Bidirectional Information Transmission in SWIPT System with Single Controlled Chopper Receiver
Abstract
1. Introduction
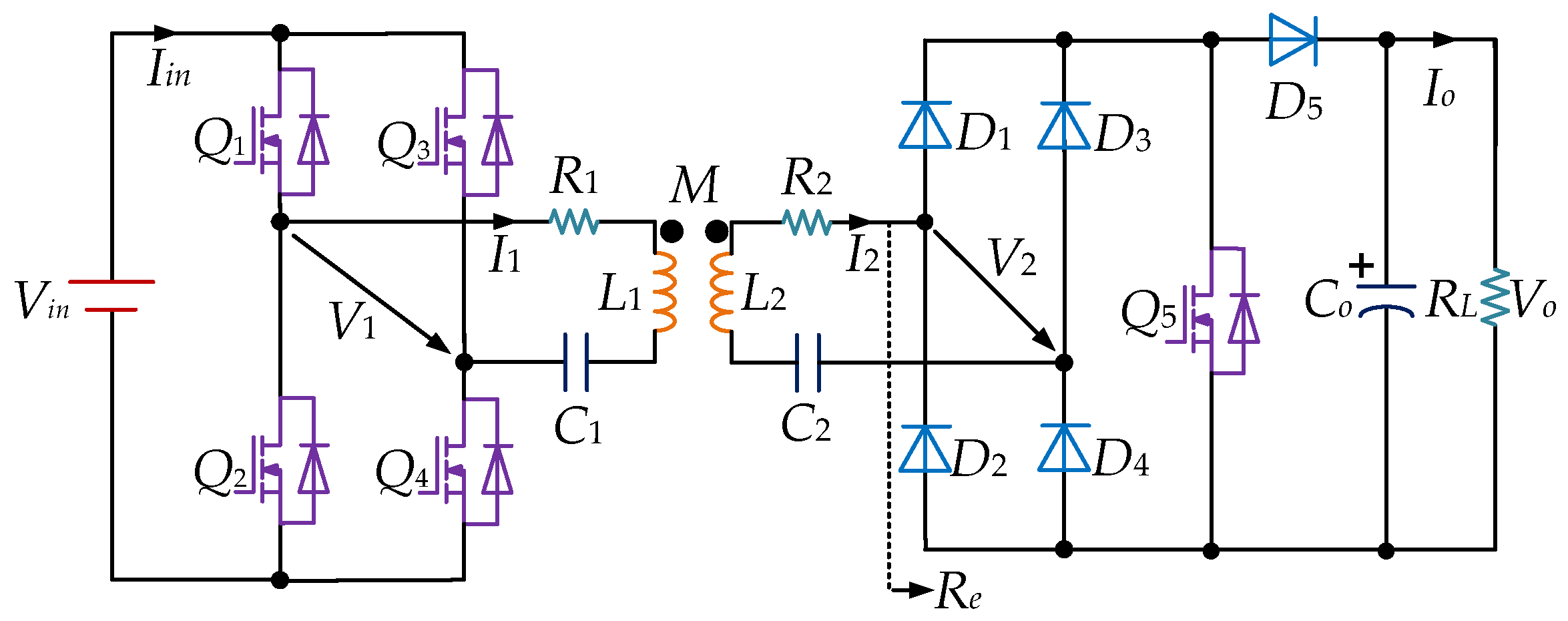
2. Model and Analysis of the Proposed SWIPT System
2.1. Model of the Proposed Topology
2.2. Analysis of Wireless Power Transfer
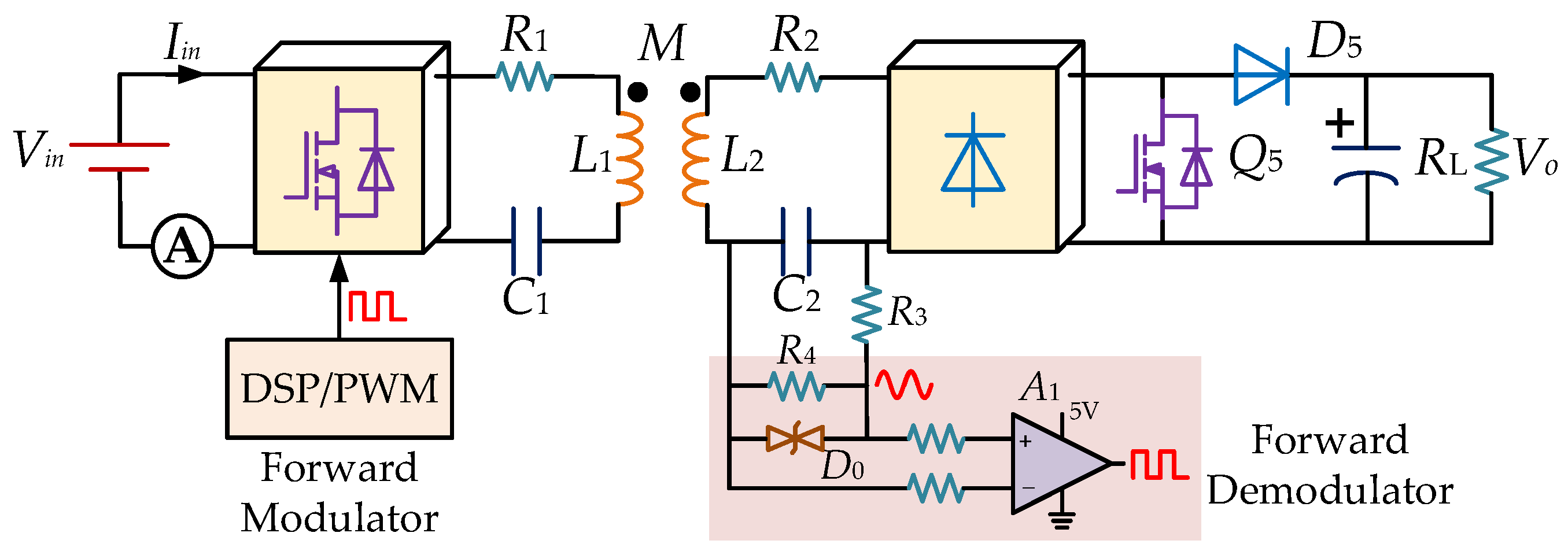
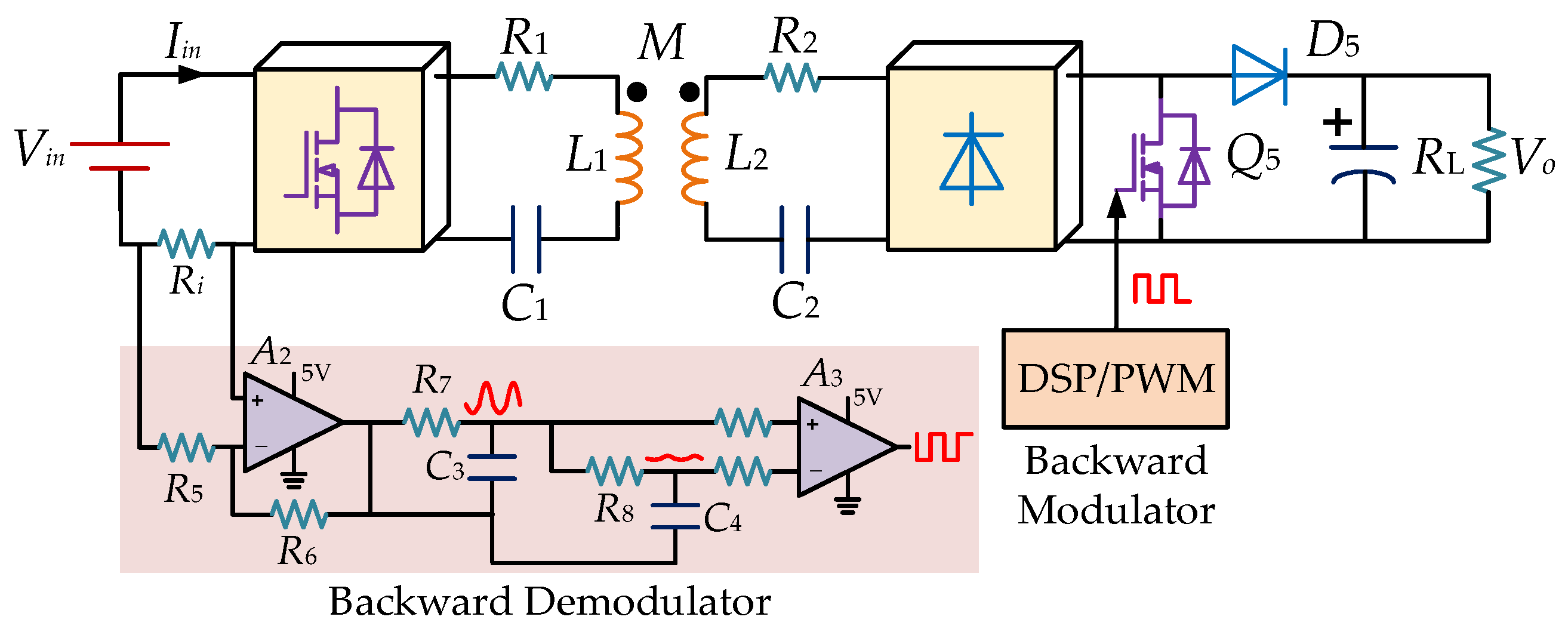
3. Principle of Information Transmission
3.1. Information Forward Transmission
3.2. Information Backward Transmission
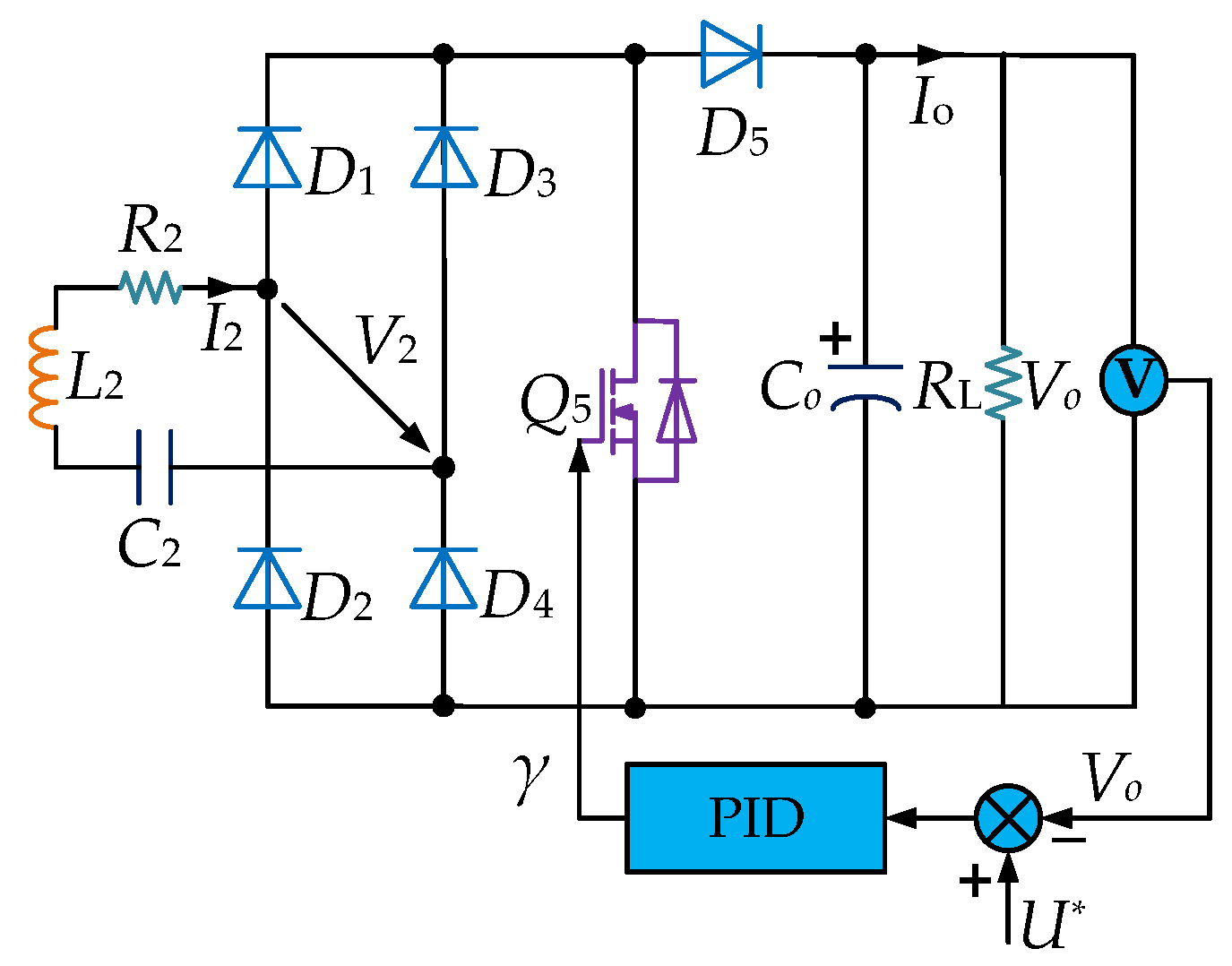
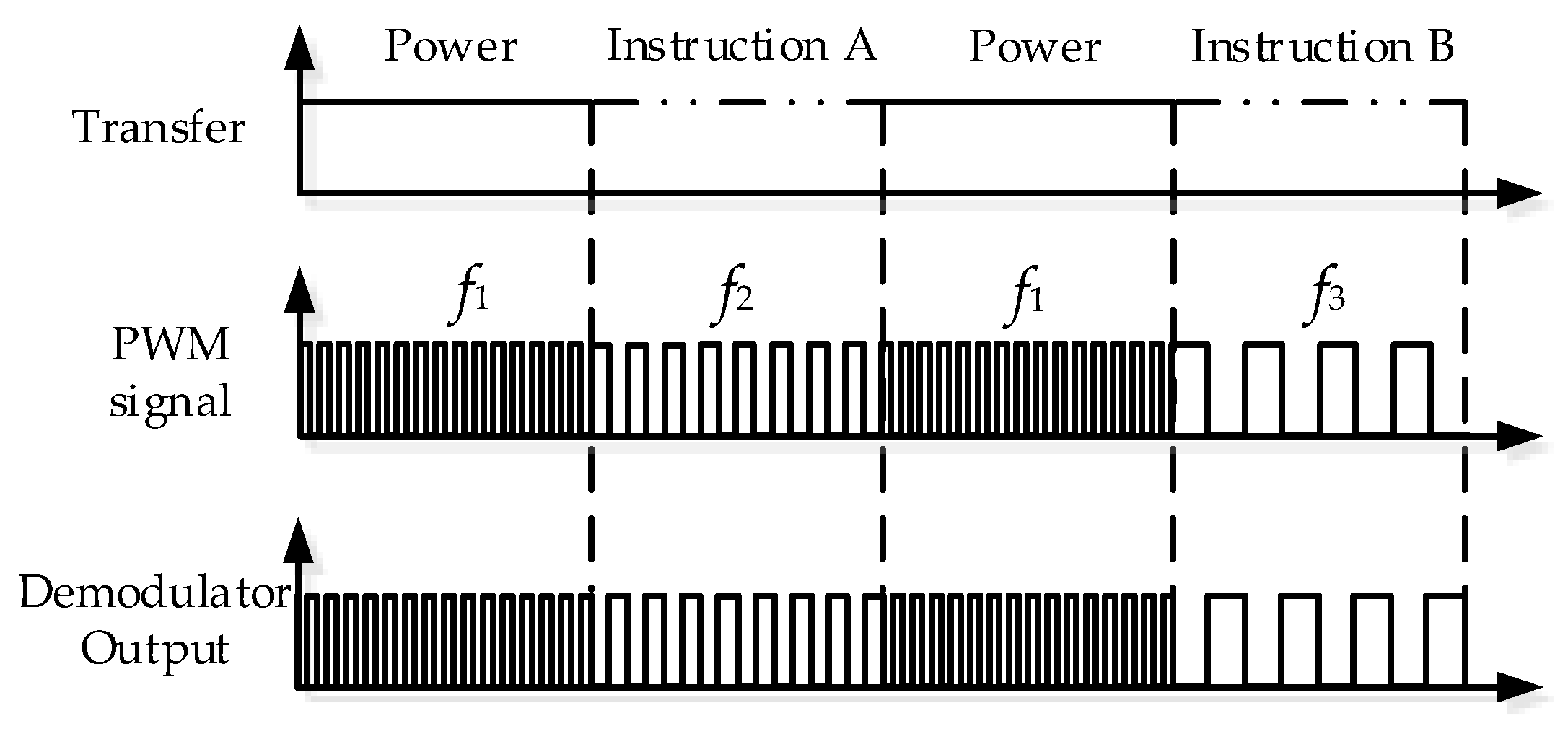
4. Method of Information Transmission
4.1. Mode A: Predefined Instruction Transmission
4.2. Mode B: Continuous Data Transmission
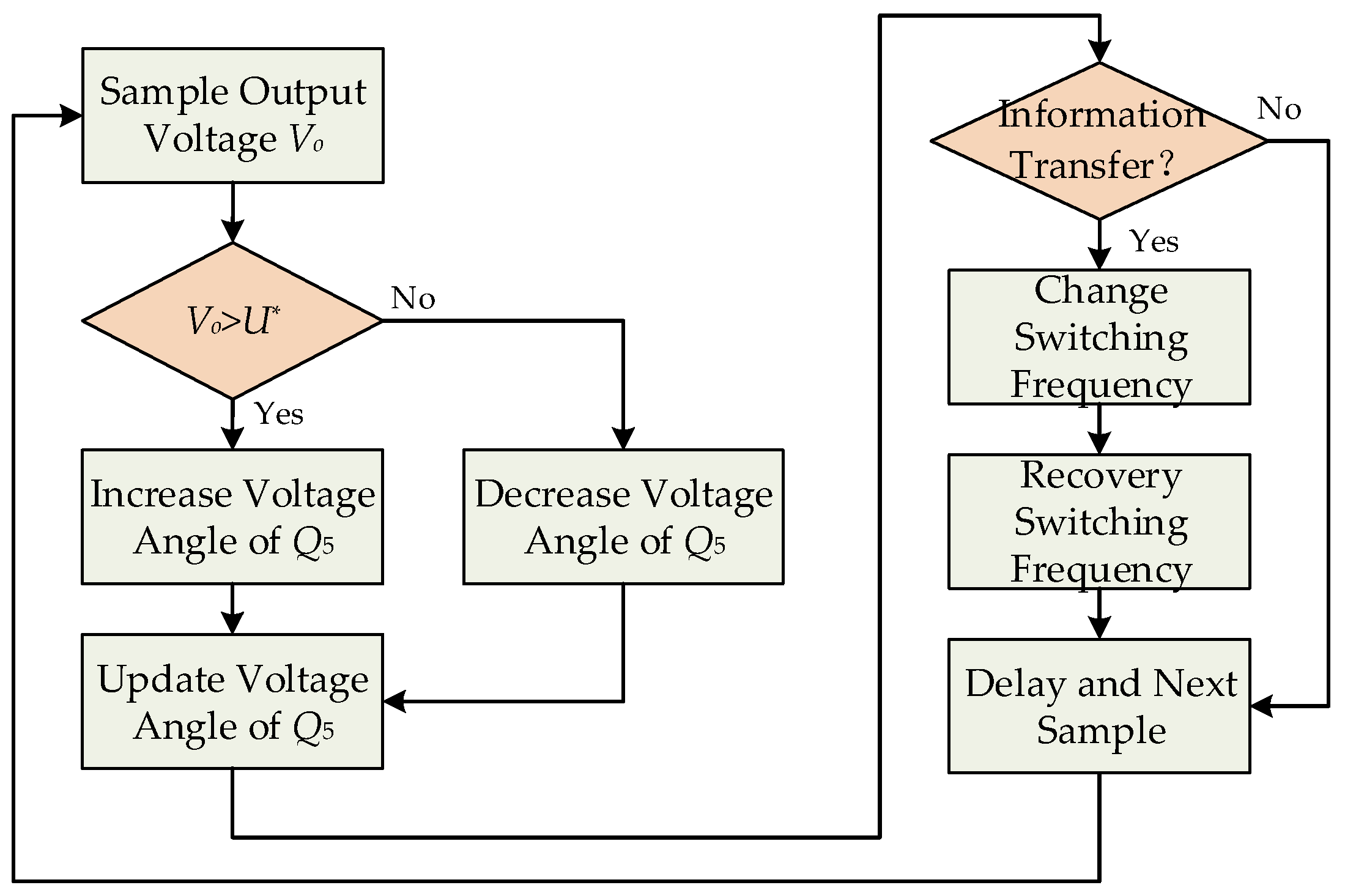
4.3. Simultaneous Power and Information Transfer Control Algorithm
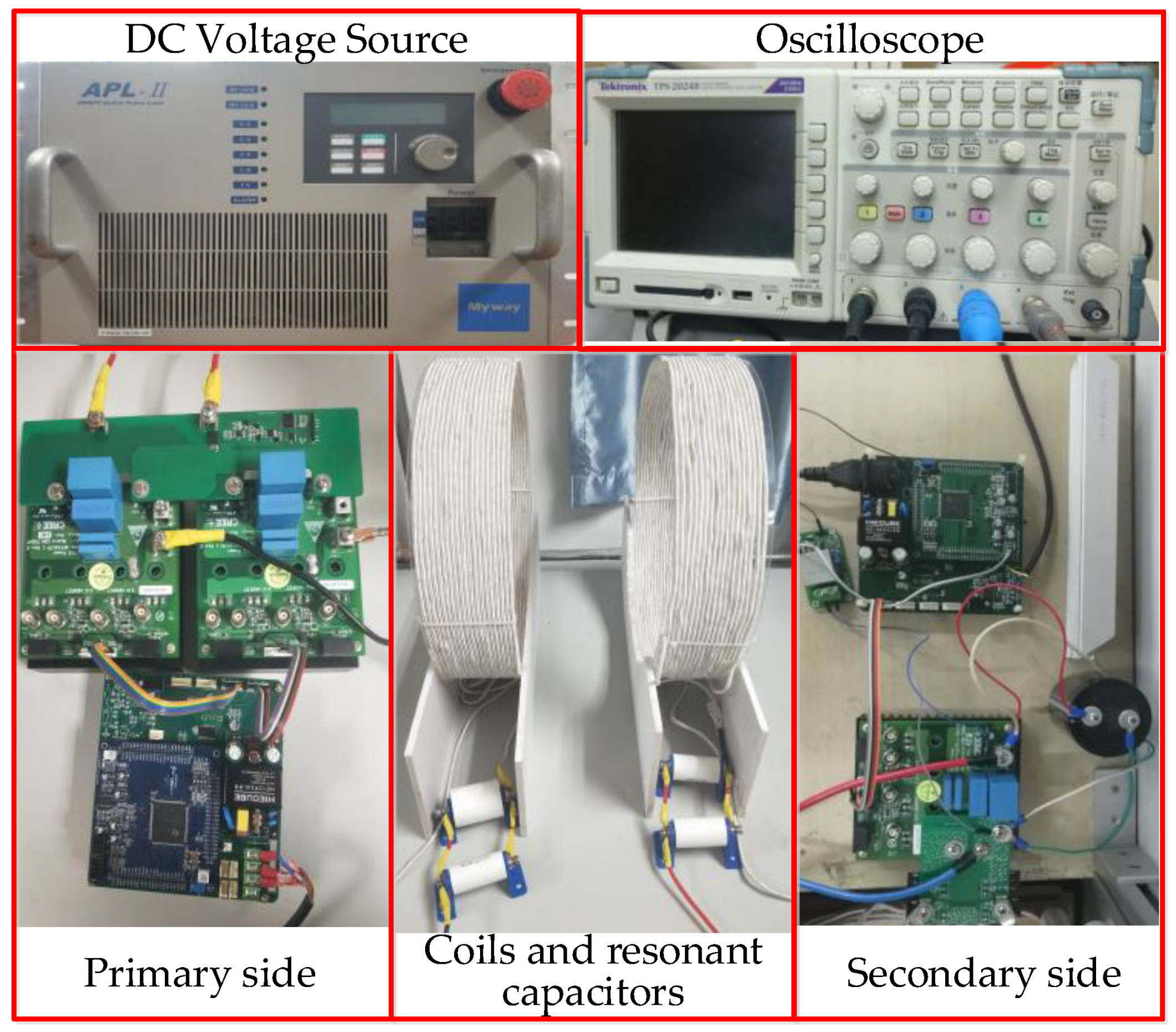
5. Verifications
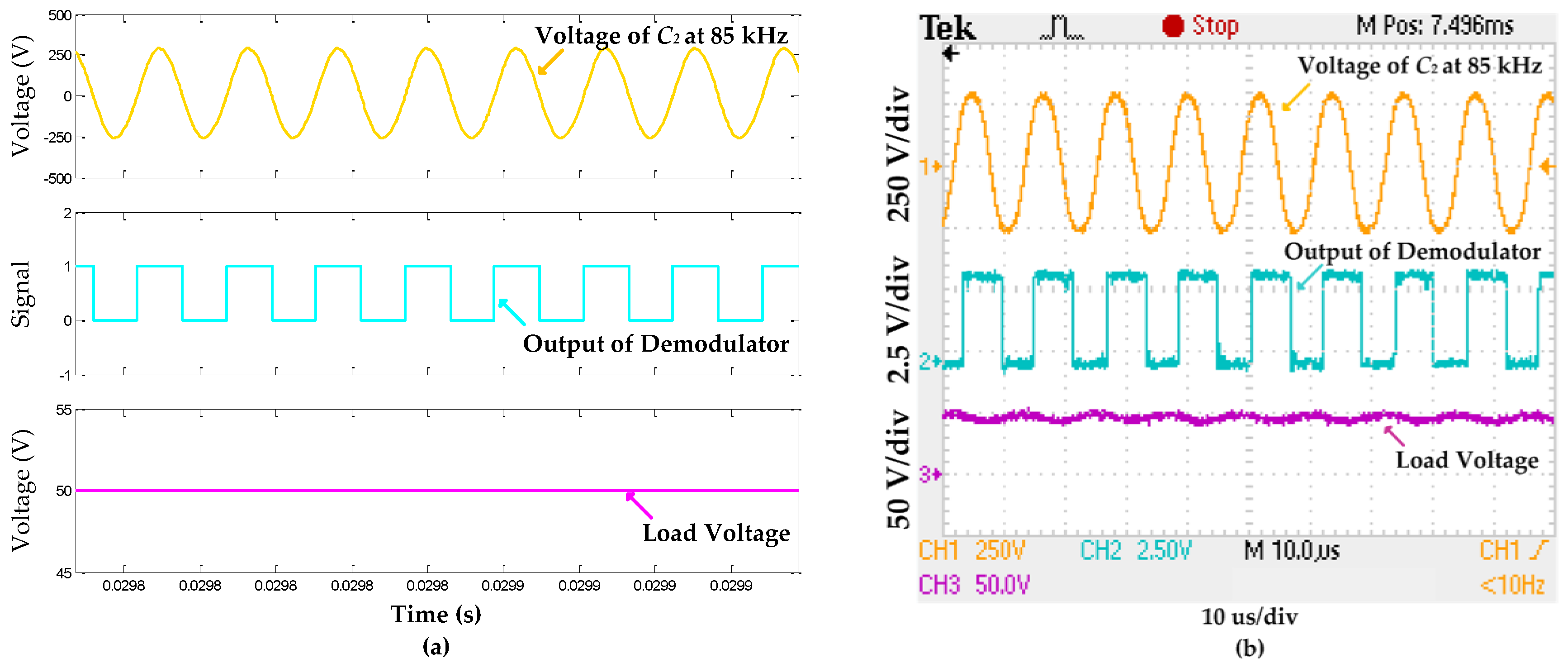
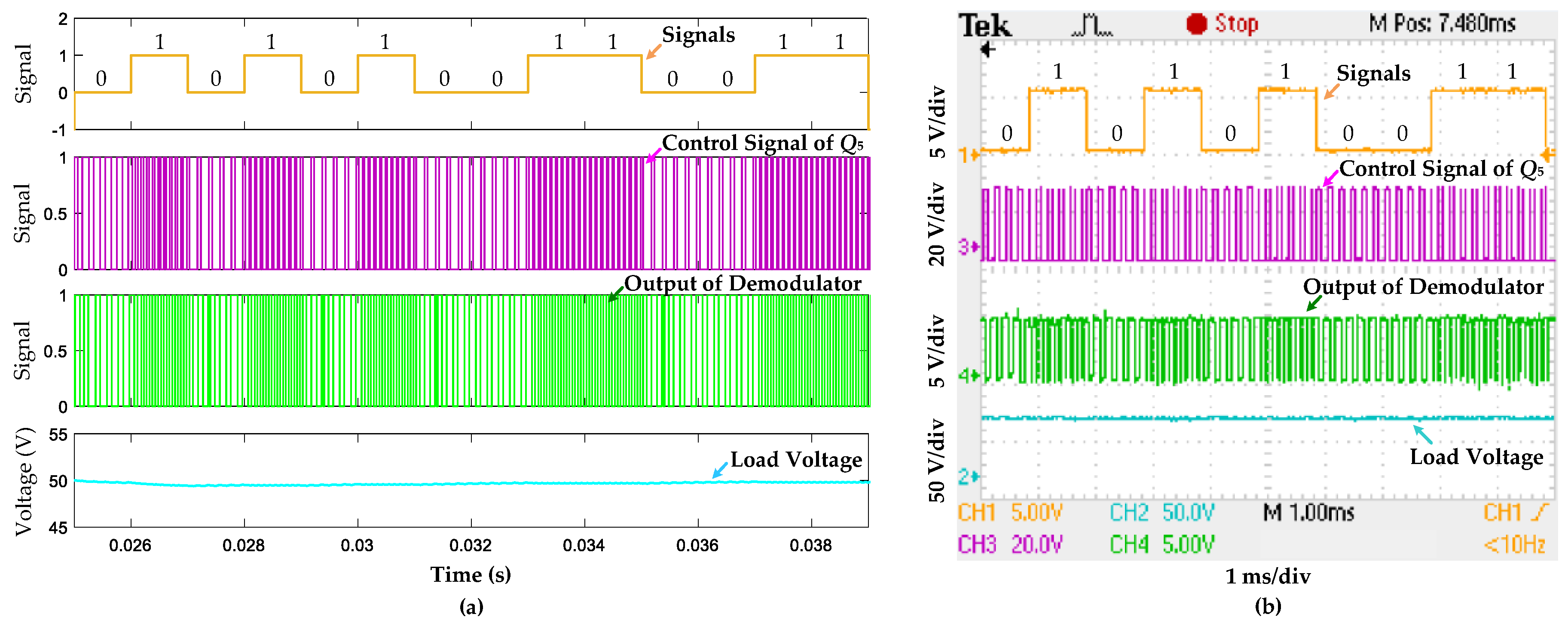
5.1. Results and Analysis of Information Forward Transmission
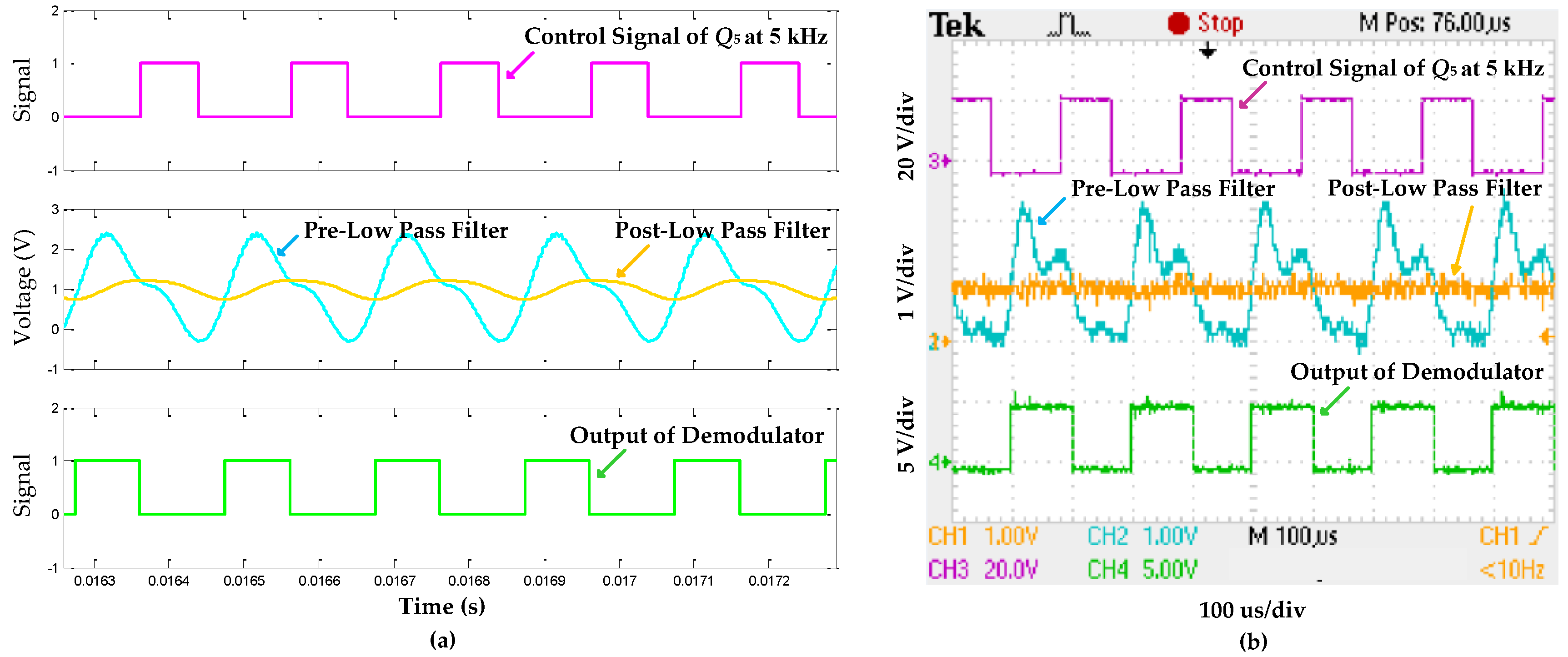
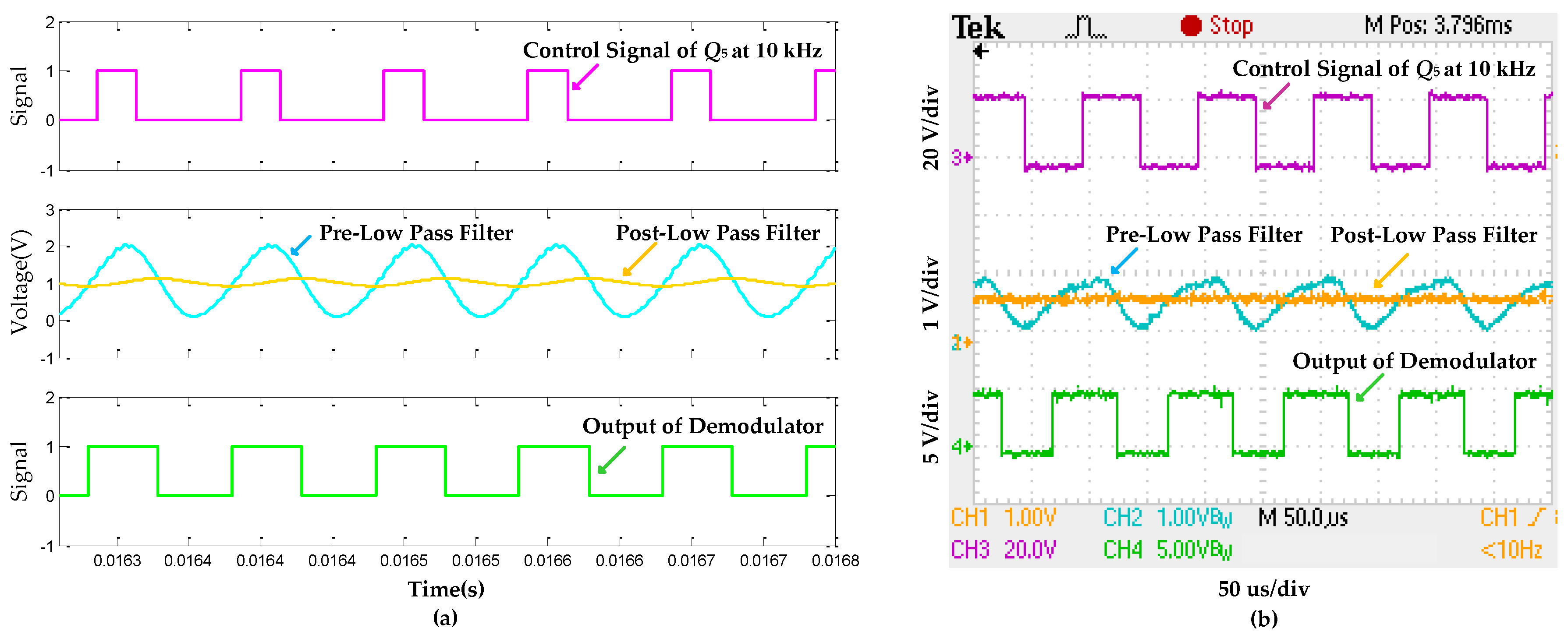
5.2. Results and Analysis of Information Backward Transmission
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garcia, D.T.; Vazque, J.; Roncero, S.P. Design, implementation issues and performance of an inductive power transfer system for electric vehicle chargers with series–series compensation. IET Power Electron. 2015, 8, 1920–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, S.Y.R.; Ho, W.C. A new generation of universal contactless battery charging platform for portable consumer electronic equipment. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2005, 20, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallan, J.; Villa, J.L.; Llombart, A. Optimal design of ICPT systems applied to electric vehicle battery charge. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 2140–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liu, X.; Jin, N.; Tang, H. Wireless Power Transfer for Battery Powering System. Electronics 2018, 7, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Houran, M.; Yang, X.; Chen, W. Magnetically Coupled Resonance WPT: Review of Compensation Topologies, Resonator Structures with Misalignment, and EMI Diagnostics. Electronics. 2018, 7, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Li, L.M. Integrated Wireless Communications and Wireless Power Transfer: An Overview. Phys. Commun. 2017, 25, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrimawithana, D.J.; Madawala, U.K.; Neath, M. A Synchronization Technique for Bidirectional IPT Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jin, N.; Yang, X.; Wang, T. A Novel Synchronization Technique for Wireless Power Transfer Systems. Electronics 2018, 7, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y. Load detection model of voltage-fed inductive power transfer system. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 5233–5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johari, R.; Krogmeier, J.V.; Love, D.J. Analysis and practical considerations in implementing multiple transmitters for wireless power transfer via coupled magnetic resonance. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 1774–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.; Dong, L.; Huang, X. Switching technique for inductive power transfer at high-Q regimes. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 2164–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, D.; Gong, C.; Qiao, W. A 3-coil simultaneous power and uplink data transmission inductive link for battery-less implantable devices. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Baltimore, MD, USA, 28–31 May 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, K.; Tang, X.; Mai, S.P.; Wang, Z.H. A Simultaneous Power and Downlink Data Transfer System with Pulse Phase Modulation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst.-II: Express Briefs. 2019, 66, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhao, C.; Lin, Z. Wireless Power and Data Transfer via a Common Inductive Link Using Frequency Division Multiplexing. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 7810–7820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, K.J.; Kim, H. Wireless information and power exchange for energy-constrained device-to-device communications. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 3175–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusamarello, V.J.; Blauth, Y.B.; De-Azambuja, R. Power transfer with an inductive link and wireless tuning. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2013, 62, 924–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yan, P.X.; Wang, Z.H. The parallel transmission of power and data with the shared channel for an inductive power transfer system. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 5495–5502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Lu, R.; Su, C. Study on wireless energy and data transmission for long-range projectile. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2013, 41, 1370–1375. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Wang, P.; Tang, Y. Analysis of dual band power and data telemetry for biomedical implants. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits System. 2012, 6, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, G.; Atasoy, O.; Dehollain, C. Wireless energy and data transfer for in-vivo epileptic focus localization. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 4172–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kalbani, A.I.; Yuce, M.R.; Redoute, J.M. Design methodology for maximum power transmission, optimal ber-snr and data rate in biomedical implants. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2013, 17, 1897–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; and Zhang, G. Design and realization of the collective meter-reading system with power lines carrier. Power System Protection and Control. 2008, 36, 77–79. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz Lantada, A.; González, B.; Carlos; Lafont, M.P. Novel system for bite-force sensing and monitoring based on magnetic near field communication. Sensors 2012, 12, 11544–11558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.G.; Fang, C.; Li, X.F. Contactless power and data transmission for underwater sensor nodes. Eurasip J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2013, 2013, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besnoff, J.; Abbasi, M.; Ricketts, D.S. High data-rate communication in near-field rfid and wireless power using higher order modulation. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2016, 64, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonkusale, S.R.; Luo, Z. A Wireless Data and Power Telemetry System Using Novel BPSK Demodulator for Non-Destructive Evaluation of Structures. In Proceedings of the IEEE SENSORS, Atlanta, GA, USA, 28–31 October 2007; pp. 300–303. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, D.; Cirmirakis, D.; Schormans, M.; Perkins, T.A.; Donaldson, N.; and Demosthenous, A. An Integrated Passive Phase-Shift Keying Modulator for Biomedical Implants with Power Telemetry over a Single Inductive Link. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2017, 11, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, S.; Sarpeshkar, R. Power-efficient impedance-modulation wireless data links for biomedical implants. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2008, 2, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Smith, B.; Schild, J.H. Data transmission from an implantable biotelemeter by load-shift keying using circuit configuration modulator. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1995, 42, 524–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.R.; Luo, Z.Y.; Sonkusale, S. Fully Digital BPSK Demodulator and Multilevel LSK Back Telemetry for Biomedical Implant Transceivers. IEEE Trans. on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs. 2009, 56, 714–718. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Yao, L.; Xue, R.F.; Li, P.; Je, M.Y. An Integrated Wireless Power Management and Data Telemetry IC for High-Compliance-Voltage Electrical Stimulation Applications. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2016, 10, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.; Kim, C.; Park, J.; Joshi, S.; Cauwenberghs, G. Energy Recycling Telemetry IC with Simultaneous 11.5 mW Power and 6.78 Mb/s Backward Data Delivery over a Single 13.56 MHz Inductive Link. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits. 2016, 51, 2664–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.; Kim, C.; Park, J.; Joshi, S.; Cauwenberghs, G. Energy-Recycling Integrated 6.78-Mbps Data 6.3-mW Power Telemetry over a Single 13.56-MHz Inductive Link. In Proceedings of the 2014 Symposium on VLSI Circuits Digest of Technical Papers, Honolulu, HI, USA, 10–13 June 2014; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]






| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Coil inductance L1, L2 | 175 μH, 219 μH |
| Capacitance C1, C2 | 20 nF, 16 nF |
| Resistance R1, R2 | 0.33 Ω, 0.47 Ω |
| Power frequency f | 85 kHz |
| Input voltage Vin | 50 V |
| Mutual inductance M | 32 μH |
| Load resistance RL | 50 Ω |
| Load voltage Vo | 50 V |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Zhao, C.; Jin, N.; He, S.; Ma, D. Bidirectional Information Transmission in SWIPT System with Single Controlled Chopper Receiver. Electronics 2019, 8, 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8091027
Wu J, Zhao C, Jin N, He S, Ma D. Bidirectional Information Transmission in SWIPT System with Single Controlled Chopper Receiver. Electronics. 2019; 8(9):1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8091027
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jie, Chongyan Zhao, Nan Jin, Shuaibiao He, and Dianguang Ma. 2019. "Bidirectional Information Transmission in SWIPT System with Single Controlled Chopper Receiver" Electronics 8, no. 9: 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8091027
APA StyleWu, J., Zhao, C., Jin, N., He, S., & Ma, D. (2019). Bidirectional Information Transmission in SWIPT System with Single Controlled Chopper Receiver. Electronics, 8(9), 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8091027





