A Multimodal Artificial Intelligence Model for Depression Severity Detection Based on Audio and Video Signals
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- We proposed a multimodal depression detection network that automatically estimates severity by extracting key facial and vocal features. It effectively addresses class imbalance and overfitting. The experiments show that the proposed architecture has a superior performance, with 83.86% accuracy, MAE of 0.1271, and MSE of 0.2133.
- (2)
- By applying model optimization techniques, the size and computational complexity of the proposed network are substantially reduced. This optimization enables lightweight deployment, making it feasible to implement the system in resource-constrained or mobile environments.
- (3)
- Through the integration of high detection accuracy, efficient data processing, and real-time deployability, this work delivers a practical solution for intelligent mental health monitoring. It provides valuable insights and technological foundations for advancing smart healthcare systems, particularly in mental health assessment and early intervention.
2. Related Works
3. Method
3.1. Dataset Construction
3.2. Data Preprocessing
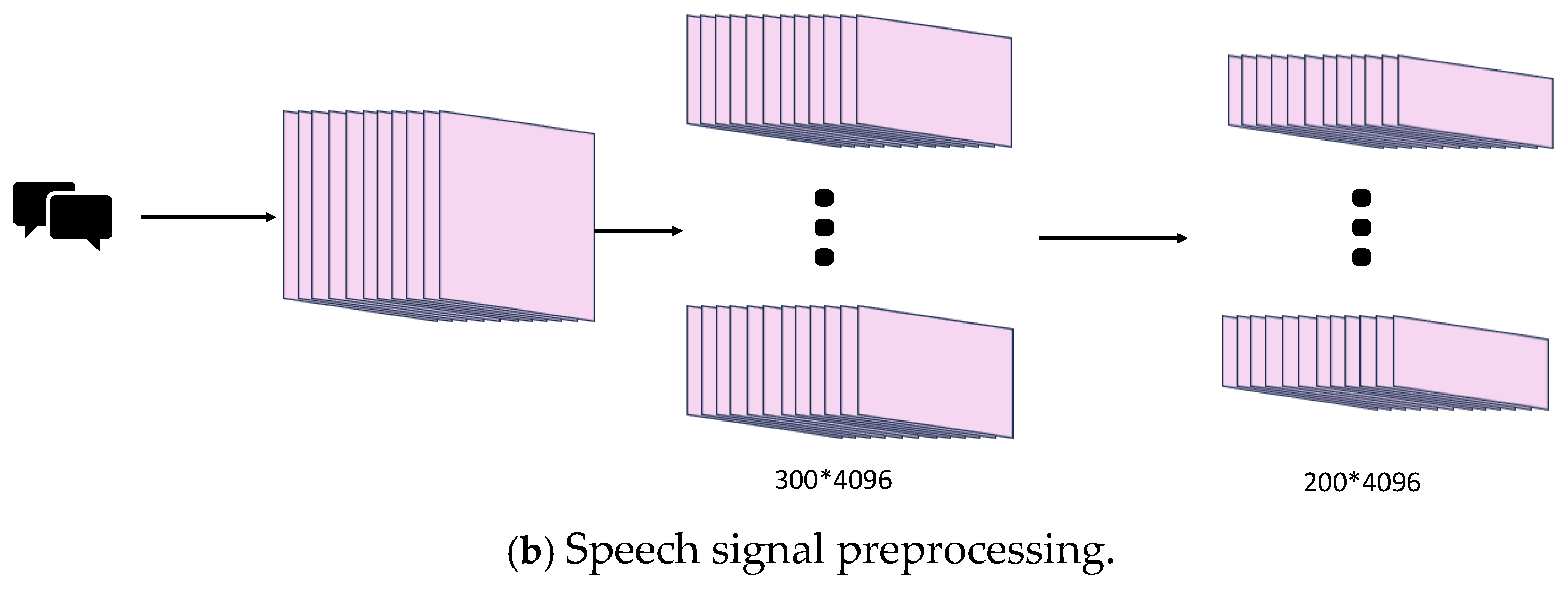
3.3. Video and Audio Signal Processing
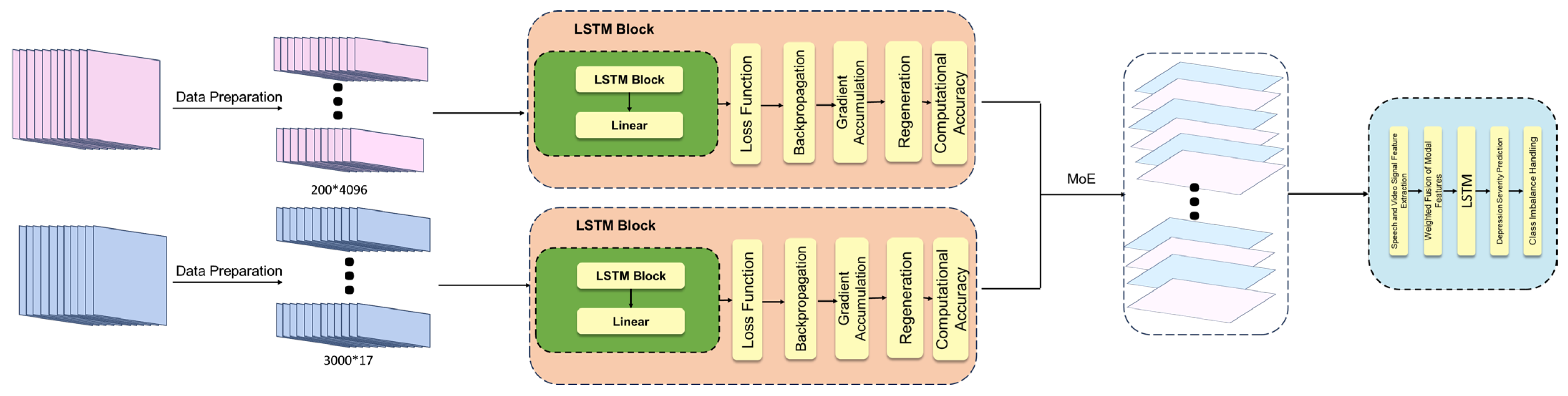
3.4. Multimodal Model
4. Results
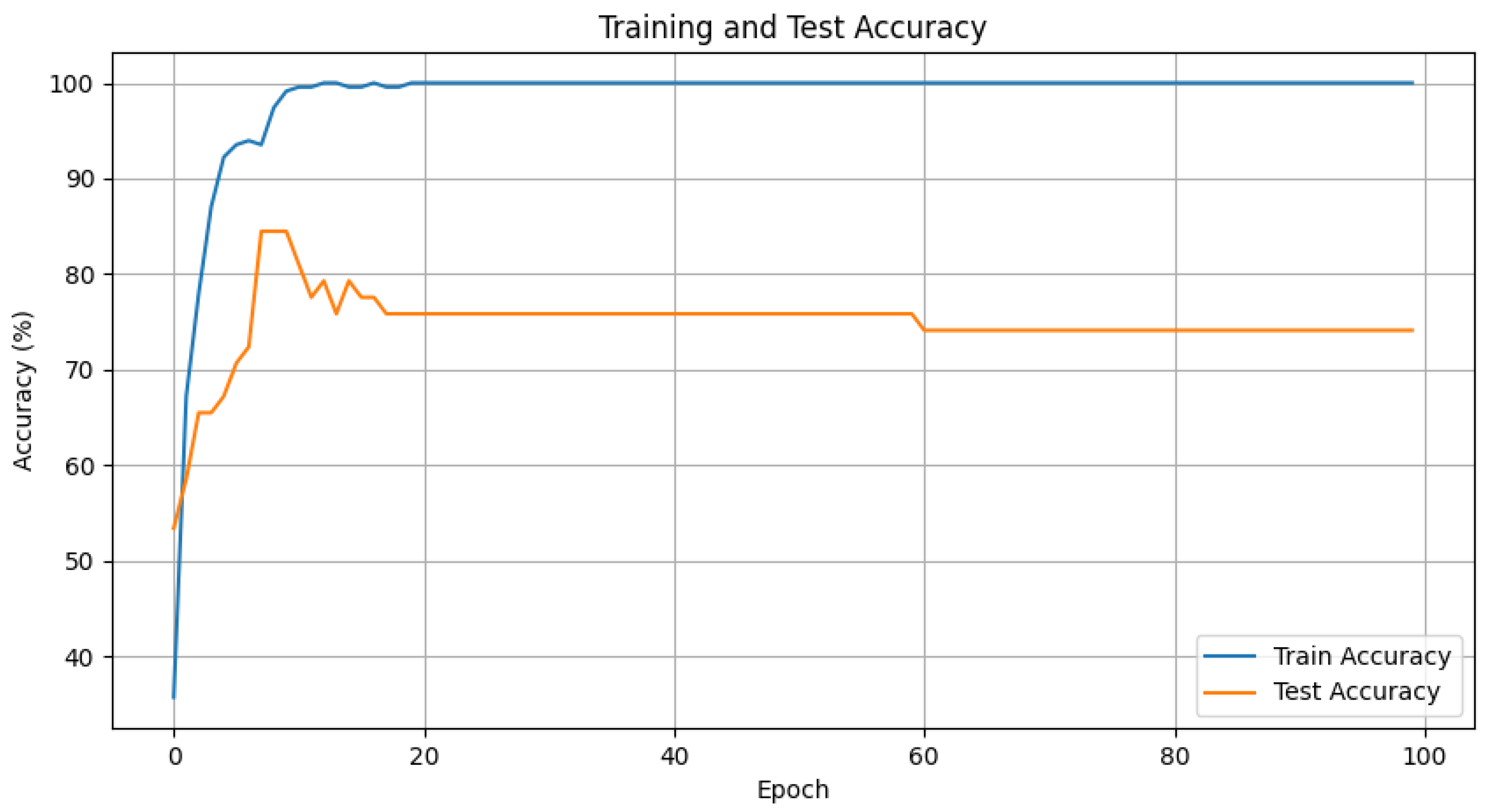
4.1. Conventional Network Experiments
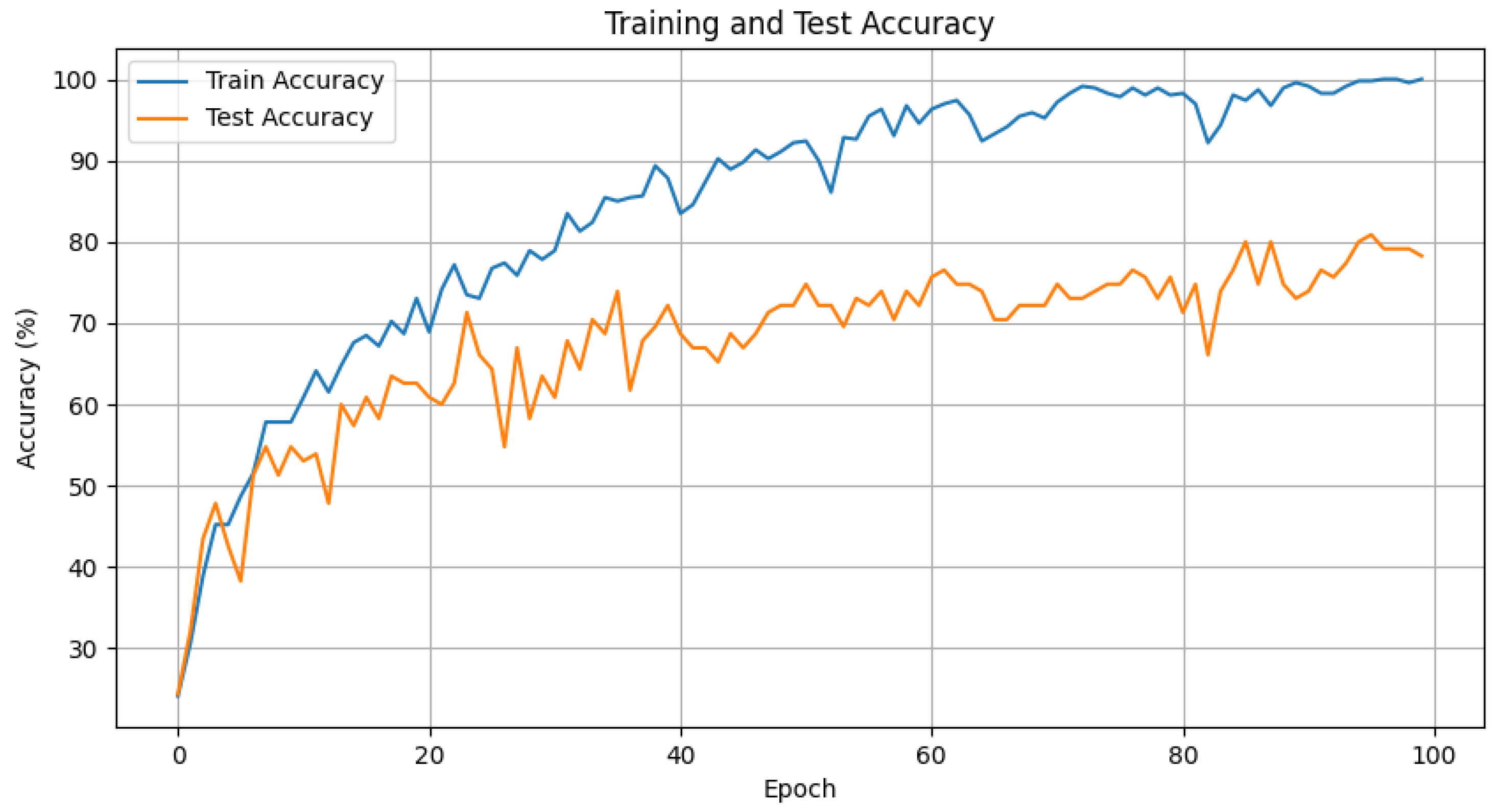
4.2. Conventional LSTM Experiments
4.3. Enhanced LSTM Experiments
4.4. Experimental Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Further exploration will be conducted into utilizing deep learning methods to identify features of depression severity, with the goal of enhancing the model’s recognition capabilities.
- (2)
- Considering the significant gender imbalance in the dataset, as well as the differences in depression prevalence, symptom manifestation, and suicide risk between males and females, the future research will emphasize the impact of gender on depression severity detection.
- (3)
- We will continue collaborate with hospitals, psychological counseling centers, and related institutions to implement automated depression severity detection technologies, ultimately contributing to smart healthcare solutions.
- (4)
- Depression in youth is both prevalent and disabling, often serving as a precursor to chronic and recurrent disorders and impairments in adulthood. However, the issue of depression among children and adolescents has not received sufficient attention from society. Therefore, the future research will place greater emphasis on depression in children and adolescents.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rakel, R.E. Depression. Prim. Care 1999, 26, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belmaker, R.H.; Agam, G. Major Depressive Disorder. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. The Global Burden of Disease: 2004 Update; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Depression and Other Common Mental Disorders: Global Health Estimates; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- France, D.; Shiavi, R.; Silverman, S.; Silverman, M.; Wilkes, M. Acoustical Properties of Speech as Indicators of Depression and Suicidal Risk. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2000, 47, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, Z.; Cheng, S.; Wu, F.; Pan, X.; Li, W.; Dong, W.; Xie, A.; Zhang, G. Electrically Conductive Two-Dimensional Metal-Organic Frameworks for Superior Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 137409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, S.; Yu, Y.; Yan, G.; Yu, M.; Guo, Y. Multi-Task Facial Activity Patterns Learning for Micro-Expression Recognition Using Joint Temporal Local Cube Binary Pattern. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2022, 103, 116616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Yuan, X.; Shangguan, Z.; Hu, X.; Hu, B. A Facial Depression Recognition Method Based on Hybrid Multi-Head Cross Attention Network. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1188434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Shang, Y.; Shao, Z.; Liu, J.; Guo, G.; Liu, T.; Ding, H.; Hu, Q. Spatial-Temporal Feature Network for Speech-Based Depression Recognition. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2023, 16, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; Fang, J.; Niu, M.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, J.; Tian, Q. MTDAN: A Lightweight Multi-Scale Temporal Difference Attention Networks for Automated Video Depression Detection. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2023, 15, 1078–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Shang, Y.; Wang, W.; Shao, Z.; Han, Z.; Liu, T.; Guo, G.; Ding, H. Multi-Feature Deep Supervised Voiceprint Adversarial Network for Depression Recognition from Speech. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2024, 89, 105704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Niu, M.; Tiwari, P.; Marttinen, P.; Su, R.; Jiang, J.; Guo, C.; Wang, H.; Ding, S.; Wang, Z.; et al. Deep Learning for Depression Recognition with Audiovisual Cues: A Review. Inf. Fusion 2022, 80, 56–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.; Tao, J.; Liu, B.; Huang, J.; Lian, Z. Multimodal Spatiotemporal Representation for Automatic Depression Level Detection. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2023, 14, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroenke, K.; Strine, T.W.; Spitzer, R.L.; Williams, J.B.; Berry, J.T.; Mokdad, A.H. The PHQ-8 as a Measure of Current Depression in the General Population. J. Affect. Disord. 2009, 114, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burdisso, S.; Reyes-Ramírez, E.; Villatoro-Tello, E.; Sánchez-Vega, F.; Monroy, A.L.; Motlicek, P. DAIC-WOZ: On the Validity of Using the Therapist’s Prompts in Automatic Depression Detection from Clinical Interviews. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.14463. [Google Scholar]
- Misgar, M.; Bhatia, M. Hopping-Mean: An Augmentation Method for Motor Activity Data Towards Real-Time Depression Diagnosis Using Machine Learning. Multimedia Tools Appl. 2024, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlman, K.; Mehltretter, J.; Benrimoh, D.; Armstrong, C.; Fratila, R.; Popescu, C.; Tunteng, J.-F.; Williams, J.; Rollins, C.; Golden, G.; et al. Development of a Differential Treatment Selection Model for Depression on Consolidated and Transformed Clinical Trial Datasets. Transl. Psychiatry 2024, 14, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Poellabauer, C. Topic Modeling Based Multi-Modal Depression Detection. In Proceedings of the 7th Annual Workshop on Audio/Visual Emotion Challenge, Mountain View, CA, USA, 23 October 2017; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, L.; Wang, L.; Diao, G. Recognition of Audio Depression Based on Convolutional Neural Network and Generative Antagonism Network Model. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 101181–101191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, J.F.; Kruez, T.S.; Matthews, I.; Yang, Y.; Nguyen, M.H.; Padilla, M.T.; Zhou, F.; De la Torre, F. Detecting Depression from Facial Actions and Vocal Prosody. In Proceedings of the 2009 3rd International Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction and Workshops, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 10–12 September 2009; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Jiang, D.; Xia, X.; Pei, E.; Oveneke, M.C.; Sahli, H. Multimodal Measurement of Depression Using Deep Learning Models. In Proceedings of the 7th Annual Workshop on Audio/Visual Emotion Challenge, Mountain View, CA, USA, 23 October 2017; pp. 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Jan, A.; Meng, H.; Gaus, Y.F.B.A.; Zhang, F. Artificial Intelligent System for Automatic Depression Level Analysis Through Visual and Vocal Expressions. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2017, 10, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Huang, W. Automatic Identification of Depressive Symptoms in College Students: An Application of Deep Learning-Based CNN (Convolutional Neural Network). Appl. Math. Nonlinear Sci. 2024, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blei, D.M.; Ng, A.Y.; Jordan, M.I. Latent Dirichlet Allocation. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2003, 3, 993–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, G.; Umapathy, K.; Krishnan, S. Trends in Audio Signal Feature Extraction Methods. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 158, 107020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, F.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, T.; Zhao, K.; Fu, X. MFED: A Database for Masked Facial Expression. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 96279–96287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huc, M.; Bush, K.; Atias, G.; Berrigan, L.; Cox, S.; Jaworska, N. Recognition of Masked and Unmasked Facial Expressions in Males and Females and Relations with Mental Wellness. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1217736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shazeer, N.; Maziarz, K.; Davis, A.; Le, Q.; Hinton, G.; Dean, J. Outrageously Large Neural Networks: The Sparsely-Gated Mixture-of-Experts Layer. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1701.06538. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs, R.A.; Jordan, M.I.; Nowlan, S.J.; Hinton, G.E. Adaptive Mixtures of Local Experts. Neural Comput. 1991, 3, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, R.; Lu, H.; Liu, M. DenseFormer-MoE: A Dense Transformer Foundation Model with Mixture of Experts for Multi-Task Brain Image Analysis. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Liu, C.; Wu, J.; Liu, F.; Zhu, J.; Li, H.B.; Chen, C.; Ouyang, C.; Rueckert, D. MedVLM-R1: Incentivizing Medical Reasoning Capability of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) via Reinforcement Learning. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.19634. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, T.; Cao, A.; Lee, G.; Johnson, J.; Lee, H. Probing Visual Language Priors in VLMs. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.00569. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Kumar, D. Detection of Stress, Anxiety, and Depression (SAD) in Video Surveillance Using ResNet-101. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2022, 95, 104681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Melo, W.C.; Granger, E.; Lopez, M.B. Facial Expression Analysis Using Decomposed Multiscale Spatiotemporal Networks. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 236, 121276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yu, X.; Huang, Z.; Palati, F.; Zhao, Z.; He, Z.; Feng, Y.; Luo, Y. Multi-Modal Fused-Attention Network for Depression Level Recognition Based on Enhanced Audiovisual Cues. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 37913–37923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, Y.; Ge, F.; Chen, D.; Shen, L.; Liu, H. An Enhanced Cross-Attention Based Multimodal Model for Depression Detection. Comput. Intell. 2025, 41, e70019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Yang, H.; Lin, L. Automatic Depression Detection: An Emotional Audio-Textual Corpus and A GRU/BiLSTM-Based Model. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022—2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 23–27 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Yuan, X.; Li, Y.; Shangguan, Z.; Zhou, L.; Hu, B. PRA-Net: Part-and-Relation Attention Network for Depression Recognition from Facial Expression. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 157, 106589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Wan, Y.; Fan, Y.; Chen, D.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, K.; Zheng, Y. DepITCM: An Audio-Visual Method for Detecting Depression. Front. Psychiatry 2025, 15, 1466507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
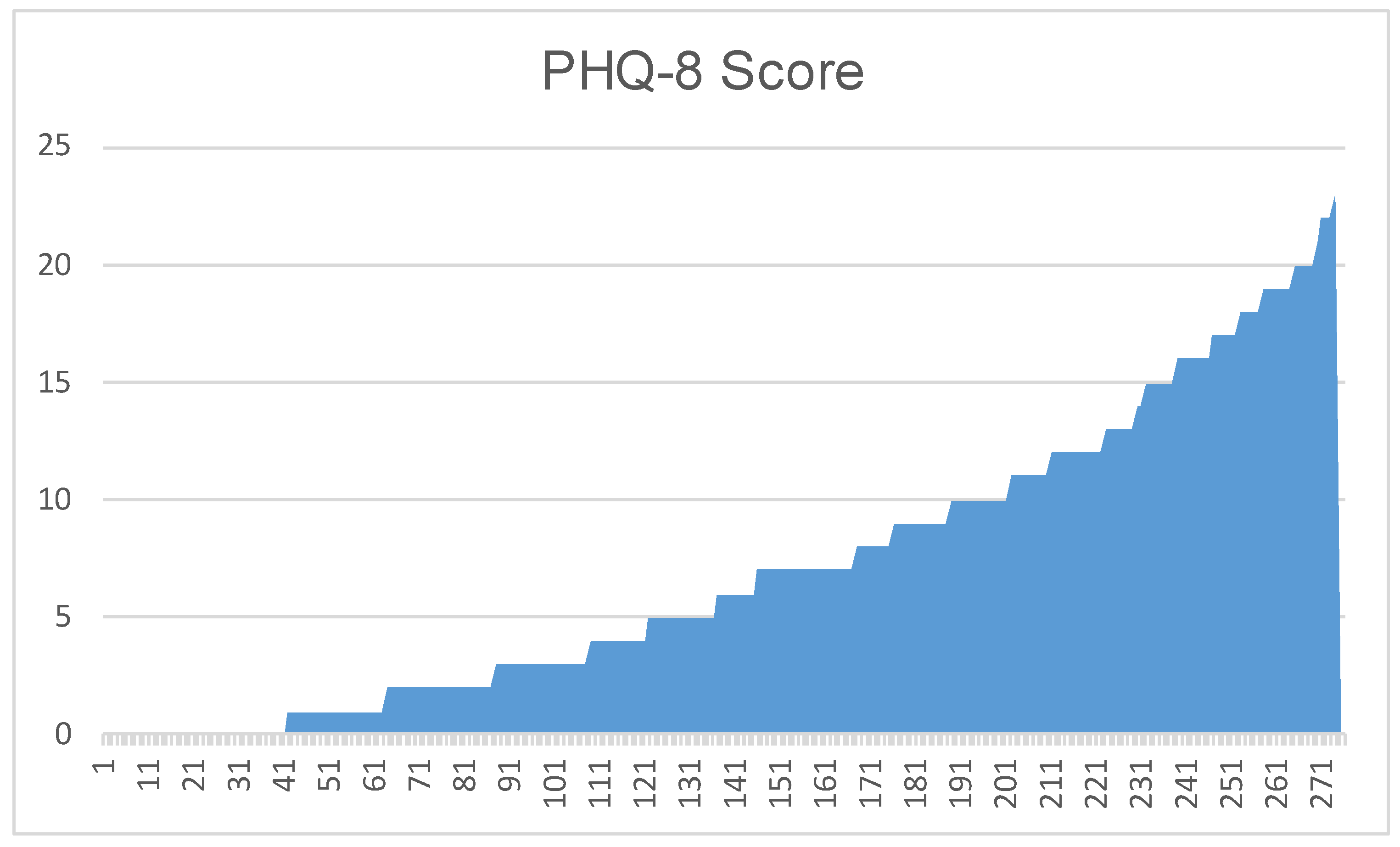
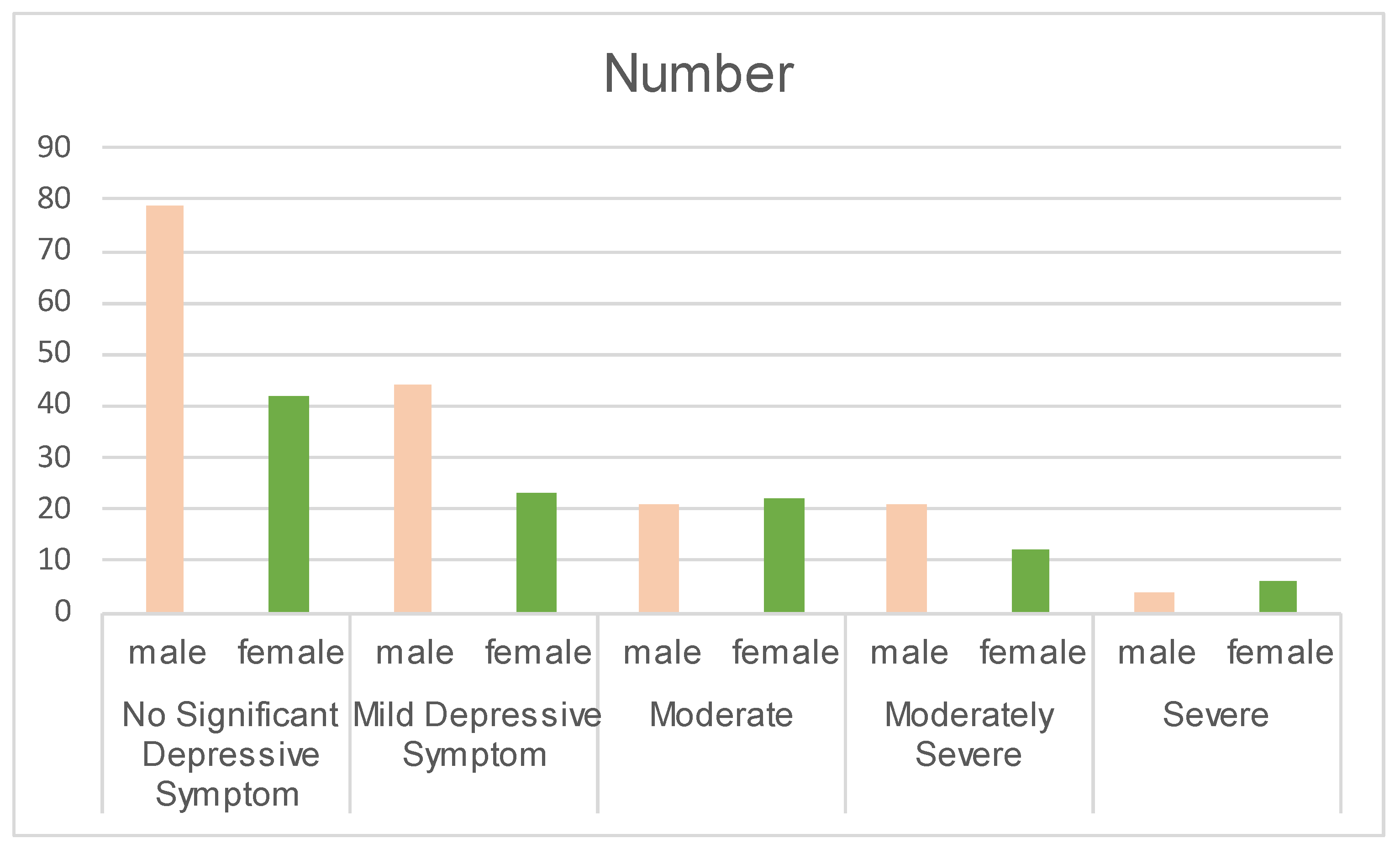



| PHQ-8 Score (/) | Severity Level |
|---|---|
| 0–4 | No Significant Depressive Symptom |
| 5–9 | Mild Depressive Symptom |
| 10–14 | Moderate |
| 15–19 | Moderately Severe |
| 20–24 | Severe |
| Action Unit (/) | Description | Action Unit (/) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Inner Brow Raiser | 2 | Outer Brow Raiser |
| 4 | Brow Lowerer | 5 | Upper Lid Raiser |
| 6 | Cheek Raiser | 7 | Lid Tightener |
| 9 | Nose Wrinkler | 10 | Upper Lip Raiser |
| 12 | Lip Corner Puller | 14 | Dimpler |
| 15 | Lip Corner Depressor | 17 | Chin Raiser |
| 20 | Lip Stretcher | 23 | Lip Tightener |
| 25 | Lips Part | 26 | Jaw Drop |
| 45 | Blink |
| Platform | Detailed Information |
|---|---|
| Processing Unit | AMD Ryzen 7 7700 8-Core Processor |
| Graphics Board | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4090 D |
| Python | 3.11.7 |
| Pytorch-cuda | 12.1 |
| Torchvision | 0.18.1 |
| Evaluation Indicators | Result |
|---|---|
| FLOPs | 0.468 (GFLOPs) |
| Average inference time per batch | 0.001655 (second) |
| Total params | 128,905 |
| Total mult-adds (UnitS.MEGABYTES) | 642.00 |
| Input size | 0.34 (MB) |
| Forward/backward pass size | 4.00 (MB) |
| Params size | 0.52 (MB) |
| Estimated total size | 4.86 (MB) |
| Size of memory footprint | 0.49 (MB) |
| Modality | Network Type | Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSE (/) | RMSE (/) | MAE (/) | Accuracy (%) | ||
| Audio | Random Forest ResNet | 1.9293 | 1.3890 | 0.0372 | 23.96% 60.87% |
| LSTM | 5.3066 | 2.3036 | 0.0350 | 79.13% | |
| Video | Random Forest ResNet | 2.6644 | 1.6323 | 0.0337 | 20.53% 66.09% |
| LSTM | 4.5769 | 2.1394 | 0.0346 | 80.87% | |
| Multi-Model | LSTM | 0.2133 | 0.3566 | 0.1271 | 83.86% |
| Modality | Network Type | Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSE (/) | RMSE (/) | MAE (/) | Accuracy (%) | ||
| Audio Video Multi-Model | Multimodal LSTM [37] AVTF-TBN [38] Proposed method Speaking HDR-DCNN [21] AVTF-TBN [29] Proposed method Topic modeling [18] DepITCM [39] AVTF-TBN [29] Proposed method | 1.9293 4.5769 0.2133 | 1.3890 2.1394 4.99 4.89 0.3566 | 0.0372 0.0346 3.96 4.62 0.1271 | 71% 61% 60.87% 82% 62% 80.87% 81.3% 57% 83.86% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y. A Multimodal Artificial Intelligence Model for Depression Severity Detection Based on Audio and Video Signals. Electronics 2025, 14, 1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14071464
Zhang L, Zhang S, Zhang X, Zhao Y. A Multimodal Artificial Intelligence Model for Depression Severity Detection Based on Audio and Video Signals. Electronics. 2025; 14(7):1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14071464
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Liyuan, Shuai Zhang, Xv Zhang, and Yafeng Zhao. 2025. "A Multimodal Artificial Intelligence Model for Depression Severity Detection Based on Audio and Video Signals" Electronics 14, no. 7: 1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14071464
APA StyleZhang, L., Zhang, S., Zhang, X., & Zhao, Y. (2025). A Multimodal Artificial Intelligence Model for Depression Severity Detection Based on Audio and Video Signals. Electronics, 14(7), 1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14071464






