A Long-Range 2.4G Network System and Scheduling Scheme for Aquatic Environmental Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Experiments of LoRa 2.4G
4. Network Architecture and the DMSF–TDMA Scheme
4.1. Network Architecture
4.2. The DMSF–TDMA Scheme
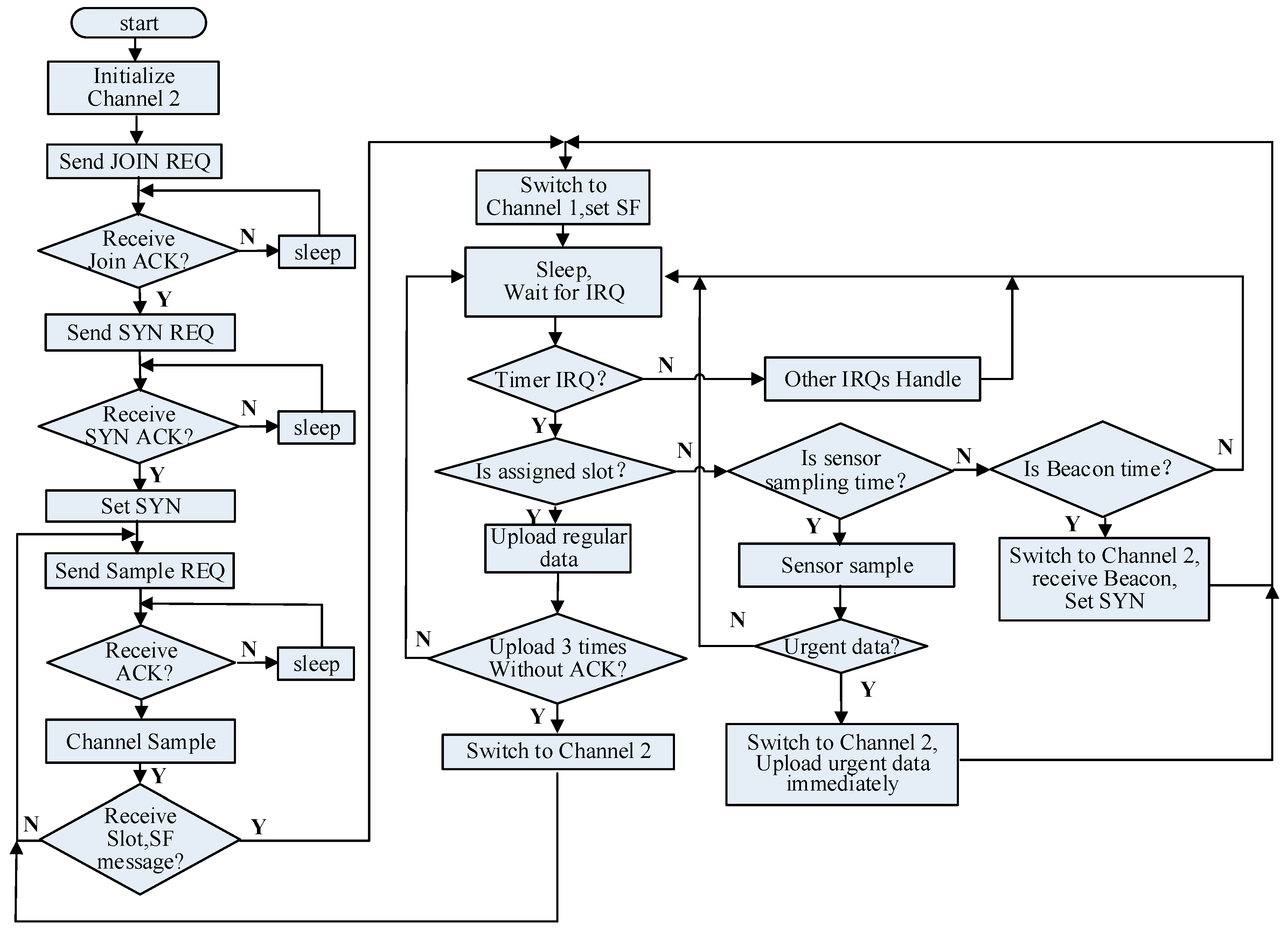
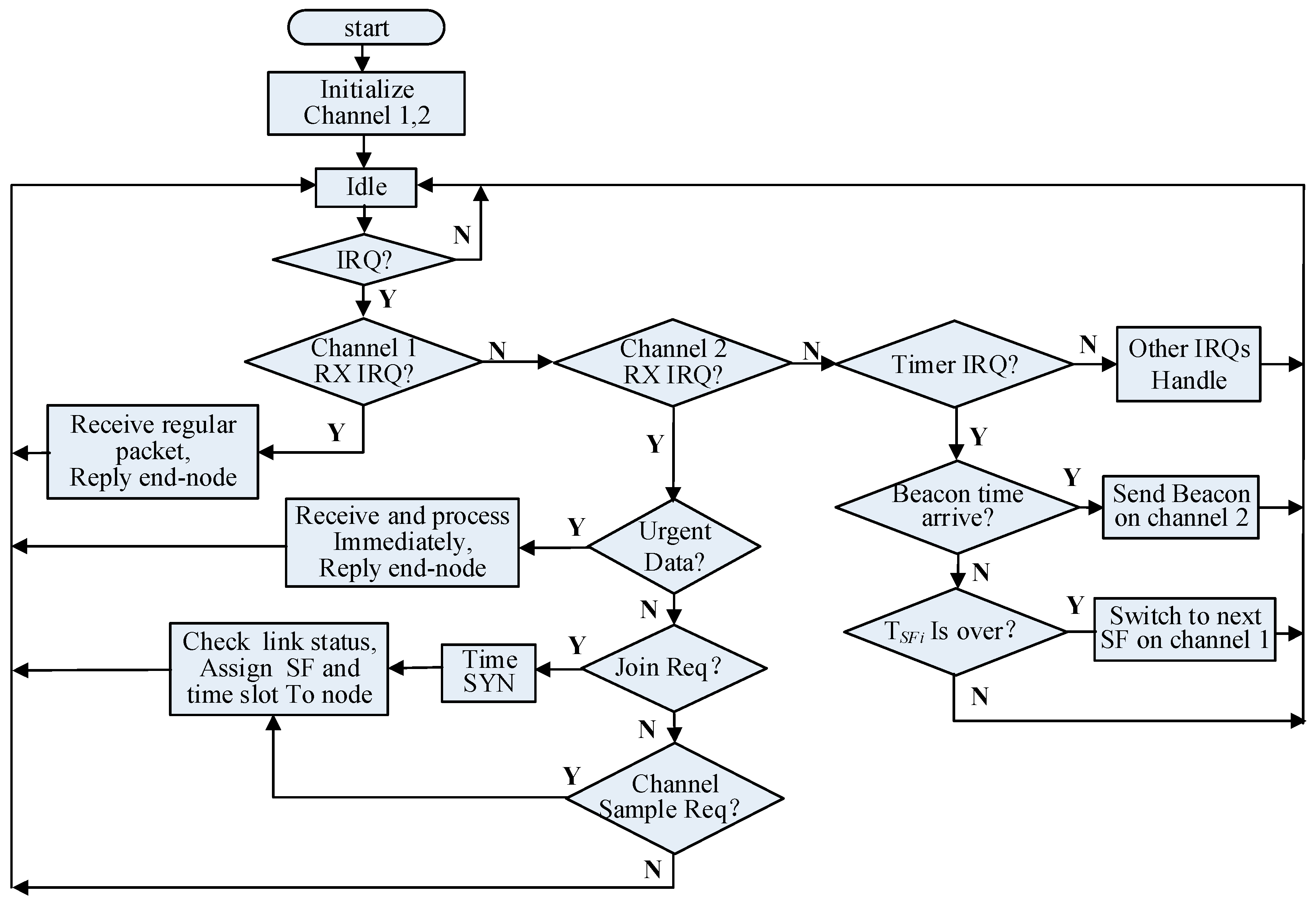
4.2.1. Schedule of Channel 1
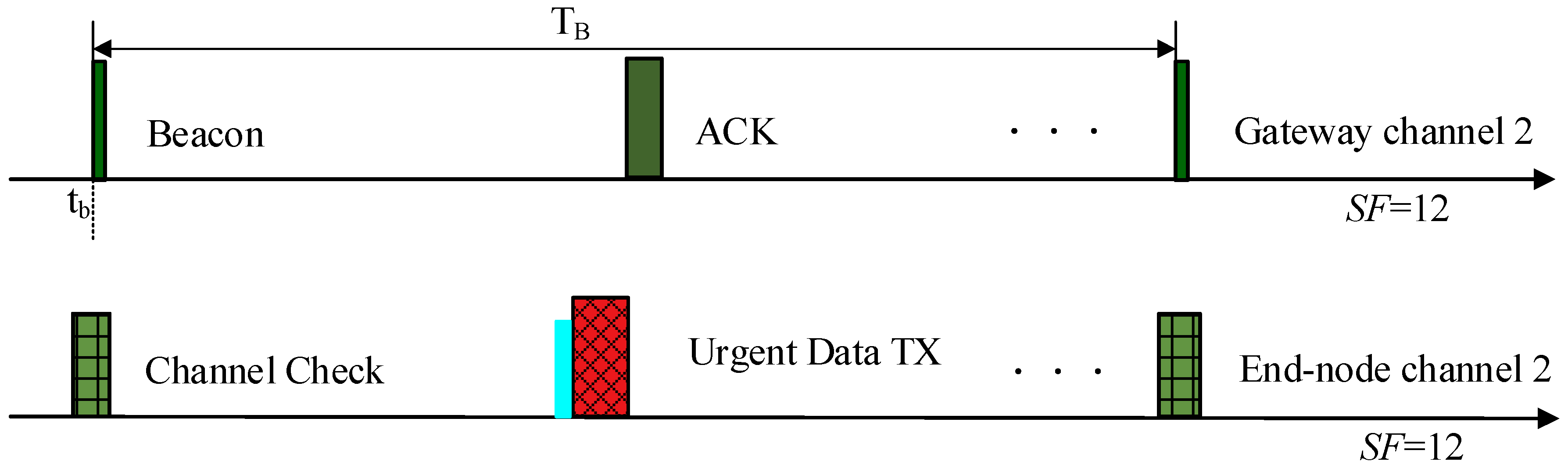
4.2.2. Schedule of Channel 2
5. Performance Evaluation
5.1. Simulation Model
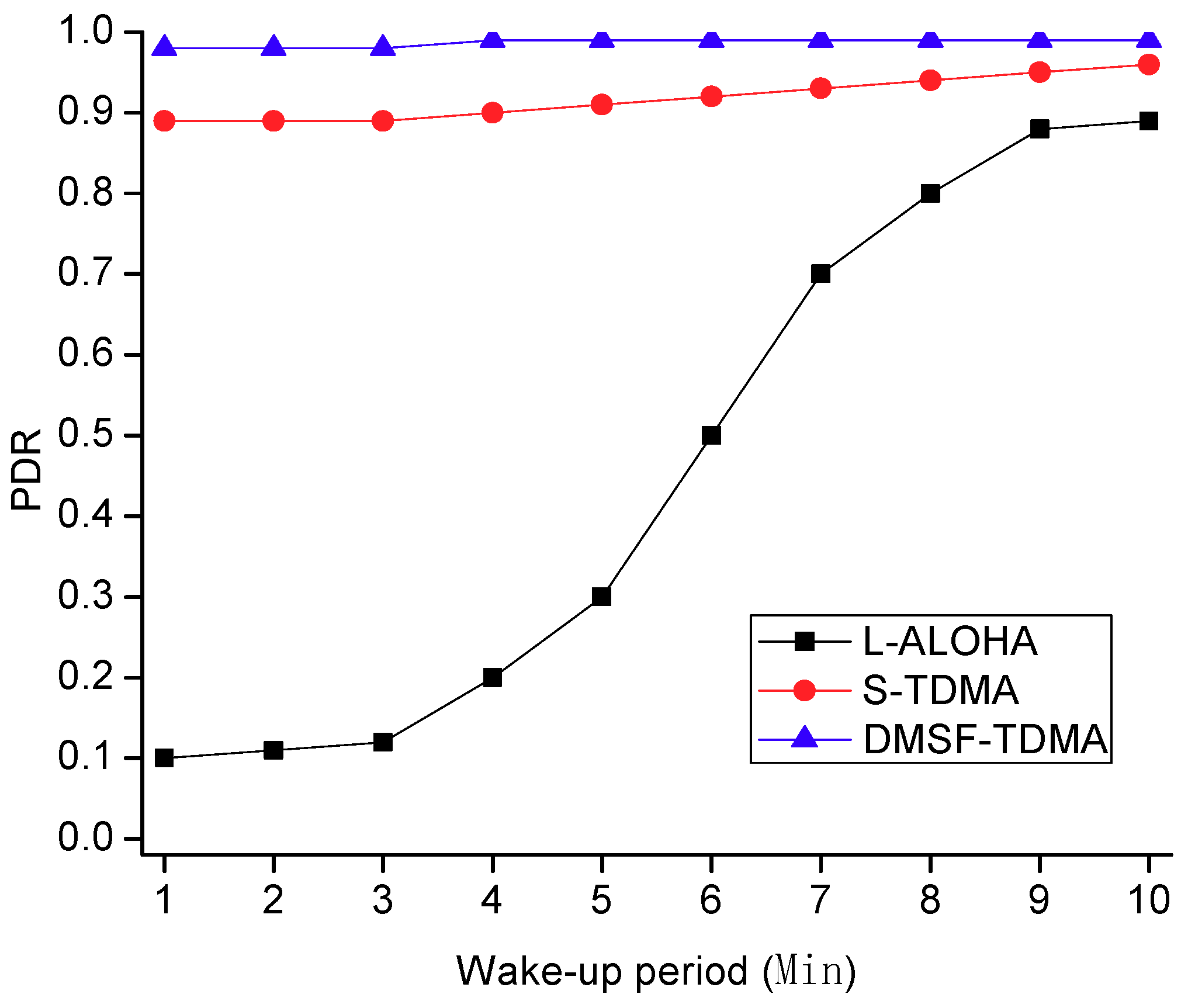
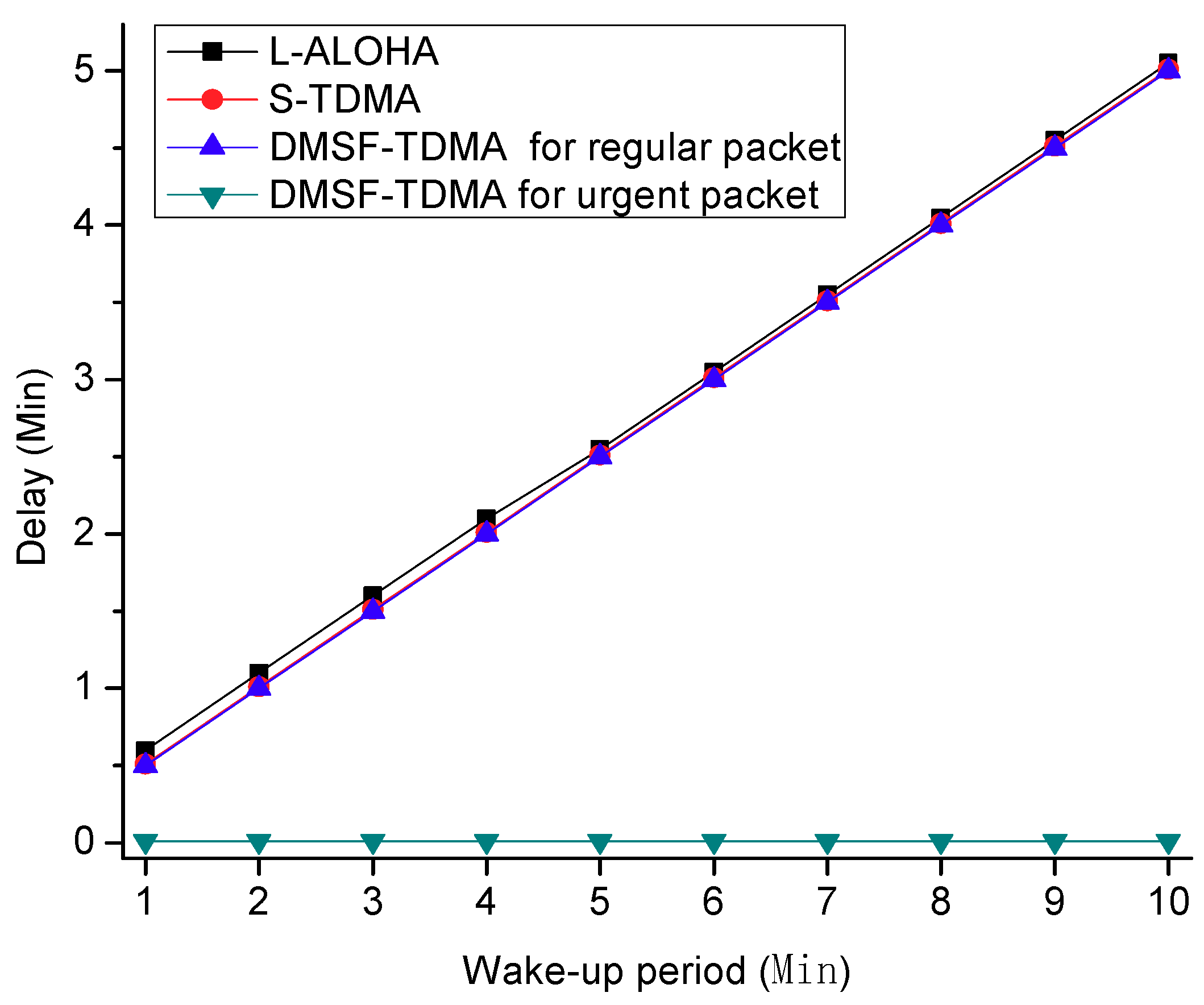
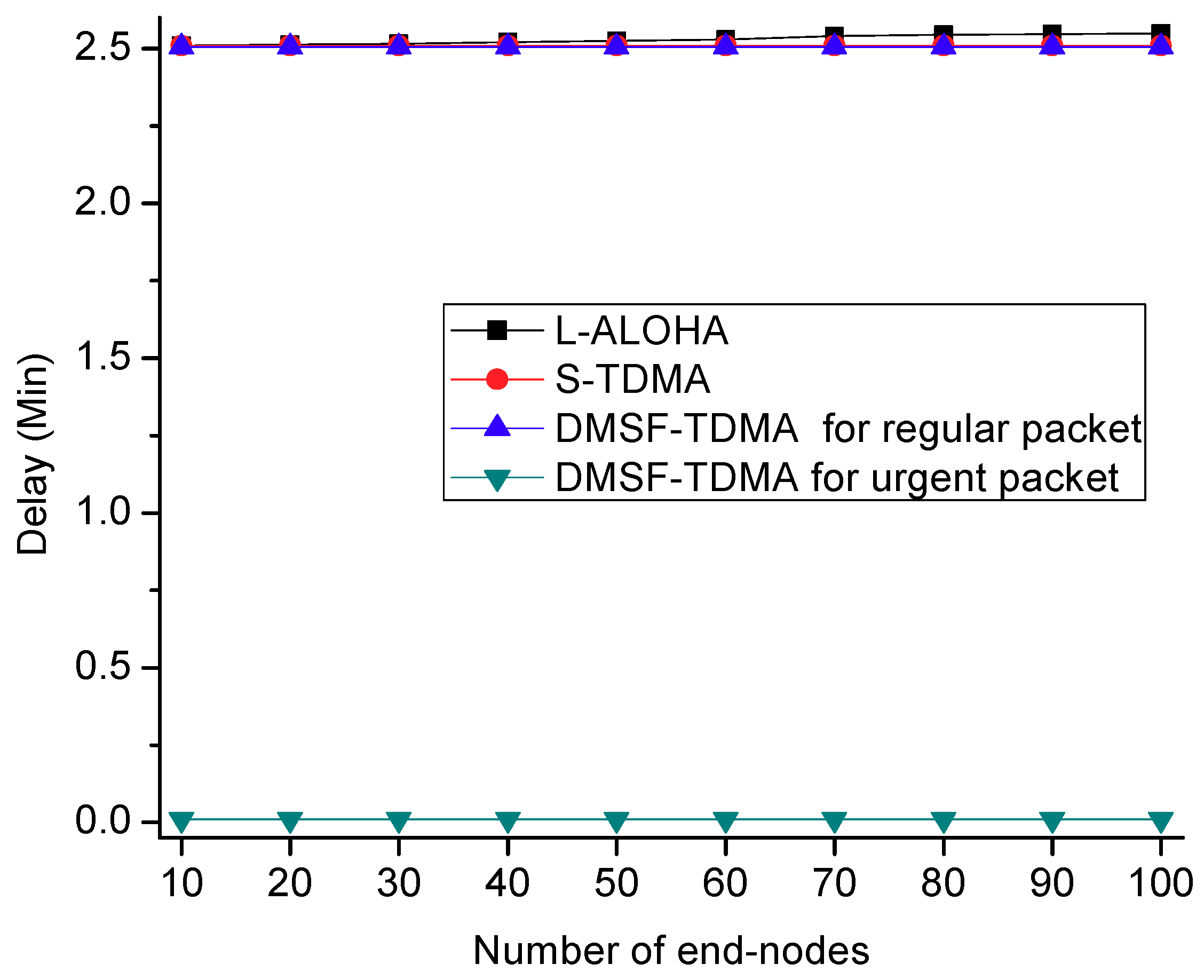
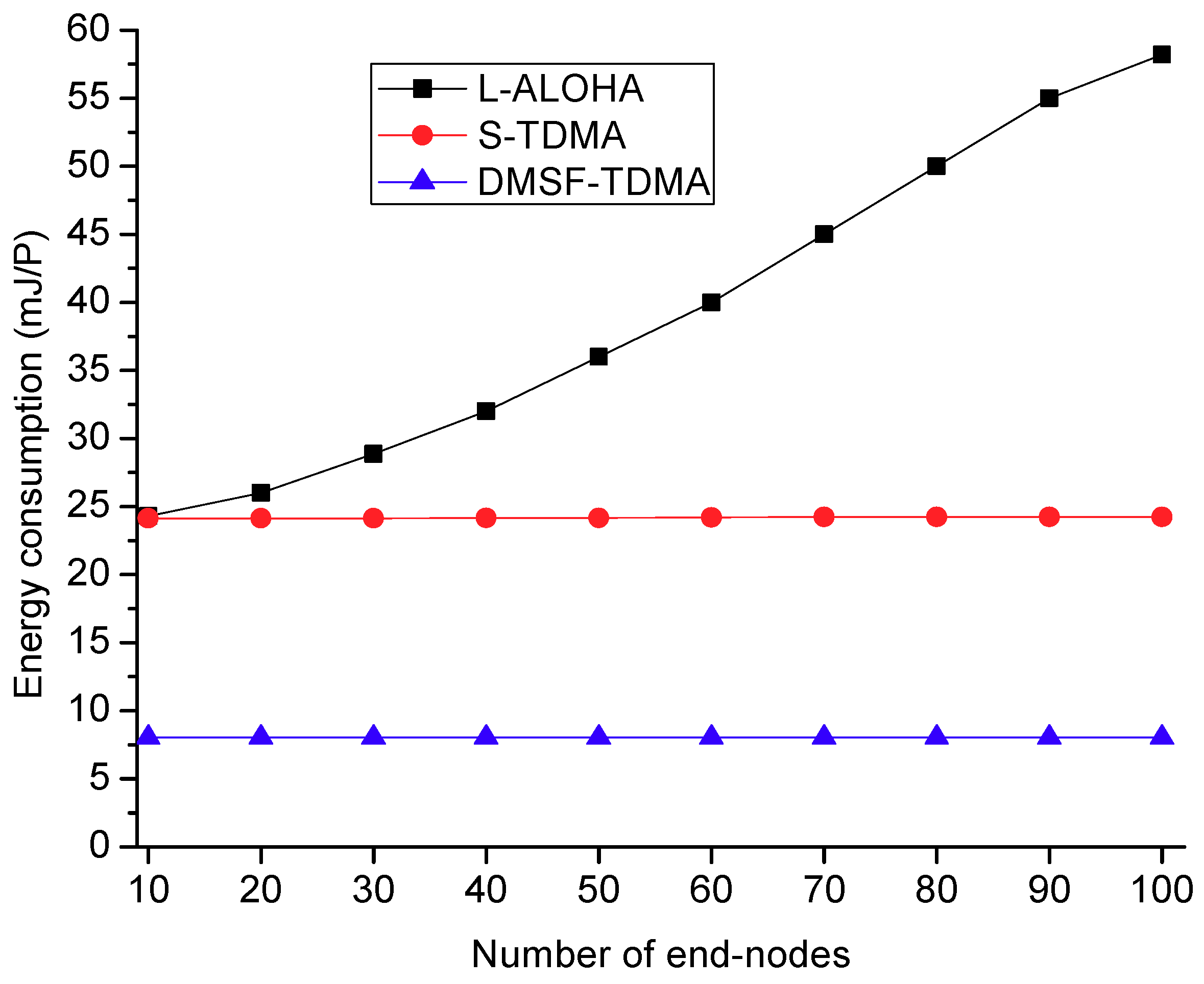
5.2. Simulation Analysis and Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gubbi, J.; Buyya, R.; Marusic, S.; Palaniswami, M. Internet of Things (IoT): A vision, architectural elements, and future directions. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2013, 29, 1645–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, D.; Sen, J. Internet of Things: Applications and challenges in technology and standardization. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2011, 55, 49–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzori, L.; Iera, A.; Morabito, G. The Internet of Things: A Survey. Comput. Netw. 2010, 54, 2787–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Guo, Q.; Shi, Z. Design of WSN node for water pollution remote monitoring. Telecommun. Syst. 2013, 53, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosma, R.H.; Verdegem, M.C.J. Sustainable aquaculture in ponds: Principles, practices and limits. Livest. Sci. 2011, 139, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marziani, C.; Alcoleas, R.; Colombo, F.; Costa, N.; Pujana, F.; Colombo, A.; Aparicio, J.; Álvarez, F.J.; Jimenez, A.; Ureña, J.; et al. A low cost reconfigurable sensor network for coastal monitoring. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on OCEANS, Santander, Spain, 6–9 June 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Albaladejo, C.; Soto, F.; Torres, R.; Sánchez, P.; López, J.A. A low-cost sensor buoy system for monitoring shallow marine environments. Sensors 2012, 12, 9613–9634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Yang, Z.; Li, M.; Guo, Z.; Guo, Y.; Hong, F.; Yang, X.; He, Y.; Feng, Y.; Liu, Y. Oceansense: Monitoring the sea with wireless sensor networks. Mob. Comput. Commun. Rev. 2010, 14, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Shen, W.; Wang, X. Applications of Wireless Sensor Networks in Marine Environment Monitoring: A Survey. Sensors 2014, 14, 16932–16954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simbeye, D.S.; Zhao, J.; Yang, S. Design and deployment of wireless sensor networks for aquaculture monitoring and control based on virtual instruments. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2014, 102, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, C.; Bellalta, B.; Sfairopoulou, A.; Oliver, M. Low energy operation in WSNs: A survey of preamble sampling MAC protocols. Comput. Netw. 2011, 55, 3351–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasi, G.; Conti, M.; Francesco, M.D.; Passarella, A. Energy conservationin wireless sensor networks: A survey. Ad Hoc Netw. 2009, 7, 537–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alippi, C.; Camplani, R.; Galperti, C.; Roveri, M. A Robust, Adaptive, Solar-Powered WSN Framework for Aquatic Environmental Monitoring. IEEE Sens. J. 2011, 11, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albaladejo Pérez, C.; Soto Valles, F.; Torres Sánchez, R.; Jiménez Buendía, M.; López-Castejón, F.; Gilabert Cervera, J. Design and Deployment of a Wireless Sensor Network for the Mar Menor Coastal Observation System. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2017, 42, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faustine, A.; Mvuma, A.N.; Mongi, H.J.; Gabriel, M.C.; Tenge, A.J.; Kucel, S.B. Wireless Sensor Networks for Water Quality Monitoring and Control within Lake Victoria Basin: Prototype Development. Wirel. Sens. Netw. 2014, 6, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yi, J.; Chen, S.; Zhu, X. A Wireless Sensor Network-Based Approach with Decision Support for Monitoring Lake Water Quality. Sensors 2015, 15, 29273–29296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongpin, L.; Guanglin, L.; Weifeng, P.; Jie, S.; Qiuwei, B. Real-time remote monitoring system for aquaculture water quality. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2015, 8, 136–143. [Google Scholar]
- Adamo, F.; Attivissimo, F.; Carducci, C.G.C.; Lanzolla, A.M.L. A Smart Sensor Network for Sea Water Quality Monitoring. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 2514–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandanapalli, S.B.; Reddy, E.S.; Davuluri, D.R.L. Efficient Design and Deployment of Aqua Monitoring Systems Using WSNs and Correlation Analysis. Int. J. Comput. Commun. Control 2015, 10, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ali, A.; Shah, G.A.; Farooq, M.O.; Ghani, U. Technologies and challenges in developing Machine-to-Machine applications: A survey. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2017, 83, 124–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekki, K.; Bajic, E.; Chaxel, F.; Meyer, F. A comparative study of LPWAN technologies for large-scale IoT deployment. ICT Express 2019, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, A.; Yi, J.; Clausen, T.; Townsley, W.M. A Study of LoRa: Long Range & Low Power Networks for the Internet of Things. Sensors 2016, 16, 1466. [Google Scholar]
- Petajajarvi, J.; Mikhaylov, K.; Pettissalo, M.; Janhunen, J.; Iinatti, J. Performance of a low-power wide-area network based on lora technology: Doppler robustness, scalability, and coverage. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2017, 13, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LoRa-Alliance. LoRaWAN Specification; Technical Report; LoRa Alliance: Beaverton, OR, USA, July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Feltrin, L.; Buratti, C.; Vinciarelli, E.; De Bonis, R.; Verdone, R. LoRaWAN: Evaluation of Link- and System-Level Performance. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 2249–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynders, B.; Wang, Q.; Tuset-Peiro, P.; Vilajosana, X.; Pollin, S. Improving reliability and scalability of lorawans through lightweight scheduling. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 1830–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ren, J.; Zhu, Q. On the application of LoRa LPWAN technology in Sailing Monitoring System. In Proceedings of the 13th Annual Conference on Wireless On-demand Network Systems and Services (WONS), Jackson, WY, USA, 21–24 February 2017; pp. 77–80. [Google Scholar]
- Petajajarvi, J.; Mikhaylov, K.; Roivainen, A.; Hanninen, T.; Pettissalo, M. On the coverage of LPWANs: Range evaluation and channel attenuation model for lora technology. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on ITS Telecommunications (ITST), Copenhagen, Denmark, 2–4 December 2015; pp. 55–59. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Iborra, R.G.; Liaño, I.; Simoes, C.; Couñago, E.; Skarmeta, A. Tracking and Monitoring System Based on LoRa Technology for Lightweight Boats. Electronics 2019, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovalekic, N.; Drndarevic, V.; Pietrosemoli, E.; Zennaro, I. Experimental Study of LoRa Transmission over Seawater. Sensors 2018, 18, 2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiou, O.; Raza, U. Low power wide area network analysis: Can LoRa scale? IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2017, 6, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylov, K.; Petäjäjärvi, J.; Haenninen, T. Analysis of capacity and scalability of the LoRa low power wide area network technology. In Proceedings of the European Wireless 2016, 22th European Wireless Conference, Oulu, Finland, 18–20 May 2016; pp. 119–125. [Google Scholar]
- Piyare, R.; Murphy, A.; Magno, M.; Benini, L. On-demand lora: Asynchronous tdma for energy efficient and low latency communication in iot. Sensors 2018, 18, 3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, C. Enabling and deploying long-range IoT image sensors with LoRa technology. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Middle East and North Africa Communications Conference (MENACOMM), Jounieh, Lebanon, 18–20 April 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Dinh, N.T.; Kim, Y. Information-centric dissemination protocol for safety information in vehicular ad-hoc networks. Wirel. Netw. 2017, 23, 1359–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, T.; Kim, Y.; Gu, T.; Vasilakos, A.V. L-mac: A wake-up time self-learning mac protocol for wireless sensor networks. Comput. Netw. 2016, 105, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SX1280 Transceivers. July 2019. Available online: https://www.semtech.com/uploads/documents/ DS_SX1280-1_V2.2.pdf (accessed on 19 July 2019).
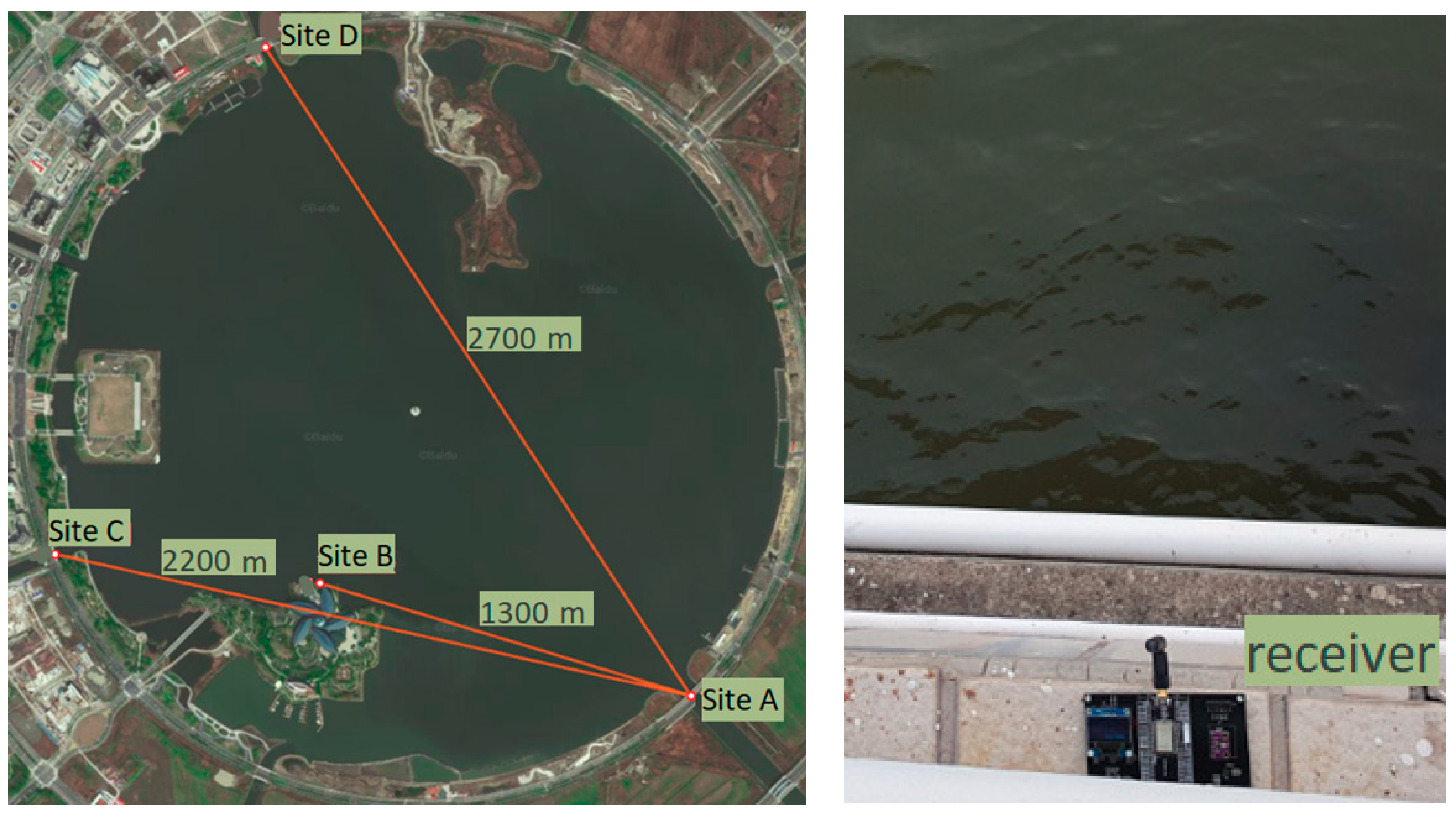
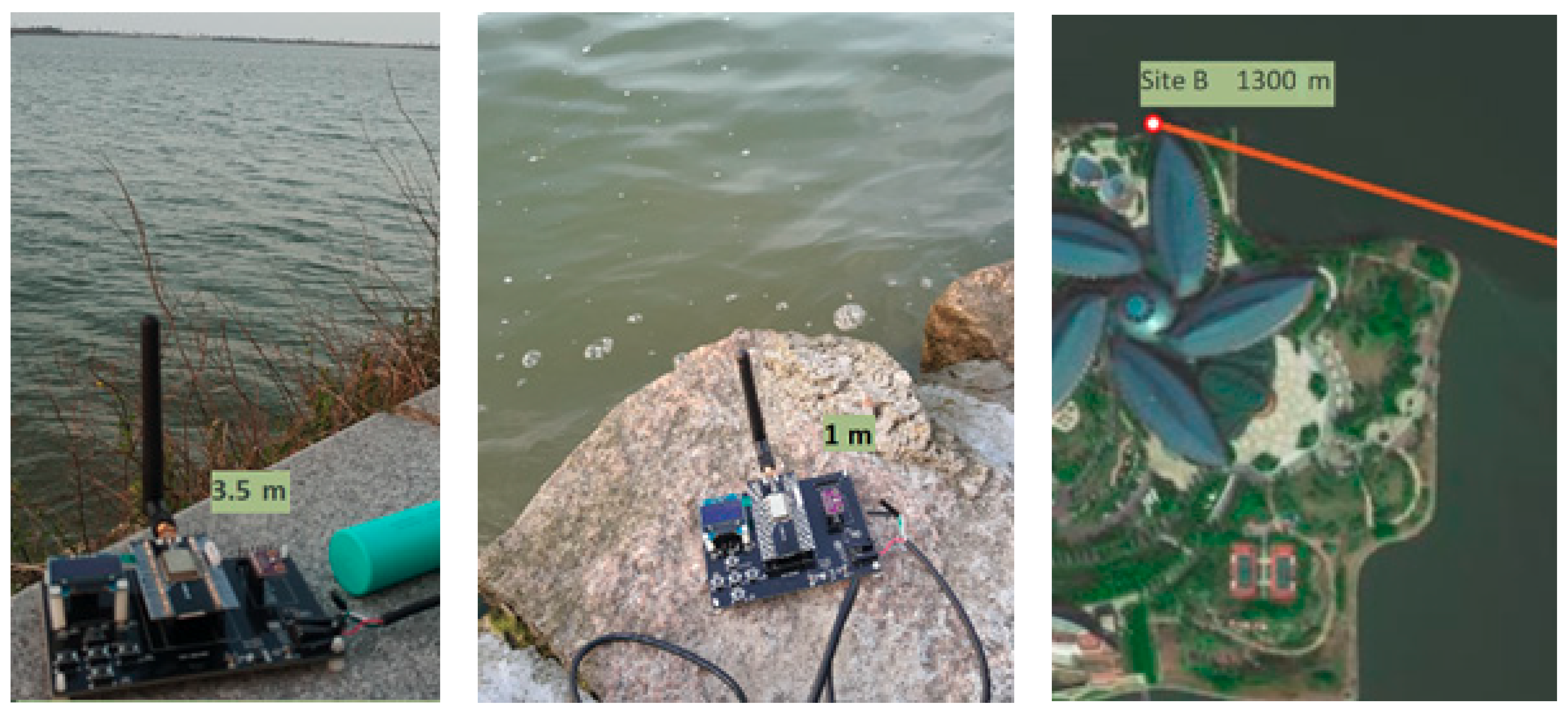



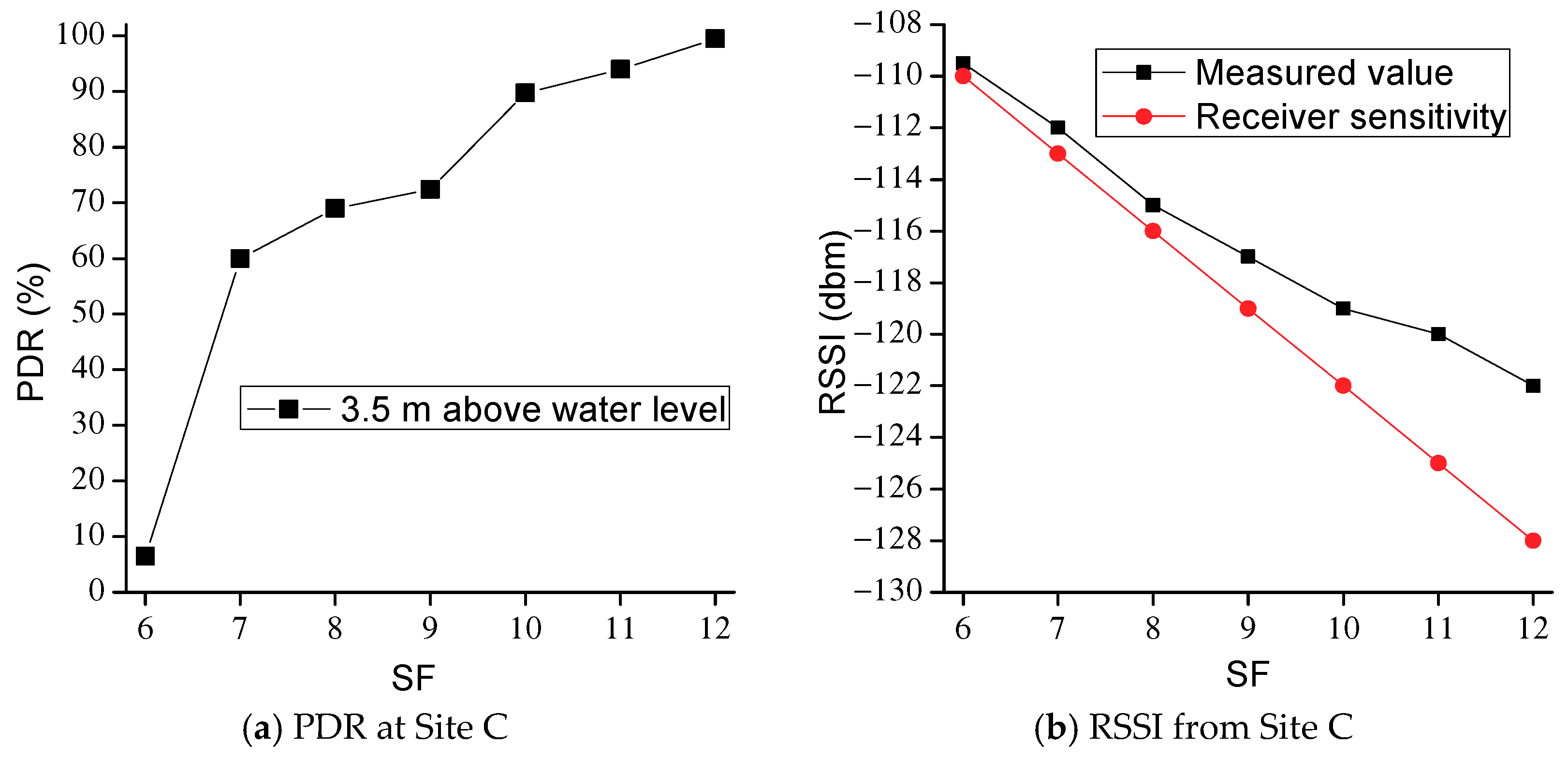
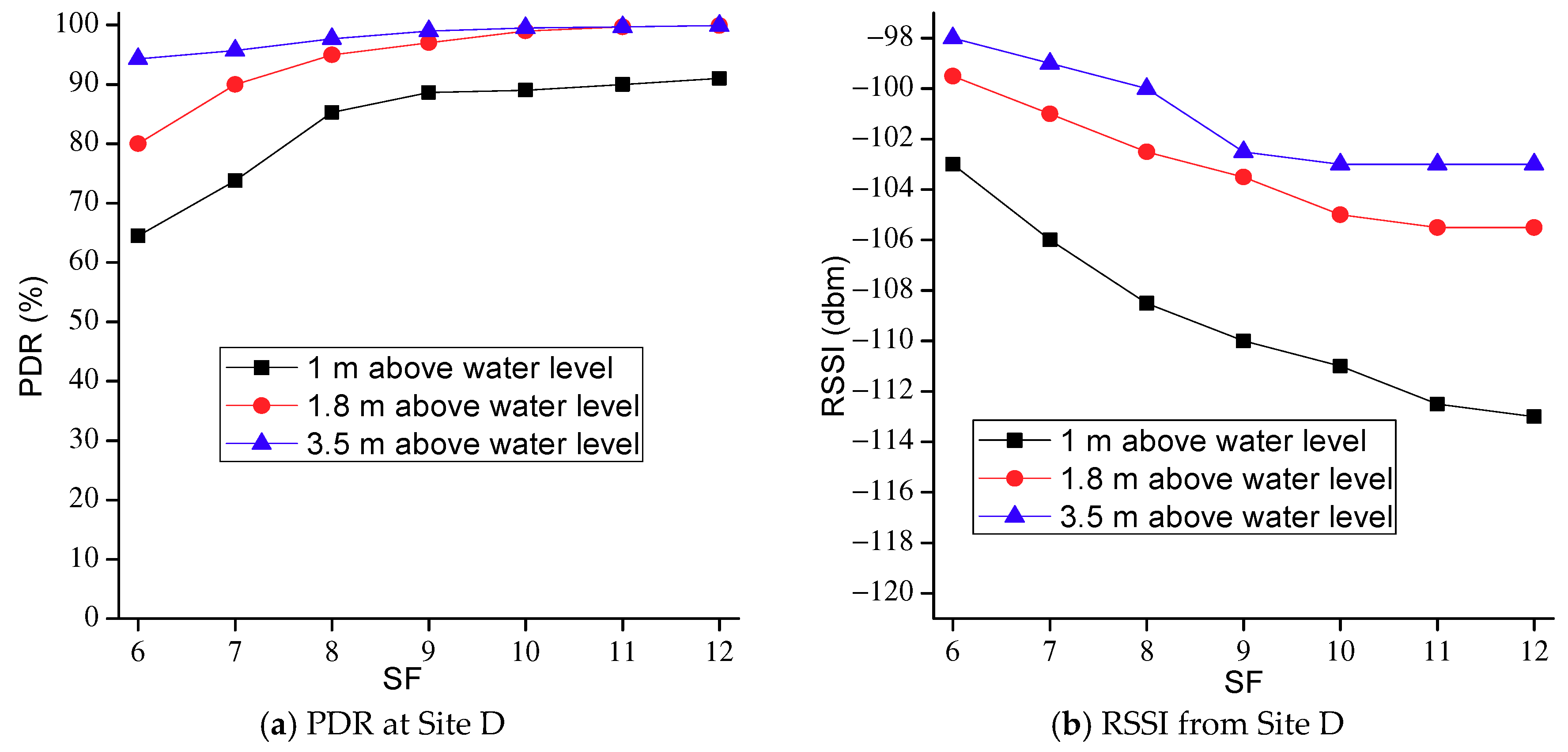

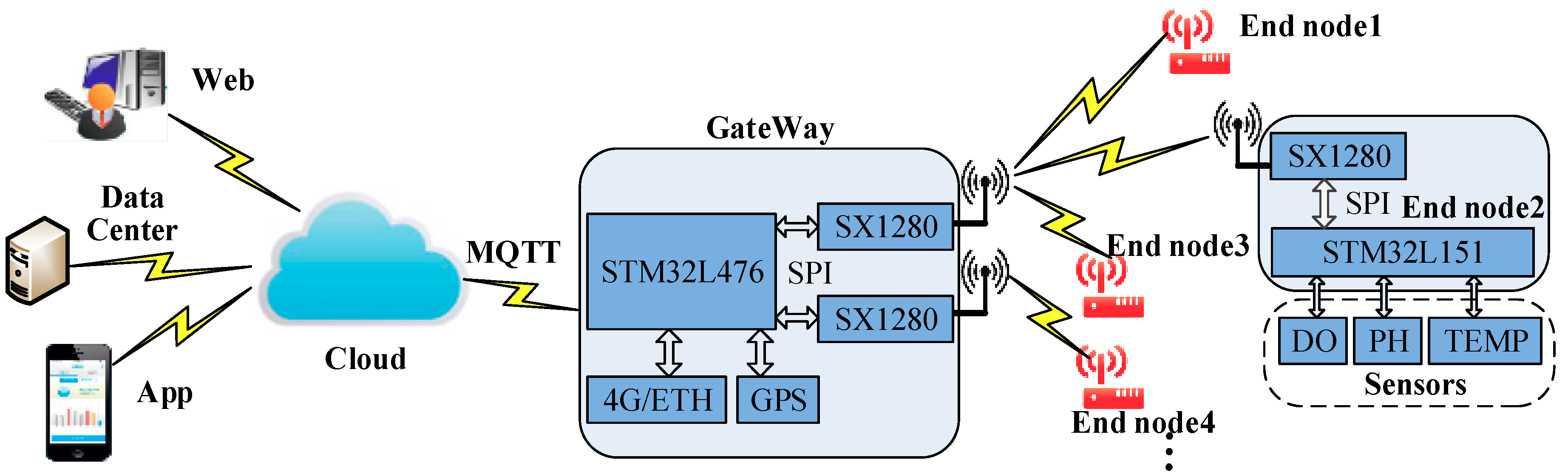

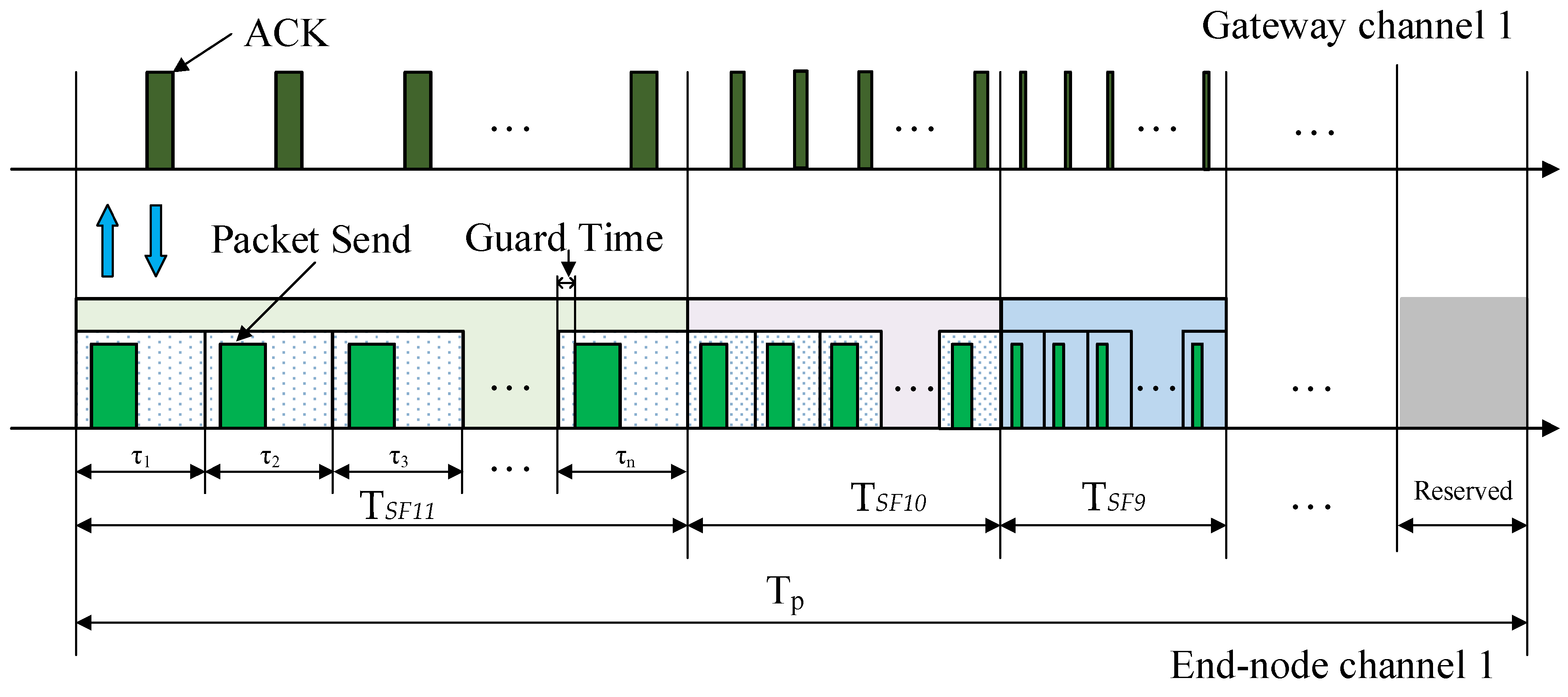



| Bandwidth (kHz) | Raw Data Rates (kb/s) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SF5 | SF6 | SF7 | SF8 | SF9 | SF10 | SF11 | SF12 | |
| 203 | 31.72 | 19.03 | 11.1 | 6.34 | 3.57 | 1.98 | 1.09 | 0.595 |
| 406 | 63.44 | 38.06 | 22.2 | 12.69 | 7.14 | 3.96 | 2.18 | 1.19 |
| 812 | 126.88 | 76.13 | 44.41 | 25.38 | 14.27 | 7.93 | 4.36 | 2.38 |
| 1625 | 253.91 | 152.34 | 88.87 | 50.78 | 28.56 | 15.87 | 8.73 | 4.76 |
| Transceiver | SX1278 | SX1280 | CC2520 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Modulation | LoRa | LoRa | IEEE 802.15.4 |
| Band | 470 MHz | 2.4 GHz | 2.4 GHz |
| Data rate (Max) | 37.5 kb/s | 202 kb/s | 250 kb/s |
| Receiver sensitivity | −148 dBm | −132 dBm | −98 dBm |
| Tx current | 29 mA @ + 13 dBm | 24 mA @ + 12.5 dBm | TX 33.6 mA @ + 5 dBm |
| RX current | 9.9 mA | 8.2 mA | 18.5 mA |
| SF | SNR | RSSI |
|---|---|---|
| 6 | 0 | −85 |
| 7 | 0 | −90 |
| 8 | −5 | −95 |
| 9 | −10 | −108 |
| 10 | −15 | −115 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| LoRa Setting | BW = 406 kHz, CR = 4/5, SF ∈ (6, 12), Preamble length = 8 symbol |
| Rx current | 6.7 mA |
| Tx current | 24 mA@ + 12.5 dBm |
| Sleep current | 0.4 μA |
| Payload | 16 Bytes |
| Beacon period | 20 min |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Cao, S.; Wang, Y. A Long-Range 2.4G Network System and Scheduling Scheme for Aquatic Environmental Monitoring. Electronics 2019, 8, 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8080909
Zhang Z, Cao S, Wang Y. A Long-Range 2.4G Network System and Scheduling Scheme for Aquatic Environmental Monitoring. Electronics. 2019; 8(8):909. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8080909
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zheng, Shouqi Cao, and Yuntengyao Wang. 2019. "A Long-Range 2.4G Network System and Scheduling Scheme for Aquatic Environmental Monitoring" Electronics 8, no. 8: 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8080909
APA StyleZhang, Z., Cao, S., & Wang, Y. (2019). A Long-Range 2.4G Network System and Scheduling Scheme for Aquatic Environmental Monitoring. Electronics, 8(8), 909. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8080909




