High-Precision Time Synchronization Based on Timestamp Mapping in Datacenter Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We present an innovative time synchronization method based on timestamp mapping, elaborate the principle and steps of the method, and make a detailed description of the implementation on an FPGA and programmable switch;
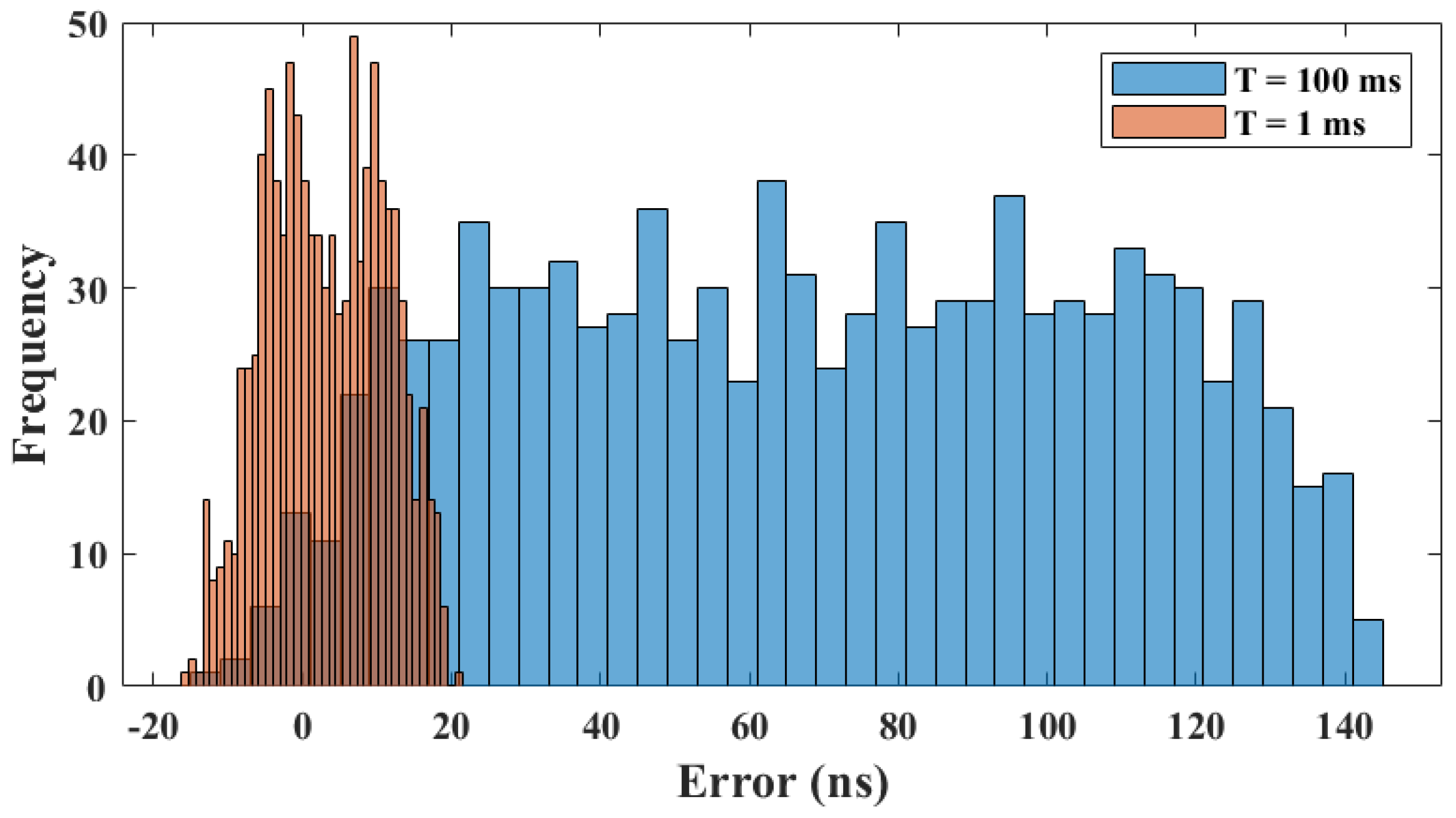
- We introduce the evaluation method and build a test platform to evaluate the feasibility and effectiveness of the method. Firstly, we investigate the effect of the synchronization period on the time synchronization performance, and secondly, we optimize the synchronization method using an offset adjustment strategy. Using the 100 ms time synchronization period and the offset adjustment strategy, the maximum synchronization error of the proposed method is found to be 19 ns, and the standard deviation is 7.8 ns. These results indicate a high level of synchronization accuracy and stability.
2. Related Work
3. Proposed Solution
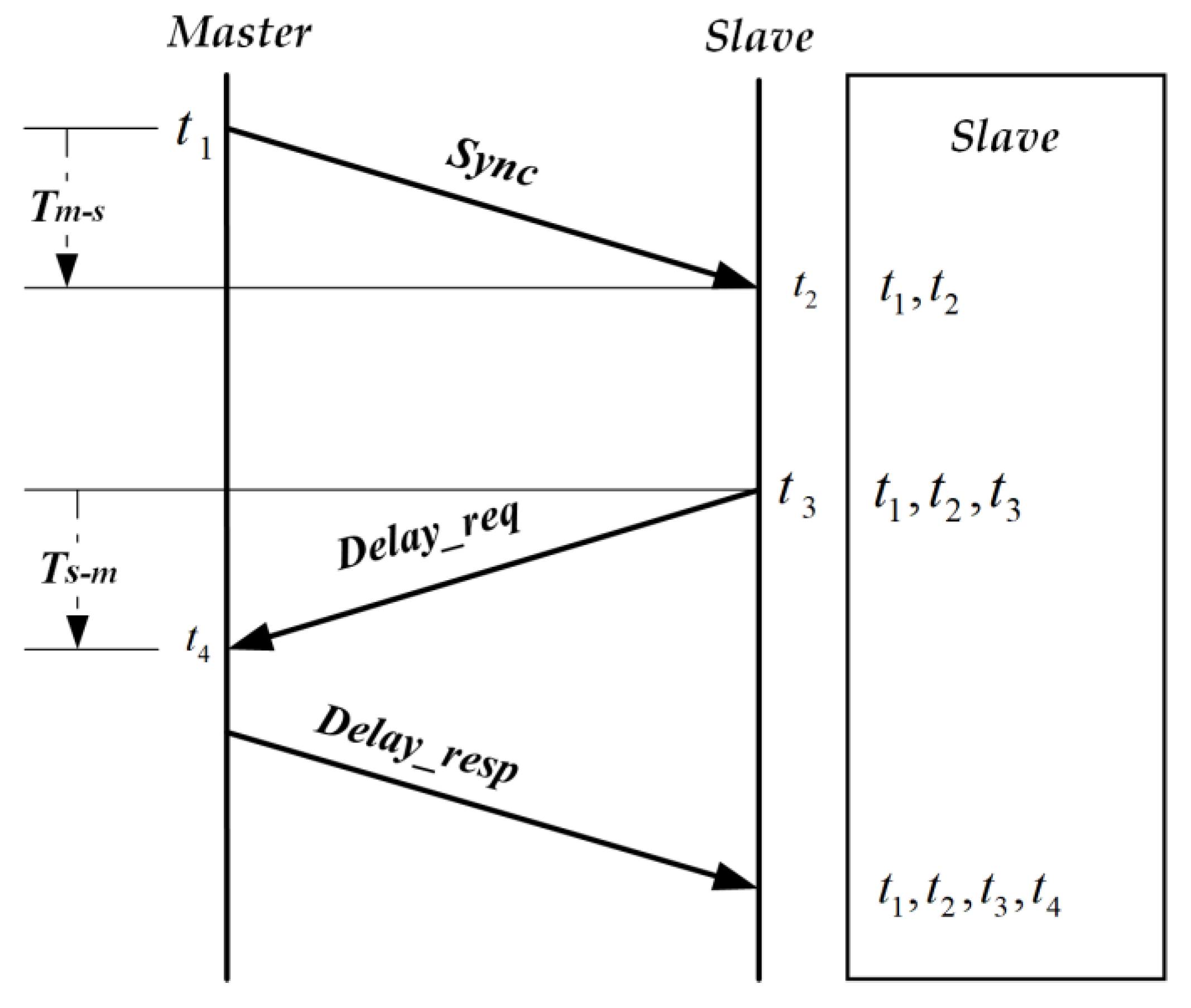
3.1. Precision Time Protocol Overview
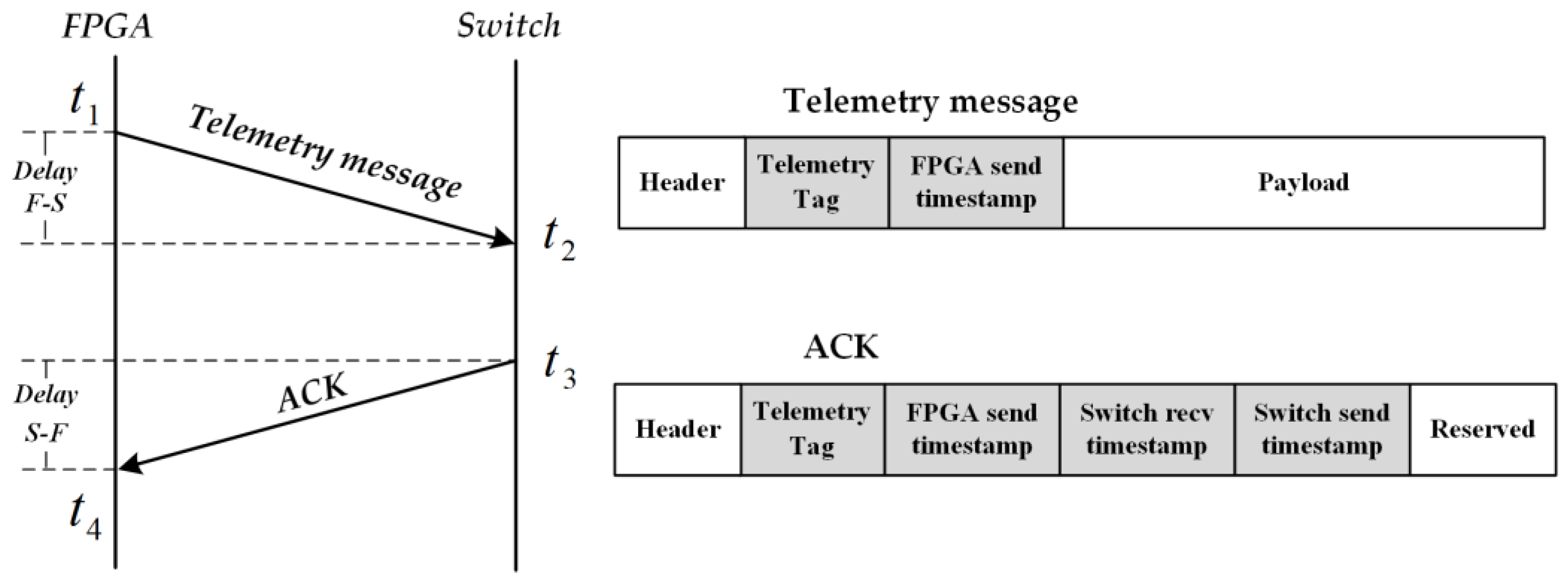
3.2. The Method Proposed in This Paper
3.3. Problems of Clock Synchronization
4. Design and Implementation
4.1. Implementation on an FPGA
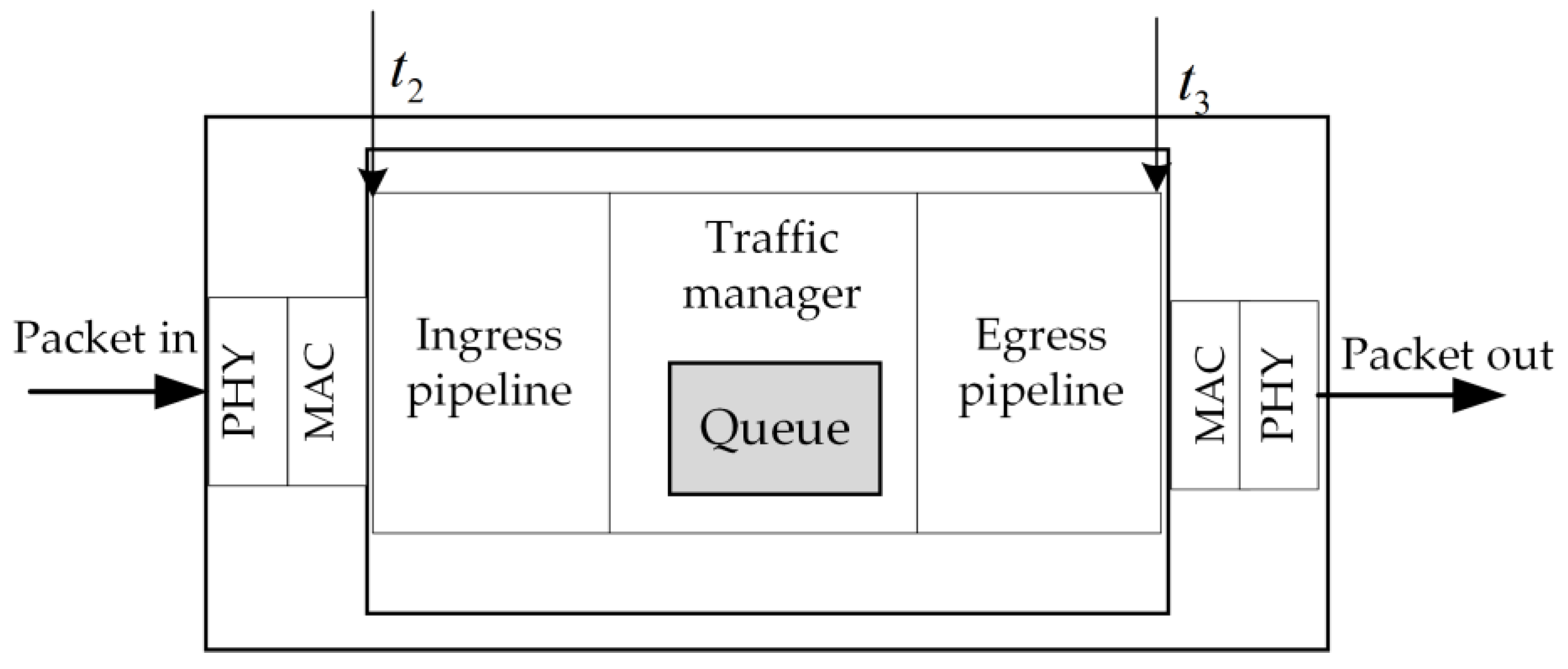
4.2. Implementation on Programmable Switch
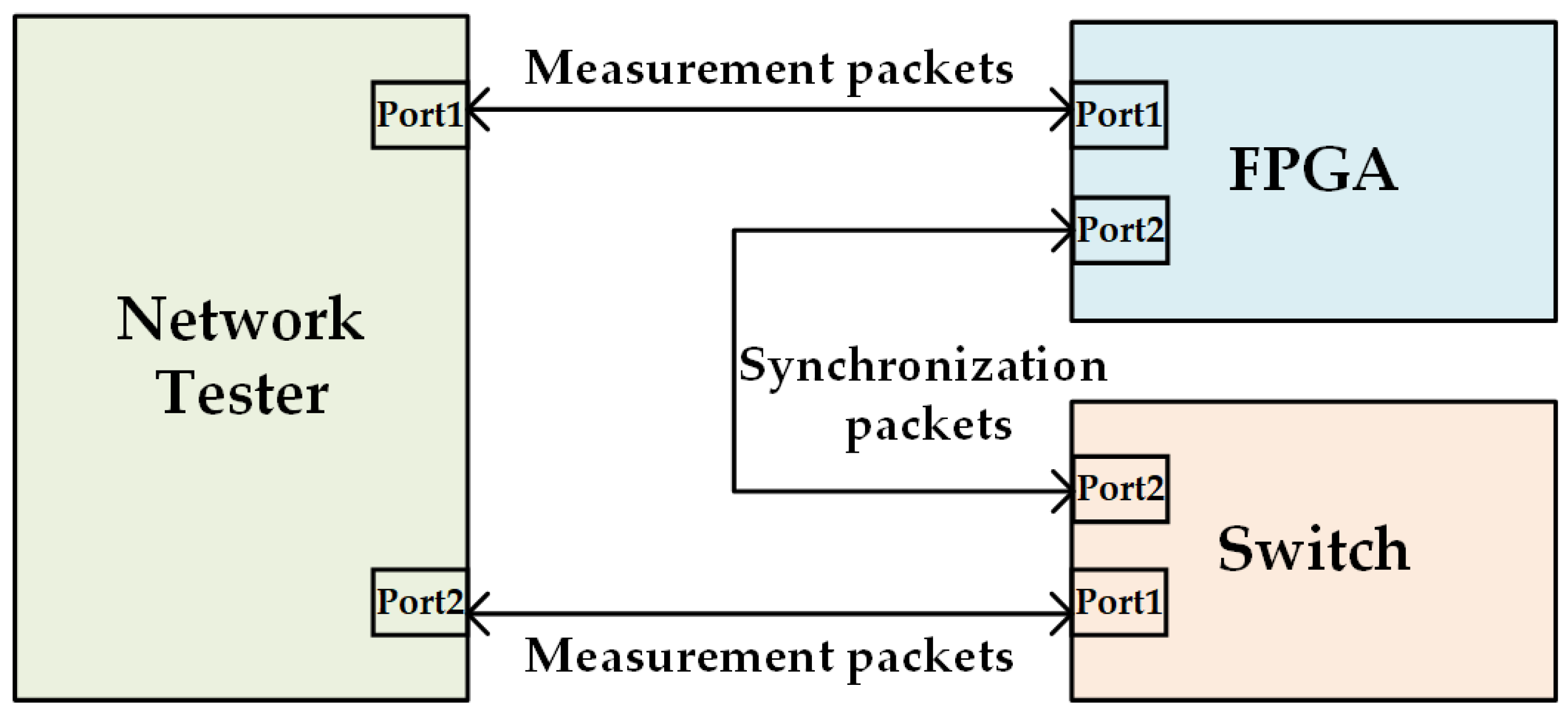
5. Evaluation
6. Results
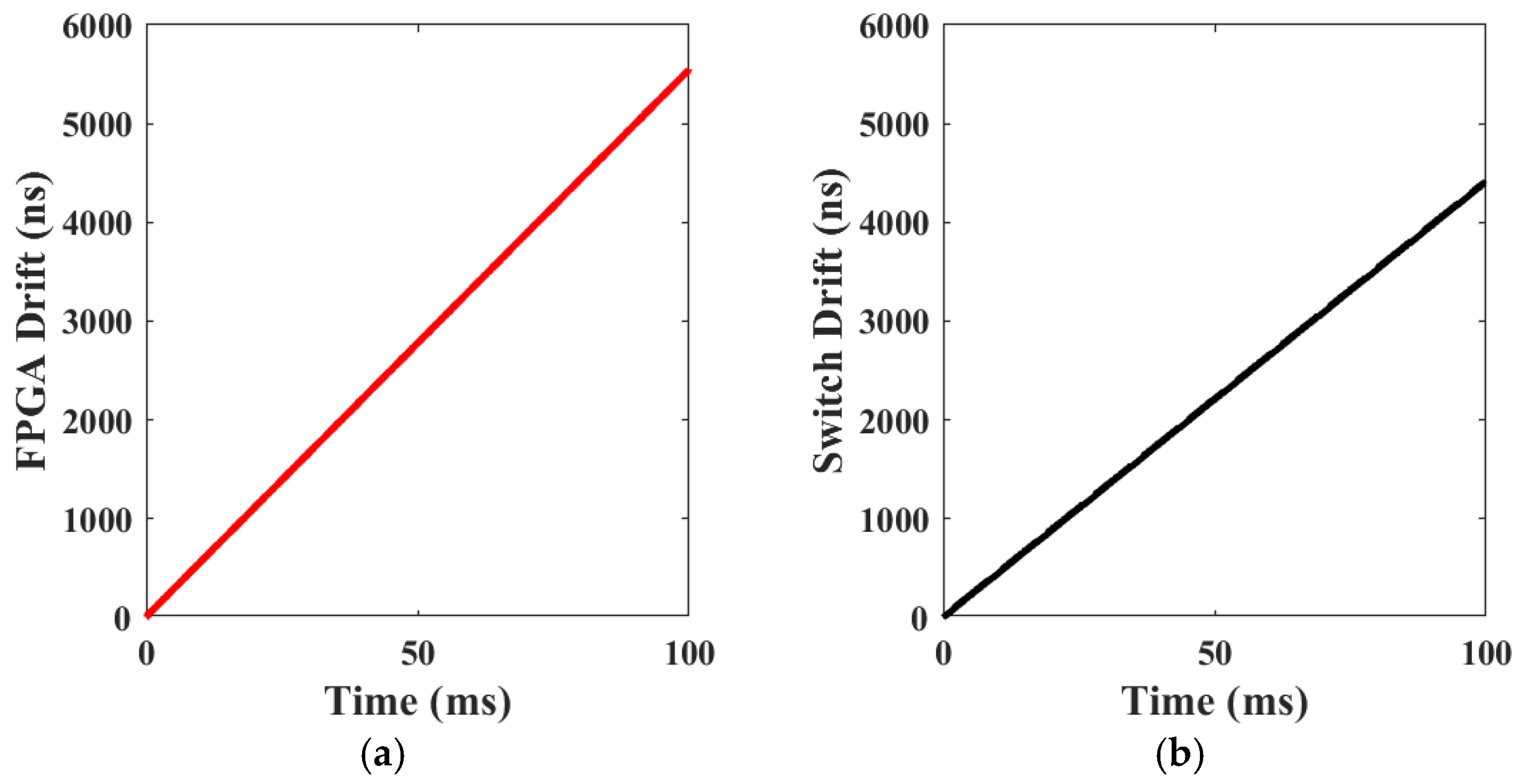
6.1. Clock Drift Measurement
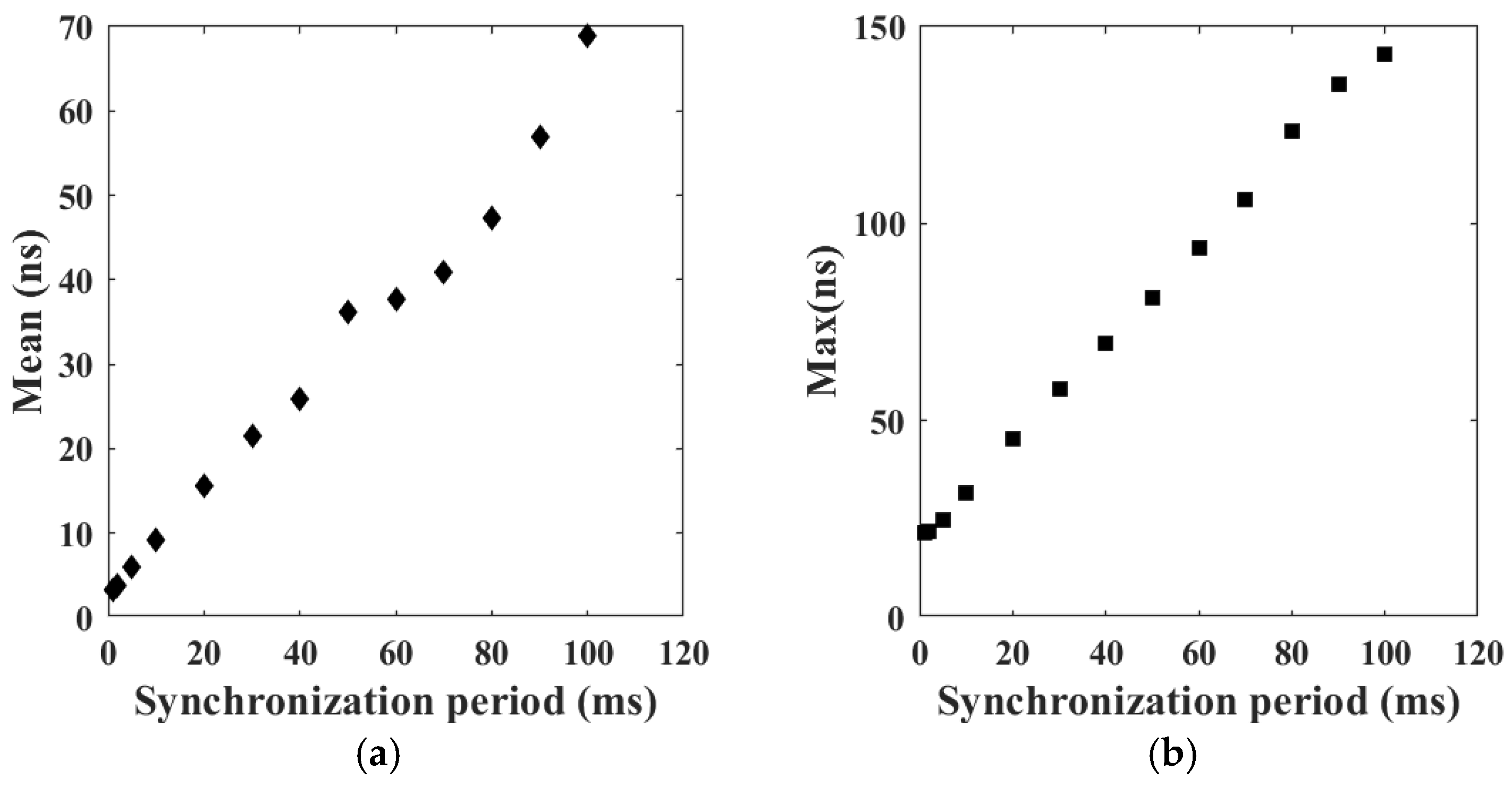
6.2. Time Synchronization Measurement
6.3. Offset Adjustment

7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lei, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Joshi, R.; Xia, Y. Nanosecond Precision Time Synchronization for Optical Data Center Networks. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.17012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, q.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Tang, X.; Shen, Z.; Wang, H. Nanosecond level time synchronization in datacenter network based on Telemetry architecture. J. Commun. 2021, 42, 117–129. [Google Scholar]
- Bosshart, P.; Daly, D.; Gibb, G.; Izzard, M.; McKeown, N.; Rexford, J.; Schlesinger, C.; Talayco, D.; Vahdat, A.; Varghese, G.; et al. P4: Programming protocol-independent packet processors. ACM SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev. 2014, 44, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kfoury, E.F.; Choueiri, S.; Mazloum, A.; AlSabeh, A.; Gomez, J.; Crichigno, J. A comprehensive survey on smartnics: Architectures, development models, applications, and research directions. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 107297–107336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Kumar, K.; Aggarwal, N. A review on P4-Programmable data planes: Architecture, research efforts, and future directions. Comput. Commun. 2021, 170, 109–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Lei, Y.; Zou, S.; Huang, J.; Li, F. Load balancing with traffic isolation in data center networks. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2022, 127, 126–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobda, C.; Mbongue, J.M.; Chow, P.; Ewais, M.; Tarafdar, N.; Vega, J.C.; Eguro, K.; Koch, D.; Handagala, S.; Leeser, M.; et al. The future of FPGA acceleration in datacenters and the cloud. ACM Trans. Reconfigurable Technol. Syst. 2022, 15, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, L.P.; Kumar, G.; Khalaf, O.I.; Wong, W.-K.; Hamad, A.A.; Rawat, S.S. Adaptive Congestion Control in IoT Networks: Leveraging One-Way Delay for Enhanced Performance. Heliyon 2024, 10, e40266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.; Park, M.; Oh, D.; Kim, B.; Lee, J. Clock synchronization for one-way delay measurement: A survey. In Proceedings of the Advanced Communication and Networking: Third International Conference, ACN 2011, Brno, Czech Republic, 15–17 August 2011; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Chefrour, D. One-way delay measurement from traditional networks to sdn: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2021, 54, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, P.G.; Joshi, R.; Chan, M.C. Precise time-synchronization in the data-plane using programmable switching asics. In Proceedings of the 2019 ACM Symposium on SDN Research, San Jose, CA, USA, 3–4 April 2019; pp. 8–20. [Google Scholar]
- Crossley, P.A.; Guo, H.; Ma, Z. Time synchronization for transmission substations using GPS and IEEE 1588. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 2016, 2, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Crossley, P. Design of a time synchronization system based on GPS and IEEE 1588 for transmission substations. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2016, 32, 2091–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, D. Internet time synchronization: The network time protocol. IEEE Trans. Commun. 1991, 39, 1482–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Guo, X.; Tian, J. Research and implementation of clock synchronization technology based on PTP. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1757, 012139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallat, A.; Schneuwly, D. Clock synchronization in telecommunications via PTP (IEEE 1588). In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium Joint with the 21st European Frequency and Time Forum, Geneva, Switzerland, 29 May–1 June 2007; pp. 334–341. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrant, J.-L.; Gilson, M.; Jobert, S.; Mayer, M.; Ouellette, M.; Montini, L.; Rodrigues, S.; Ruffini, S. Synchronous Ethernet: A method to transport synchronization. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2008, 46, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrant, J.-L.; Gilson, M.; Jobert, S.; Mayer, M.; Montini, L.; Ouellette, M.; Rodrigues, S.; Ruffini, S. Synchronous Ethernet and IEEE 1588 in Telecoms: Next Generation Synchronization Networks; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.S.; Wang, H.; Shrivastav, V.; Weatherspoon, H. Globally synchronized time via datacenter networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM SIGCOMM Conference, Florianópolis, Brazil, 22–26 August 2016; pp. 454–467. [Google Scholar]
- Moreira, P.; Serrano, J.; Wlostowski, T.; Loschmidt, P.; Gaderer, G. White rabbit: Sub-nanosecond timing distribution over ethernet. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Symposium on Precision Clock Synchronization for Measurement, Control and Communication, Brescia, Italy, 12–16 October 2009; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Serrano, J.; Lipinski, M.; Wlostowski, T.; Gousiou, E.; van der Bij, E.; Cattin, M.; Daniluk, G. The white rabbit project. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Beam Instrumentation Conference, Oxford, UK, 16–19 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rafii, A.; Sun, W.; Chow, P. Pharos: A multi-FPGA performance monitor. In Proceedings of the 2021 31st International Conference on Field-Programmable Logic and Applications (FPL), Dresden, Germany, 30 August–3 September 2021; pp. 257–262. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, H.; Fu, P.; Qiao, J.; Li, Y. The implementation of IEEE 1588 clock synchronization protocol based on FPGA. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Houston, TX, USA, 14–17 May 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakakis, E.; Sparsø, J.; Schoeberl, M. Hardware assisted clock synchronization with the ieee 1588-2008 precision time protocol. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Real-Time Networks and Systems, Chasseneuil-du-Poitou, France, 10–12 October 2018; pp. 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Grölle, D.; Schulz, L.-C.; Wehner, R.; Hausheer, D. Poster: High-Speed Per-Packet Checksums on the Intel Tofino. In Proceedings of the 6th on European P4 Workshop, Paris, France, 5–8 December 2023; pp. 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, D.; Zaballa, E.O.; Zang, M.; Atutxa, A.; Sasiain, J.; Pruski, A.; Rojas, E.; Higuero, M.; Jacob, E. A comprehensive latency profiling study of the Tofino P4 programmable ASIC-based hardware. Comput. Commun. 2024, 218, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Wu, J.; Xie, M.; Yu, Z. A new design for precision clock synchronization based on FPGA. In Proceedings of the 2009 16th IEEE-NPSS Real Time Conference, Beijing, China, 10–15 May 2009; pp. 411–414. [Google Scholar]


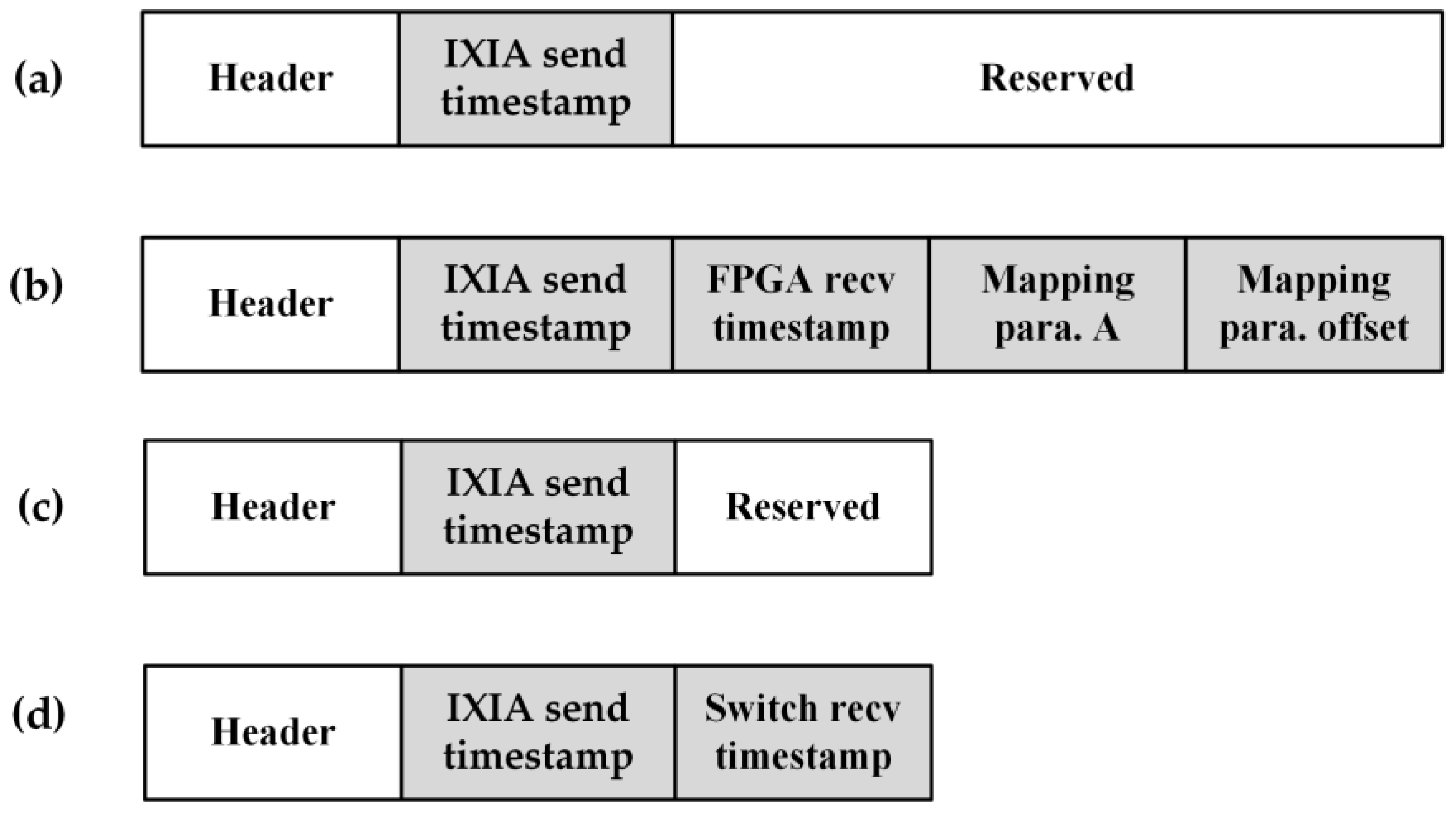
| Modules | LUT | Registers | BRAM | CARRY8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Telemetry tagging | 2217 | 5759 | 8.5 | 7 |
| TX timestamp insertion | 1790 | 1254 | 0 | 288 |
| RX timestamp insertion | 1897 | 1240 | 0 | 336 |
| Timestamp generator | 2012 | 64 | 0 | 0 |
| Storage | 185 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| Others (mux/demux et al.) | 1369 | 4018 | 1 | 4 |
| Total | 9470 | 12435 | 9.5 | 635 |
| Modules | Power Consumption (W) |
|---|---|
| Telemetry tagging | 0.101 |
| TX timestamp insertion | 0.037 |
| RX timestamp insertion | 0.028 |
| Timestamp generator | 0.013 |
| Storage | 0.003 |
| Others (mux/demux et al.) | 0.097 |
| Total | 0.279 |
| Synchronization Period (ms) | Mean (ns) | Std (ns) | Max_Error (ns) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.25 | 7.88 | 21 |
| 2 | 3.76 | 7.91 | 21 |
| 5 | 5.99 | 8.08 | 24 |
| 10 | 9.18 | 8.68 | 31 |
| 20 | 15.61 | 10.93 | 45 |
| 30 | 21.50 | 14.17 | 57 |
| 40 | 25.82 | 17.12 | 69 |
| 50 | 36.17 | 20.76 | 81 |
| 60 | 37.67 | 22.56 | 93 |
| 70 | 40.91 | 27.62 | 106 |
| 80 | 47.37 | 33.23 | 123 |
| 90 | 56.94 | 37.45 | 135 |
| 100 | 68.96 | 39.36 | 143 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Chen, B.; Duan, D.; Liu, L. High-Precision Time Synchronization Based on Timestamp Mapping in Datacenter Networks. Electronics 2025, 14, 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14030610
Li L, Chen B, Duan D, Liu L. High-Precision Time Synchronization Based on Timestamp Mapping in Datacenter Networks. Electronics. 2025; 14(3):610. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14030610
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Lin, Baihua Chen, Dexuan Duan, and Lei Liu. 2025. "High-Precision Time Synchronization Based on Timestamp Mapping in Datacenter Networks" Electronics 14, no. 3: 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14030610
APA StyleLi, L., Chen, B., Duan, D., & Liu, L. (2025). High-Precision Time Synchronization Based on Timestamp Mapping in Datacenter Networks. Electronics, 14(3), 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14030610





