A Survey of Algorithms and Systems for Evacuating People in Confined Spaces
Abstract
1. Introduction
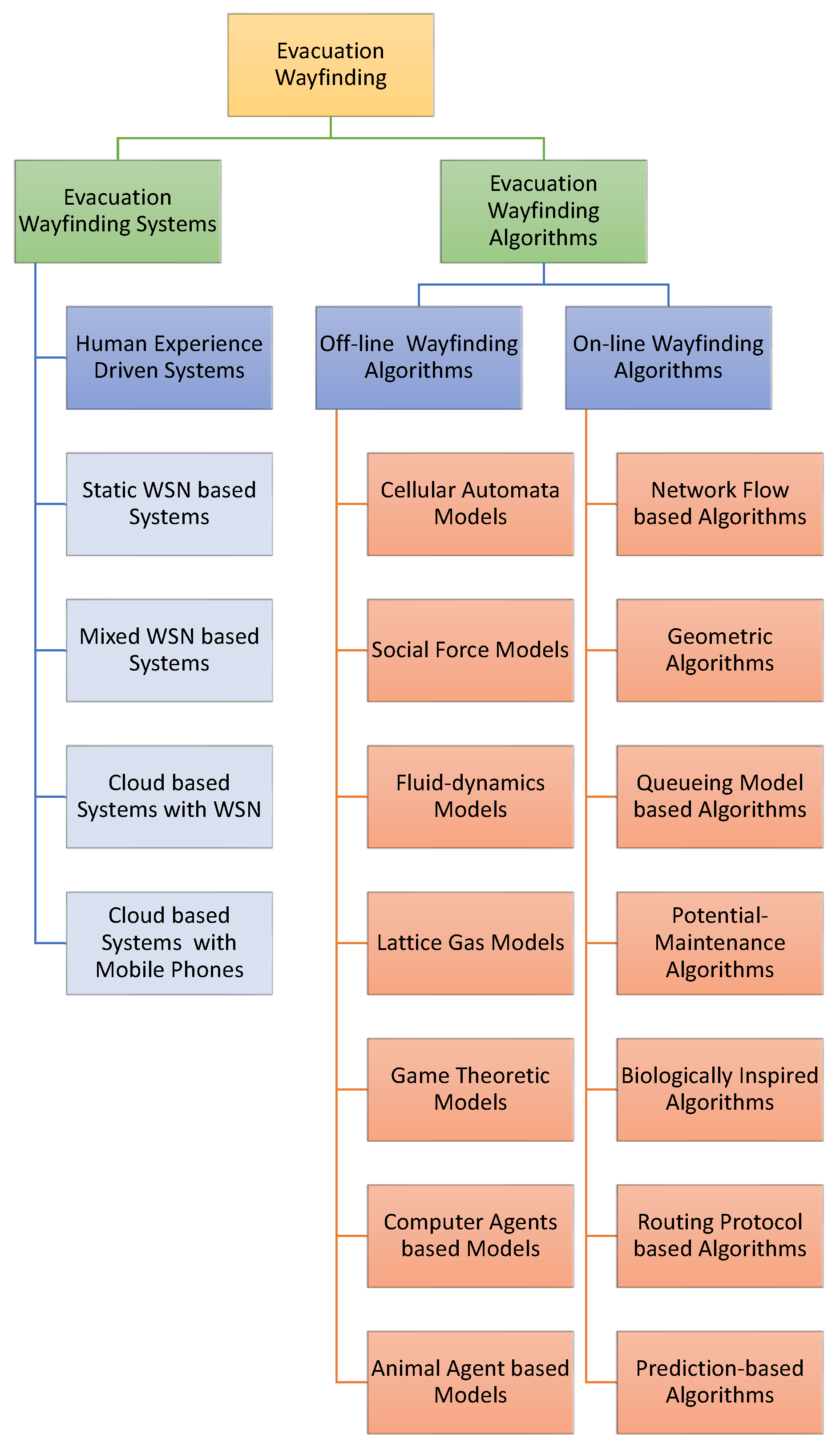
2. Evacuation Wayfinding Systems
2.1. Human Experience Driven-Systems
2.2. Static Wireless Sensor Network-Based Systems
2.3. Static and Mobile Wireless Sensor Network-Based Systems
2.4. Integrated Systems Based on Wireless Sensor Networks and Cloud Computing
2.5. Integrated Systems Based on Smartphones and Cloud Computing
3. Evacuation Wayfinding Algorithms
3.1. Off-Line Evacuation Wayfinding Algorithms
3.1.1. Cellular Automata Model-Based Algorithms
3.1.2. Social Force Model-Based Algorithms
3.1.3. Fluid-Dynamics Model-Based Algorithms
3.1.4. Lattice Gas Model-Based Algorithms
3.1.5. Game Theoretic Model-Based Algorithms
3.1.6. Computer Agent-Based Algorithms
3.1.7. Animal Agent-Based Algorithms
3.2. On-Line Evacuation Wayfinding Algorithms
3.2.1. Network Flow-Based Algorithms
3.2.2. Geometric Algorithms
3.2.3. Queueing Model-Based Algorithms
3.2.4. Potential-Maintenance Algorithms
3.2.5. Biologically-Inspired Algorithms
3.2.6. Routing Protocol-Based Algorithms
3.2.7. Prediction-Based Algorithms
4. Conclusions and Challenges
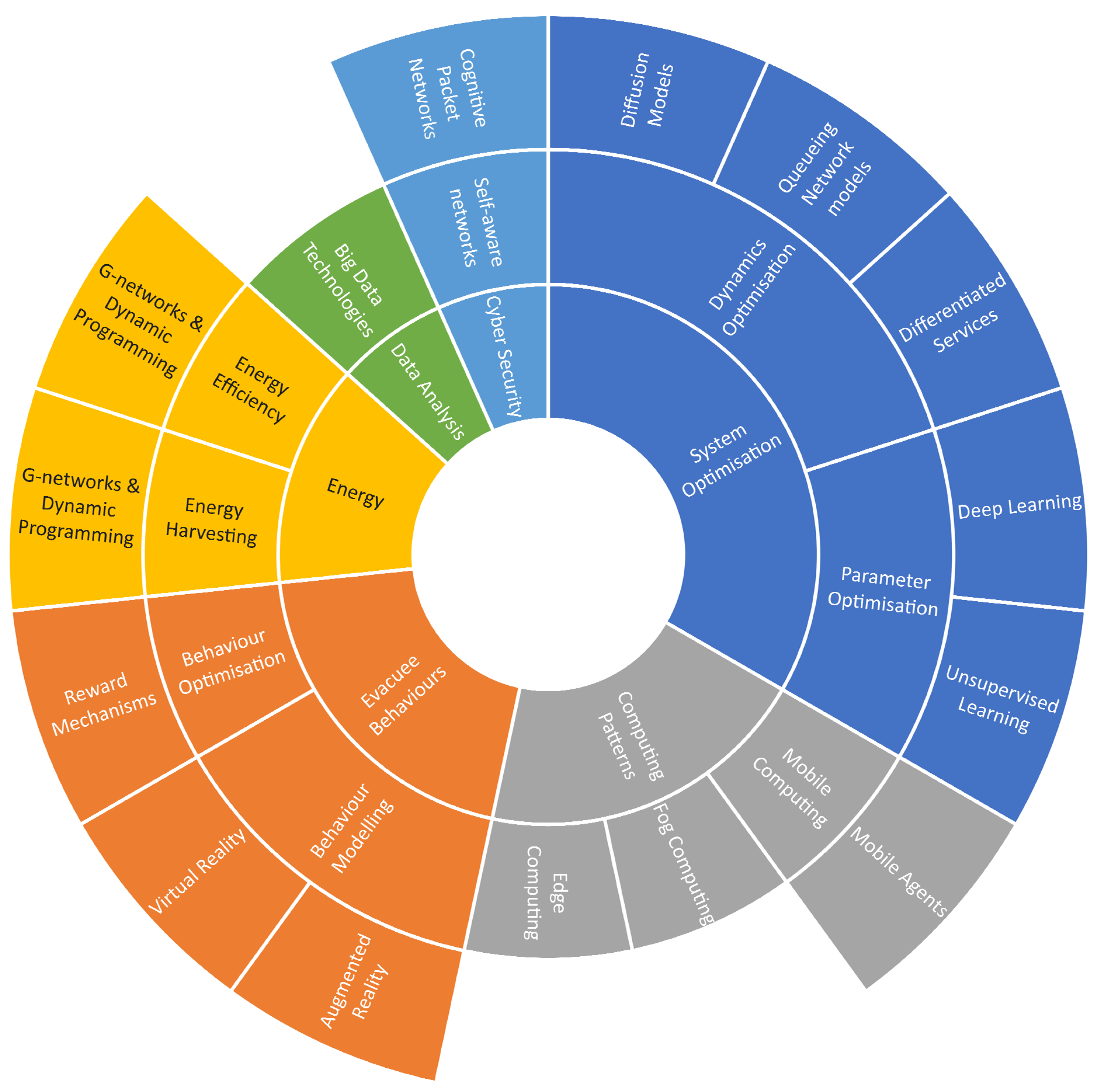
Emerging Challenges and Opportunities
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gelenbe, E.; Koçak, T. Area-based results for mine detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelenbe, E.; Wu, F.J. Future research on cyber-physical emergency management systems. Future Internet 2013, 5, 336–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, R.T.; Kitts, C.A.; Neumann, M. Experimental Implementation and Verification of Scalar Field Ridge, Trench, and Saddle Point Maneuvers Using Multirobot Adaptive Navigation. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 62950–62961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimakis, N.; Filippoupolitis, A.; Gelenbe, E. Distributed Building Evacuation Simulator for Smart Emergency Management. Comput. J. 2010, 53, 1384–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddow, G.; Bullock, J.; Coppola, D.P. Introduction to Emergency Management; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gelenbe, E.; Cao, Y. Autonomous search for mines. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1998, 108, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelenbe, E.; Hussain, K.; Kaptan, V. Simulating autonomous agents in augmented reality. J. Syst. Softw. 2005, 74, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belardo, S.; Karwan, K.R.; Wallace, W. An investigation of system design considerations for emergency management decision support. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1984, 14, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmet, L.; Francis, R.; Saunders, P. Network models for building evacuation. Fire Technol. 1982, 18, 90–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, T. Graph processing by which to evacuate a mine. In Proceedings of the 1990 Symposium on Applied Computing, Fayetteville, AR, USA, 5–6 April 1990; pp. 137–141. [Google Scholar]
- Southworth, F.; Chin, S.M.; Cheng, P. A telemetric monitoring and analysis system for use during large scale population evacuations. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Road Traffic Monitoring, London, UK, 7–9 February 1989; pp. 99–103. [Google Scholar]
- Griffith, D. The critical problems of hurricane evacuation and alternative solutions. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 82, Washington, DC, USA, 20–22 September 1982; pp. 990–994. [Google Scholar]
- Zorpette, G. Evacuation planning for Lilco’s Shoreham plant: Lack of an approved emergency evacuation strategy may prevent full operation of a $5 billion nuclear power plant on long Island’s north shore. IEEE Spectr. 1987, 24, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serpa, D.P.; Walker, D.M.; Jenckes, T.A. Emergency Monitoring, Assessment and Response System for Diablo Canyon Nuclear Power Plant. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 1981, 28, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelenbe, E. A diffusion model for packet travel time in a random multi-hop medium. ACM Trans. Sens. Networks (Tosn) 2007, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippoupolitis, A.; Gelenbe, E. A distributed decision support system for Building Evacuation. In Proceedings of the 2nd Conference on Human System Interactions, Catania, Italy, 21–23 May 2009; pp. 323–330. [Google Scholar]
- Gelenbe, E.; Sevcik, K. Analysis of update synchronization for multiple copy data bases. IEEE Trans. Comput. 1979, 100, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, Y.C.; Pan, M.S.; Tsai, Y.Y. Wireless sensor networks for emergency navigation. Computer 2006, 39, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, V.D.; Corson, M.S. A highly adaptive distributed routing algorithm for mobile wireless networks. In Proceedings of the Sixteenth Annual Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications Societies. Driving the Information Revolution, Kobe, Japan, 7–12 April 1997; Volume 3, pp. 1405–1413. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; De Rosa, M.; Rus, D. Distributed algorithms for guiding navigation across a sensor network. In Proceedings of the 9th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, San Diego, CA, USA, 14–19 September 2003; pp. 313–325. [Google Scholar]
- Koditschek, D.E. Robot planning and control via potential functions. Robot. Rev. 1989, 1, 349–367. [Google Scholar]
- Gorbil, G.; Gelenbe, E. Opportunistic communications for emergency support systems. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2011, 5, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelenbe, E.; Gorbil, G. Wireless networks in emergency management. In Proceedings of the First ACM International Workshop on Practical Issues and Applications in Next Generation Wireless Networks, Istanbul, Turkey, 26 August 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Gorbil, G.; Gelenbe, E. Resilient emergency evacuation using opportunistic communications. In Computer and Information Sciences III; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 249–257. [Google Scholar]
- Pelusi, L.; Passarella, A.; Conti, M. Opportunistic networking: data forwarding in disconnected mobile ad hoc networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2006, 44, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippoupolitis, A.; Gorbil, G.; Gelenbe, E. Autonomous navigation systems for emergency management in buildings. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), Houston, TX, USA, 5–9 December 2011; pp. 1056–1061. [Google Scholar]
- Zubair, S.; bnt Fisal, N.; Yerima, S.; Salihu, B.; Salihu, Y. CoWiSMoN: A framework for cognitive wireless sensor mobile network system for emergency rescue management. In Proceedings of the 2011 3rd IEEE International Conference Adaptive Science and Technology (ICAST), Abuja, Nigeria, 24–26 November 2011; pp. 237–241. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, Y.; Sashima, A.; Ikeda, T.; Kurumatani, K. Indoor Emergency Evacuation Service on Autonomous Navigation System using Mobile Phone. In Proceedings of the Second International Symposium Universal Communication, Osaka, Japan, 15–16 December 2008; pp. 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Tseng, Y.C.; Wang, Y.C.; Cheng, K.Y.; Hsieh, Y.Y. iMouse: An Integrated Mobile Surveillance and Wireless Sensor System. Computer 2007, 40, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Li, H.; Ota, K.; Yang, L.; Zhu, H. Multicloud-Based Evacuation Services for Emergency Management. IEEE Cloud Comput. 2014, 1, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.; Wu, S.J. An Integrated Building Fire Evacuation System with RFID and Cloud Computing. In Proceedings of the 2011 Seventh International Conference on Intelligent Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing (IIH-MSP), Dalian, China, 14–16 October 2011; pp. 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, M.; Ming, Z.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.T.; Xiang, Y. Enabling Cloud Computing in Emergency Management Systems. IEEE Cloud Comput. 2014, 1, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelenbe, E.; Bi, H. Emergency Navigation without an Infrastructure. Sensors 2014, 14, 15142–15162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelenbe, E.; Mahmoodi, T. Energy-aware routing in the cognitive packet network. Energy 2011, 68, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Gelenbe, E. Energy packet networks: adaptive energy management for the cloud. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Cloud Computing Platforms, Bern, Switzerland, 10–13 April 2012; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Helbing, D.; Farkas, I.; Vicsek, T. Simulating dynamical features of escape panic. Nature 2000, 407, 487–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhao, D.; Li, J.; Fang, T. Simulation of the kin behavior in building occupant evacuation based on cellular automaton. Build. Environ. 2005, 40, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwynne, S.; Galea, E.; Owen, M.; Lawrence, P.J.; Filippidis, L. ; others. A review of the methodologies used in evacuation modelling. Fire Mater. 1999, 23, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhong, T.; Liu, M. Modeling crowd evacuation of a building based on seven methodological approaches. Build. Environ. 2009, 44, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfram, S. Statistical mechanics of cellular automata. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1983, 55, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandini, S.; Manzoni, S.; Vizzari, G. Situated Cellular Agents: A model to simulate crowding dynamics. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. Spec. Issue Cell. Autom. 2004, 87, 669–676. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Song, W. Cellular automaton simulation of pedestrian counter flow considering the surrounding environment. Phys. Rev. E 2007, 75, 046112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spartalis, E.; Georgoudas, I.G.; Sirakoulis, G.C. CA Crowd Modeling for a Retirement House Evacuation with Guidance. In Cellular Automata; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 481–491. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, F.; Wohak, O.; Schadschneider, A. Study of Influence of Groups on Evacuation Dynamics Using a Cellular Automaton Model. Transp. Res. Procedia 2014, 2, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helbing, D.; Molnar, P. Social force model for pedestrian dynamics. Phys. Rev. E 1995, 51, 4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, D.; Dorso, C. Microscopic dynamics of pedestrian evacuation. Phys. Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2005, 354, 606–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfried, A.; Steffen, B.; Lippert, T. Basics of modelling the pedestrian flow. Phys. Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2006, 368, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, L. The statistics of crowd fluids. Nature 1971, 229, 381–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helbing, D.; Farkas, I.J.; Molnar, P.; Vicsek, T. Simulation of pedestrian crowds in normal and evacuation situations. Pedestr. Evacuation Dyn. 2002, 21, 21–58. [Google Scholar]
- Fredkin, E.; Toffoli, T. Conservative Logic; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Tajima, Y.; Takimoto, K.; Nagatani, T. Scaling of pedestrian channel flow with a bottleneck. Phys. Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2001, 294, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takimoto, K.; Nagatani, T. Spatio-temporal distribution of escape time in evacuation process. Phys. Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2003, 320, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogendoorn, S.; HL Bovy, P. Simulation of pedestrian flows by optimal control and differential games. Optim. Control. Appl. Methods 2003, 24, 153–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.M.; Huang, H.C.; Wang, P.; Yuen, K. A game theory based exit selection model for evacuation. Fire Saf. J. 2006, 41, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehtamo, H.; Heliövaara, S.; Hostikka, S.; Korhonen, T. Modeling evacuees’ exit selection with best response dynamics. In Pedestrian and Evacuation Dynamics 2008; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 309–319. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Cheng, Y. Modeling cooperative and competitive behaviors in emergency evacuation: A game-theoretical approach. Comput. Math. Appl. 2011, 62, 4627–4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonabeau, E. Agent-based modeling: Methods and techniques for simulating human systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 7280–7287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarboutis, N.; Marmaras, N. Searching efficient plans for emergency rescue through simulation: the case of a metro fire. Cogn. Technol. Work 2004, 6, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstone, R.L.; Janssen, M.A. Computational models of collective behavior. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2005, 9, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Han, C.S.; Dauber, K.; Law, K.H. A multi-agent based framework for the simulation of human and social behaviors during emergency evacuations. AI Soc. 2007, 22, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saloma, C.; Perez, G.J.; Tapang, G.; Lim, M.; Palmes-Saloma, C. Self-organized queuing and scale-free behavior in real escape panic. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 11947–11952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altshuler, E.; Ramos, O.; Núñez, Y.; Fernández, J.; Batista-Leyva, A.; Noda, C. Symmetry breaking in escaping ants. Am. Nat. 2005, 166, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelechano, N.; Malkawi, A. Evacuation simulation models: Challenges in modeling high rise building evacuation with cellular automata approaches. Autom. Constr. 2008, 17, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, G.J.; Tapang, G.; Lim, M.; Saloma, C. Streaming, disruptive interference and power-law behavior in the exit dynamics of confined pedestrians. Phys. Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2002, 312, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstedde, C.; Klauck, K.; Schadschneider, A.; Zittartz, J. Simulation of pedestrian dynamics using a two-dimensional cellular automaton. Physica A 2004, 295, 507–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Kashimori, Y.; Kambara, T. A model describing collective behaviors of pedestrians with various personalities in danger situations. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Neural Information Processing, Singapore, 18–22 November 2002; Volume 4, pp. 2083–2087. [Google Scholar]
- Hecht-Nielsen, R. Applications of counter-propagation networks. Neural Netw. 1988, 1, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.L. A continuum theory for the flow of pedestrians. Transp. Res. Part Methodol. 2002, 36, 507–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, R.M.; Rosini, M.D. Pedestrian flows and non-classical shocks. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 2005, 28, 1553–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lighthill, M.J.; Whitham, G.B. On kinematic waves. II. A theory of traffic flow on long crowded roads. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1955, 229, 317–345. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.P. The Riemann problem for general systems of conservation laws. J. Differ. Equ. 1975, 18, 218–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thouless, D.J. The Quantum Mechanics of Many-Body Systems; Dover Publications: Mineola, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kirchner, A.; Klüpfel, H.; Nishinari, K.; Schadschneider, A.; Schreckenberg, M. Simulation of competitive egress behavior: comparison with aircraft evacuation data. Phys. Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2003, 324, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fudenberg, D.; Tirole, J. Game Theory; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1991; Volume 393. [Google Scholar]
- Nash, J. Non-cooperative games. Ann. Math. 1951, 54, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Asada, M. Motion sketch: Acquisition of visual motion guided behaviors. In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference Artificial Intelligence, Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–25 August 1995; Volume 1, pp. 126–132. [Google Scholar]
- March, J.G. Primer on Decision Making: How Decisions Happen; Simon and Schuster: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Kuligowski, E.D.; Peacock, R.D.; Hoskins, B. A Review of Building Evacuation Models; US Department of Commerce, National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gelenbe, E.; Wu, F.J. Large scale simulation for human evacuation and rescue. Comput. Math. Appl. 2012, 64, 3869–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, R. A Negative Exponential Solution to an Evacuation Problem; National Bureau of Standards, Center for Fire Research: Springfield, VA, USA, 1984.
- Kisko, T.M.; Francis, R.L. EVACNET+: A computer program to determine optimal building evacuation plans. Fire Saf. J. 1985, 9, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Huang, Y.; Shekhar, S. Evacuation planning: a capacity constrained routing approach. In Intelligence and Security Informatics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 111–125. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Q.; George, B.; Shekhar, S. Capacity constrained routing algorithms for evacuation planning: A summary of results. In Advances in Spatial and Temporal Databases; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 291–307. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.Y.; Chen, W.T.; Shen, Y.T. A distributed area-based guiding navigation protocol for wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 14th IEEE International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Systems, Melbourne, Australia, 8–10 December 2008; pp. 647–654. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z. Sensor network navigation without locations. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2013, 24, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacGregor Smith, J. State-dependent queueing models in emergency evacuation networks. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 1991, 25, 373–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, F.R.; Smith, J.M.; Queiroz, D. Service and capacity allocation in M/G/c/c state-dependent queueing networks. Comput. Oper. Res. 2005, 32, 1545–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanov, A.; Smith, J.M. Multi-objective evacuation routing in transportation networks. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2009, 198, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lino, P.; Maione, G.; Maione, B. Modeling and simulation of crowd egress dynamics in a discrete event environment. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Control Applications (CCA) & Intelligent Control, Intelligent Control, Petersburg, Russia, 8–10 July 2009; pp. 843–848. [Google Scholar]
- Desmet, A.; Gelenbe, E. Graph and analytical models for emergency evacuation. Future Internet 2013, 5, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H. Evacuee Flow Optimisation Using G-Network with Multiple Classes of Positive Customers. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 24th International Symposium on Modeling, Analysis and Simulation of Computer and Telecommunication Systems (MASCOTS), London, UK, 19–21 September 2016; pp. 135–143. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, H.; Abdelrahman, O.H. Energy-Aware Navigation in Large-Scale Evacuation Using G-networks. Probab. Eng. Inform. Sci. 2018, 32, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.T.; Chen, P.Y.; Wu, C.H.; Huang, C.F. A load-balanced guiding navigation protocol in wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Globecom 2008 Global Telecommunications Conference, New Orleans, LA, USA, 30 November–4 December 2008; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Gelenbe, E.; Timotheou, S. Random neural networks with synchronized interactions. Neural Comput. 2008, 20, 2308–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankowska, A.; Schut, M.; Ferreira-Schut, N. A wireless actuator-sensor neural network for evacuation routing. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Sensor Technologies and Applications, Athens/Glyfada, Greece, 18–23 June 2009; pp. 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Fang, Z.; Li, Q.; Zong, X. Multiobjective evacuation route assignment model based on genetic algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2010 18th International Conference on Geoinformatics, Beijing, China, 18–20 June 2010; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Filippoupolitis, A. Emergency Simulation and Decision Support Algorithms. Ph.D. Thesis, Imperial College London (University of London), London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, H.; Desmet, A.; Gelenbe, E. Routing Emergency Evacuees with Cognitive Packet Networks. In Proceedings of the 28th International Symposium on Computer and Information Sciences (ISCIS’13), Paris, France, 28–29 October 2013; Springer: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, H.; Gelenbe, E. Routing diverse evacuees with Cognitive Packets. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops (PERCOM Workshops), Budapest, Hungary, 24–28 March 2014; pp. 291–296. [Google Scholar]
- Hasofer, A.; Odigie, D. Stochastic modelling for occupant safety in a building fire. Fire Saf. J. 2001, 36, 269–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, M.; Leather, H.; Arvind, D. Emergency evacuation using wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 32nd IEEE Conference on Local Computer Networks, Dublin, Ireland, 15–18 October 2007; pp. 851–857. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.; Potter, S.; Beckett, G.; Pringle, G.; Welch, S.; Koo, S.H.; Wickler, G.; Usmani, A.; Torero, J.L.; Tate, A. FireGrid: an e-infrastructure for next-generation emergency response support. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2010, 70, 1128–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radianti, J.; Granmo, O.C.; Sarshar, P.; Goodwin, M.; Dugdale, J.; Gonzalez, J.J. A spatio-temporal probabilistic model of hazard-and crowd dynamics for evacuation planning in disasters. Appl. Intell. 2015, 42, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.; Gelenbe, E. Cloud enabled emergency navigation using faster-than-real-time simulation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communication Workshops (PerCom Workshops), St. Louis, MO, USA, 23–27 March 2015; pp. 475–480. [Google Scholar]
- Ford, D.; Fulkerson, D.R. Flows in Networks; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ahuja, R.K.; Magnanti, T.L.; Orlin, J.B. Network Flows; Alfred P. Sloan School of Management, Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Graves, G.W.; Brown, G.G.; Bradley, G.H. Design and Implementation of Large-Scale Primal Transshipment Algorithms. Manag. Sci. 1977, 24, 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Hoppe, B.; Tardos, É. Polynomial time algorithms for some evacuation problems. In Proceedings of the Fifth Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms, Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, Arlington, VA, USA, 23–25 January 1994; pp. 433–441. [Google Scholar]
- Hoppe, B.; Tardos, É. The quickest transshipment problem. Math. Oper. Res. 2000, 25, 36–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megiddo, N. Optimal flows in networks with multiple sources and sinks. Math. Program. 1974, 7, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minieka, E. Maximal, lexicographic, and dynamic network flows. Oper. Res. 1973, 21, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, E.W. A note on two problems in connexion with graphs. Numer. Math. 1959, 1, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Calinescu, G.; Wan, P.J. Distributed construction of a planar spanner and routing for ad hoc wireless networks. In Proceedings of the Twenty-First Annual Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications Societies, New York, NY, USA, 23–27 June 2002; Volume 3, pp. 1268–1277. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.Y.; Calinescu, G.; Wan, P.J.; Wang, Y. Localized delaunay triangulation with application in ad hoc wireless networks. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2003, 14, 1035–1047. [Google Scholar]
- Bruck, J.; Gao, J.; Jiang, A. MAP: Medial axis based geometric routing in sensor networks. Wirel. Netw. 2007, 13, 835–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelenbe, E.; Pujolle, G. Introduction aux réSeaux de Files d’Attente; Eyrolles: Paris, France, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Gelenbe, E.; Muntz, R.R. Probabilistic models of computer systems, Part I (Exact Results). Acta Inform. 1976, 7, 35–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelenbe, E. A unified approach to a class of page replacement algorithms. IEEE Trans. Comput. 1973, 22, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruin, J.J. Pedestrian Planning and Design; Metropolitan Association of Urban Designers and Environmental Planners, Inc. In Pedestrian Planning and Design; Metropolitan Association of Urban Designers and Environmental Planners, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Tregenza, P. The Design of Interior Circulation; Van Nostrand Reinhold: New York, NY, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, R.L.; Chalmet, L.G. Network Models for Building Evacuation: A Prototype Primer; Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering, University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Yuhaski, S.J., Jr.; Smith, J.M. Modeling circulation systems in buildings using state dependent queueing models. Queueing Syst. 1989, 4, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, J.Y.; Smith, J.M. Generalized M/G/c/c state dependent queueing models and pedestrian traffic flows. Queueing Syst. 1994, 15, 365–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerbachea, L.; Smith, J.M. The generalized expansion method for open finite queueing networks. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1987, 32, 448–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerbache, L.; Smith, J.M. Asymptotic behavior of the expansion method for open finite queueing networks. Comput. Oper. Res. 1988, 15, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.M.; Gershwin, S.B.; Papadopoulos, C.T. Performance Evaluation and Optimization of Production Lines; Baltzer Science Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; Volume 93. [Google Scholar]
- Lino, P.; Pizzileo, B.; Maione, G.; Maione, B. Tuning and Validation of a Discrete-Event Model of the Egress Dynamics from Buildings. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2011, 44, 8743–8748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Luh, P.B.; Chang, S.C.; Sun, J. Modeling and optimization of crowd guidance for building emergency evacuation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering, Washington, DC, USA, 23–26 August 2008; pp. 328–334. [Google Scholar]
- Watts, J.M. Computer models for evacuation analysis. Fire Saf. J. 1987, 12, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, F.R.; Smith, J.M.; Medeiros, R. An M/G/C/C state-dependent network simulation model. Comput. Oper. Res. 2005, 32, 919–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelenbe, E.; Labed, A. G-networks with multiple classes of signals and positive customers. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1998, 108, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelenbe, E. G-networks with triggered customer movement. J. Appl. Probab. 1993, 30, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.; Szewczyk, R.; Woo, A.; Hollar, S.; Culler, D.; Pister, K. System architecture directions for networked sensors. ACM SIGOPS Oper. Syst. Rev. 2000, 34, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.S.; Tsai, C.H.; Tseng, Y.C. Emergency guiding and monitoring applications in indoor 3D environments by wireless sensor networks. Int. J. Sens. Netw. 2006, 1, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelenbe, E.; Schmajuk, N.; Staddon, J.; Reif, J. Autonomous search by robots and animals: A survey. Robot. Auton. Syst. 1997, 22, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, T.M. Machine Learning; McGraw Hill: Burr Ridge, IL, USA, 1997; Volume 45. [Google Scholar]
- John, H. Adaptation in Natural and Artificial Systems; University of Michigan Press: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Gelenbe, E.; Liu, P.; Laine, J. Genetic algorithms for route discovery. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B 2006, 36, 1247–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K.; Agrawal, S.; Pratap, A.; Meyarivan, T. A fast elitist non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm for multi-objective optimization: NSGA-II. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2000, 1917, 849–858. [Google Scholar]
- Eppstein, D. Finding the k shortest paths. SIAM J. Comput. 1998, 28, 652–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadatseresht, M.; Mansourian, A.; Taleai, M. Evacuation planning using multiobjective evolutionary optimization approach. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2009, 198, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Han, C.S.; Law, K.H. A multi-agent based simulation framework for the study of human and social behavior in egress analysis. In Proceedings of the ASCE International Conference on Computing in Civil Engineering, Cancun, Mexico, 12–15 July 2005; Volume 92. [Google Scholar]
- Samadzadegan, F.; Yadegari, M. A biologically-inspired optimization algorithm for urban evacuation planning in disaster management. In Proceedings of the ACRS, Hanoi, Vietnam, 1–5 November 2010; Volume 1, pp. 573–578. [Google Scholar]
- Karaboga, D. An Idea Based on Honey Bee Swarm for Numerical Optimization; Technical Report-tr06; Erciyes University Press: Kayseri, Turkey, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gelenbe, E.; Lent, R.; Xu, Z. Towards networks with cognitive packets. In Performance and QoS of Next Generation Networking; Springer: London, UK, 2001; pp. 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Gelenbe, E.; Lent, R.; Xu, Z. Design and performance of cognitive packet networks. Perform. Eval. 2001, 46, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelenbe, E. Sensible decisions based on QoS. Comput. Manag. Sci. 2003, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahdat, A.; Becker, D. Epidemic Routing for Partially Connected ad Hoc Networks; Technical Report CS-200006; Duke University: Durham, NC, USA,, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Gorbil, G.; Gelenbe, E. Resilience and security of opportunistic communications for emergency evacuation. In Proceedings of the 7th ACM Workshop on Performance Monitoring and Measurement of Heterogeneous Wireless and Wired Networks, Paris, France, 21–23 November 2012; pp. 115–124. [Google Scholar]
- Gelenbe, E. Réseaux neuronaux aléatoires stables. Comptes Rendus de l’Académie des Sciences. Série 2 1990, 310, 177–180. [Google Scholar]
- Gelenbe, E. Random neural networks with negative and positive signals and product form solution. Neural Comput. 1989, 1, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelenbe, E.; Stafylopatis, A. Global behavior of homogeneous random neural systems. Appl. Math. Model. 1991, 15, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelenbe, E. Learning in the recurrent random neural network. Neural Comput. 1993, 5, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmet, A.; Gelenbe, E. A Parametric Study of CPN’s Convergence Process. In Information Sciences and Systems 2014; Springer: Cham, Switerland, 2014; pp. 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, H. Routing Diverse Evacuees with the Cognitive Packet Network Algorithm. Future Internet 2014, 6, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinwande, O.; Bi, H.; Gelenbe, E. Managing Crowds in Hazards With Dynamic Grouping. IEEE Access 2015, 3, 1060–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olenick, S.M.; Carpenter, D.J. An updated international survey of computer models for fire and smoke. J. Fire Prot. Eng. 2003, 13, 87–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, S.H.; Fraser-Mitchell, J.; Upadhyay, R.; Welch, S. Sensor-linked fire simulation using a Monte-Carlo approach. Fire Saf. Sci. 2008, 9, 1389–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Murphy, K.P. Dynamic Bayesian Networks: Representation, Inference and Learning. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Berkeley, Berkeley, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Gelenbe, E. Adaptive dispatching of tasks in the cloud. IEEE Trans. Cloud Comput. 2018, 6, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelenbe, E.; Loukas, G. A self-aware approach to denial of service defence. Comput. Netw. 2007, 51, 1299–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelenbe, E. Dealing with software viruses: a biological paradigm. Inf. Secur. Tech. Rep. 2007, 12, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, G.; Loukas, G.; Gelenbe, E. Detecting denial of service attacks with bayesian classifiers and the random neural network. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Fuzzy Systems Conference, London, UK, 23–26 July 207; pp. 1–6.
- Brun, O.; Yin, Y.; Gelenbe, E.; Kadioglu, Y.M.; Augusto-Gonzalez, J.; Ramos, M. Deep Learning with Dense Random Neural Networks for Detecting Attacks against IoT-connected Home Environments. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 134, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelenbe, E. Adaptive management of energy packets. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 38th International Computer Software and Applications Conference Workshops (COMPSACW), Vasteras, Sweden, 21–25 July 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Gelenbe, E. A sensor node with energy harvesting. ACM SIGMETRICS Perform. Eval. Rev. 2014, 42, 37–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, C.E.; Gelenbe, E. Video quality and traffic QoS in learning-based subsampled and receiver-interpolated video sequences. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2000, 18, 150–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelenbe, E.; Yin, Y. Deep learning with random neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2016; pp. 1633–1638. [Google Scholar]
- Nourbakhsh, I.R.; Sycara, K.; Koes, M.; Yong, M.; Lewis, M.; Burion, S. Human-robot teaming for search and rescue. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2005, 4, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelenbe, E. The first decade of G-networks. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2000, 126, 231–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxma, O.J.; Gelenbe, E. Two symmetric queues with alternating service and switching times. In Models of Computer System Performance, Proceedings of the 10th IFIP WG7. 3 International Symposium on Computer Performance Modelling, Measurement and Evaluation, Paris, France, 19–21 December 1984; North-Holland Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1985; pp. 409–431. [Google Scholar]
- Gelenbe, E. Steady-state solution of probabilistic gene regulatory networks. Phys. Rev. E 2007, 76, 031903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aversa, R.; Di Martino, B.; Rak, M.; Venticinque, S. Cloud agency: A mobile agent based cloud system. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Complex, Intelligent and Software Intensive Systems (CISIS), Krakow, Poland, 15–18 February 2010; pp. 132–137. [Google Scholar]
| System Type | Period |
|---|---|
| Human experience-driven systems | 1970s–1990s |
| Static WSN-based systems | 1995–present |
| Mixed WSN-based systems | 2006–present |
| WSN and cloud-based systems | 2007–present |
| Cloud-based systems and mobile phones | 2011–present |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bi, H.; Gelenbe, E. A Survey of Algorithms and Systems for Evacuating People in Confined Spaces. Electronics 2019, 8, 711. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8060711
Bi H, Gelenbe E. A Survey of Algorithms and Systems for Evacuating People in Confined Spaces. Electronics. 2019; 8(6):711. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8060711
Chicago/Turabian StyleBi, Huibo, and Erol Gelenbe. 2019. "A Survey of Algorithms and Systems for Evacuating People in Confined Spaces" Electronics 8, no. 6: 711. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8060711
APA StyleBi, H., & Gelenbe, E. (2019). A Survey of Algorithms and Systems for Evacuating People in Confined Spaces. Electronics, 8(6), 711. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8060711






