BEMF-Net: A Boundary-Enhanced Multi-Scale Feature Fusion Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A boundary-enhanced multi-scale feature fusion network called BEMF-Net is proposed to automatically delineate renal tumors in endoscopic images and highlight the lesion regions, thereby achieving effective tumor extraction.
- A multi-scale feature fusion attention module called MFA is proposed. This module refines and enriches backbone features through convolutional branches of different receptive fields, thereby integrating more comprehensive local and global information.
- We propose a hybrid cross-modal attention module called HCA for the dual purpose of modeling long-range interactions and encoding local appearance details, which equips the decoder to represent features more effectively.
- We propose a boundary selective attention module called BSA, which specializes in dealing with boundary regions and heightens the model’s perceptual acuity towards edges, so that different levels of features are boundary-aware.
2. Related Works
2.1. Traditional Image Segmentation
2.2. CNN-Based Methods
2.3. Transformer-Based Methods
2.4. Segmentation Methods for Kidney Tumors
3. Proposed Method
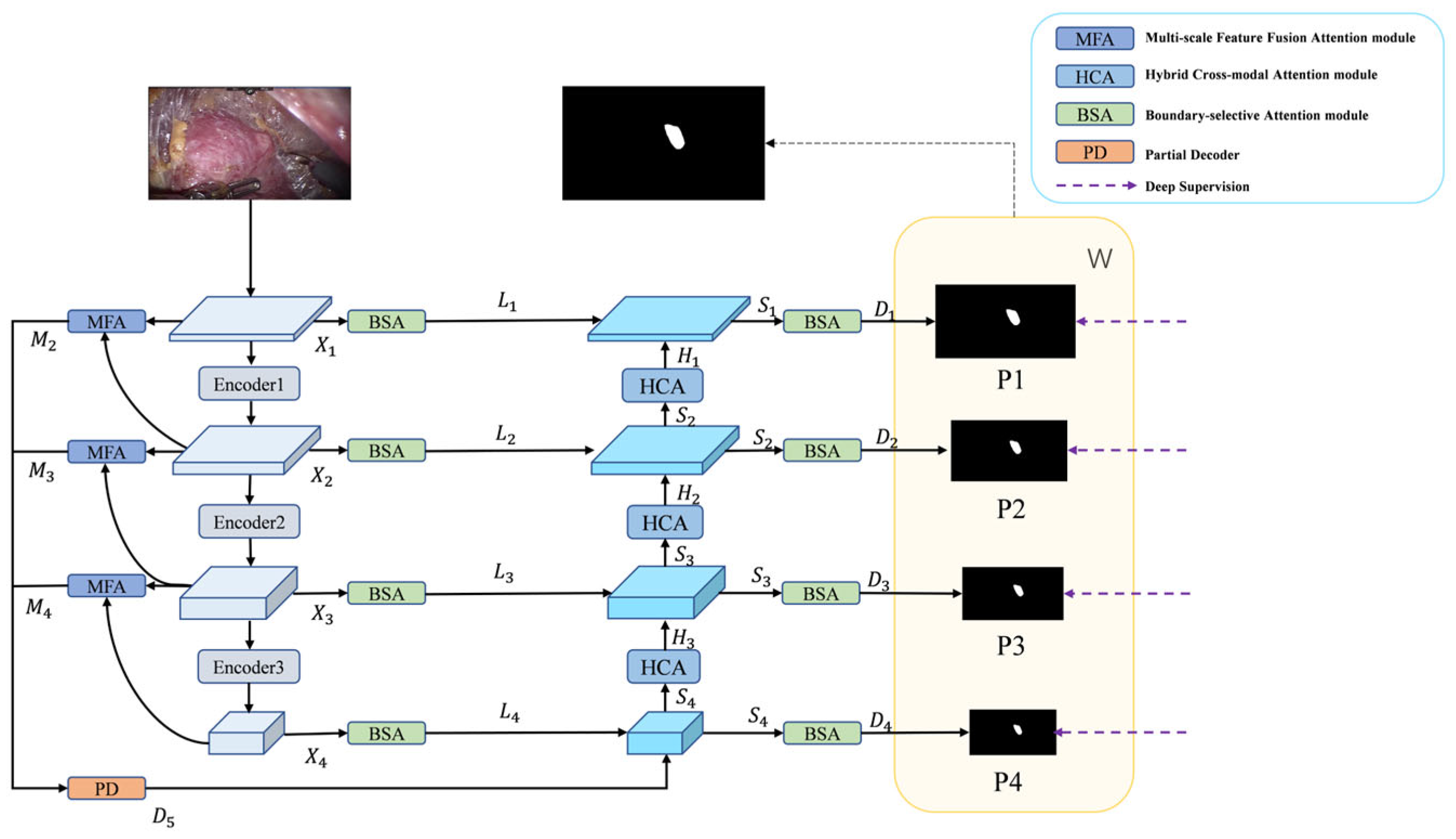
3.1. Overview
3.2. PVTv2 Backbone Network
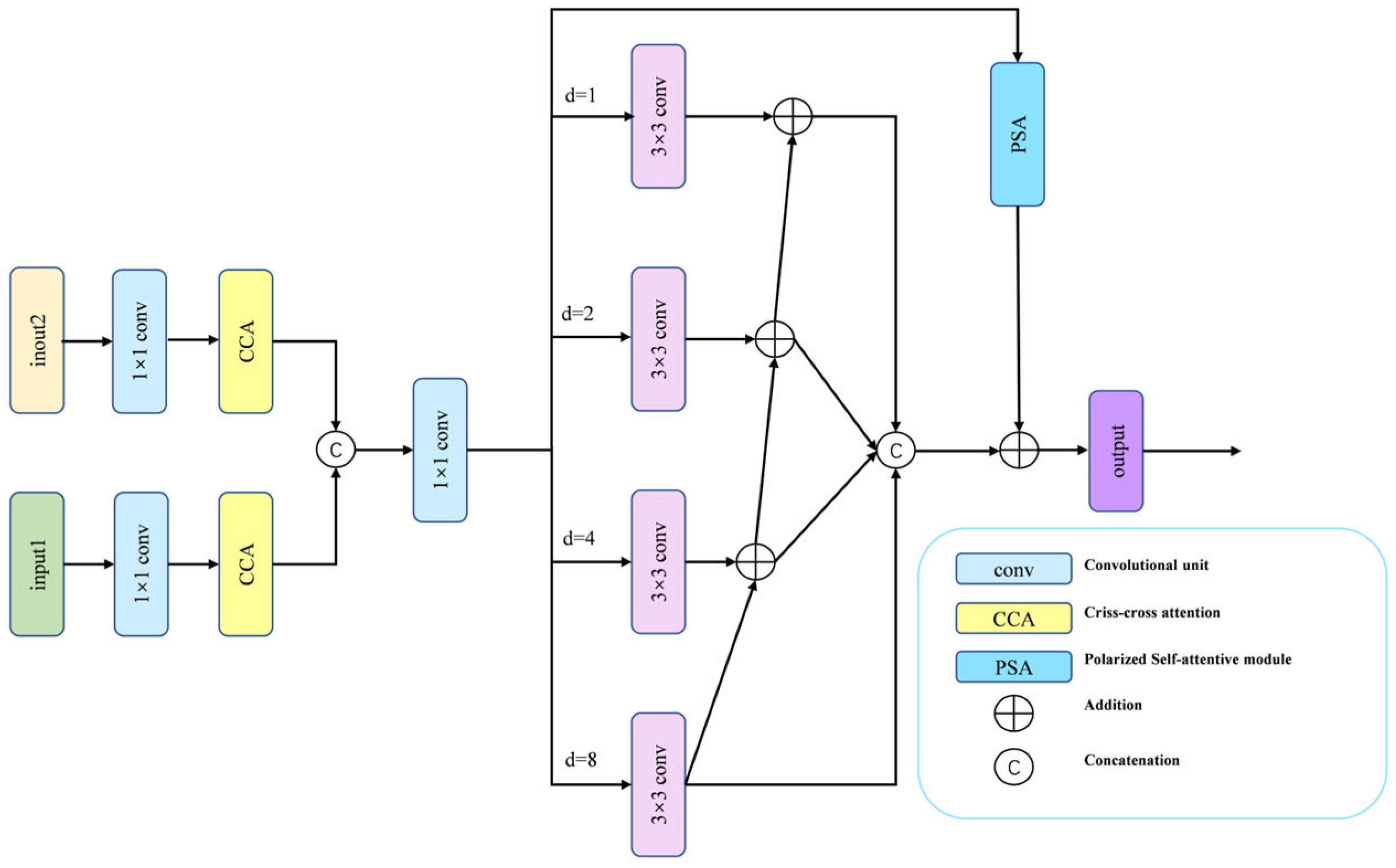
3.3. Multi-Scale Feature Fusion Attention Module
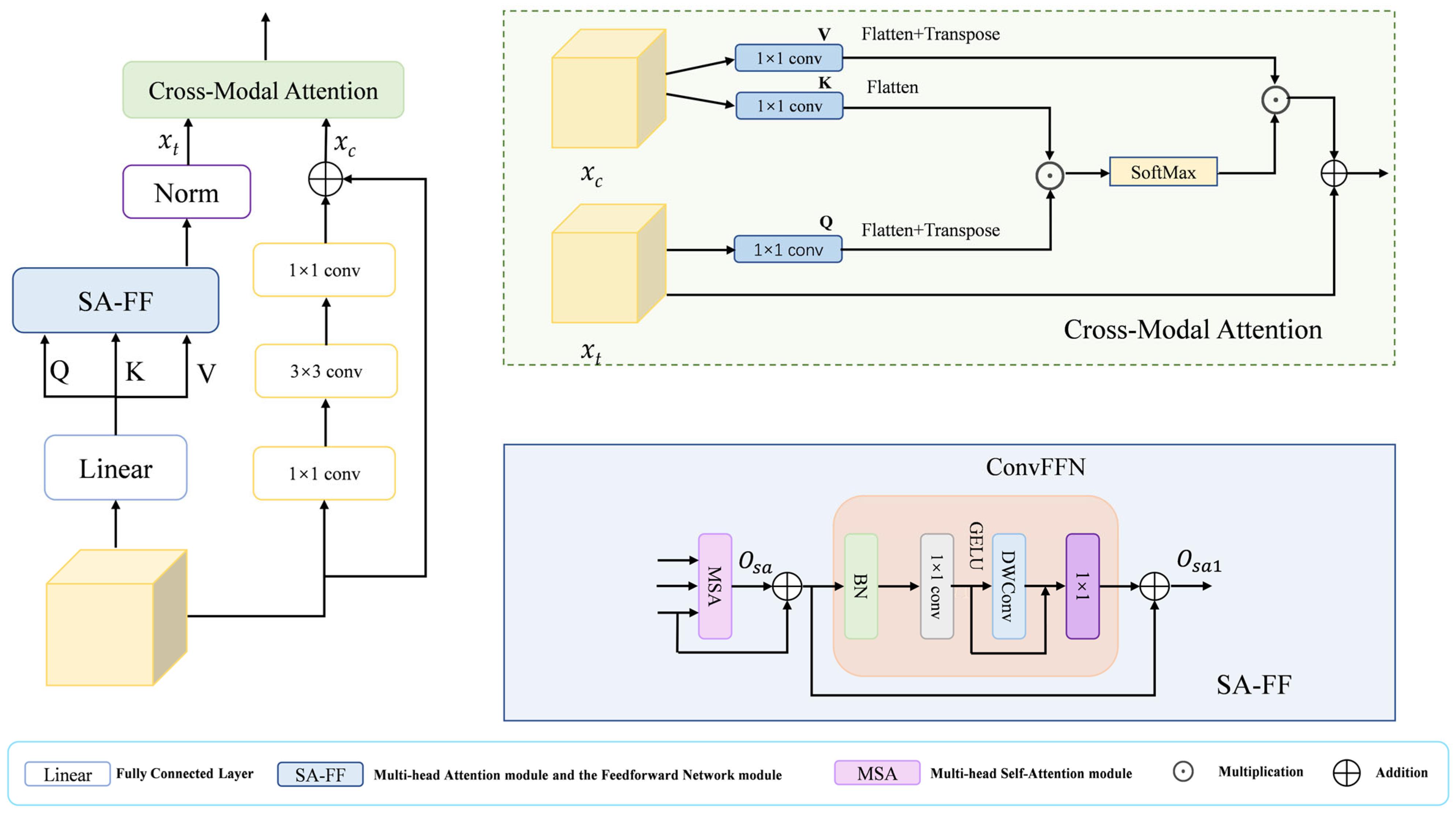
3.4. Hybrid Cross-Modal Attention Module
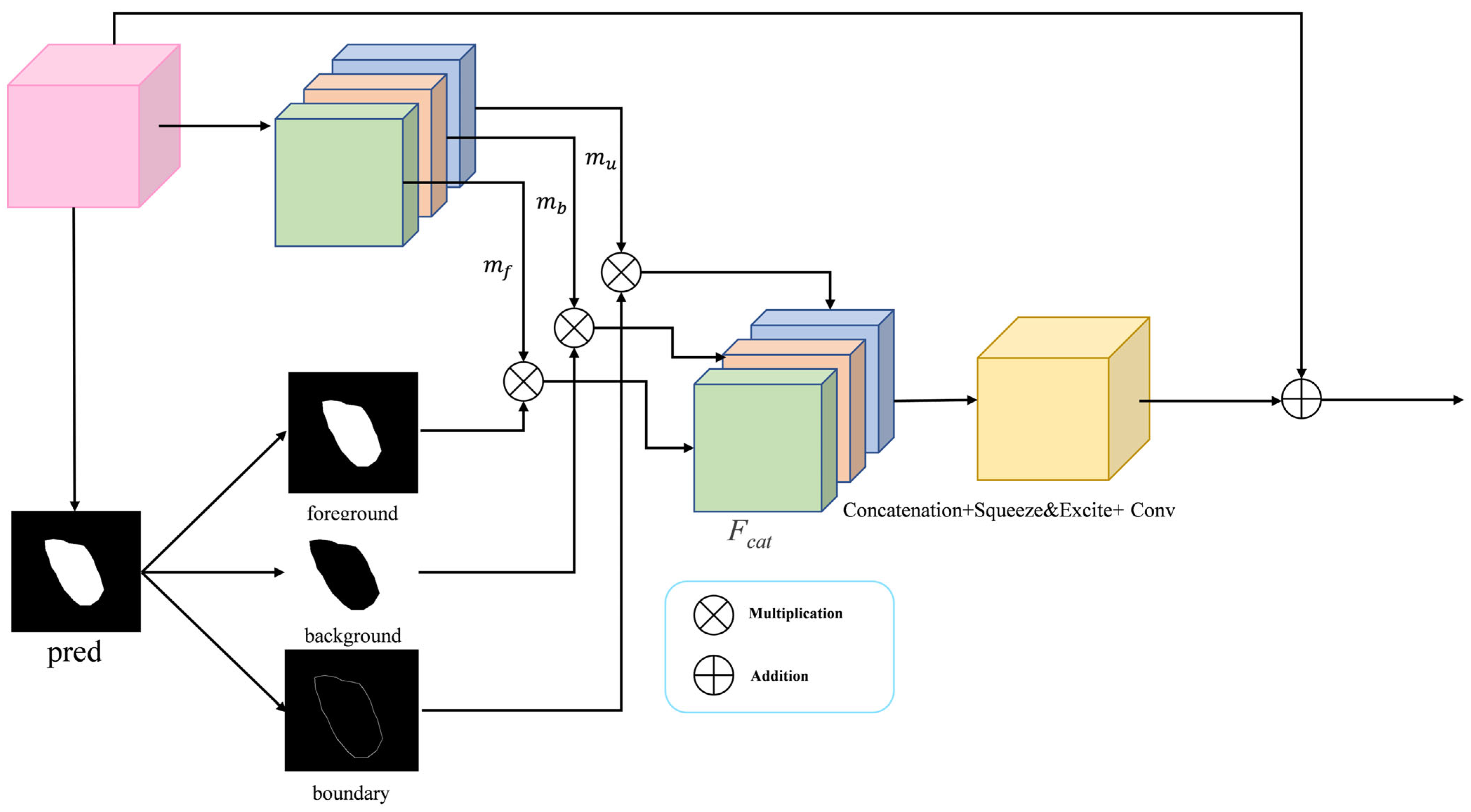
3.5. Boundary-Selective Attention Module
3.6. Loss Function
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.2.1. Experimental Set-Up and Evaluation Metrics
4.2.2. Quantitative Experiments
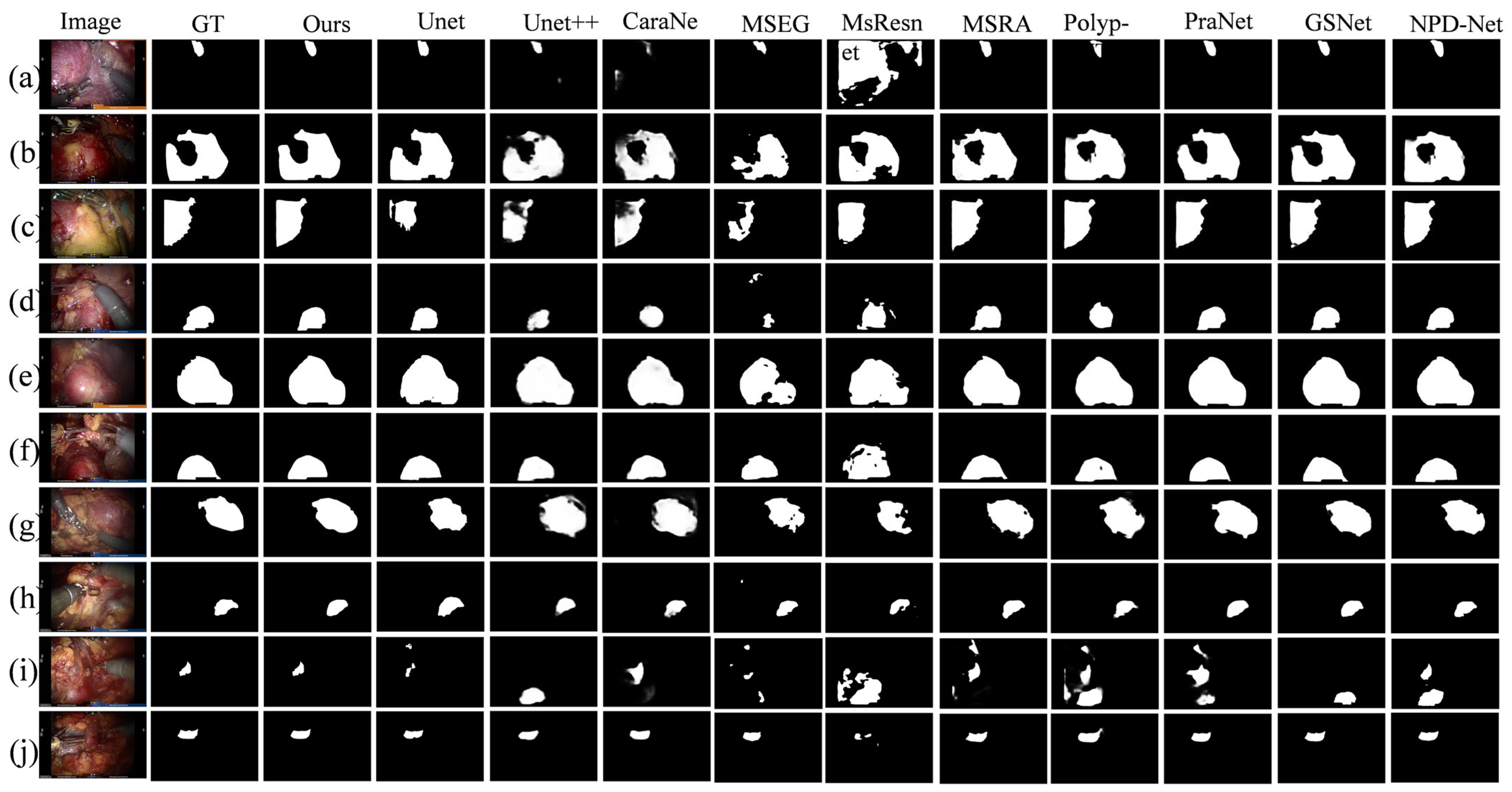
4.2.3. Qualitative Experiments
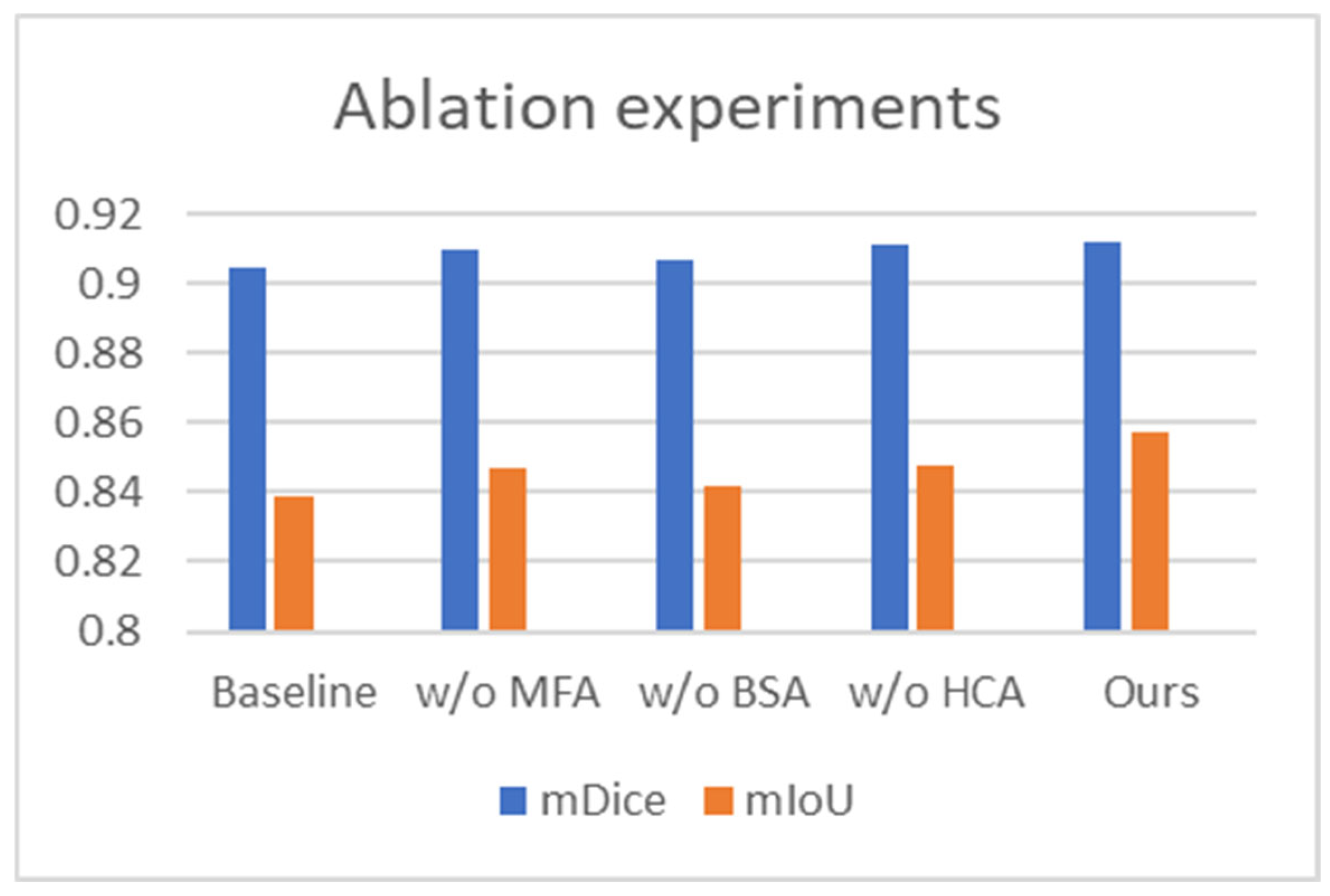
4.2.4. Ablation Experiments
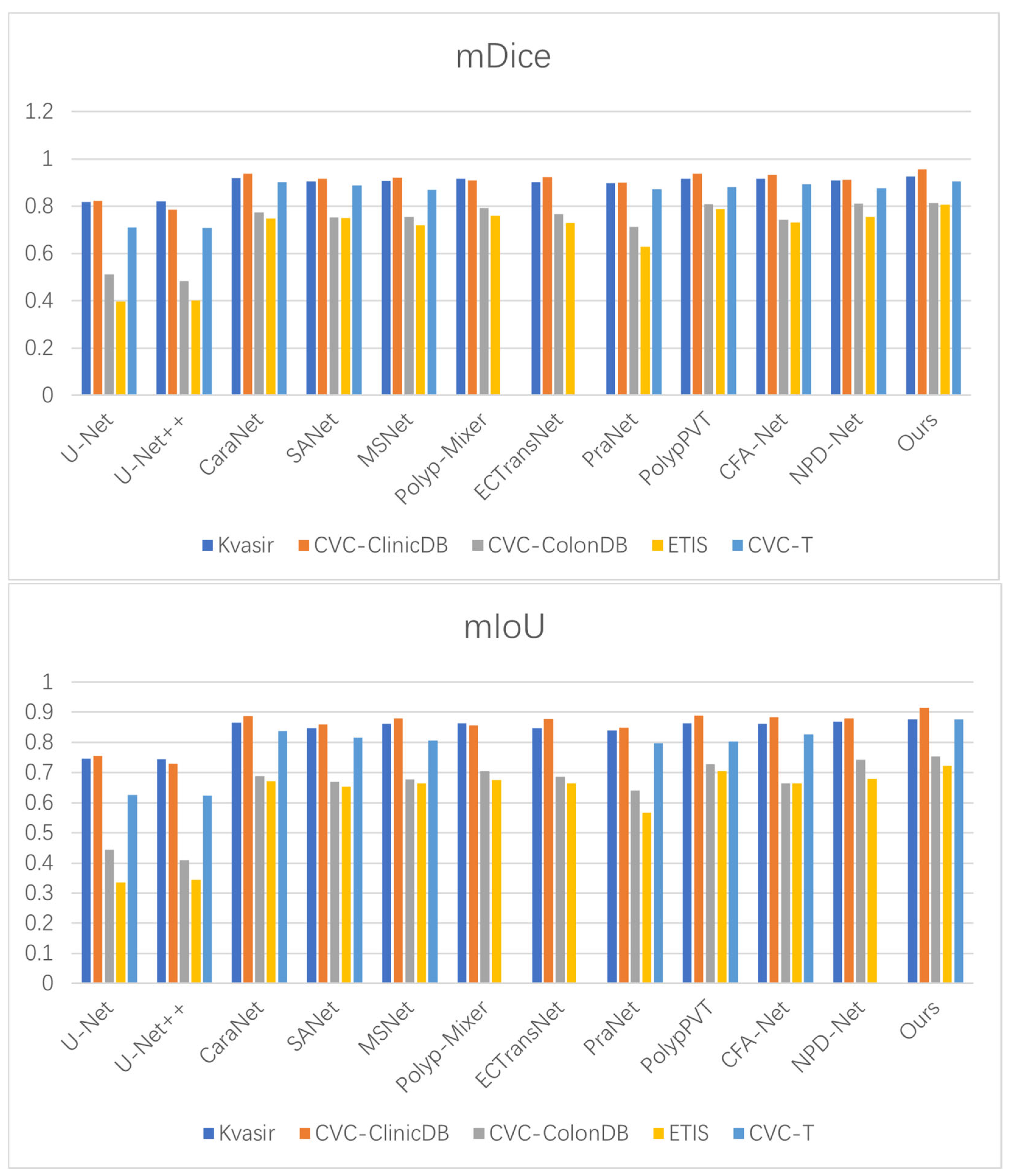
4.2.5. Generalization Experiments
4.2.6. Computational Efficiency
5. Discussion
5.1. Effectiveness
5.2. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, X.; Li, X.; Shi, C.; Ren, H.; Mumtaz, I. Dual-Feature Fusion Attention Network for Small Object Segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 160, 107065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015, 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Siddiquee, M.M.R.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. UNet++: A Nested U-Net Architecture for Medical Image Segmentation. In Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support, Proceedings of the 4th International Workshop, DLMIA 2018, and 8th International Workshop, ML-CDS 2018, Granada, Spain, 20 September 2018; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 11045, pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Lian, S.; Luo, Z.; Li, S. Weighted res-UNet for high-quality retina vessel segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2018 9th International Conference on Information Technology in Medicine and Education (ITME), Hangzhou, China, 19–21 October 2018; pp. 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, D.; Smedsrud, P.H.; Riegler, M.A.; Johansen, D.; De Lange, T.; Halvorsen, P.; Johansen, H.D. Resunet++: An advanced architecture for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Multimedia (ISM), San Diego, CA, USA, 9–11 December 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, D.; Riegler, M.A.; Johansen, D.; Halvorsen, P.; Johansen, H.D. DoubleU-Net: A deep convolutional neural network for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 33rd International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), Rochester, MN, USA, 28–30 July 2020; pp. 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alom, M.Z.; Yakopcic, C.; Hasan, M.; Taha, T.M.; Asari, V.K. Recurrent Residual U-Net for Medical Image Segmentation. J. Med. Imaging 2019, 6, 014006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglovikov, V.; Shvets, A. TernausNet: U-Net with VGG11 Encoder Pre-Trained on ImageNet for Image Segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.05746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An Image is Worth 16×16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Luo, X.; Adeli, E.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; Yuille, A.L.; Zhou, Y. TransUNet: Transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.04306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xie, E.; Li, X.; Fan, D.P.; Song, K.; Liang, D.; Lu, T.; Luo, P.; Shao, L. Pyramid Vision Transformer: A Versatile Backbone for Dense Prediction without Convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 6000–6010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wei, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Huang, T.S.; Shi, H. AlignSeg: Feature-Aligned Segmentation Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzini, D. Guided Upsampling Network for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the BMVC 2018: British Machine Vision Conference, Newcastle, UK, 3–6 September 2018; p. 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Peng, C.; Xue, X.; Sun, J. Exfuse: Enhancing Feature Fusion for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, D.L.; Xu, C.; Prince, J.L. Current methods in medical image segmentation. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2000, 2, 315–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohle, R.; Toennies, K.D. A New Approach for Model-Based Adaptive Region Growing in Medical Image Analysis. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2001, 2124, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.T.; Lei, C.C.; Hung, S.W. Computer-aided kidney segmentation on abdominal CT images. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2006, 10, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, H.; Chang, S.; Tao, C.; Wang, J.H.; Kaya, D.; Bae, K.T. Semiautomated segmentation of kidney from high-resolution multidetector computed tomography images using a graph-cuts technique. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2009, 33, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caselles, V.; Kimmel, R.; Sapiro, G. Geodesic active contours. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1997, 22, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, R.; Kawashima, A.; Takahashi, N.; Silva, A.; Vrtiska, T.; Leng, S.; Fletcher, J.; McCollough, C. Applications of dual energy CT in urologic imaging: An update. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 50, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grasso, M. Bladder cancer: A major public health issue. Eur. Urol. Suppl. 2008, 7, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Ni, J.; Elazab, A.; Wu, J. TA-Net: Triple Attention Network for Medical Image Segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 137, 104836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, D.P.; Ji, G.P.; Zhou, T.; Chen, G.; Fu, H.; Shen, J.; Shao, L. PraNet: Parallel Reverse Attention Network for Polyp Segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Lima, Peru, 4–8 October 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.H.; Wu, H.-Y.; Lin, Y.L. Hardnet-mseg: A simple encoder-decoder polyp segmentation neural network that achieves over 0.9 mean dice and 86 fps. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.07172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, A.; Guan, S.; Ko, H.; Loew, M.H. CaraNet: Context Axial Reverse Attention Network for Segmentation of Small Medical Objects. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2022: Image Processing, San Diego, CA, USA, 20–24 February 2022; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2022; pp. 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zeng, G.; Li, F.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H. FRBNet: Feedback refinement boundary network for semantic segmentation in breast ultrasound images. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 86, 105194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer Using Shifted Windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xie, E.; Li, X.; Fan, D.P.; Song, K.; Liang, D.; Lu, T.; Luo, P.; Shao, L. PVT v2: Improved Baselines with Pyramid Vision Transformer. Comput. Vis. Media 2022, 8, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Wang, W.; Fan, D.P.; Li, J.; Fu, H.; Shao, L. Polyp-PVT: Polyp Segmentation with Pyramid Vision Transformers. CAAI Artif. Intell. Res. 2023, 2, 9150015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Long, C.; Li, S.; Yang, J.; Jiang, F.; Zhou, R. MSRAformer: Multiscale Spatial Reverse Attention Network for Polyp Segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 151, 106274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cruz, L.B.; Araújo, J.D.L.; Ferreira, J.L.; Diniz, J.O.B.; Silva, A.C.; de Almeida, J.D.S.; de Paiva, A.C.; Gattass, M. Kidney segmentation from computed tomography images using deep neural network. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 123, 103906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Li, L.; Lian, S.; Chen, S.; Luo, Z. SERU: A cascaded SE-ResNeXT U-Net for kidney and tumor segmentation. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2020, 32, e5738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geethanjali, T.M.; Dinesh, M.S. Semantic segmentation of tumors in kidneys using attention U-Net models. In Proceedings of the 2021 5th International Conference on Electrical, Electronics, Communication, Computer Technologies and Optimization Techniques (ICEECCOT), Mysuru, India, 14–15 December 2021; pp. 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.; Zhang, G.; Liu, H.; Qin, Y.; Chen, Y. DCCTNet: Kidney Tumors Segmentation Based On Dual-Level Combination Of CNN And Transformer. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 27–30 October 2024; pp. 3112–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Xie, C.; Li, F.; Wang, J.; Lv, C.; Xie, G.; Nan, Y. A triple-stage self-guided network for kidney tumor segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 17th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Iowa City, IA, USA, 3–7 April 2020; pp. 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Su, L.; Huang, Q. Cascaded Partial Decoder for Fast and Accurate Salient Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–21 June 2019; pp. 3907–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhojanapalli, S.; Chakrabarti, A.; Glasner, D.; Li, D.; Unterthiner, T.; Veit, A. Understanding robustness of transformers for image classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10231–10241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Wei, Y.; Huang, L.; Huang, T.S. CCNet: Criss-Cross Attention for Semantic Segmentation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:1811.11721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, A.; Loew, M. Cfpnet: Channel-wise Feature Pyramid for Real-time Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Anchorage, AK, USA, 19–22 September 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, S.; Rastegari, M.; Caspi, A.; Shapiro, L.; Hajishirzi, H. ESPNet: Efficient Spatial Pyramid of Dilated Convolutions for Semantic Segmentation. Proc. ECCV 2018, 11212, 552–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, F.; Fan, X.; Huang, D. Polarized Self-Attention: Towards High-quality Pixel-wise Regression. arXiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Wang, S.; Huang, Q. F3Net: Fusion, Feedback and Focus for Salient Object Detection. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; pp. 12321–12328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.C.; Fu, C.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, F.Y.; Zhao, Y.L.; Sham, C.W. HSNet: A hybrid semantic network for polyp segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 150, 106173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Zhao, X.; Lv, L.; Zhang, L.; Sun, W.; Lu, H. Growth Simulation Network for Polyp Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision Conference, Xiamen, China, 13–15 October 2023; pp. 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Liao, T.; Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Xiao, G. A novel non-pretrained deep supervision network for polyp segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 2024, 154, 110554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, D.; Smedsrud, P.H.; Riegler, M.A.; Halvorsen, P.; de Lange, T.; Johansen, D.; Johansen, H.D. Kvasir-seg: A segmented polyp dataset. In Proceedings of the MultiMedia Modeling: 26th International Conference, MMM 2020, Daejeon, South Korea, 5–7 January 2020; pp. 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, J.; Sánchez, F.J.; Fernández-Esparrach, G.; Gil, D.; Rodríguez, C.; Vilariño, F. WM-DOVA maps for accurate polyp highlighting in colonoscopy: Validation vs. saliency maps from physicians. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2015, 43, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajbakhsh, N.; Gurudu, S.R.; Liang, J. Automated Polyp Detection in Colonoscopy Videos Using Shape and Context Information. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2015, 35, 630–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, D.; Bernal, J.; Sánchez, F.J.; Fernández-Esparrach, G.; López, A.M.; Romero, A.; Drozdzal, M.; Courville, A. A benchmark for endoluminal scene segmentation of colonoscopy images. J. Healthc. Eng. 2017, 2017, 4037190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.; Histace, A.; Romain, O.; Dray, X.; Granado, B. Toward Embedded Detection of Polyps in WCE Images for Early Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2013, 9, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Xu, C.; Nie, C.; Han, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, C. DBE-Net: Dual Boundary Guided Attention Exploration Network for Polyp Segmentation. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsch, D.; Neuhäuser, M. Wilcoxon-Signed-Rank Test. In International Encyclopedia of Statistical Science; Lovric, M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Fang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, E. Polyp Segmentation of Colonoscopy Images by Exploring the Uncertain Areas. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 52971–52981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.K.; Li, Z.G.; Li, C.Y.; Gao, H.Y. ECTransNet: An automatic polyp segmentation network based on multi-scale edge complementary. J. Digit. Imaging 2023, 36, 2427–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.H.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, Y.H.; Zhang, Z.Q. Polyp-Mixer: An efficient context-aware MLP-based paradigm for polyp segmentation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 33, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Zhou, Y.; He, K.L.; Gong, C.; Yang, J.; Fu, H.Z.; Shen, D.Z. Cross-level Feature Aggregation Network for Polyp Segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 140, 109555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
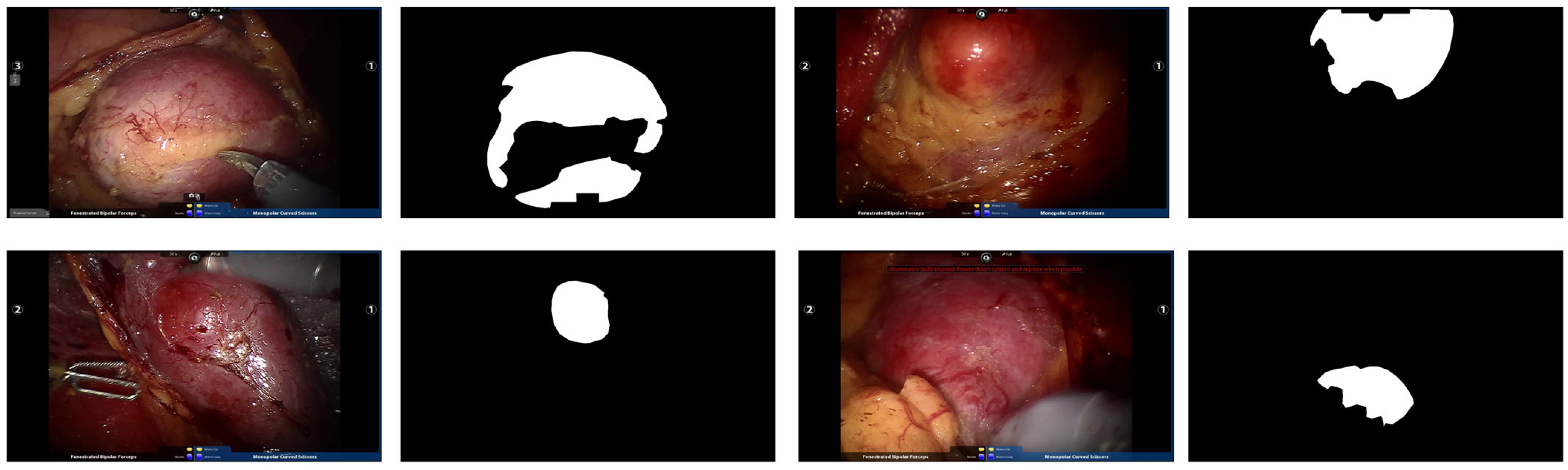
| Dataset | Image Size | Image Number | Train Number | Test Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Re-TMRS | Variable | 2823 | 2258 | 565 |
| Kvasir-SEG | Variable | 1000 | 900 | 100 |
| CVC-ClinicDB | 384 × 288 | 612 | 550 | 62 |
| CVC-ColonDB | 574 × 500 | 380 | 0 | 380 |
| ETIS | 1225 × 966 | 196 | 0 | 196 |
| CVC-T | 574 × 500 | 60 | 0 | 60 |
| Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net | 0.780 | 0.699 | 0.021 | 0.884 | 12.477 |
| U-Net++ | 0.804 | 0.726 | 0.023 | 0.895 | 12.210 |
| CaraNet | 0.833 | 0.757 | 0.022 | 0.911 | 12.442 |
| HarDMSEG | 0.791 | 0.702 | 0.022 | 0.890 | 12.394 |
| Multi-scale-Resnet | 0.545 | 0.457 | 0.094 | 0.745 | 18.671 |
| MSRAformer | 0.893 | 0.826 | 0.014 | 0.942 | 11.341 |
| PolypPVT | 0.854 | 0.798 | 0.020 | 0.922 | 12.151 |
| PraNet | 0.897 | 0.828 | 0.013 | 0.945 | 10.853 |
| HSNet | 0.908 | 0.836 | 0.012 | 0.951 | 10.544 |
| GSNet | 0.909 | 0.838 | 0.012 | 0.951 | 10.345 |
| NPD-Net | 0.906 | 0.833 | 0.012 | 0.883 | 10.826 |
| Ours | 0.912 | 0.857 | 0.011 | 0.952 | 10.336 |
| Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 0.905 | 0.839 | 0.013 | 0.945 | 10.634 |
| w/o MFA | 0.910 | 0.847 | 0.012 | 0.950 | 10.554 |
| w/o BSA | 0.907 | 0.842 | 0.012 | 0.946 | 10.609 |
| w/o HCA | 0.911 | 0.848 | 0.012 | 0.951 | 10.563 |
| Ours | 0.912 | 0.857 | 0.011 | 0.952 | 10.336 |
| Kvasir | CVC-ClinicDB | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | ||||||
| U-Net | 0.818 | 0.746 | 0.019 | 0.823 | 0.755 | 0.019 |
| U-Net++ | 0.821 | 0.743 | 0.022 | 0.784 | 0.729 | 0.022 |
| CaraNet | 0.918 | 0.865 | 0.007 | 0.936 | 0.887 | 0.007 |
| SANet | 0.904 | 0.847 | 0.012 | 0.916 | 0.859 | 0.012 |
| MSNet | 0.907 | 0.862 | 0.008 | 0.921 | 0.879 | 0.008 |
| Polyp-Mixer | 0.916 | 0.864 | —— | 0.908 | 0.856 | —— |
| ECTransNet | 0.901 | 0.847 | —— | 0.923 | 0.878 | —— |
| PraNet | 0.898 | 0.840 | 0.009 | 0.899 | 0.849 | 0.009 |
| PolypPVT | 0.917 | 0.864 | 0.006 | 0.937 | 0.889 | 0.006 |
| CFA-Net | 0.915 | 0.861 | 0.007 | 0.933 | 0.883 | 0.007 |
| NPD-Net | 0.909 | 0.869 | 0.008 | 0.912 | 0.879 | 0.007 |
| Ours | 0.925 | 0.876 | 0.023 | 0.955 | 0.915 | 0.006 |
| CVC-ColonDB | ETIS | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | ||||||
| U-Net | 0.512 | 0.444 | 0.061 | 0.398 | 0.335 | 0.036 |
| U-Net++ | 0.483 | 0.410 | 0.064 | 0.401 | 0.344 | 0.035 |
| CaraNet | 0.773 | 0.689 | 0.042 | 0.747 | 0.672 | 0.017 |
| SANet | 0.753 | 0.670 | 0.043 | 0.750 | 0.654 | 0.015 |
| MSNet | 0.755 | 0.678 | 0.041 | 0.719 | 0.664 | 0.020 |
| Polyp-Mixer | 0.791 | 0.706 | —— | 0.759 | 0.676 | —— |
| ECTransNet | 0.766 | 0.687 | —— | 0.728 | 0.665 | —— |
| PraNet | 0.712 | 0.640 | 0.045 | 0.628 | 0.567 | 0.031 |
| PolypPVT | 0.808 | 0.727 | 0.031 | 0.787 | 0.706 | 0.013 |
| CFA-Net | 0.743 | 0.665 | 0.039 | 0.732 | 0.665 | 0.014 |
| NPD-Net | 0.811 | 0.742 | 0.028 | 0.754 | 0.679 | 0.017 |
| Ours | 0.814 | 0.753 | 0.012 | 0.805 | 0.722 | 0.012 |
| CVC-T | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Model | |||
| U-Net | 0.710 | 0.627 | 0.022 |
| U-Net++ | 0.707 | 0.624 | 0.008 |
| CaraNet | 0.903 | 0.838 | 0.007 |
| SANet | 0.888 | 0.815 | 0.008 |
| MSNet | 0.869 | 0.807 | 0.010 |
| PraNet | 0.871 | 0.797 | 0.010 |
| PolypPVT | 0.880 | 0.802 | 0.011 |
| CFA-Net | 0.893 | 0.827 | 0.008 |
| NPD-Net | 0.876 | 0.804 | 0.007 |
| Ours | 0.904 | 0.876 | 0.006 |
| Model | Input Size | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net | (3, 352, 352) | 31.044 | 103.489 |
| U-Net++ | (3, 352, 352) | 47.195 | 37.923 |
| CaraNet | (3, 352, 352) | 46.640 | 21.750 |
| HarDMSEG | (3, 352, 352) | 17.424 | 11.400 |
| PolypPVT | (3, 352, 352) | 25.108 | 10.018 |
| PraNet | (3, 352, 352) | 30.498 | 13.150 |
| HSNet | (3, 352, 352) | 29.257 | 10.943 |
| GSNet | (3, 352, 352) | 81.980 | 30.430 |
| NPD-Net | (3, 352, 352) | 29.210 | 14.540 |
| Ours | (3, 352, 352) | 31.095 | 13.002 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Xu, C.; Li, Z. BEMF-Net: A Boundary-Enhanced Multi-Scale Feature Fusion Network. Electronics 2026, 15, 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics15020430
Zhang J, Xu C, Li Z. BEMF-Net: A Boundary-Enhanced Multi-Scale Feature Fusion Network. Electronics. 2026; 15(2):430. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics15020430
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jiayi, Chao Xu, and Zhengping Li. 2026. "BEMF-Net: A Boundary-Enhanced Multi-Scale Feature Fusion Network" Electronics 15, no. 2: 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics15020430
APA StyleZhang, J., Xu, C., & Li, Z. (2026). BEMF-Net: A Boundary-Enhanced Multi-Scale Feature Fusion Network. Electronics, 15(2), 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics15020430






