An Efficient Super-Resolution Network Based on Aggregated Residual Transformations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
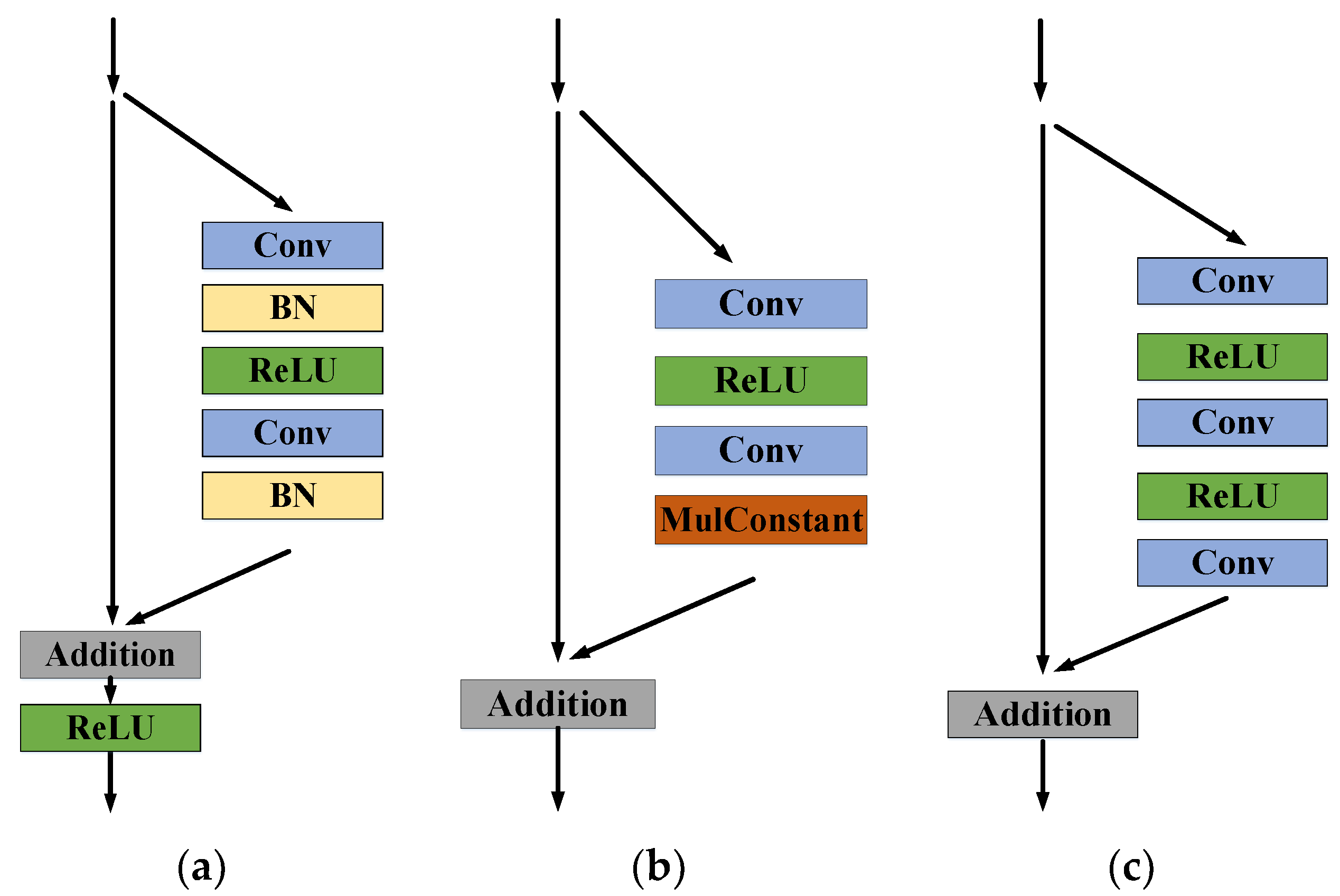
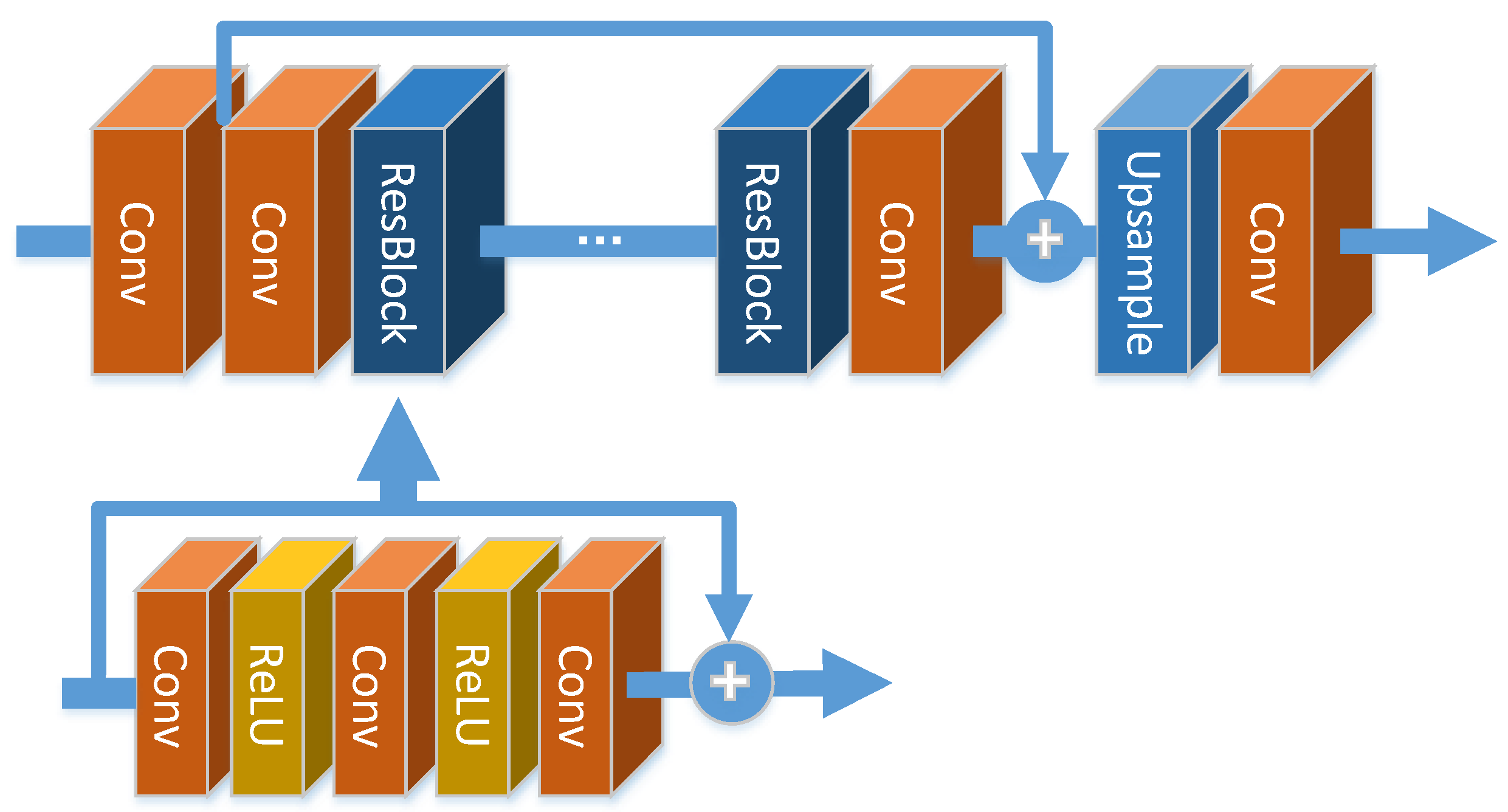
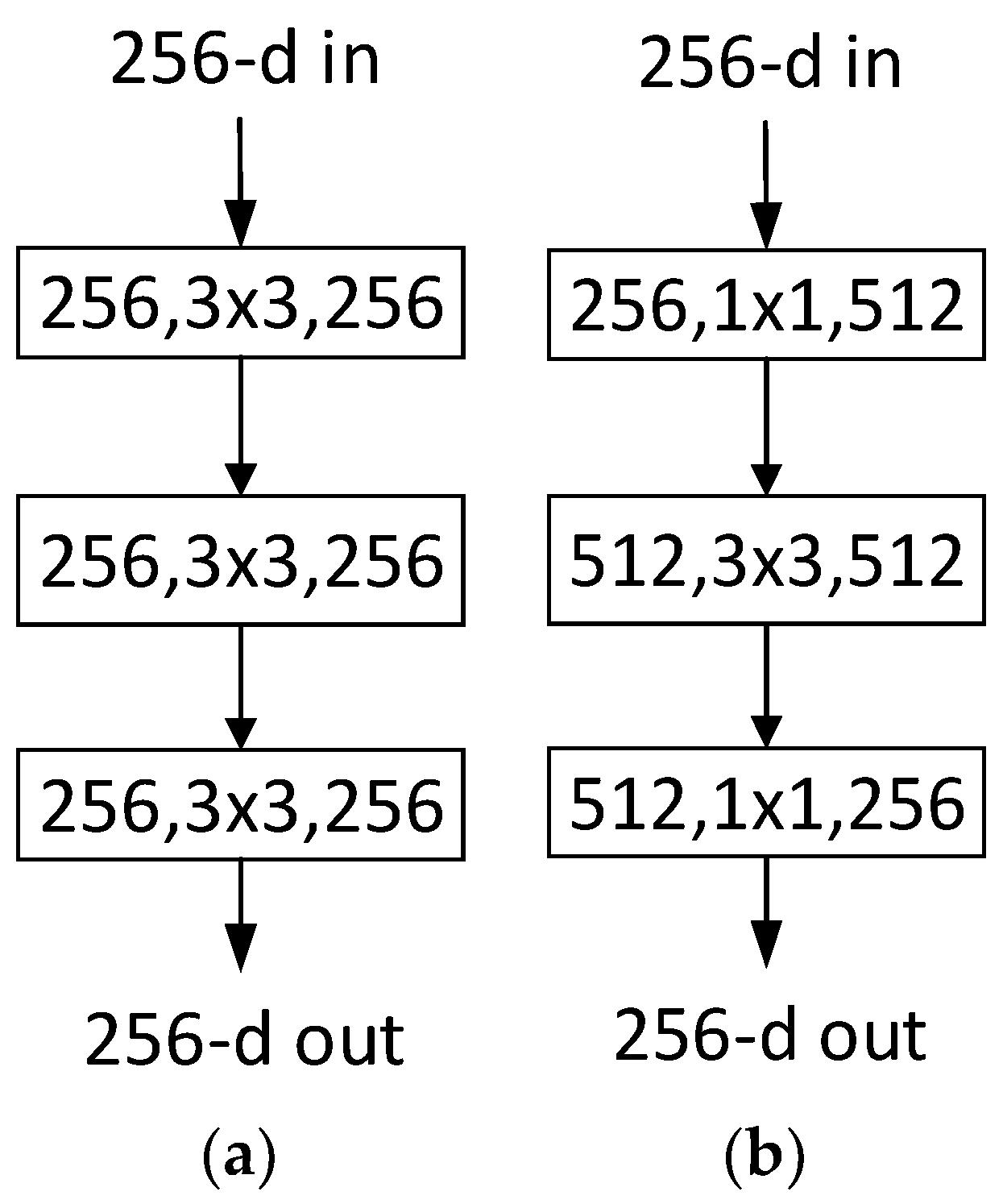
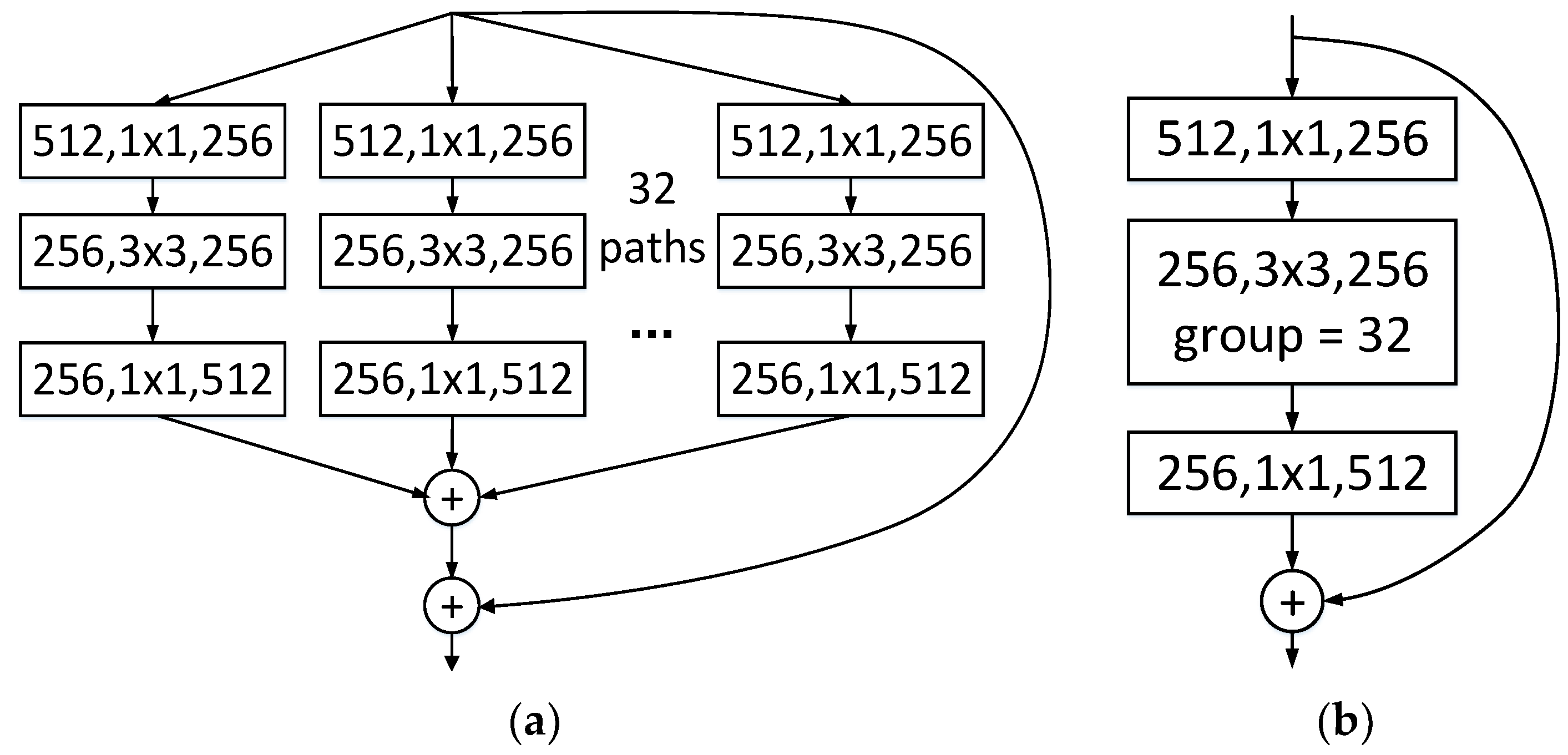
3. Methods
4. Experiment
4.1. Datasets
4.2. PSNR and SSIM Criteria
4.3. Training Details
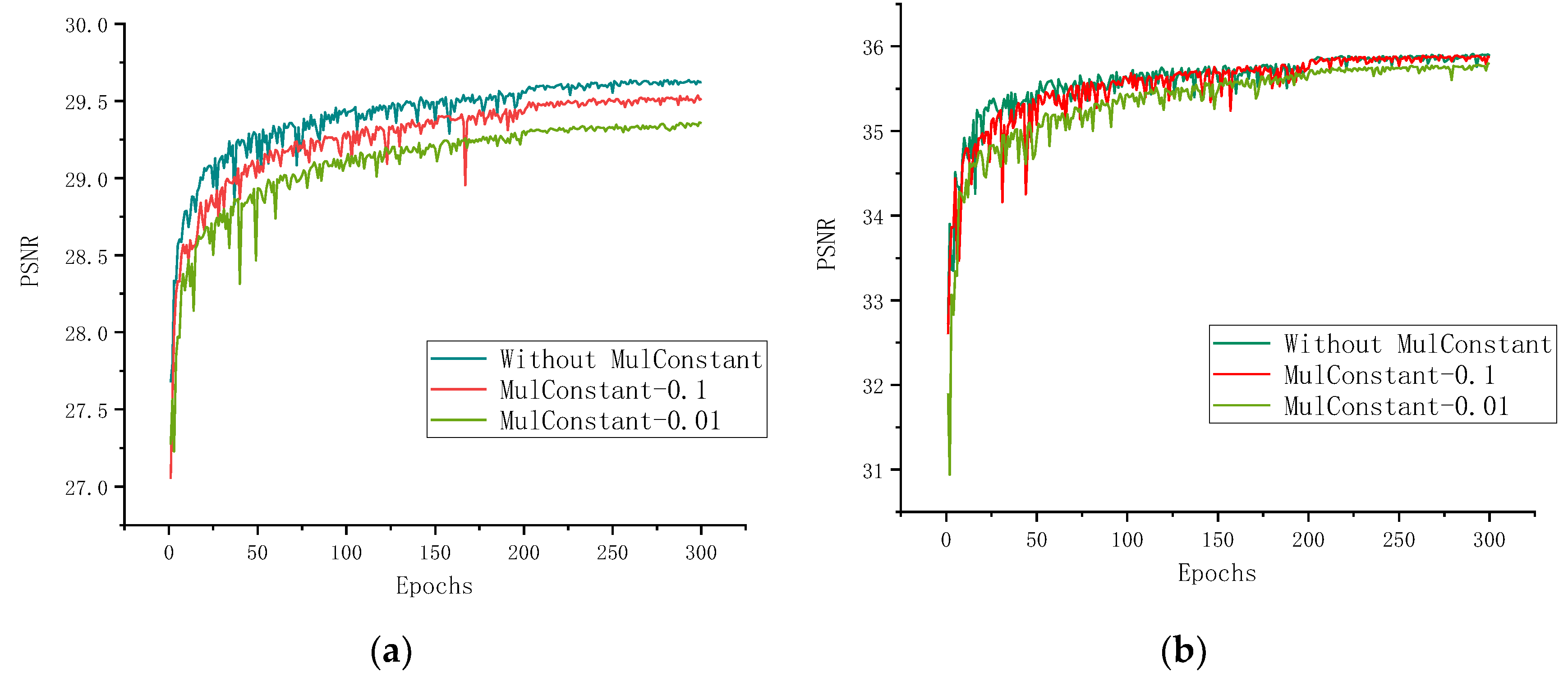
4.4. Comparison between the Cases with and without MulConstant Layer
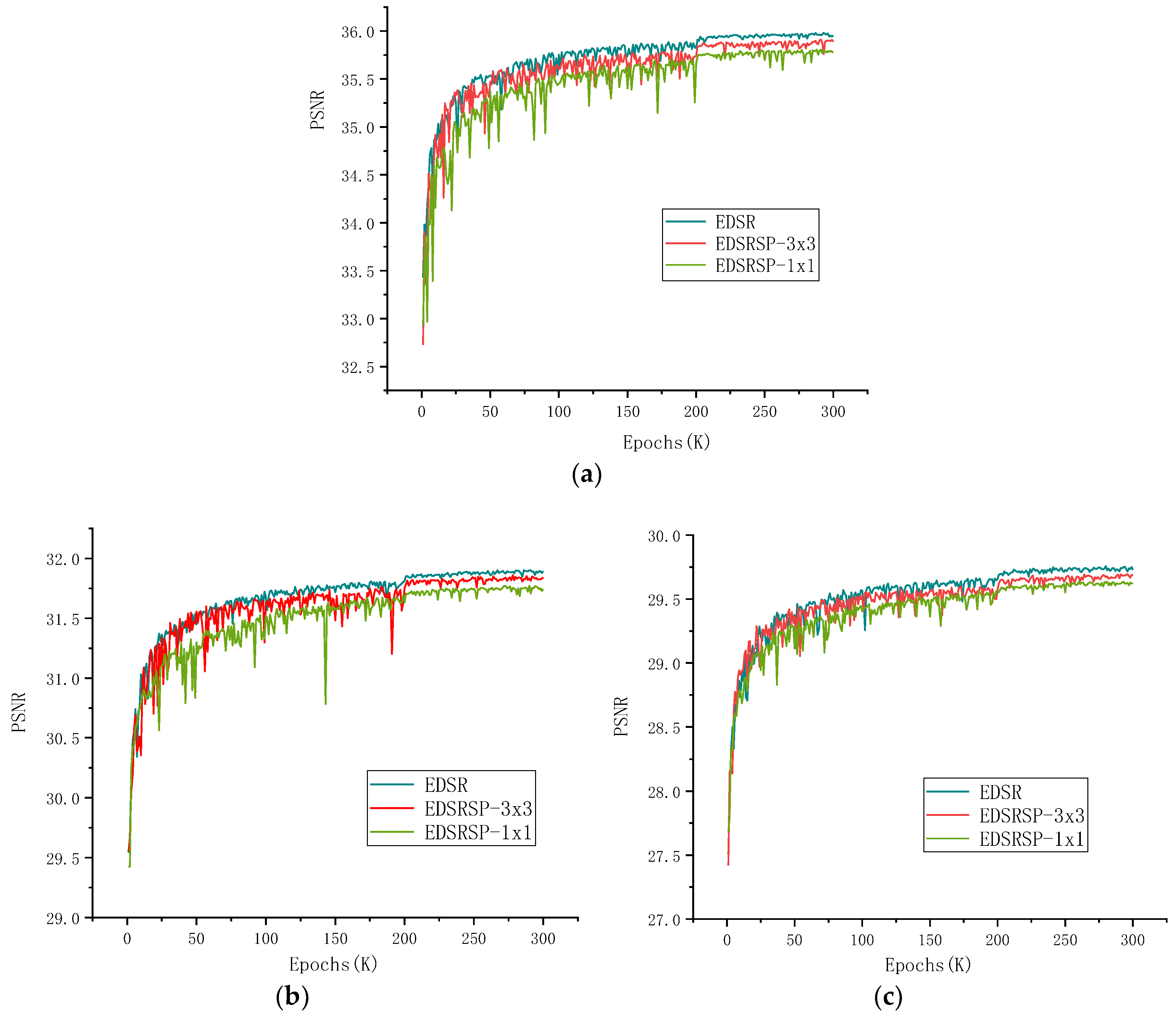
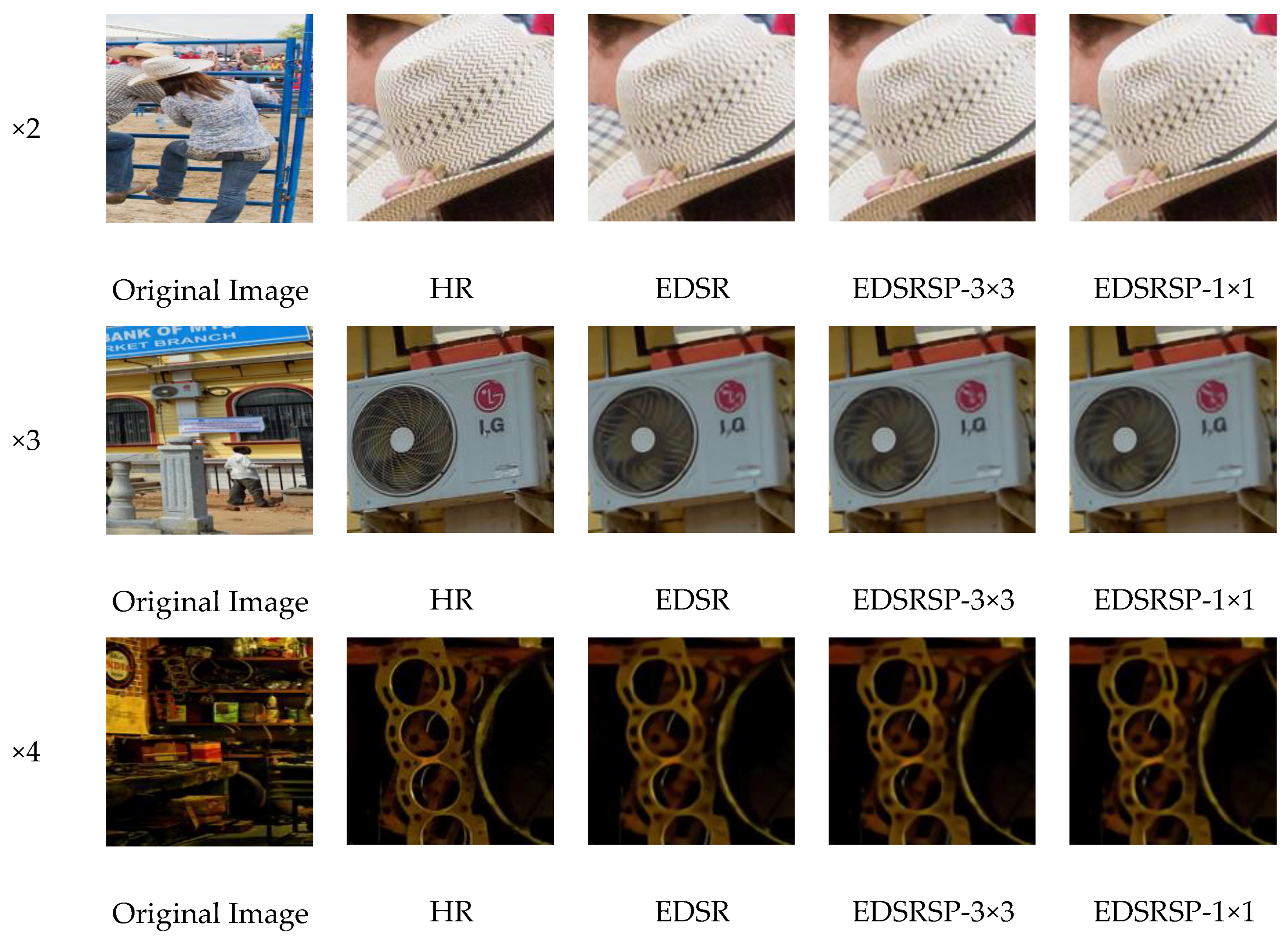
4.5. Evaluation on DIV2K Dataset
4.6. Evaluation on Other Datasets
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lim, B.; Son, S.; Kim, H.; Nah, S.; Lee, K.M. Enhanced deep residual networks for single image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Thornton, M.W.; Atkinson, P.M.; Holland, D.A. Sub-pixel mapping of rural land cover objects from fine spatial resolution satellite sensor imagery using super-resolution pixel-swapping. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 473–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenspan. Super-resolution in medical imaging. Comput. J. 2008, 52, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuszewski, J.; Sikorska-Łukasiewicz, K. Neural network application for emitter identification. In Proceedings of the 18th International Radar Symposium (IRS), Prague, Czech Republic, 28–30 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dudczyk, J.; Kawalec, A. Adaptive forming of the beam pattern of microstrip antenna with the use of an artificial neural network. Int. J. Antenn. Propag. 2012, 2012, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudczyk, J. A method of feature selection in the aspect of specific identification of radar signals. Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci.-Tech. 2017, 65, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrow, D.; Matuszewski, J. Objects detection and recognition system using artificial neural networks and drones. In Proceedings of the 2017 Signal Processing Symposium (SPSympo), Jachranka Village, Poland, 12–14 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.; Yeung, D.-Y.; Xiong, Y. Super-resolution through neighbor embedding. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Washington, DC, USA, 27 June–2 July 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua, M.; Roumy, A.; Guillemot, C.; Alberi-Morel, M.L. Low-complexity single-image super-resolution based on nonnegative neighbor embedding. In Proceedings of the 23rd British Machine Vision Conference Location (BMVC), Guildford, UK, 3–7 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, K.; Tao, D. Image super-resolution with sparse neighbor embedding. IEEE Trans. Image Process 2012, 21, 3194–3205. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roweis, S.T.; Saul, L.K.J.S. Nonlinear dimensionality reduction by locally linear embedding. Science 2000, 290, 2323–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeyde, R.; Elad, M.; Protter, M. On single image scale-up using sparse-representations. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Curves and Surfaces (ICCS), Avignon, France, 24–30 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Wang, Z.; Lin, Z.; Cohen, S.; Huang, T. Coupled dictionary training for image super-resolution. IEEE T. Image Process 2012, 21, 3467–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timofte, R.; De Smet, V.; Van Gool, L. A+: Adjusted anchored neighborhood regression for fast super-resolution. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV), Singapore, 1–2 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Wright, J.; Huang, T.S. Image super-resolution via sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Image Process 2010, 19, 2861–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Kwon Lee, J.; Mu Lee, K. Deeply-recursive convolutional network for image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Kwon Lee, J.; Mu Lee, K. Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; He, K.; Tang, X. Learning a deep convolutional network for image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ledig, C.; Theis, L.; Huszár, F.; Caballero, J.; Cunningham, A.; Acosta, A.; Aitken, A.; Tejani, A.; Totz, J.; Wang, Z. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hassibi, B.; Stork, D.G. Second order derivatives for network pruning: Optimal brain surgeon. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Denver, CO, USA, 1 April 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Aharon, M.; Elad, M.; Bruckstein, A. K-SVD: An algorithm for designing overcomplete dictionaries for sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2006, 54, 4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Ioffe, S.; Vanhoucke, V.; Alemi, A.A. Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning. In Proceedings of the Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-17), San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.; Girshick, R.; Dollár, P.; Tu, Z.; He, K. Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Harrahs and Harveys, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3–8 December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Timofte, R.; Agustsson, E.; Van Gool, L.; Yang, M.-H.; Zhang, L.; Lim, B.; Son, S.; Kim, H.; Nah, S.; Lee, K.M. Ntire 2017 challenge on single image super-resolution: Methods and results. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, D.; Fowlkes, C.; Tal, D.; Malik, J. A database of human segmented natural images and its application to evaluating segmentation algorithms and measuring ecological statistics. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 9–12 July 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Huynh-Thu, Q.; Ghanbari, M. Scope of validity of PSNR in image/video quality assessment. Electron. Lett. 2008, 44, 800–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Model | Number of Residual Blocks | Total Parameters of Residual Blocks |
|---|---|---|
| EDSR | 32 | ~32,749 K |
| 256, 3 × 3, 256 | ||
| 256, 3 × 3, 256 | ||
| EDSRSP-3×3 | 21 | ~25,160 K |
| 256, 3 × 3, 256 | ||
| 256, 3 × 3, 256, 32 | ||
| 256, 3 × 3, 256 | ||
| EDSRSP-1×1 | 21 | ~7053 K |
| 256, 1 × 1, 512 | ||
| 512, 3 × 3, 512, 32 | ||
| 512, 1 × 1, 256 |
| Dataset | Scale | EDSR | EDSRSP-3×3 | EDSRSP-1×1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIV2K | ×2 | 35.80/0.9676 | 35.71/0.9673 | 35.60/0.9670 |
| ×3 | 32.17/0.9345 | 32.06/0.9337 | 31.99/0.9331 | |
| ×4 | 30.07/0.9057 | 29.97/0.9050 | 29.88/0.9045 |
| Scale | EDSR | EDSRSP-3×3 | EDSRSP-1×1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ×2 | 12.562 | 9.966 | 6.472 |
| ×3 | 7.700 | 6.348 | 4.665 |
| ×4 | 4.426 | 3.363 | 2.442 |
| Dataset | Scale | EDSR | EDSRSP-3×3 | EDSRSP-1×1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Set5 | ×2 | 38.08/0.960 | 38.04/0.9599 | 37.99/0.9598 |
| ×3 | 34.59/0.9275 | 34.48/0.9267 | 34.40/0.9261 | |
| ×4 | 32.36/0.8950 | 32.21/0.8937 | 32.15/0.8926 | |
| Set14 | ×2 | 33.71/0.9185 | 33.65/0.9180 | 33.58/0.9169 |
| ×3 | 30.35/0.8435 | 30.32/0.8428 | 30.24/0.8412 | |
| ×4 | 28.60/0.7831 | 28.57/0.7821 | 28.51/0.7809 | |
| B100 | ×2 | 32.30/0.9009 | 32.24/0.9004 | 32.20/0.8995 |
| ×3 | 29.20/0.8080 | 29.16/0.8067 | 29.12/0.8055 | |
| ×4 | 27.64/0.7390 | 27.60/0.7378 | 27.57/0.7366 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, H.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, M.; Qin, H. An Efficient Super-Resolution Network Based on Aggregated Residual Transformations. Electronics 2019, 8, 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8030339
Liu Y, Zhang G, Wang H, Zhao W, Zhang M, Qin H. An Efficient Super-Resolution Network Based on Aggregated Residual Transformations. Electronics. 2019; 8(3):339. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8030339
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yan, Guangrui Zhang, Hai Wang, Wei Zhao, Min Zhang, and Hongbo Qin. 2019. "An Efficient Super-Resolution Network Based on Aggregated Residual Transformations" Electronics 8, no. 3: 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8030339
APA StyleLiu, Y., Zhang, G., Wang, H., Zhao, W., Zhang, M., & Qin, H. (2019). An Efficient Super-Resolution Network Based on Aggregated Residual Transformations. Electronics, 8(3), 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8030339







