Cross-Attention Guided Local Feature Enhanced Multi-Branch Network for Person Re-Identification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Holistic Feature Representation Learning
2.2. Local Feature Learning in ReID
2.3. Attention in ReID
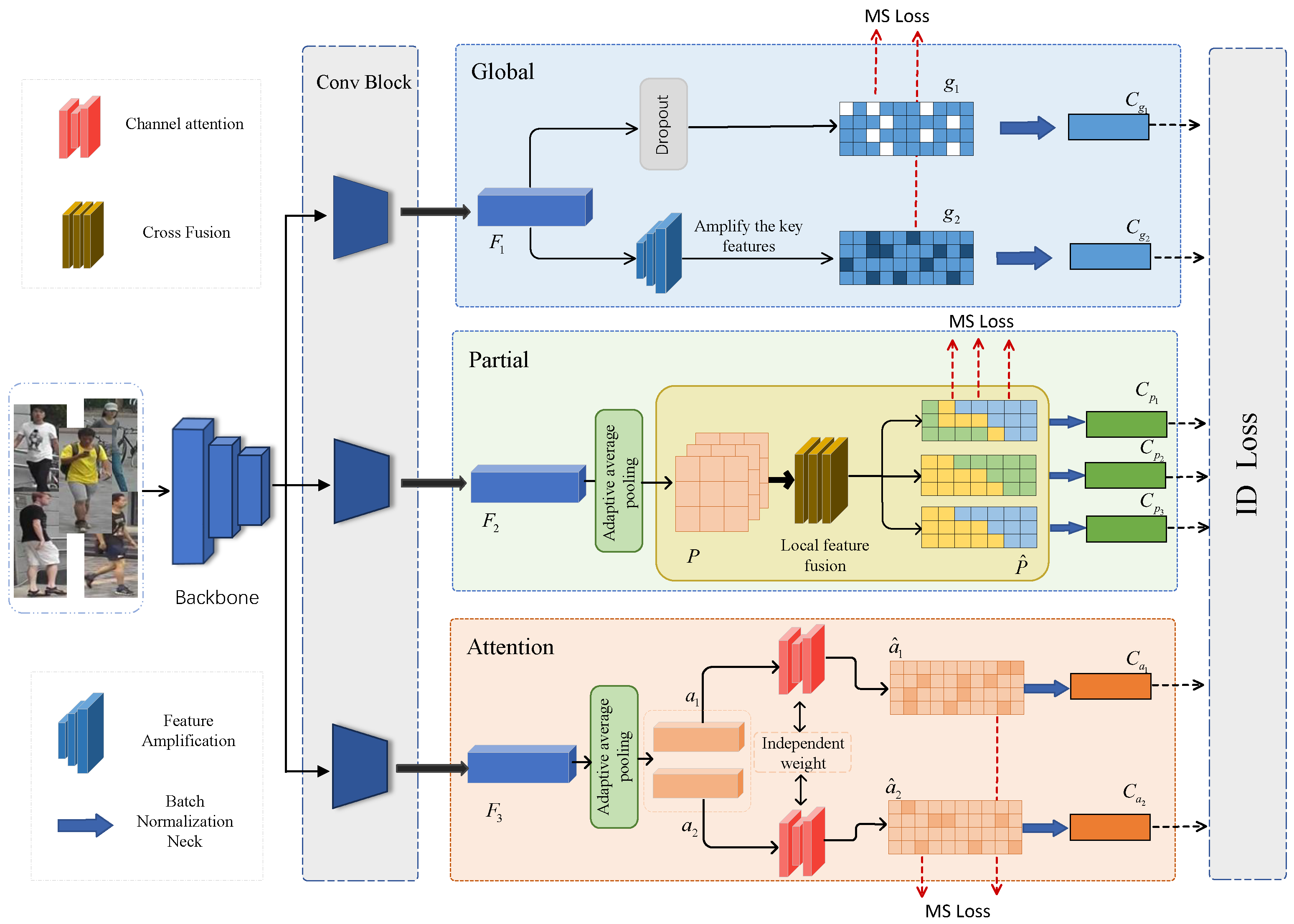
3. Methods
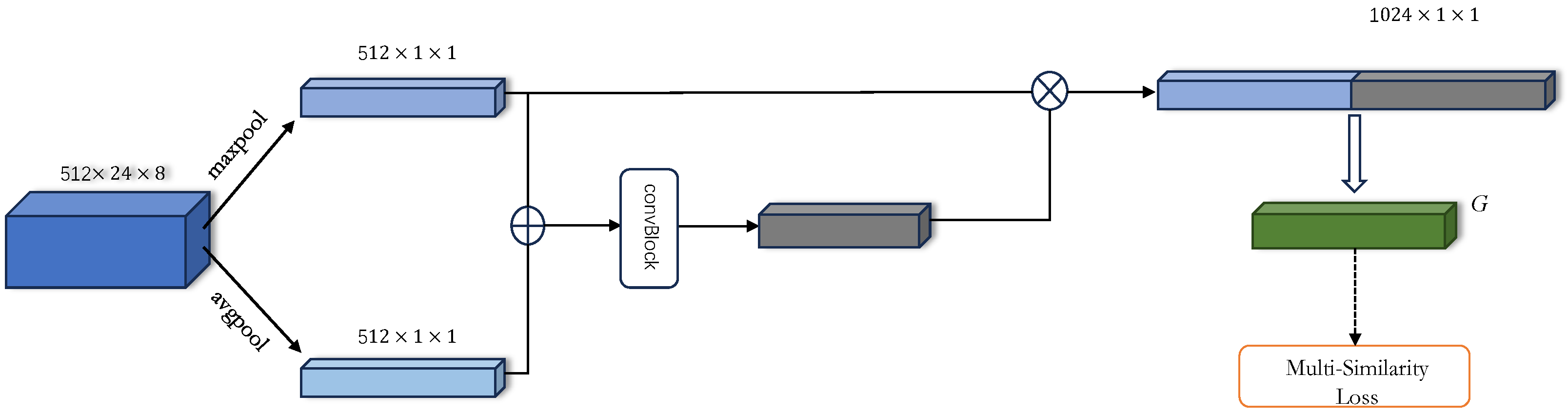
3.1. Feature Amplification Module
3.2. Cross Fusion Module
3.3. Training Loss
4. Results
4.1. Datasets and Evaluation Metrics
4.2. Implementation Details
4.3. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Methods
4.4. Ablation Studies
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, H.; Yao, M.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, H.; Jia, W.; Fu, X.; Wang, Y. Manifold-based Incomplete Multi-view Clustering via Bi-Consistency Guidance. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024, 26, 10001–10014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Peng, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, M. Progressive learning with multi-scale attention network for cross-domain vehicle re-identification. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2022, 65, 160103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. Intelligent multi-camera video surveillance: A review. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2013, 34, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loy, C.C.; Xiang, T.; Gong, S. Multi-camera activity correlation analysis. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 1988–1995. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Dai, P.; Chen, J.; Lin, C.W.; Wu, Y.; Huang, F.; Zhong, B.; Ji, R. Discover cross-modality nuances for visible-infrared person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 4330–4339. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, B.; Chu, Q.; Lu, Y.; Yu, N. Joint color-irrelevant consistency learning and identity-aware modality adaptation for visible-infrared cross modality person re-identification. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2021, 35, 3520–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zheng, Z.; Wu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Yan, C.; Yang, Y. Improving person re-identification by attribute and identity learning. Pattern Recognit. 2019, 95, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Chen, X.; Huang, K. Human parsing based alignment with multi-task learning for occluded person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), London, UK, 6–10 July 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Ni, B.; Yan, Y.; Zhou, P.; Cheng, S.; Hu, J. Pose transferrable person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 4099–4108. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Jiang, G.; Wang, H. Adaptive Memorization with Group Labels for Unsupervised Person Re-identification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 33, 5802–5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Wang, H.; Yao, M.; Fu, X. Focus More on What? Guiding Multi-Task Training for End-to-End Person Search. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yang, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S.; Yu, G.; Zhou, E.; Sun, J. High-order information matters: Learning relation and topology for occluded person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 6449–6458. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Zhou, X. Learning discriminative features with multiple granularities for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 26th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 22–26 October 2018; pp. 274–282. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, M.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Fu, X. Between/Within View Information Completing for Tensorial Incomplete Multi-view Clustering. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024, 27, 1538–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zheng, L.; Yang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Wang, S. Beyond part models: Person retrieval with refined part pooling (and a strong convolutional baseline). In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 480–496. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, F.; Deng, C.; Sun, X.; Jiang, X.; Guo, X.; Yu, Z.; Huang, F.; Ji, R. Pyramidal person re-identification via multi-loss dynamic training. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 8514–8522. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, G.; Hu, G.; Wang, X.; Mazur, N.; Zhu, Z.; Haner, M. EXAM: A framework of learning extreme and moderate embeddings for person re-ID. J. Imaging 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, F.; Ji, X.; Teepe, T.; Hörmann, S.; Gilg, J.; Rigoll, G. Lightweight multi-branch network for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Anchorage, AK, USA, 19–22 September 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1129–1133. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Yang, Y.; Hauptmann, A.G. Person re-identification: Past, present and future. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1610.02984. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, K. Learning deep context-aware features over body and latent parts for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 384–393. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Li, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Wang, J. Deeply-learned part-aligned representations for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 3219–3228. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Sun, X.; Fan, B.; Tang, C.; Zeng, H. Deep attention aware feature learning for person re-identification. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 126, 108567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheissari, N.; Sebastian, T.B.; Hartley, R. Person reidentification using spatiotemporal appearance. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’06), New York, NY, USA, 17–22 June 2006; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2006; Volume 2, pp. 1528–1535. [Google Scholar]
- Prosser, B.J.; Zheng, W.S.; Gong, S.; Xiang, T.; Mary, Q. Person re-identification by support vector ranking. In Proceedings of the BMVC, Aberystwyth, UK, 31 August–3 September 2010; Volume 2, p. 6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Yao, M.; Jiang, G.; Mi, Z.; Fu, X. Graph-Collaborated Auto-Encoder Hashing for Multiview Binary Clustering. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 35, 10121–10133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Jiang, G.; Peng, J.; Deng, R.; Fu, X. Towards adaptive consensus graph: Multi-view clustering via graph collaboration. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022, 25, 6629–6641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, H.; Tian, M.; Sheng, L.; Shao, J.; Yi, S.; Yan, J.; Wang, X. Hydraplus-net: Attentive deep features for pedestrian analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 350–359. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, G.; Peng, J.; Wang, H.; Mi, Z.; Fu, X. Tensorial multi-view clustering via low-rank constrained high-order graph learning. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 32, 5307–5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Ham, B. Relation network for person re-identification. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2020, 34, 11839–11847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, I.; Asai, A.; Shindo, H.; Takeda, H.; Matsumoto, Y. Luke: Deep contextualized entity representations with entity-aware self-attention. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.01057. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, J.; Nie, L.; Shao, J.; Liu, W.; Chua, T.S. Sca-cnn: Spatial and channel-wise attention in convolutional networks for image captioning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5659–5667. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zhu, X.; Gong, S. Harmonious attention network for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 2285–2294. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Yan, K.; Lu, S.; Jia, H.; Xie, X.; Gao, W. Attention driven person re-identification. Pattern Recognit. 2019, 86, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Deng, W.; Hu, J. Mixed high-order attention network for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 371–381. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Lan, C.; Zeng, W.; Jin, X.; Chen, Z. Relation-aware global attention for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 3186–3195. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, K.; Yang, Y.; Cavallaro, A.; Xiang, T. Omni-scale feature learning for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 3702–3712. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Hermans, A.; Beyer, L.; Leibe, B. In defense of the triplet loss for person re-identification. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.07737. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.; Gu, Y.; Liao, X.; Lai, S.; Jiang, W. Bag of tricks and a strong baseline for deep person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Han, X.; Huang, W.; Dong, D.; Scott, M.R. Multi-similarity loss with general pair weighting for deep metric learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 5022–5030. [Google Scholar]
- Buolamwini, J.; Gebru, T. Gender Shades: Intersectional Accuracy Disparities in Commercial Gender Classification. In Proceedings of the 1st Conference on Fairness, Accountability and Transparency, New York, NY, USA, 23–24 February 2018; Friedler, S.A., Wilson, C., Eds.; Volume 81, pp. 77–91. [Google Scholar]
- Datta, A.; Swamidass, S.J. Fair-Net: A network architecture for reducing performance disparity between identifiable sub-populations. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.00720. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Shen, L.; Tian, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Tian, Q. Scalable person re-identification: A benchmark. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1116–1124. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zhao, R.; Xiao, T.; Wang, X. Deepreid: Deep filter pairing neural network for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 152–159. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Zheng, L.; Yang, Y. Unlabeled samples generated by gan improve the person re-identification baseline in vitro. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 3754–3762. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.; Luo, H.; Wang, P.; Wang, F.; Li, H.; Jiang, W. Transreid: Transformer-based object re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 15013–15022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, K.; Guo, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Tang, M. Aaformer: Auto-aligned transformer for person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 35, 17307–17317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shen, J.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Gavves, E. Nformer: Robust person re-identification with neighbor transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 7297–7307. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Luo, H.; Fan, X.; Xiang, W.; Sun, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, C.; Sun, J. Alignedreid: Surpassing human-level performance in person re-identification. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.08184. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, R.; Dong, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Yang, Y. Auto-reid: Searching for a part-aware convnet for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 3750–3759. [Google Scholar]



| Methods | Market1501 | CHUK03-D | DukeMTMC-reID | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank 1 | mAP | Rank 1 | mAP | Rank 1 | mAP | |
| AlignedReID [50] | 91.8 | 79.1 | 61.5 | 59.6 | 82.1 | 69.7 |
| PCB [15] | 92.4 | 77.3 | 61.3 | 54.2 | 81.9 | 65.3 |
| HA-CNN [32] | 91.2 | 75.7 | 41.7 | 38.6 | 80.5 | 63.8 |
| Auto-ReID [51] | 94.5 | 85.1 | 73.3 | 69.3 | - | - |
| MHN [34] | 95.1 | 85.0 | 71.7 | 65.4 | 89.1 | 77.2 |
| OSNet [36] | 94.8 | 84.9 | 72.3 | 67.8 | 88.6 | 73.5 |
| DAAF-BoT [22] | 95.1 | 87.9 | 64.9 | 63.1 | 87.9 | 77.9 |
| GCP [29] | 95.2 | 88.9 | 74.4 | 69.6 | 89.7 | 78.6 |
| MGN [13] | 95.7 | 86.9 | 66.8 | 66.0 | 88.7 | 78.4 |
| NFormer [49] | 94.7 | 91.1 | 79.0 | 76.4 | 90.6 | 85.7 |
| TransReID [47] | 95.2 | 88.9 | 75.1 | 72.9 | 90.7 | 82.0 |
| AAformer [48] | 95.4 | 88.0 | 78.1 | 77.2 | 90.1 | 80.9 |
| ours | 96.0 | 90.2 | 82.6 | 79.7 | 90.8 | 81.9 |
| Branch | Market-1501 | CUHK03-D | DukeMTMC-reID | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank-1 | mAP | Rank-1 | mAP | Rank-1 | mAP | |
| Global (G) | 94.7 | 87.6 | 78.0 | 74.7 | 88.4 | 74.8 |
| Part (P) | 95.1 | 87.3 | 73.8 | 70.6 | 88.7 | 77.9 |
| Attention (A) | 92.8 | 84.5 | 71.5 | 67.2 | 85.0 | 71.7 |
| G and P | 95.8 | 90.1 | 81.6 | 79.1 | 90.6 | 80.8 |
| G and A | 94.6 | 88.3 | 78.5 | 75.2 | 88.7 | 78.0 |
| P and A | 95.0 | 88.6 | 75.3 | 73.4 | 89.5 | 79.3 |
| All | 96.0 | 90.2 | 82.6 | 79.7 | 90.8 | 81.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Yang, J. Cross-Attention Guided Local Feature Enhanced Multi-Branch Network for Person Re-Identification. Electronics 2025, 14, 1626. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14081626
Wang X, Yang J. Cross-Attention Guided Local Feature Enhanced Multi-Branch Network for Person Re-Identification. Electronics. 2025; 14(8):1626. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14081626
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaoyong, and Jianxi Yang. 2025. "Cross-Attention Guided Local Feature Enhanced Multi-Branch Network for Person Re-Identification" Electronics 14, no. 8: 1626. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14081626
APA StyleWang, X., & Yang, J. (2025). Cross-Attention Guided Local Feature Enhanced Multi-Branch Network for Person Re-Identification. Electronics, 14(8), 1626. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14081626





