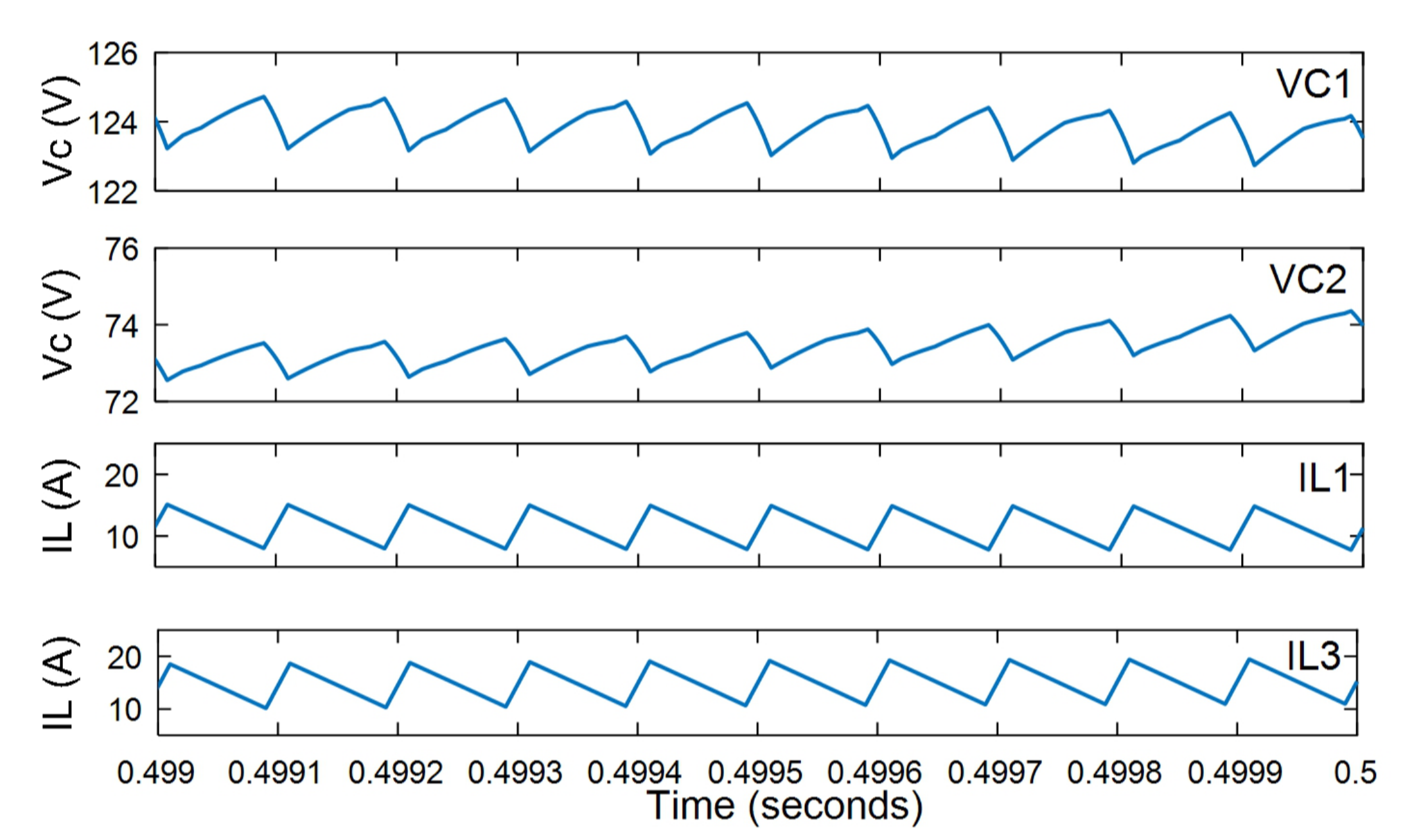
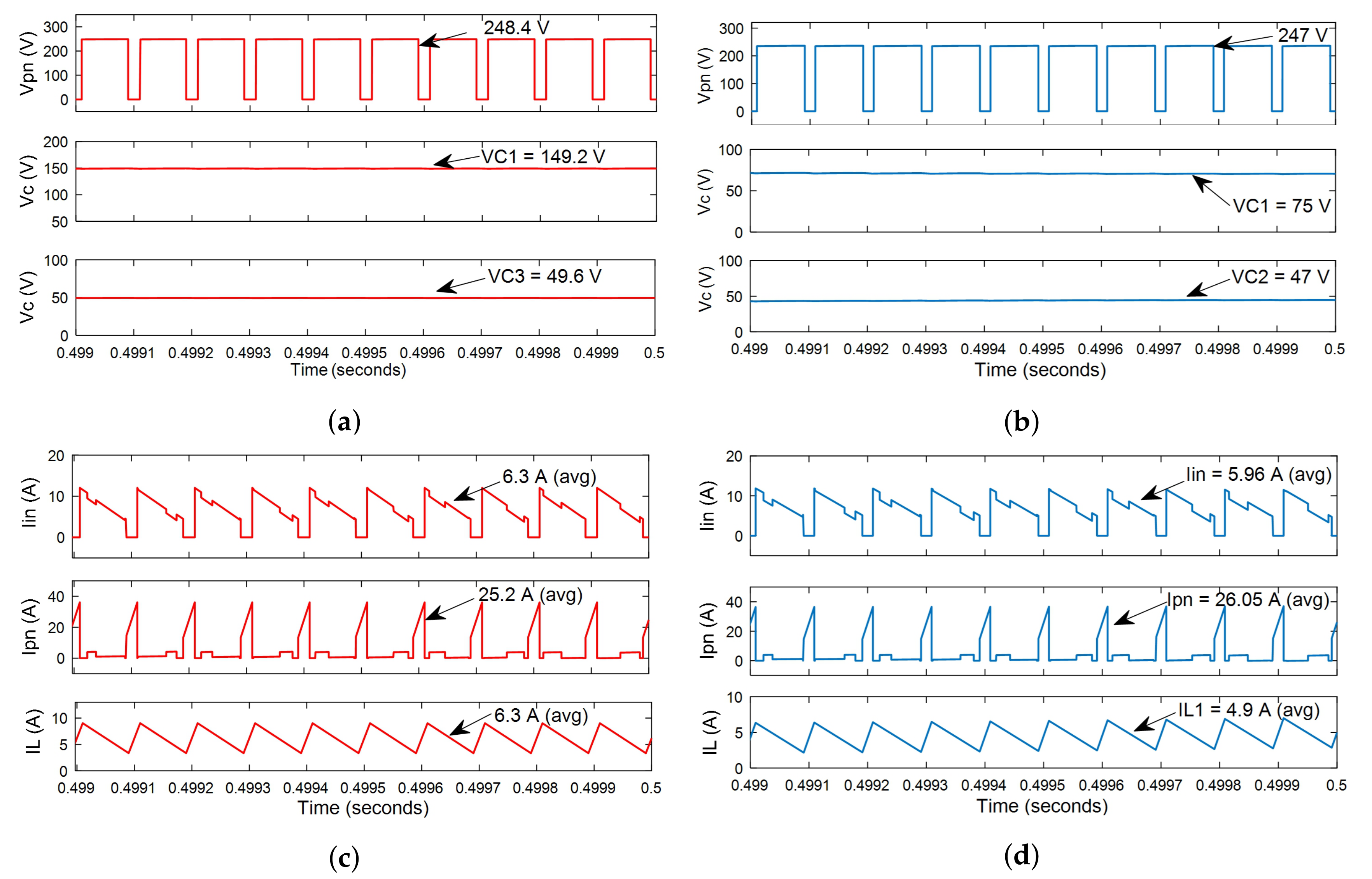
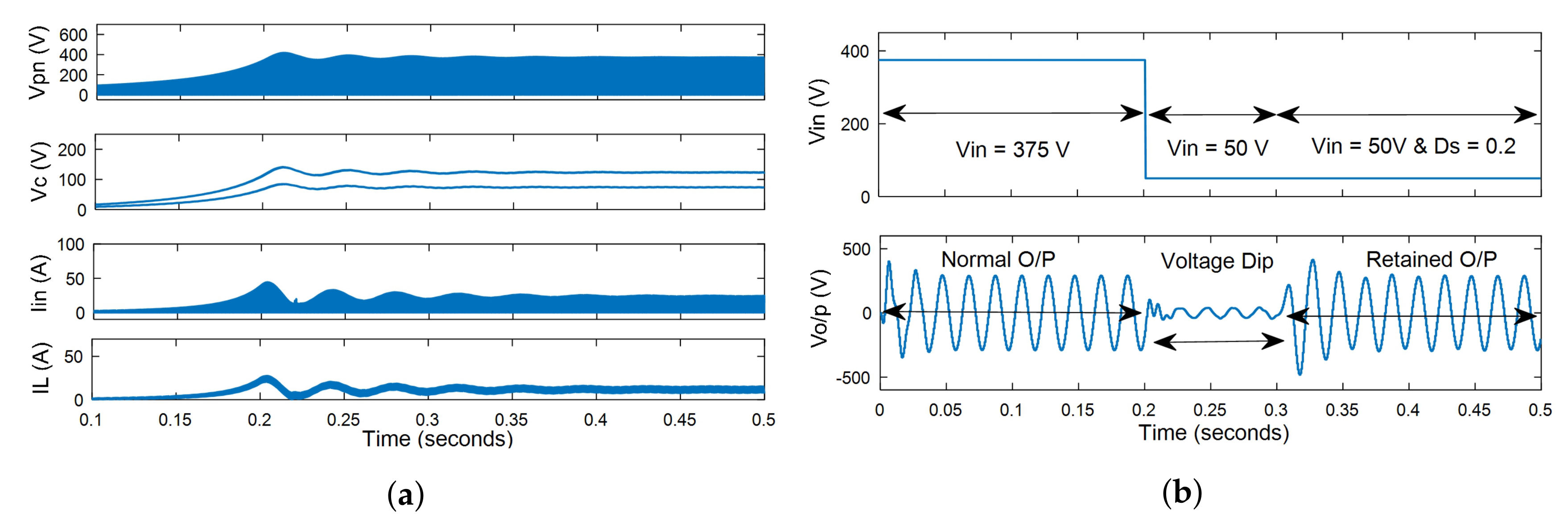
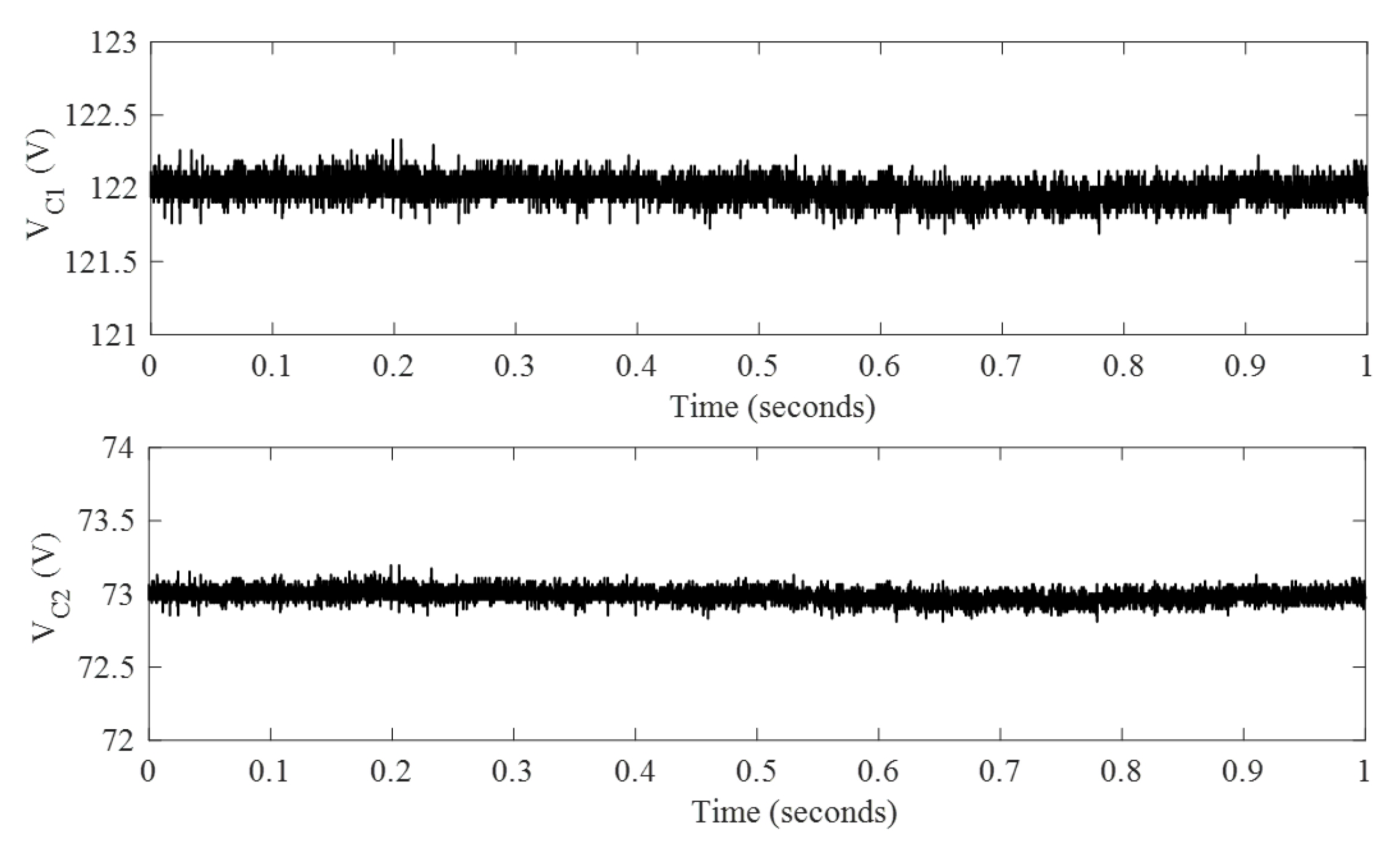
7. Simulation Results
- Analysis of the voltage and current characteristics with the fixed input voltage and shoot-through duty ratio.
- Analysis of the voltage and current characteristics with the fixed input voltage and boost factor but different shoot-through duty ratios.
- Analysis of the voltage and current characteristics with the fixed input voltage but slower variations in the shoot-through duty ratio.
- Analysis of dynamic voltage compensation characteristics.
- Case 1: analysis of the voltage and current characteristics with the fixed input voltage and shoot-through duty ratio.
- Case 2: analysis of the voltage and current characteristics with the fixed input voltage and boost factor but different shoot-through duty ratios.
- Case 3: analysis of the voltage and current characteristics with the fixed input voltage but slower variations in the shoot-through duty ratio.
- Case 4: analysis of dynamic voltage compensation characteristics
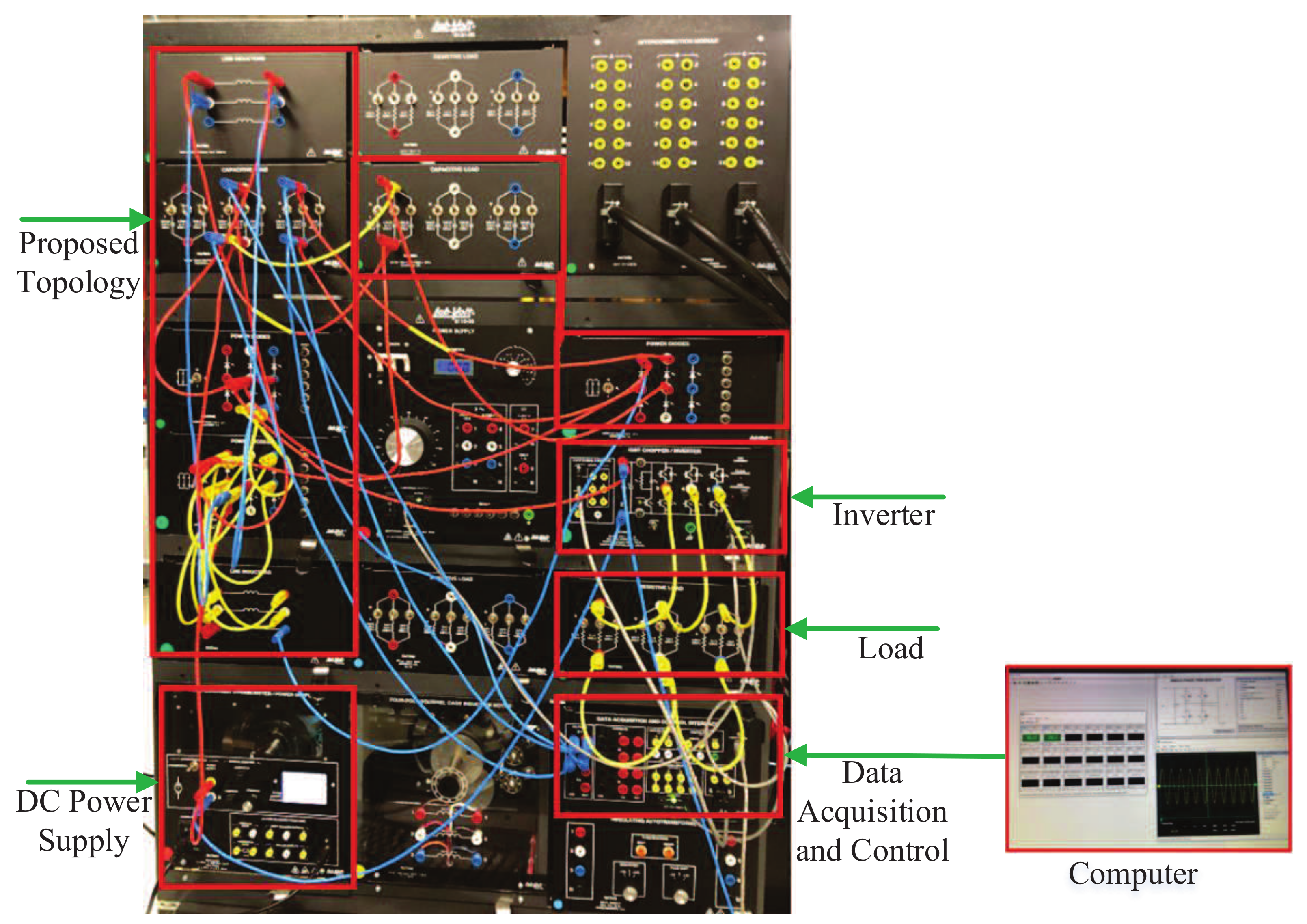
8. Experimental Validation
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, F.Z. Z-source inverter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2003, 39, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangaprakash, S.; Krishnan, A. Implementation and critical investigation on modulation schemes of three phase impedance source inverter. Iran. J. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2010, 6, 84–92. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, F.Z.; Joseph, A.; Wang, J.; Shen, M.; Chen, L.; Pan, Z.; Ortiz-Rivera, E.; Huang, Y. Z-source inverter for motor drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2005, 20, 857–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Shen, M.; Peng, F.Z.; Wang, J. Z-Source Inverter for Residential Photovoltaic Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2006, 21, 1776–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.W.; Keyhani, A. Control of a fuel cell based Z-source converter. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2007, 22, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.Z.; Shen, M.; Holland, K. Application of Z-source inverter for traction drive of fuel cell—Battery hybrid electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2007, 22, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, B.; Liu, X.; Cui, S. Analysis of a single-phase Z-source inverter for battery discharging in vehicle to grid applications. Energies 2011, 4, 2224–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, P.; Shen, W.X. Single-phase uninterruptible power supply based on Z-source inverter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 2997–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonar, S.; Maity, T.; Minu, M. Single phase transformerless wide range ac boost voltage regulator based on z-source network. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2013, 47, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, S. Stator Current Harmonic Reduction in a Novel Half Quasi-Z-Source Wind Power Generation System. Energies 2016, 9, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshi, N.; Padmanaban, S.; Ionel, D.; Mihet-Popa, L.; Azam, F. Hybrid PV-Wind, Micro-Grid Development Using Quasi-Z-Source Inverter Modeling and Control—Experimental Investigation. Energies 2018, 11, 2277. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Xie, S.; Zhang, C.; Xu, Z. Improved Z-source inverter with reduced Z-source capacitor voltage stress and soft-start capability. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2009, 24, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.; Peng, F.Z. Four quasi-Z-source inverters. In Proceedings of the Power Electronics Specialists Conference, Rhodes, Greece, 15–19 June 2008; pp. 2743–2749. [Google Scholar]
- Loh, P.C.; Gao, F.; Blaabjerg, F. Embedded EZ-source inverters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2010, 46, 256–267. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.; Ge, B.; Bi, D.; Peng, F.Z. Analysis and control of quasi-Z source inverter with battery for grid-connected PV system. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2013, 46, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wei, J.; Xie, S. Grid-tied photovoltaic system with series Z-source inverter. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2013, 7, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Yu, K.; Luo, F.L. Switched inductor Z-source inverter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2010, 25, 2150–2158. [Google Scholar]
- Gajanayake, C.J.; Luo, F.L.; Gooi, H.B.; So, P.L.; Siow, L.K. Extended-boost Z-source inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2010, 25, 2642–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.K.; Lim, Y.C.; Choi, J.H. Two switched-inductor quasi-Z-source inverters. Iet Power Electron. 2012, 5, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.; Zheng, J.; Mei, J. Novel switched-inductor quasi-Z-source inverter. J. Power Electron. 2014, 14, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, A.V.; Chun, T.W.; Kim, H.G. Extended boost active-switched-capacitor/switched-inductor quasi-Z-source inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 5681–5690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, E.; Asl, E.S.; Babayi, M.H.; Laali, S. Developed embedded switched-Z-source inverter. IET Power Electron. 2016, 9, 1828–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhani, N.; Kannan, R.; Romlie, M.F. Modified Topology of Z-Source Inverter by Switched Inductor with Series Impedance Network. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Intelligent and Advanced System (ICIAS), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 13–14 August 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhani, N.; Kannan, R.; Romlie, M.F. Steady state performance analysis of one switched inductor series Z-source inverter. In Proceedings of the 5th IET International Conference on Clean Energy and Technology (CEAT2018), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 5–6 September 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzelecki, R.; Adamowicz, M.; Strzelecka, N.; Bury, W. New type T-source inverter. In Proceedings of the Compatibility and Power Electronics, CPE’09, Badajoz, Spain, 20–22 May 2009 ; pp. 191–195. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M.; Li, D.; Loh, P.C.; Blaabjerg, F. Tapped-inductor Z-source inverters with enhanced voltage boost inversion abilities. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Sustainable Energy Technologies (ICSET), Kandy, Sri Lanka, 6–9 December 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, W.; Peng, F.Z.; Cha, H. Trans-Z-source inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2011, 26, 3453–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamowicz, M.; Strzelecki, R.; Peng, F.Z.; Guzinski, J.; Rub, H.A. New type LCCT-Z-source inverters. In Proceedings of the 2011-14th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications (EPE 2011), Birmingham, UK, 30 August–1 September 2011; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, M.K.; Lim, Y.C.; Kim, Y.G. TZ-source inverters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 5686–5695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, P.C.; Li, D.; Blaabjerg, F. Γ-Z-source inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 4880–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, H.; Madadi, H. Enhanced-boost Z-source inverters with switched Z-impedance. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.; Eslahchi, A.H.; Mardaneh, M. Two Symmetric Extended-Boost Embedded Switched-Inductor Quasi-Z-Source Inverter With Reduced Ripple Continuous Input Current. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 5096–5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, A.V.; Chun, T.W. Modified Capacitor-Assisted Z-Source Inverter Topology with Enhanced Boost Ability. J. Power Electron. 2017, 17, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Li, W.; Gu, Y.; Cui, W.; He, X. Improved transformerless inverter with common-mode leakage current elimination for a photovoltaic grid-connected power system. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Soon, T.K.; Mekhilef, S. A single phase doubly grounded semi-Z-source inverter for photovoltaic (PV) systems with maximum power point tracking (MPPT). Energies 2014, 7, 3618–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhani, N.; Kannan, R.; Mahmud, M.A.; Romlie, M.F. Performance Analysis of a Modernized Z-Source Inverter for Robust Boost Control in Photovoltaic Power Conditioning Systems. Electronics 2019, 8, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemmen, R.S. Analysis for the effect of inverter ripple current on fuel cell operating condition. J. Fluids Eng. 2003, 125, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertasgin, G.; Whaley, D.M.; Ertugrul, N.; Soong, W.L. Analysis of DC Link Energy Storage for Single-Phase Grid-Connected PV Inverters. Electronics 2019, 8, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Joseph, A.; Huang, Y.; Peng, F.Z.; Qian, Z. Design and Development of a 50kW Z-Source Inverter for Fuel Cell Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2006 CES/IEEE 5th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference, Shanghai, China, 14–16 August 2006; Volume 2, pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Joseph, A.; Wang, J.; Peng, F.Z.; Adams, D.J. Comparison of Traditional Inverters and Z-Source Inverter for Fuel Cell Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2007, 22, 1453–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, C.T.; Shen, A.; Dzung, P.Q.; Anh, N.B.; Phu, N.X. A comparison of control methods for Z-source inverter. Energy Power Eng. 2012, 4, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capacitors Datasheets. Available online: http://Capacitors datasheets/www.mouser.com (accessed on 25 March 2019).



| No | Parameters | MCA-ZSI | Proposed SL-SBZSI |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Boost factor, B | ||
| 2 | Capacitor voltage, | ||
| 3 | Capacitor voltage, | ||
| 4 | Voltage gain, G | ||
| 5 | Inductor current, | ||
| 6 | Input current, | ||
| 7 | ST current, | ||
| 8 | Load current, |
| No | Parameters | Symbols | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Input voltage | 50 V | |
| 2 | Capacitance | 500 F | |
| 3 | Inductance | 700 H | |
| 4 | Switching frequency | 10 kHz | |
| 5 | Output filter | 1 mH, 110 F | |
| 6 | Load | 60 /phase |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Subhani, N.; Kannan, R.; Mahmud, M.A.; Roy, T.K.; Romlie, M.F. Analysis of Steady-State Characteristics for a Newly Designed High Voltage Gain Switched Inductor Z-Source Inverter. Electronics 2019, 8, 940. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8090940
Subhani N, Kannan R, Mahmud MA, Roy TK, Romlie MF. Analysis of Steady-State Characteristics for a Newly Designed High Voltage Gain Switched Inductor Z-Source Inverter. Electronics. 2019; 8(9):940. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8090940
Chicago/Turabian StyleSubhani, Nafis, Ramani Kannan, Md. Apel Mahmud, Tushar Kanti Roy, and Mohd Fakhizan Romlie. 2019. "Analysis of Steady-State Characteristics for a Newly Designed High Voltage Gain Switched Inductor Z-Source Inverter" Electronics 8, no. 9: 940. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8090940
APA StyleSubhani, N., Kannan, R., Mahmud, M. A., Roy, T. K., & Romlie, M. F. (2019). Analysis of Steady-State Characteristics for a Newly Designed High Voltage Gain Switched Inductor Z-Source Inverter. Electronics, 8(9), 940. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8090940







