Spatial–Adaptive Replay for Foreground Classes in Class-Incremental Semantic Segmentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We study the task of the replay-based incremental semantic segmentation of classes in autonomous driving scenarios, in particular the problem of selecting replay classes. We argue that the replay of foreground classes is more necessary.
- We propose a new replay method, SAF, that enables the replay of foreground classes with less memory occupation.
- Experiments conducted on the Cityscapes and BDD100K datasets demonstrate that SAF achieves outstanding performance in semantic segmentation of autonomous driving scenarios.
2. Related Work
2.1. Incremental Learning
2.2. Class-Incremental Semantic Segmentation
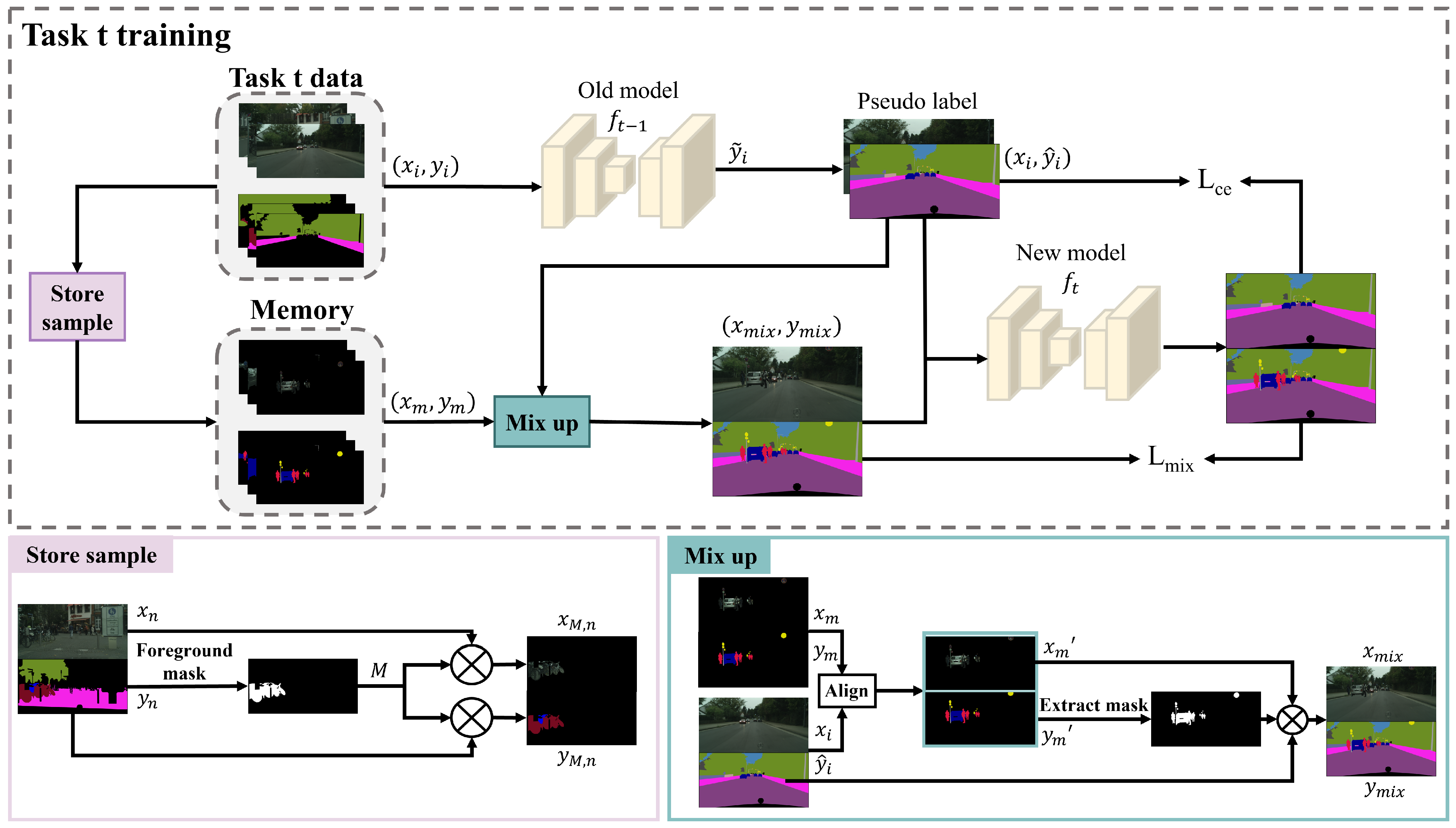
3. Methodology
3.1. Setting
3.2. Overall Architecture
3.3. Foreground Classes Replay
3.4. SAM
3.5. Total Loss
4. Experiment
4.1. Experiment Setting
4.1.1. Datasets
4.1.2. Implementation Details
4.1.3. Metrics
4.2. Comparison with Cityscapes
4.3. Comparison with BDD100K
4.4. Replay Memory-Required Analysis
4.5. Ablation Studies
4.5.1. Effectiveness Assessment of Components
4.5.2. Hyperparameter
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bono, F.M.; Radicioni, L.; Cinquemani, S. A novel approach for quality control of automated production lines working under highly inconsistent conditions. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 122, 106149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Luo, B.; Yu, L.; Chen, B.; Yang, C. BASeg: Boundary aware semantic segmentation for autonomous driving. Neural Netw. 2023, 157, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tavera, A.; Cermelli, F.; Masone, C.; Caputo, B. Pixel-by-pixel cross-domain alignment for few-shot semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2022; pp. 1626–1635. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.; Pan, H.; Sun, W.; Jia, Y. Deep dual-resolution networks for real-time and accurate semantic segmentation of road scenes. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.06085. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Rao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, B.; Zhou, J.; Lu, J. Unleashing text-to-image diffusion models for visual perception. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 5729–5739. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, F.; Hu, H.; Bai, X. Side adapter network for open-vocabulary semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 2945–2954. [Google Scholar]
- McCloskey, M.; Cohen, N.J. Catastrophic interference in connectionist networks: The sequential learning problem. In Psychology of Learning and Motivation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1989; Volume 24, pp. 109–165. [Google Scholar]
- Michieli, U.; Zanuttigh, P. Incremental learning techniques for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cermelli, F.; Mancini, M.; Bulo, S.R.; Ricci, E.; Caputo, B. Modeling the background for incremental learning in semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 9233–9242. [Google Scholar]
- Michieli, U.; Zanuttigh, P. Continual semantic segmentation via repulsion-attraction of sparse and disentangled latent representations. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 1114–1124. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, D.; Oh, Y.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.; Ham, B. Decomposed knowledge distillation for class-incremental semantic segmentation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 10380–10392. [Google Scholar]
- Cha, S.; Kim, B.; Yoo, Y.; Moon, T. Ssul: Semantic segmentation with unknown label for exemplar-based class-incremental learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 10919–10930. [Google Scholar]
- Maracani, A.; Michieli, U.; Toldo, M.; Zanuttigh, P. Recall: Replay-based continual learning in semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 7026–7035. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Cong, R.; Luo, Y.; Ip, H.; Kwong, S. Saving 100× storage: Prototype replay for reconstructing training sample distribution in class-incremental semantic segmentation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 36, 35988–35999. [Google Scholar]
- Van de Ven, G.M.; Siegelmann, H.T.; Tolias, A.S. Brain-inspired replay for continual learning with artificial neural networks. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4069. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kalb, T.; Roschani, M.; Ruf, M.; Beyerer, J. Continual learning for class-and domain-incremental semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Nagoya, Japan, 11–17 July 2021; pp. 1345–1351. [Google Scholar]
- Kalb, T.; Mauthe, B.; Beyerer, J. Improving replay-based continual semantic segmentation with smart data selection. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 25th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Macau, China, 8–12 October 2022; pp. 1114–1121. [Google Scholar]
- Cordts, M.; Omran, M.; Ramos, S.; Rehfeld, T.; Enzweiler, M.; Benenson, R.; Franke, U.; Roth, S.; Schiele, B. The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3213–3223. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Xian, W.; Chen, Y.; Liu, F.; Madhavan, V.; Darrell, T. Bdd100k: A diverse driving dataset for heterogeneous multitask learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 2636–2645. [Google Scholar]
- Wickramasinghe, B.; Saha, G.; Roy, K. Continual learning: A review of techniques, challenges, and future directions. IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell. 2023, 5, 2526–2546. [Google Scholar]
- Aljundi, R.; Babiloni, F.; Elhoseiny, M.; Rohrbach, M.; Tuytelaars, T. Memory aware synapses: Learning what (not) to forget. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 139–154. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Hoiem, D. Learning without forgetting. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 2935–2947. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Castro, F.M.; Marín-Jiménez, M.J.; Guil, N.; Schmid, C.; Alahari, K. End-to-end incremental learning. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 233–248. [Google Scholar]
- Douillard, A.; Cord, M.; Ollion, C.; Robert, T.; Valle, E. Podnet: Pooled outputs distillation for small-tasks incremental learning. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part XX 16. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 86–102. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, T.; Socher, R.; Xiong, C. Learn to grow: A continual structure learning framework for overcoming catastrophic forgetting. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 3925–3934. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.; Mazumder, P.; Rai, P.; Namboodiri, V.P. Rectification-based knowledge retention for continual learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 15282–15291. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, S.; Xie, J.; He, X. Der: Dynamically expandable representation for class incremental learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 3014–3023. [Google Scholar]
- Rebuffi, S.A.; Kolesnikov, A.; Sperl, G.; Lampert, C.H. icarl: Incremental classifier and representation learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–25 July 2017; pp. 2001–2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Herranz, L.; Liu, X.; Van De Weijer, J.; Raducanu, B. Memory replay gans: Learning to generate new categories without forgetting. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2018, 31, 5966–5976. [Google Scholar]
- Hayes, T.L.; Kafle, K.; Shrestha, R.; Acharya, M.; Kanan, C. Remind your neural network to prevent catastrophic forgetting. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 466–483. [Google Scholar]
- Michieli, U.; Zanuttigh, P. Knowledge distillation for incremental learning in semantic segmentation. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2021, 205, 103167. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27, 2672–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Klingner, M.; Bär, A.; Donn, P.; Fingscheidt, T. Class-incremental learning for semantic segmentation re-using neither old data nor old labels. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 23rd International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Rhodes, Greece, 20–23 September 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Douillard, A.; Chen, Y.; Dapogny, A.; Cord, M. Plop: Learning without forgetting for continual semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 4040–4050. [Google Scholar]
- Araujo, V.; Hurtado, J.; Soto, A.; Moens, M.F. Entropy-based stability-plasticity for lifelong learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 3721–3728. [Google Scholar]
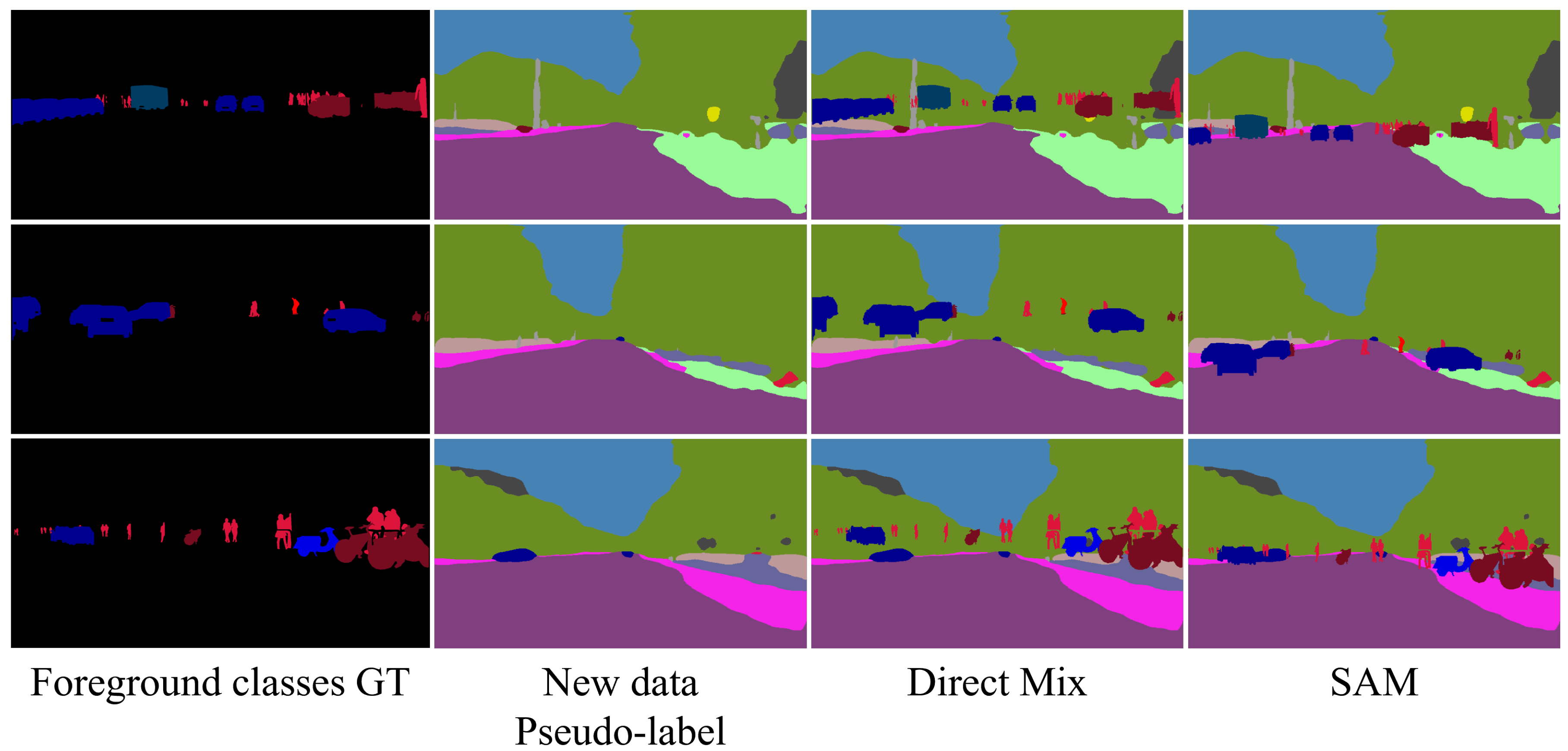

| Methods | 13-6 (2 Steps) | 13-3 (3 Steps) | 13-1 (7 Steps) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1–13 | 14–19 | All | 1–13 | 14–16 | 17–19 | All | 1–13 | 14–19 | All | |
| offline | 76.9 | 71.4 | 75.2 | 76.9 | 64.8 | 78.2 | 75.2 | 76.9 | 71.4 | 75.2 |
| FT | 41.3 | 61.7 | 47.7 | 30.8 | 34.2 | 67.7 | 37.1 | 3.9 | 10.7 | 6.1 |
| CIL [35] | 62.7 | 64.9 | 63.4 | 62.3 | 52.3 | 70.3 | 61.9 | 58.9 | 38.0 | 52.3 |
| PLOP [36] | 66.0 | 64.1 | 65.4 | 65.3 | 56.0 | 69.5 | 64.5 | 62.2 | 40.9 | 55.4 |
| SSUL [12] | 63.9 | 66.7 | 64.8 | 62.1 | 52.6 | 71.4 | 62.1 | 56.2 | 50.7 | 54.4 |
| MiB [9] | 64.7 | 65.9 | 65.1 | 64.3 | 55.7 | 70.6 | 63.9 | 62.9 | 41.3 | 56.0 |
| Replay (size = 16) | 65.3 | 59.3 | 63.4 | 64.9 | 44.0 | 65.3 | 61.7 | 62.2 | 26.1 | 50.8 |
| Replay (size = 128) | 68.1 | 58.7 | 65.1 | 67.5 | 52.7 | 63.6 | 64.5 | 67.0 | 46.0 | 60.4 |
| Ours (size = 128) | 67.6 | 63.0 | 66.1 | 67.1 | 51.3 | 69.2 | 64.9 | 65.7 | 46.3 | 59.6 |
| Ours + MiB | 68.9 | 65.4 | 67.8 | 68.5 | 54.3 | 70.9 | 66.6 | 67.3 | 48.7 | 61.4 |
| Methods | 13-6 (2 Steps) | 13-1 (7 Steps) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1–13 | 14–19 | All | 1–13 | 14–19 | All | |
| Offline | 59.8 | 51.7 | 57.2 | 59.8 | 51.7 | 57.2 |
| FT | 26.7 | 37.1 | 30.0 | 0.1 | 1.8 | 0.6 |
| PLOP [36] | 42.9 | 41.4 | 42.4 | 36.2 | 33.1 | 35.2 |
| MiB [9] | 38.7 | 43.0 | 40.1 | 37.9 | 35.9 | 37.3 |
| Replay (size = 16) | 39.9 | 38.4 | 39.4 | 37.1 | 19.7 | 36.9 |
| Replay (size = 128) | 44.2 | 37.8 | 42.2 | 41.9 | 32.4 | 38.9 |
| Ours (size = 128) | 43.0 | 40.5 | 42.2 | 41.3 | 32.9 | 38.6 |
| Ours + MiB | 43.9 | 42.7 | 43.5 | 41.7 | 33.6 | 39.1 |
| Methods | Incremental Setting | Size | Memory |
|---|---|---|---|
| Replay (simple) | 13-6 | 16 | 35.6 MB |
| 128 | 285 MB | ||
| 19-0 | 16 | 35.6 MB | |
| 128 | 285 MB | ||
| SAF | 13-6 | 128 | 10.1 MB |
| 19-0 | 128 | 36.2 MB |
| Components | Cityscapes 13-1 (7 Steps) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1–13 | 14–19 | All | |
| Simple replay | 62.2 | 26.1 | 50.8 |
| +Foreground-class replay | 64 | 42.6 | 57.2 |
| +Spatial–adaptive alignment | 65.7 | 46.3 | 59.6 |
| +MiB [9] | 67.3 | 48.7 | 61.4 |
| Hyperparameter | Cityscapes 13-1 (7 Steps) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1–13 | 14–19 | All | |
| 10 | 66.1 | 40.9 | 58.1 |
| 1 | 65.7 | 46.3 | 59.6 |
| 0.1 | 64.8 | 46.6 | 59 |
| 0.01 | 63.3 | 46.8 | 58.1 |
| 0.001 | 60.9 | 46.7 | 56.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, W.; Gu, Z.; Xu, M.; Lu, X. Spatial–Adaptive Replay for Foreground Classes in Class-Incremental Semantic Segmentation. Electronics 2025, 14, 1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14071338
Huang W, Gu Z, Xu M, Lu X. Spatial–Adaptive Replay for Foreground Classes in Class-Incremental Semantic Segmentation. Electronics. 2025; 14(7):1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14071338
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Wei, Zhuoming Gu, Mengfan Xu, and Xiaofeng Lu. 2025. "Spatial–Adaptive Replay for Foreground Classes in Class-Incremental Semantic Segmentation" Electronics 14, no. 7: 1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14071338
APA StyleHuang, W., Gu, Z., Xu, M., & Lu, X. (2025). Spatial–Adaptive Replay for Foreground Classes in Class-Incremental Semantic Segmentation. Electronics, 14(7), 1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14071338





