TIANet: A Defect Classification Structure Based on the Combination of CNN and ViT
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Background
1.2. Related Work
2. Methodology
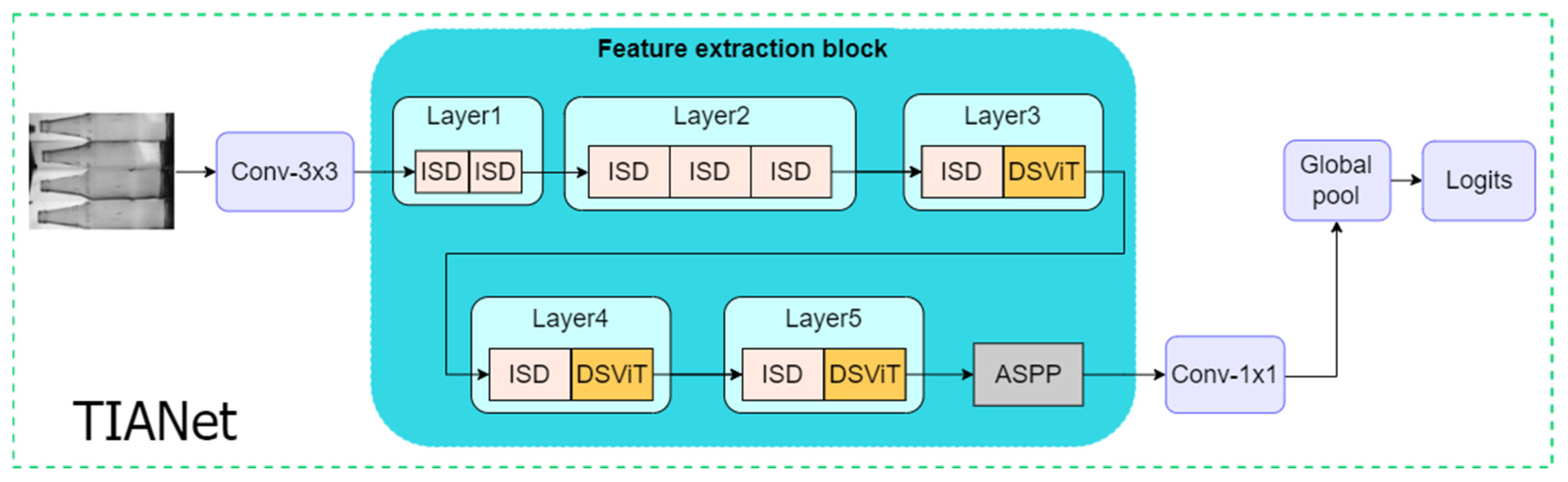
2.1. TIANet Structure Design
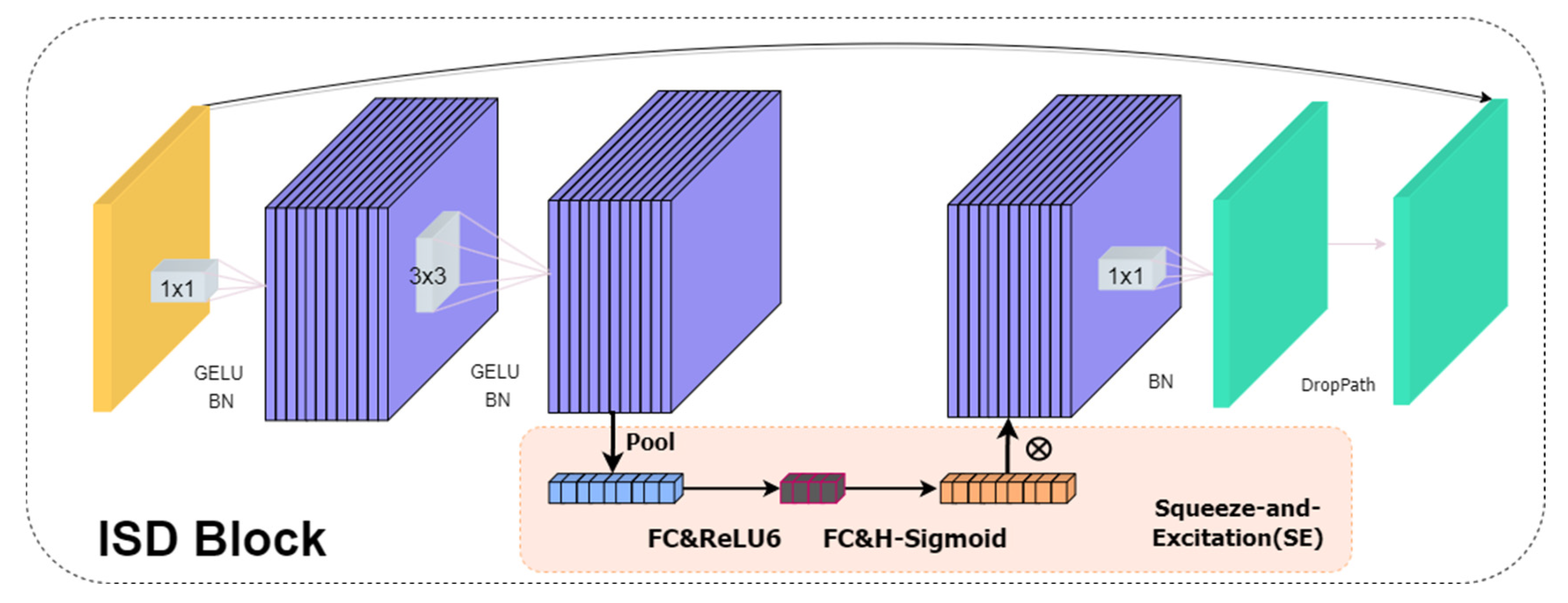
2.2. ISD Block
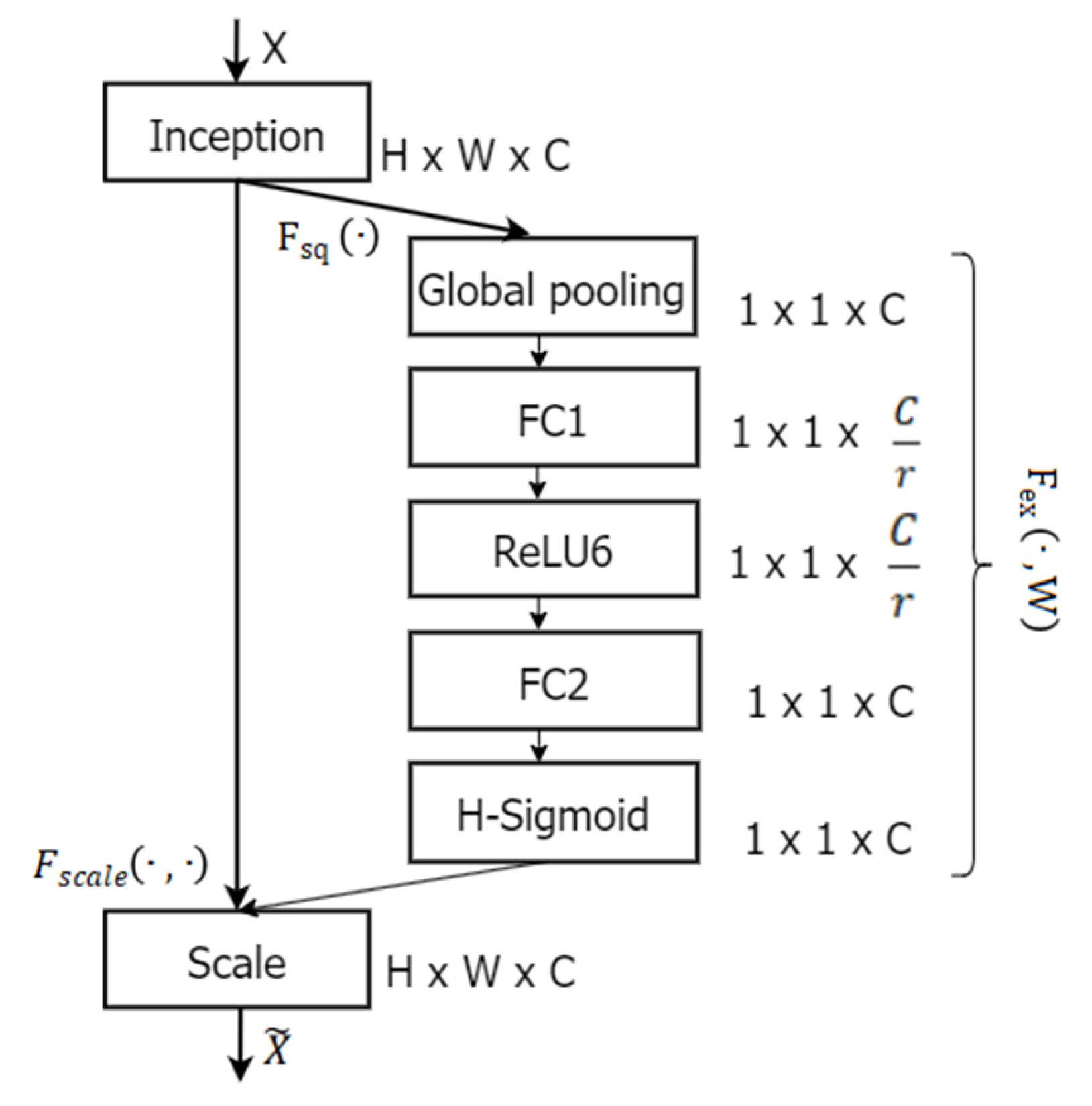
2.2.1. Optimize the Squeeze-and-Excitation Attention
2.2.2. Path Drop Mechanism
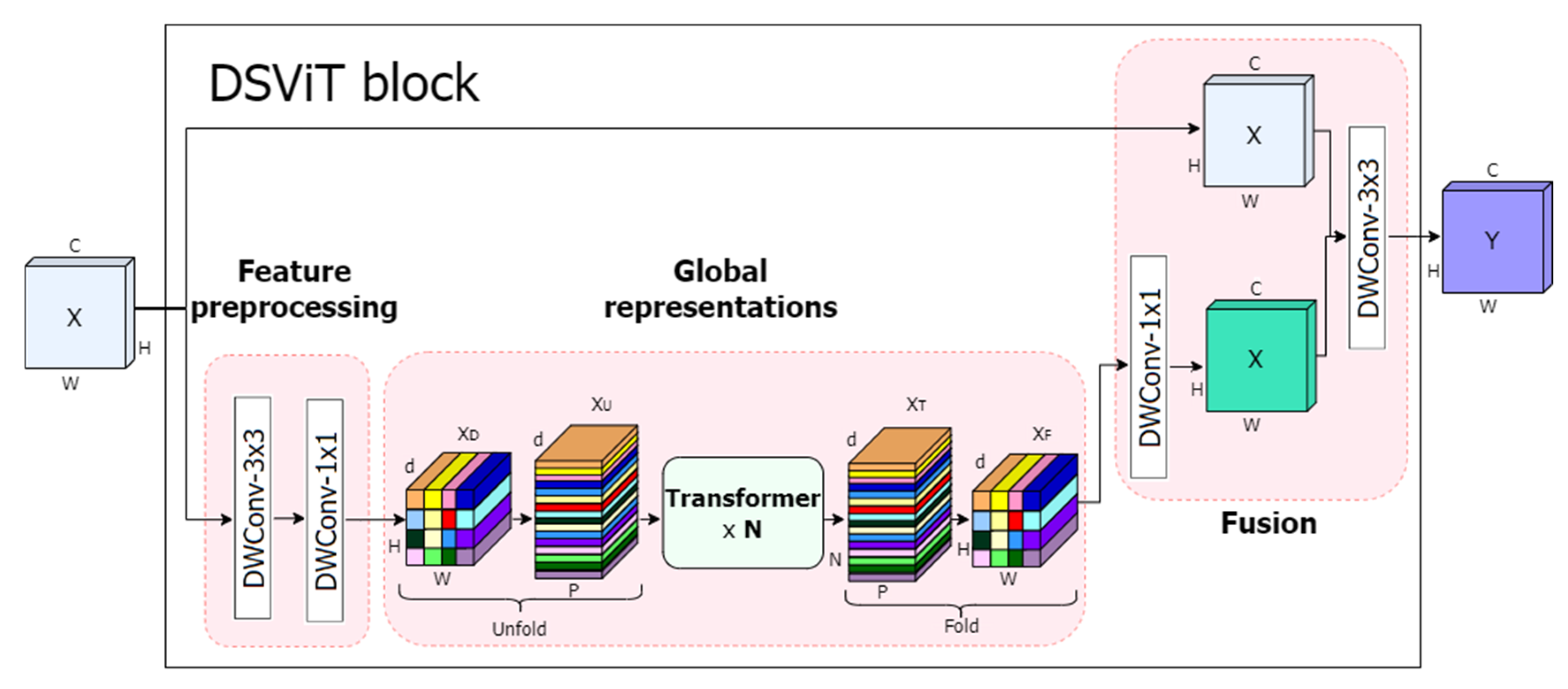
2.3. DSViT Block
- (1)
- Feature preprocessing: This process mainly includes two stages: deep convolution and pointwise convolution, with the purpose of converting the input tensor into to adapt to the input requirements of the Transformer module.
- (2)
- Global representation: It mainly includes three stages: unfolding operation, Transformer encoding, and folding operation, and its purpose is to capture global information by dealing with long-range non-local dependencies with spatial inductive bias.
- (3)
- Feature fusion: This process should include three stages: low-dimensional projection, joining operation, and fusion convolution. The aim is to combine the global features processed by Transformer with the local features extracted by the ISD block.
2.4. ASPP Block

3. Data and Experiments
3.1. Datasets
3.2. Experimental Environment
3.3. Analysis of Experimental Results
3.3.1. Evaluation Metrics
3.3.2. Comparative Test
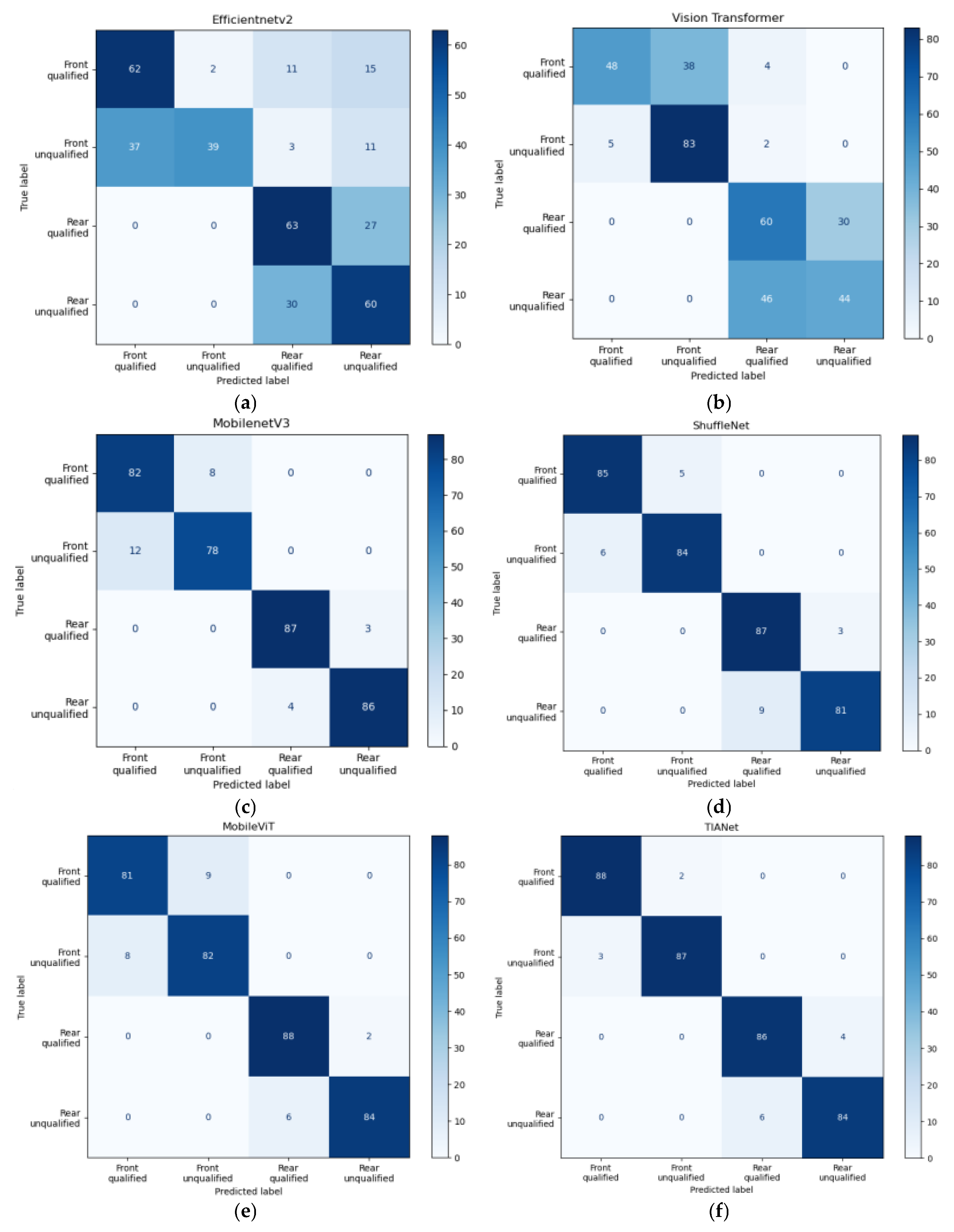
3.3.3. Confusion Matrix
3.4. Ablation Experiments
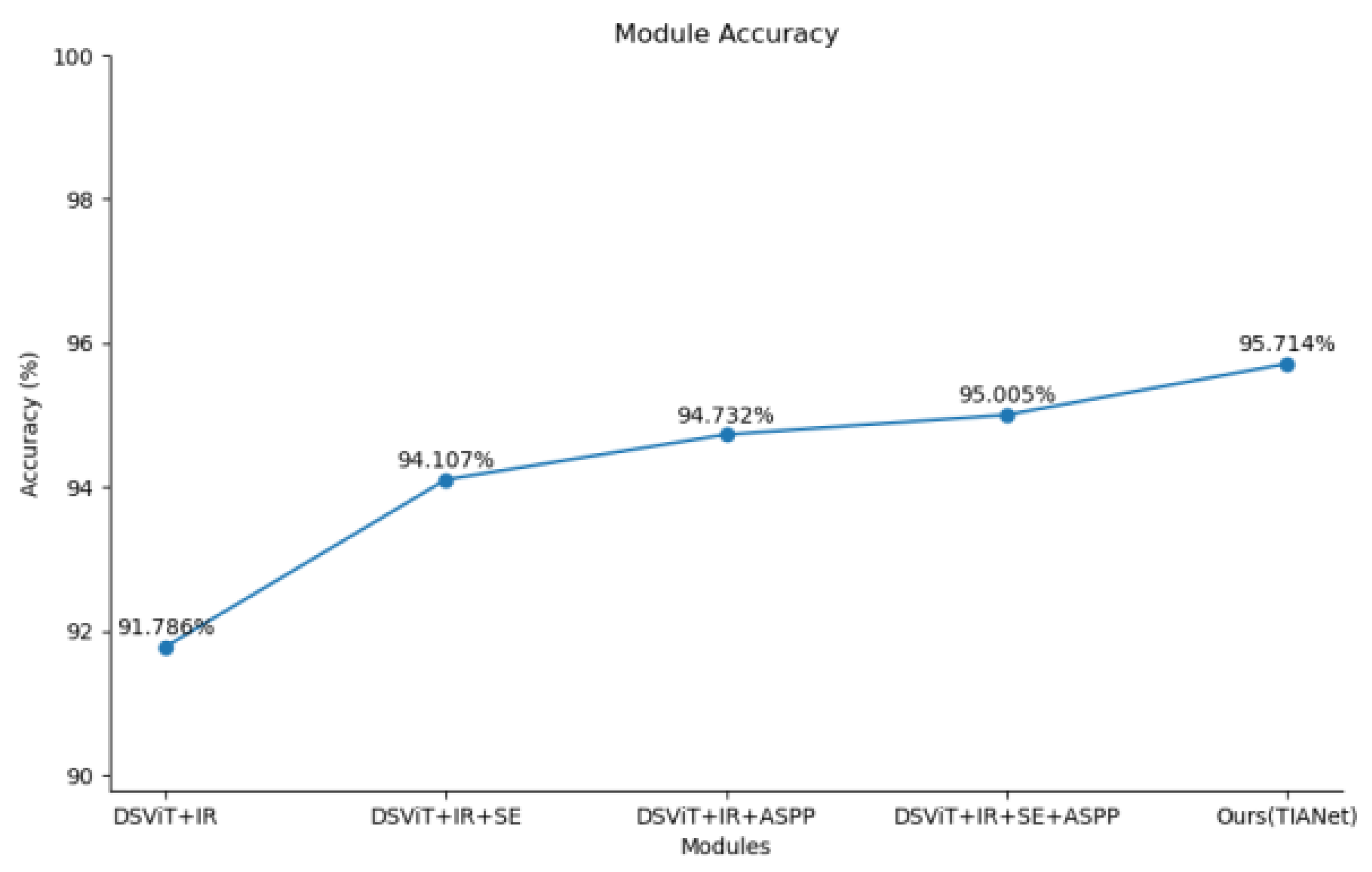
3.4.1. Recommended Module Ablation
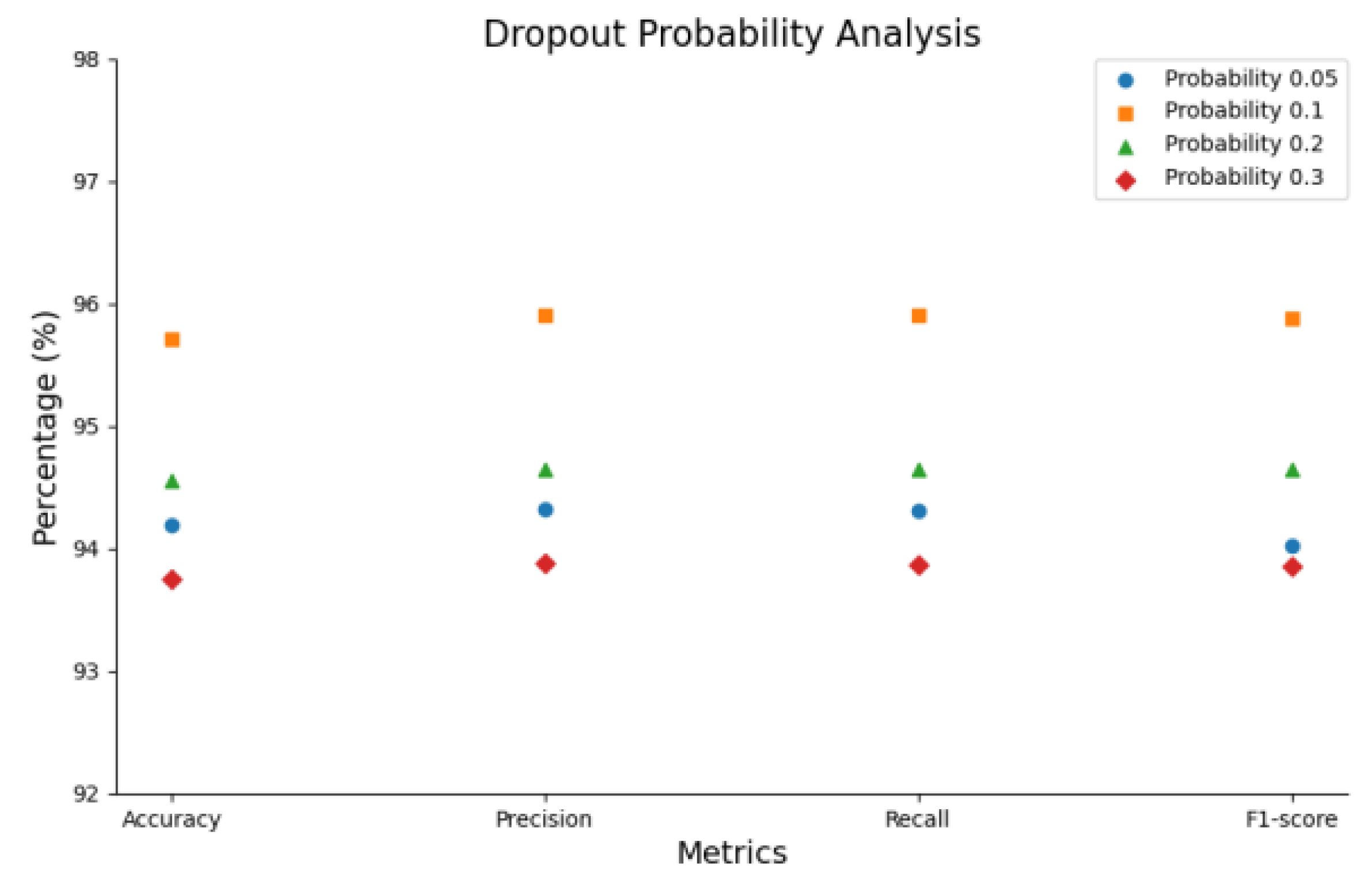
3.4.2. Probabilistic Analysis of the Path Drop Mechanism
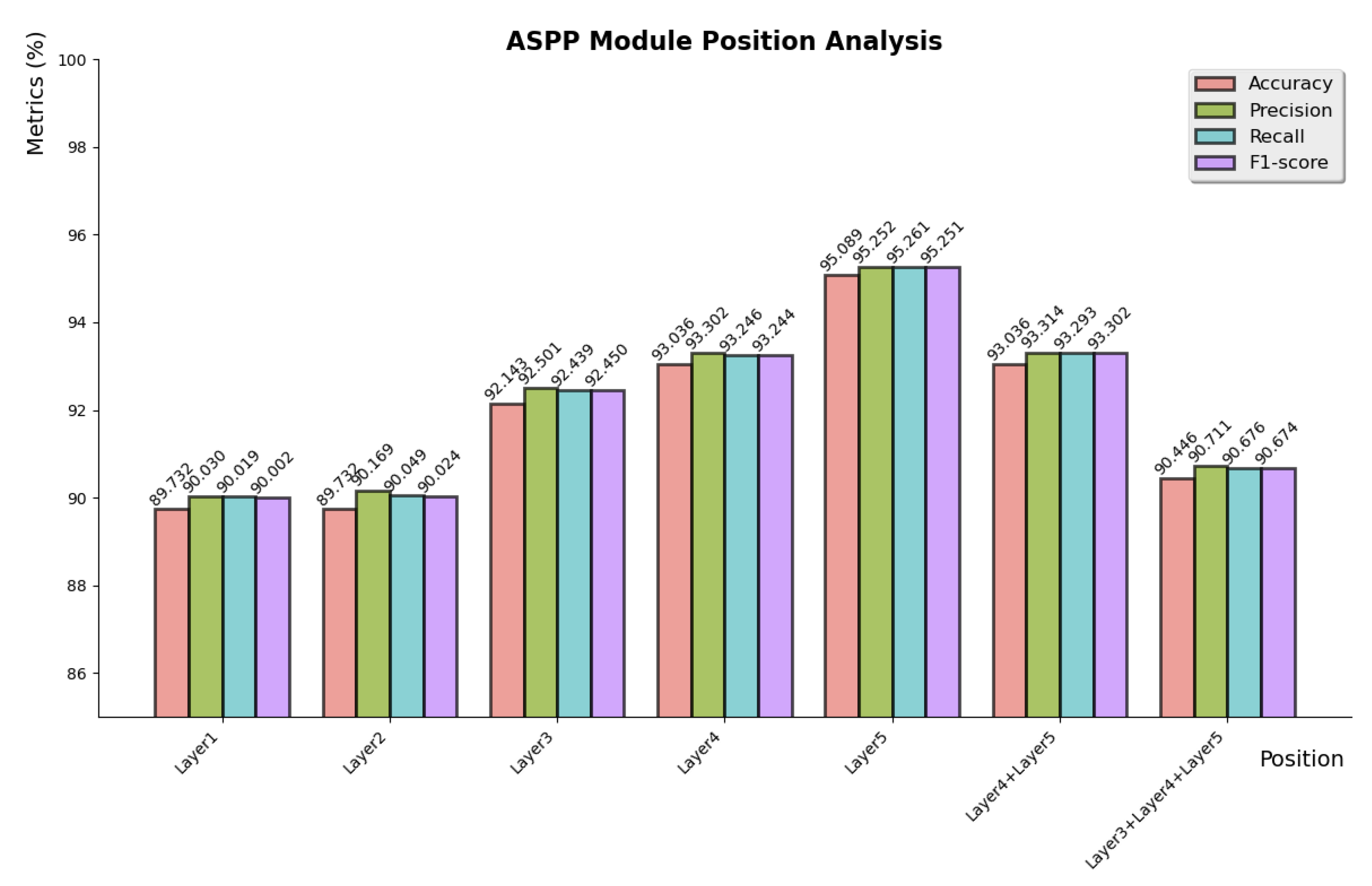
3.4.3. ASPP Module Insert Position Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TIANet | A defect classification structure based on the combination of CNN and ViT |
| ViT | Vision transformer |
| ISD | Local feature extraction |
| DSViT | Global feature extraction |
| ASPP | Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling |
| SE | Squeeze-and-Excitation attention |
| BN | Batch normalization |
References
- Xian, R.; Xiong, X.; Peng, H.; Wang, J.; de Arellano Marrero, A.R.; Yang, Q. Feature fusion method based on spiking neural convolutional network for edge detection. Pattern Recognit. 2024, 147, 110112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Duanmu, L.; Zhai, Z.J.; Wang, Z. Application and improvement of Canny edge-detection algorithm for exterior wall hollowing detection using infrared thermal images. Energy Build. 2022, 274, 112421. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Li, L.; Wen, S.; Liang, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, F.; Yang, Y. Metalens for accelerated optoelectronic edge detection under ambient illumination. Nano Lett. 2023, 24, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhateja, V.; Nigam, M.; Bhadauria, A.S.; Arya, A.; Zhang, E.Y.-D. Human visual system based optimized mathematical morphology approach for enhancement of brain MR images. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2024, 15, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.; Wang, J.; Mao, X.; Zhao, Z.; Gao, X.; Lu, W. An improved faster R-CNN method for landslide detection in remote sensing images. J. Geovis. Spat. Anal. 2024, 8, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Solihin, M.I.; Ardiyanto, I.; Zhao, Y.; Li, W.; Cai, B.; Chen, C. A streamlined approach for intelligent ship object detection using EL-YOLO algorithm. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 15254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; He, L.; Zhang, M.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, W.; Wu, Z. Improving the Performance of the Single Shot Multibox Detector for Steel Surface Defects with Context Fusion and Feature Refinement. Electronics 2023, 12, 2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.F.R.; Fan, Q.; Panda, R. CrossViT: Cross-attention multi-scale vision transformer for image classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 357–366. [Google Scholar]
- Bazi, Y.; Bashmal, L.; Rahhal, M.M.A.; Dayil, R.A.; Ajlan, N.A. Vision transformers for remote sensing image classification. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S. An image is worth 16 × 16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Z.; Sedra, D.; Weinberger, K.Q. Deep networks with stochastic depth. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2016, 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 646–661. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, K.; Zhou, C.; Ruan, Y.; Li, Y. MobileNetV2 model for image classification. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Information Technology and Computer Application, Guangzhou, China, 18–20 December 2020; pp. 476–480. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Targ, S.; Almeida, D.; Lyman, K. ResNet in ResNet: Generalizing residual architectures. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.08029. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Koltun, V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.07122. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Mao, H.; Wu, C.Y.; Feichtenhofer, C.; Darrell, T.; Xie, S. A convnet for the 2020s. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, Louisiana, 21–24 June 2022; pp. 11976–11986. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, A.; Mohri, M.; Zhong, Y. Cross-entropy loss functions: Theoretical analysis and applications. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23 July 2023; pp. 23803–23828. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. EfficientNetV2: Smaller models and faster training. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Online, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 10096–10106. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Lin, M.; Sun, J. ShuffleNet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 6848–6856. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chu, G.; Chen, L.-C.; Chen, B.; Tan, M.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, R.; Vasudevan, V.; et al. Searching for MobileNetV3. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1314–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, S.; Rastegari, M. MobileViT: Light-weight, general-purpose, and mobile-friendly vision transformer. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.02178. [Google Scholar]
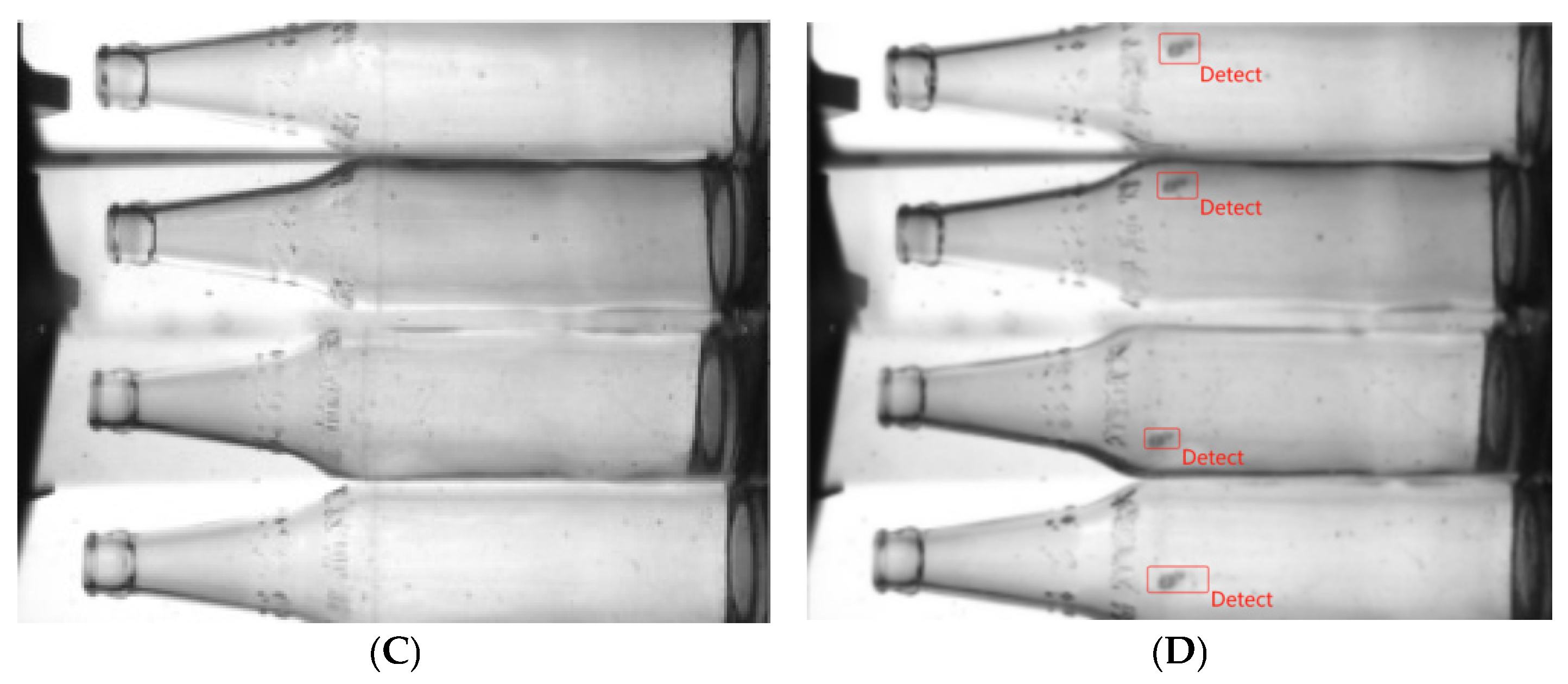


| No | Model | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | EfficientNetV2 | 60.357 | 60.985 | 60.341 | 59.682 |
| 2 | Vision Transformer | 63.571 | 66.051 | 63.553 | 62.104 |
| 3 | ShuffleNet | 93.929 | 94.025 | 93.976 | 93.975 |
| 4 | MobileNetV3 | 91.857 | 93.163 | 92.125 | 92.014 |
| 5 | MobileViT | 92.186 | 93.067 | 92.067 | 92.066 |
| 6 | Ours (TIANet) | 95.714 | 95.903 | 95.903 | 95.882 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Zhao, F.; An, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, K.; Guo, Q. TIANet: A Defect Classification Structure Based on the Combination of CNN and ViT. Electronics 2025, 14, 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14081502
Wang H, Zhao F, An X, Zhao Y, Li K, Guo Q. TIANet: A Defect Classification Structure Based on the Combination of CNN and ViT. Electronics. 2025; 14(8):1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14081502
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hongjuan, Fangzheng Zhao, Xinjun An, Youjun Zhao, Kunxi Li, and Quanbing Guo. 2025. "TIANet: A Defect Classification Structure Based on the Combination of CNN and ViT" Electronics 14, no. 8: 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14081502
APA StyleWang, H., Zhao, F., An, X., Zhao, Y., Li, K., & Guo, Q. (2025). TIANet: A Defect Classification Structure Based on the Combination of CNN and ViT. Electronics, 14(8), 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14081502






