Iterative Learning Control for V-Shaped Electrothermal Microactuator
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Configuration and Working Principle of the V-Shaped Electrothermal Microactuator
3. Simscape Model of V-Shaped Beam System
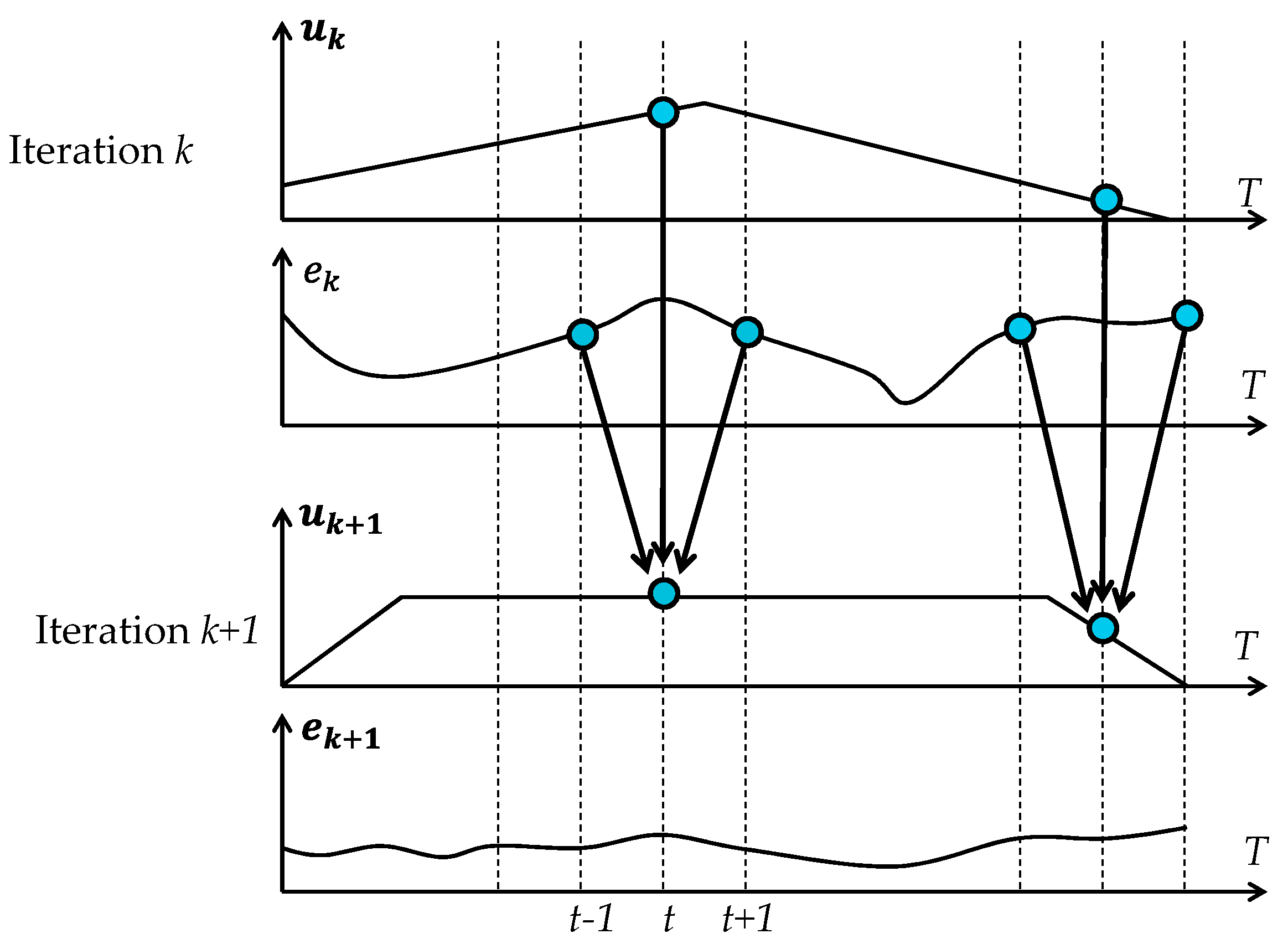
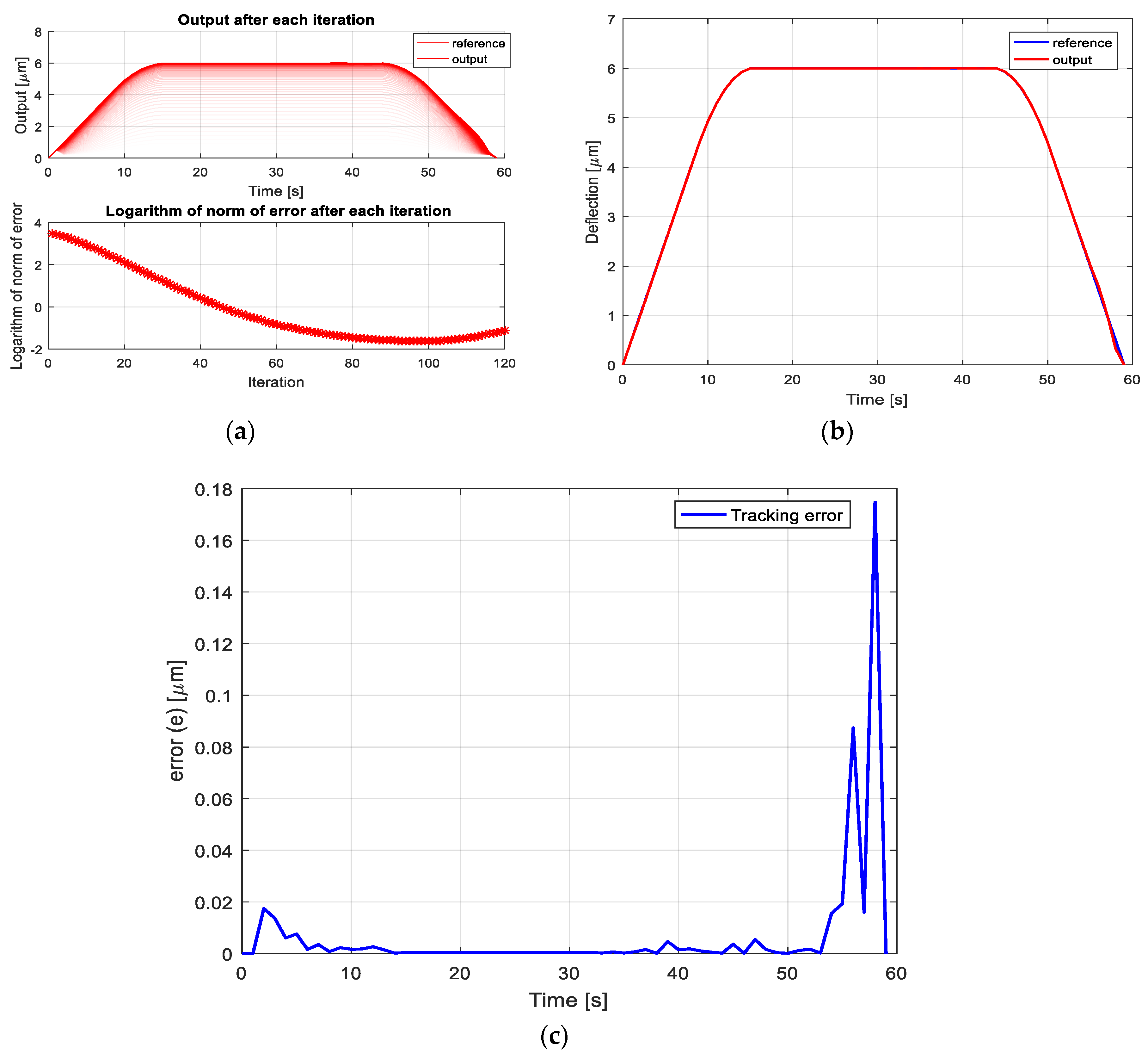
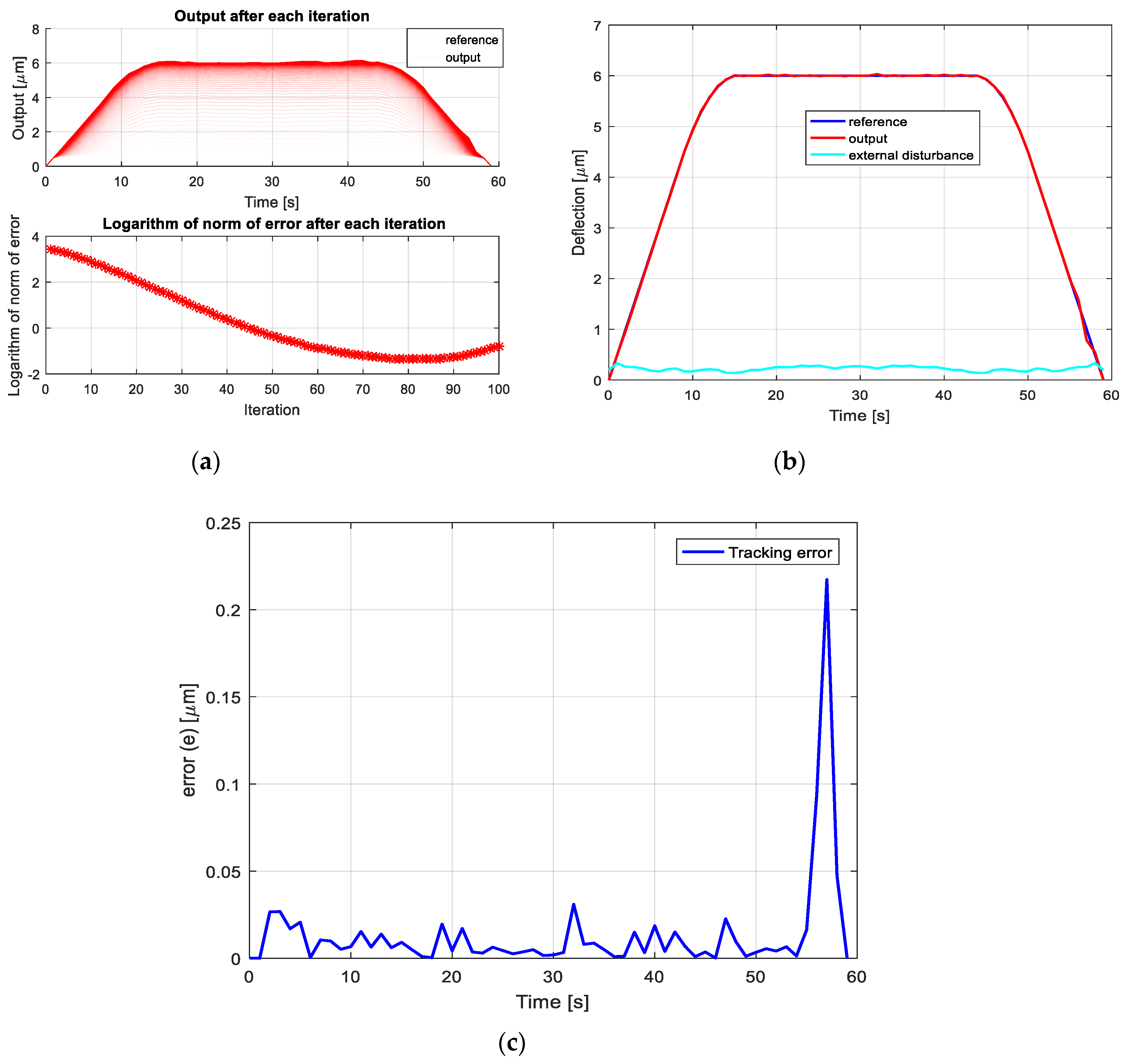
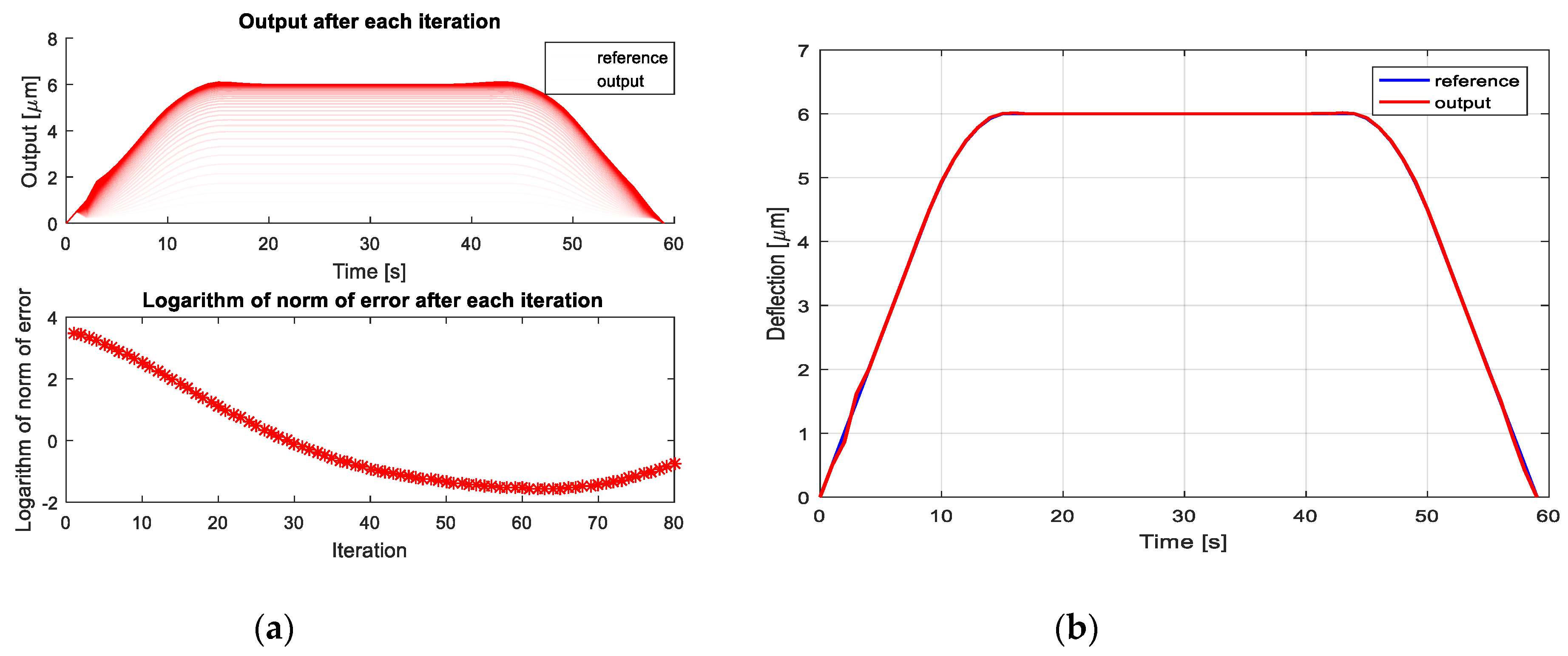
4. Iterative Learning Controller Design for VEM, Simulations and Discussion
- First, during the trial, the whole input , with 0 ≤ t ≤ T is sent to the controlled plant for producing its complete response .
- Afterward, at the moment when the current trial is finished, the output tracking error (5) is calculated based on a particularly chosen learning algorithm to determining the input for the next trial, which should produce a smaller tracking error than the previous input . In other words, a suitably chosen learning function (3) is that, which should generate continuously:for For a particular circumstance, that the input–output operator :as well as the chosen learning function (3) of an additional structure:are linear, then the requirement (6) will be satisfied, if the following sufficient condition:where denotes the identity operator.
- 3.
- Finally, the learning process will be continued repetitively for , until the condition (4) is satisfied.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sinclair, M.J. A high force low area MEMS thermal actuator. In Proceedings of the ITHERM 2000, the Seventh Intersociety Conference on Thermal and Thermomechanical Phenomena in Electronic Systems (Cat. No. 00CH37069), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 23–26 May 2000; pp. 127–132. [Google Scholar]
- Mayyas, M.; Stephanou, H. Electrothermoelastic modeling of MEMS gripper. Microsyst. Technol. 2009, 15, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloney, J.M.; Schreiber, D.S.; Devoe, D.L. Large-force electrothermal linear micromotors. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2003, 14, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, T.; Xu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, Y.; Ren, W. Design of a large displacement thermal actuator with a cascaded V-beam amplification for MEMS safety-and-arming devices. Microsyst. Technol. 2015, 21, 2367–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Chen, X. Mechanical performance of a cascaded V-shaped electrothermal actuator. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2013, 10, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Chu, L.L.; Oliver, A.D.; Gianchandani, Y.B. Bent-beam electrothermal actuators-Part II: Linear and rotary microengines. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2001, 10, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messenger, R.K. Modeling and Control of Surface Micromachined Thermal Actuators. Master Thesis, Brigham Young University, Provo, UT, USA, 21 May 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X. Dynamic modelling and analysis of V-and Z-shaped electrothermal microactuators. Microsyst. Technol. 2017, 23, 3775–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzung, N.T.; Nam, D.P.; Dich, N.Q. Modelling and Control Design of a V-shaped Thermal Actuator System via Partial Derivative Equation Approach. In Proceedings of the ICMRE 2019, Rome, Italy, 16–19 February 2019; pp. 78–82. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, A.; Aphale, S.S. A survey of modeling and control techniques for micro-and nanoelectromechanical systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C Appl. Rev. 2010, 41, 350–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez, R.; Pissaloux, E.E. Modelling and temperature control of shape memory alloys with fast electrical heating. Int. J. Mech. Control 2012, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Walraven, J.A.; Baker, M.S.; Headley, T.J.; Plass, R.A. Compliant Thermo-Mechanical MEMS Actuators; Final Report; Sandia National Laboratories: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 2004.
- Zhu, Y.; Bazaei, A.; Moheimani, S.R.; Yuce, M.R. Design, modeling, and control of a micromachined nanopositioner with integrated electrothermal actuation and sensing. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2011, 20, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Mechefske, C.; Lai, Y. Micro thermal actuator with integrated capacitive position sensor. In Proceedings of the 2009 2nd Microsystems and Nanoelectronics Research Conference, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 13–14 October 2009; pp. 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Vagia, M.; Nikolakopoulos, G.; Tzes, A. Intelligent robust controller design for a micro-actuator. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2006, 47, 299–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enikov, E.T.; Kedar, S.S.; Lazarov, K.V. Analytical model for analysis and design of V-shaped thermal microactuators. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2005, 14, 788–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Chen, G. Modeling V-shape Thermal In-plane Microactuator using Chained Beam-Constraint-Model. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Manipulation, Manufacturing and Measurement on the Nanoscale (3M-NANO), Taipei, Taiwan, 27–31 October 2014; pp. 244–248. [Google Scholar]
- Jamshidi, M.; Zilouchian, A. Intelligent Control Systems Using Soft Computing Methodologies; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Antsaklis, P.J. Intelligent control. In wiley Encyclopedia of Electrical and Electronics Engineering; Webster, J., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Torino, Italy, 1999; pp. 493–503. [Google Scholar]
- Uchiyama, M. Formation of high-speed motion pattern of a mechanical arm by trial. Trans. Soc. Instrum. Control Eng. 1978, 14, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-K.; Li, K.-S. Iterative learning control for robotic contouring. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Control and Automation, Christchurch, New Zealand, 9–11 December 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Arimoto, S.; Kawamura, S.; Miyazaki, F. Bettering operation of robots by learning. J. Robot. Syst. 1984, 1, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, S. An iterative learning control method with application for CNC machine tools. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1996, 32, 66–72. [Google Scholar]
- de Roover, D.; Bosgra, O.H. Synthesis of robust multivariable iterative learning controllers with application to a wafer stage motion system. Int. J. Control 2000, 73, 968–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havlicsek, H.; Alleyne, A. Nonlinear control of an electrohydraulic injection molding machine via iterative adaptive learning. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 1999, 4, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, A.D.; Lewin, P.L.; Brown, D.J. Practical implementation of a real-time iterative learning position controller. Int. J. Control 2000, 73, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.R.; Lee, K.S.; Ahn, H.J.; Lee, J.H. Experimental application of a quadratic optimal iterative learning control method for control of wafer temperature uniformity in rapid thermal processing. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 2003, 16, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.L. Iterative Learning Control for Deterministic Systems; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.-X.; Tan, Y. Linear and Nonlinear Iterative Learning Control; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Norrlöf, M. Iterative Learning Control-Analysis, Design, and Experiments; Diss, No.653; Linkoepings University: Linkoepings, Sweden, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, K.L.; Dahleh, M.; Bhattacharyya, S.P. Iterative learning for trajectory control. In Proceedings of the 28th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Tampa, FL, USA, 13–15 December 1989; pp. 860–865. [Google Scholar]
- Vita, V.; Vitas, A.; Chatzarakis, G.E. Design, implementation and evaluation of an optimal iterative learning control algorithm. Wseas Trans. Circuits Syst. 2011, 10, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Getting Started with Simscape. MathLab Tutorials. R2019b. Available online: https://ch.mathworks.com/help/physmod/simscape/getting-started-with-simscape.html (accessed on 15 October 2019).
- Tian, S.; Liu, Q.; Dai, X.; Zhang, J. A PD-type iterative learning control algorithm for singular discrete systems. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2016, 2016, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, D.H.; Amann, N.; Rogers, E. Iterative learning control-an overview of recent algorithms. Appl. Math. Comput. Sci. 1995, 5, 425–438. [Google Scholar]
- Owens, D.H.; Hätönen, J. Iterative learning control-The state of the art. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2004, 37, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharayil, D.A.B.M.; Alleyne, A.G. A survey of iterative learning control: A learning-based method for high performance tracking control. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 2006, 26, 96–114. [Google Scholar]
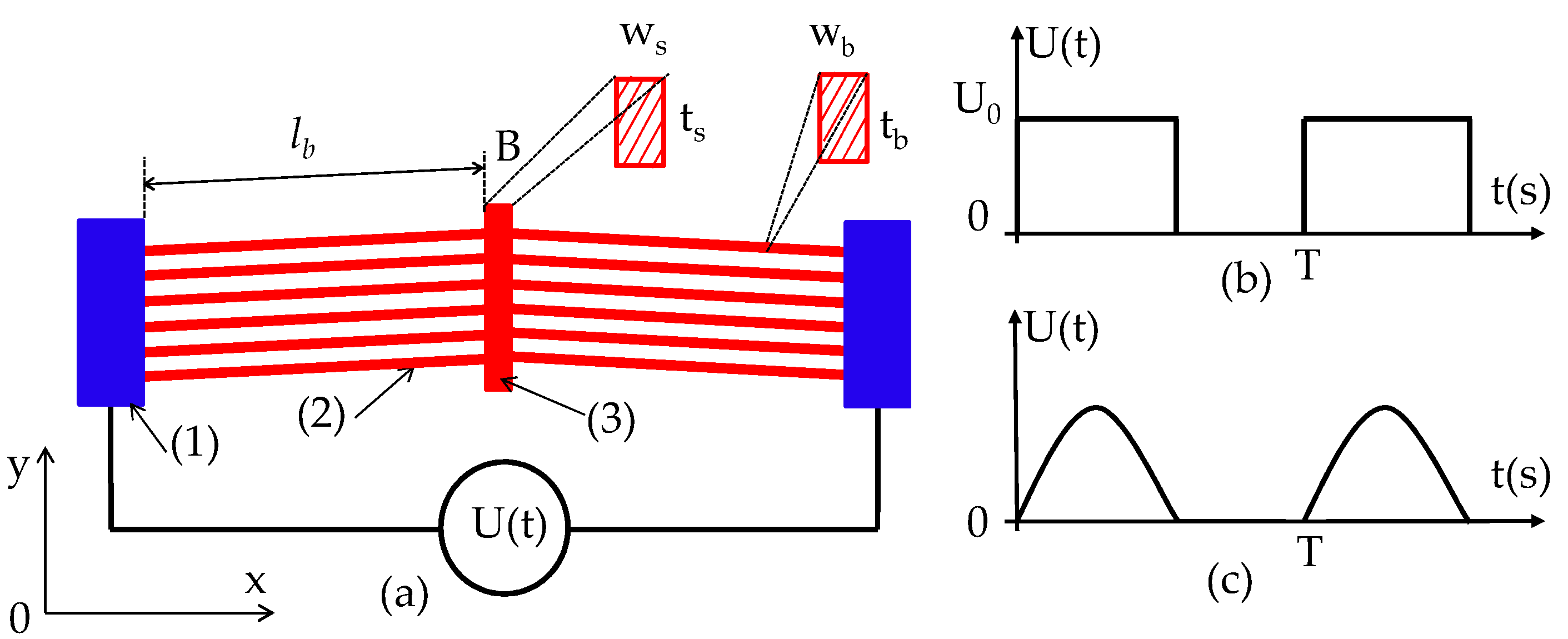

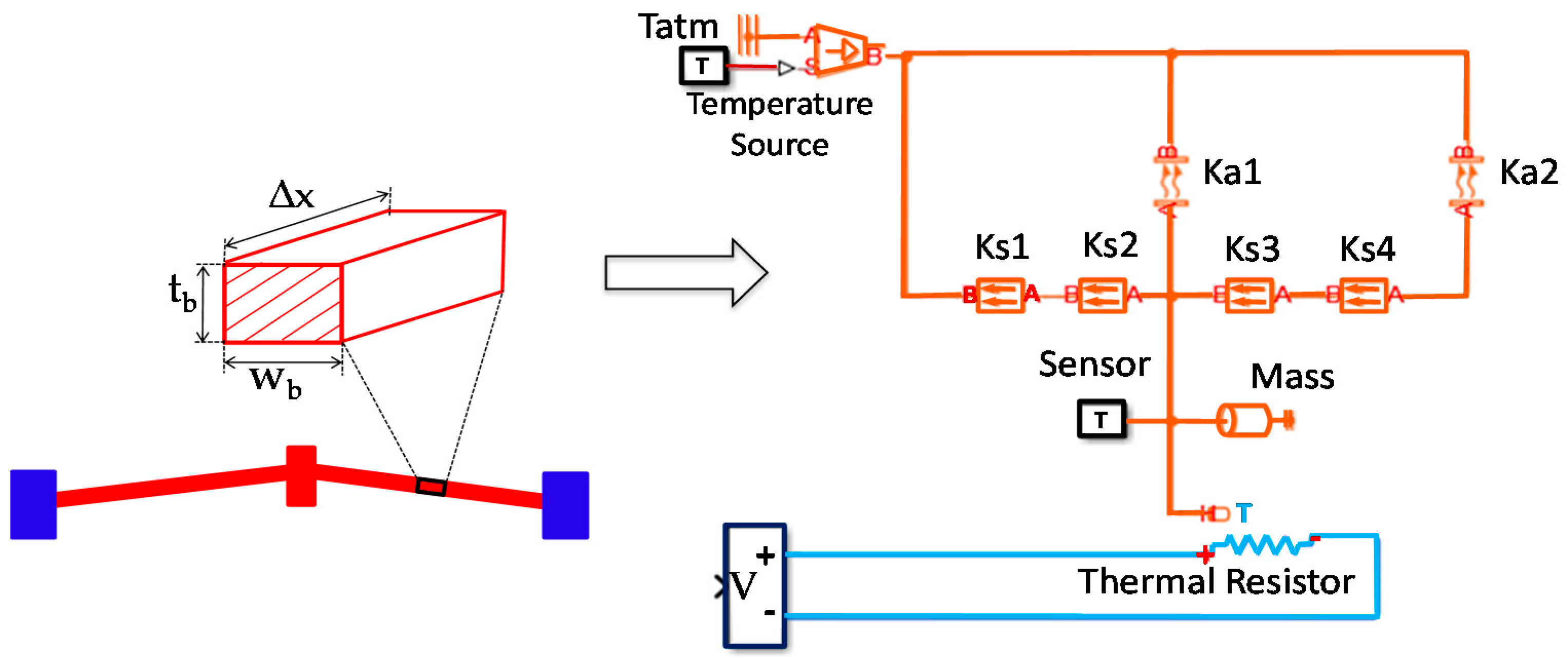
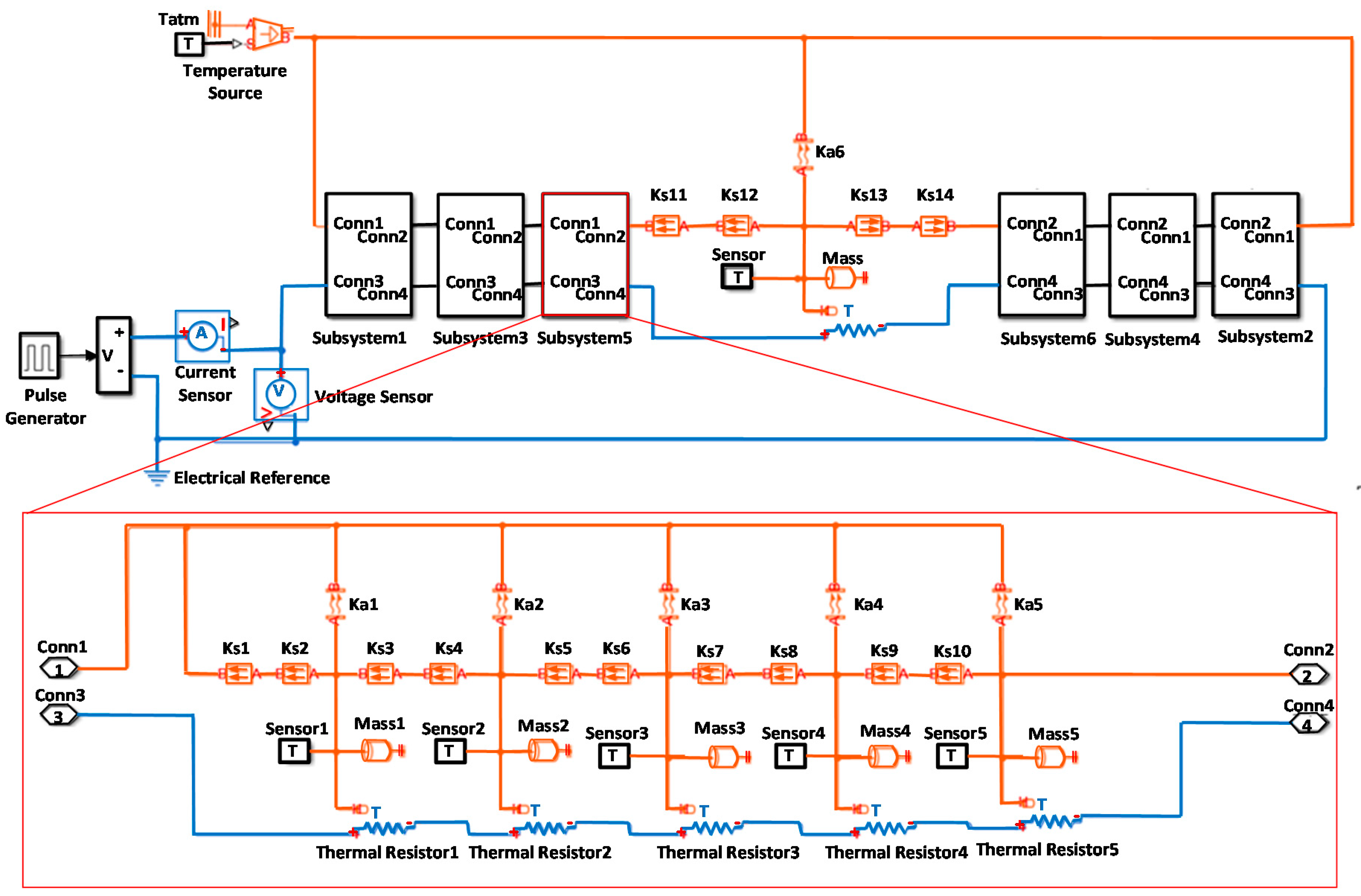




| Parameters | Symbol | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Length of a single beam | lb | 320 | µm |
| Width of a single beam | wb | 4.5 | µm |
| The thickness of beam | tb | 30 | µm |
| The length of the shuttle | ls | 125 | µm |
| The width of the shuttle | ws | 40 | µm |
| The thickness of the shuttle | ts | 30 | µm |
| Air gap | ga | 4 | µm |
| Parameters | Symbol | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specific weight | D | 2330 | Kg/m3 |
| Specific heat | Cp | 710 | J/Kg°C |
| Resistivity at room temperature | ρ0 | 1200 | Ωmm |
| Thermal conductivity of silicon | Ks | 146 | W/m°C |
| Thermal conductivity of air | Ka | 0.026 | W/m°C |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dzung, N.T.; Phuc, P.H.; Dich, N.Q.; Phuoc, N.D. Iterative Learning Control for V-Shaped Electrothermal Microactuator. Electronics 2019, 8, 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8121410
Dzung NT, Phuc PH, Dich NQ, Phuoc ND. Iterative Learning Control for V-Shaped Electrothermal Microactuator. Electronics. 2019; 8(12):1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8121410
Chicago/Turabian StyleDzung, Nguyen Tien, Pham Hong Phuc, Nguyen Quang Dich, and Nguyen Doan Phuoc. 2019. "Iterative Learning Control for V-Shaped Electrothermal Microactuator" Electronics 8, no. 12: 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8121410
APA StyleDzung, N. T., Phuc, P. H., Dich, N. Q., & Phuoc, N. D. (2019). Iterative Learning Control for V-Shaped Electrothermal Microactuator. Electronics, 8(12), 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8121410





