Incorporating a Model-Driven Approach into an Embedded Software Course
Abstract
1. Introduction
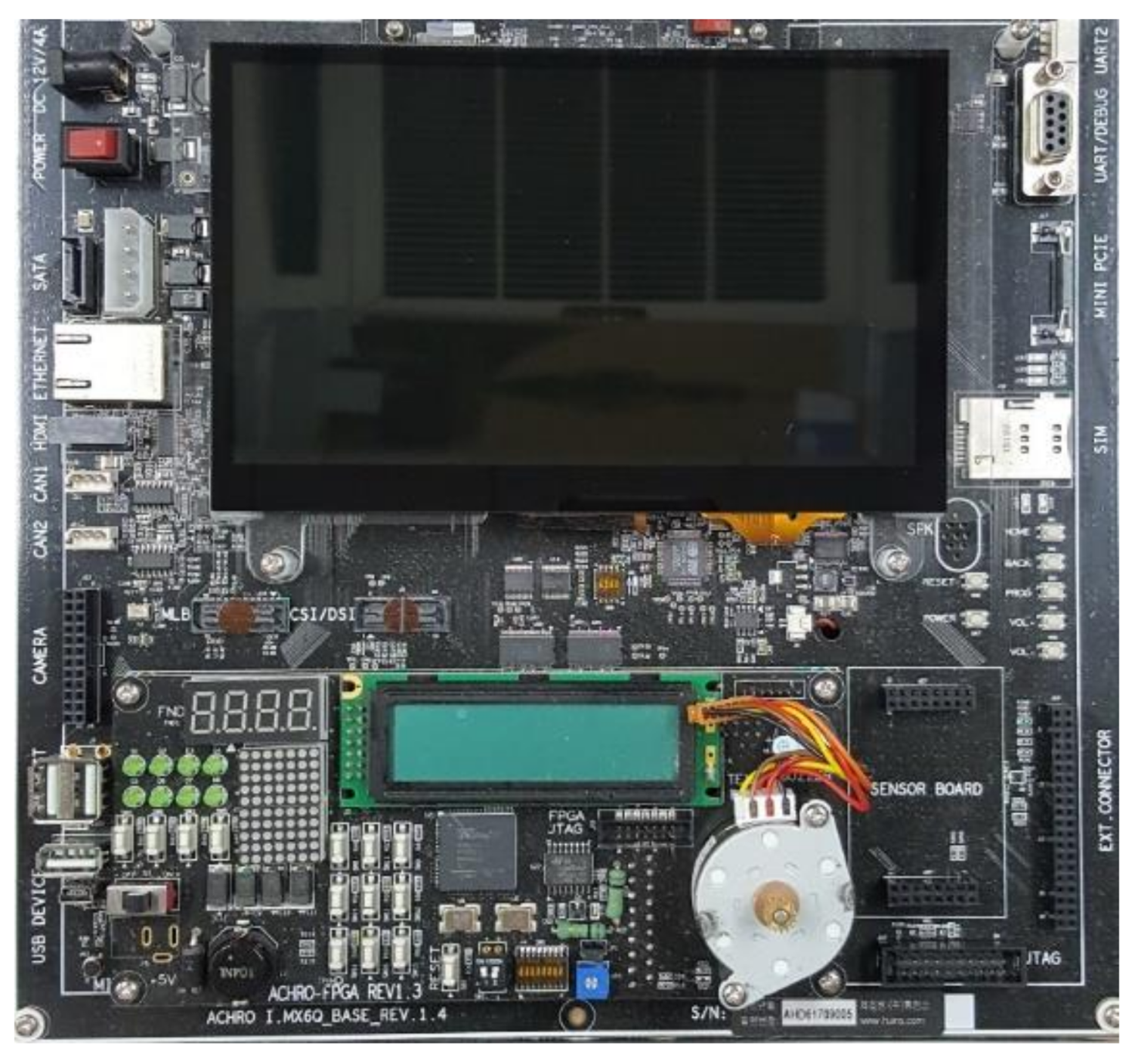
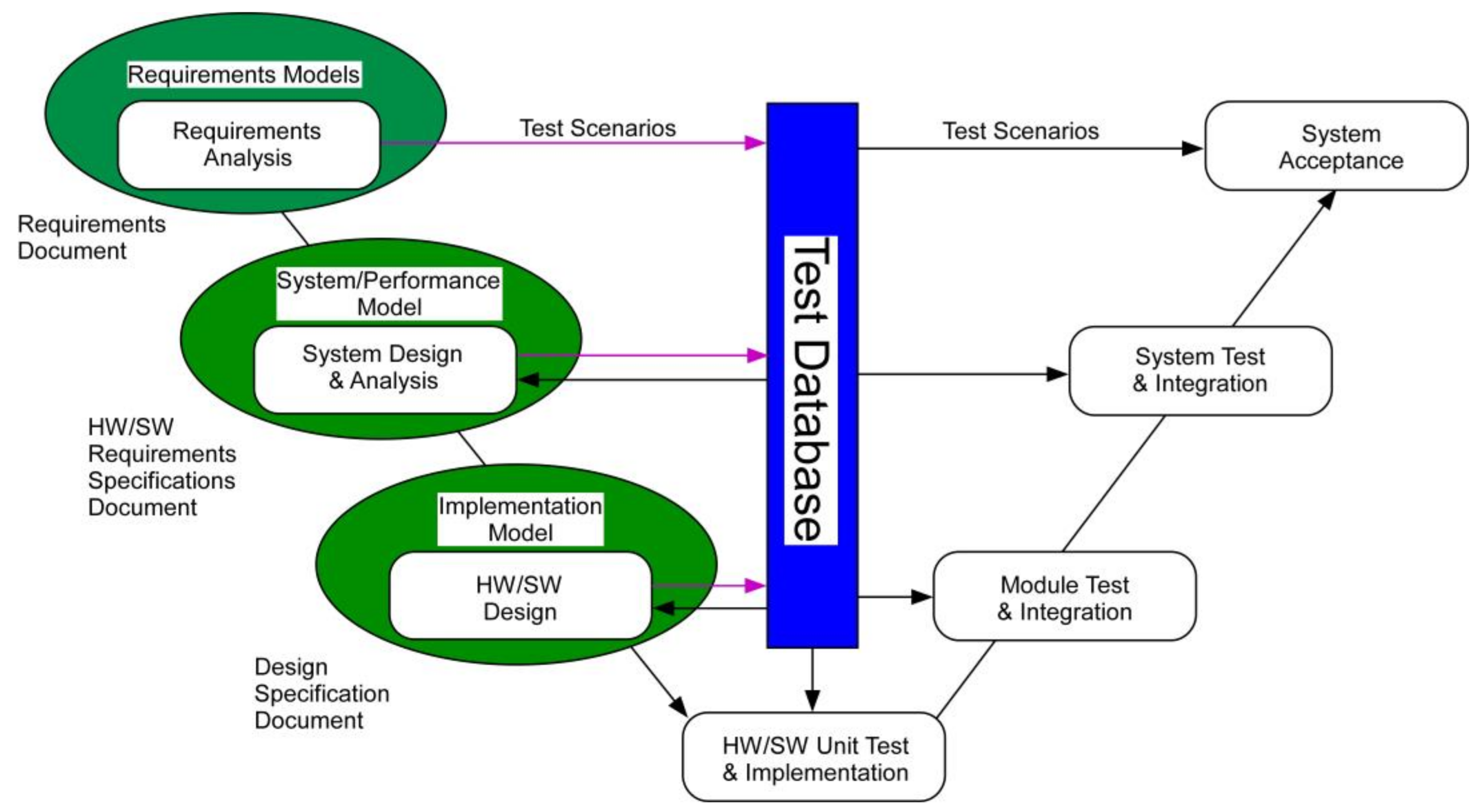
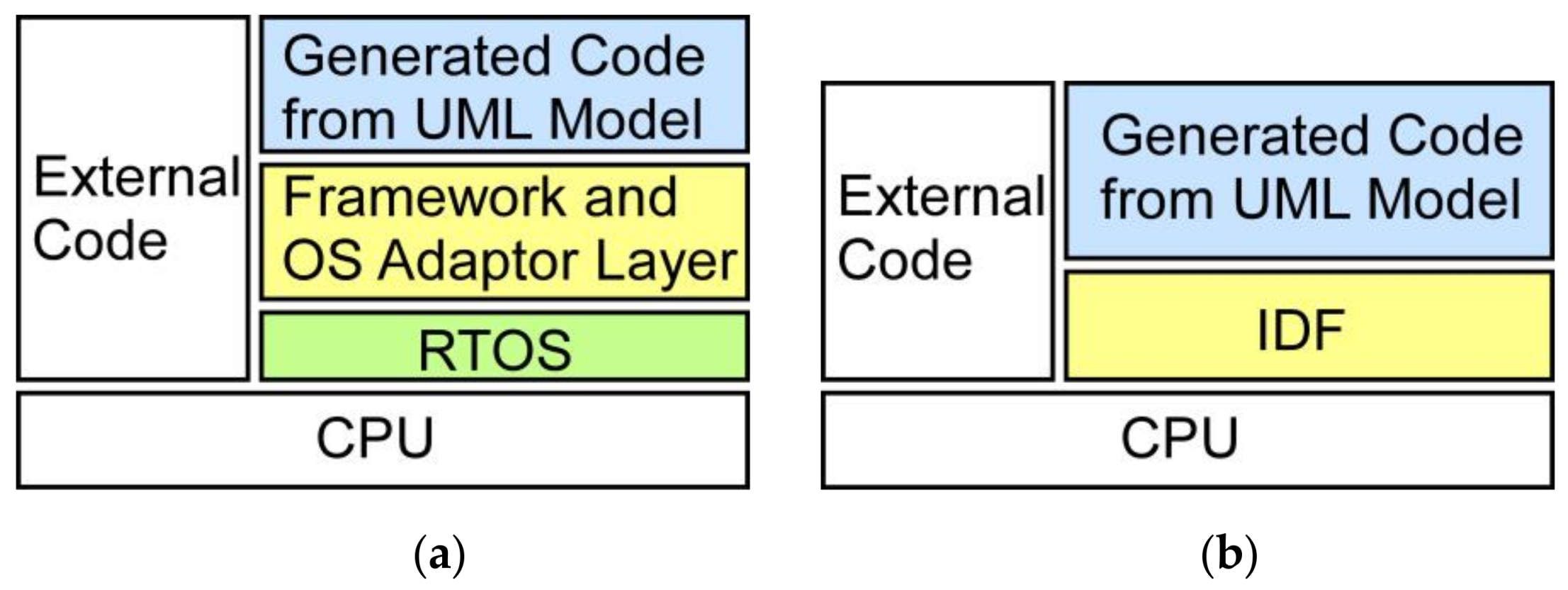
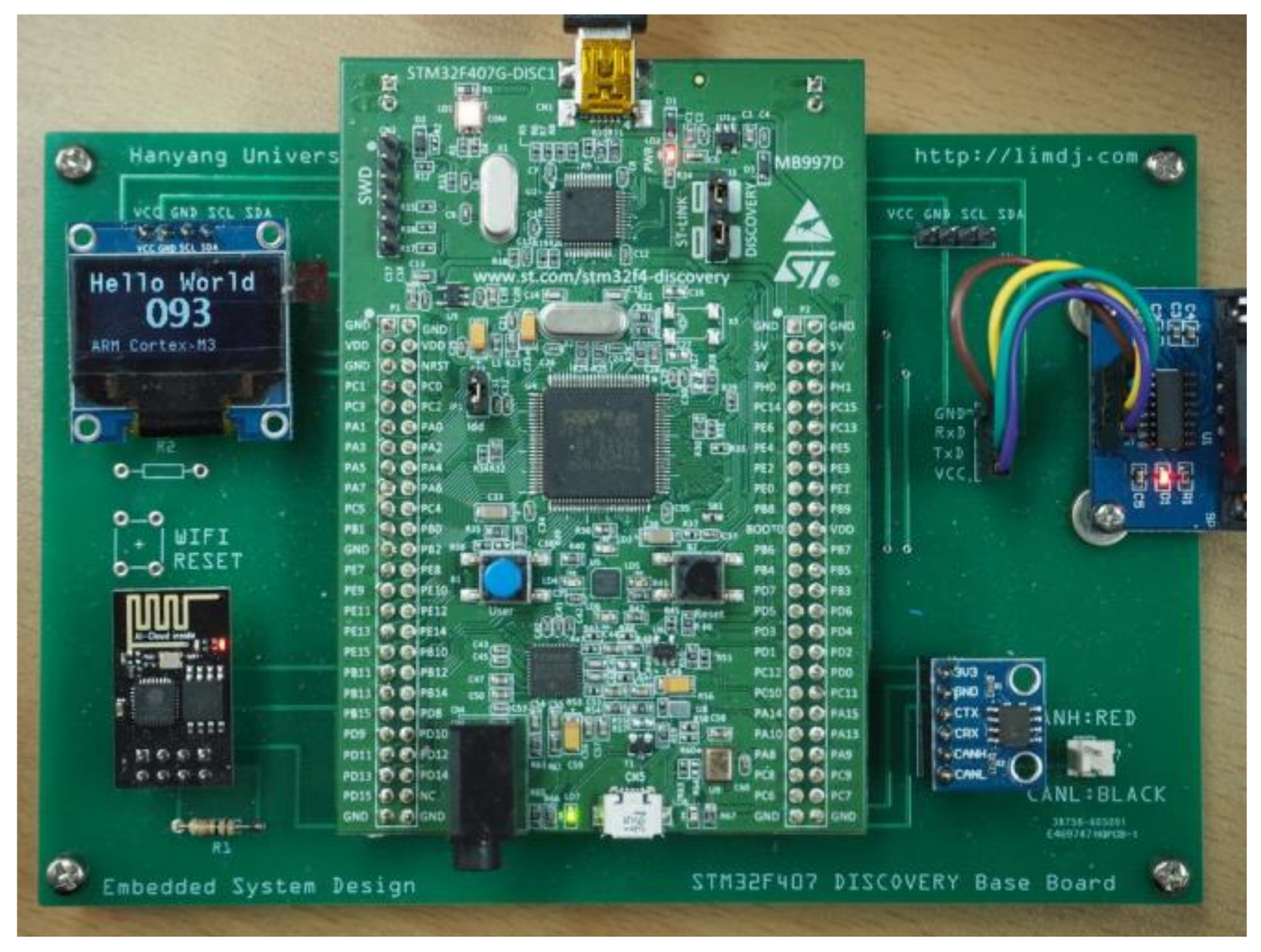
2. Embedded Platforms and the Software Modeling Tool
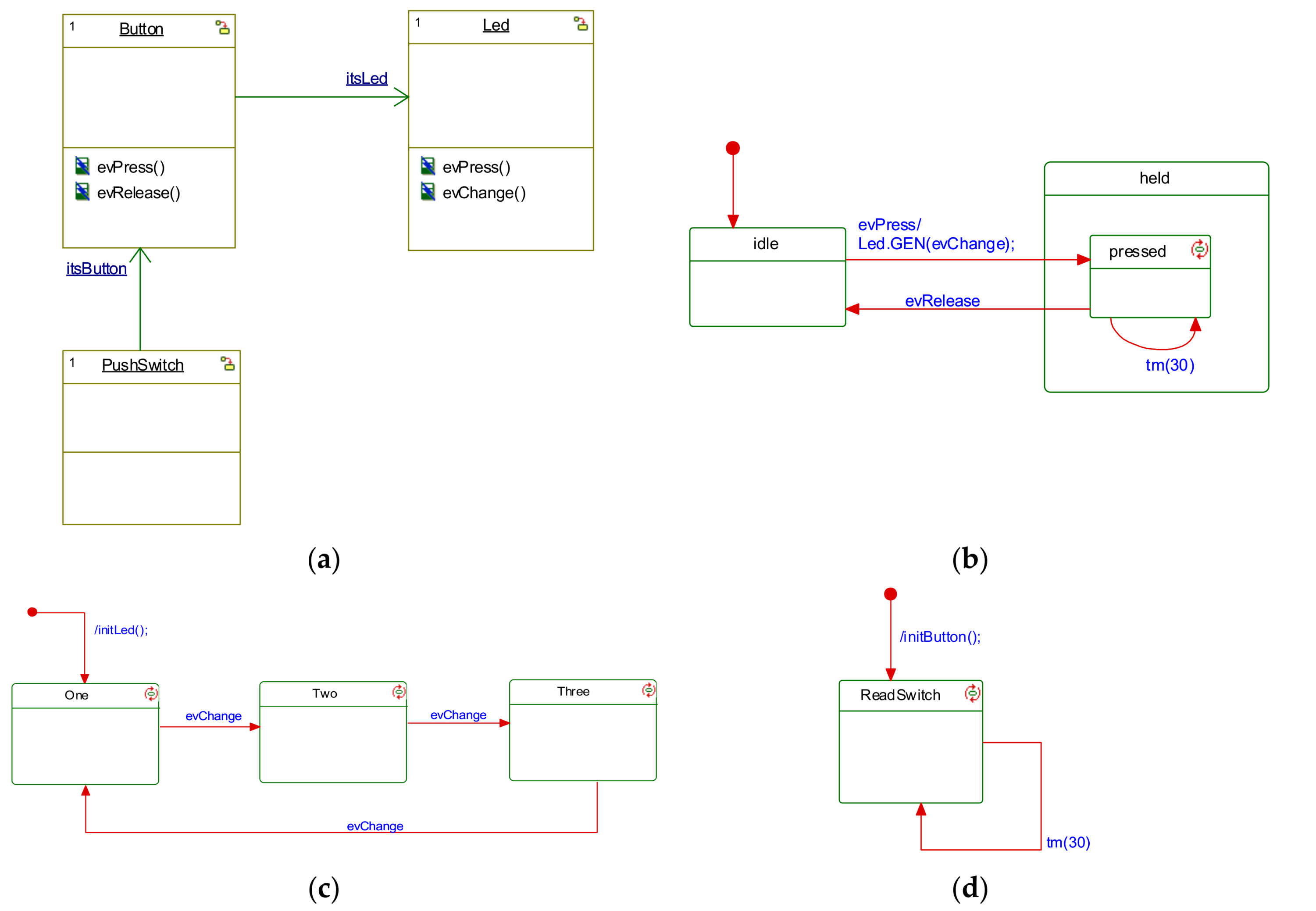
3. Course Overview and Lab Assignments
4. Student Feedback
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liggesmeyer, P.; Trapp, M. Trends in Embedded Software Engineering. IEEE Softw. 2009, 26, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangiovanni-Vincentelli, A.; Di Natale, M. Embedded system design for automotive applications. Computer 2007, 40, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staron, M. Automotive Software Architectures: An Introduction; Springer International Publishing AG: Basel, Switzerland, 2017; p. 52. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 26262-9:2011(en) Road vehicles—Functional safety—Part 9: Automotive Safety Integrity Level (ASIL)-oriented and safety-oriented analyses. Available online: https://www.iso.org/obp/ui#iso:std:iso:26262:-9:ed-1:v1:en (accessed on 28 August 2019).
- Martin, G. UML for embedded systems specification and design: motivation and overview. In Proceedings of the 2002 Design, Automation and Test in Europe Conference and Exhibition, Paris, France, 4–8 March 2002; pp. 773–775. [Google Scholar]
- Seidewitz, E. What models mean. IEEE Softw. 2003, 20, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- France, R.B.; Ghosh, S.; Dinh-Trong, T.; Solberg, A. Model-driven development using UML 2.0: Promises and pitfalls. Computer 2006, 39, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Object Management Group. Available online: http://www.omg.org (accessed on 28 August 2019).
- Running animated models. Available online: https://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/en/SSB2MU_8.4.0/com.ibm.rhp.animation.doc/topics/rhp_c_dm_rning_anm_models.html (accessed on 28 August 2019).
- Model Based Testing with TestConductor and Automatic Test Generation (ATG). Available online: https://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/SSB2MU_8.2.1/com.btc.tcatg.user.doc/topics/com.btc.tcatg.user.doc.html (accessed on 28 August 2019).
- Introduction to Microcontroller-Based Systems. Available online: https://ece.osu.edu/courses/introduction-microcontroller-based-systems-2560 (accessed on 28 August 2019).
- Introductory Microcomputer Interfacing Laboratory. Available online: https://www2.eecs.berkeley.edu/Courses/EEC145M/ (accessed on 28 August 2019).
- Design of Microprocessor-Based Systems. Available online: http://eecs.umich.edu/eecs/academics/courses/eecs-373.html (accessed on 28 August 2019).
- Advanced Embedded Software Development. Available online: https://sites.google.com/colorado.edu/ecen5013/home (accessed on 28 August 2019).
- Advanced Embedded Software. Available online: https://my.eng.utah.edu/~cs5785/ (accessed on 28 August 2019).
- Embedded and Real Time Software. Available online: https://cs.brown.edu/courses/csci1600/ (accessed on 28 August 2019).
- Mellor, S.J.; Clark, A.N.; Futagami, T. Model-driven development - Guest editor’s introduction. IEEE Softw. 2003, 20, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selic, B. The pragmatics of model-driven development. IEEE Softw. 2003, 20, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Schwerin, M. Software engineering in a nutshell for Electrical Engineering students. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Global Engineering Education Conference (EDUCON), Istanbul, Turkey, 3–5 April 2014; pp. 788–793. [Google Scholar]
- Muppala, J. Experience with an embedded systems software course. ACM SIGBED Review 2005, 2, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.U.; Geihs, K.; Gutbrodt, F.; Gohner, P.; Trauter, R. Model-driven development of real-time systems with UML 2.0 and C. In Proceedings of the Fourth Workshop on Model-Based Development of Computer-Based Systems and Third International Workshop on Model-Based Methodologies for Pervasive and Embedded Software (MBD-MOMPES’06), Potsdam, Germany, 30–30 March 2006; pp. 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mura, M.; Sami, M.G. Code Generation from Statecharts: Simulation of Wireless Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of the 2008 11th EUROMICRO Conference on Digital System Design Architectures, Methods and Tools, Parma, Italy, 3–5 September 2008; pp. 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.K. Model-Driven Engineering and Safety-Critical Embedded Software. Computer 2009, 42, 93–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM Rational Rhapsody. Available online: https://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/SSB2MU_8.4.0/com.ibm.rhp.homepage.doc/helpindex_rhapsody.html (accessed on 28 August 2019).
- Krasner, J.L. Reducing OEM Development Costs and Enabling Embedded Design Efficiencies Using UML. In Embedded Market Forecasters; American Technology International Inc.: Framingham, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]

| Category | Lecture | Lab |
|---|---|---|
| Conventional Method for Linux | Introduction to Embedded Linux | Embedded Linux Applications Development Environment |
| Real-Time Kernel Concepts | Multi Threads, Semaphore, Mutex | |
| Device Drivers | Applications using LED, FND, and LCD drivers | |
| Linux Architecture | Applications using Interrupt Drivers, Digital Clock, on Embedded Linux | |
| Building a Linux Kernel | Building a Linux Kernel including Device Drivers | |
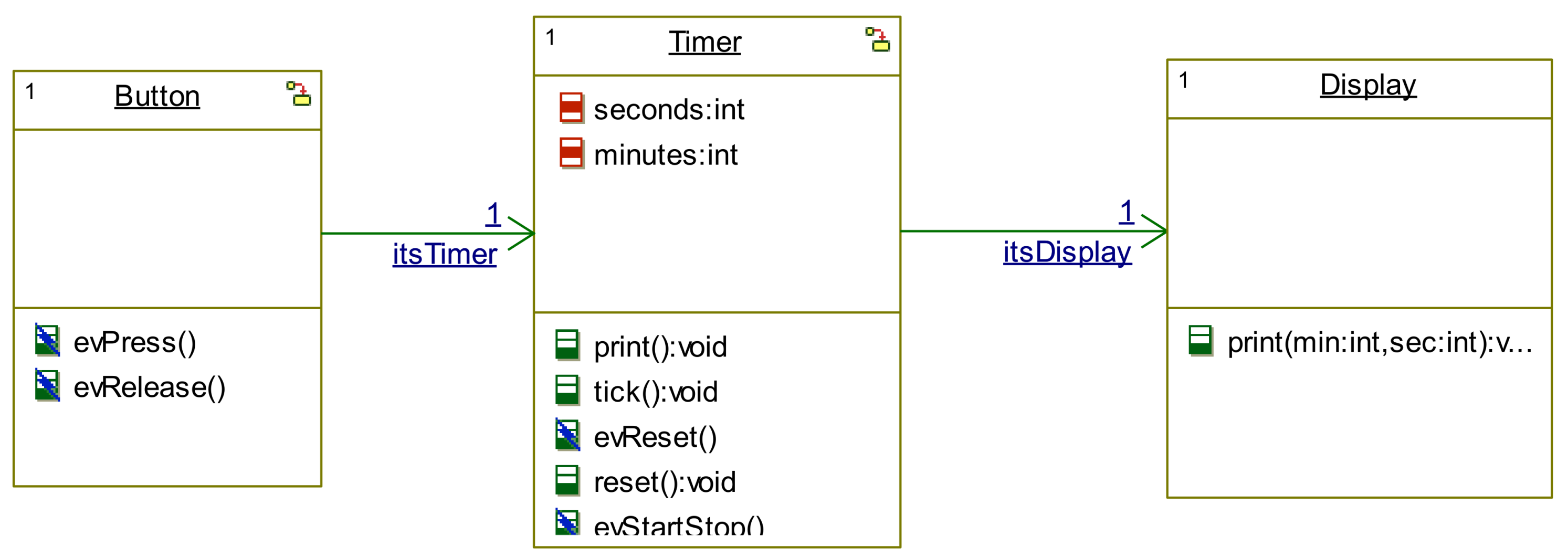
| Model-driven Method for Linux | Concepts of Model-driven Design | Hello World Example, Counter |
| Concepts of Model-driven Design | Stopwatch | |
| Midterm Exam | ||
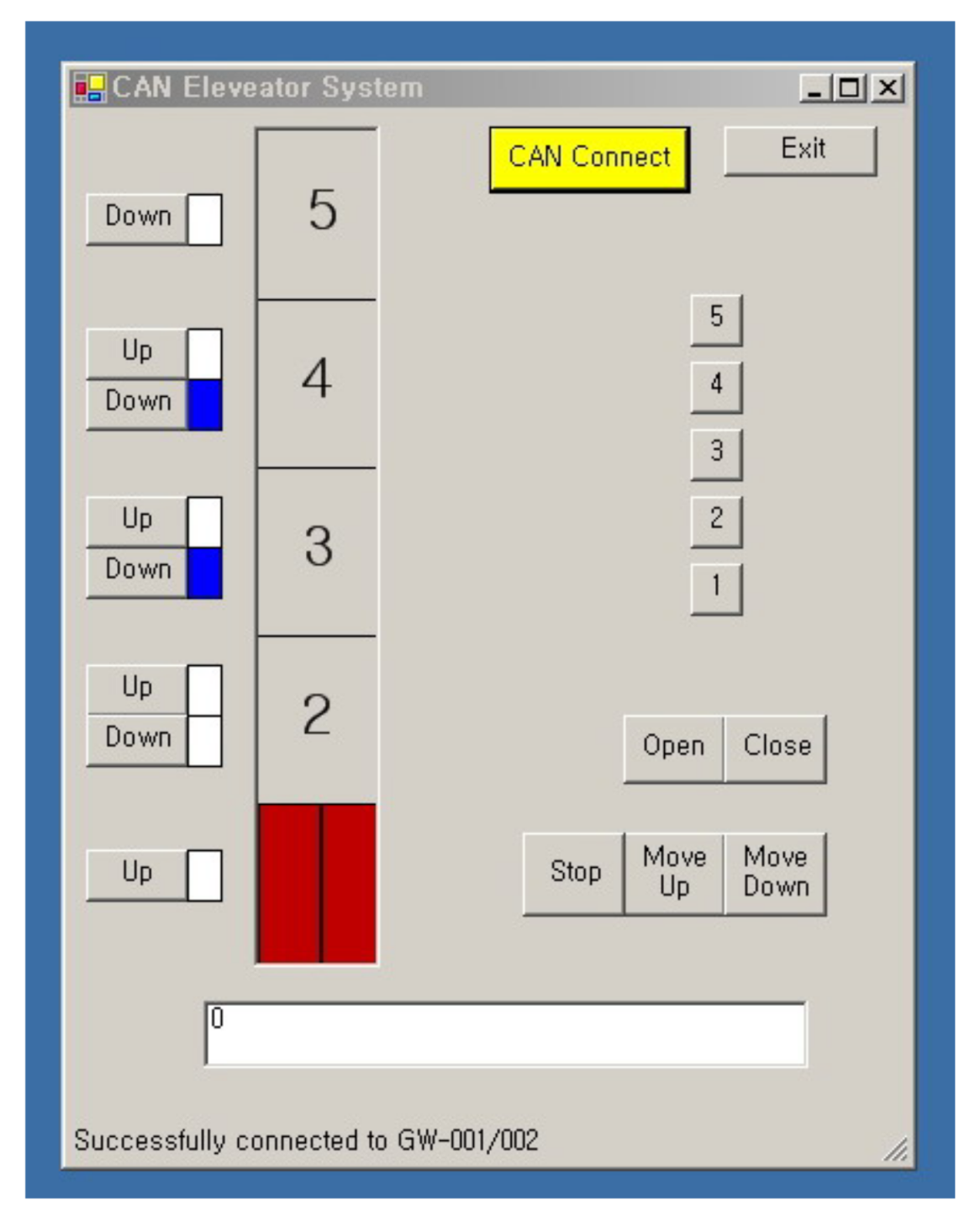
| Concepts of Model-driven Design | Linux CAN Communication | |
| Conventional Method for ARM Cortex-M | ARM Cortex-M Processors | Cortex-M serial ports |
| ARM Cortex-M Processors | Cortex-M I2C | |
| ARM Cortex-M Processors | Cortex-M CAN | |
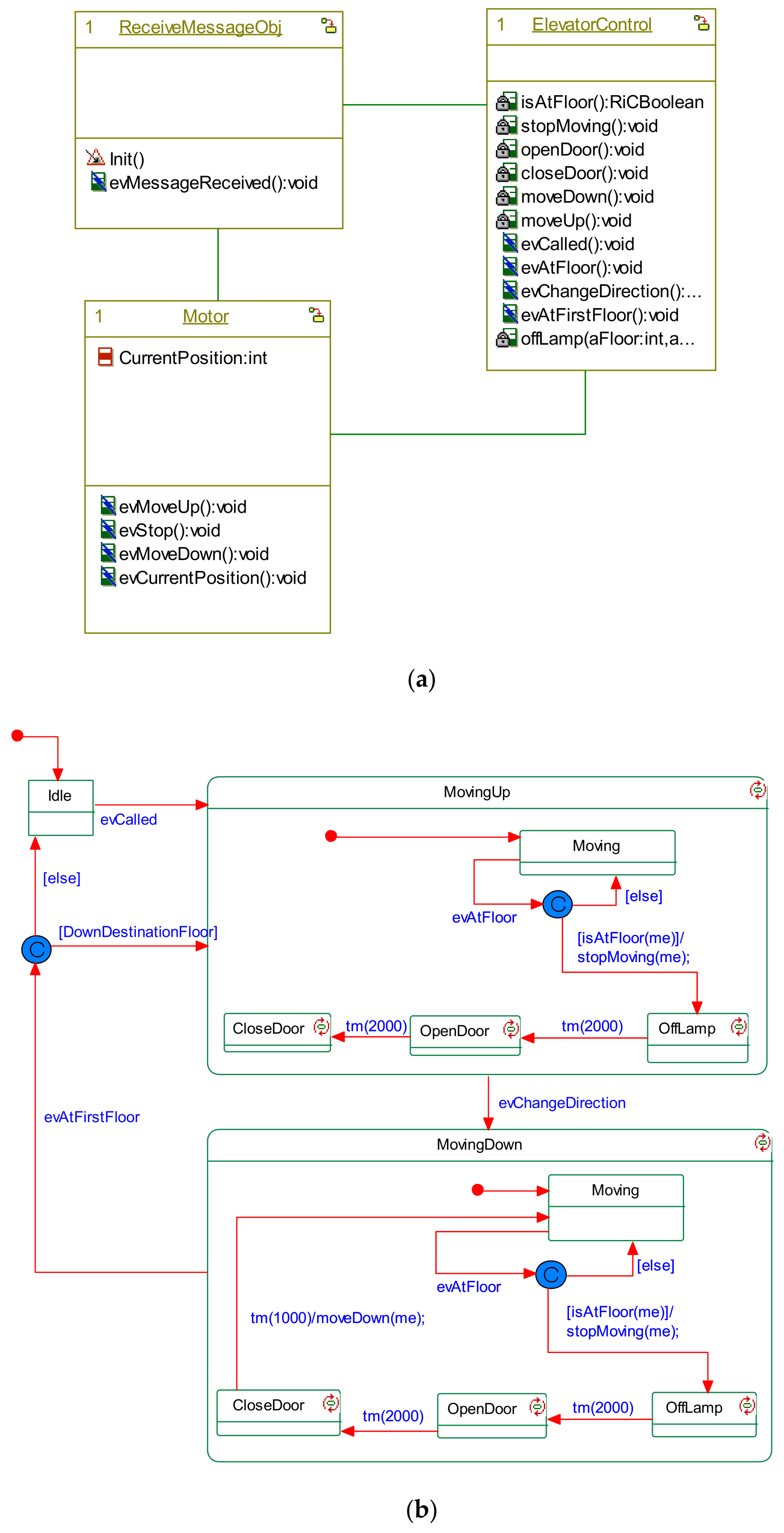
| Final Project (Model-driven and Conventional) | Design Project | Elevator Controller |
| Design Project | Elevator Controller | |
| Design Project | Elevator Controller | |
| Final Exam |
| Questions | SA | A | N | D | SD | AVG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Syllabus was helpful in choosing this course | 13 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 4.41 |
| Course objectives were concrete and clear | 14 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 4.41 |
| The instructor effectively presented concepts and techniques | 12 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 4.36 |
| The instructor provided helpful feedback | 12 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 4.36 |
| The instructor is enthusiastic about teaching | 12 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 4.36 |
| The instructor stimulated my interest in the subject matter | 13 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 4.36 |
| I gained worthwhile knowledge in this course | 14 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 4.41 |
| Questions | SA | A | N | D | SD | AVG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Syllabus was helpful in choosing this course | 6 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 4.18 |
| Course objectives were concrete and clear | 6 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 4.18 |
| The instructor effectively presented concepts and techniques | 6 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 4.18 |
| The instructor provided helpful feedback | 5 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 4.00 |
| The instructor is enthusiastic about teaching | 5 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 4.00 |
| The instructor stimulated my interest in the subject matter | 5 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 4.09 |
| I gained worthwhile knowledge in this course | 5 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 4.09 |
| Model-Driven | Legacy Code (C) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Architectural Design | Pros | Visualization | None |
| Cons | Need to learn modeling language | Hard to capture the whole picture | |
| Detail Design | Pros | Intuitive design with state chart | Familiar source code design |
| Cons | Need to learn state chart designs | Difficult to design complex functions | |
| Coding | Pros | Automatic code generation | Flexible |
| Cons | Less flexible Increased code size | Hard to understand code written by other programmers | |
| Debugging | Pros | State chart animation | Familiar source code debugger |
| Cons | Hard to find errors in generated code | No animation |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, D.-J. Incorporating a Model-Driven Approach into an Embedded Software Course. Electronics 2019, 8, 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8091004
Lim D-J. Incorporating a Model-Driven Approach into an Embedded Software Course. Electronics. 2019; 8(9):1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8091004
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Dong-Jin. 2019. "Incorporating a Model-Driven Approach into an Embedded Software Course" Electronics 8, no. 9: 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8091004
APA StyleLim, D.-J. (2019). Incorporating a Model-Driven Approach into an Embedded Software Course. Electronics, 8(9), 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8091004




