Lamb Wave Near-Field Source Localization Method for Corrosion Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Lamb Wave Near-Field DOA Estimation Based on CS
2.1. Theory of CS
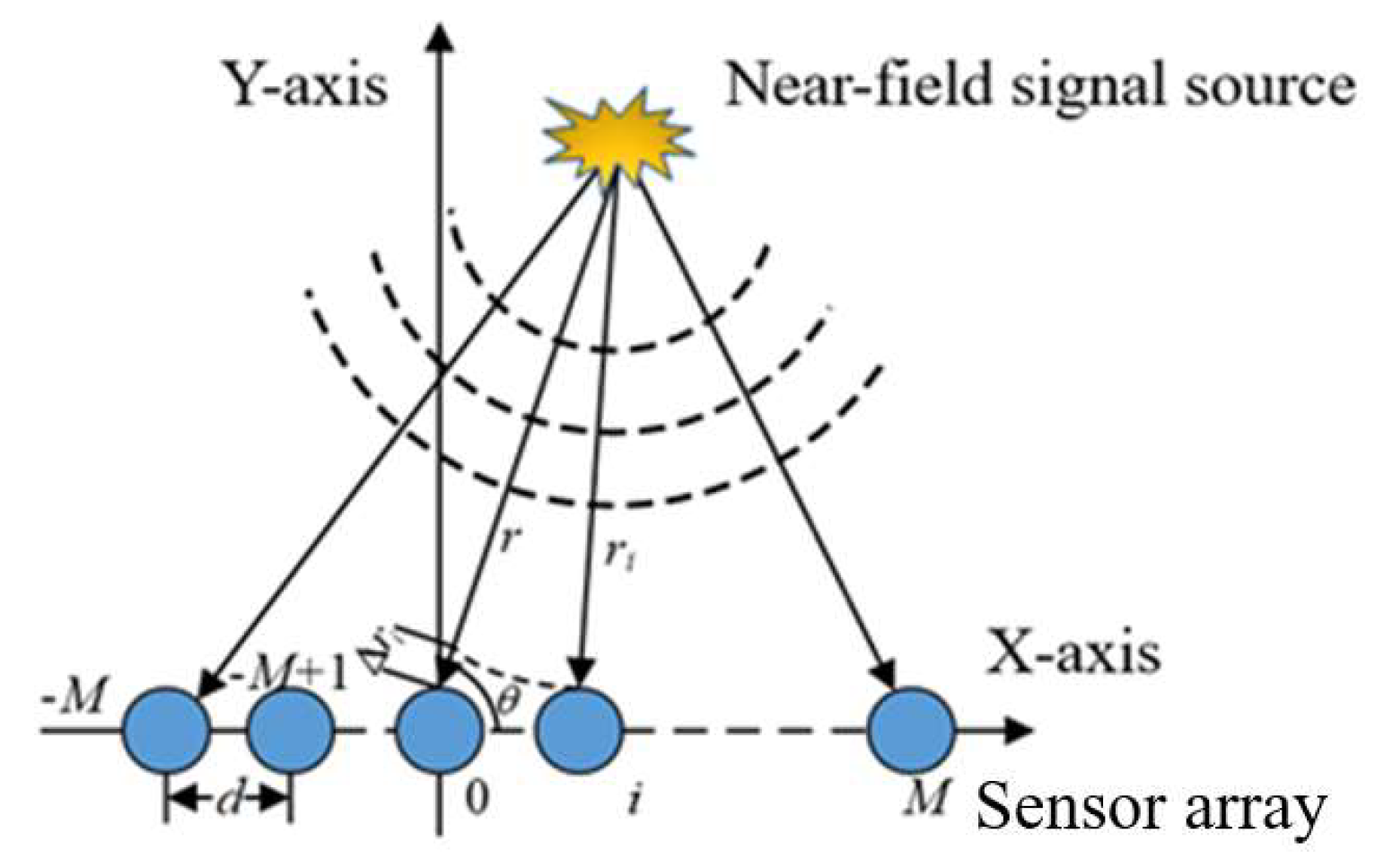
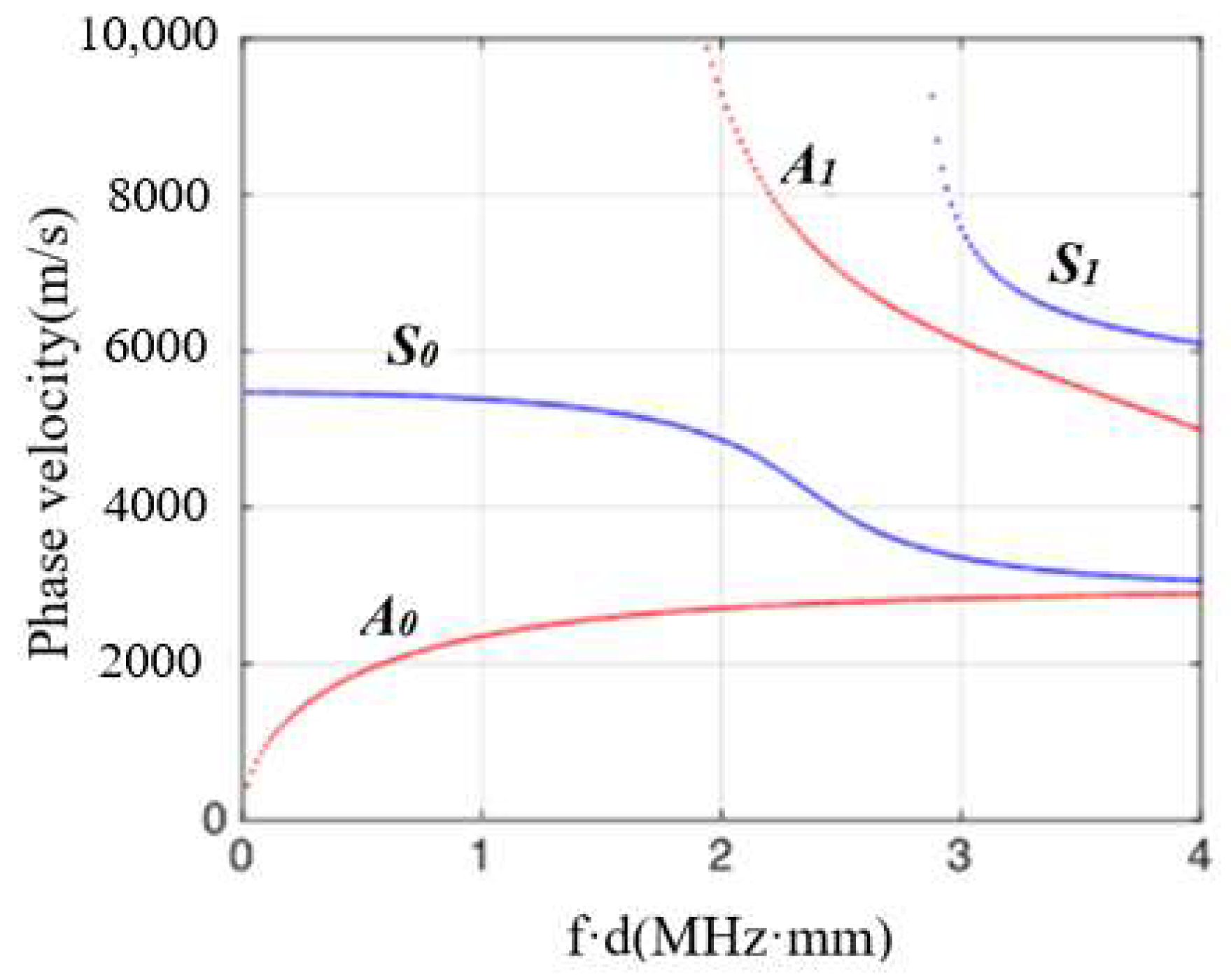
2.2. Lamb Wave Near-Field Array Model
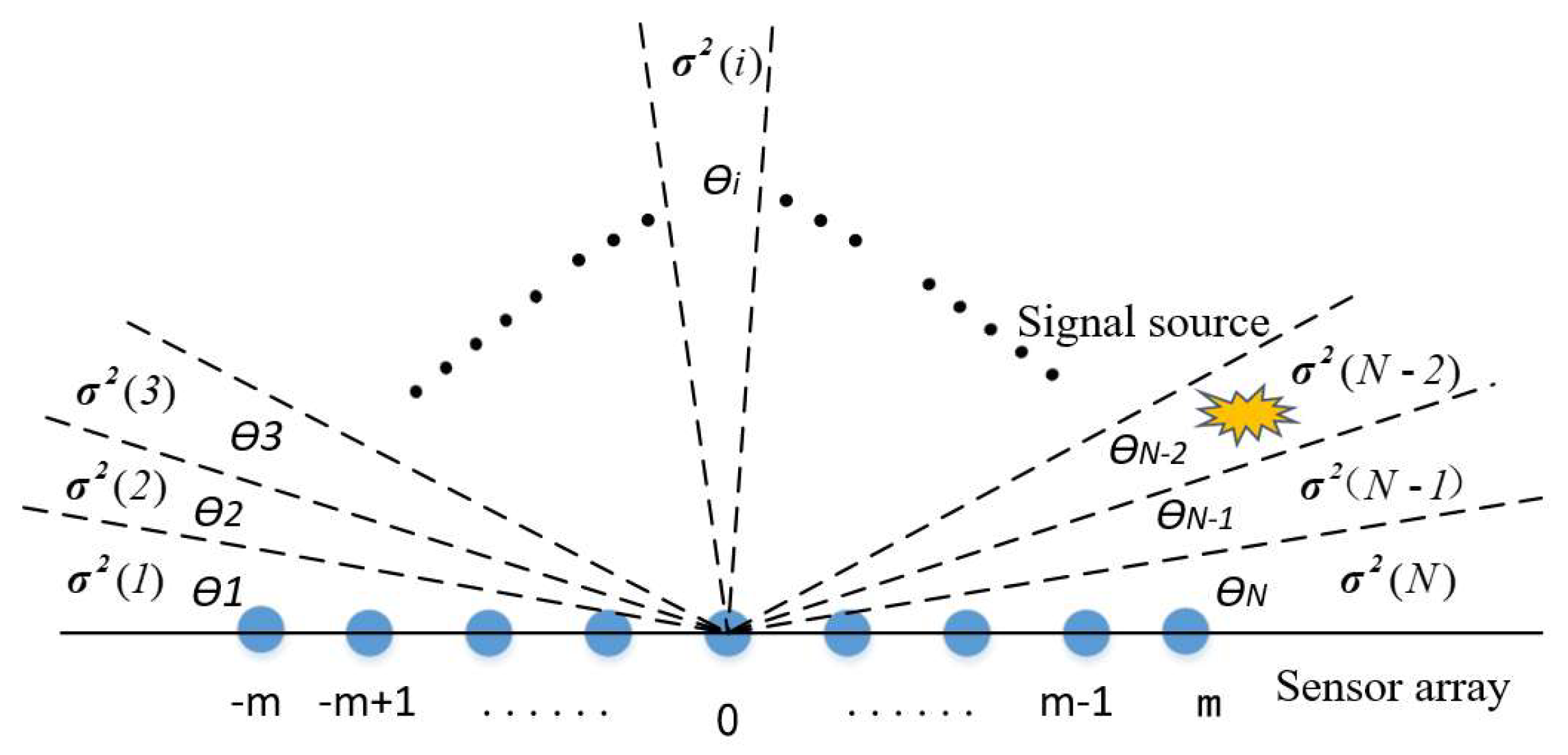
2.3. DOA Estimation Based on CS
3. Lamb Wave Near-Field Distance Estimation
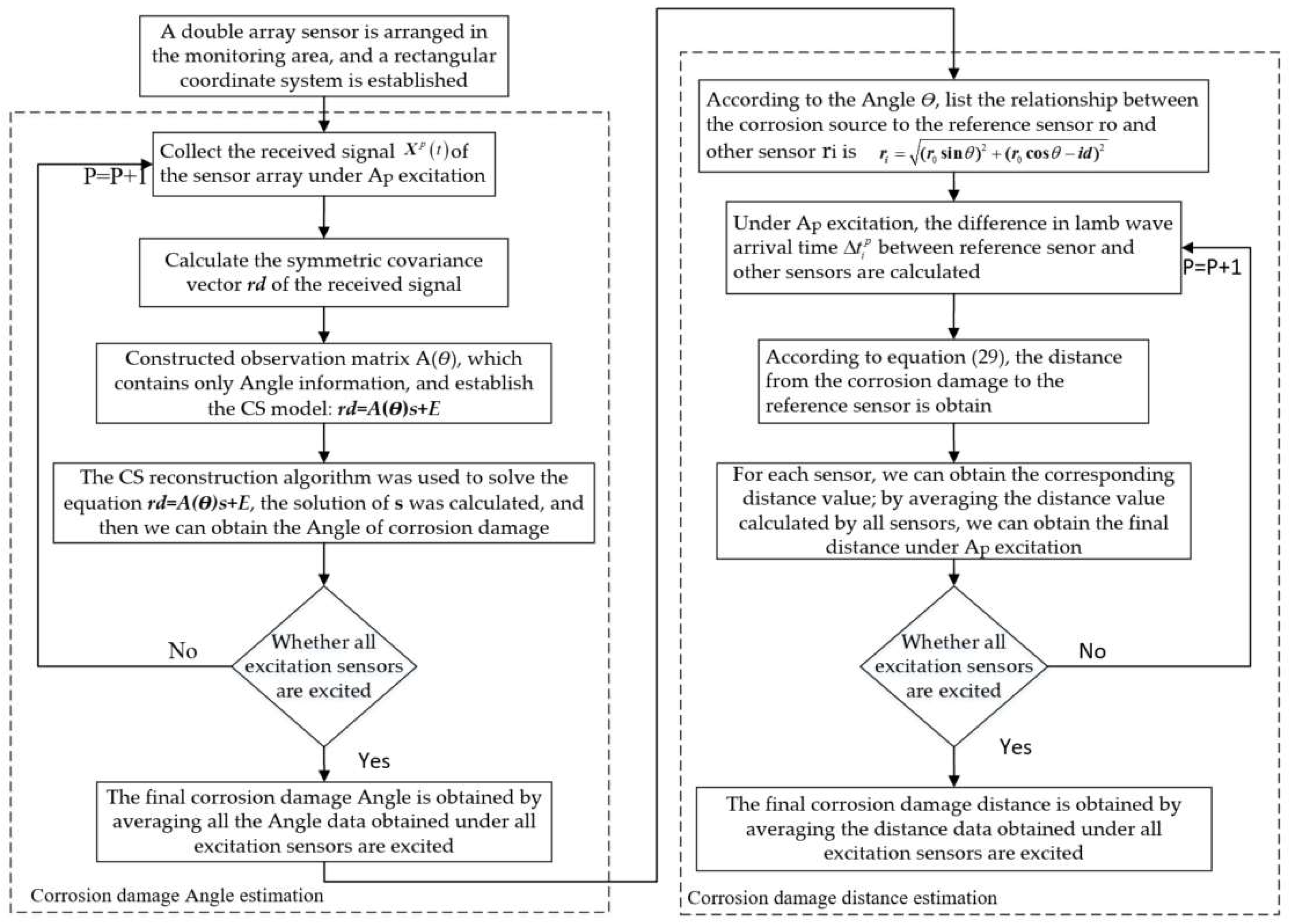
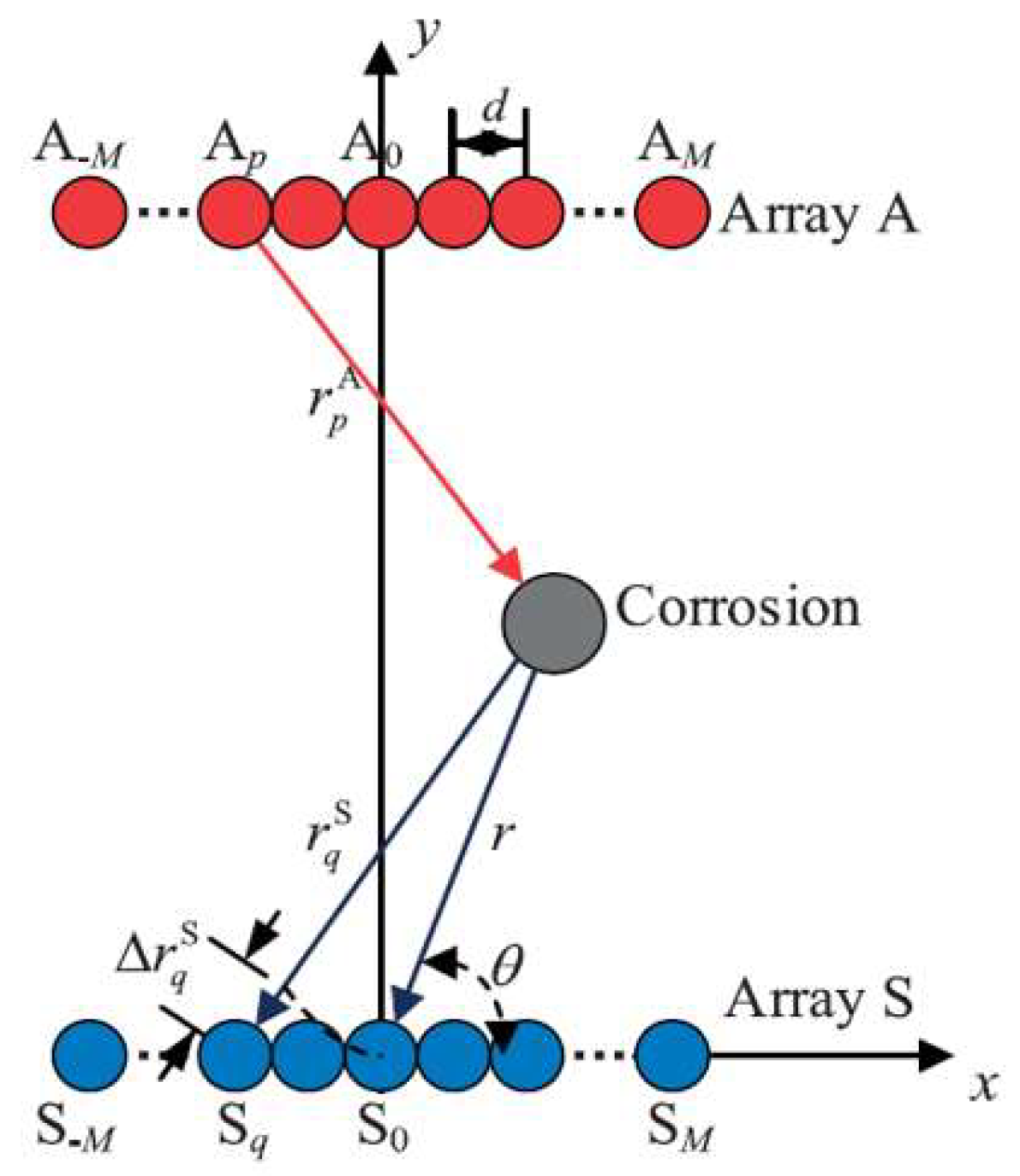
4. Lamb Wave Near-Field Source Location
5. Experimental Verification
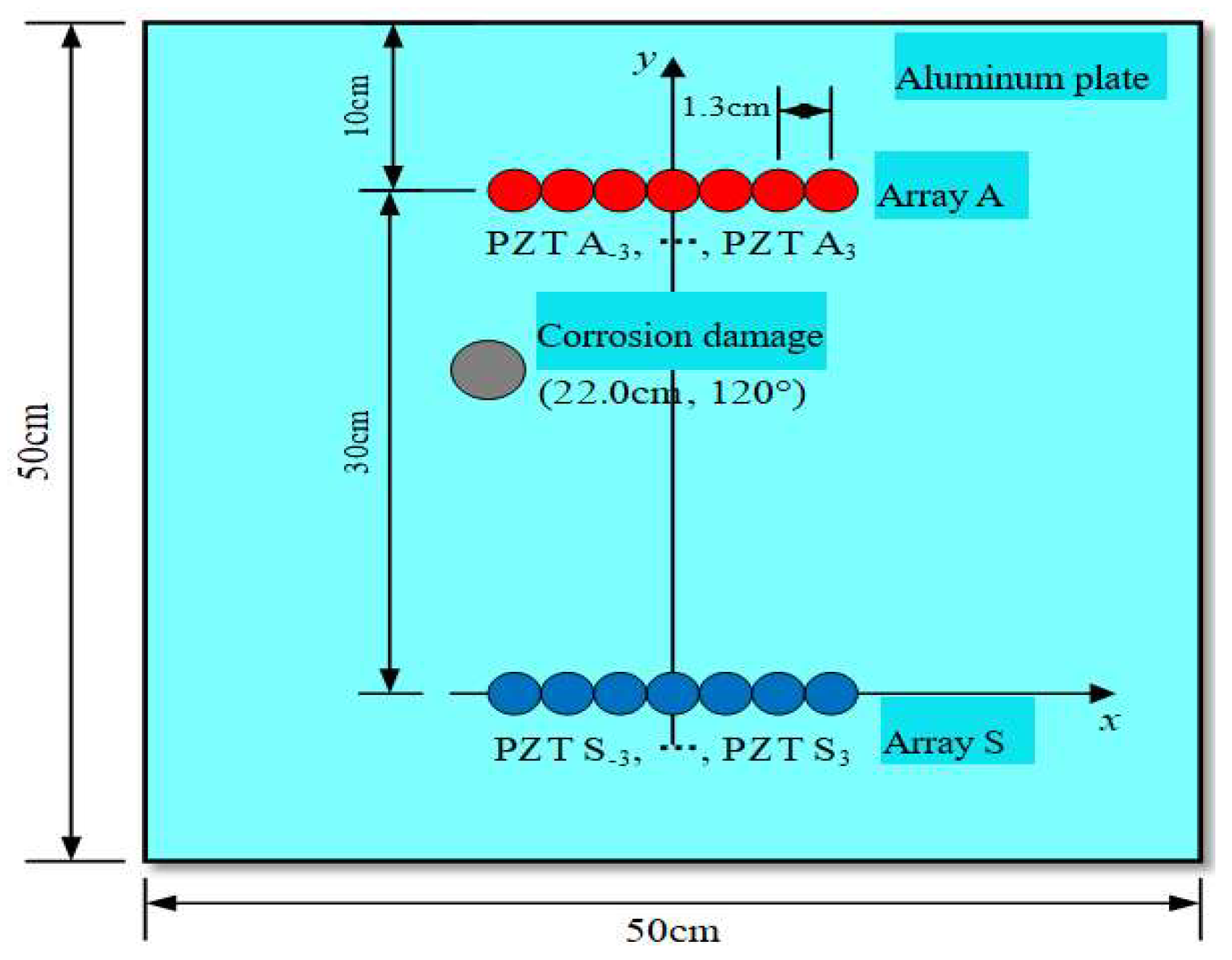
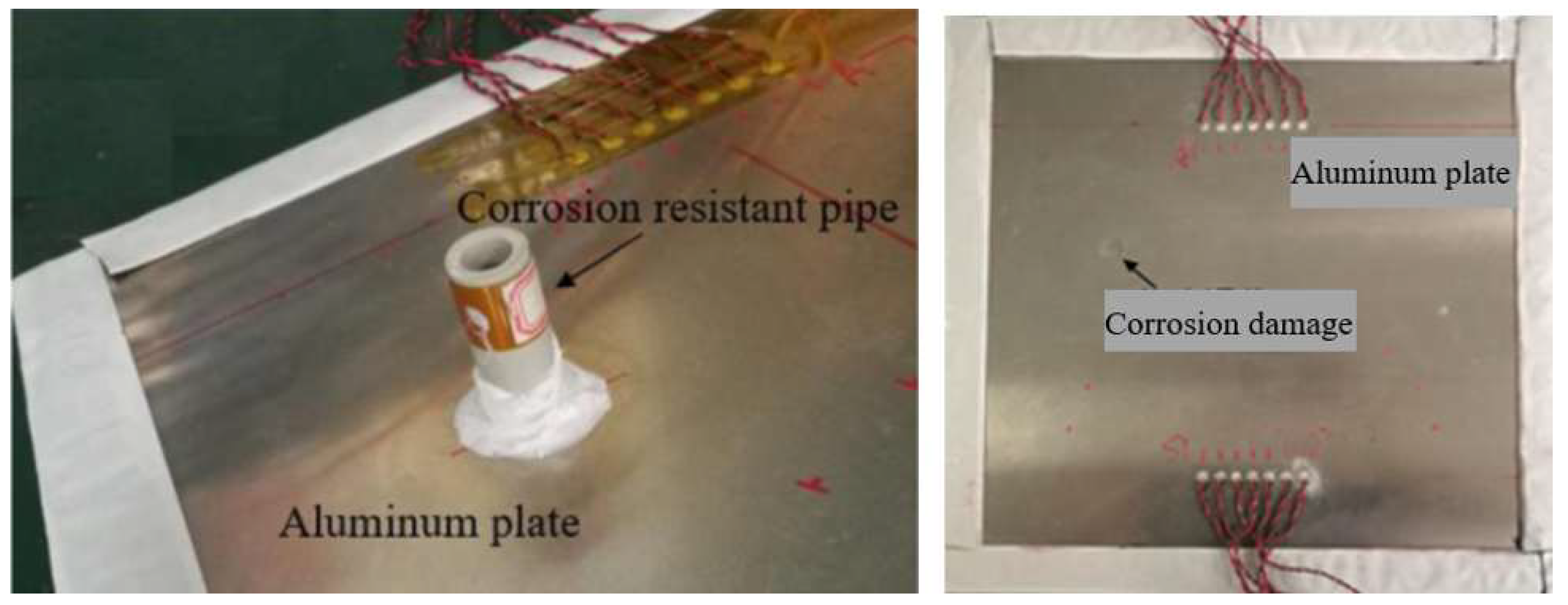
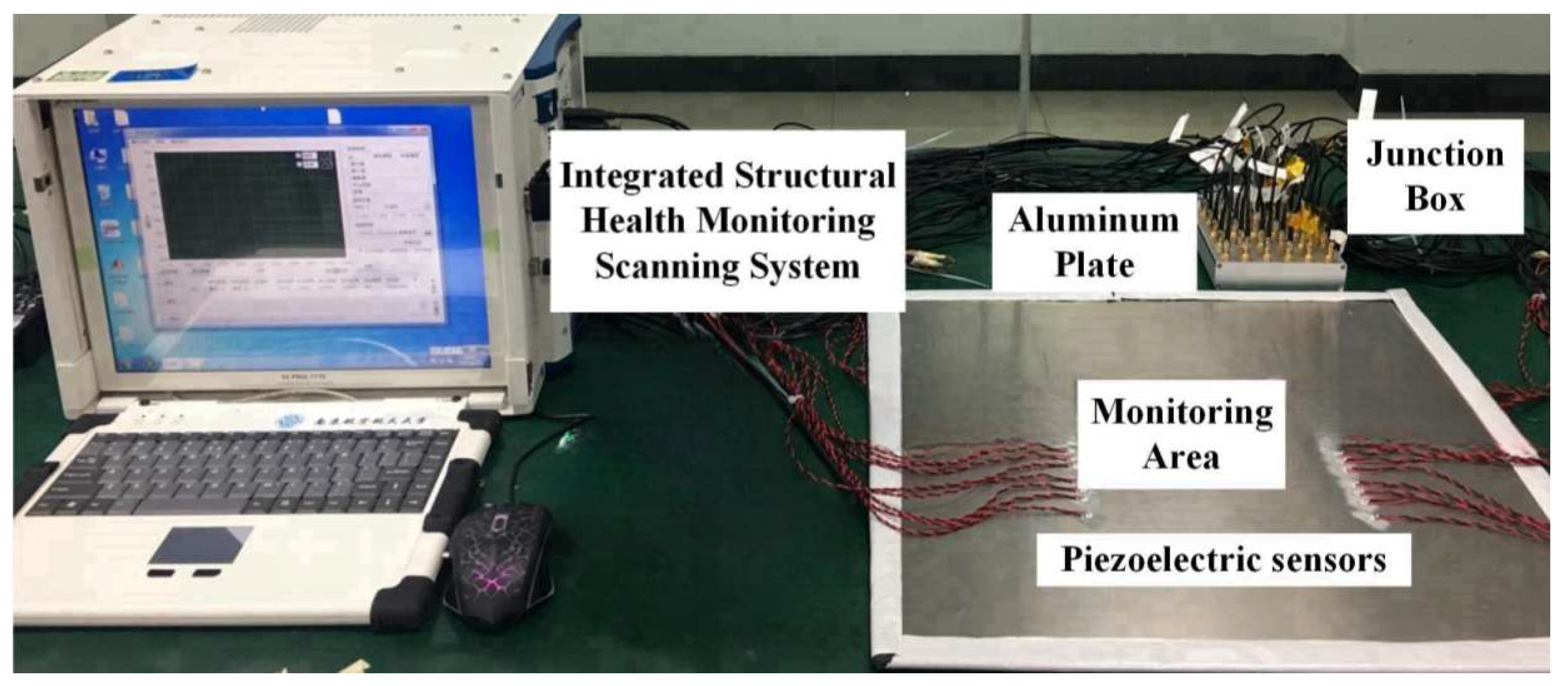
5.1. Experimental Setup
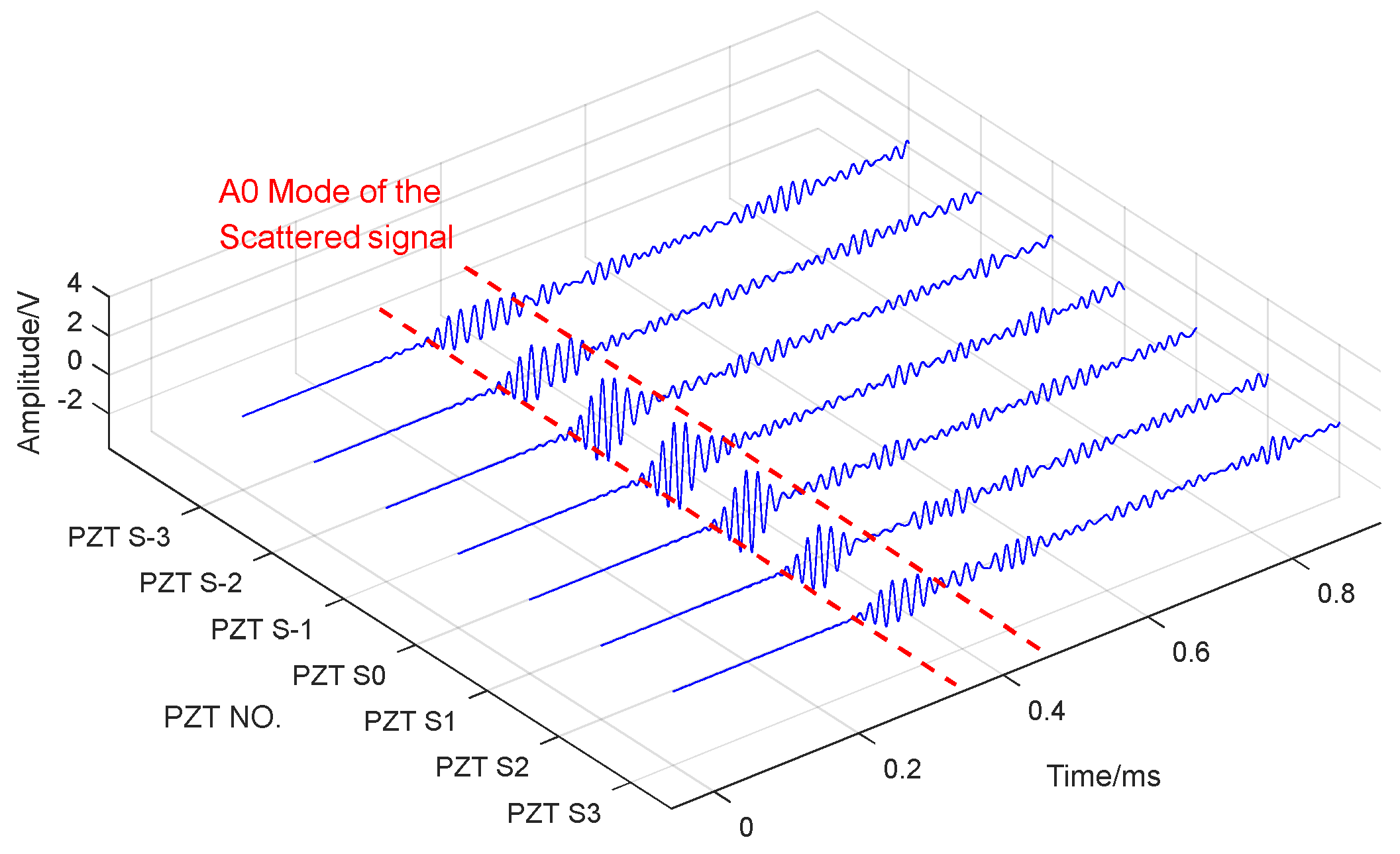
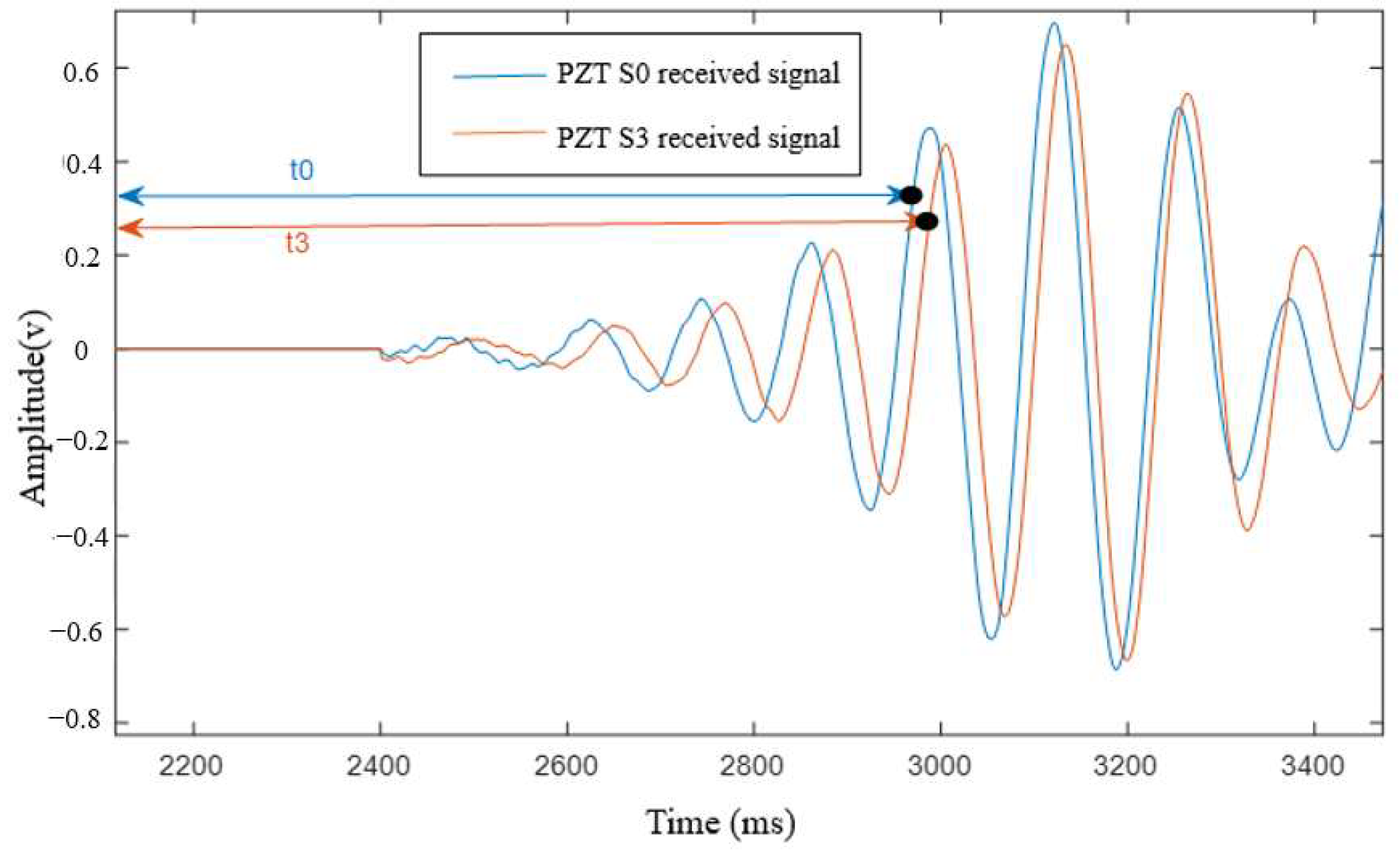
5.2. Experimental Results
5.2.1. Corrosion Angle Location
5.2.2. Corrosion Distance Location
5.2.3. Location Result Analysis
6. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DOA | Direction of Arrival CS compressive sensing. |
| MUSIC | Multiple signal classification. |
| LWNFL | Lamb wave near-field source location. |
| CS | Compressed sensing. |
| SHM | Structural health monitoring. |
| PZT | Piezoelectric. |
References
- Alexopoulos, N.D.; Dalakouras, C.J.; Skarvelis, P.; Kourkoulis, S.K. Accelerated corrosion exposure in ultra thin sheets of 2024 aircraft aluminium alloy for GLARE applications. Corros. Sci. 2012, 55, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, D.F.; Tavares, S.M.O.; Silva, L.F.; Moreira, P.M.G.P.; Castro, P.M. Advanced design for lightweight structures: Review and prospects. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2014, 69, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.Q.; Qiu, L.; Yuan, S.F.; Fang, F. Multi–damage imaging of composite structures under environmental and operational conditions using guided wave and Gaussian mixture model. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 115017–115031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, X.L.; Li, W.Z.; Wang, Y.S.; Sun, H. Piezoelectric transducer–based structural health monitoring for aircraft applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.F.; Ren, Y.Q.; Qiu, L.; Mei, H. A multi-response-based wireless impact monitoring network for aircraft composite structures. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 7712–7722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Q.; Yuan, S.F.; Guo, F.Y.; Qiu, L. Transmitter beamforming and weighted image fusion-based multiple signal classification algorithm for corrosion monitoring. Struct. Health Monit. 2019, 18, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Xu, C.; Deng, M.; Zhao, Y.; Bi, X.; Hu, N. Experimental investigation of the surface corrosion damage in plates based on nonlinear Lamb wave methods. NDT E Int. 2021, 121, 102466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, F.; Cao, Q.; Pan, H.; Lin, Z. CNN-LSTM hybrid model to promote signal processing of ultrasonic guided lamb waves for damage detection in metallic pipelines. Sensors 2023, 23, 7059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Luo, Z.; Zeng, L.; Lin, J. Detection and localization of corrosion using the combination information of multiple Lamb wave modes. Ultrasonics 2024, 138, 107246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozo, F.; Tibaduiza, D.A.; Vidal, Y. Sensors for structural health monitoring and condition monitoring. Sensors 2021, 21, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Leary, D.P. The Direction-of-Arrival Problem: Coming at You. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2003, 5, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engholm, M.; Stepinski, T. Direction of arrival estimation of Lamb waves using circular arrays. Struct. Health Monit. 2011, 10, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, S.K. Impact source localization in plate utilizing multiple signal classification. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2013, 227, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Zhong, Y.; Qiu, L.; Wang, Z. Two-dimensional near-field multiple signal classification algorithm-based impact localization. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2015, 26, 703–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Yuan, S.; Qiu, L. Multi-impact source localisation on aircraft composite structure using uniform linear PZT sensors array. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2015, 11, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Yuan, S.; Qiu, L. An improved two-dimensional multiple signal classification approach for impact localization on a composite structure. Struct. Health Monit. 2015, 14, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Yuan, S.; Qiu, L. Multiple damage detection on aircraft composite structures using near-field MUSIC algorithm. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2014, 214, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalal, B.; Yang, X.; Wu, X.; Long, T.; Sarkar, T.K. Efficient direction-of-arrival estimation method based on variable-step-size LMS algorithm. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2019, 18, 1576–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Chien, Y.R.; Qian, G. Low complexity error-censoring RLS algorithm for DOA estimation. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 17237–17244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, G.; Feng, C.; Tang, J. Improved DOA estimation algorithm for co-prime linear arrays using root- MUSIC algorithm. Electron. Lett. 2017, 53, 1277–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Z. Maximum likelihood estimation of DOD and DOA for bistatic MIMO radar. Signal Process. 2013, 93, 1349–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubeigt, C.; Vincent, F.; Ortega, L.; Vila-Valls, J.; Chaumette, E. Approximate maximum likelihood time-delay estimation for two closely spaced sources. Signal Process. 2023, 210, 109056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarty, S.; Habets, E.A. Multi-speaker DOA estimation using deep convolutional networks trained with noise signals. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2019, 13, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Chen, B.; Yang, T.; Liu, D. Improved de-multipath neural network models with self-paced feature-to-feature learning for DOA estimation in multipath environment. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 5068–5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoho, D.L. Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2006, 52, 1289–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candes, E.J.; Tao, T. Decoding by linear programming. IEEE Trans. Theory 2005, 59, 4203–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candes, E.J.; Romberg, J.; Tao, T. Robust uncertainty principles: Exact signal recognition from highly incomplete frequency information. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2006, 52, 489–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malioutov, D.M.; Cetin, M.; Willsky, A.S. A sparse signal reconstruct on perspective for source localization with sensor arrays. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2005, 53, 3010–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, H.A.; Raja, M.A.Z.; Chaudhary, N.I.; Qureshi, I.M.; Malik, A.N. A robust multi sample compressive sensing technique for DOA estimation using sparse antenna array. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 140848–140861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, K.; Ganguly, S.; Kishore, K.P. Performance comparison of reconstruction algorithms in compressive sensing based single snapshot doa estimation. IETE J. Res. 2022, 68, 2876–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Shen, X.; Jiang, M.; Zhao, K. Off-Grid DOA Estimation Based on Compressed Sensing on Multipath Environment. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2023, 2023, 9315869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Hao, C. Super-resolution TOA and AOA estimation for OFDM radar systems based on compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2022, 58, 5730–5740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, P. Compressed sensing-based DOA estimation with antenna phase errors. Electronics 2019, 8, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Chen, T.; Wang, P.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, R.; Bai, Y. A direction-of-arrival estimation algorithm based on compressed sensing and density-based spatial clustering and its application in signal processing of MEMS vector hydrophone. Sensors 2021, 21, 2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraniuk, R.G. A lecture on compressive sensing. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2007, 24, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaig, Y.; Donoho, D.L. Extensions of compressed sensing. Signal Process. 2006, 86, 549–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


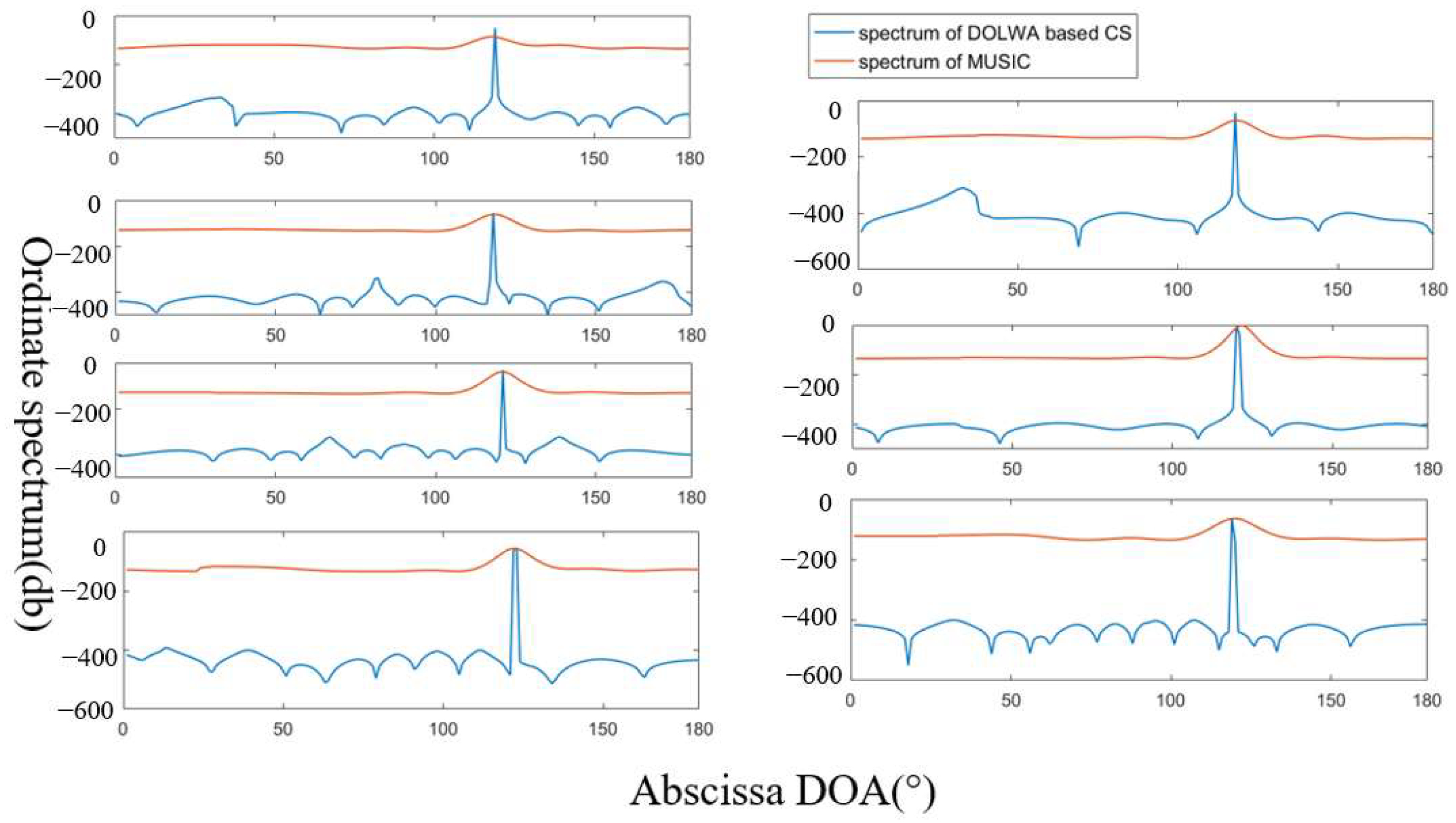

| Excitation Sensor | Actual Angle | MUSIC Algorithm | Lamb Wave Near-Field DOA Estimation Based on CS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Localization | Error | Localization | Error | ||
| PZT A-3 | 120° | 117.0° | 3° | 116.6° | 3.4° |
| PZT A-2 | 120° | 122.2° | 2.2° | 118.2° | 1.8° |
| PZT A-1 | 120° | 123.2° | 3.2° | 116.8° | 3.2° |
| PZT A0 | 120° | 118.0° | 2° | 117.6° | 2.4° |
| PZT A1 | 120° | 117.4° | 2.6° | 118.2° | 1.8° |
| PZT A2 | 120° | 122.2° | 2.2° | 122.0° | 2.0° |
| PZT A3 | 120° | 122.8° | 2.8° | 122.2° | 2.2° |
| Excitation Sensor | Actual Distance | MUSIC | Lamb Wave Near-Field Distance Estimation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Localization Result | Error | Localization Result | Error | ||
| PZT A-3 | 220 mm | 196 mm | 24 mm | 246 mm | 26 mm |
| PZT A-2 | 220 mm | 240 mm | 20 mm | 207 mm | 13 mm |
| PZT A-1 | 220 mm | 236 mm | 16 mm | 239 mm | 19 mm |
| PZT A0 | 220 mm | 201 mm | 19 mm | 208 mm | 12 mm |
| PZT A1 | 220 mm | 205 mm | 15 mm | 206 mm | 14 mm |
| PZT A2 | 220 mm | 244 mm | 24 mm | 200 mm | 20 mm |
| PZT A3 | 220 mm | 191 mm | 29 mm | 194mm | 26 mm |
| Location Results | Error | DOA Power Spectrum | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Angle | Distance | Angle | Distance | ||
| MUISC | 117.4° | 205 mm | 2.6° | 15 mm | Increases slowly, wider spectrum range, small peak difference at corrosion angle |
| LWNFL | 118.8° | 214.3 mm | 1.2° | 5.7 mm | Increases steeply, narrower spectrum range, small peak difference at corrosion angle |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xin, Z.; Bao, Q.; Zheng, F. Lamb Wave Near-Field Source Localization Method for Corrosion Monitoring. Electronics 2025, 14, 907. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14050907
Xin Z, Bao Q, Zheng F. Lamb Wave Near-Field Source Localization Method for Corrosion Monitoring. Electronics. 2025; 14(5):907. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14050907
Chicago/Turabian StyleXin, Zengnian, Qiao Bao, and Fei Zheng. 2025. "Lamb Wave Near-Field Source Localization Method for Corrosion Monitoring" Electronics 14, no. 5: 907. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14050907
APA StyleXin, Z., Bao, Q., & Zheng, F. (2025). Lamb Wave Near-Field Source Localization Method for Corrosion Monitoring. Electronics, 14(5), 907. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14050907






