A Lightweight Denoising Network with TCN–Mamba Fusion for Modulation Classification
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose a unified lightweight AMC framework that addresses the challenges of low-SNR robustness, local feature extraction, and global dependency modeling in a single design, improving performance in both noisy environments and real-time applications.
- The NATM is introduced to enhance effective SNR, significantly improving robustness under low-SNR conditions where traditional methods struggle.
- A parallel dual-branch architecture integrates TCN and Mamba modules, effectively balancing local symbol-level feature extraction and global long-range dependency modeling.
2. Related Work
2.1. Temporal Convolutional Networks (TCN)
2.2. Mamba and State-Space Models
2.3. Denoising and Robust AMC
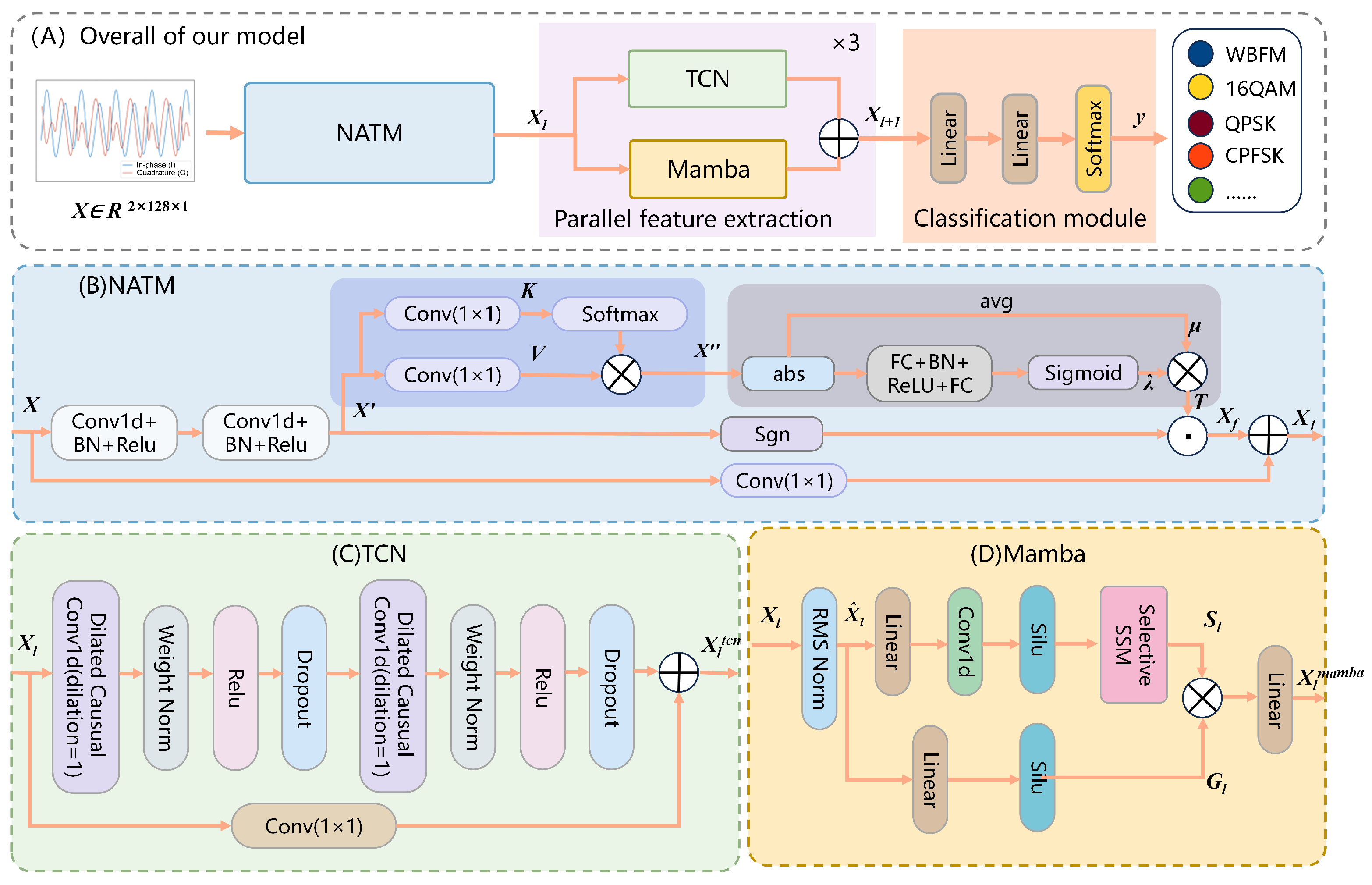
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Problem Formulation
3.2. Proposed Model
3.2.1. Non-Local Adaptive Thresholding Module (NATM)
3.2.2. Parallel Feature Extraction
3.2.3. Classification Module
3.3. Datasets and Experimental Settings
3.3.1. Datasets
3.3.2. Leakage-Controlled Partitioning
- GroupKFold: Partitioned by capture ID to ensure that no contiguous IQ segments are shared between splits [18].
3.3.3. Training Setup
3.3.4. Reproducibility and Confidence Intervals
4. Results
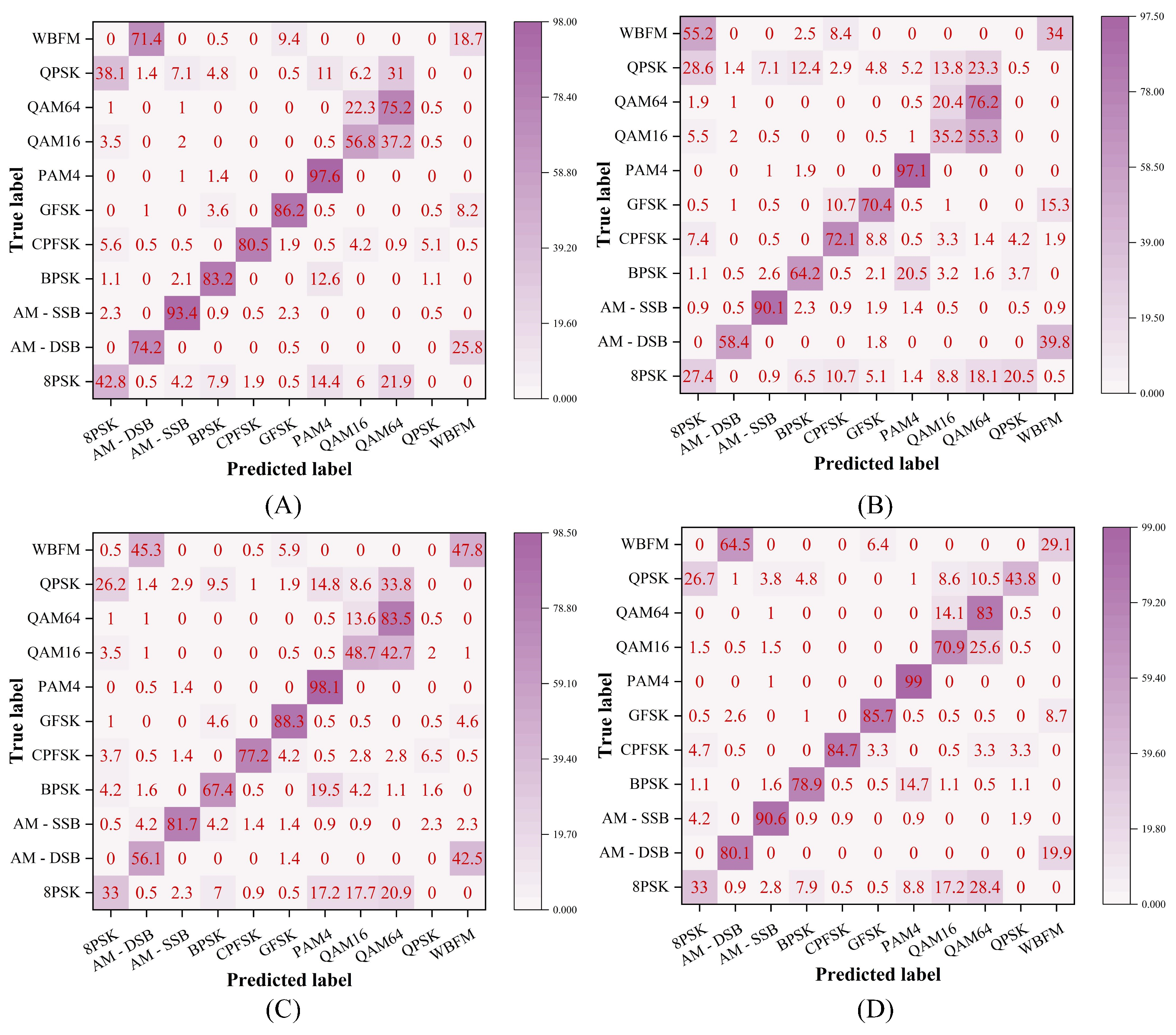
4.1. Performance Evaluation on Different Datasets
4.2. Efficiency Analysis
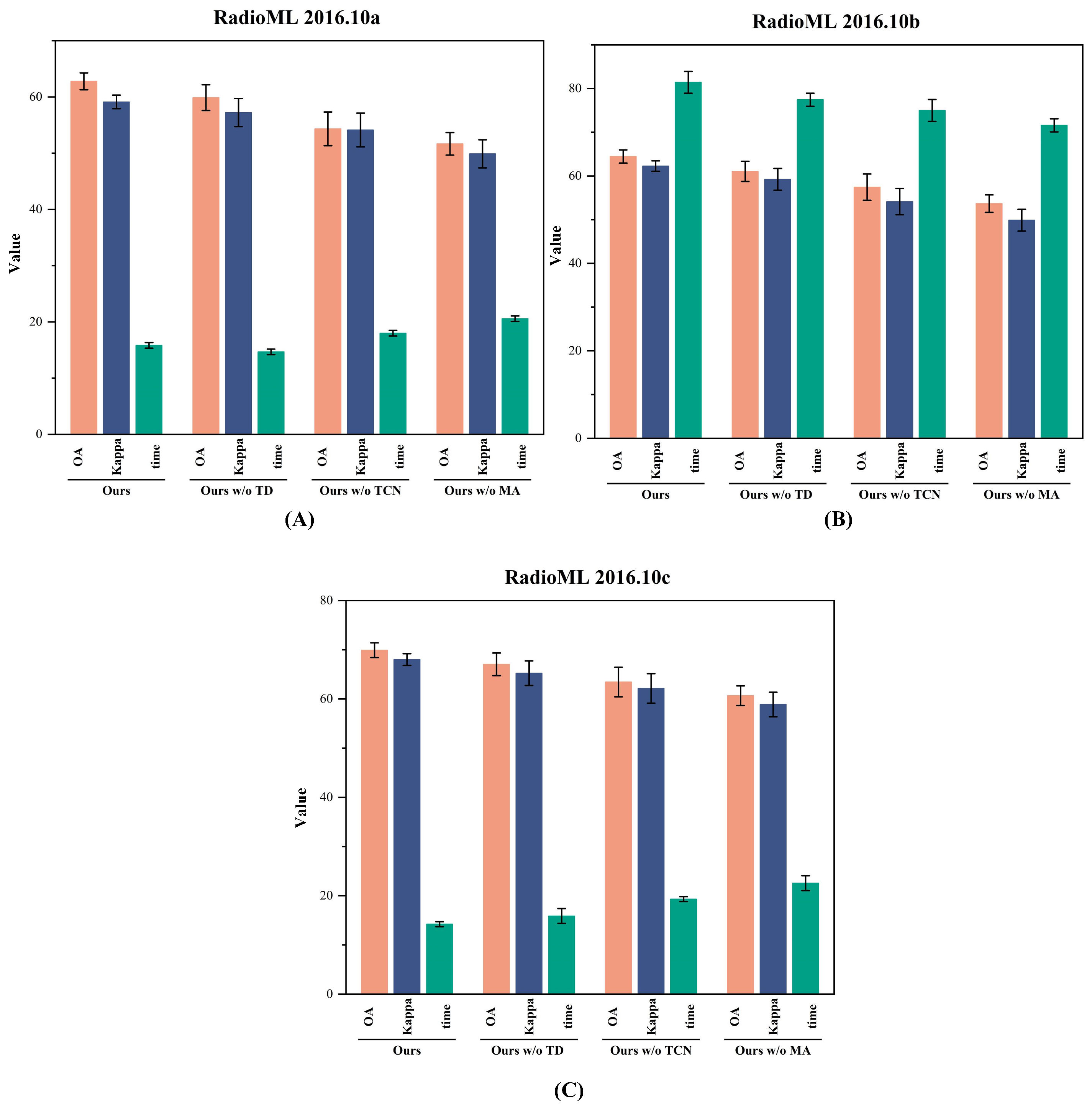
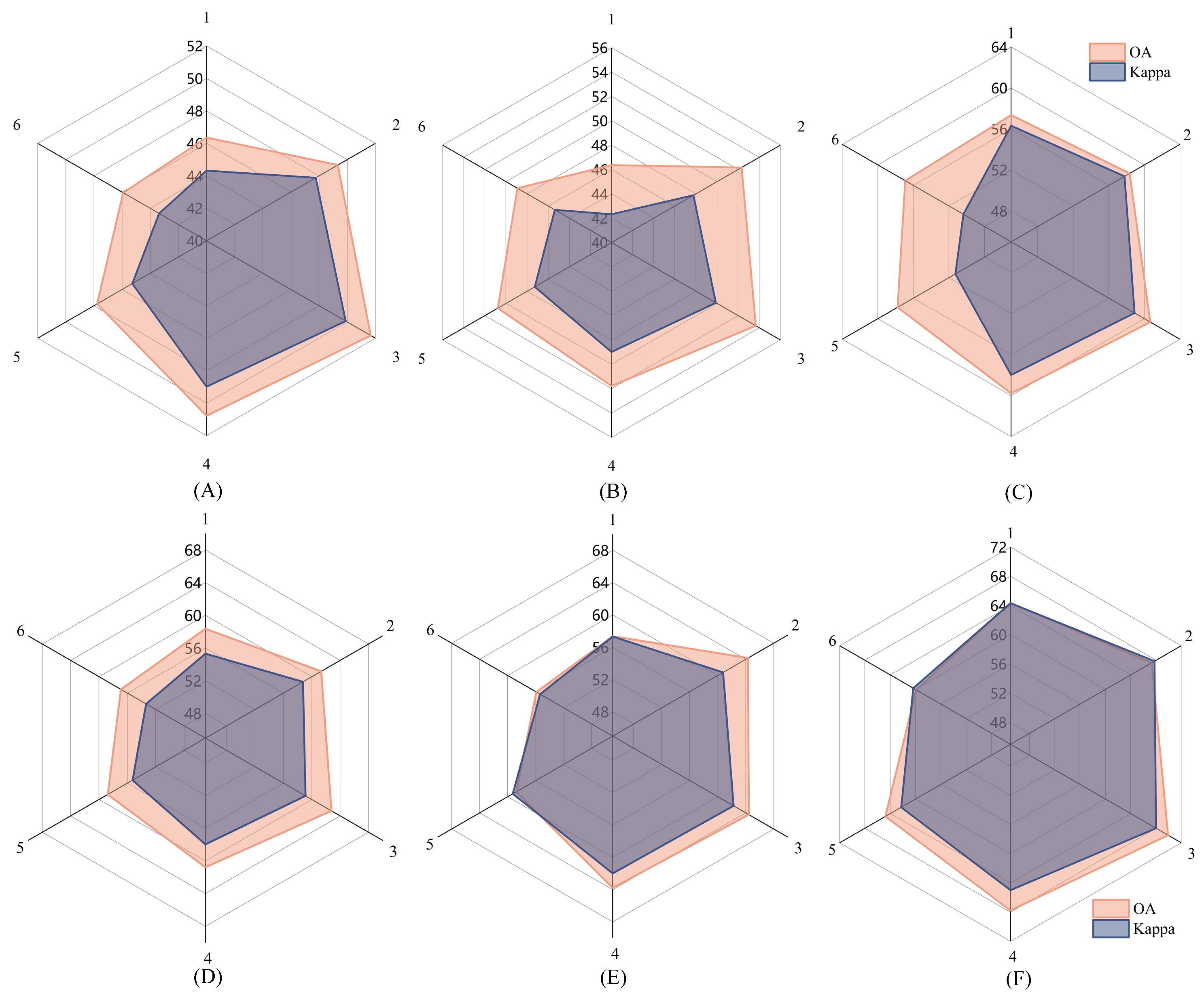
4.3. Ablation Study
- Ours w/o MA: NATM + TCN.
- Ours w/o TCN: NATM + Mamba.
- Ours w/o NATM: Dual branches without NATM.
- Ours: Complete architecture.
4.4. Fusion Method Comparison
- Sum (ours): Element-wise addition of branch outputs after each layer.
- Concat: Concatenation followed by a linear projection to match dimensionality.
- Gated: A learnable weight-based gating mechanism for adaptive fusion.
4.5. Performance Evaluation at Different SNRs
4.6. Impacts of Model Structure Design on Model Performance
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dobre, O.A.; Abdi, A.; Bar-Ness, Y.; Su, W. Survey of Automatic Modulation Classification Techniques: Classical Approaches and New Trends. IET Commun. 2007, 1, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, T.J.; Roy, T.; Clancy, T.C. Over-the-Air Deep Learning Based Radio Signal Classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2018, 12, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, S.; Meert, W.; Giustiniano, D.; Lenders, V.; Pollin, S. Deep Learning Models for Wireless Signal Classification with Distributed Low-Cost Spectrum Sensors. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2018, 4, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, N.; O’Shea, T.J. Deep Architectures for Modulation Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Dynamic Spectrum Access Networks (DySPAN), Baltimore, MD, USA, 6–9 March 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Lu, C.; Sun, Y.; Yang, M.; Liu, C.; Ou, C. Automatic ECG Classification Using Continuous Wavelet Transform and Convolutional Neural Network. Entropy 2021, 23, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, F.; Yue, C.; Han, C. A lightweight and efficient neural network for modulation recognition. Digit. Signal Process. 2022, 123, 103444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Jiang, J.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, H.; Huang, D.; Lu, Y. Improving Computation and Memory Efficiency for Real-world Transformer Inference on GPUs. Acm Trans. Archit. Code Optim. 2023, 20, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanghieri, M.; Benatti, S.; Burrello, A.; Kartsch, V.; Conti, F.; Benini, L. Robust Real-Time Embedded EMG Recognition Framework Using Temporal Convolutional Networks on a Multicore IoT Processor. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2020, 14, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Ma, Q.; Ding, W. Multiscale Correlation Networks Based on Deep Learning for Automatic Modulation Classification. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2023, 30, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Zhao, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y. Spectrum interference-based two-level data augmentation method in deep learning for automatic modulation classification. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 7723–7745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Gan, F.; Cao, X.; Liu, W. Signal Modulation Classification Based on the Transformer Network. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2022, 8, 1348–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.C.; Han, D.S. Deep Learning-Based Automatic Modulation Classification With Blind OFDM Parameter Estimation. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 108305–108317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Shi, J.; Li, Z.; Du, M.; Liu, F.; Zeng, F. Contrastive Semi-Supervised Learning With Pseudo-Label for Radar Signal Automatic Modulation Recognition. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 30399–30411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Cao, Y.; Li, G.; Li, X. MAMC—Optimal on Accuracy and Efficiency for Automatic Modulation Classification with Extended Signal Length. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2024, 28, 2864–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Yang, S.; Feng, Z.; Jiao, L. MCLHN: Toward Automatic Modulation Classification via Masked Contrastive Learning with Hard Negatives. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2024, 23, 14304–14319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Deng, T.; Gavin, B.; Ball, E.A.; Seed, L. A Ultra-Low Cost and Accurate AMC Algorithm and Its Hardware Implementation. IEEE Open J. Comput. Soc. 2024, 6, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Chen, S.; Ma, Y.; Gao, Y.; Yang, S. Learning Temporal–Spectral Feature Fusion Representation for Radio Signal Classification. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2025, 21, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Jin, Z. Latent Modulated Function for Computational Optimal Continuous Image Representation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 26026–26035. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, A.; Dao, T. Mamba: Linear-Time Sequence Modeling with Selective State Spaces. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2312.00752. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, S.; Kolter, J.Z.; Koltun, V. An Empirical Evaluation of Generic Convolutional and Recurrent Networks for Sequence Modeling. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.01271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Fei, Z. GIGNet: A Graph-in-Graph Neural Network for Automatic Modulation Recognition. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2025, 74, 10058–10062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, T.T.; Argyriou, A.; Puspitasari, A.A.; Cotton, S.L.; Lee, B.M. Efficient Automatic Modulation Classification for Next-Generation Wireless Networks. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw. 2025, 10, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Tian, X.; Yu, Z.; Yang, M.; Elhanshi, A.; Saponara, S. Robust automatic modulation classification using asymmetric trilinear attention net with noisy activation function. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 141, 109861. [Google Scholar]
- An, T.; Lee, B.M. Robust Automatic Modulation Classification in Low Signal to Noise Ratio. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 7860–7872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T. Ghost Convolutional Neural Network-Based Lightweight Semantic Communications for Wireless Image Classification. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2025, 14, 886–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, T.; West, N. Radio Machine Learning Dataset Generation with GNU Radio. In Proceedings of the GNU Radio Conference, Boulder, CO, USA, 12–16 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y. Large-Scale Real-World Radio Signal Recognition with Deep Learning. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2022, 35, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekbiyik, K.; Ekti, A.; Görçin, A.; Kurt, G.; Keçeci, C. Robust and Fast Automatic Modulation Classification with Convolutional Neural Networks under Multipath Fading Channels. In Proceedings of the IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC-Spring), Antwerp, Belgium, 25–28 May 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, H.S.; Ali, M.H.E.; Ismail, M.; Shaaban, M.N.; Mohamed, M.L.; Atallah, H.A. Automatic Modulation Classification: Convolutional Deep Learning Neural Networks Approaches. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 98695–98705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, J.K.; Darr, M.J. Interpretable AI for Time-Series: Multi-Model Heatmap Fusion with Global Attention and NLP-Generated Explanations. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2507.00234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. PyTorch: An Imperative Style, High-Performance Deep Learning Library. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; pp. 8024–8035. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, C.; Yang, S.; Feng, Z. Complex-Valued Depthwise Separable Convolutional Neural Network for Automatic Modulation Classification. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 2522310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, B. CA-CNN-GRU Communication Modulation Signal Classification Method Based on Multi-Scale Feature. IET Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2025. Early View. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveen, S.; Kounte, M.R.; Ahmed, M.R. Low Latency Deep Learning Inference Model for Distributed Intelligent IoT Edge Clusters. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 160607–160621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
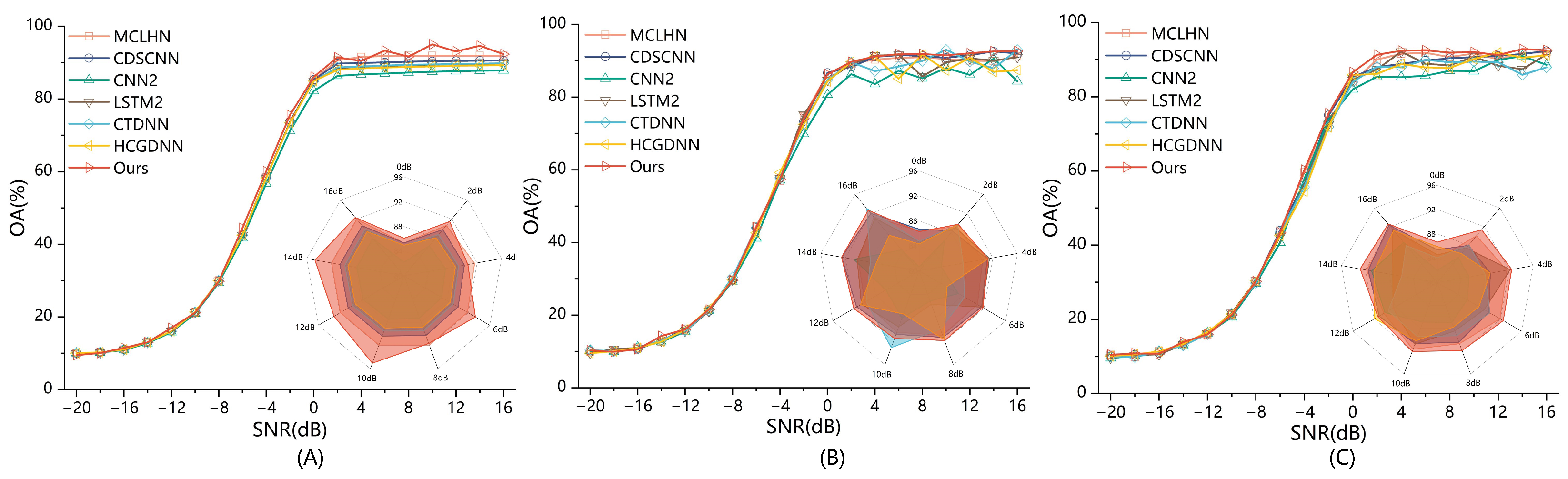
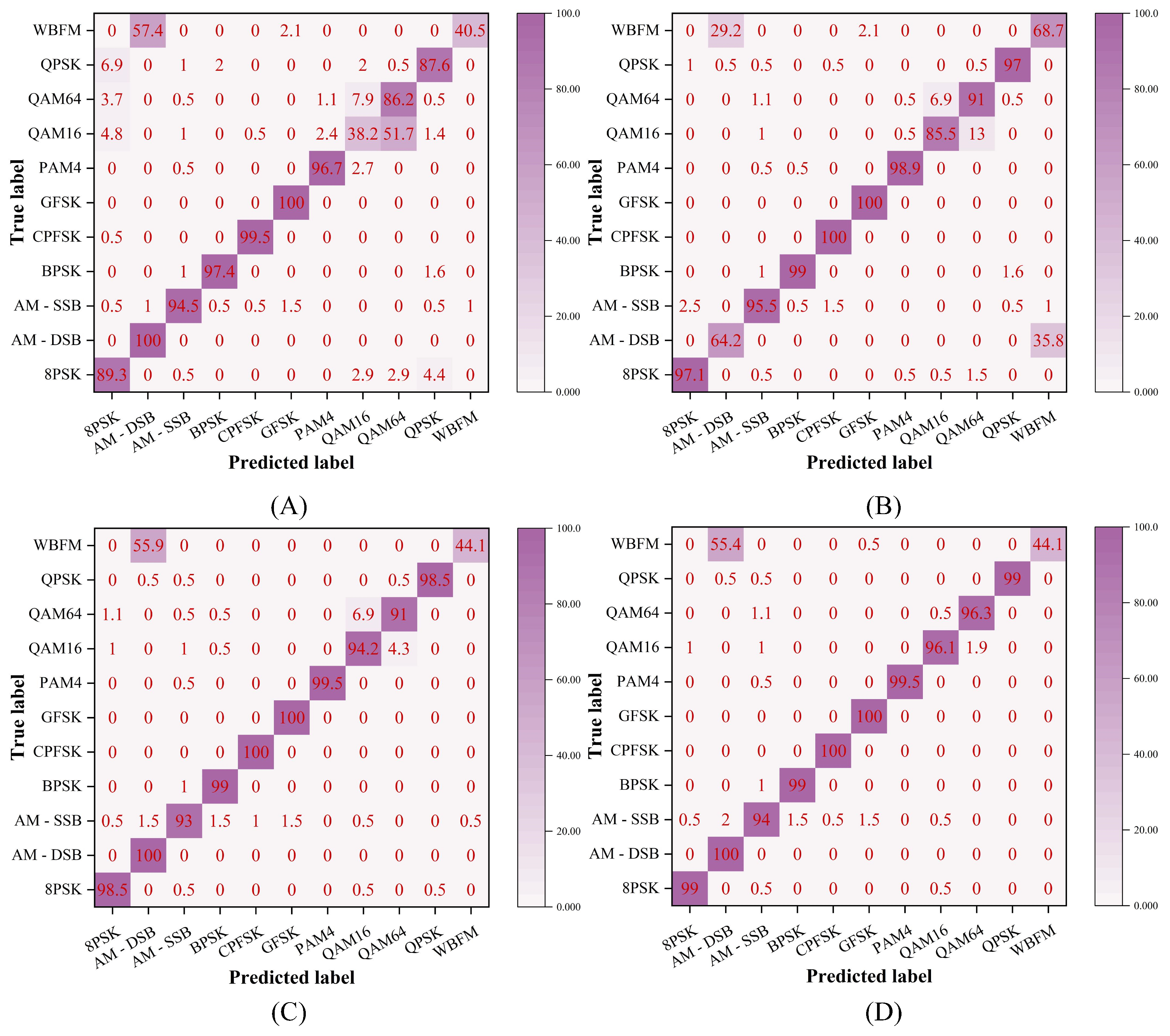
| Model | 2016.10A | 2016.10B | 2018.01A |
|---|---|---|---|
| CDSCNN [32] | 51.20 | 56.44 | 48.73 |
| CNN2 [26] | 50.17 | 54.12 | 47.55 |
| LSTM2 [3] | 49.52 | 55.84 | 49.12 |
| CTDNN [4,5] | 53.84 | 56.72 | 50.66 |
| HCGDNN [33] | 54.97 | 56.74 | 51.21 |
| MCLHN [15] | 56.83 | 59.68 | 53.90 |
| Ours | 59.12 | 62.26 | 55.37 |
| Model | Params (M) | FLOPs (G) | Latency (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CTDNN | 5.63 (GPU) | ||
| HCGDNN | 8.21 (GPU) | ||
| MCLHN | 11.40 (GPU) | ||
| Ours | 4.75 (GPU) |
| Module | Dataset | OA (%) | Kappa (%) | Latency (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Denoise-only | RadioML 2016.10A | 53.4 ± 0.3 | 49.2 ± 0.3 | 2.85 |
| TCN-only | RadioML 2016.10A | 55.8 ± 0.2 | 51.1 ± 0.3 | 2.73 |
| Mamba-only | RadioML 2016.10A | 58.0 ± 0.2 | 53.0 ± 0.3 | 2.68 |
| Denoise-only | RadioML 2016.10B | 55.1 ± 0.3 | 50.7 ± 0.3 | 2.87 |
| TCN-only | RadioML 2016.10B | 57.4 ± 0.3 | 52.5 ± 0.3 | 2.74 |
| Mamba-only | RadioML 2016.10B | 59.6 ± 0.2 | 54.0 ± 0.3 | 2.69 |
| Denoise-only | RadioML 2018.01A | 56.8 ± 0.2 | 51.8 ± 0.3 | 2.91 |
| TCN-only | RadioML 2018.01A | 59.1 ± 0.2 | 53.9 ± 0.3 | 2.75 |
| Mamba-only | RadioML 2018.01A | 61.2 ± 0.2 | 55.6 ± 0.2 | 2.70 |
| Fusion Method | 2018.01A (OA) | Params (M) | Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sum (ours) | 55.37 ± 0.2 | ||
| Concat | 54.77 ± 0.3 | ||
| Gated Fusion | 53.33 ± 0.3 |
| SNR (dB) | OA (%) | Kappa (%) | Macro-F1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| −4 | 58.0 ± 0.5 | 56.0 ± 0.6 | 57.0 ± 0.4 |
| 0 | 58.6 ± 0.4 | 56.2 ± 0.5 | 57.0 ± 0.3 |
| 4 | 65.3 ± 0.3 | 63.1 ± 0.3 | 64.0 ± 0.3 |
| 8 | 72.5 ± 0.2 | 70.8 ± 0.3 | 71.3 ± 0.2 |
| 12 | 77.6 ± 0.3 | 76.0 ± 0.4 | 76.4 ± 0.3 |
| 16 | 80.4 ± 0.2 | 79.0 ± 0.3 | 79.3 ± 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Kong, Y.; Ge, Y.; Guo, Z. A Lightweight Denoising Network with TCN–Mamba Fusion for Modulation Classification. Electronics 2026, 15, 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics15010188
Kong Y, Ge Y, Guo Z. A Lightweight Denoising Network with TCN–Mamba Fusion for Modulation Classification. Electronics. 2026; 15(1):188. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics15010188
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Yubo, Yang Ge, and Zhengbing Guo. 2026. "A Lightweight Denoising Network with TCN–Mamba Fusion for Modulation Classification" Electronics 15, no. 1: 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics15010188
APA StyleKong, Y., Ge, Y., & Guo, Z. (2026). A Lightweight Denoising Network with TCN–Mamba Fusion for Modulation Classification. Electronics, 15(1), 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics15010188








