High-Precision Low-Power Interface Circuit for Two-Dimensional Integrated Magnetic Switches
Abstract
1. Introduction
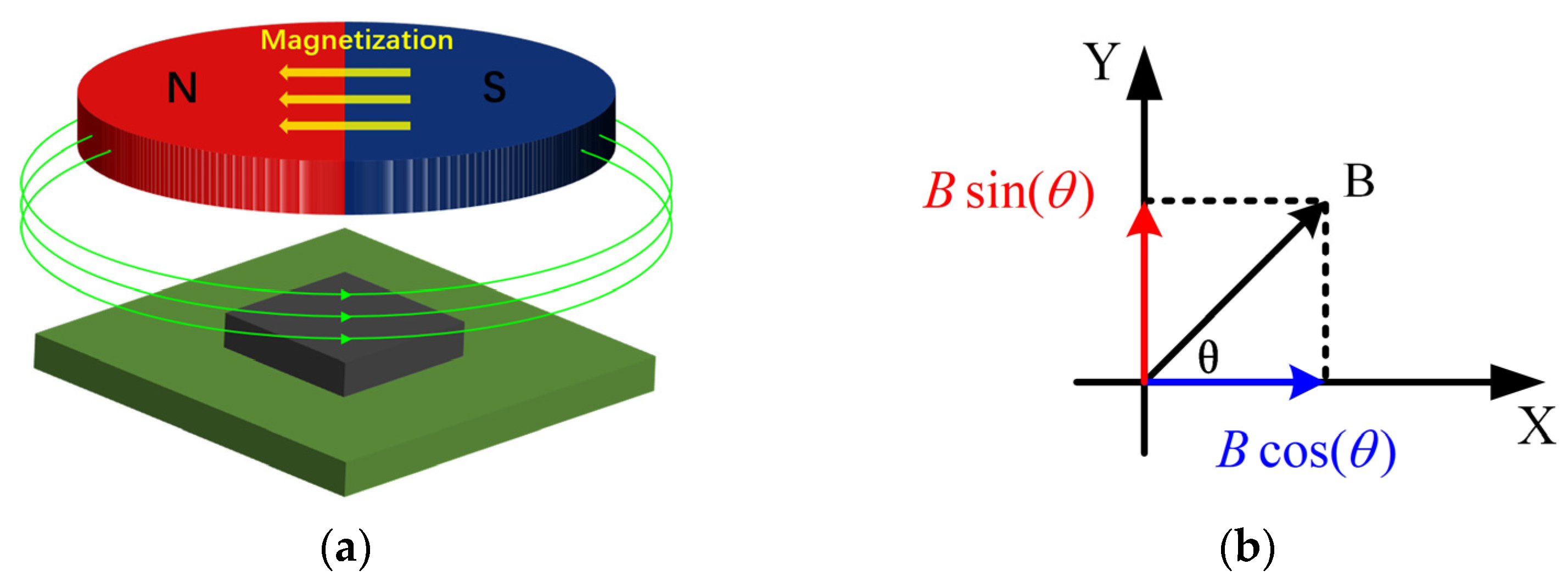
2. Basic Detection Principle of the 2D Integrated Magnetic Switch
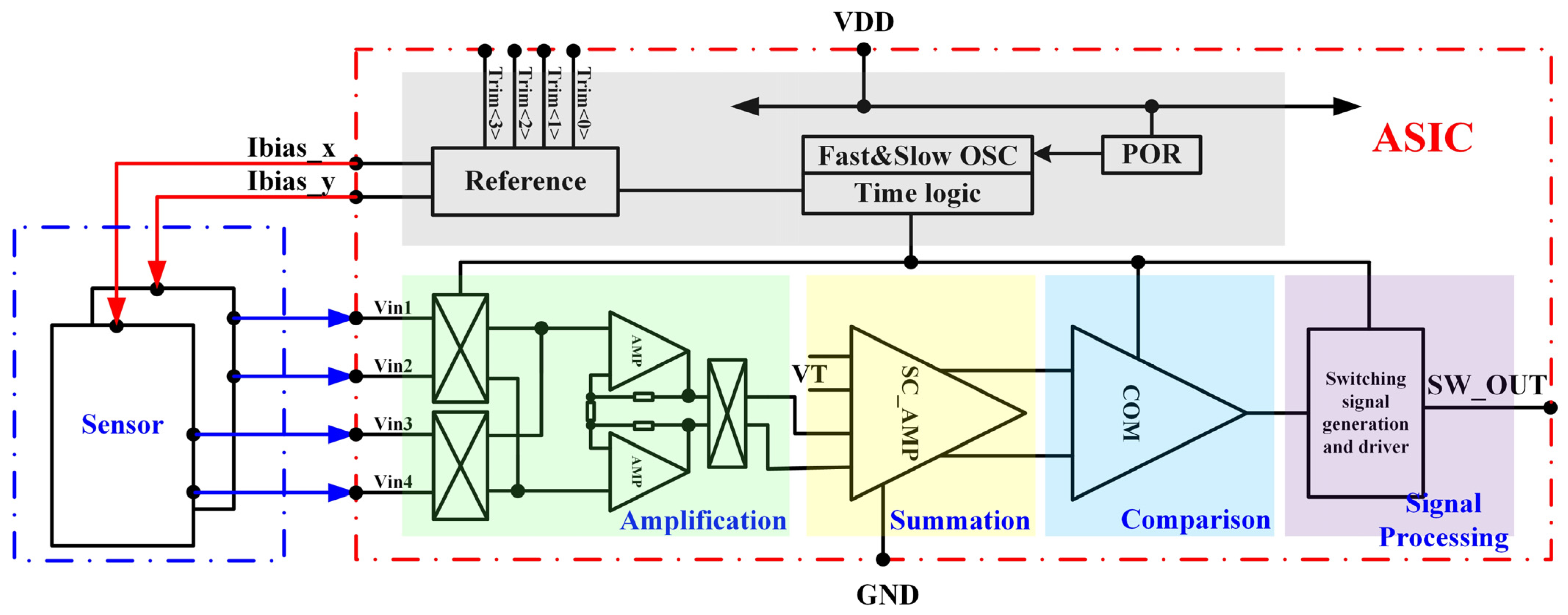
3. Interface Circuit Architecture and Principle
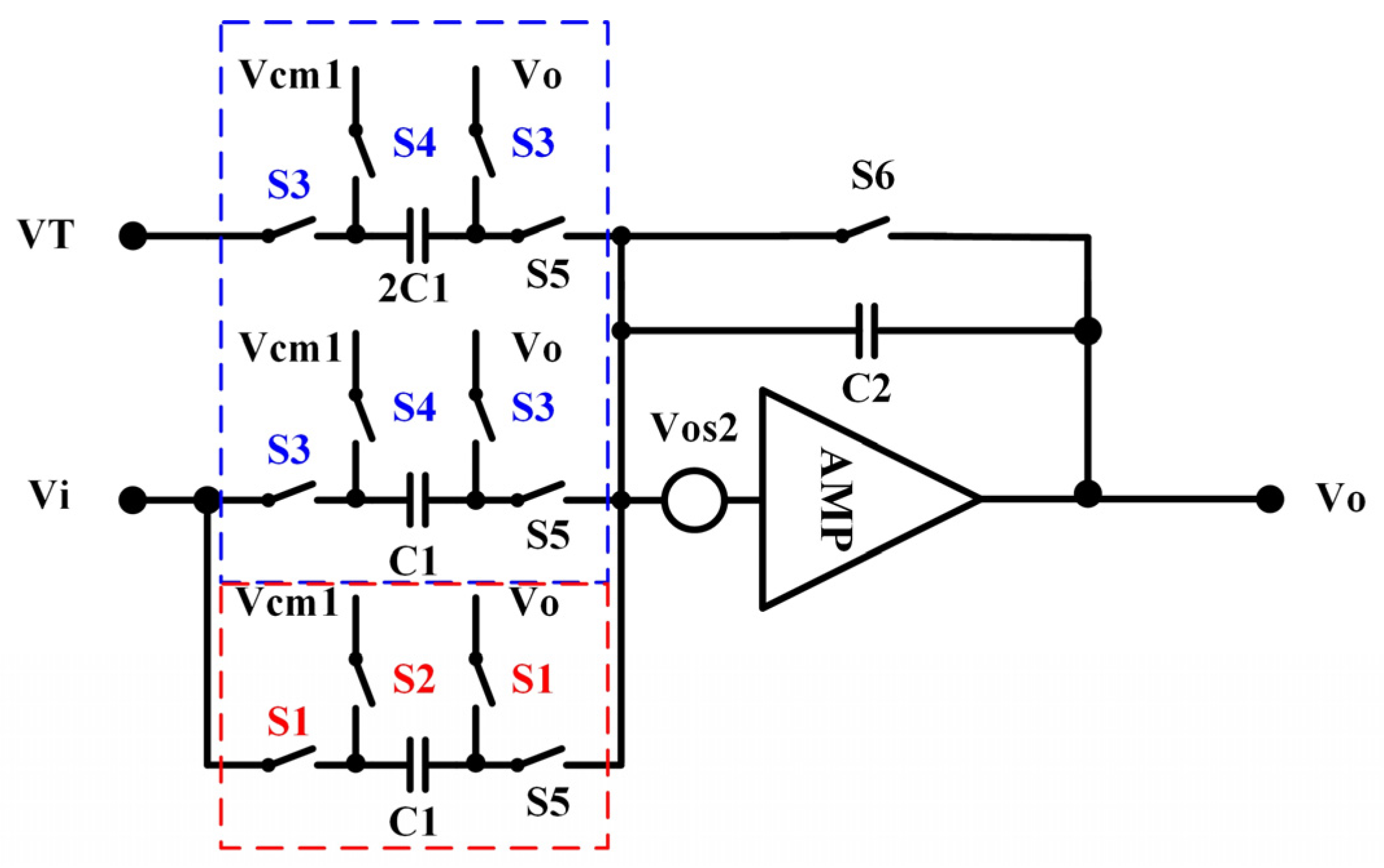
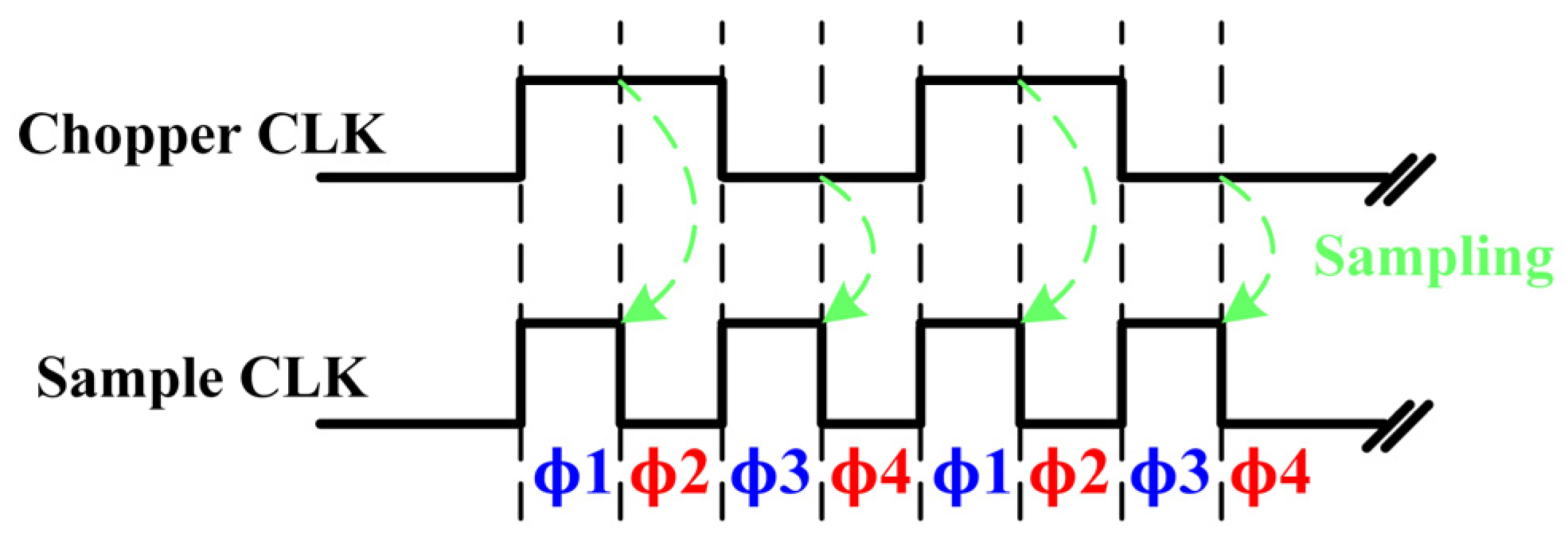
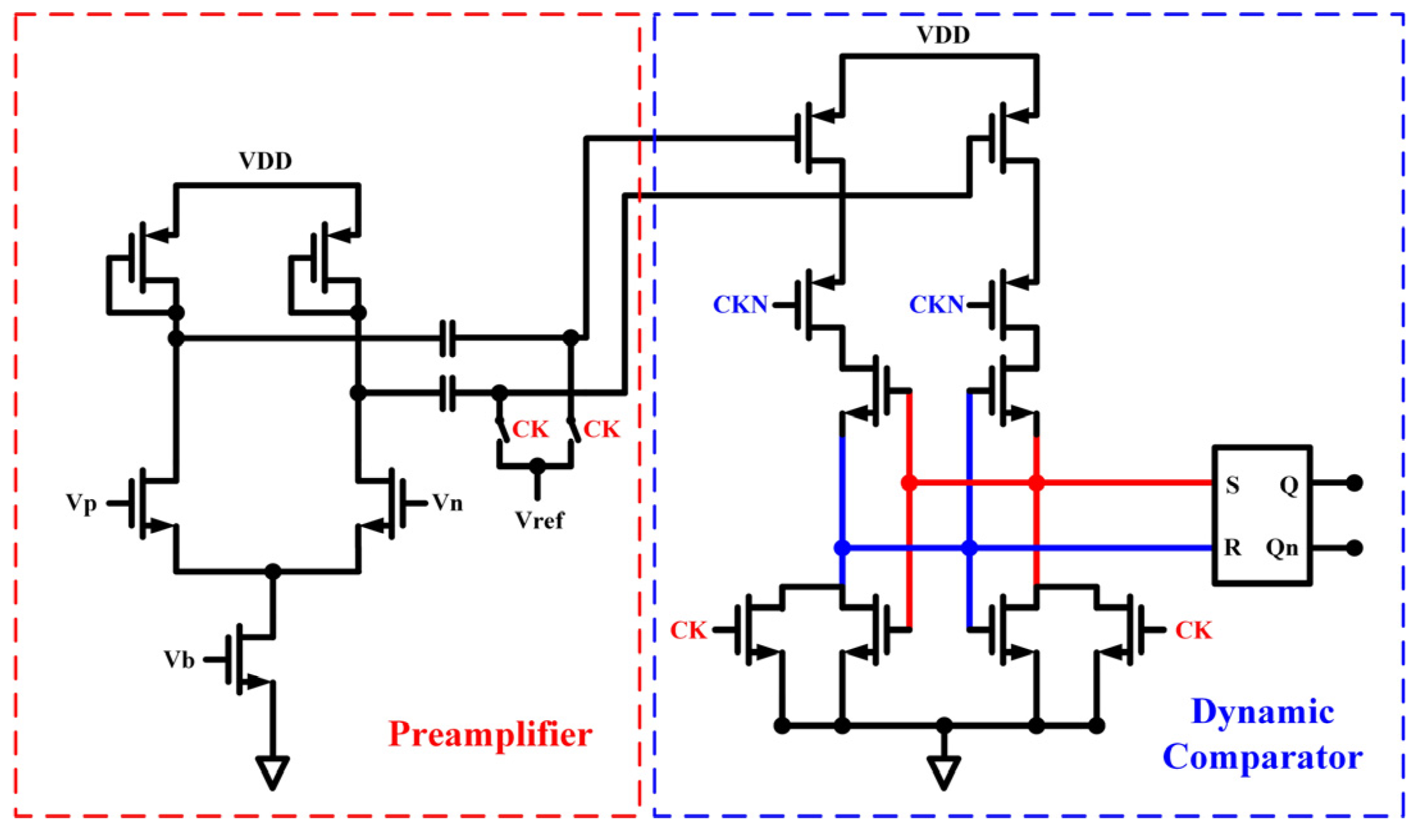
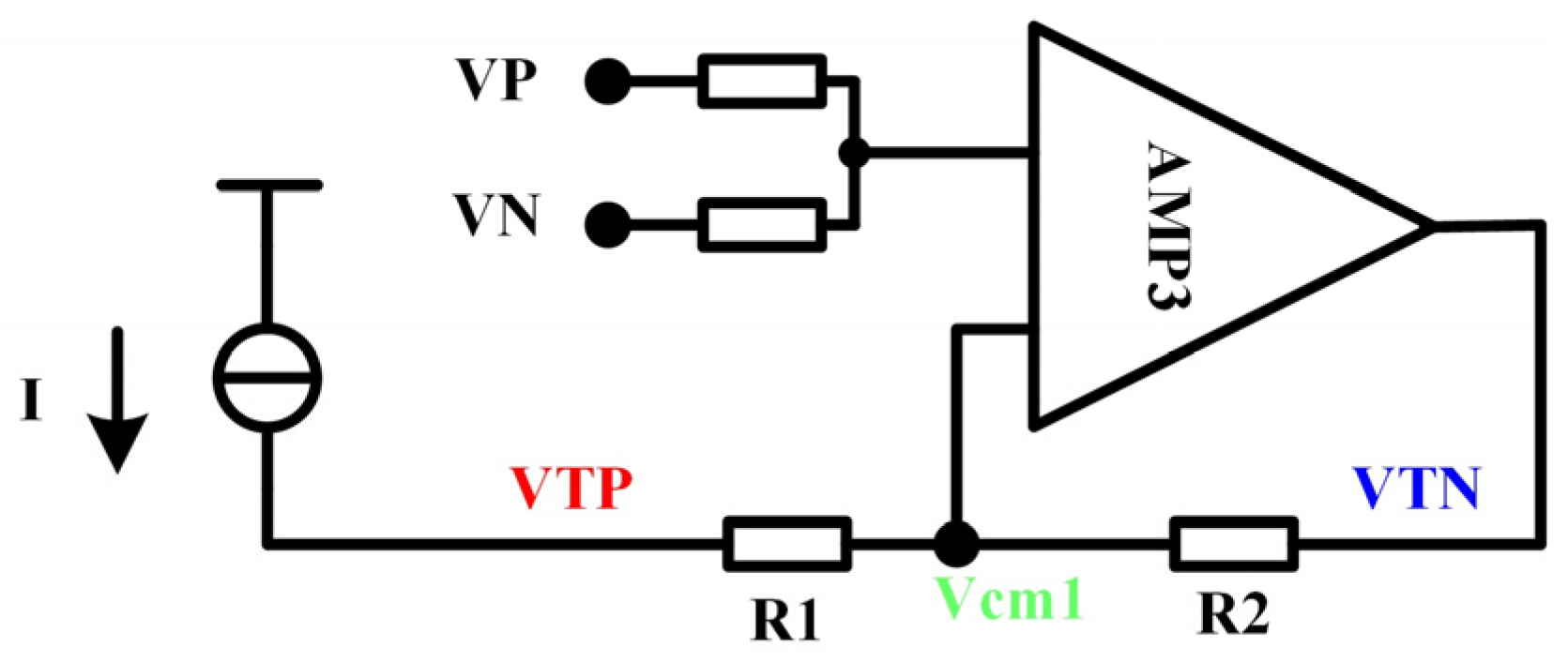
3.1. High-Precision Signal Processing Path
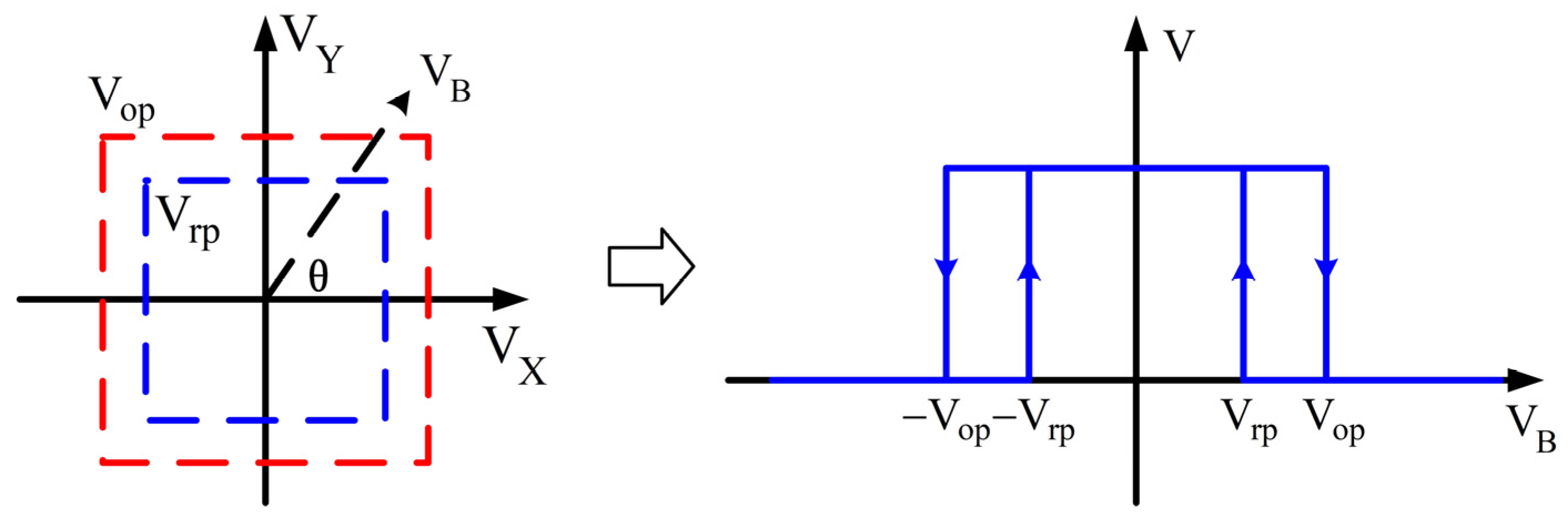
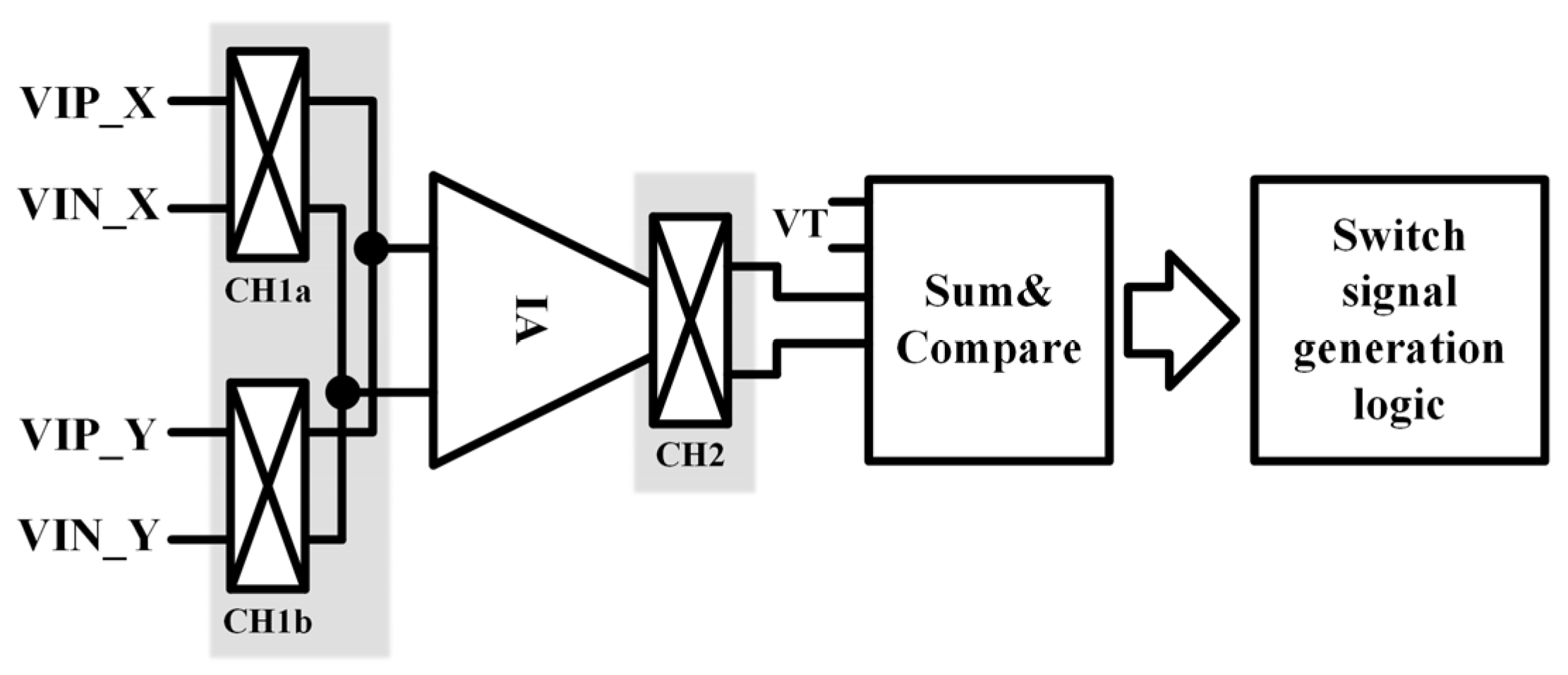
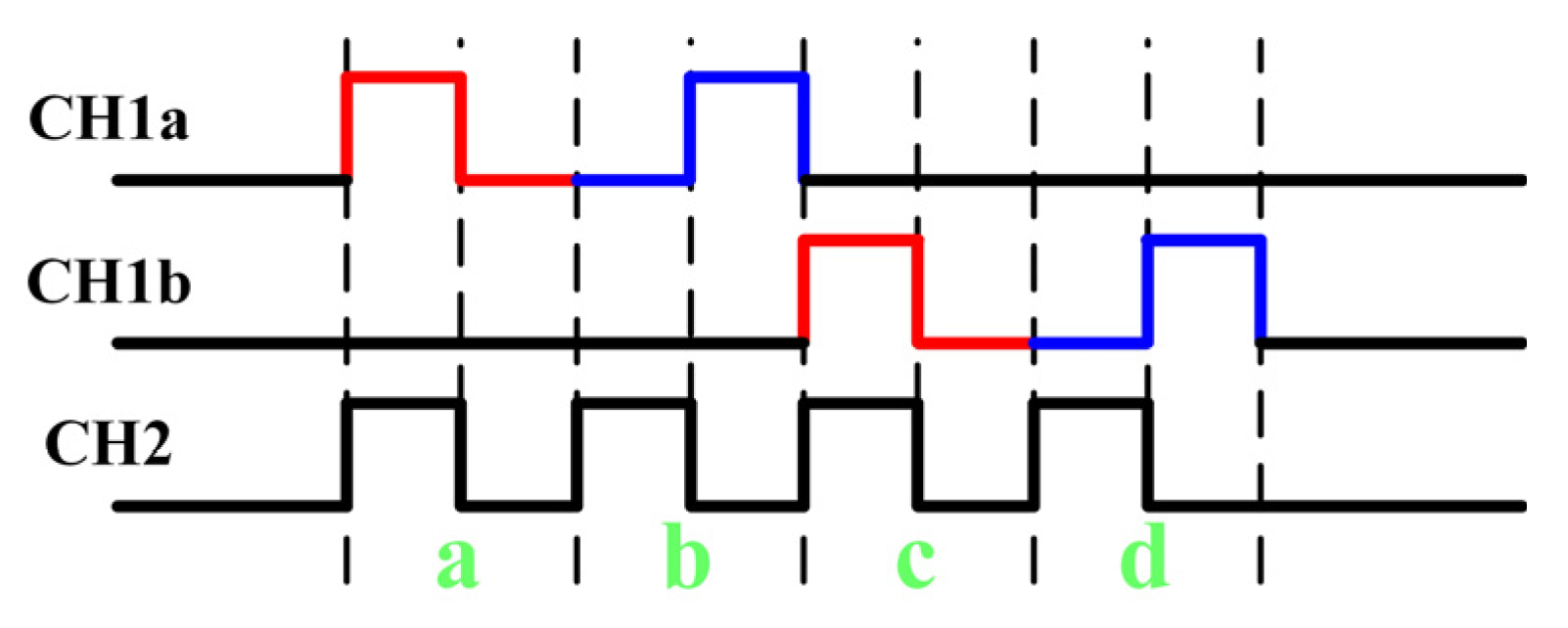
3.2. Switch Signal Algorithm
3.3. Switching Threshold and Hysteresis Range Design
3.4. Sleep and Wake-Up Mode
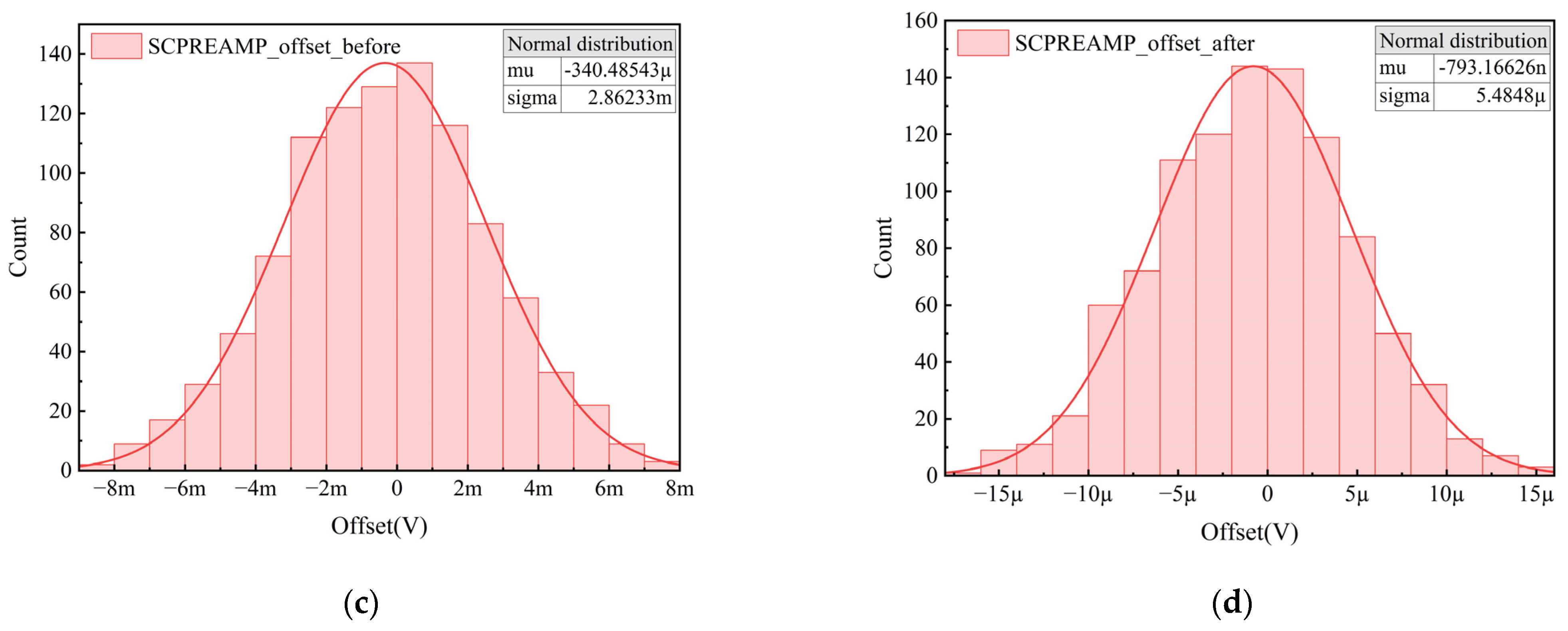
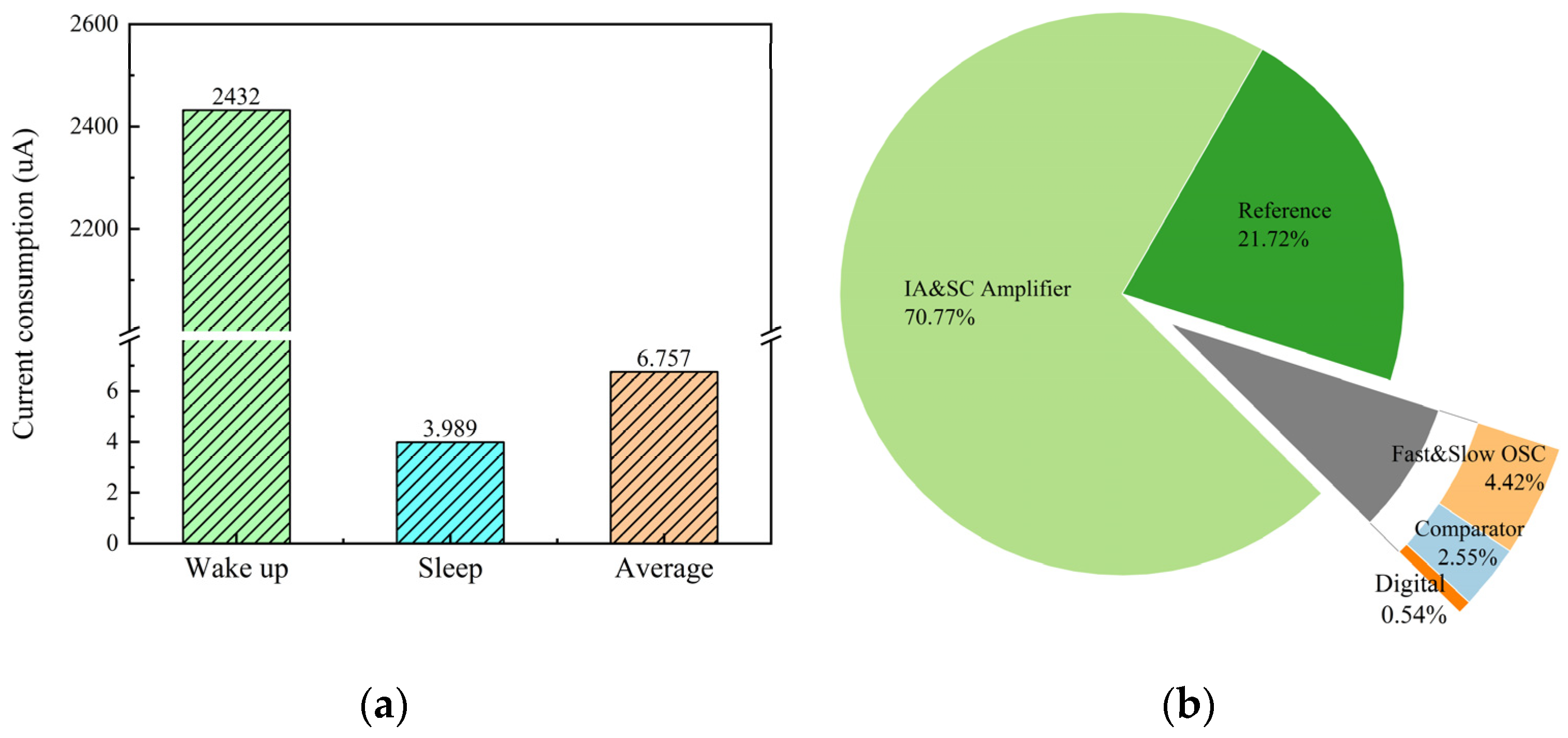
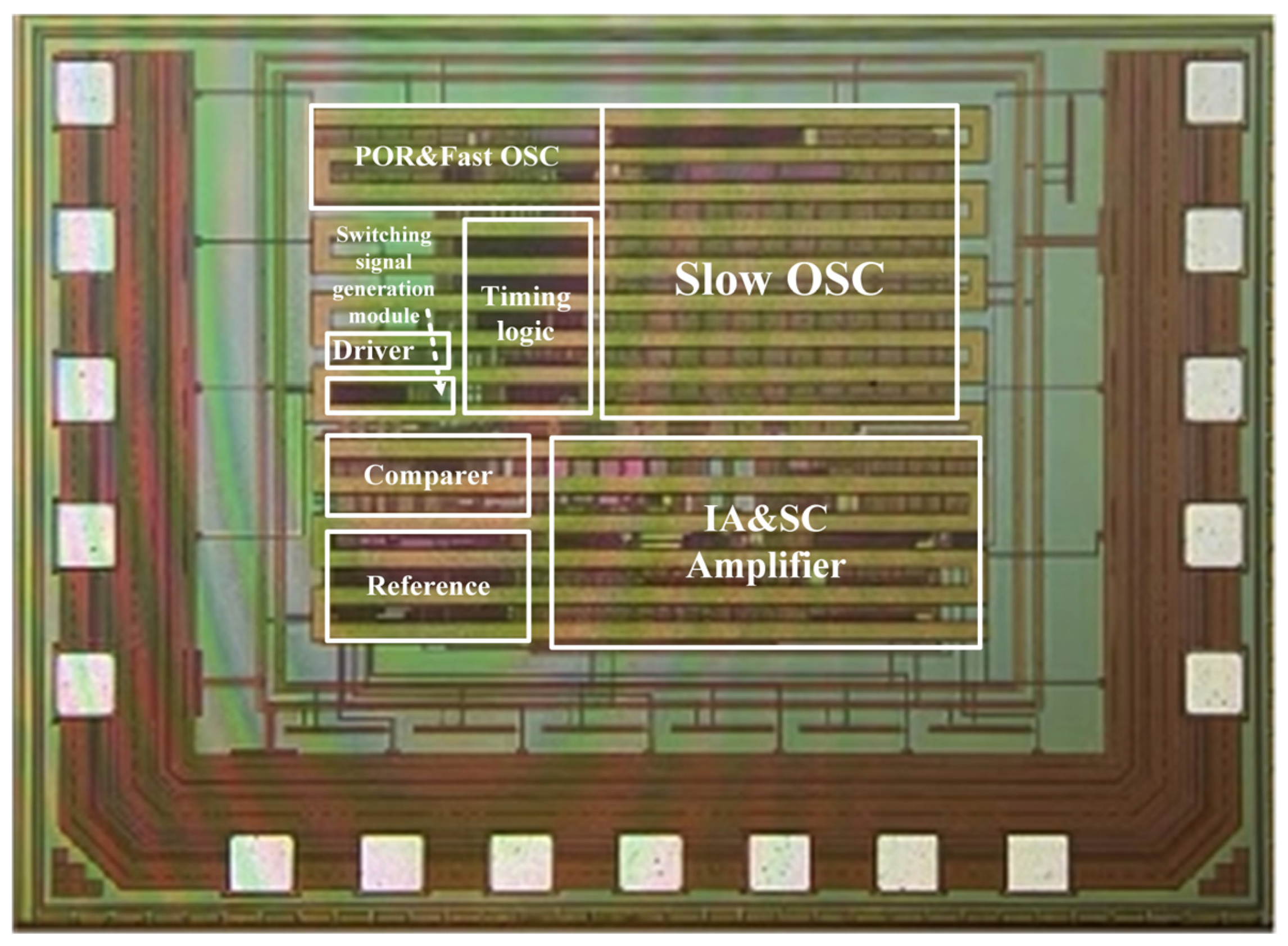
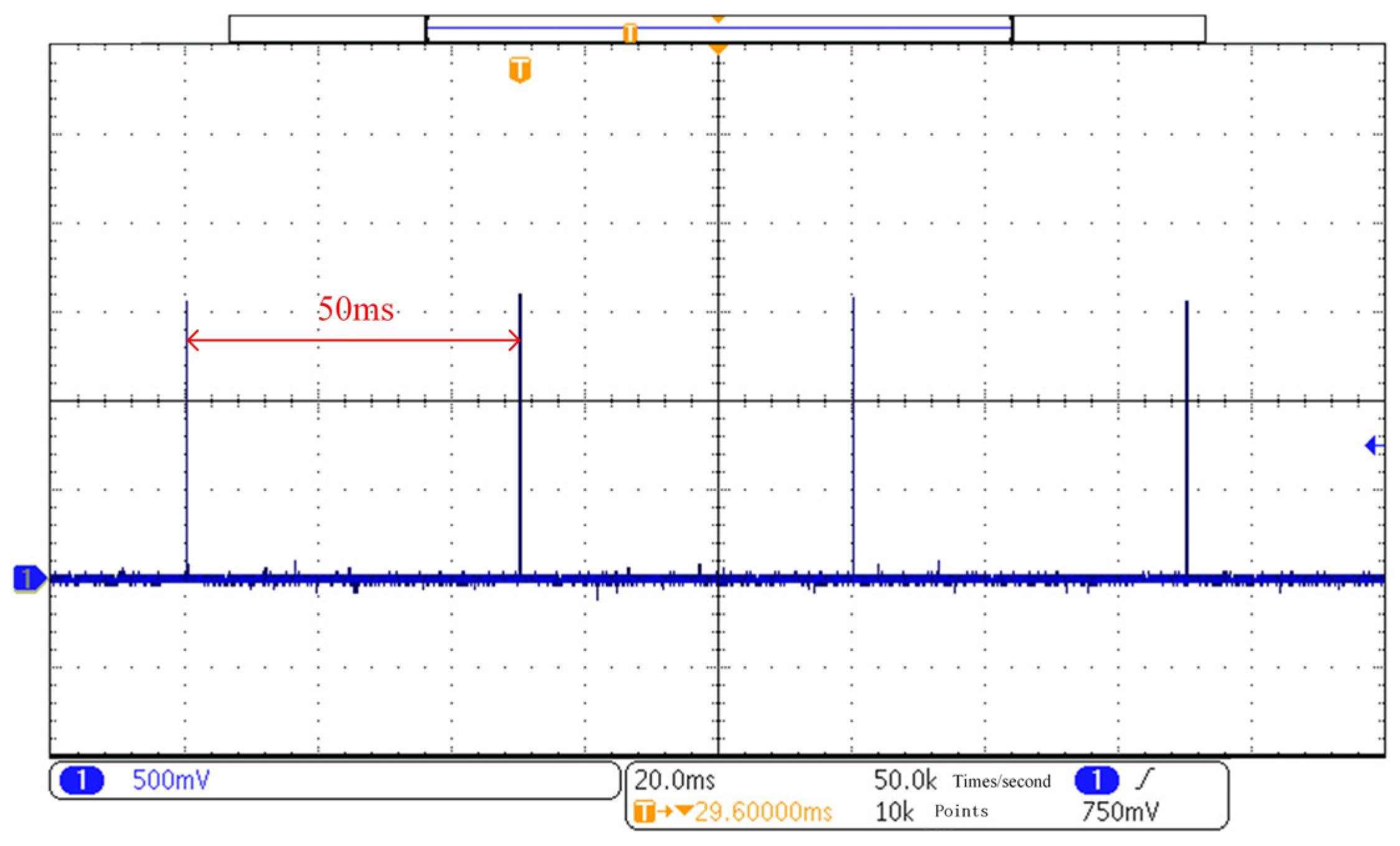
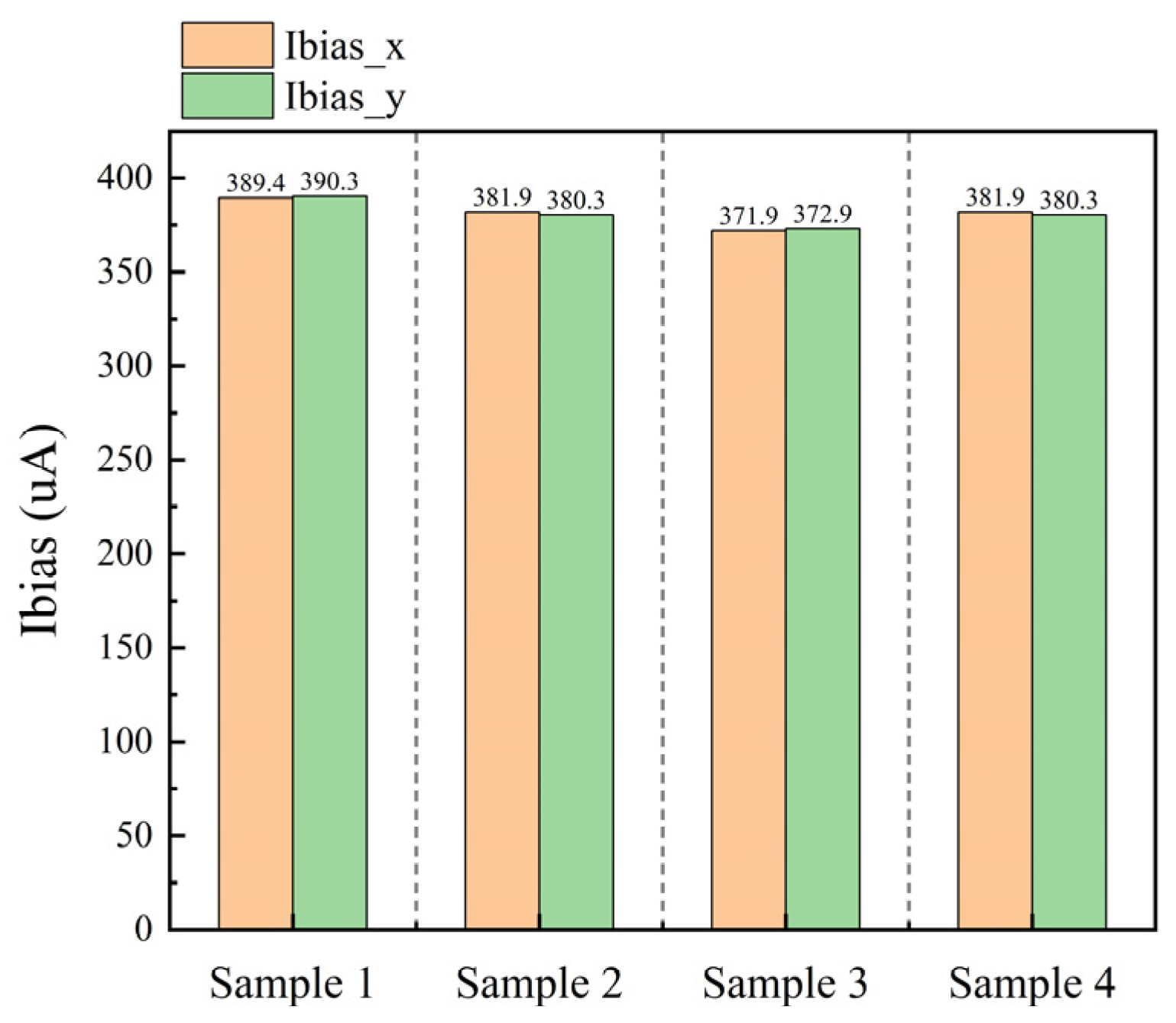
4. Results and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gerard, C.M.; Meijer, M.S. Smart Sensor System; Antony Rowe Ltd.: Chippenham, UK, 2008; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Tang, Y.; Lin, S. A monolithic CMOS Hall switch sensor system with high precision and low power consumption. In Proceedings of the 2019 6th International Conference on Electrical and Electronics Engineering (ICEEE), Istanbul, Turkey, 16–17 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, S.; Yuan, C.; Duan, N. Design of the CMOS switching hall sensor circuit. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Sensor Networks and Signal Processing (SNSP), Xi’an, China, 28–31 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.C.; Qian, Z.H.; Huang, X.W. Integrated GMR magnetic switch for implantable medical devices. In Proceedings of the 2010 Asia Pacific Conference on Postgraduate Research in Microelectronics and Electronics (PrimeAsia), Shanghai, China, 22–24 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, R.; Kofi, A.A.; Johan, H.H. A chopper current-feedback instrumentation amplifier with a 1m Hz 1/f noise corner and an AC-coupled ripple reduction loop. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2009, 44, 3232–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johan, F.W.; Kofi, A.A.; Johan, H.H. Dynamic Offset Compensated CMOS Amplifiers; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 43–64. [Google Scholar]
- Ronis, N.; Mariano, G.I. Design and characterization of Hall Plates in a 0.5 um CMOS process. In Proceedings of the 2016 Argentine Conference of Micro-Nanoelectronics, Technology and Applications (CAMTA), Neuquen, Argentina, 4–5 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Popovic, R.S. Hall Effect Devices, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; pp. 30–49. [Google Scholar]
- Asahi Kasei Microdevices. Available online: https://www.akm.com/global/en/products/hall-sensor/hall-element/ (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Guo, S.Z. Integrated three-dimensional Hall switch sensor based on independent optimized Hall devices. Microelectron. J. 2023, 135, 105756. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.K.; Seong, I.C. A low noise Hall Effect Sensor Readout Circuit. IDEC J. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2019, 5, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, R.S.; Guo, S.Z.; Yang, S.Z. Low-Power CMOS Integrated Hall Switch Sensor. Act. Passive Electron. Compon. 2017, 1, 5375619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.C.; Qian, Z.H.; Bai, R.; Li, J.P. The Omnipolar Integrated Magnetic Switch Based on GMR. Key Eng. Mater. 2013, 562, 1234–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Johan, H.H.; Kofi, A.A. Precision Instrumentation Amplifiers and Read-Out Integrated Circuits; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 128–213. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Q.W.; Kofi, A.A.; Johan, H.H. Capacitively-Coupled Chopper Amplifiers; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 106–154. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.N.; Wang, B.; Amine, B. Analysis of output ripple shape and amplitude in chopper instrumentation amplifier. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2021, 69, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, C.E.; Gabor, C.T. Circuit techniques for reducing the effects of op-amp imperfections: Autozeroing, correlated double sampling, and chopper stabilization. Proc. IEEE 1996, 84, 1584–1614. [Google Scholar]
- Mountrichas, L.; Siskos, S. A novel switching scheme for offset storage cancellation technique, for GS/s range ADCS. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference Proceedings, Graz, Austria, 13–16 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Kofi, A.A. A multi-path CMOS Hall sensor with integrated ripple reduction loops. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference (A-SSCC), Xiamen, China, 9–11 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Razavi, R. Design of Analog CMOS Integrated Circuit, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 503–507. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, P.E. CMOS Analog Circuit Design, 3rd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 488–492. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, J.H. Chip on Board: Technology for Multichip Modules; Chapman & Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 57–65. [Google Scholar]









| Magnetic Sensor Element | Sensitivity (mV/(V×mT)) | Output Voltage of 10 mT (mV) |
|---|---|---|
| GaAs Hall element [9] | 0.183–0.367 | 1.83–3.67 |
| InAs Hall element [9] | 0.6–0.967 | 6–9.67 |
| InSb Hall element [9] | 0.82–7.4 | 8.2–74 |
| Silicon-based Hall element [7] | 0.03–0.0408 | 0.3–0.408 |
| AMR 1 | 1–10 | 10–100 |
| Parameters | [12] | [10] | [13] | This Work |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Process (μm) | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.5 | 0.18/BCD |
| ) | 0.396 | 1.46 | NA | 1.18 |
| Supply voltage (V) | 3.3 | 3.3 | 5 | 5 |
| Operating point voltage (mV) | 0.41 | 0.41 | 40.5–55.35 | 0–13.52 |
| Release point voltage (mV) | 0.26 | 0.28 | 27–36.9 | 0–13.52 |
| Hysteresis voltage (mV) | 0.15 | 0.13 | 3.6–28.35 | 0–7.32 |
| Operating frequency (Hz) | 20 | NA | NA | 20 |
| Average current consumption (μA) | 7.89 | >14.85 | NA | 6.757 |
| Trim code (bit) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| Dimensions | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y. High-Precision Low-Power Interface Circuit for Two-Dimensional Integrated Magnetic Switches. Electronics 2025, 14, 1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14071299
Xu Y, Zhao Q, Li Y, Zhao Y. High-Precision Low-Power Interface Circuit for Two-Dimensional Integrated Magnetic Switches. Electronics. 2025; 14(7):1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14071299
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Yongkang, Qiming Zhao, Yao Li, and Yiqiang Zhao. 2025. "High-Precision Low-Power Interface Circuit for Two-Dimensional Integrated Magnetic Switches" Electronics 14, no. 7: 1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14071299
APA StyleXu, Y., Zhao, Q., Li, Y., & Zhao, Y. (2025). High-Precision Low-Power Interface Circuit for Two-Dimensional Integrated Magnetic Switches. Electronics, 14(7), 1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14071299






