Automated Low-Cost Photogrammetric Acquisition of 3D Models from Small Form-Factor Artefacts
Abstract
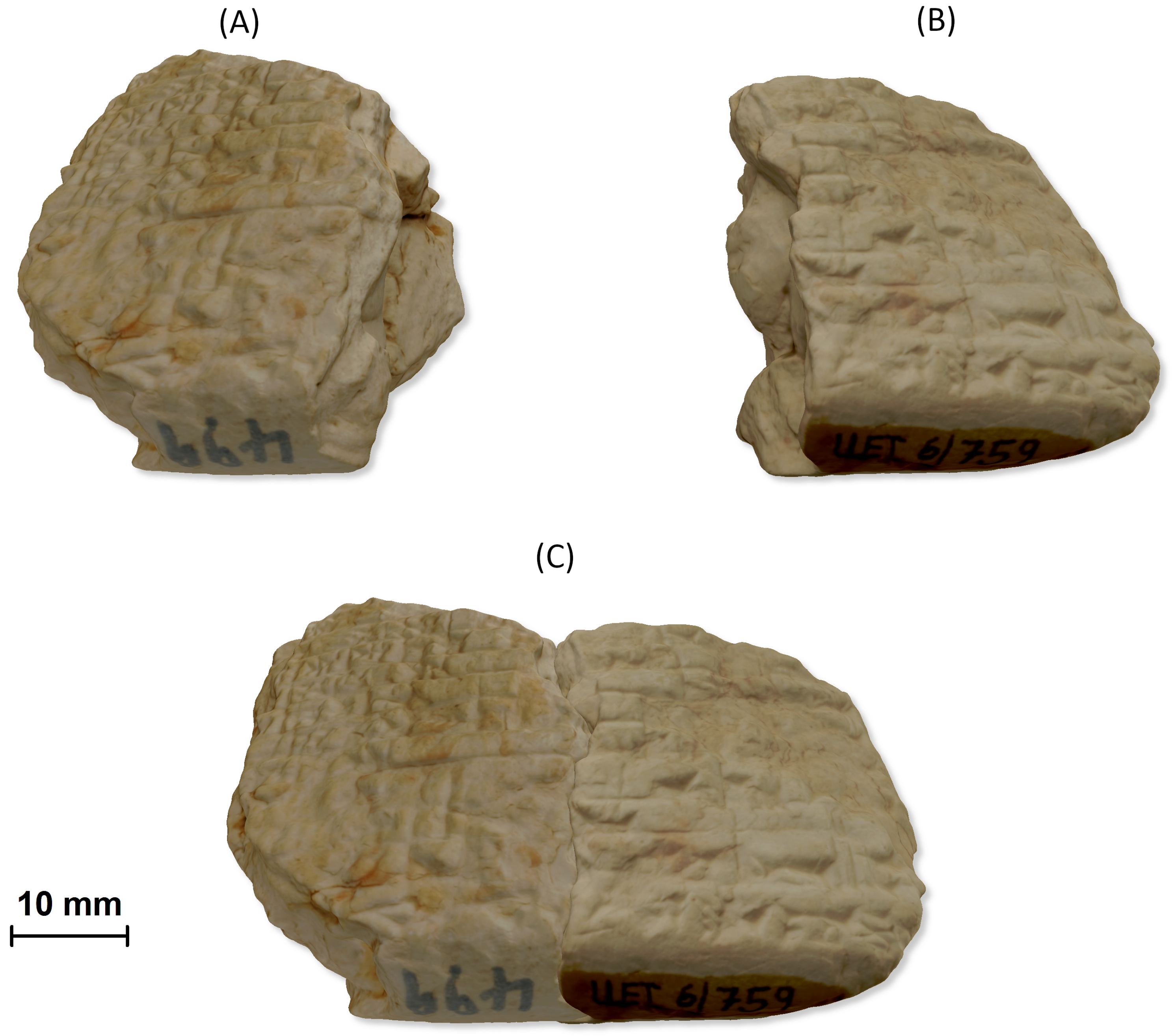
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
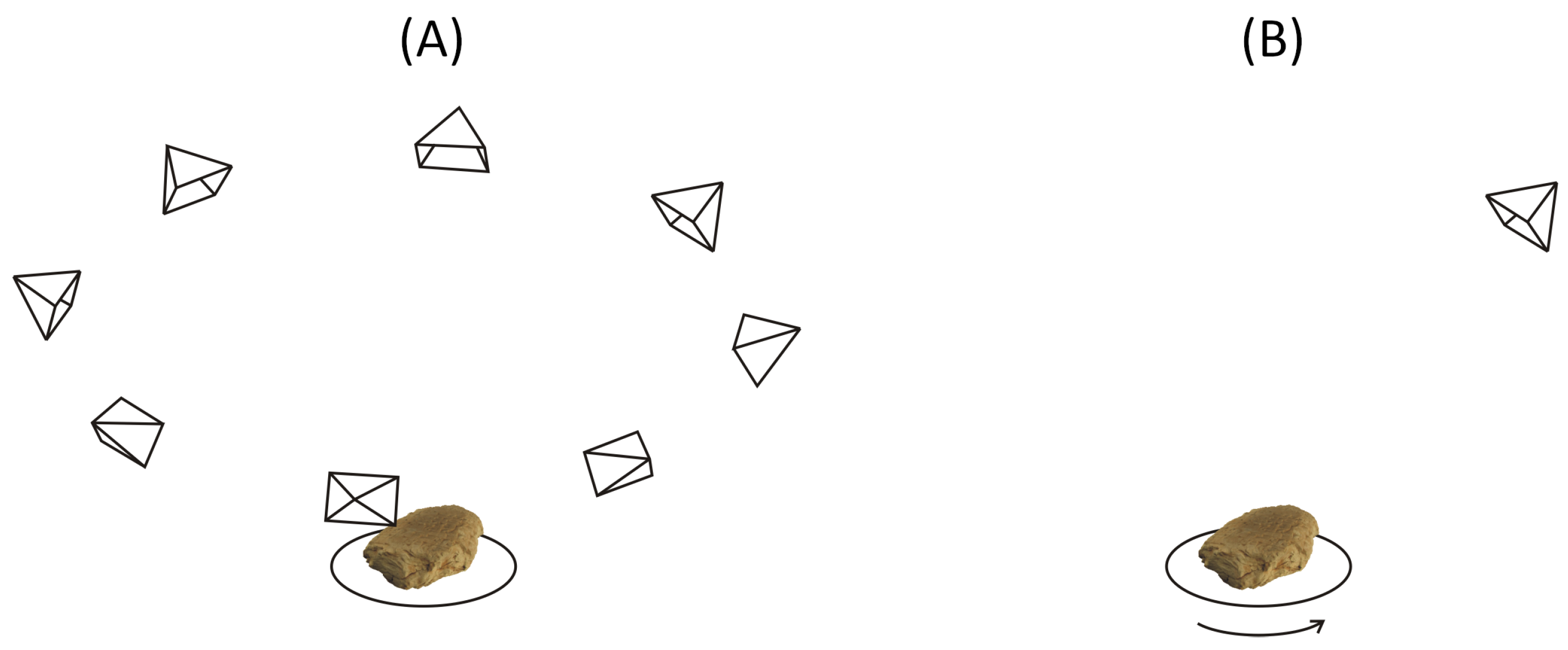
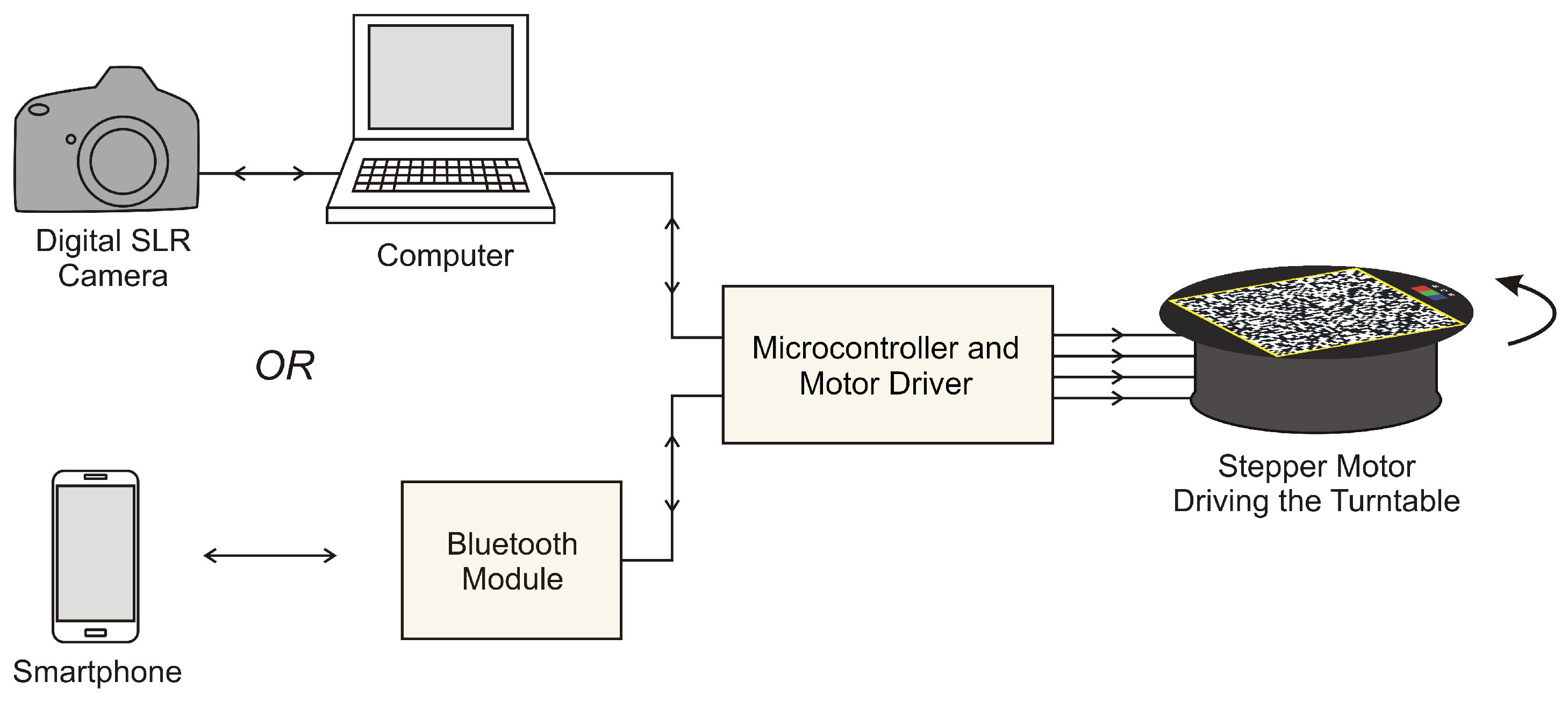
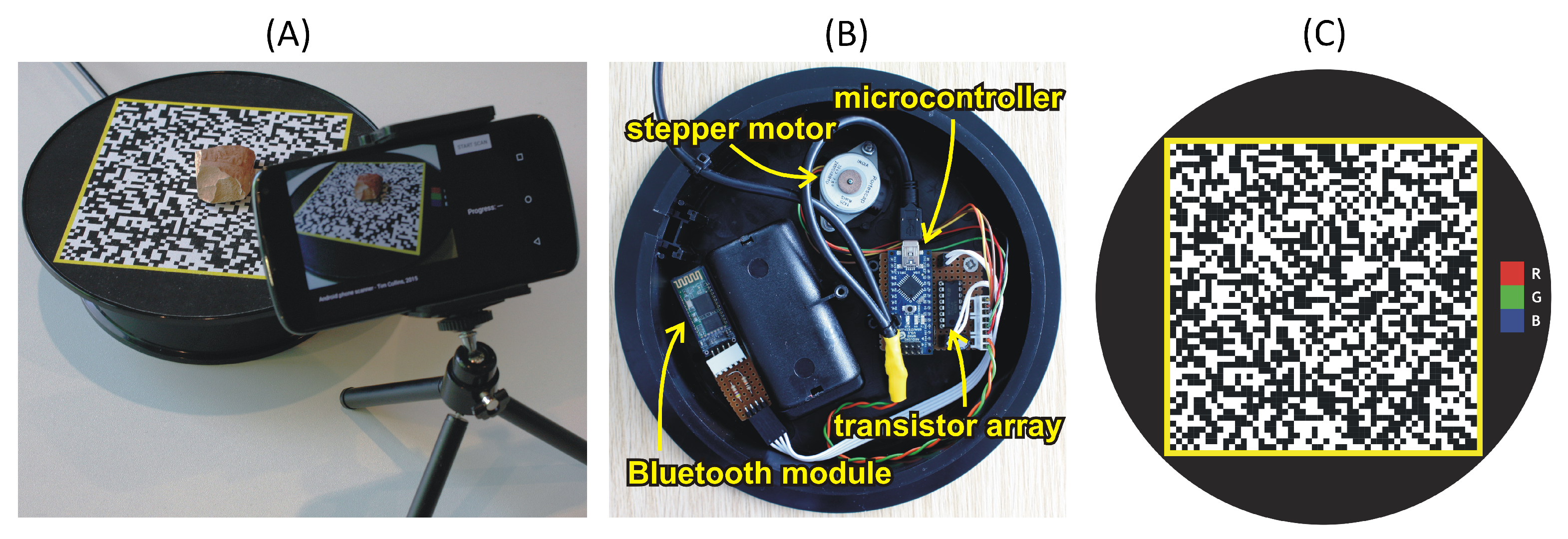
2.1. Rotary Acquisition System
2.2. Acquisition Software
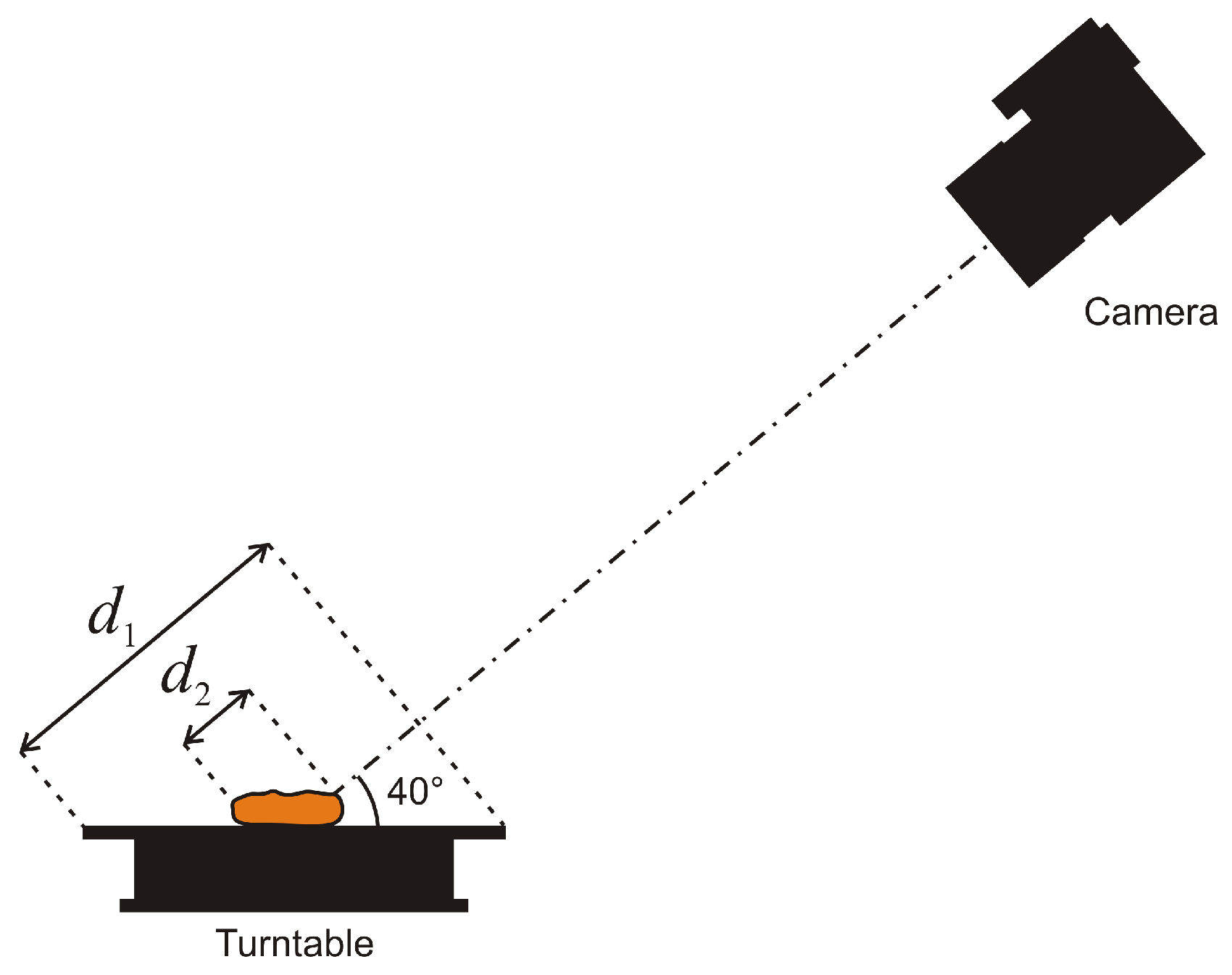
2.3. Photography
2.3.1. Depth-of-Field
2.3.2. Lighting
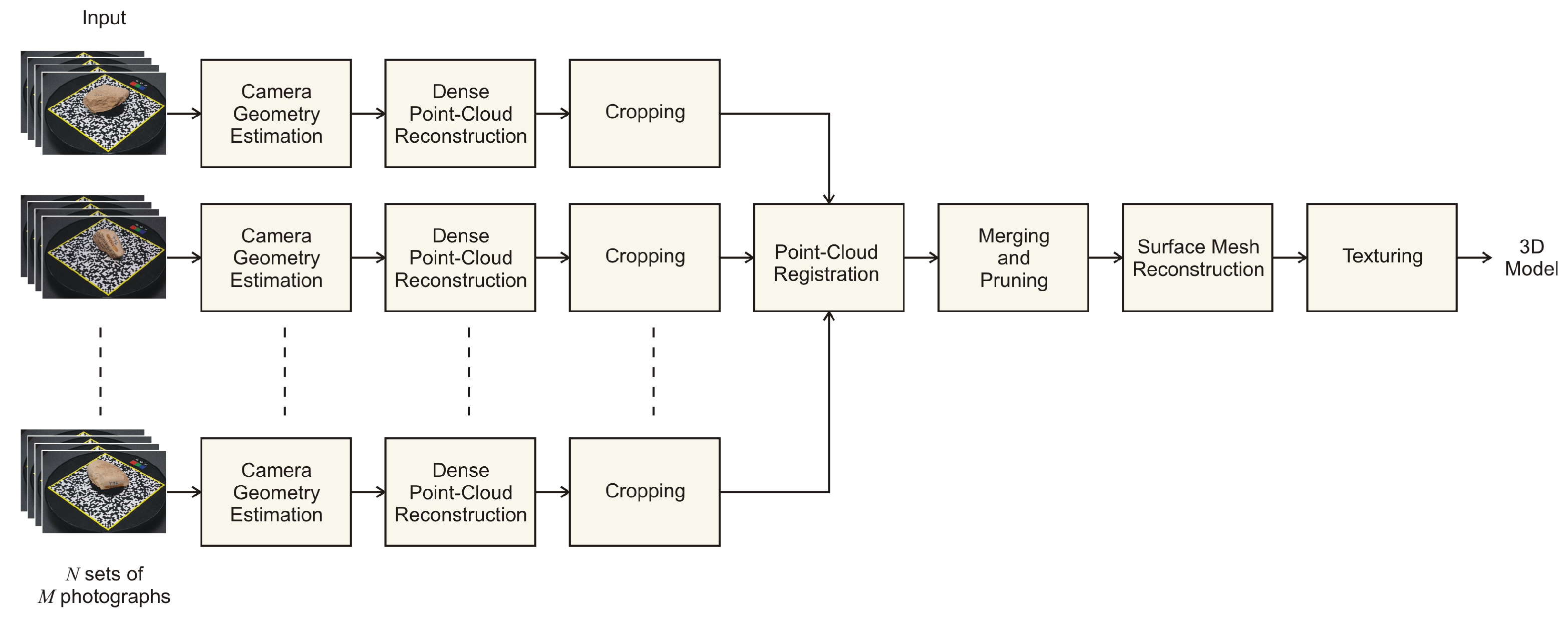
2.4. Image Processing
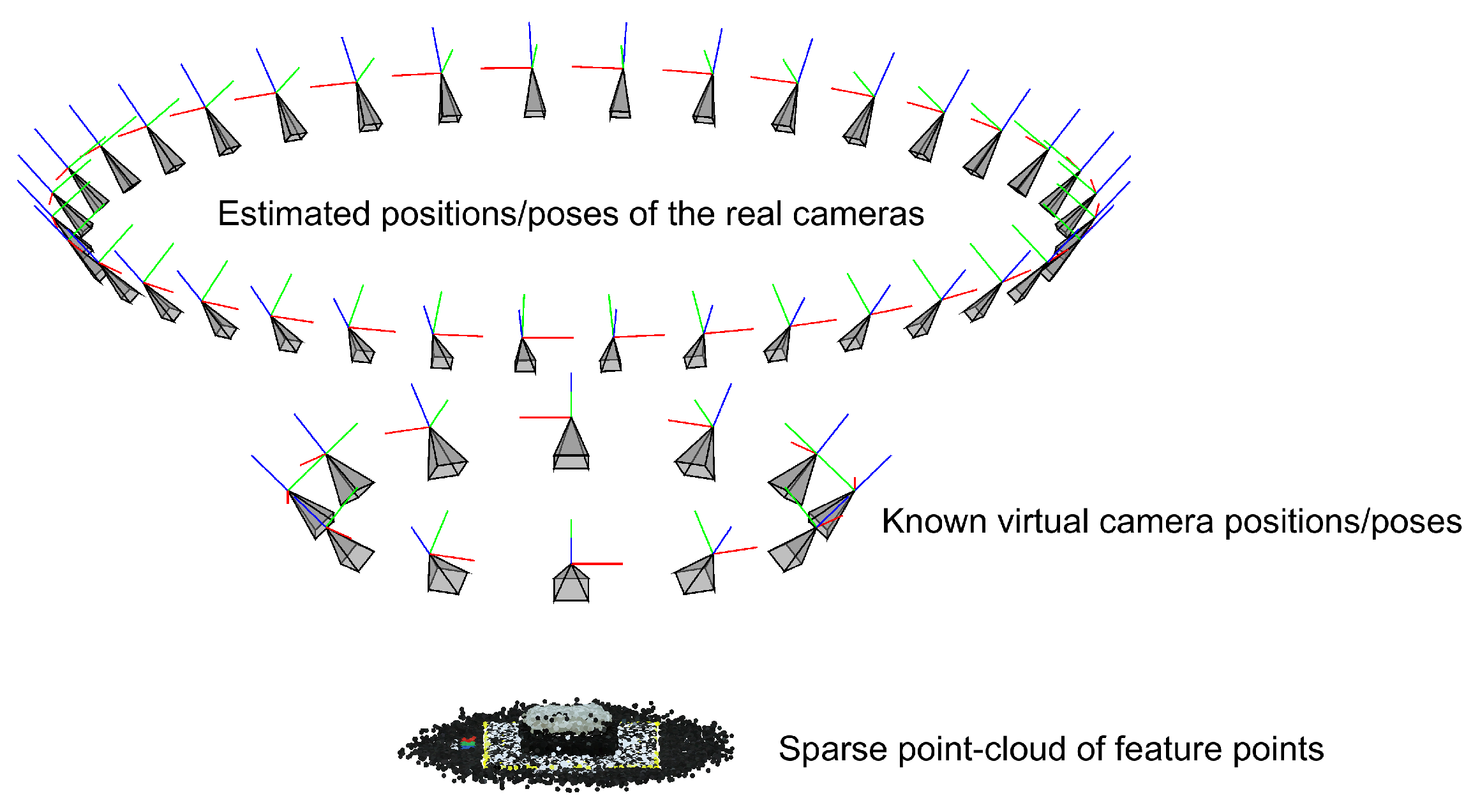
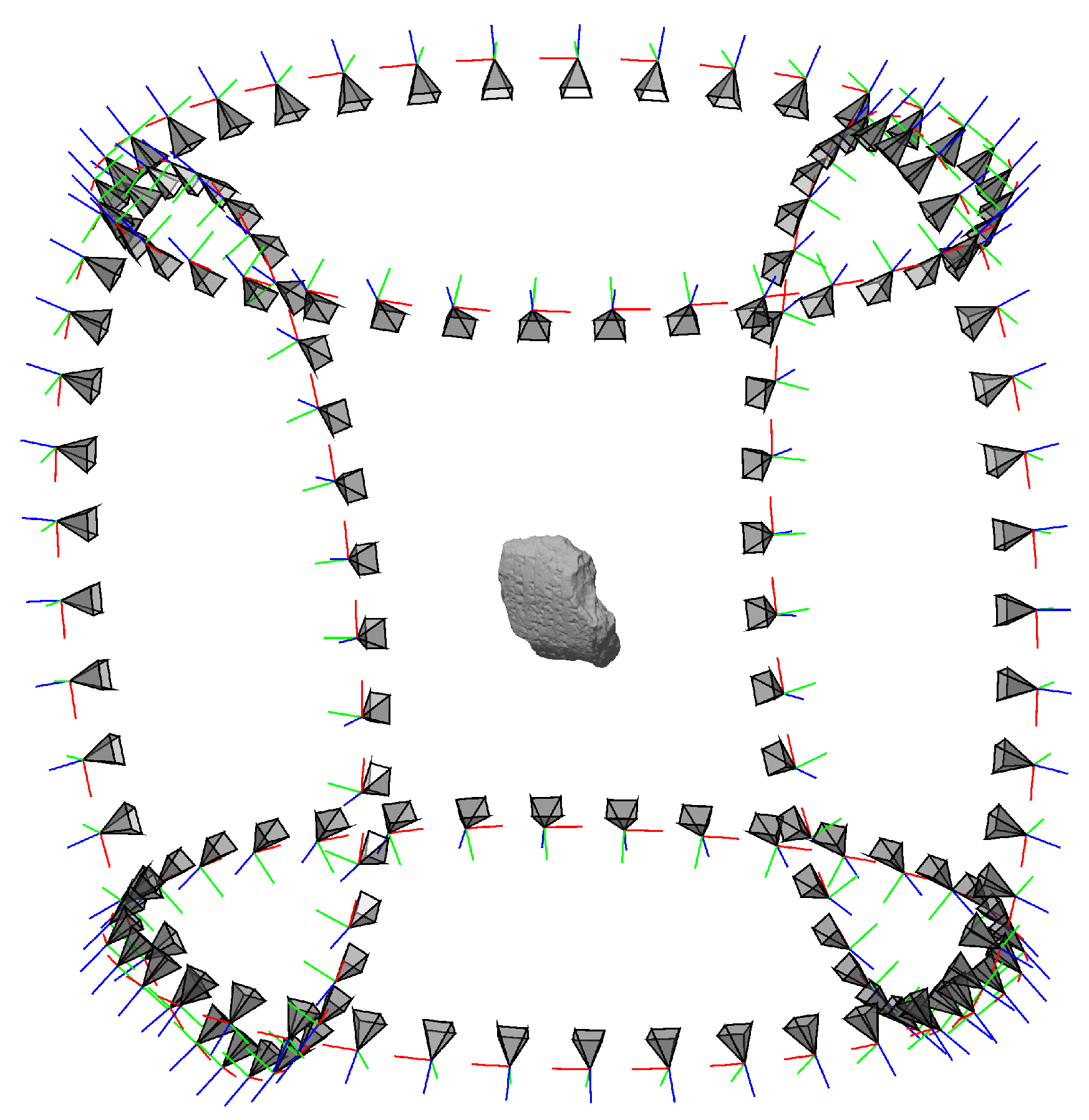
2.4.1. Camera Properties and Geometry Estimation
2.4.2. Dense Point-Cloud Reconstruction
2.4.3. Cropping
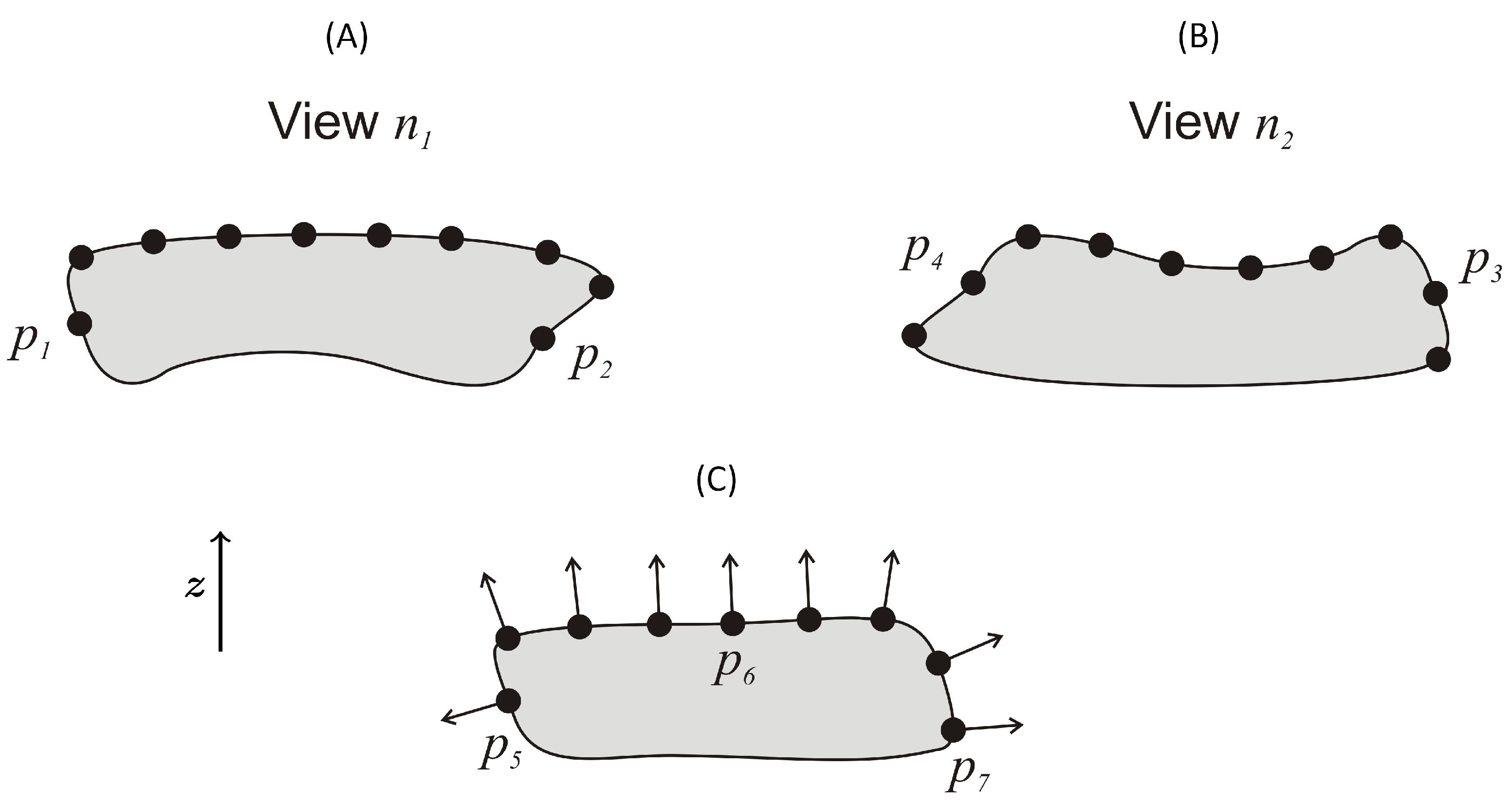
2.4.4. Point-Cloud Registration
- Automatic coarse alignment of point-clouds using the Super 4PCS algorithm [37],
- Fine alignment using a Weighted Iterative Closest Point (W-ICP) algorithm.
2.4.5. Meshing
2.4.6. Texturing
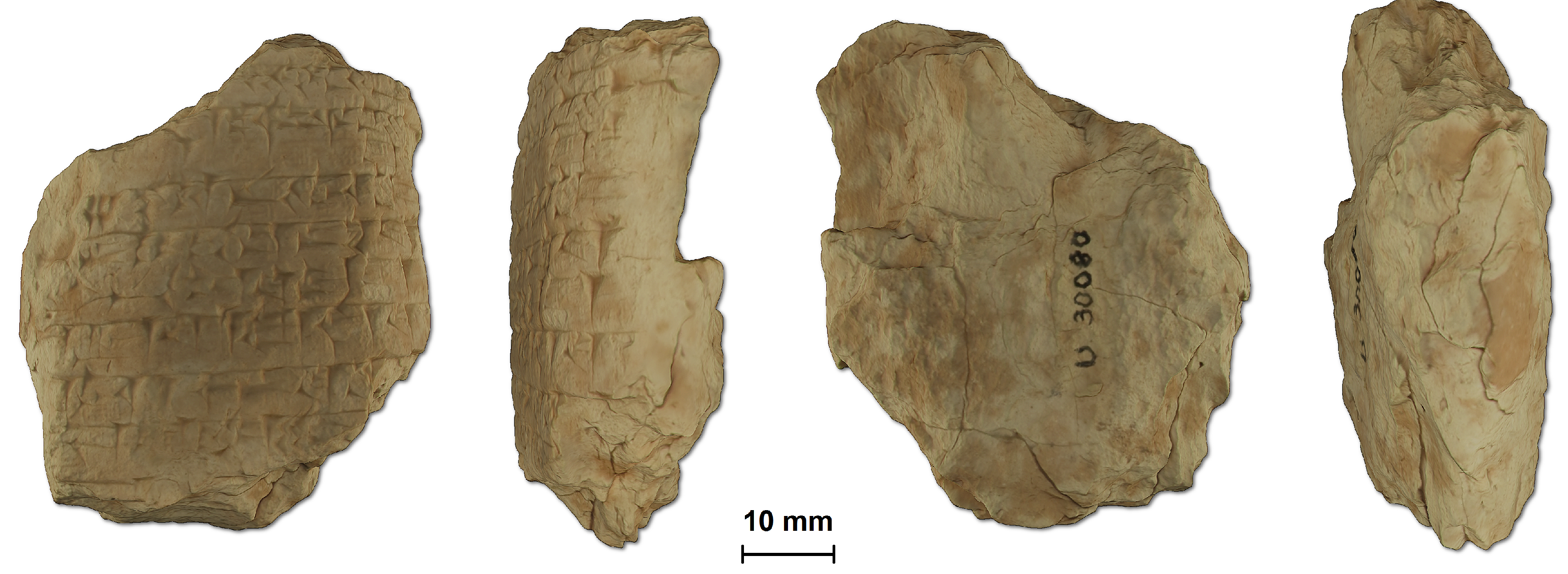
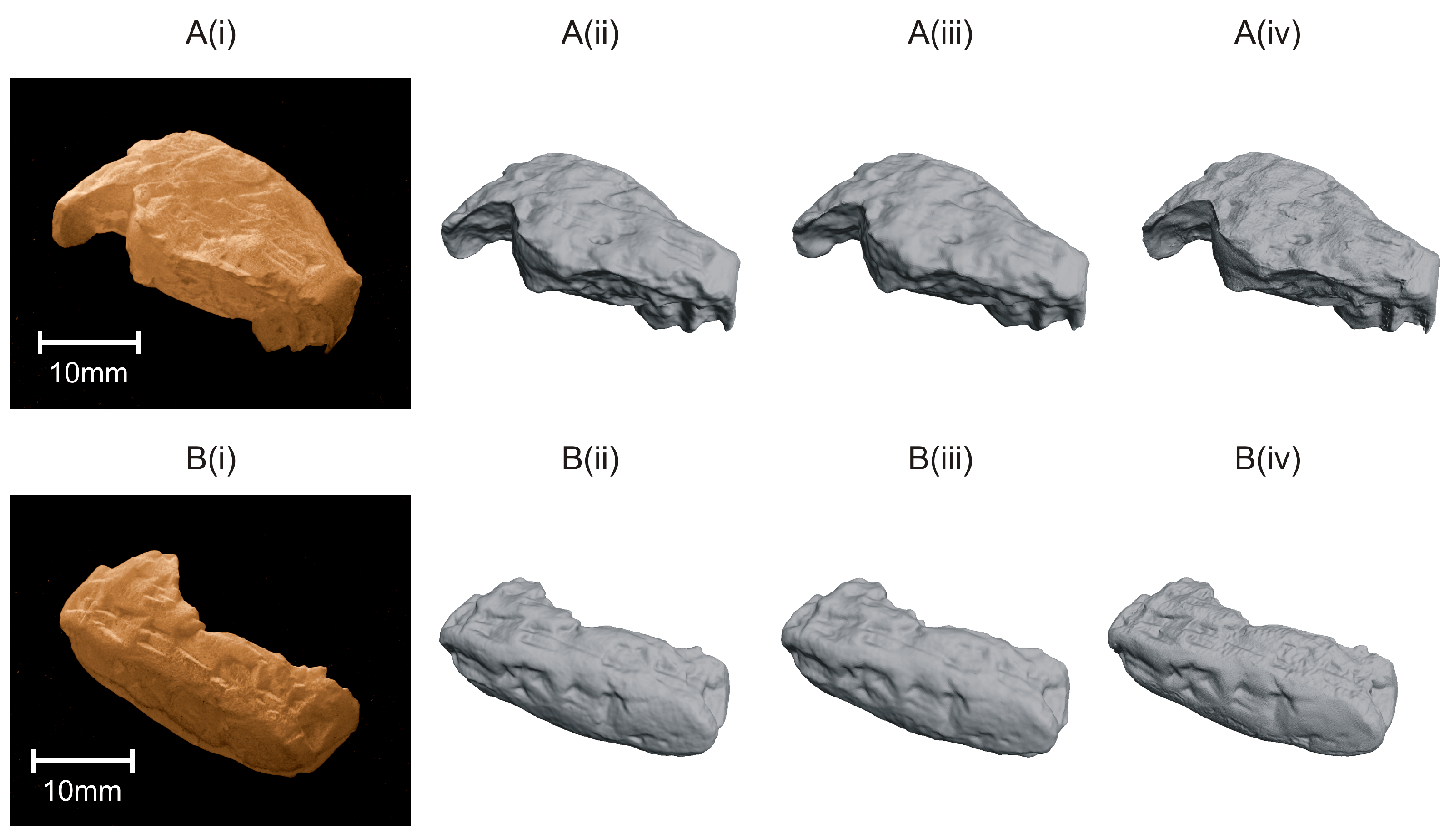
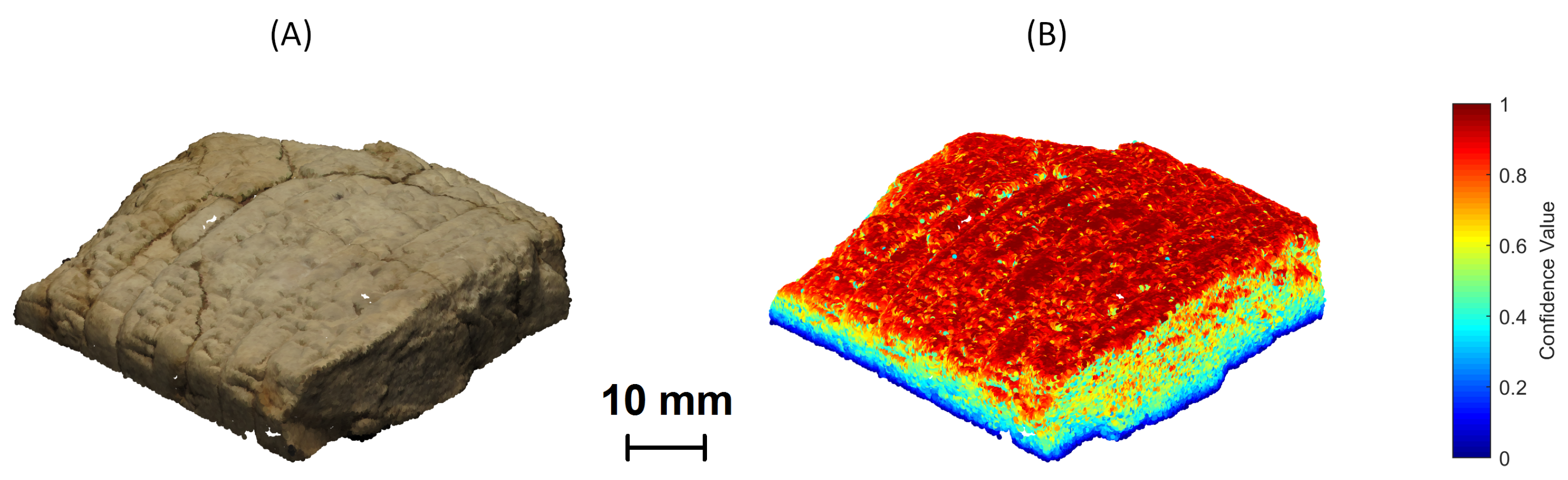
3. Performance Evaluation
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations. General Assembly Resolution 69/281: Saving the Cultural Heritage of Iraq. 2015. Available online: http://www.un.org/en/ga/69/resolutions.shtml (accessed on 26 November 2019).
- Vincent, M.L.; Gutierrez, M.F.; Coughenour, C.; Manuel, V.; Bendicho, L.M.; Remondino, F.; Fritsch, D. Crowd-Sourcing the 3D Digital Reconstructions of Lost Cultural Heritage. In Proceedings of the 2015 Digital Heritage, Granada, Spain, 28 September–2 October 2015; Volume 1, pp. 171–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IDA. The Million Image Database Project, The Institute for Digital Archaeology. 2015. Available online: http://digitalarchaeology.org.uk/projects/ (accessed on 26 November 2019).
- VCTR. Virtual Cuneiform Tablet Reconstruction Project. 2016. Available online: http://virtualcuneiform.org/ (accessed on 26 November 2019).
- Gehlken, E.; Collins, T.; Woolley, S.I.; Hanes, L.; Lewis, A.; Hernandez-Munoz, L.; Ch’ng, E. From Uruk to Ur: Automated Matching of Virtual Tablet Fragments. In Proceedings of the 62nd Rencontre Assyriologique Internationale, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 11–15 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ch’ng, E.; Woolley, S.I.; Gehlken, E.; Lewis, A.; Hernandez-Munoz, L.; Collins, T. The Development of a Collaborative Virtual Environment for 3D Reconstruction of Cuneiform Tablets. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Virtual Systems & Multimedia (VSMM), Hong Kong, China, 9–12 December 2014; pp. 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ch’ng, E.; Lewis, A.; Gehlken, R.E.; Woolley, S.I. A Theoretical Framework for Stigmergetic Reconstruction of Ancient Text. In Visual Heritage in the Digital Age; Springer-Verlag: London, UK, 2013; pp. 43–65. [Google Scholar]
- CDLI. Cuneiform Digital Library Initiative. 2019. Available online: http://cdli.ucla.edu/ (accessed on 26 November 2019).
- Lewis, A.; Ch’ng, E. A Photogrammetric Analysis of Cuneiform Tablets for the Purpose of Digital Reconstruction. Int. J. Herit. Digit. Era 2012, 1, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Woolley, S.I.; Flowers, N.J.; Arvanitis, T.N.; Livingstone, A.; Davis, T.R.; Ellison, J. 3D Capture, Representation and Manipulation of Cuneiform Tablets. In Proceedings SPIE (Three Dimensional Image Capture and Applications IV); SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2001; Volume 4298, pp. 103–110. Available online: https://www.spiedigitallibrary.org/conference-proceedings-of-SPIE/4298 (accessed on 26 November 2019).
- Collins, T.; Woolley, S.I.; Lewis, A.; Hernandez-Munoz, L.; Ch’ng, E.; Gehlken, E. Computer-Assisted Reconstruction of Virtual Fragmented Cuneiform Tablets. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Virtual Systems & Multimedia (VSMM), Hong Kong, China, 9–12 December 2014; pp. 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, A.R.; Cooper, D.B. Computational Reconstruction of Ancient Artifacts. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2008, 25, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pevar, A.; Verswyvel, L.; Stam Georgoulis, N.C.; Proesmans, M.; Van Gool, L. Real-Time Photometric Stereo. In Proceedings of the 55th Photogrammetric Week, Stuttgart, Germany, 7–11 September 2015; pp. 185–206. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/34653128.pdf (accessed on 26 November 2019).
- MacDonald, L.; Toschi, I.; Nocerino, E.; Hess, M.; Remondino, F.; Robson, S. Accuracy of 3D Reconstruction in an Illumination Dome. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2016, 41, 69–76. Available online: https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/id/eprint/1503889/1/isprs-archives-XLI-B5-69-2016.pdf (accessed on 26 November 2019). [CrossRef]
- Boehler, W.; Marbs, A. 3D Scanning and Photogrammetry for Heritage Recording: A Comparison. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Geoinformatics, Gävle, Sweden, 7–9 June 2004; pp. 291–298. Available online: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.452.3508&rep=rep1&type=pdf (accessed on 26 November 2019).
- Ahmadabadian, A.H.; Robson, S.; Boehm, J.; Shortis, M.; Wenzel, K.; Fritsch, D. A Comparison of Dense Matching Algorithms for Scaled Surface Reconstruction Using Stereo Camera Rigs. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 78, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolae, C.; Nocerino, E.; Menna, F.; Remondino, F. Photogrammetry Applied to Problematic Artefacts. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2014, 40, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remondino, F.; Pizzo, S.D.; Kersten, T.P.; Troisi, S. Low-Cost and Open-Source Solutions for Automated Image Orientation—A Critical Overview. In Progress in Cultural Heritage Preservation, EuroMed 2012; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 7616, pp. 40–54. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-642-34234-9_5 (accessed on 26 November 2019).
- Bourke, P. Automated 3D Model Reconstruction From Photographs. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Virtual Systems & Multimedia (VSMM), Hong Kong, China, 9–12 December 2014; pp. 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besl, P.J.; McKay, N.D. A Method for Registration of 3D Shapes. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1992, 14, 239–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lempitsky, V.; Ivanov, D. Seamless Mosaicing of Image-Based Texture Maps. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 17–22 June 2007; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabove, P.; Grasso, N.; Piras, M. Smartphone-Based Photogrammetry for the 3D Modeling of a Geomorphological Structure. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, A.; Lemaire, E. A Smartphone Photogrammetry Method for Digitizing Prosthetic Socket Interiors. Prosthetics Orthot. Int. 2017, 41, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arduino. Arduino Nano. 2015. Available online: https://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/arduinoBoardNano (accessed on 26 November 2019).
- Texas Instruments. ULN200x, ULQ200x High-Voltage, High-Current Darlington Transistor Arrays. 1976. Available online: http://www.ti.com/lit/ds/symlink/uln2003a.pdf (accessed on 26 November 2019).
- Porter, S.T.; Roussel, M.; Soressi, M. A Simple Photogrammetry Rig for the Reliable Creation of 3D Artifact Models in the Field. Adv. Archaeol. Pract. 2016, 4, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canon. Canon Digital Camera Software Developers’ Kit. 2014. Available online: https://developercommunity.usa.canon.com/canon (accessed on 26 November 2019).
- Google Inc. Android Studio IDE. 2014. Available online: https://developer.android.com/sdk (accessed on 26 November 2019).
- Kraus, K. Photogrammetry: Geometry From Images and Laser Scans; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- James, M.R.; Robson, S. Straightforward Reconstruction of 3D Surfaces and Topography With a Camera: Accuracy and Geoscience Application. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.G. Object Recognition From Local Scale-Invariant Features. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Kerkyra, Greece, 20–27 September 1999; Volume 2, pp. 1150–1157. [Google Scholar]
- Triggs, B.; McLauchlan, P.F.; Hartley, R.I.; Fitzgibbon, A.W. Bundle Adjustment: A Modern Synthesis. In Vision Algorithms: Theory and Practice; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 298–372. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Agarwal, S.; Curless, B.; Seitz, S.M. Multicore Bundle Adjustment. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Providence, RI, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 3057–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, Y.; Ponce, J. Accurate, Dense, and Robust Multi-View Stereopsis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2010, 32, 1362–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, Y.; Curless, B.; Seitz, S.M.; Szeliski, R. Towards Internet-Scale Multi-View Stereo. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 1434–1441. [Google Scholar]
- Agisoft. Agisoft Photoscan. 2016. Available online: http://www.agisoft.com/ (accessed on 26 November 2019).
- Mellado, N.; Aiger, D.; Mitra, N.J. Super 4PCS Fast Global Pointcloud Registration via Smart Indexing. In Proceedings of the Computer Graphics Forum, Cardiff, UK, 9–11 July 2014; Volume 33, pp. 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Medioni, G. Object Modeling by Registration of Multiple Range Images. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Sacramento, CA, USA, 9–11 April 1991; Volume 3, pp. 2724–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazhdan, M.; Bolitho, M.; Hoppe, H. Poisson Surface Reconstruction. In Proceedings of the Fourth Eurographics Symposium on Geometry Processing, Cagliari, Italy, 26–28 June 2006; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Cignoni, P.; Callieri, M.; Corsini, M.; Dellepiane, M.; Ganovelli, F.; Ranzuglia, G. MeshLab: An Open-Source Mesh Processing Tool. In Proceedings of the Eurographics Italian Chapter Conference, Salerno, Italy, 2008; pp. 129–136. Available online: https://dblp.org/db/conf/egItaly/egItaly2008 (accessed on 26 November 2019).
- Falkingham, P.L. Generating a Photogrammetric Model Using Visual SFM, and Post-Processing With Meshlab; Technical Report; Brown University: Providence, RI, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C. VisualSFM: A Visual Structure from Motion System. 2012. Available online: http://ccwu.me/vsfm/ (accessed on 26 November 2019).
- Boehler, W.; Vicent, M.B.; Marbs, A. Investigating Laser Scanner Accuracy. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2003, 34, 696–701. [Google Scholar]
- Koutsoudis, A.; Ioannakis, G.; Vidmar, B.; Arnaoutoglou, F.; Chamzas, C. Using Noise Function-Based Patterns to Enhance Photogrammetric 3D Reconstruction Performance of Featureless Surfaces. J. Cult. Herit. 2015, 16, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DAVID Group. DAVID-SLS-2. 2015. Available online: http://www.david-3d.com/en/products/sls-2 (accessed on 26 November 2019).
- Girardeau-Montaut, D. CloudCompare. 2003. Available online: http://www.cloudcompare.org/ (accessed on 26 November 2019).
- Hess, M.; Robson, S.; Serpico, M.; Amati, G.; Pridden, I.; Nelson, T. Developing 3D Imaging Programmes–Workflow and Quality Control. J. Comput. Cult. Herit. 2015, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, T.; Woolley, S.I.; Ch’ng, E.; Hernandez-Munoz, L.; Gehlken, E.; Nash, D.; Lewis, A.; Hanes, L. A Virtual 3D Cuneiform Tablet Reconstruction Interaction. In Proceedings of the 31st British Computer Society Human Computer Interaction Conference, Sunderland, UK, 3–6 July 2017; p. 73. [Google Scholar]
- Woolley, S.I.; Ch’ng, E.; Hernandez-Munoz, L.; Gehlken, E.; Collins, T.; Nash, D.; Lewis, A.; Hanes, L. A Collaborative Artefact Reconstruction Environment. In Proceedings of the 31st British Computer Society Human Computer Interaction Conference, Sunderland, UK, 3–6 July 2017; BCS Learning & Development Ltd.: Sunderland, UK, 2017; p. 53. [Google Scholar]
- Gehlken, E.; Collins, T.; Woolley, S.I.; Hanes, L.; Lewis, A.; Hernandez-Munoz, L.; Ch’ng, E. Searching the Past in the Future—Joining Cuneiform Tablet Fragments in Virtual Collections. In Proceedings of the 63rd Rencontre Assyriologique Internationale, Marburg, Germany, 24–28 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, T.; Woolley, S.; Gehlken, E.; Ch’ng, E. Computational Aspects of Model Acquisition and Join Geometry for the Virtual Reconstruction of the Atrahasis Cuneiform Tablet. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Virtual Systems & Multimedia (VSMM), Dublin, Ireland, 31 October–4 November 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolley, S.; Gehlken, E.; Ch’ng, E.; Collins, T. Virtual Archaeology: How We Achieved the First, Long-Distance Reconstruction of a Cultural Artefact. The Conversation, Art and Culture. 2018. Available online: https://theconversation.com/virtual-archaeology-how-we-achieved-the-first-long-distance-reconstruction-of-a-cultural-artefact-91725 (accessed on 26 November 2019).



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Collins, T.; Woolley, S.I.; Gehlken, E.; Ch’ng, E. Automated Low-Cost Photogrammetric Acquisition of 3D Models from Small Form-Factor Artefacts. Electronics 2019, 8, 1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8121441
Collins T, Woolley SI, Gehlken E, Ch’ng E. Automated Low-Cost Photogrammetric Acquisition of 3D Models from Small Form-Factor Artefacts. Electronics. 2019; 8(12):1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8121441
Chicago/Turabian StyleCollins, Tim, Sandra I. Woolley, Erlend Gehlken, and Eugene Ch’ng. 2019. "Automated Low-Cost Photogrammetric Acquisition of 3D Models from Small Form-Factor Artefacts" Electronics 8, no. 12: 1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8121441
APA StyleCollins, T., Woolley, S. I., Gehlken, E., & Ch’ng, E. (2019). Automated Low-Cost Photogrammetric Acquisition of 3D Models from Small Form-Factor Artefacts. Electronics, 8(12), 1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8121441





