SolidTrack: A Novel Method for Robust and Reliable Multi-Pedestrian Tracking
Abstract
1. Introduction
- RQ1: How robust are the existing SOTA TBD methods to variations in threshold values?
- RQ2: To what extent do our proposed methods demonstrate greater robustness to variations in threshold values compared to existing SOTA TBD methods?
- Robustness Analysis: We conducted extensive experiments on SOTA TBD methods, revealing how their performance varies with changes in , providing valuable insights into their robustness in dynamic environments.
- SolidTrack: We introduced SolidTrack, a novel approach, by integrating the SOLIDER-ReID model into the MOT task, which significantly enhances robustness against variations in , as demonstrated by improved experimental results.
- Performance on Benchmark Datasets: We achieved SOTA performance on the MOT17 and MOT20 test sets, showcasing the reliability and effectiveness of the proposed method in real-world tracking scenarios.
2. Related Work
2.1. Object Detection
2.1.1. Two-Stage Algorithms
2.1.2. One-Stage Algorithms
2.2. Data Association
2.2.1. Similarity Metrics
Motion Model
Appearance Model
2.2.2. Matching Method
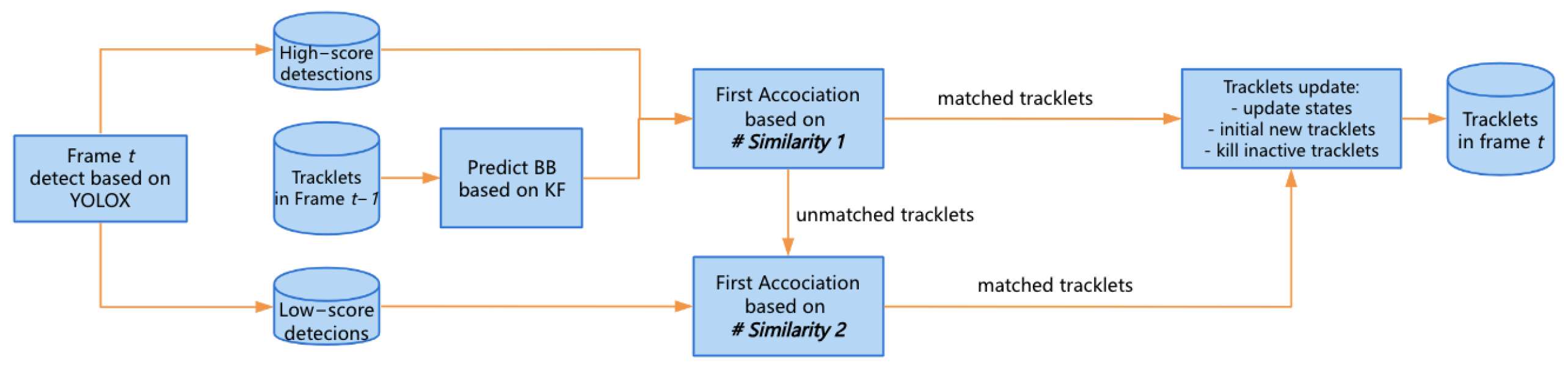
3. SolidTrack
- SOLIDER-ReID: With advancements in Transformer [39] and self-supervised training, Chen et al. [19] proposed a semantic-controllable self-supervised learning framework called SOLIDER. This framework leverages prior knowledge from human images to train representations enriched with semantic information. Additionally, the pre-trained model from SOLIDER can be fine-tuned via a semantic controller input, allowing for the generation of representations with varying degrees of semantic information to meet the specific needs of downstream tasks, such as person re-identification, pedestrian detection, pose estimation, etc. The reason why we choose SOLIDER-ReID to extract appearance feature is that SOLIDER-ReID significantly outperforms other ReID methods and has made substantial progress in addressing the occlusion issue in person-ReID compared to traditional CNN methods. For more details, please refer to [19].
SolidTrack Framework
4. Experiment and Results
4.1. Settings
4.1.1. Datasets
4.1.2. Metrics
4.1.3. Implementation Details
4.1.4. Comparison Methods
4.2. Results
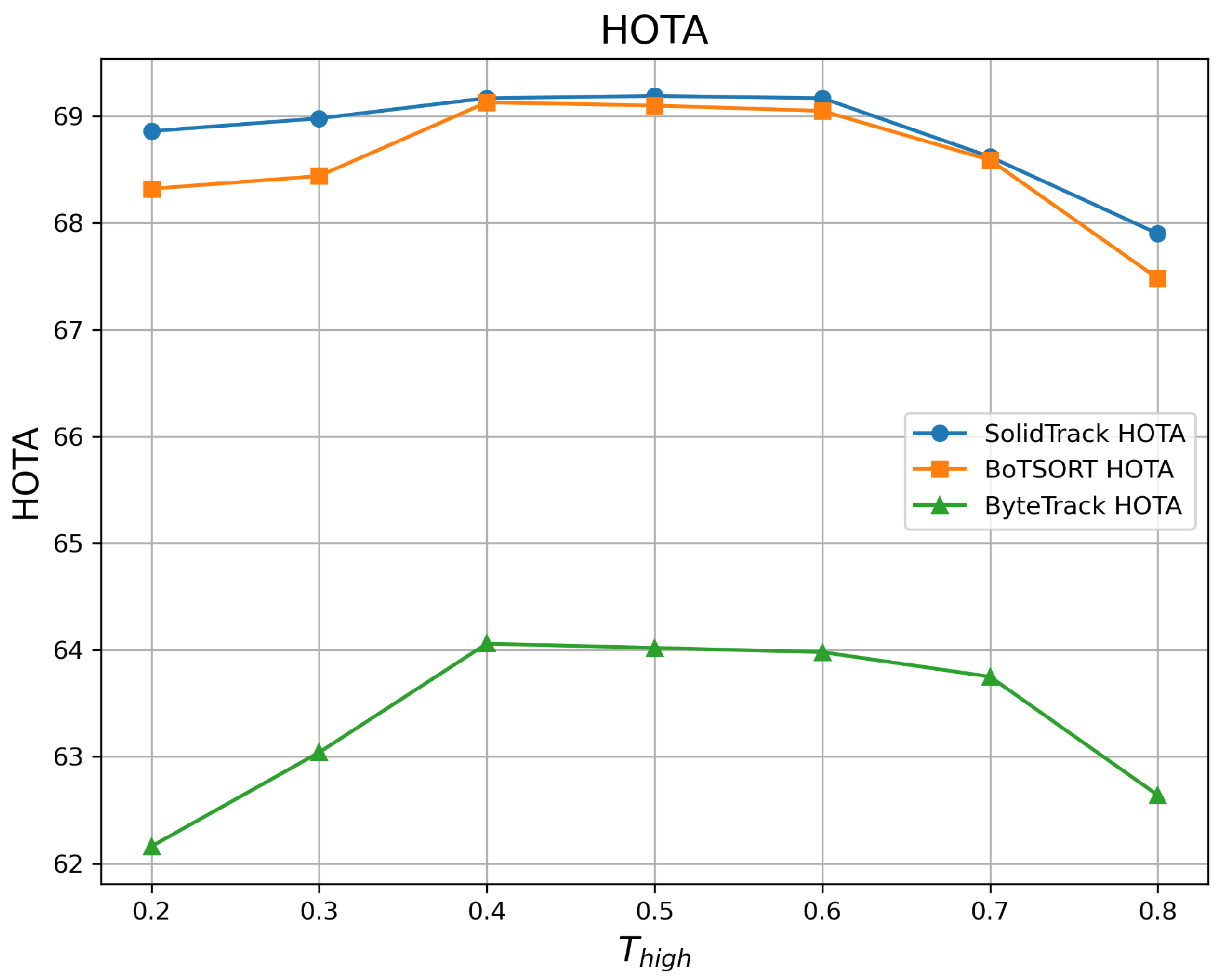
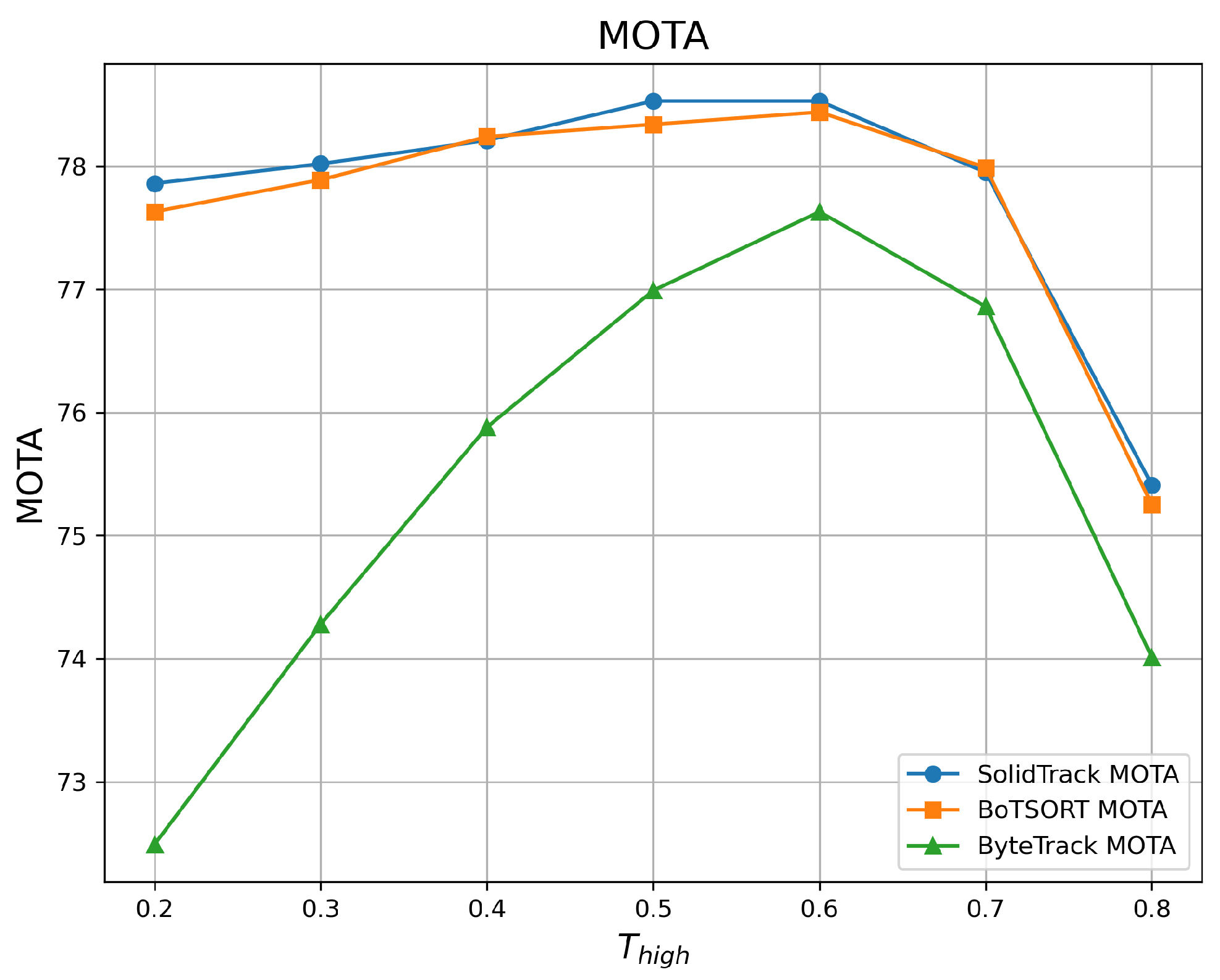
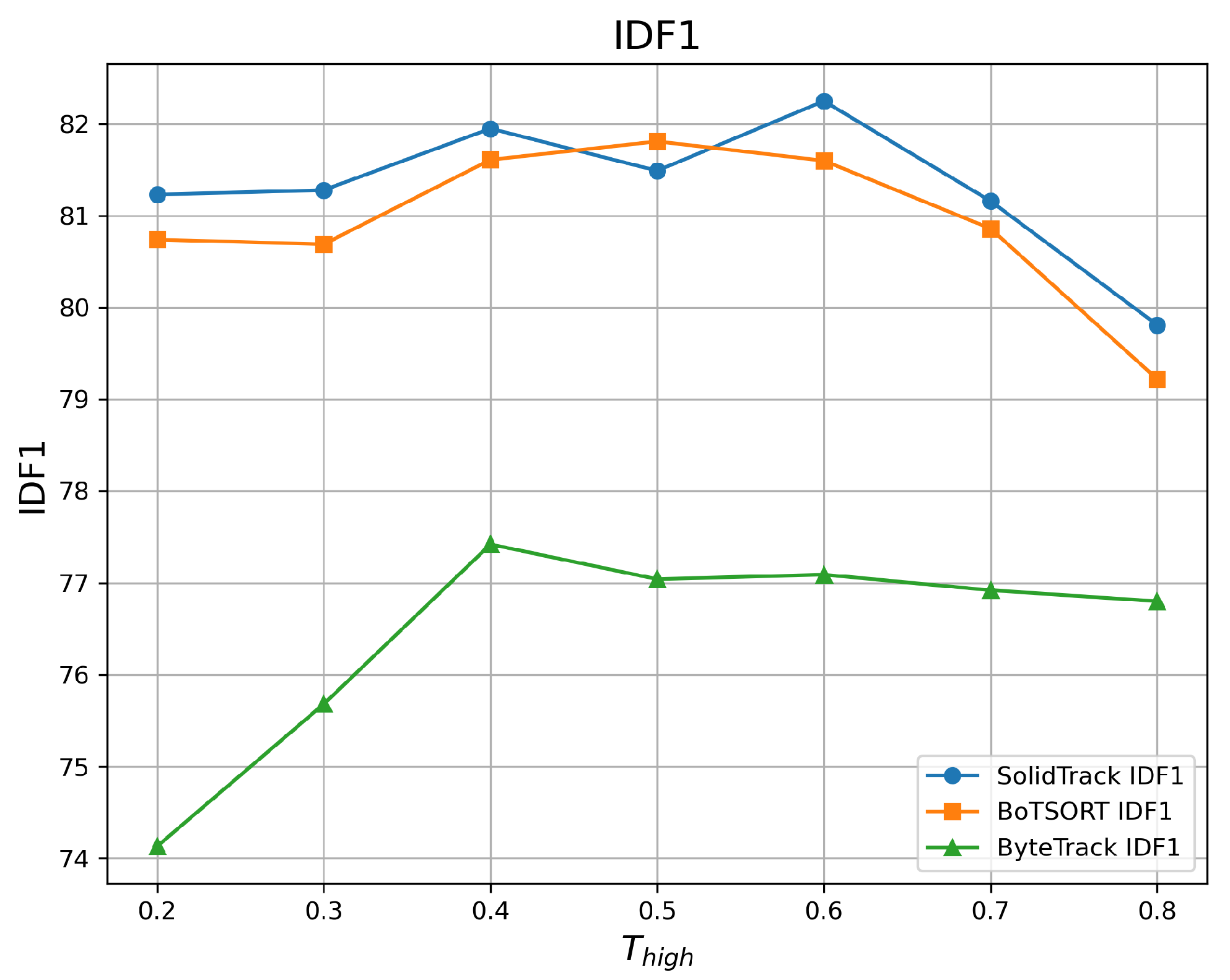
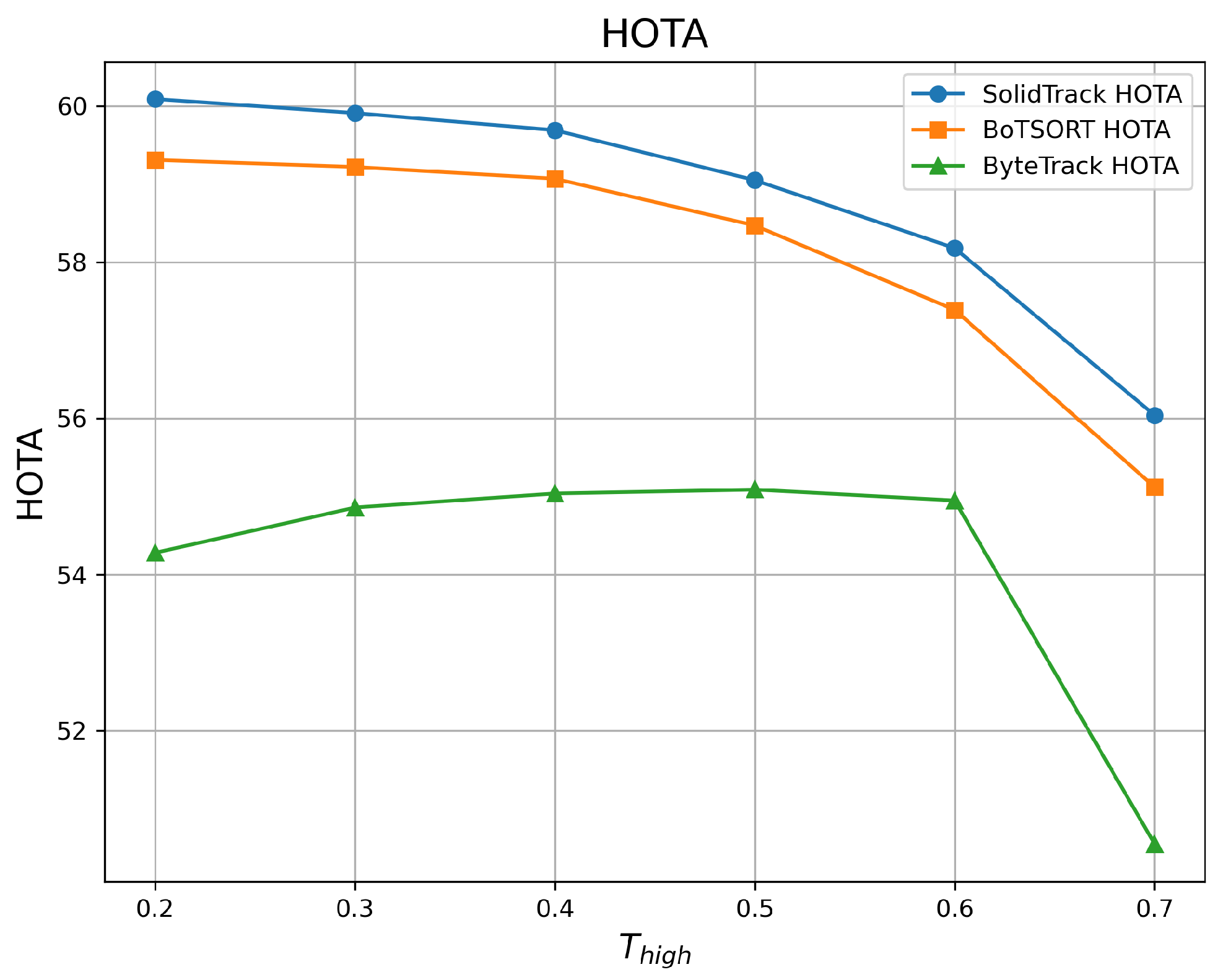
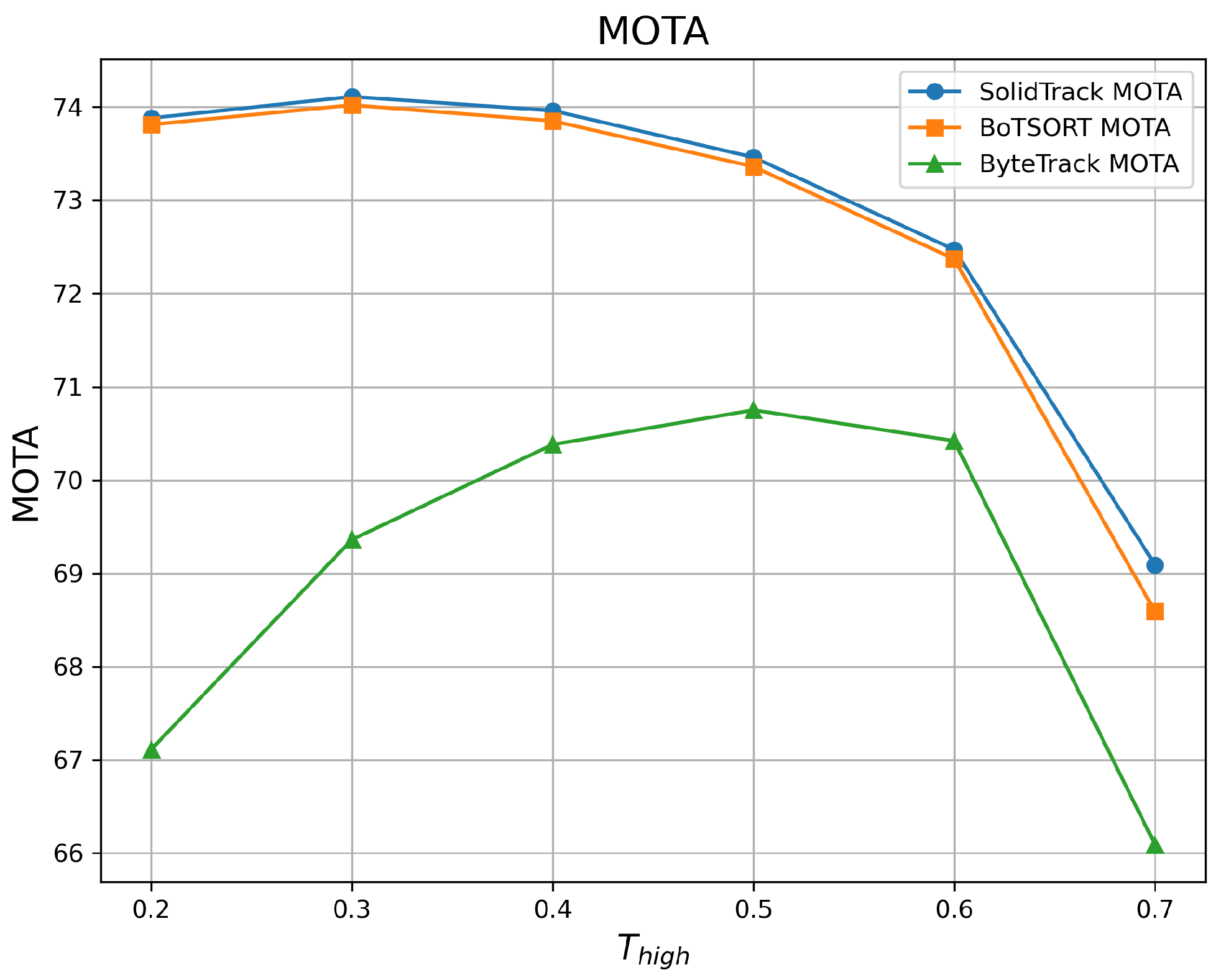
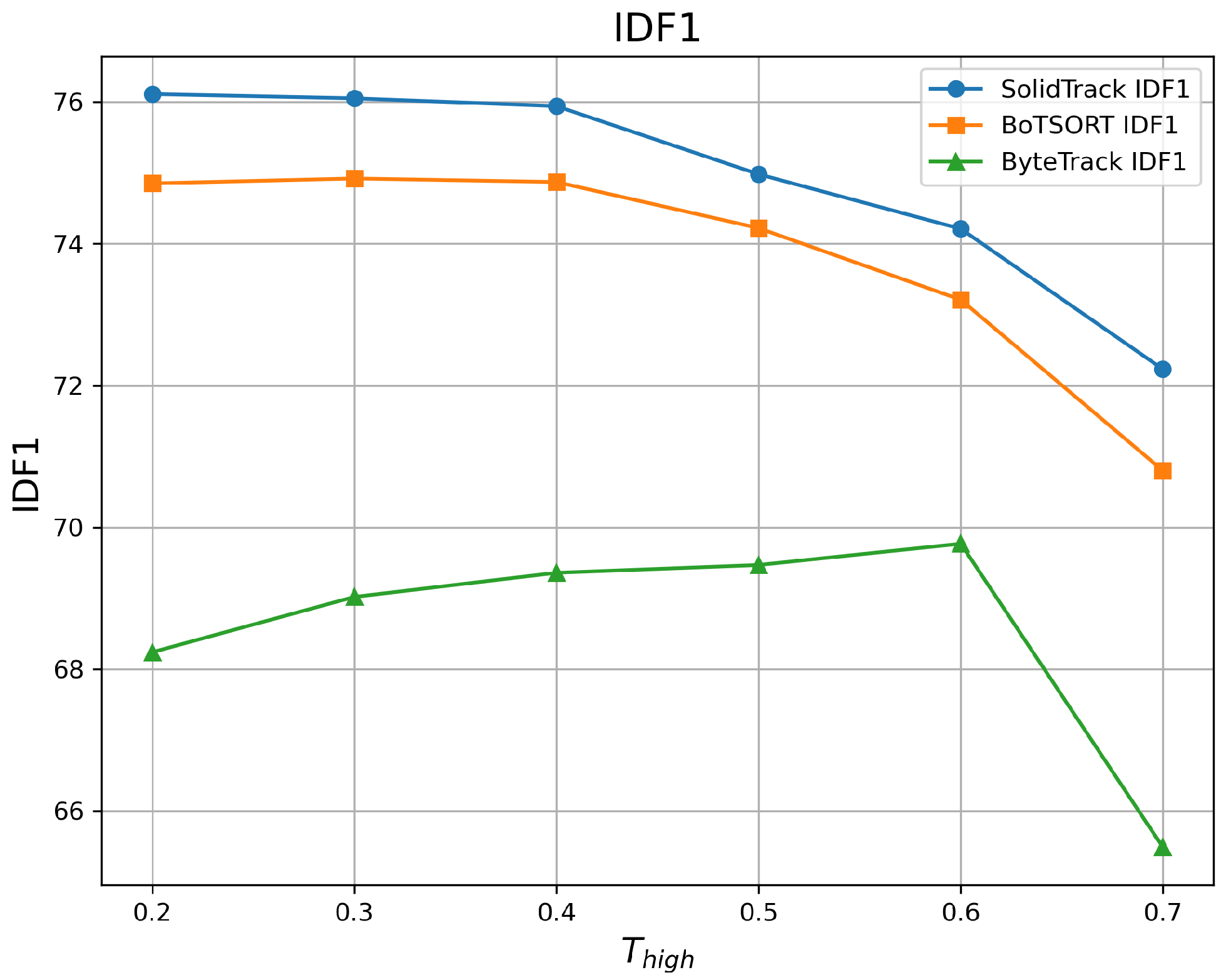
4.2.1. Robustness Evaluation Against Detection Score Thresholds
4.2.2. Benchmark Evaluation
MOT17
MOT20
5. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Algorithm A1 Pseudo-code of SolidTrack |
| Require: A video sequence V; object detector Det; detection score threshold Ensure: Tracks of the video
|
References
- Luo, W.; Xing, J.; Milan, A.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W.; Kim, T.K. Multiple object tracking: A literature review. Artif. Intell. 2021, 293, 103448. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, M.; Jin, L.; Jiang, Y.; Bie, J. Multiple object tracking using a dual-attention network for autonomous driving. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 14, 842–848. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Jin, L.; He, Y.; Huo, Z.; Wang, G.; Sun, X. Detector–tracker integration framework for autonomous vehicles pedestrian tracking. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, A.; Singh, S. Trends in video object tracking in surveillance: A survey. In Proceedings of the 2019 Third International Conference on I-SMAC (IoT in Social, Mobile, Analytics and Cloud) (I-SMAC), Palladam, India, 12–14 December 2019; pp. 729–733. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez-Bravo, D.M.; Murciego, Á.L.; Mendes, A.S.; San Blás, H.S.; Bajo, J. Multi-object tracking in traffic environments: A systematic literature review. Neurocomputing 2022, 494, 43–55. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, J.; Lin, M.C. Avot: Audio-visual object tracking of multiple objects for robotics. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; pp. 10045–10051. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zheng, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, S. Towards real-time multi-object tracking. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 107–122. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, C.; Ma, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y. Learning discriminative activated simplices for action recognition. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017; Volume 31. [Google Scholar]
- Bewley, A.; Ge, Z.; Ott, L.; Ramos, F.; Upcroft, B. Simple online and realtime tracking. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 25–28 September 2016; pp. 3464–3468. [Google Scholar]
- Wojke, N.; Bewley, A.; Paulus, D. Simple online and realtime tracking with a deep association metric. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Beijing, China, 17–20 September 2017; pp. 3645–3649. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Li, W.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Shi, X.; Yan, J. Poi: Multiple object tracking with high performance detection and appearance feature. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016 Workshops, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–10 and 15–16 October 2016; Proceedings, Part II 14. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- Aharon, N.; Orfaig, R.; Bobrovsky, B.Z. BoT-SORT: Robust associations multi-pedestrian tracking. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.14651. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, P.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, D.; Weng, F.; Yuan, Z.; Luo, P.; Liu, W.; Wang, X. Bytetrack: Multi-object tracking by associating every detection box. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, S.H.; Yoon, K.J. Robust online multi-object tracking based on tracklet confidence and online discriminative appearance learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1218–1225. [Google Scholar]
- Berclaz, J.; Fleuret, F.; Turetken, E.; Fua, P. Multiple object tracking using k-shortest paths optimization. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 33, 1806–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, P.; Meinhardt, T.; Leal-Taixe, L. Tracking without bells and whistles. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 941–951. [Google Scholar]
- Dendorfer, P.; Rezatofighi, H.; Milan, A.; Shi, J.; Cremers, D.; Reid, I.; Roth, S.; Schindler, K.; Leal-Taixé, L. Mot20: A benchmark for multi object tracking in crowded scenes. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.09003. [Google Scholar]
- Milan, A.; Leal-Taixé, L.; Reid, I.; Roth, S.; Schindler, K. MOT16: A benchmark for multi-object tracking. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.00831. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Xu, X.; Jia, J.; Luo, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Jin, R.; Sun, X. Beyond appearance: A semantic controllable self-supervised learning framework for human-centric visual tasks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 15050–15061. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Cao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yang, S.; Xu, L.; Xu, M. Visible-Infrared Person Re-identification with Real-world Label Noise. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Liu, L. A survey of detection-based video multi-object tracking. Displays 2022, 75, 102317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE international Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Z.; Vasconcelos, N. Cascade r-cnn: Delving into high quality object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6154–6162. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Proceedings, Part I 14. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1708.02002. [Google Scholar]
- Law, H.; Deng, J. Cornernet: Detecting objects as paired keypoints. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 734–750. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, K.; Bai, S.; Xie, L.; Qi, H.; Huang, Q.; Tian, Q. Centernet: Keypoint triplets for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6569–6578. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Sun, J. Yolox: Exceeding yolo series in 2021. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.08430. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, R.G.; Hwang, P.Y. Introduction to random signals and applied Kalman filtering: With MATLAB exercises and solutions. In Introduction to Random Signals and Applied Kalman Filtering: With MATLAB Exercises and Solutions; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Song, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Su, F.; Gong, T.; Meng, H. Strongsort: Make deepsort great again. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2023, 25, 8725–8737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Xu, L.; Yu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Mu, C.; Xu, M. Deep-IRTarget: An automatic target detector in infrared imagery using dual-domain feature extraction and allocation. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2021, 24, 1735–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Odashima, S.; Masui, S.; Jiang, S. Hard to track objects with irregular motions and similar appearances? make it easier by buffering the matching space. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 2–7 January 2023; pp. 4799–4808. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017. Available online: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2017/file/3f5ee243547dee91fbd053c1c4a845aa-Paper.pdf (accessed on 15 February 2025).
- Zheng, L.; Shen, L.; Tian, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Tian, Q. Scalable person re-identification: A benchmark. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1116–1124. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardin, K.; Stiefelhagen, R. Evaluating multiple object tracking performance: The clear mot metrics. EURASIP J. Image Video Process. 2008, 2008, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ristani, E.; Solera, F.; Zou, R.; Cucchiara, R.; Tomasi, C. Performance measures and a data set for multi-target, multi-camera tracking. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; pp. 17–35. [Google Scholar]
- Luiten, J.; Osep, A.; Dendorfer, P.; Torr, P.; Geiger, A.; Leal-Taixé, L.; Hota, B.L. A higher order metric for evaluating multi-object tracking. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 548–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Method | SolidTrack | BoT-SORT | ByteTrack | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HOTA↑ | MOTA↑ | IDF1↑ | HOTA↑ | MOTA↑ | IDF1↑ | HOTA↑ | MOTA↑ | IDF1↑ | |
| 0.2 | 68.86 | 77.86 | 81.23 | 68.32 | 77.63 | 80.74 | 62.16 | 72.49 | 74.13 |
| 0.3 | 68.98 | 78.02 | 81.28 | 68.44 | 77.89 | 80.69 | 63.04 | 74.28 | 75.68 |
| 0.4 | 69.17 | 78.21 | 81.95 | 69.13 | 78.24 | 81.61 | 64.06 | 75.88 | 77.42 |
| 0.5 | 69.19 | 78.53 | 81.49 | 69.10 | 78.34 | 81.81 | 64.02 | 76.99 | 77.04 |
| 0.6 | 69.17 | 78.53 | 82.25 | 69.05 | 78.44 | 81.60 | 63.98 | 77.63 | 77.09 |
| 0.7 | 68.62 | 77.95 | 81.16 | 68.59 | 77.99 | 80.86 | 63.75 | 76.86 | 76.92 |
| 0.8 | 67.90 | 75.41 | 79.81 | 67.48 | 75.25 | 79.22 | 62.64 | 74.01 | 76.80 |
| Mean ↑ | 68.84 | 77.78 | 81.31 | 68.59 | 77.69 | 80.93 | 63.38 | 75.45 | 76.44 |
| Var ↓ | 0.216 | 1.171 | 0.603 | 0.346 | 1.229 | 0.783 | 0.587 | 3.578 | 1.339 |
| Method | SolidTrack | BoT-SORT | ByteTrack | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HOTA↑ | MOTA↑ | IDF1↑ | HOTA↑ | MOTA↑ | IDF1↑ | HOTA↑ | MOTA↑ | IDF1↑ | |
| 0.2 | 60.09 | 73.88 | 76.11 | 59.31 | 73.81 | 74.85 | 54.28 | 67.11 | 68.24 |
| 0.3 | 59.91 | 74.11 | 76.05 | 59.22 | 74.02 | 74.92 | 54.86 | 69.36 | 69.02 |
| 0.4 | 59.69 | 73.96 | 75.94 | 59.07 | 73.85 | 74.87 | 55.04 | 70.38 | 69.36 |
| 0.5 | 59.05 | 73.46 | 74.98 | 58.47 | 73.36 | 74.22 | 55.09 | 70.75 | 69.47 |
| 0.6 | 58.18 | 72.47 | 74.21 | 57.39 | 72.37 | 73.21 | 54.95 | 70.42 | 69.77 |
| 0.7 | 56.04 | 69.09 | 72.23 | 55.12 | 68.59 | 70.80 | 50.55 | 66.09 | 65.49 |
| 0.8 | 35.86 | 33.20 | 42.01 | 35.83 | 33.15 | 42.03 | 28.03 | 33.65 | 31.67 |
| Mean ↑ | 58.83 | 72.83 | 74.92 | 58.10 | 72.67 | 73.81 | 54.13 | 69.02 | 68.56 |
| Var ↓ | 2.349 | 3.699 | 2.298 | 2.631 | 4.348 | 2.607 | 3.158 | 3.827 | 2.532 |
| Tracker | MOTA ↑ | IDF1 ↑ | HOTA ↑ | FP ↓ | FN ↓ | IDs ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tube_TK | 63.0 | 58.6 | 48.0 | 27,060 | 177,483 | 4137 |
| MOTR | 65.1 | 66.4 | - | 45,486 | 149,307 | 2049 |
| CTracker | 66.6 | 57.4 | 49.0 | 22,284 | 160,491 | 5529 |
| CenterTrack | 67.8 | 64.7 | 52.2 | 18,498 | 160,332 | 3039 |
| QuasiDense | 68.7 | 66.3 | 53.9 | 26,589 | 146,643 | 3378 |
| GSDT | 73.2 | 66.5 | 55.2 | 26,397 | 120,666 | 3891 |
| Semi-TCL | 73.3 | 73.2 | 59.8 | 22,944 | 124,980 | 2790 |
| FairMOT | 73.7 | 72.3 | 59.3 | 27,507 | 117,477 | 3303 |
| RelationTrack | 73.8 | 74.7 | 61.0 | 27,999 | 118,623 | 1374 |
| PermaTrackPr | 73.8 | 68.9 | 55.5 | 28,998 | 115,104 | 3699 |
| TransMOT | 76.7 | 75.1 | 61.7 | 36,231 | 93,150 | 2346 |
| ReMOT | 77.0 | 72.0 | 59.7 | 33,204 | 93,612 | 2853 |
| MAATrack | 79.4 | 75.9 | 62.0 | 37,320 | 77,661 | 1452 |
| OCSORT | 78.0 | 77.5 | 63.2 | 15,129 | 107,055 | 1950 |
| StrongSORT++ | 79.6 | 79.5 | 64.4 | 27,876 | 86,205 | 1194 |
| ByteTrack | 80.3 | 77.3 | 63.1 | 25,491 | 83,721 | 2196 |
| BoT-SORT | 80.5 | 80.2 | 65.0 | 22,521 | 86,037 | 1212 |
| SolidTrack (ours) | 80.6 | 80.0 | 65.0 | 26,305 | 81,698 | 1306 |
| Tracker | MOTA ↑ | IDF1 ↑ | HOTA ↑ | FP ↓ | FN ↓ | IDs ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MLT | 48.9 | 54.6 | 43.2 | 45,660 | 216,803 | 2187 |
| FairMOT | 61.8 | 67.3 | 54.6 | 103,440 | 88,901 | 5243 |
| TransCenter | 61.9 | 50.4 | - | 45,895 | 146,347 | 4653 |
| TransTrack | 65.0 | 59.4 | 48.5 | 27,197 | 150,197 | 3608 |
| CorrTracker | 65.2 | 69.1 | - | 79,429 | 95,855 | 5183 |
| Semi-TCL | 65.2 | 70.1 | 55.3 | 61,209 | 114,709 | 4139 |
| CSTrack | 66.6 | 68.6 | 54.0 | 25,404 | 144,358 | 3196 |
| GSDT | 67.1 | 67.5 | 53.6 | 31,913 | 135,409 | 3131 |
| RelationTrack | 67.2 | 70.5 | 56.5 | 61,134 | 104,597 | 4243 |
| SOTMOT | 68.6 | 71.4 | - | 57,064 | 101,154 | 4209 |
| MAATrack | 73.9 | 71.2 | 57.3 | 24,942 | 108,744 | 1331 |
| OCSORT | 75.7 | 76.3 | 62.4 | 19,067 | 105,894 | 942 |
| StrongSORT++ | 73.8 | 77.0 | 62.6 | 16,632 | 117,920 | 770 |
| ByteTrack | 77.8 | 75.2 | 61.3 | 26,249 | 87,594 | 1223 |
| BoT-SORT | 77.8 | 77.5 | 63.3 | 24,638 | 88,863 | 1257 |
| SolidTrack (ours) | 77.9 | 77.5 | 63.4 | 24,572 | 88,742 | 1228 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, D.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y. SolidTrack: A Novel Method for Robust and Reliable Multi-Pedestrian Tracking. Electronics 2025, 14, 1370. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14071370
Wu D, Huang Z, Zhang Y. SolidTrack: A Novel Method for Robust and Reliable Multi-Pedestrian Tracking. Electronics. 2025; 14(7):1370. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14071370
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Dongjie, Zhen Huang, and Yong Zhang. 2025. "SolidTrack: A Novel Method for Robust and Reliable Multi-Pedestrian Tracking" Electronics 14, no. 7: 1370. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14071370
APA StyleWu, D., Huang, Z., & Zhang, Y. (2025). SolidTrack: A Novel Method for Robust and Reliable Multi-Pedestrian Tracking. Electronics, 14(7), 1370. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14071370






