Robot Motion Control via an EEG-Based Brain–Computer Interface by Using Neural Networks and Alpha Brainwaves
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. BCI Types
2.2. Brainwaves for EEG-BCIs
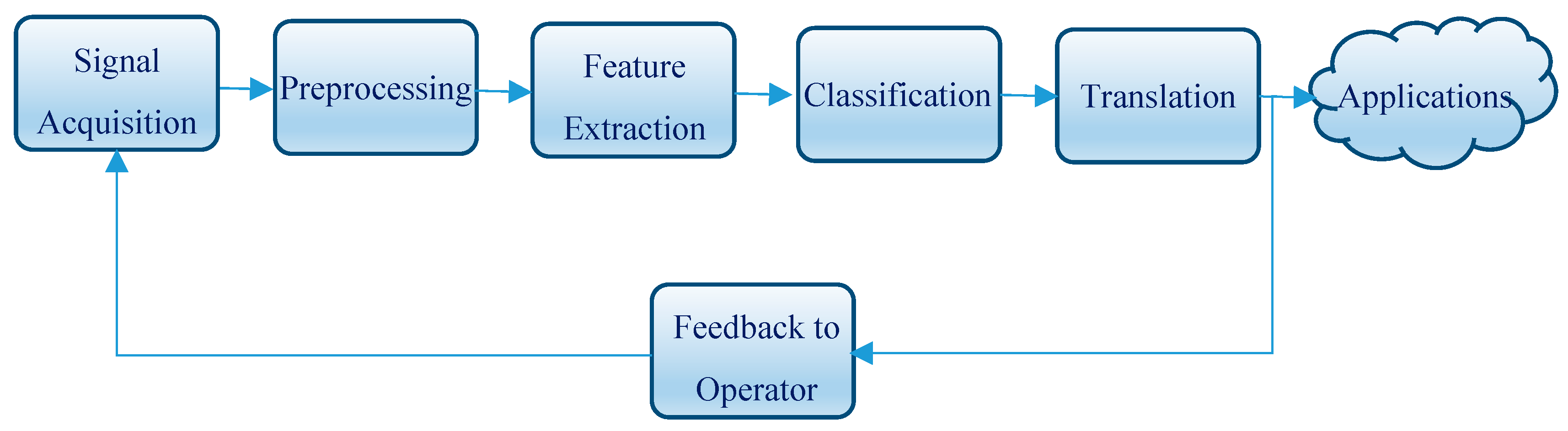
2.3. BCI Operation
2.4. BCI-Based Robot Control
3. Materials and Methods
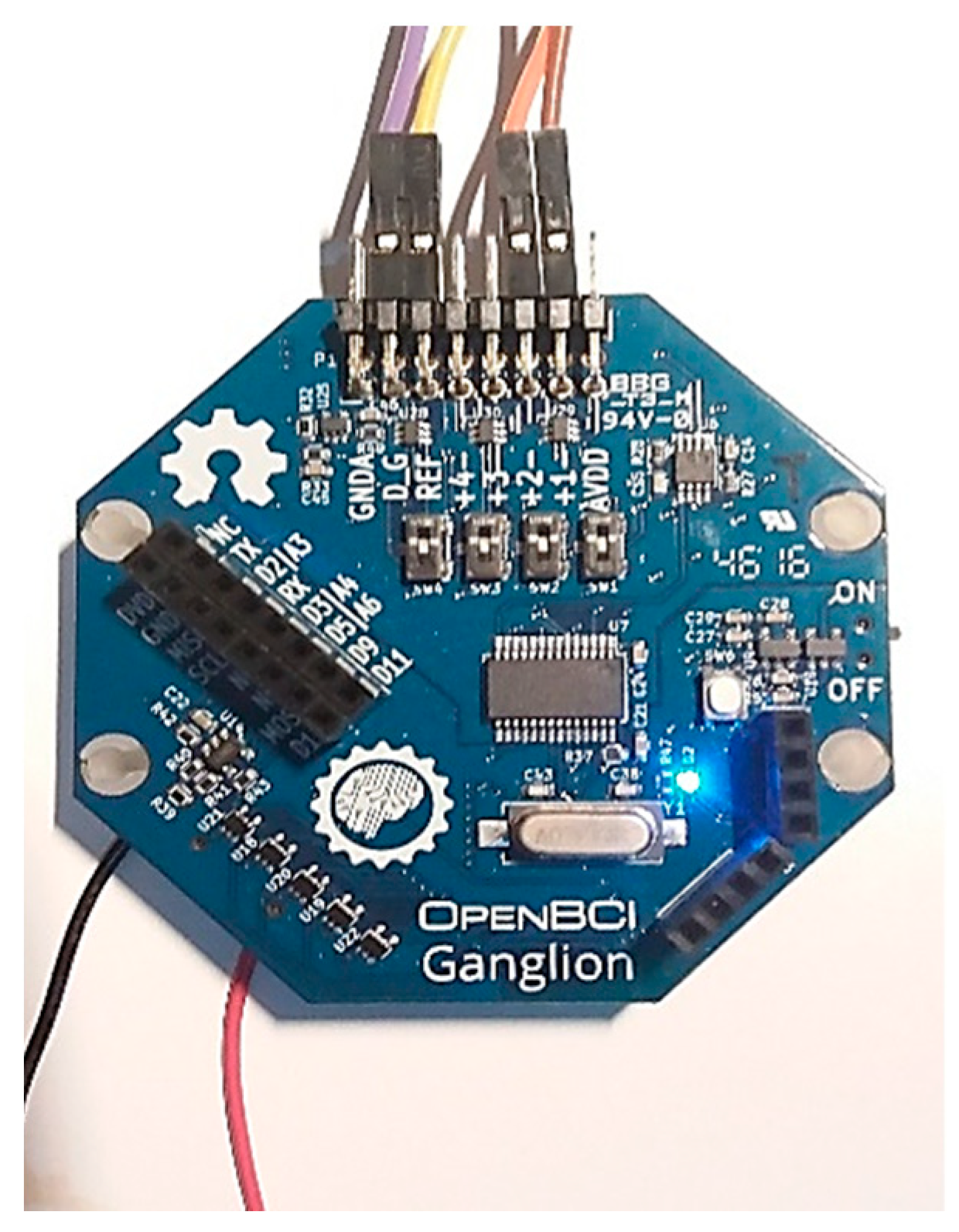
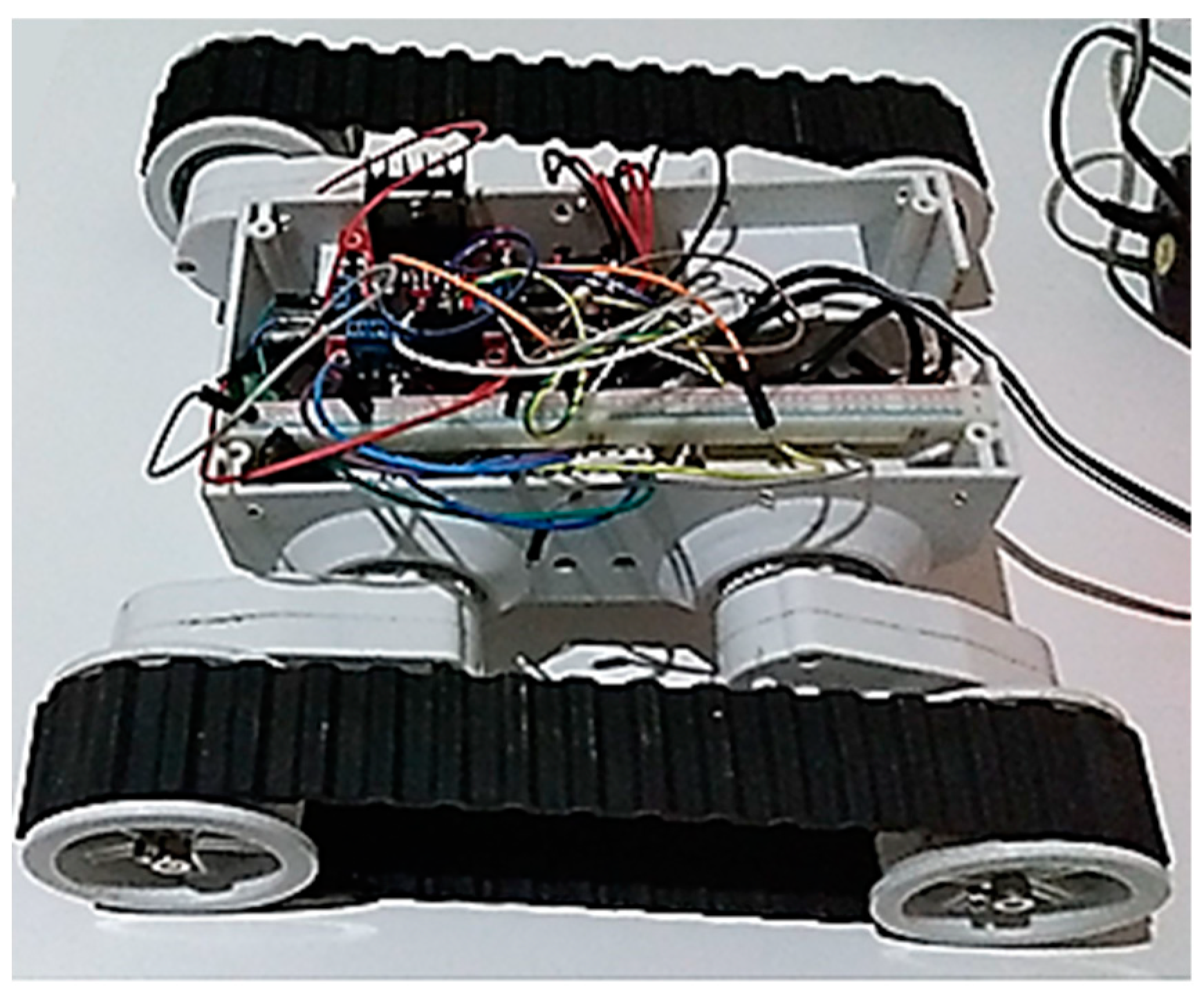
3.1. Experimental Equipment
3.1.1. BCI Unit
3.1.2. Robotic Unit
3.2. Experimental Procedure
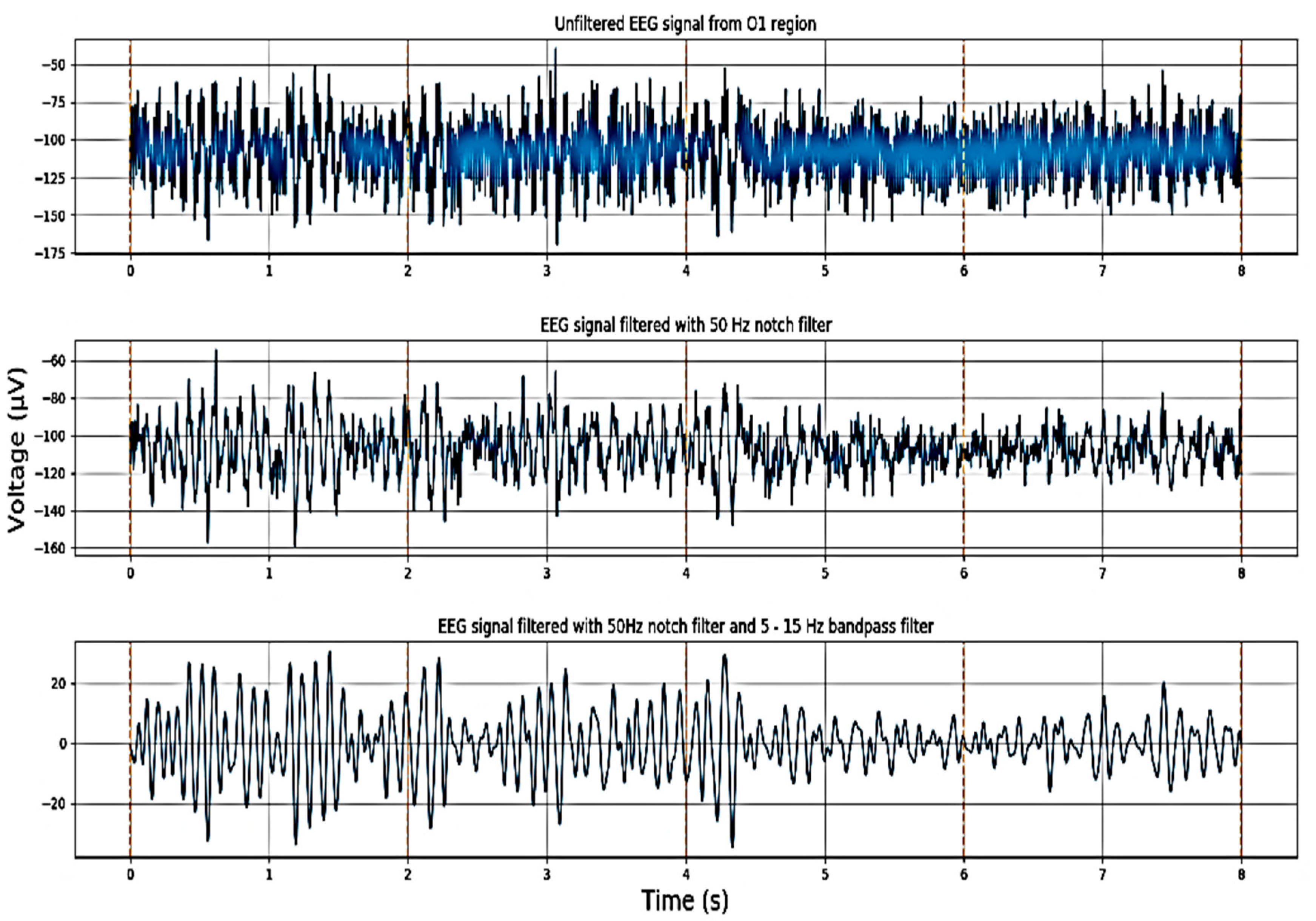
3.2.1. Signal Acquisition
3.2.2. Preprocessing and Feature Extraction
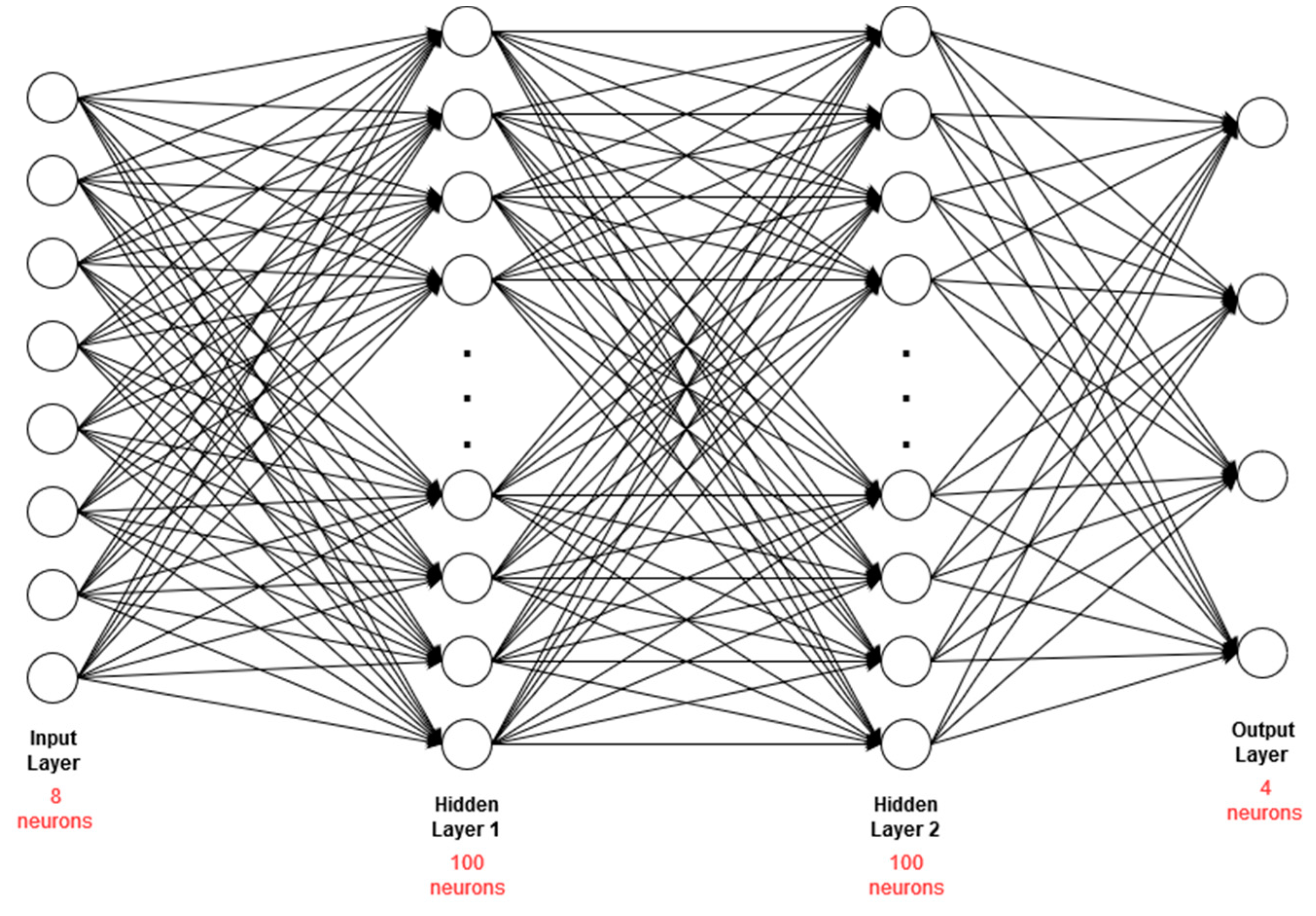
3.2.3. Classification and Translation
4. Results and Discussion
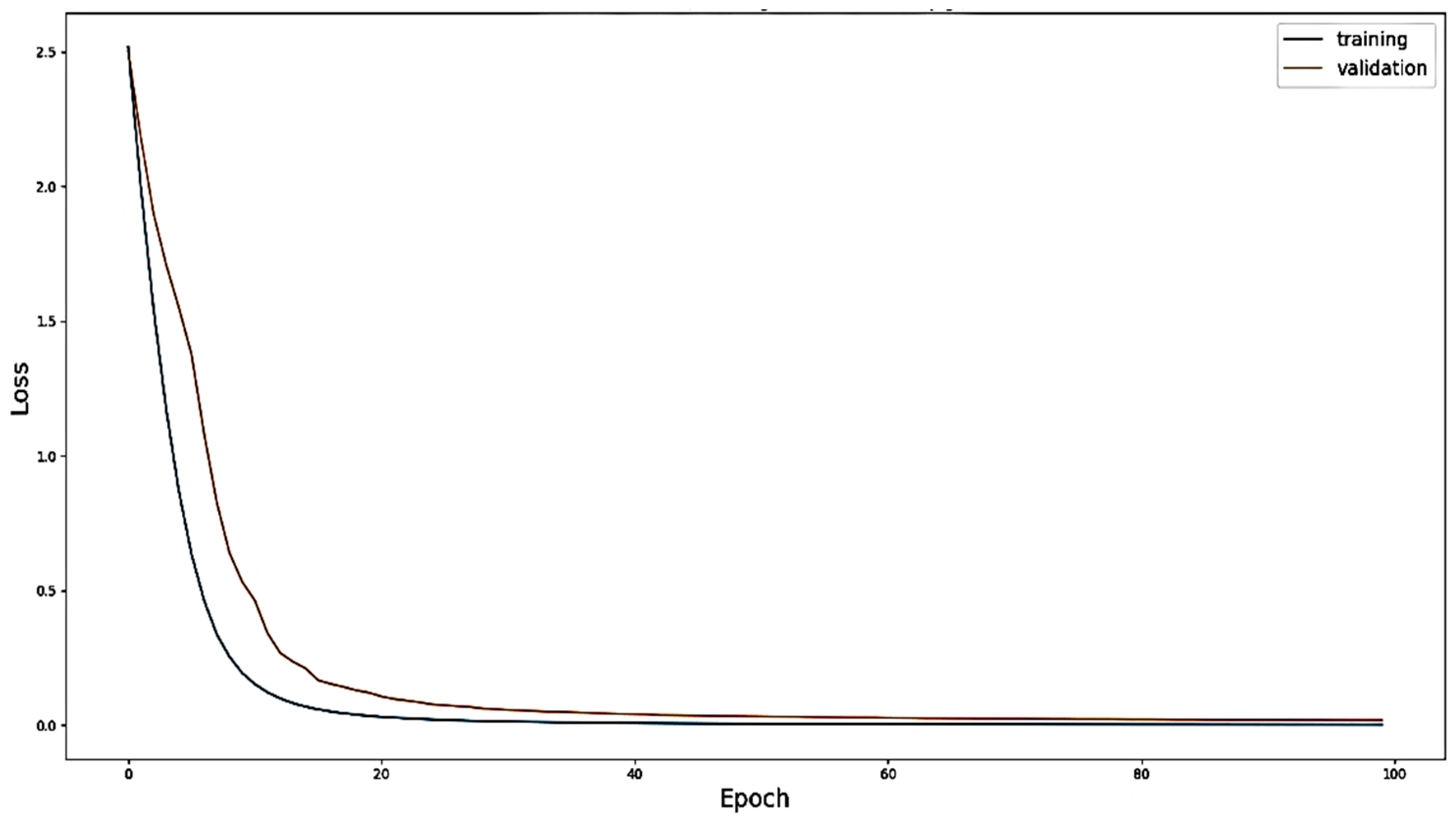
4.1. Evaluation with Offline Data
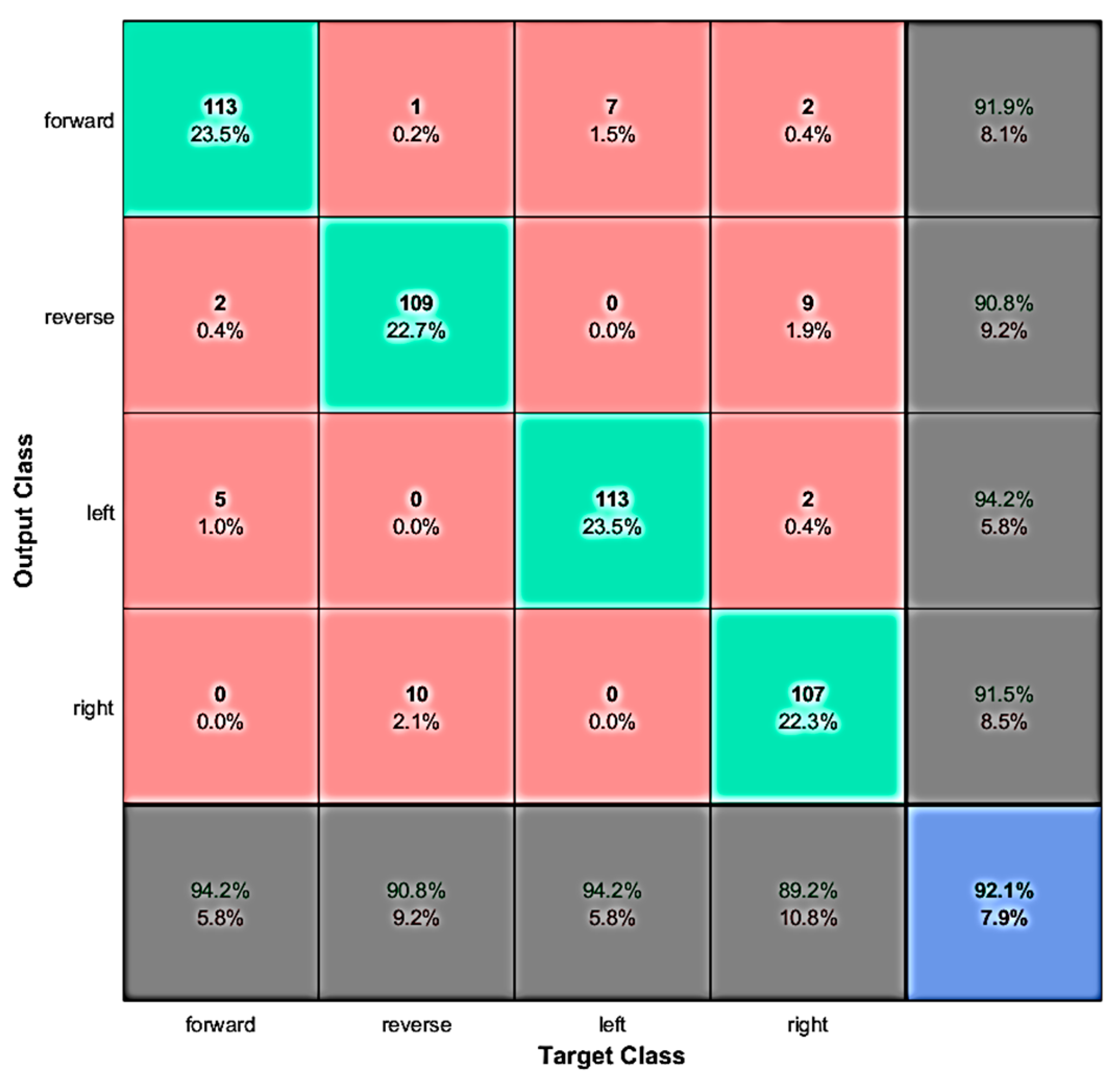
4.2. Real-Time Evaluation
4.3. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dixon, A.M.; Allstot, E.G.; Gangopadhyay, D.; Allstot, D.J. Compressed sensing system considerations for ECG and EMG wireless biosensors. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2012, 6, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdiz, J.; Pires, G.; Nunes, U.J. Emotional state detection based on EMG and EOG biosignals: A short survey. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 5th Portuguese Meeting on Bioengineering (ENBENG), Coimbra, Portugal, 16–18 February 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Valais, I.; Koulouras, G.; Fountos, G.; Michail, C.; Kandris, D.; Athinaios, S. Design and Construction of a Prototype ECG Simulator. EJST 2014, 9, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Subha, D.P.; Joseph, P.K.; Acharya, R.; Lim, C.M. EEG signal analysis: A survey. J. Med. Syst. 2010, 34, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolpaw, J.R.; Birbaumer, N.; McFarland, D.J.; Pfurtscheller, G.; Vaughan, T.M. Brain–computer interfaces for communication and control. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2002, 113, 767–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkader, S.N.; Atia, A.; Mostafa, M.S.M. Brain computer interfacing: Applications and challenges. Egypt. Inform. J. 2015, 16, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katona, J.; Kovari, A. A Brain–Computer Interface Project Applied in Computer Engineering. IEEE Trans. Educ. 2016, 59, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katona, J.; Kovari, A. The Evaluation of BCI and PEBL-Based Attention Tests. Acta Polytechnica Hungarica 2018, 15, 225–249. [Google Scholar]
- Katona, J.; Kovari, A. Examining the learning efficiency by a brain-computer interface system. Acta Polytechnica Hungarica 2018, 15, 251–280. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas-Alonso, L.F.; Gomez-Gil, J. Brain computer interfaces, a review. Sensors 2012, 12, 1211–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, L.; Fan, X.A.; Liu, Y. EEG-based brain-controlled mobile robots: A survey. IEEE Trans. Hum. Mach. Syst. 2013, 43, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minguillon, J.; Lopez-Gordo, M.A.; Pelayo, F. Trends in EEG-BCI for daily-life: Requirements for artifact removal. Biom. Signal Proces. Control 2017, 31, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmavathi, R.; Ranganathan, V. A review on EEG based brain computer interface systems. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. 2014, 4, 683–696. [Google Scholar]
- Gandhi, V. Brain-Computer Interfacing for Assistive Robotics: Electroencephalograms, Recurrent Quantum Neural Networks and User-Centric Graphical Interfaces, 1st ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2014; pp. 29–30. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandridis, A.; Chondrodima, E.; Giannopoulos, N.; Sarimveis, H. A Fast and Efficient Method for Training Categorical Radial Basis Function Networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2017, 28, 2831–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandridis, A.; Chondrodima, E.; Sarimveis, H. Radial Basis Function network training using a non-symmetric partition of the input space and Particle Swarm Optimization. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2013, 24, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotte, F.; Bougrain, L.; Cichocki, A.; Clerc, M.; Congedo, M.; Rakotomamonjy, A.; Yger, F. A review of classification algorithms for EEG-based brain-computer interfaces: A 10 year update. J. Neural Eng. 2018, 15, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Matsunaga, K.; Wang, H.O. Electroencephalogram based control of an electric wheelchair. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2005, 21, 762–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Cichocki, A. Control of a wheelchair by motor imagery in real time. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Data Engineering and Automated Learning, Daejeon, Korea, 2–5 November 2008; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; pp. 330–337. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, A.; Silva, R.L.; Celeste, W.C.; Bastos, T.F.; Filho, M.S. Human–machine interface based on muscular and brain signals applied to a robotic wheelchair. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2007, 90, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandel, C.; Luth, T.; Laue, T.; Röfer, T.; Graser, A.; Krieg-Bruckner, B. Navigating a smart wheelchair with a brain–computer interface interpreting steady-state visual evoked potentials. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, St. Louis, MO, USA, 10–15 October 2009; pp. 1118–1125. [Google Scholar]
- Rebsamen, B.; Burdet, E.; Guan, C.; Zhang, H.; Teo, C.L.; Zeng, Q.; Ang, M.; Laugier, C. A brain controlled wheelchair based on P300 and path guidance. In Proceedings of the 1st IEEE/RAS-EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, Pisa, Italy, 20–22 February 2006; pp. 1001–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Iturrate, I.M.; Antelis, J.; Kubler, A.; Minguez, J. A noninvasive brain-actuated wheelchair based on a p300 neurophysiological protocol and automated navigation. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2009, 25, 614–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benevides, A.B.; Bastos, T.F.; Filho, M.S. Proposal of brain–computer interface architecture to command a robotic wheelchair. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium in Industrial Electronics, Gdansk, Poland, 27–30 June 2011; pp. 2249–2254. [Google Scholar]
- Samson, V.R.R.; Kitti, B.P.; Kumar, S.P.; Babu, D.S.; Monica, C. Electroencephalogram-Based OpenBCI Devices for Disabled People. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Micro-Electronics, Electromagnetics and Telecommunications, Visakhapatnam, India, 6–7 January 2017; pp. 229–238. [Google Scholar]
- Olejarczyk, E.; Bogucki, P.; Sobieszek, A. The EEG split α peak: Phenomenological origins and methodological aspects of detection and evaluation. Front. Neurosc. 2017, 11, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, G.C.; Swetapadma, A.; Pattnaik, P.K. Enhancing the performance of motor imagery classification to design a robust brain computer interface using feed forward back-propagation neural network. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2018, 9, 2871–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subasi, A.; Erçelebi, E. Classification of EEG signals using neural network and logistic regression. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2005, 78, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Boer, P.T.; Kroese, D.P.; Mannor, S.; Rubinstein, R.Y. A tutorial on the cross-entropy method. Ann. Oper. Res. 2005, 134, 19–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Abadi, M.; Barham, P.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M.; Ghemawat, S.; Irving, G.; Isard, M.; et al. TensorFlow: A system for large-scale machine learning. In Proceedings of the 12th USENIX Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation (OSDI 16), Savannah, GA, USA, 2–4 November 2016; pp. 265–283. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. Keras: The python deep learning library. Astrophys. Source Code Libr. 2018. Available online: https://keras.io/k (accessed on 19 November 2019).
- Wada, Y.; Takizawa, Y.; Zheng-Yan, J.; Yamaguchi, N. Gender differences in quantitative EEG at rest and during photic stimulation in normal young adults. Clin. Electroencephalogr. 1994, 25, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsi-Cabrera, M.; Ramos, J.; Guevara, M.A.; Arce, C.; Gutierrez, S. Gender Differences m in the Eeg During Cognitive Activity. Int. J. Neurosci. 1993, 72, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, S.; Fazel-Rezai, R.; Asadpour, V. A review of hybrid brain-computer interface systems. Adv. Hum. Comput. Interact. 2013, 2013, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zantalis, F.; Koulouras, G.; Karabetsos, S.; Kandris, D. A Review of Machine Learning and IoT in Smart Transportation. Future Internet 2019, 11, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarifarmand, A.; Badamchizadeh, M.A. EEG Artifacts Handling in a Real Practical Brain-Computer Interface Controlled Vehicle. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabilit. Eng. 2019, 27, 2000–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, E.; Rangel, J.C.; Gomez-Donoso, F.; Bauer, Z.; Cazorla, M.; García-Rodríguez, J. Finding the place: How to train and use convolutional neural networks for a dynamically learning robot. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 8–13 July 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]

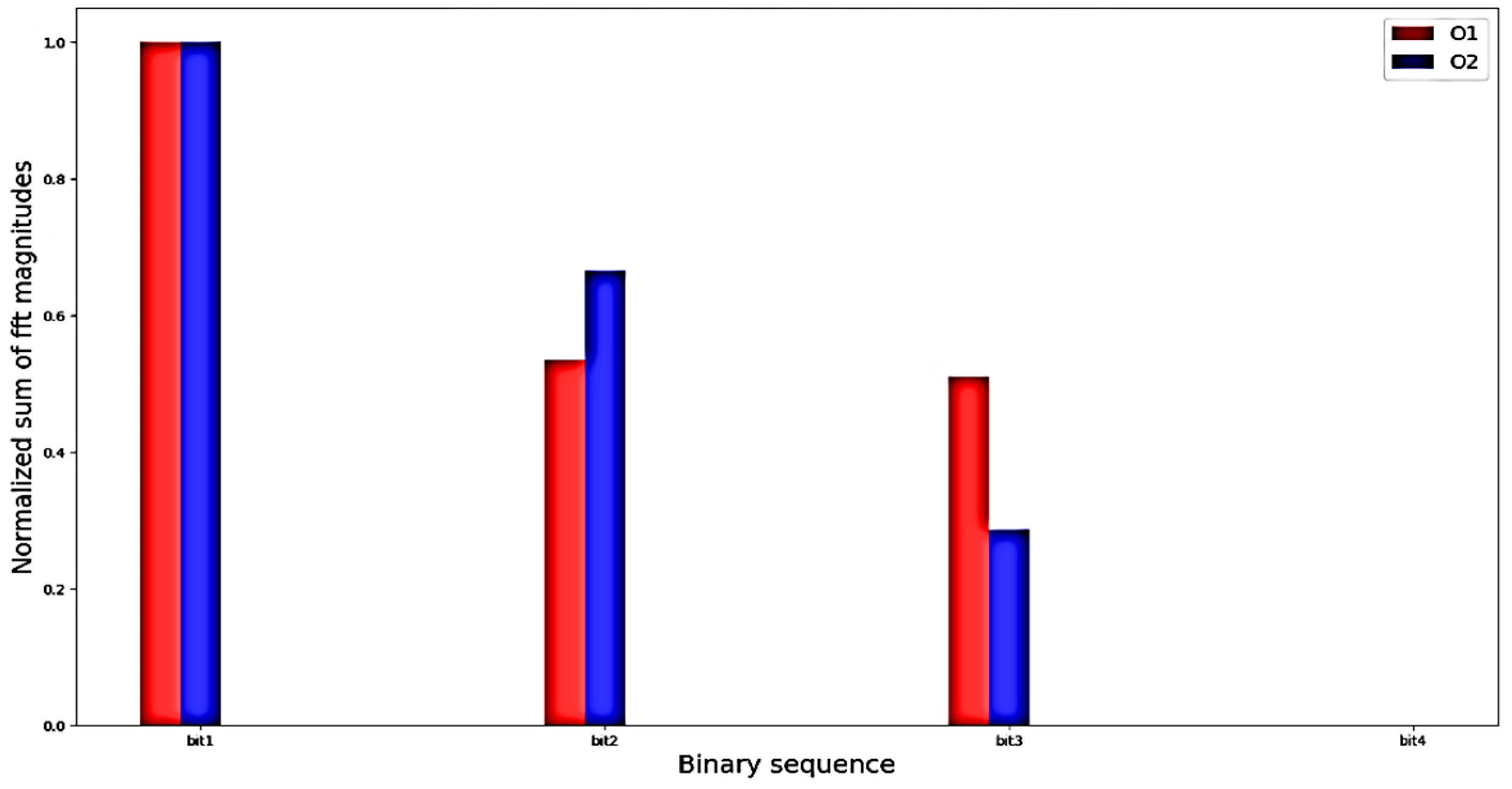
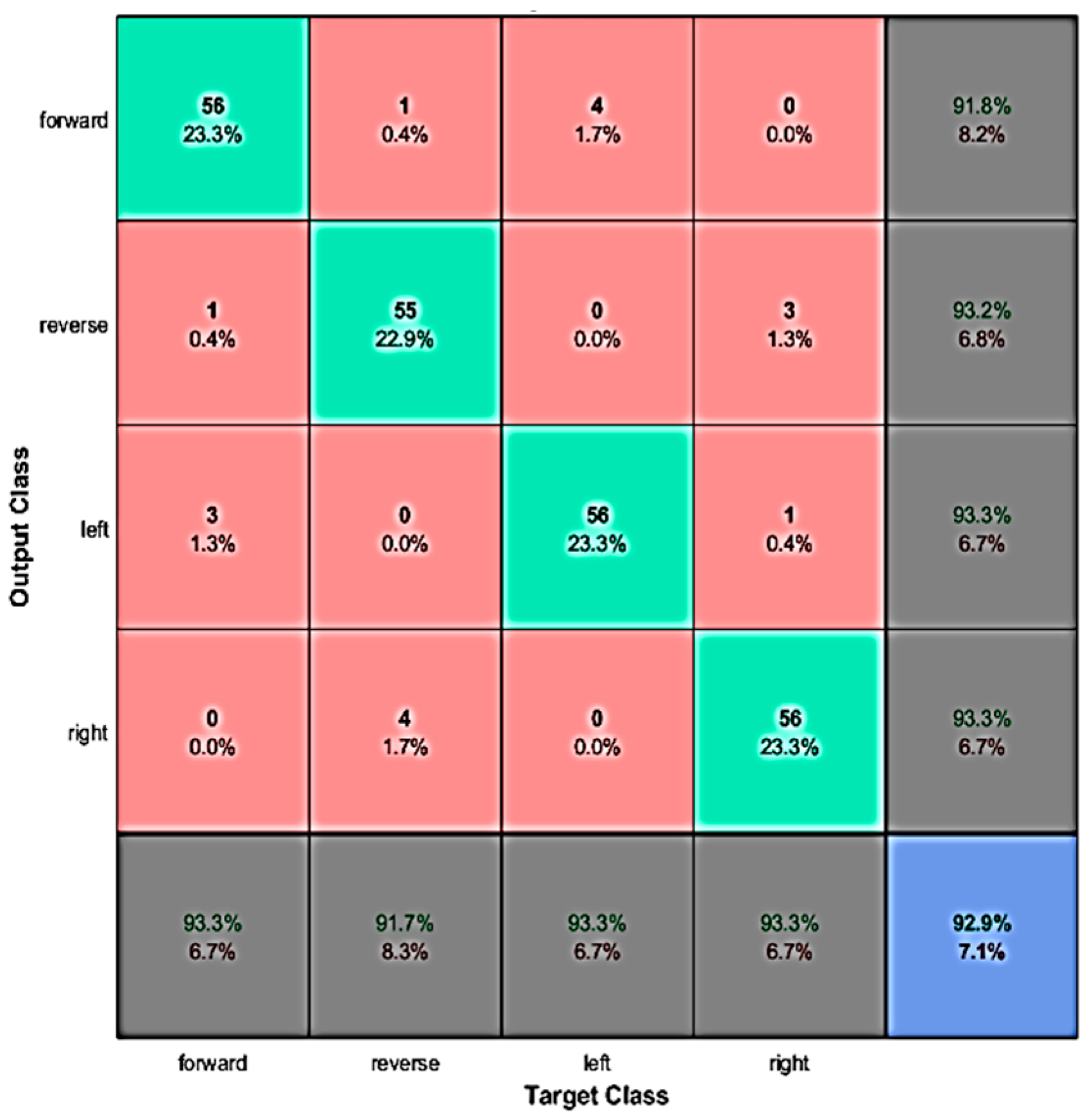
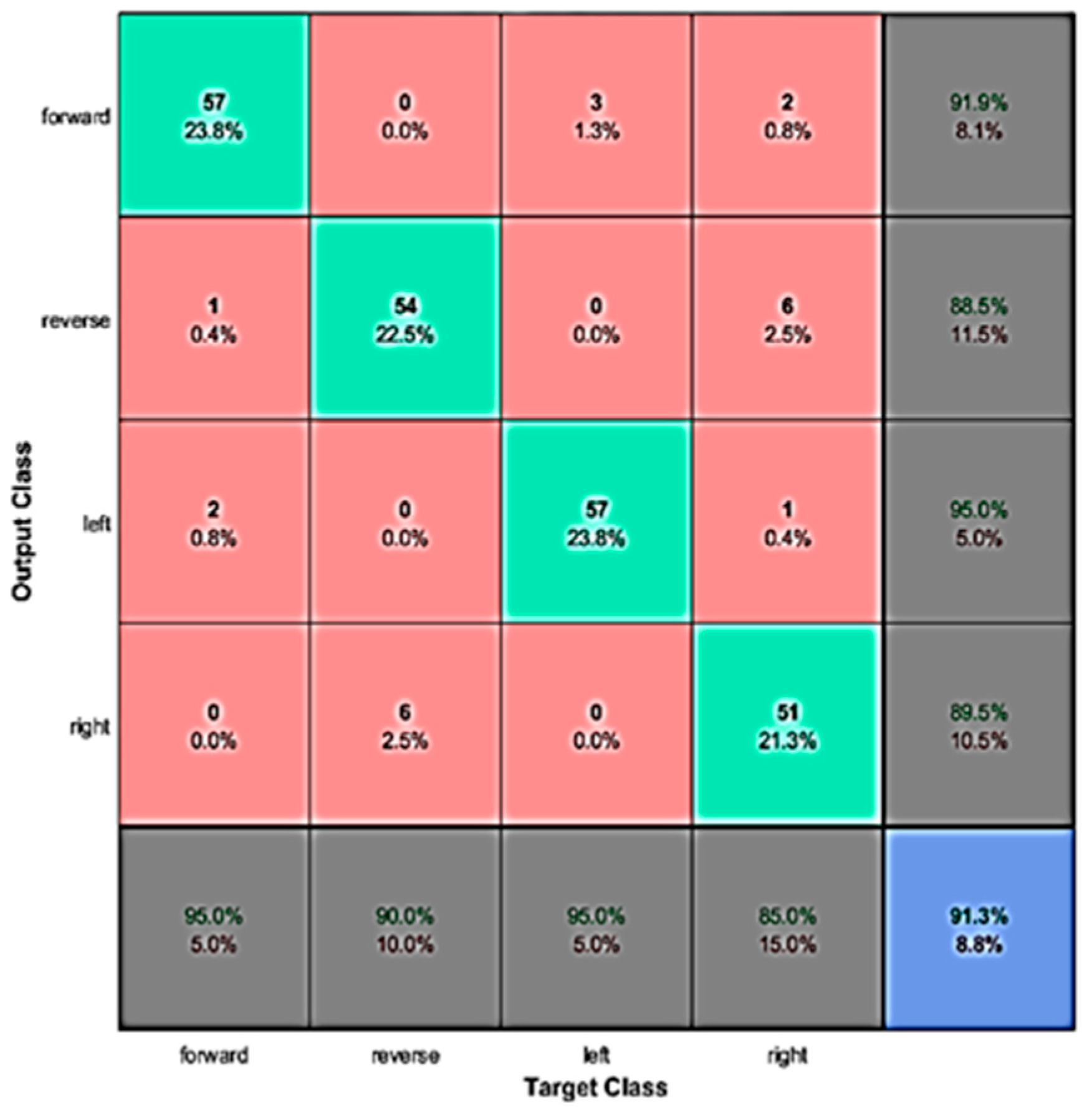
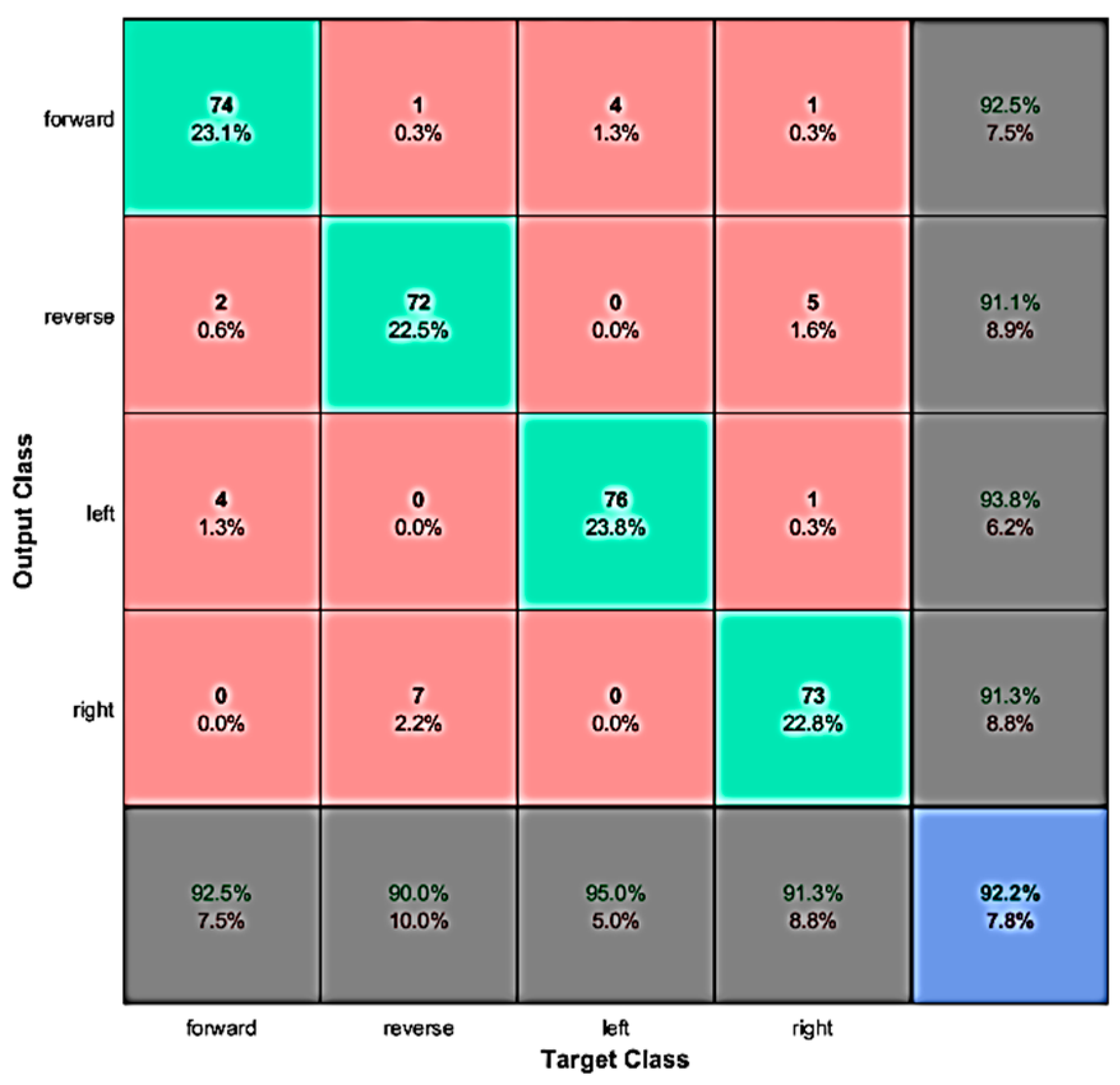

| Binary Sequence | Robotic Movement |
|---|---|
| ‘1010’ | Forward |
| ‘0101’ | Reverse |
| ‘1100’ | Left |
| ‘0011’ | Right |
| Command | ‘1010’ | ‘0101’ | ‘1100’ | ‘0011’ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forward | ‘1010’ | 0 | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| Reverse | ‘0101’ | 4 | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| Left | ‘1100’ | 2 | 2 | 0 | 4 |
| Right | ‘0011’ | 2 | 2 | 4 | 0 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Korovesis, N.; Kandris, D.; Koulouras, G.; Alexandridis, A. Robot Motion Control via an EEG-Based Brain–Computer Interface by Using Neural Networks and Alpha Brainwaves. Electronics 2019, 8, 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8121387
Korovesis N, Kandris D, Koulouras G, Alexandridis A. Robot Motion Control via an EEG-Based Brain–Computer Interface by Using Neural Networks and Alpha Brainwaves. Electronics. 2019; 8(12):1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8121387
Chicago/Turabian StyleKorovesis, Nikolaos, Dionisis Kandris, Grigorios Koulouras, and Alex Alexandridis. 2019. "Robot Motion Control via an EEG-Based Brain–Computer Interface by Using Neural Networks and Alpha Brainwaves" Electronics 8, no. 12: 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8121387
APA StyleKorovesis, N., Kandris, D., Koulouras, G., & Alexandridis, A. (2019). Robot Motion Control via an EEG-Based Brain–Computer Interface by Using Neural Networks and Alpha Brainwaves. Electronics, 8(12), 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8121387








