Abstract
Physically Unclonable Functions (PUFs) are a cryptographic primitive that exploit the unique physical characteristics of Integrated Circuits (ICs). A PUF can be modeled as a black-box challenge–response system. The number and size of challenge–response pairs (CRPs) supported by a PUF determine and condition its strength. Ring Oscillators (RO)-based PUF, which are one of the most implemented on FPGA, suffer from a low number and size of CRPs. In this work, we propose an innovative mechanism to expand the size of the CRPs in a RO-PUF by using multiple bits of the two ROs under comparison. To satisfy the reliability and enhance the quality of these responses, we either switch the remaining ROs that are not used for the comparison off or use them as a background noise. We validated our proposal using FPGA measurements. The results show that, with the same number of Ring Oscillators, the CRP size can be doubled with a minimum area overhead.
1. Introduction
Sub-micron manufacturing processes are subject to process variations that result in different physical transistor properties despite having the same design sizes [1]. These unavoidable and uncontrollable imperfections can be used to create unique and unclonable electronic fingerprints, which are commonly known as Physically Unclonable Functions (PUFs) [1]. PUFs are an asset in many security-related applications such as IC authentication, cryptographic key generation and Intellectual Property (IP) protection mechanisms [2]. Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) require special attention as their reconfigurable nature opens doors to a wide set of security threats, including IP theft attacks that can be attained once the chip is deployed [3]. To combat IP attacks, Ring Oscillators-based PUFs (RO-PUFs) have been frequently deployed as they are one of the most affordable solutions [4] in secure embedded systems. The main drawback of RO-PUFs is that they offer a low number of challenge–response pairs (CRPs) [5]. A CRP can be described by a mathematical function that maps a challenge to its associated PUF responses (i.e., )). A large number of CRPs is desirable as they depend less on noise (as more stable RO-PUF pairs can be selected), prevent replay attacks due to a larger CRP set, increase security due to longer and stronger keys, and serve a bigger IC population as different chips have a larger probability ending up in a different CRP set [6,7].
Several proposals have been presented in the literature to expand and/or enhance the number of CRPs in RO-PUFs. They are based on either modifying the RO structure or adding post-processing operations. In [8], the authors proposed a modification of the basic RO structure to enhance the PUF response. Their target is to increase the size of the response by increasing the response reliability. They realized this by replacing the basic RO with transient effect ring oscillators (TERO) and adding some circuitry to compute the average frequency of each TERO [8]. The main drawback of this proposal is that it requires multiple measurements to obtain the mean value of transient fluctuations for each TERO loop that lead to serious power and area overheads [9]. Using the same line of thought, other works propose a tuneable approach such as the Configurable-ROs (CROs) [5,10] or the use of signature post-processing [6,7,11]. For instance, in [6], the authors proposed to use the euclidean distances of RO frequencies as weighting factors. In addition to the circuit area and power consumption overheads, this proposal is vulnerable to side channel attacks as it involves arithmetic units such as square-root and multiplier units [9]. All above prior state-of-the-art methods either suffer from a high area penalty or are vulnerable against side attacks.
In this work, we present a new quantization method to expand the CRP size of RO-PUFs. More specifically, we intend to quantify the frequency difference of two RO PUFs using different intervals in order to obtain multiple bits from each comparison. This new quantification method could lead to unreliable responses, as the RO frequencies are affected by operational conditions (such as noise, supply voltage, etc.) and environmental conditions (such as temperature). To overcome this problem, we propose using the remaining RO-PUFs (i.e., the ones not used for comparison) in different background noise configurations. By exploiting them, we are able to select more reliable RO-PUF pairs.
The main contributions of this work are summarized as follows:
- A new quantization method allows us to increase the size of CRPs by exploiting multiple bits of a RO-PUF response.
- A new RO pair-selection mechanism based on the reliability of the PUF responses involves different levels of background noise.
- The evaluation of a physical implementation of the quantization method and different background configurations using 25 Xilinx Spartan 3E FPGA boards is presented.
- A validation of the methodology using some of the most extended PUF quality metrics (uniformity, bit-aliasing, reliability and uniqueness) for different operating conditions (i.e., core voltage variations) is presented.
Overall, the proposed methodology exhibits strong PUF quality metrics with a lower area overhead than other state-of-the-art solutions.
The remainder of the article is structured as follows: Section 2 shows a brief introduction to the CRP concept and related work. In Section 3, the proposed methodology to enhance the CRP set is presented. Experimental results and analysis are presented in Section 4 and Section 5. Finally, some conclusions are drawn in Section 6.
2. Background
In this section, we provide a background on PUFs and CRPs schemes, along with an introduction of the impact of the background noise on these circuits.
2.1. Basics of Ring Oscillator-Based PUFs and CRPs
In 2007, Suh and Devadas introduced the basic RO-PUF [12]. This PUF derives a single bit response by comparing the frequency of two identically laid-out ROs. A RO is a simple digital oscillator typically composed of an odd number of inverters in a ring configuration that will oscillate at a specific frequency. RO oscillation frequencies are determined by the design specification (e.g., number of stages, delay elements, place and route, etc.), random process variations that have a unique effect on every single device cause by the manufacturing processes, and the operational conditions (i.e., supply voltage, temperature, surrounding logic, etc.). RO-PUFs exploit the unique variations of the manufacturing processes to create an unclonable fingerprint of the device. To create this fingerprint, the traditional RO-PUF architecture depicted in Figure 1 is used; it measures the frequencies of a RO couple using two counters and subsequently compares these two frequencies to generate a response bit based on the following:
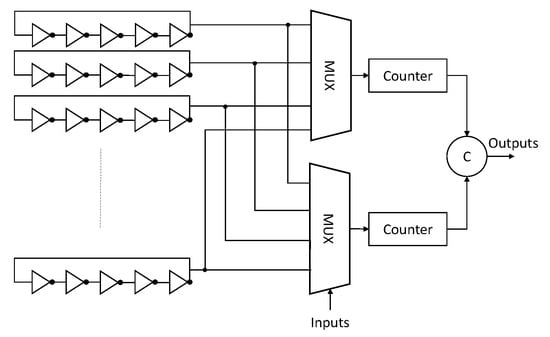
Figure 1.
RO-PUF general scheme.
A n-bit signature can be generated by comparing several ROs. These ROs are typically implemented in a two-dimensional matrix using hard-macros. This CRP generation method based on ranking of individual RO frequencies has some limitations from a security point of view [6,13]. A major limitation is related to the straightforward comparison between frequencies, which allows an attacker that has knowledge of two response pairs to derive the response of a third one; e.g., when 1 ( < ) and = 0 ( < ) = 0 ( < ). Another major limitation is the loss of information in the comparison process, as only the sign bit of the frequency difference between ROs is considered and not the frequency itself. Therefore, a higher number of ROs are required to distinguish between several chips. Finally, the placement of ROs has a big impact on the RO frequencies. Systematic process variations may dominate the generated frequency responses if the RO pairs under comparison are randomly selected [14]. To overcome this limitation, several proposals ranging from comparing only oscillators which are direct neighbors to signature post-processing can be found in the literature [6,14].
2.2. Impact of Switching Activity on RO-PUFs
Generally, increasing the switching activity in an FPGA implies an increase in power consumption which leads to a higher heat dissipation. Consequently, the temperature will rise—originated from flowing currents in the FPGA—and the switching speed is affected.
The effects of a background noise generated by different components of the PUF scheme (e.g., RO-PUFs that are not under comparison, counter logic, muxes and comparator in Figure 1) have been widely studied [14,15]. In [15], the authors explored the effects of the logic surrounding the RO matrix. They studied different relative placements of the RO counters and Chipscope logic (used to measure the RO frequencies). The authors concluded that the impact of the surrounding logic on the RO frequencies was negligible. In addition, they evaluated the effect of intrusive logic near the ROs; they measured a RO frequency decrease of around 0.4%. In [14], the effects of the switching activity generated by neighboring ROs are studied. The authors applied an enable/disable strategy to all the ROs contained in the matrix. Their results show an almost negligible effect on reliability when all the ROs are activated. Nevertheless, to the best of our knowledge, a study of different enable/disable strategies and their impact on the quality metrics and RO frequencies is missing.
3. Proposed Method
In this section, we introduce the proposed method to generate multiple bits of each RO frequency difference while maintaining reliability by using different background configurations. We present the methodology using a bottom-up approach. Firstly, we detail the considered background noise configurations; this is required to understand the proposed methodology better. Subsequently, we present the new quantization method that is used to expand the number of bits for each CRP. Finally, we describe the methodology that increases the reliability of the responses.
3.1. Background Noise Configuration
The idea behind different background noise configurations is to impact the frequency of ROs under comparison by intentionally enabling other ROs from the RO-PUF matrix as a noise source. We considered four background configurations, as shown in Figure 2. Configuration-A is the typical configuration where only the two ROs under comparison are activated. In Configuration-B, the ROs of the same column of one of the ROs under comparison are activated. Configuration-C expands on Configuration-B by having the neighboring columns also activated. Configuration-D activates all the ROs in the matrix. It is important to note that we selected only column configurations (instead of rows), as they have a higher impact as a result of the FPGA power line distribution.
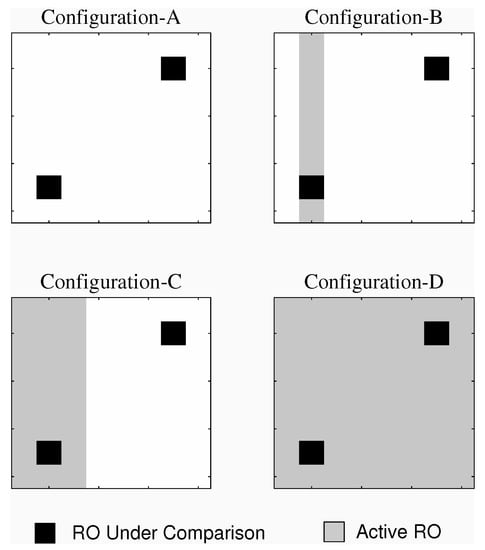
Figure 2.
Different background noise configurations for two RO-PUFs under comparison.
Before explaining how to take advantage of the different background configurations, it is crucial to have an approximation of their impact. To that end, a RO-PUF matrix has been implemented in a Spartan-3E FPGA. The implemented matrix consists of 512 identical ROs (four inverters and a NAND gate) evenly distributed in a grid of 16 × 32. To guarantee an identical lay-out (i.e., the same structure and routing for the ROs), we created a hard macro that constrains each RO to a single slice. We placed the auxiliary components (such as muxes, RO-counters, comparators, etc.) in other FPGA regions. Finally, we instrumented the design with Xilinx Chipscope [16] to read out the RO counters. Chipscope logic was restricted to an FPGA zone where the interference with the RO frequencies is negligible.
Figure 3 displays four histograms of the 512 measured frequencies for the different background configurations. As expected, the switching activity generated by the active ROs causes a frequency decrement. Note that, although the absolute frequency of the RO-PUFs changes, the change in differential value (i.e., the comparison result of the two ROs under comparison) in the case of the same background configurations is negligible, as observed by the state-of-the-art. This can be clearly seen also from the similar standard deviations that the four configurations have. In addition, the figure shows that Configurations B and C also affect, although to a lesser extent, the RO frequency. If such background configurations are used, they will reduce the reliability of CRPs as the frequency difference of two ROs is less. To overcome this limitation, we propose to carry out the frequency acquisition in two separate steps:
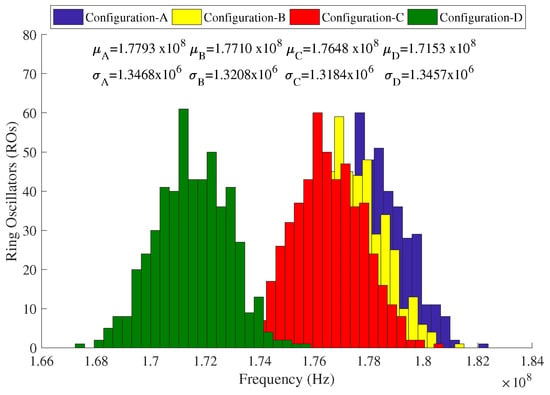
Figure 3.
RO frequency histograms for studied configurations.
- The user introduces a challenge that contains the two ROs under comparison while selecting one of the four background configuration randomly or based on user preference. The frequency of only one of the ROs under comparison is acquired.
- In this step, the the RO frequency of the second RO under comparison is acquired. However, during this step, a different background configuration can be used.
This two-step approach allows the user to select between more background configurations and hence select those responses that enhance the reliability. A detailed description of the expansion and enhancement of CRPs is presented next.
3.2. CRP Expansion
The results depicted in Figure 3 show that the frequencies of Configuration-D have almost no overlap with the other three configurations. As a result, any comparison where Configuration-D is involved with one of the other three background configurations will lead to a somewhat predictable output (i.e., the selected RO with Configuration-D will likely be slower). Hence, this mode is discarded for CRP expansion. A straightforward way of increasing the number of CRPs is using the traditional rank-based method (Equation (1)) together with the proposed two-step frequency acquisition scheme. In this way, an upper bound on the number of possible pairwise comparisons can be expressed by , where the numbers 3 represents the different background configurations, N is the number of ROs and the number 2 denotes that the order between each two RO pairs is not accounted for. It is clear that many of the RO pairs are correlated [12]. For example, the comparison between two ROs using the same background configuration (Configuration-A, -B or -C) will likely lead to the same result. To avoid security issues, a more restricted set of RO pairs has to be considered where the dependencies are not included. One of the popular method is to use a chain strategy [13], where only neighboring ROs are selected for comparison. This results in the following RO-pairs: ; ; and . Note that only one background configuration is used for each RO pair. The chain strategy results in a lower bound of N pairs.
The quantization phase of the traditional rank-based method in Figure 4a only takes into account the sign bit of the comparison, omitting some interesting information as the frequency differences between ROs. Although this loss of information results in more reliable responses, a large penalty is paid in terms of unused bits. To overcome this drawback and expand the number of bits generated by each challenge, we propose to define four contiguous intervals in the frequency range with equal probabilities (i.e., quartiles). As shown in Figure 4b, each comparison generates a 2-bit response thereby doubling the number of bits responses compared to the traditional method. Other divisions can be explored to increase the number of bits per challenge when the penalty in reliability is acceptable. To increase the reliability, we present an CRP reliability enhancement scheme in the next section.
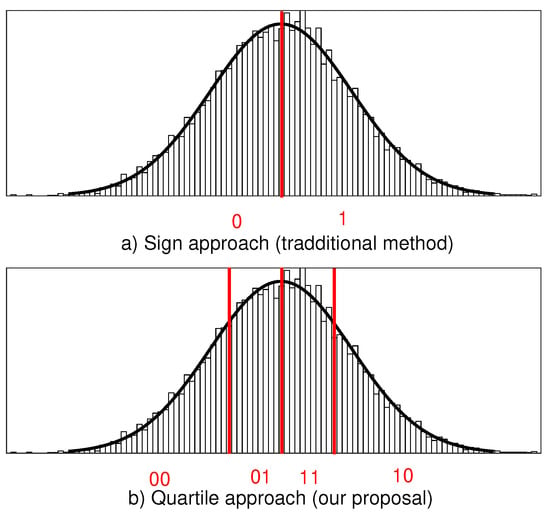
Figure 4.
Frequency difference histograms.
3.3. CRP Reliability Enhancement
To enhance the PUF response, several actions can be carried out.
Firstly, the selection strategy of RO pairs has to be chosen carefully in order to avoid security issues related to the spatial distribution of ROs [14]. The chain strategy where only neighboring ROs are selected for comparison can be adopted, as it reduces the effects of operational conditions such as voltage and temperature.
Second, we propose to compare ROs using all the aforementioned configurations and select the pairs with the most reliable responses during the enrolment process. This is in line with previous selection methods where pairs have been selected with the highest frequency difference [5]. To determine the best configurations, we first randomly select the background configuration (i.e., Configuration-A, -B or -C) of each RO pair of the chain to measure the frequency response of one of the ROs. Subsequently, we measure the frequency response of the other RO using all four different background configurations; note that Configuration-D is only used for enhancement purposes. Therefore, for each of the N RO pairs, we obtain four m-bit results, where m specifies the number of bits taken from the difference between the two RO frequencies under comparison. In this work, we consider only, as shown in Figure 4b.
If the four responses are exactly the same or when three of the four responses are the same and the remaining response is in an adjacent quartile (see also Figure 4b), the output will be labeled as a strong response pair. If three of the four responses have the same value and the remaining is not in an adjacent quartile, the output will be labeled as a weak response pair. Only RO pairs that generate strong and weak responses pairs are allowed in the signature generation process; the remaining combinations are discarded. As an extra enhancement method, we have used an adjacent code to codify the output of quartiles. With this measure, only one bit of two will change in the case of a shift in frequency. Additional enhancement can be achieved by fixing a minimum number of strong bits in the complete PUF response.
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Set-Up
To evaluate the proposed CRP expansion and enhancement schemes, we implemented them on 25 Xilinx Spartan 3E FPGA Starter boards (XC3S500E), where FPGAs came from different manufacturing lots. Some of these 25 FPGAs have been used for teaching purposes, so their electrical characteristics could be biased. In each FPGA, 512 identically laid out ROs were implemented in the middle of the FPGA. As in [17], each RO was confined to a single Configurable Logic Block (CLB) to guarantee local routing among the inverting stages. The rest of the PUF blocks (multiplexer, counters, enable/disable logic, etc.) were implemented in other FPGAs zones to mitigate their impact on an RO’s frequency. The area of the design consisted of 2914 four-input LUTs (31% of total area) and 627 registers (6% of total area). We added an UART interface to communicate with the host computer to control the background configurations and read the frequency responses out. The proposed methodology was validated using the main quality metrics uniformity, bit-aliasing, reliability and uniqueness under typical operating conditions and under different supply voltages. In addition, the min-entropy of the PUF responses was calculated using NIST statistical tests [18].
4.2. Performance Evaluation of the PUF Responses
Figure 5 depicts for each FPGA the average frequencies of the 512 ROs for the different background configurations; each RO was measured 100 times for all background configurations. The figure clearly shows that the frequency trend observed in Figure 3 is applicable in all FPGAs. The average frequencies for the different background configurations ranged from 157.94 MHz (lowest average frequency for Configuration-D) to 199.64 MHz (highest average frequency for Configuration-A). With respect to Configuration-A, the mean shift measured from all FPGAs equaled 620 KHz (0.34%) for Configuration-B, 1.28 MHz (0.71%) for Configuration-C and 6.27 MHz (3.5%) for Configuration-D.
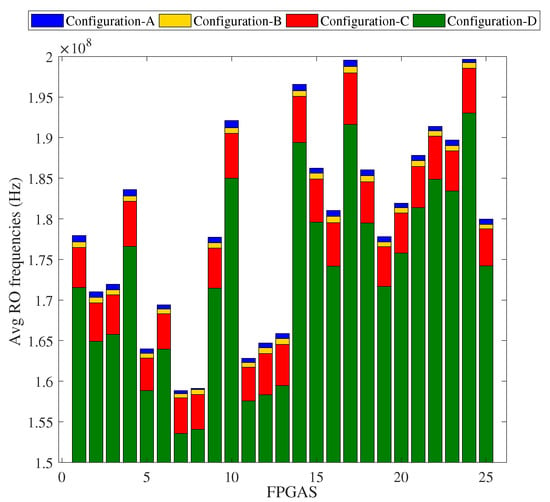
Figure 5.
Average frequencies of 25 FPGAs for the proposed configurations.
From the 512 chained RO pairs, 370 pairs satisfied the strong and weak response pair requirement. For convenience, we randomly selected from the 370 pairs only 100 pairs to analyze and evaluate their quality. As already mentioned, the following metrics were used for this: uniformity, bit-aliasing, reliability and uniqueness. These metrics are widely used by the scientific community and are included in the first proposal of a standard test for the assessment of the quality of PUFs [19].
4.2.1. Uniformity
A binary PUF is uniform when the n bit response contains an equal number of 0 s and 1 s. The uniformity can be calculated as follows [20]:
where represents the lth-bit of an n-bit response of FPGA i. Note that our method has an n that is twice as large as compared to the conventional approach, as we doubled the number of bits taken from each comparison. The results of the uniformity metric for the 25 FPGAs are shown in Figure 6. The obtained results are close to the ideal value, i.e., a uniformity of 50%. In fact, the average value of all the 25 FPGAs is 50.01%.
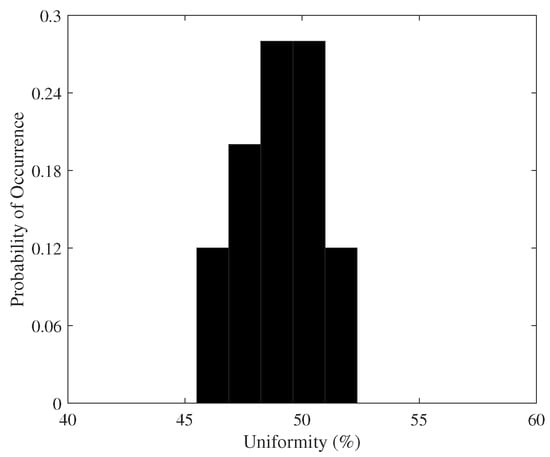
Figure 6.
Uniformity of PUF responses.
4.2.2. Bit-Aliasing
The design and operation conditions can affect the frequency of the RO responses. Consequently, some RO responses might give a fixed value (e.g., “00” or “01”) in all devices. To measure this undesirable behavior, the bit-aliasing metric was used. Mathematically, it is described as follows [20]:
where k is the number of devices and is the lth-bit of an n-bit response of the device i. The ideal bit aliasing value of a response equals 50%; this indicates that there is an equal distribution of “0 s” and “1 s” between the different devices. Figure 7 shows a histogram of the bit-aliasing distribution. Although the response is centered around the ideal value, it can be observed that some bits have a fixed value in all FPGAs (i.e., a 0% or 100% bit-aliasing value). The RO pairs that generate these fixed values in all the FPGAs can be discarded at enrolment phase.
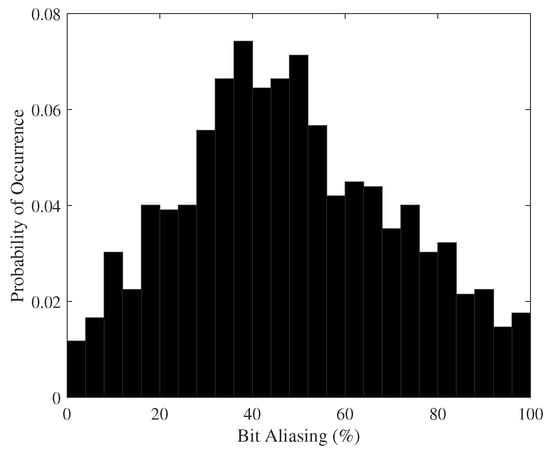
Figure 7.
Bit-aliasing histogram of PUF responses.
4.2.3. Reliability
The stability and reliability of the response over time is a crucial aspect of a PUF. Generating the same response under different operational and environmental conditions and after a long deployment time in the field (aging) is essential for a PUF. The reliability is typically quantified as described below [20]:
where x is the number of samples of a n-bit response and is the Hamming distance between the yth sample and the reference response. In our experiment, we took x = 300 samples for each RO response over a period of three weeks in normal conditions (i.e., core voltage of 1.2 V and room temperature of C). Therefore, we collected a total amount of 300 (samples) × 25 (FPGAs) × 100 (ROs) × 2 (number of used bits per comparsion) = 1.5 million bits. Figure 8 shows the histogram of these bits, i.e., the results of the reliability. The reliability of the responses is generally high with a mean value of 98.95%. It is noteworthy that only one FPGA of the set has slightly worse results. This may be due to noise (such as the noise generated by power supply problems), making the responses unstable for this particular FPGA (D427923).
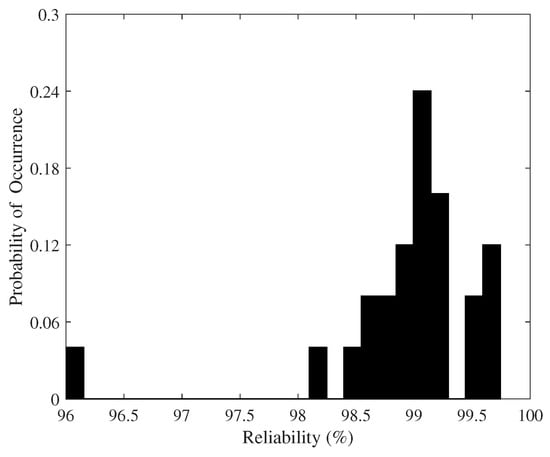
Figure 8.
Probability of the occurrence of reliability.
4.2.4. Uniqueness
Uniqueness is a metric that represents the ability of a PUF to discriminate between two devices. Basically, it measures how different the responses of the devices are when the same challenge is applied. The uniqueness can be mathematically described as below [20]:
where k is the number of devices and is the Hamming distance between the n-bits responses of chip i and j. The ideal value of uniqueness is 50%. The distribution of the uniqueness metric for the 25 FPGAs is shown in Figure 9. On average, the uniqueness obtained for the enhanced proposal is 48.86% with a standard deviation of 3.43. The minimum and maximum values of the uniqueness are 43.76% and 53.96%, respectively.
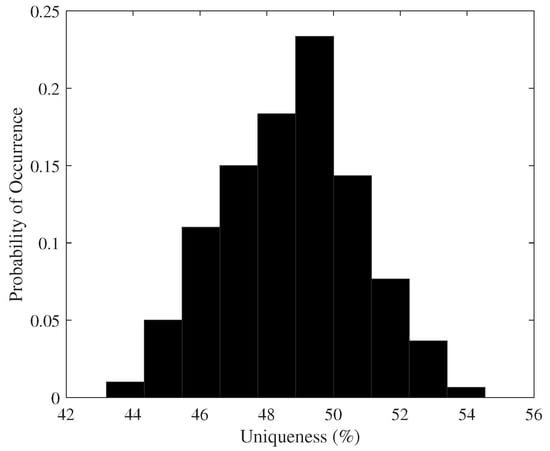
Figure 9.
Probability of the occurrence of uniqueness.
4.2.5. Entropy
Entropy estimation is important when PUF responses are used for key generation. Among the different estimation proposals, the NIST recommendations stand out, including several statistical tests aimed at estimating the min-entropy of a random number generator [18]. This suite includes 10 different tests that have been particularly designed to avoid overestimation entropy in non-independent and identically distributed sources (non-IID).
The ideal value of min-entropy in perfectly independent and identically distributed entropy sources is 1. The estimated min-entropy for the PUF responses dataset is 0.794207—this corresponds to the minimum value obtained for the 10 tests, as shown in Table 1. This value has been obtained for the collision test. This test [21] gives a measure of the mean number of samples to the first collision in a dataset, where a collision is any repeated value. For our particular dataset, the bit-aliasing has a negative contribution to the entropy estimation. As mentioned above, the fixed values in all the FPGAs can be discarded at the enrolment phase to improve the min-entropy for this specific test.

Table 1.
NIST min-entropy results.
4.3. Impact of Environmental Variations
As aforementioned, the stability of the PUF response under different operations conditions is of paramount importance. The reliability of the responses was analyzed using 5 of the 25 boards. To model the impact of environment, we considered variations in the supply core voltage ranging from 1.0 V to 1.6 V in steps of 0.1 V. The reference response was obtained at the nominal FPGA supply voltage provided by the manufacturer (i.e., 1.2 V). Figure 10 shows the impact of voltage variation on the reliability. The voltage variations cause a lower reliability with a minimal value of 93.3% (1.1 V). Note however that these results are in general still good. The worst results were obtained for FPGA D427923, which was purposefully selected as it had the lowest reliability and therefore would give a lower bound on this metric. As expected, the reliability is high near the nominal core voltage (1.2 V) and gets worse as soon as the supply voltage deviates from this point.
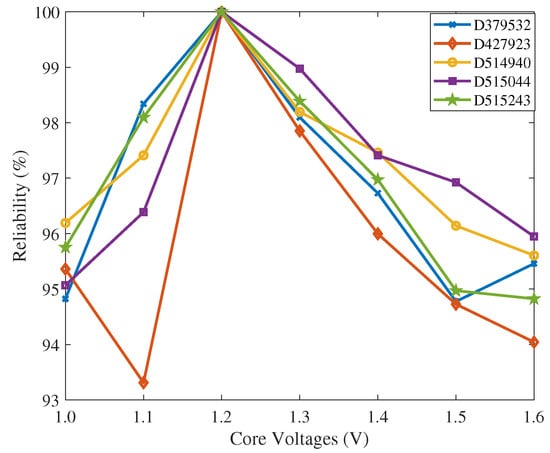
Figure 10.
Probability of the occurrence of reliability vs. core voltages.
The quality metrics presented above are in line with the results presented in other enhanced RO-PUFs works [5,9]. Therefore, our methodology is able to double the number of CRPs with a negligible area overhead compared to the traditional RO-PUFs.
5. Discussion
In this section, we discuss the main advantages and disadvantages of our proposal in comparison with the state-of-the-art solutions.
The traditional RO-PUFs [12] are only used in CRPs using Configuration-A. Our approach improves this by selecting different background configurations.
In contrast to the state-of-the-art solutions [5,8], our proposal keeps the original RO implementation intact while it modifies slightly the RO enable/disable control circuit to enable different backgrounds configurations. As a result, it has a minor impact on the area. In addition, our methodology can be easily integrated with different types of post-processing techniques ([5,22,23]), since the original RO-PUF structure is maintained. These post-processing blocks are necessary to avoid well-known attacks such as the modeling attack presented in [24]. Another advantage of our proposal is the flexibility it offers. Users can select between: (1) an implementation that extends (i.e., doubles) the number of CRPs with a slight increase in area cost; and (2) an implementation that saves hardware resources by implementing fewer ROs while maintaining the same set of CRPs. This flexibility can be useful when selecting a fuzzy extractor as post-processing block. For example, given the entropy results and reliability obtained, we could use a fuzzy extractor that focuses on the sketch phase rather than the privacy amplification phase. Another possibility is the usage of a powerful fuzzy extractor [22] along with our methodology using more divisions to quantize the different RO frequency differences.
Besides the above advantages, the increasing switching activity introduced by the different background configurations causes a higher noise level, which in turn leads to more randomness in the response with respect to the traditional RO-PUF. This is confirmed by the results of the uniqueness, bit-aliasing, uniformity and entropy metrics.
Finally, it is worth noting that our proposed scheme can be efficiently used in authentication protocols. The inclusion of the different configurations leads to a more robust authentication protocol when the ROS are controlled by a system of synchronized PRNGs [25]. The user selects the ROs under comparison while the PRNG determines the configurations. The users know the PRNG states in advance if they are trusted. Therefore, when the PRNG is desynchronized, the user can identify that an untrusted user (attacker) is trying to gain access to the device. There are several limitations of our approached that need to be addressed. First, the power consumption will be higher than traditional RO-PUFs due to the higher switching activity. In addition, the power consumption may reveal the used background configurations. To overcome this drawback, we propose shuffling the order of ROs under comparison to obfuscate which ROs are measured each time. Moreover, the higher switching activity might also be negatively impacted by intra-die variations, which in turn affect the reliability of the response. However, based on the results presented in the previous section, this effect is negligible. Second, the acquisition of the RO frequencies in two different steps might introduce measurement errors as clock variations impact the measured frequencies. Nevertheless, the quantization method adopted by our proposal together with the enhancement method have proven to be an effective countermeasure against these phenomena. Finally, our methodology takes four times longer to enrol the ROs than the traditional RO-PUFs.
6. Conclusions
One of the main restrictions of PUF functions is the limited number of CRPs that can be generated. This is a key-point problem as they are used to distinguish/identify several chips and generate a strong cryptographic key. In this article, we improve the number of CRPs by considering different background configurations for one of the ROs under comparison. Our proposal was tested with an FPGA design. Our results show that we are able to expand the CPRs, while preserving the desired performance metrics (uniformity, bit-aliasing, reliability and uniqueness), which are required for a good PUF. In particular, the proposed method takes advantage of the background activity generated by the ROs already on-board of the original RO-PUF design. The overhead in terms of area is negligible, while a penalty is paid in terms of power consumption. Our scheme can be used to advance any application that depends on CRPs, such as IC identification or IP protection.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed equally to the work presented in this paper.
Funding
This work was partially supported by Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovacion y Universidades under a Jose Castillejo grant(2018); the MINECO grants ESP-2015-68245-C4-1-P and TIN2016-79095-C2-2-R; and the CAM grant S2013/ICE-3095.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Gassend, B.; Clarke, D.; van Dijk, M.; Devadas, S. Silicon Physical Random Functions. In Proceedings of the 9th ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security (CCS’02), Washington, DC, USA, 18–22 November 2002; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampon, J.; Perillat, R.; Torres, L.; Benoit, P.; Natale, G.D.; Barbareschi, M. Digital Right Management for IP Protection. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium on VLSI, Montpellier, France, 8–10 July 2015; pp. 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qu, G. A survey on security and trust of FPGA-based systems. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Field-Programmable Technology (FPT), Shanghai, China, 10–12 December 2014; pp. 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karri, R.; Sinanoglu, O.; Rajendran, J. Physical Unclonable Functions and Intellectual Property Protection Techniques. In Fundamentals of IP and SoC Security: Design, Verification, and Debug; Bhunia, S., Ray, S., Sur-Kolay, S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Swtzerland, 2017; pp. 199–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, A.; Schaumont, P. Improved Ring Oscillator PUF: An FPGA-friendly Secure Primitive. J. Cryptol. 2011, 24, 375–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, A.; Kim, I.; Schaumont, P. A Robust Physical Unclonable Function With Enhanced Challenge-Response Set. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2012, 7, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kömürcü, G.; Pusane, A.E.; Dündar, G. Enhanced challenge-response set and secure usage scenarios for ordering-based ring oscillator-physical unclonable functions. IET Circuits Devices Syst. 2015, 9, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossuet, L.; Ngo, X.T.; Cherif, Z.; Fischer, V. A PUF Based on a Transient Effect Ring Oscillator and Insensitive to Locking Phenomenon. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. 2014, 2, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wang, X.; Rahman, F.; Tehranipoor, M. iPUF: Interconnect PUF with Self-Masking Circuit for Performance Enhancement. In Proceedings of the 2017 18th International Workshop on Microprocessor and SOC Test and Verification (MTV), Austin, TX, USA, 11–12 December 2017; pp. 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Lai, K.; Qu, G. A highly flexible ring oscillator PUF. In Proceedings of the 2014 51st ACM/EDAC/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 1–5 June 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delavar, M.; Mirzakuchaki, S.; Mohajeri, J. A Ring Oscillator-Based PUF With Enhanced Challenge-Response Pairs. Can. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2016, 39, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, G.E.; Devadas, S. Physical Unclonable Functions for Device Authentication and Secret Key Generation. In Proceedings of the 2007 44th ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 4–8 June 2007; pp. 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Merli, D.; Stumpf, F.; Eckert, C. Improving the Quality of Ring Oscillator PUFs on FPGAs. In Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Embedded Systems Security (WESS’10), Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 24 October 2010; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 9:1–9:9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yu, Y.; Wang, C.; Cui, Y.; O’Neill, M. RO PUF design in FPGAs with new comparison strategies. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Lisbon, Portugal, 24–27 May 2015; pp. 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbareschi, M.; Natale, G.D.; Bruguier, F.; Benoit, P.; Torres, L. Ring oscillators analysis for security purposes in Spartan-6 FPGAs. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2016, 47, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xilinx. ChipScope Pro Software and Cores, User Guide; Xilinx Inc.: San Jose, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Maiti, A.; Casarona, J.; McHale, L.; Schaumont, P. A large scale characterization of RO-PUF. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Hardware-Oriented Security and Trust (HOST), Anaheim, CA, USA, 13–14 June 2010; pp. 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, M.S.; Barker, E.; Kelsey, J.; McKay, K.A.; Baish, M.L.; Boyle, M. NIST Special Publication 800-90B: Recommendation for the Entropy Sources Used for Random Bit Generation; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2018.
- Wilde, F.; Gammel, B.M.; Pehl, M. Spatial Correlation Analysis on Physical Unclonable Functions. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2018, 13, 1468–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, A.; Gunreddy, V.; Schaumont, P. A Systematic Method to Evaluate and Compare the Performance of Physical Unclonable Functions. Available online: https://eprint.iacr.org/2011/657 (accessed on 29 January 2019).
- Hagerty, P.; Draper, T.H.J. Entropy Bounds and Statistical Tests. In Proceedings of the NIST Random Bit Generation Workshop, Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 5–6 December 2012; pp. 1319–1327. [Google Scholar]
- Herder, C.; Ren, L.; van Dijk, M.; Yu, M.; Devadas, S. Trapdoor computational fuzzy extractors and stateless cryptographically-secure physical unclonable functions. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2017, 14, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Herder, C.; Ren, L.; Nguyen, P.H.; Fuller, B.; Devadas, S.; van Dijk, M. FPGA Implementation of a Cryptographically-Secure PUF Based on Learning Parity with Noise. Cryptography 2017, 1, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, R.; Frank, S.; Jan, S.; Gideon, D.; Srinivas, D.; Jürgen, S. Modeling Attacks on Physical Unclonable Functions. In Proceedings of the 17th ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security (CCS’10), Chicago, IL, USA, 4–8 October 2010; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burmester, M.; Munilla, J. Lightweight RFID Authentication with Forward and Backward Security. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. Secur. 2011, 14, 11:1–11:26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).