LLM-SPSS: An Efficient LLM-Based Secure Partitioned Storage Scheme in Distributed Hybrid Clouds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Technologies
2.1. Large Language Models
2.2. MapReduce Distributed Computing Framework
2.3. Cloud Storage Partitioning Technologies
3. LLM-SPSS: An Efficient LLM-Based Secure Partitioned Storage Scheme in Distributed Hybrid Clouds
3.1. System Architecture
3.2. Sensitive Data Labeling Model and Fine-Tuning Design
3.2.1. Problem Definition
3.2.2. Model Selection
3.2.3. Large Language Model Fine-Tuning
3.2.4. Sensitive Label Generation Process
| Algorithm 1 Sensitive- Data Labeling Workflow |
|
3.3. Data Partitioning and MapReduce Parallel Processing
| Algorithm 2 Map Phase: Local Sensitive Data Labeling |
|
3.4. Reduce Phase: Result Aggregation and Global Label Generation
| Algorithm 3 Reduce Phase: Result Aggregation |
|
3.5. Hybrid Cloud Data Partitioned Storage
4. Experimental Design and Implementation
4.1. Dataset and Preprocessing
4.2. Experimental Environment and Configuration
4.3. Experimental Design and Results
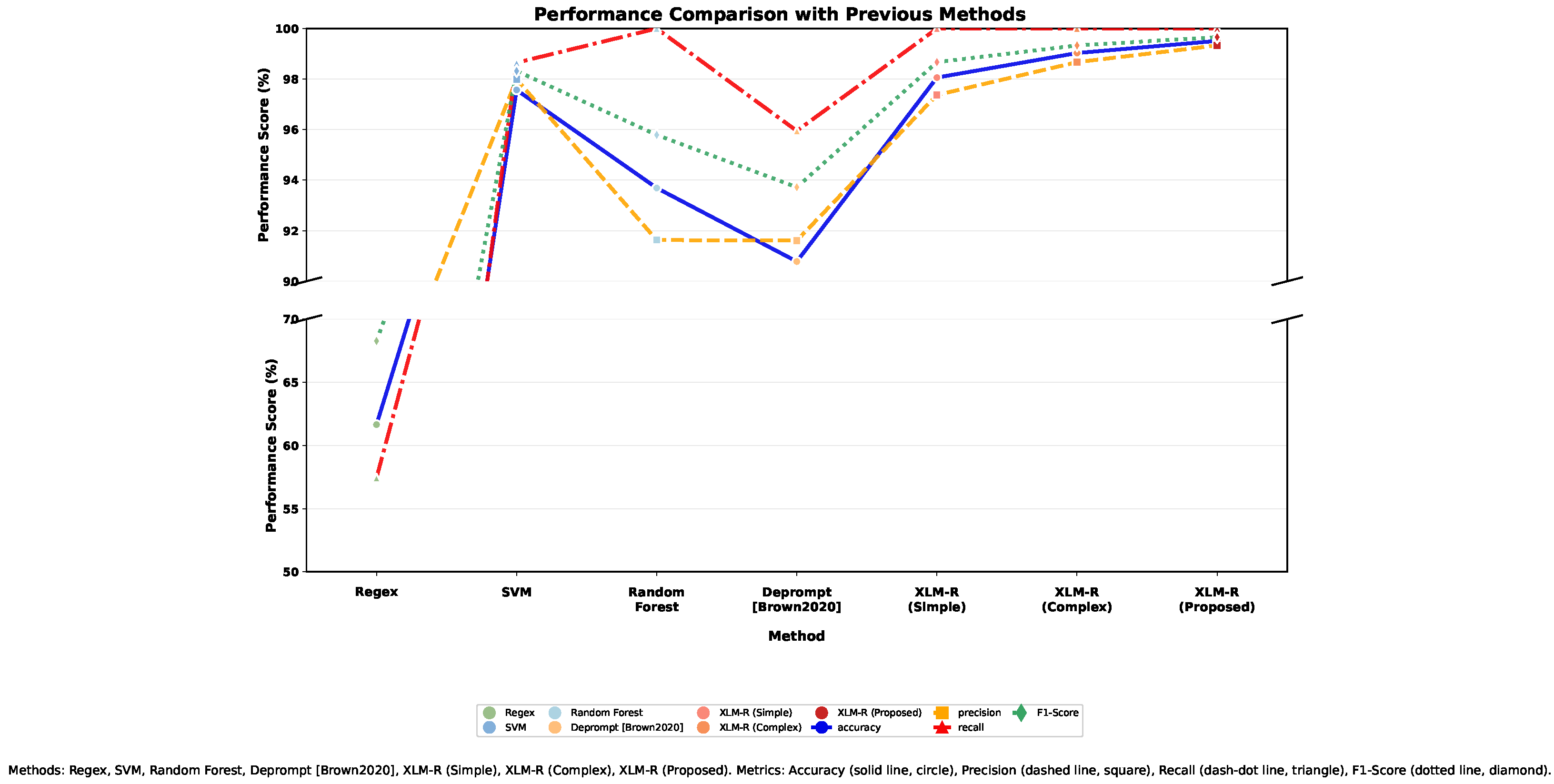
4.3.1. Comparison with Traditional Schemes
4.3.2. Comparison of Training Strategies
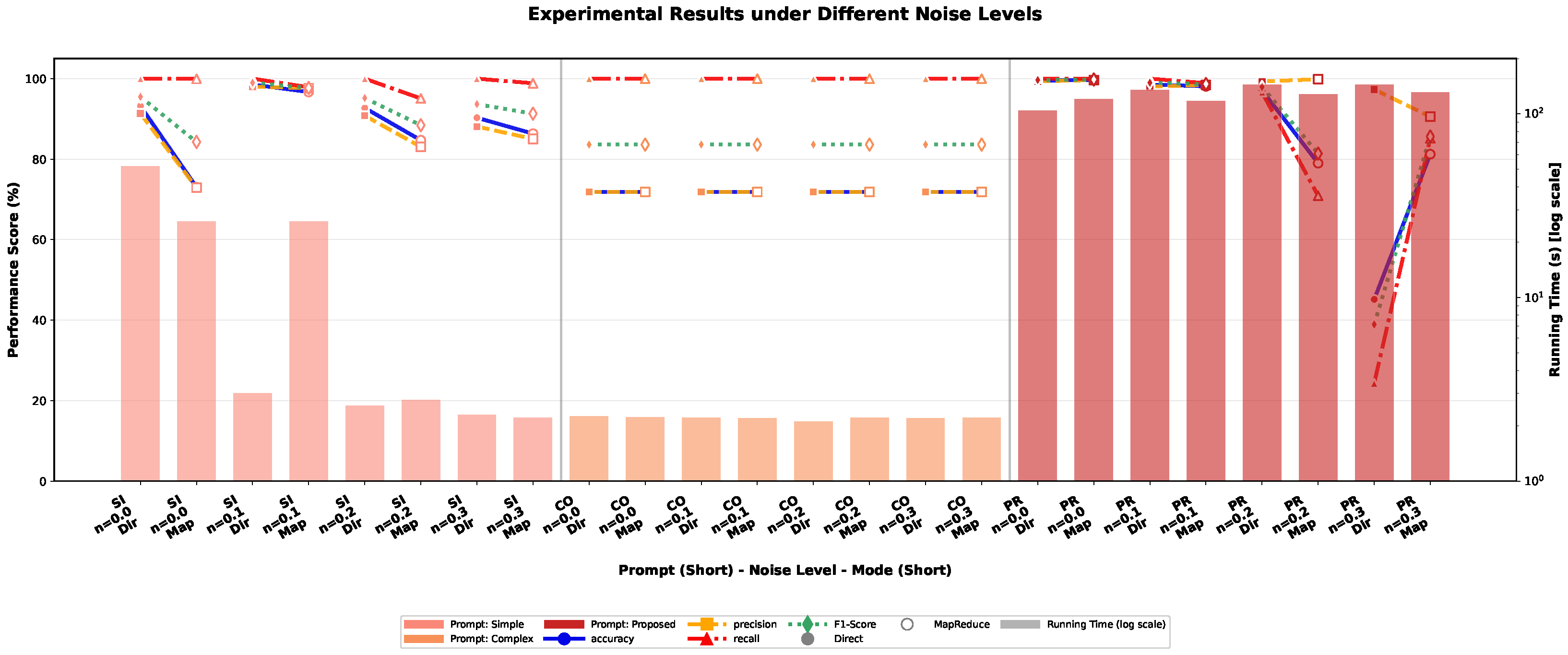
4.3.3. Robustness Evaluation Under Noisy Conditions
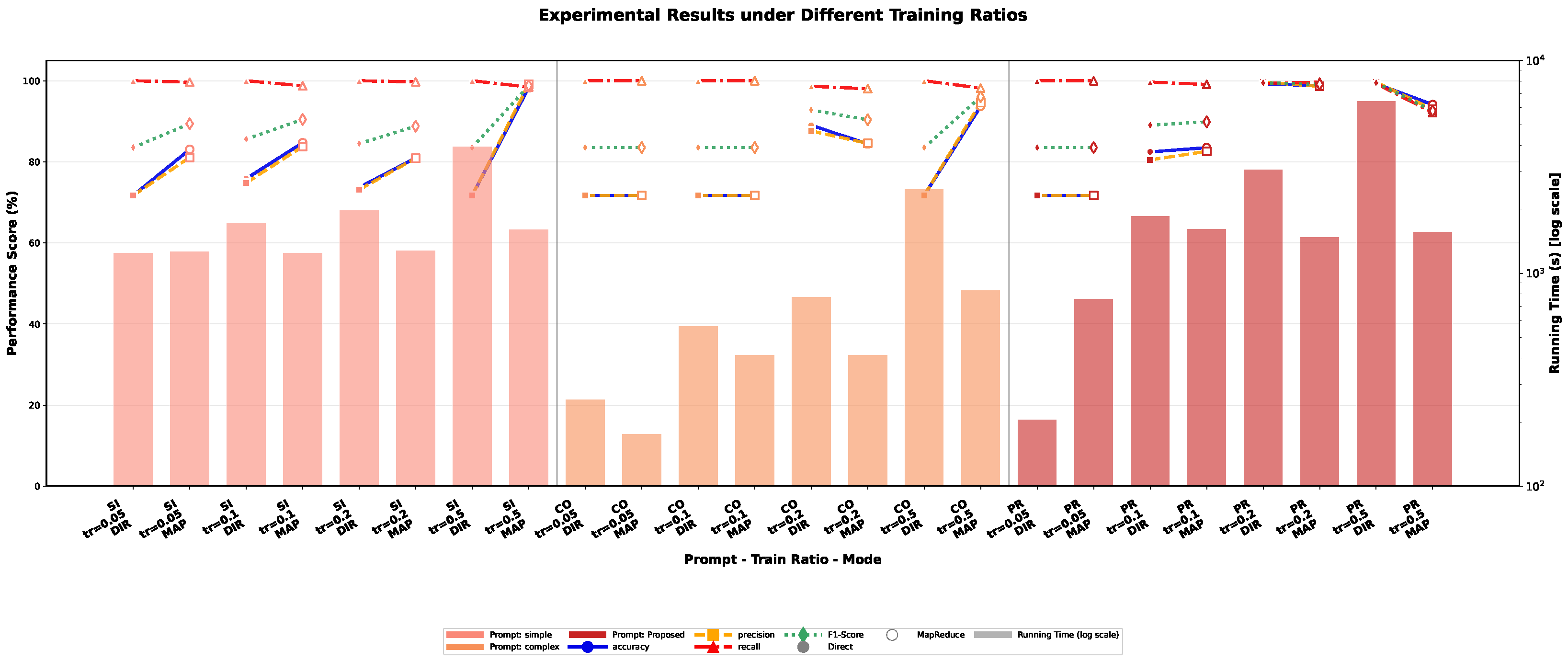
4.3.4. Impact of Training Data Scale on Model Performance
4.3.5. Comparison of Large Language Models of Similar Scale
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Full Complex Prompt Template
- Please judge whether the text contains sensitive information.
- Sensitive information includes the following categories with detailed
- definitions:
References
- Gantz, J.; Reinsel, D. Extracting Value from Chaos; IDC iView White Paper; IDC: Framingham, MA, USA, 2011; Available online: https://www.emc.com/digital_universe (accessed on 28 November 2025).
- Gartner, Inc. Gartner Forecasts Worldwide Public Cloud End-User Spending to Total $723 Billion in 2025, Press Release; Gartner: Stamford, CT, USA, 19 November 2024. Available online: https://www.gartner.com/en/newsroom/press-releases/2024-11-19-gartner-forecasts-worldwide-public-cloud-end-user-spending-to-total-723-billion-dollars-in-2025 (accessed on 28 November 2025).
- Sawle, P.; Baraskar, T. Survey on Data Classification and Data Encryption Techniques Used in Cloud Computing. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2016, 135, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, M.A.; Mohammadi, M.; Hashemi, S. Regular Expression Search over Encrypted Data in the Cloud. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Cloud Computing Technology and Science (CloudCom), Singapore, 15–18 December 2014; pp. 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenRaven. Introduction to Regex Based Data Classification for the Cloud. OpenRaven. 2022. Available online: https://www.openraven.com/articles/introduction-to-regex-based-data-classification-for-the-cloud-writing-and-developing-dataclasses-for-scale (accessed on 28 November 2025).
- Mainetti, L.; Elia, A. Detecting Personally Identifiable Information Through Natural Language Processing: A Step Forward. Appl. Syst. Innov. 2025, 8, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Peng, H.; Li, J.; Xia, C.; Yang, R.; Sun, L.; Yu, P.S.; He, L. A Survey on Text Classification: From Shallow to Deep Learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.00364. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.00364 (accessed on 28 November 2025).
- Tang, W. Using Machine Learning to Help Detect Sensitive Information. ISACA Now Blog, 13 November 2023. Available online: https://www.isaca.org/resources/news-and-trends/isaca-now-blog/2023/using-machine-learning-to-help-detect-sensitive-information (accessed on 25 June 2024).
- Sun, X.; Liu, G.; He, Z.; Li, H.; Li, X. DePrompt: Desensitization and Evaluation of Personal Identifiable Information in Large Language Model Prompts. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.08930. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2408.08930 (accessed on 25 June 2024).
- Rama, B.K.; Thaiyalnayaki, S. A Novel Integration of Machine Learning-Based Data Classification with Optimized Cryptographic Techniques for Secure Cloud Storage. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 2025, 103, 1808–1816. Available online: https://www.jatit.org/volumes/Vol103No5/14Vol103No5.pdf (accessed on 28 November 2025).
- Addula, S.R.; Meesala, M.K.; Ravipati, P.; Sajja, G.S. A Hybrid Autoencoder and Gated Recurrent Unit Model Optimized by Honey Badger Algorithm for Enhanced Cyber Threat Detection in IoT Networks. Secur. Priv. 2025, 8, e70086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, B.; Wang, L. A Survey of Semantics-Aware Performance Optimization for Data-Intensive Computing. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.11540. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.-W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-Training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (NAACL-HLT 2019), Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; pp. 4171–4186. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language Models Are Few-Shot Learners. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 33 (NeurIPS 2020), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 6–12 December 2020; pp. 1877–1901. [Google Scholar]
- Boehnke, J.; Pontikes, E.; Bhargava, H.K. Decoding Unstructured Text: Enhancing LLM Classification Accuracy with Redundancy and Confidence, Technical Report; Graduate School of Management, University of California Davis: Davis, CA, USA, 7 June 2024. Available online: https://d30i16bbj53pdg.cloudfront.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/Decoding-Unstructured-Text-Enhancing-LLM-Classification.pdf (accessed on 28 November 2025).
- Howard, J.; Ruder, S. Universal Language Model Fine-Tuning for Text Classification (ULMFiT). arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.06146. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1801.06146 (accessed on 28 November 2025).
- Zhou, Z.; Li, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, S.; Chao, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Shi, Q.; Tan, Z.; Han, X.; et al. LLM × MapReduce: Simplified Long-Sequence Processing using Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the 63rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), Vienna, Austria, 27 July–1 August 2025; pp. 27664–27678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, J.; Ghemawat, S. MapReduce: Simplified Data Processing on Large Clusters. Commun. ACM 2008, 51, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitin, G.; Xing, L.; Dai, Y. Optimal data partitioning in cloud computing system with random server assignment. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2017, 70, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Li, M. Enhanced Secure Storage and Data Privacy Management System for Big Data Based on Multilayer Model. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 32285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2017, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Chen, W.; Luo, Y.; Long, Y.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lin, B.; Cai, D.; He, X. Model Compression and Efficient Inference for Large Language Models: A Survey. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.09748. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.09748 (accessed on 28 November 2025).
- Hu, Z.; Wang, L.; Lan, Y.; Xu, W.; Lim, E.-P.; Bing, L.; Xu, X.; Poria, S.; Lee, R.K.-W. LLM-Adapters: An Adapter Family for Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning of Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP 2023), Singapore, 6–10 December 2023; pp. 5254–5276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Eisner, J. Learning How to Ask: Querying LMs with Mixtures of Soft Prompts. In Proceedings of the 2021 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (NAACL 2021), Online, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 5203–5212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffel, C.; Shazeer, N.; Roberts, A.; Lee, K.; Narang, S.; Matena, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, P.-J. Exploring the Limits of Transfer Learning with a Unified Text-to-Text Transformer. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2020, 21, 5485–5551. [Google Scholar]
- Conneau, A.; Khandelwal, K.; Goyal, N.; Chaudhary, V.; Wenzek, G.; Guzmán, F.; Grave, E.; Ott, M.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Stoyanov, V. Unsupervised Cross-lingual Representation Learning at Scale. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL 2020), Online, 5–10 July 2020; pp. 8440–8451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, N.; Chaudhary, V.; Wenzek, G.; Guzmán, F.; Grave, E.; Ott, M.; Stoyanov, V.; Zettlemoyer, L. Larger-Scale Transformers for Multilingual Masked Language Modeling. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.01373. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.01373 (accessed on 28 November 2025).
- Chai, Y.; Liang, Y.; Duan, N. Cross-Lingual Ability of Multilingual Masked Language Models: A Study of Language Structure. In Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL 2022), Dublin, Ireland, 22–27 May 2022; pp. 3041–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T. Hadoop: The Definitive Guide, 3rd ed.; O’Reilly Media: Sebastopol, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Nghiem, P.P.; Figueira, S.M. Towards Efficient Resource Provisioning in MapReduce. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2016, 95, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Cheng, L.; Boutaba, R. Cloud Computing: State-of-the-Art and Research Challenges. J. Internet Serv. Appl. 2010, 1, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyya, R.; Broberg, J.; Goscinski, A. Cloud Computing: Principles and Paradigms; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Agyekum, J.; Mazumdar, S.; Scheich, C. ADAPT: An effective data-aware multicloud data placement framework. Cluster Comput. 2025, 28, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yolchuyev, A.; Levendovszky, J. Data Chunks Placement Optimization for Hybrid Cloud Storage Systems. Future Internet 2021, 13, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simo, D.R.; Hernández-Cartagena, A.; Vázquez-Chávez, J.; Hernández, G.; Pulido, A. Sensitive-Data-Detection: Dataset and Code for Sensitive Data Detection. GitHub Repository. Available online: https://github.com/SimoDR/sensitive-data-detection (accessed on 28 November 2025).
- Taylor, J.; Smith, A.; Johnson, R.; Brown, L.; Davis, M. Synthetic Data for Privacy-Preserving Clinical Risk Prediction. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, A.; Mahmoud, M. A Systematic Review of Synthetic Data Generation Techniques Using Generative AI. Electronics 2024, 13, 3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Type | Description | Example/Template |
|---|---|---|
| None | No instruction is prepended. The raw text is fed directly into the model. | [Text] |
| Simple | A concise, direct instruction listing the sensitive categories. | “Determine whether the following text contains sensitive information (health, political, judicial, religious, sexual orientation, racial): [Text]” |
| Complex | A structured, multi-line instruction providing definitions for each sensitive category. | (Full template provided in Appendix A for reproducibility) |
| Component | Specification |
|---|---|
| CPU | Intel(R) Xeon(R) Platinum 8358 CPU @ 2.60 GHz |
| GPU | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090 |
| RAM | 128 GiB |
| OS | Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (64-bit) |
| Experimental Aspect | Configurations/Values |
|---|---|
| Comparison Baselines | Regex, SVM, Random Forest, DePrompt [9] |
| Our Model (XLM-R) Variants | No Prompt, Simple Prompt, Complex Prompt (see Table 1) |
| Training Strategy | Direct (single node), MapReduce (four-node simulation) |
| Noise Robustness | Noise levels: 0%, 10%, 20%, 30% |
| Data Scale Sensitivity | Training data proportions: 5%, 20%, 50%, 100% |
| Model Scale Comparison | XLM-R-base, XLM-R-large, InfoXLM-base |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Zhou, R.; Che, B.; Yang, L. LLM-SPSS: An Efficient LLM-Based Secure Partitioned Storage Scheme in Distributed Hybrid Clouds. Electronics 2026, 15, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics15010030
Zhou R, Che B, Yang L. LLM-SPSS: An Efficient LLM-Based Secure Partitioned Storage Scheme in Distributed Hybrid Clouds. Electronics. 2026; 15(1):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics15010030
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Ran, Bichen Che, and Liangbin Yang. 2026. "LLM-SPSS: An Efficient LLM-Based Secure Partitioned Storage Scheme in Distributed Hybrid Clouds" Electronics 15, no. 1: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics15010030
APA StyleZhou, R., Che, B., & Yang, L. (2026). LLM-SPSS: An Efficient LLM-Based Secure Partitioned Storage Scheme in Distributed Hybrid Clouds. Electronics, 15(1), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics15010030





