Federated Distributed Network Traffic Classification Based on Deep Mutual Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Mitigating Data Heterogeneity: We introduce a deep mutual learning mechanism to mitigate the performance degradation of conventional federated learning under non-IID data. This mechanism fosters knowledge exchange among clients, enhancing model generalization across diverse distributions by preventing overfitting to localized patterns.
- The FLDML Framework: We propose the FLDML framework. Its core innovation is a server-side mutual learning phase, where client models are co-trained on a public dataset to assimilate a more robust and generalized representation, complementing their local training on private data.
- A Lightweight Local Model: We design a lightweight local model architecture that integrates a 1D-CNN with Batch Normalization (BN), termed BN-CNN. This design is tailored for efficient feature extraction from preprocessed traffic sequences. Experiments on the ISCX VPN-NonVPN 2016 dataset confirm that BN-CNN achieves superior accuracy and F1-score over traditional baselines.
- Comprehensive Validation: Through extensive comparative experiments on the ISCX dataset, we demonstrate that FLDML achieves higher traffic classification accuracy than both a centralized BN-CNN baseline and classical federated algorithms like FedAvg, effectively balancing performance with the privacy benefits of decentralized training.
2. Related Work
2.1. Conventional Network Traffic Classification
2.2. Federated Learning for Network Traffic Classification
2.3. Deep Mutual Learning
3. Materials and Methods
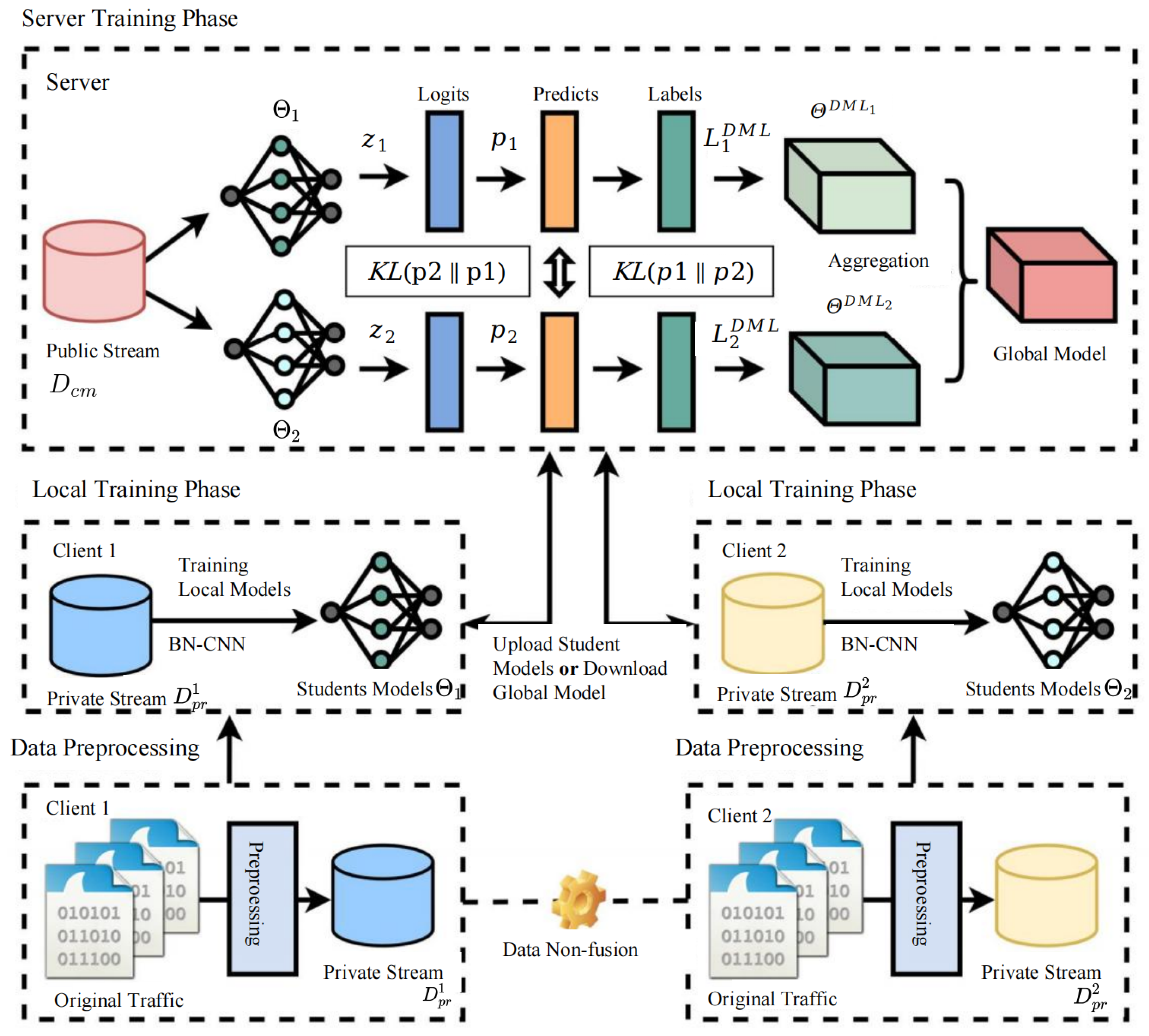
3.1. Overview
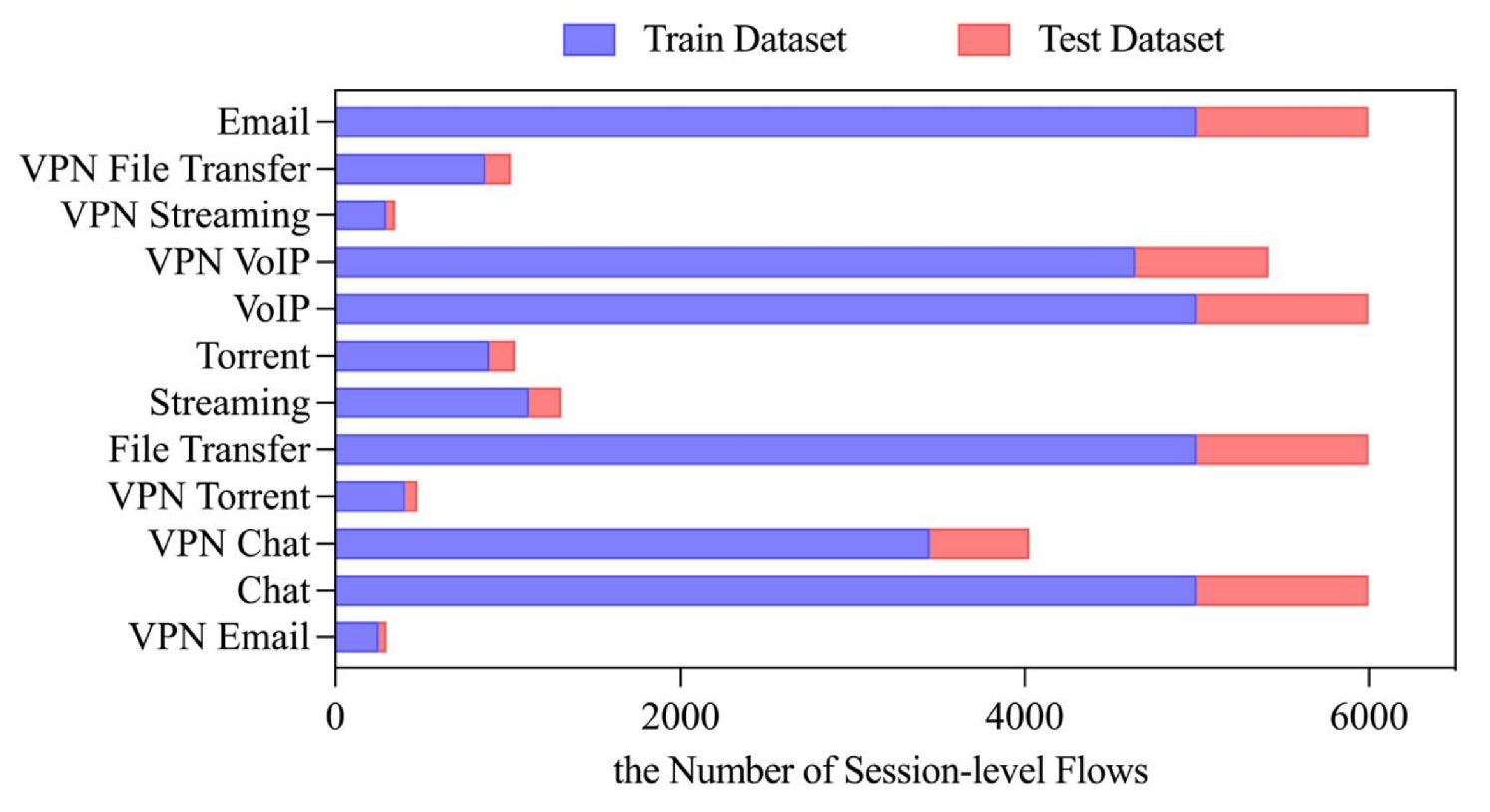
3.2. Datasets
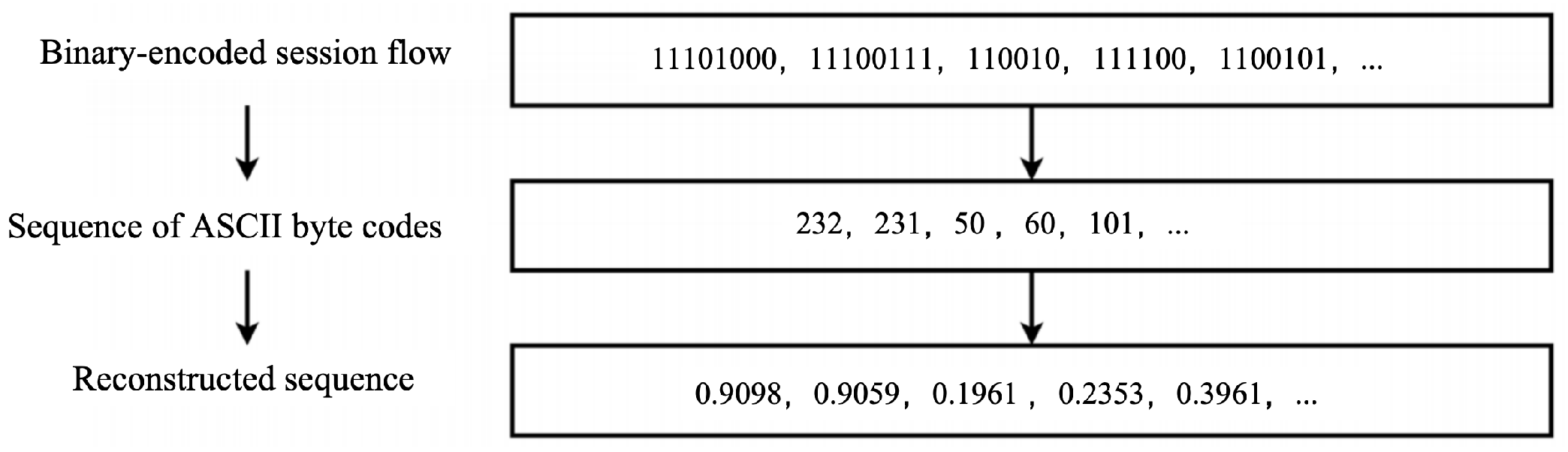
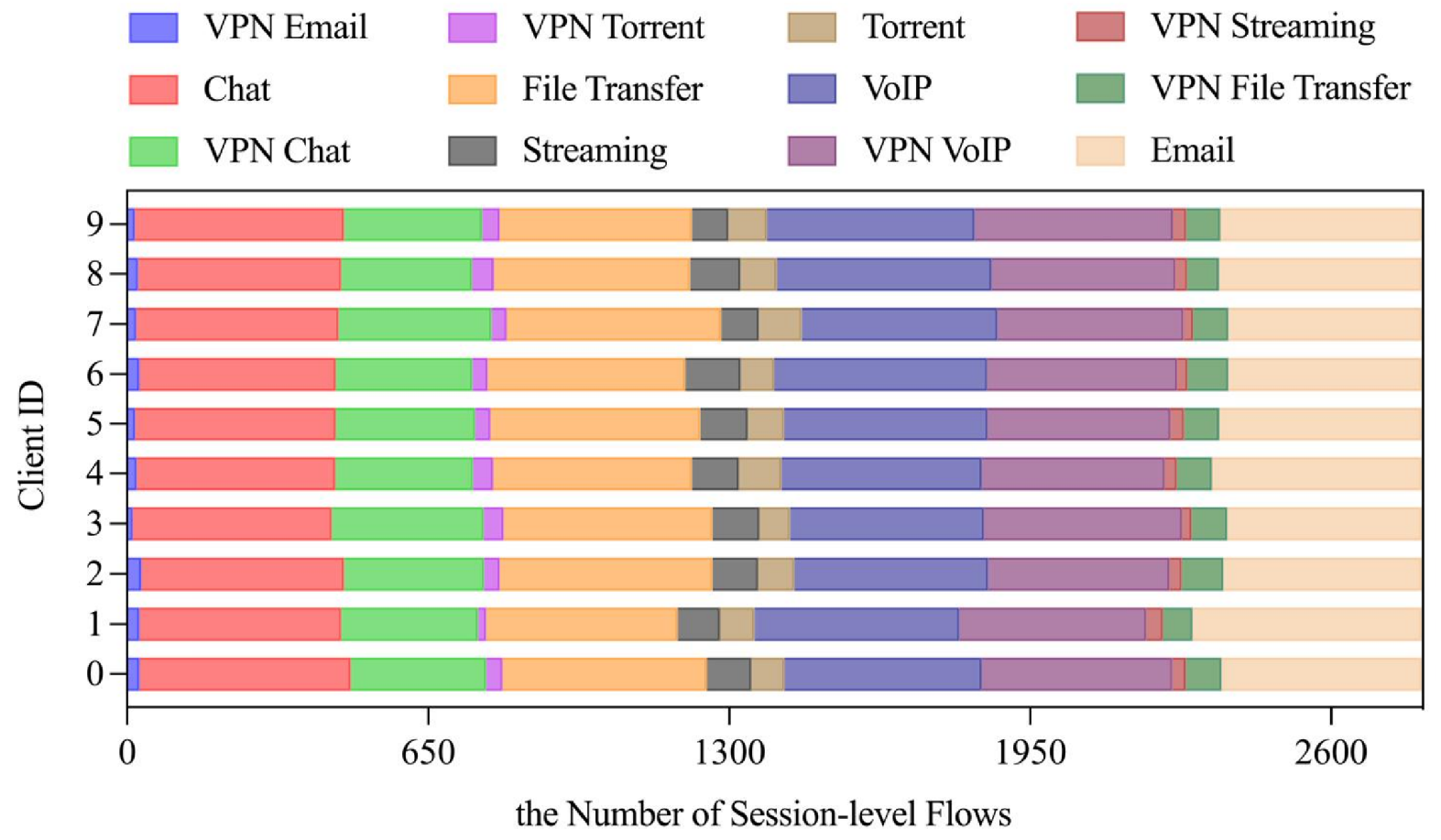
3.3. Client-Side Data Preprocessing
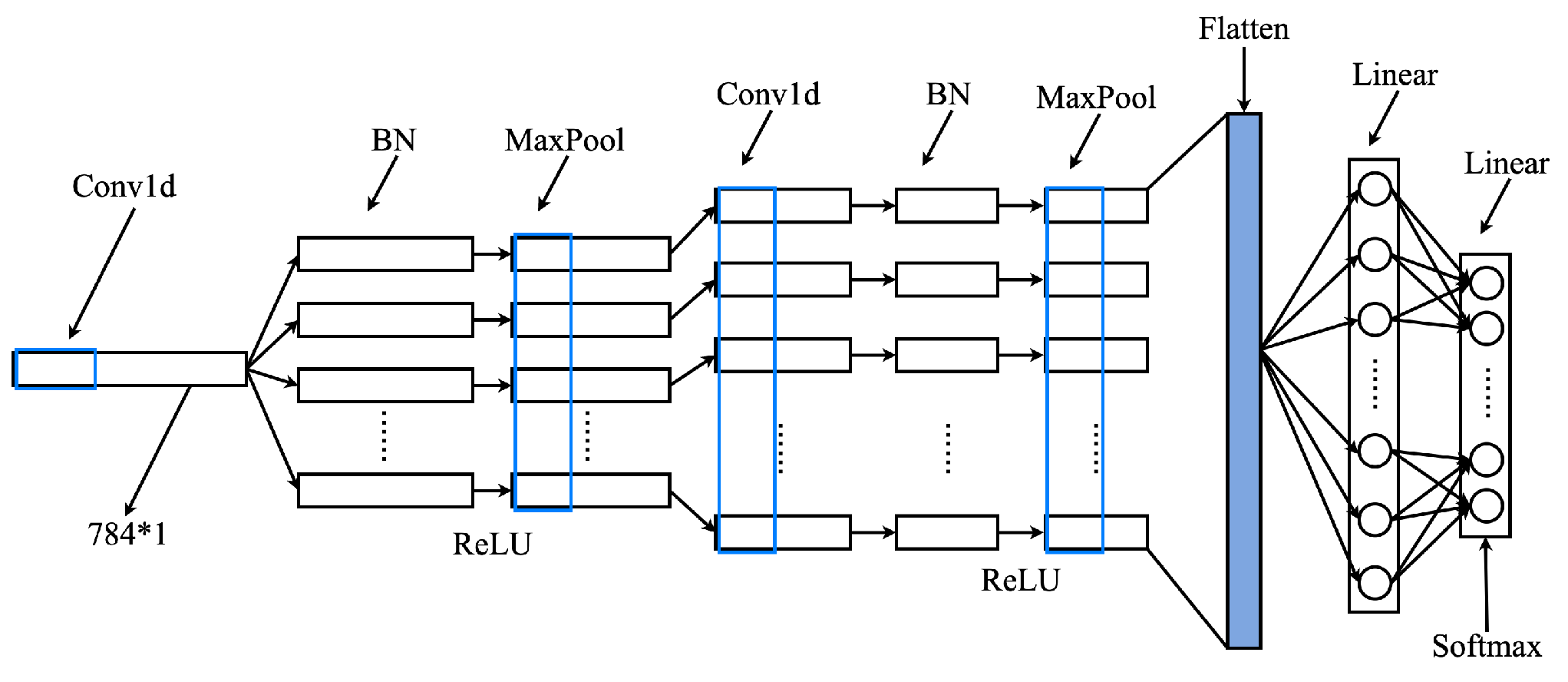
3.4. Client-Side Local Model Training
3.5. Server-Side Student Models Learn from Each Other and Model Average Aggregation Stages
3.6. The FLDML Algorithm
| Algorithm 1 FLDML Algorithm |
| Require: K, Number of clients of the network operator; B, Small batch size; E, Client model training rounds; F, Students model rounds of learning from each other; , Learning rate; ,, Private stream, public stream Data preprocessing: for each client k = 1, 2, …, K do end for Server-side training: for each epoch t = 1, 2, …, T do for each client in paralled do end for for each client , do for each epoch do end for end for end for Client local training: for each local epoch from 1 to E do for each do end for end for return |
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
4.1. Experimental Settings
4.2. Experimental Evaluation
4.3. Experimental Results and Analysis
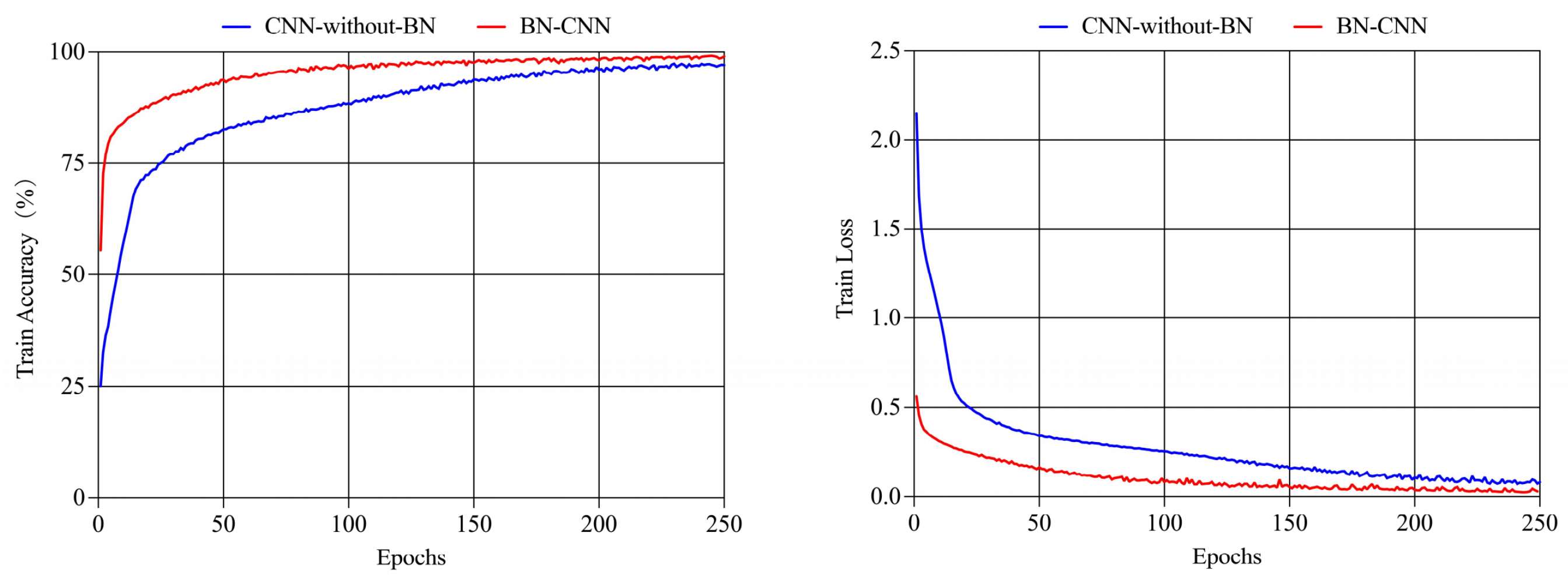
4.3.1. Evaluation of the Local Model
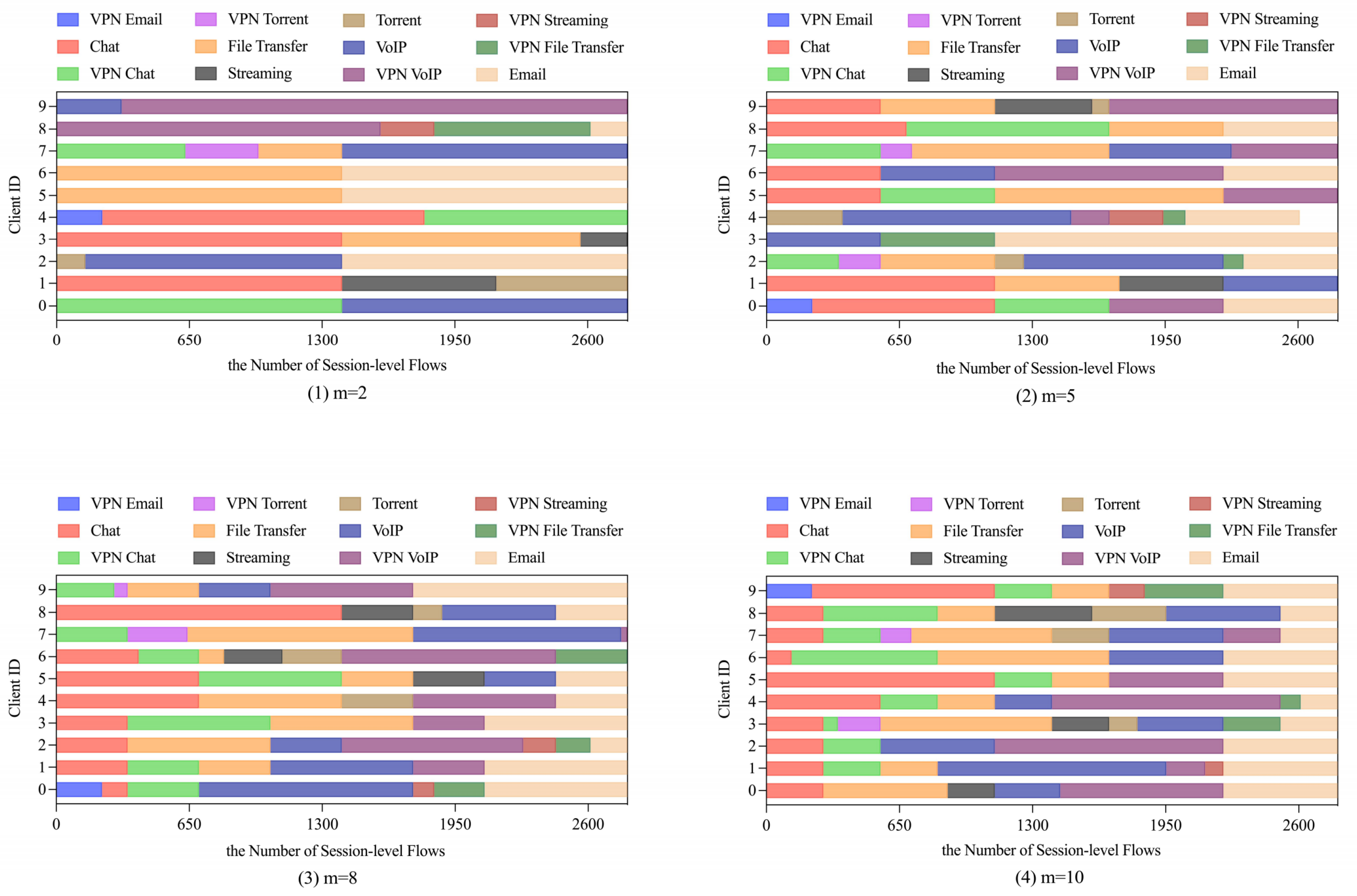
4.3.2. Evaluation of FLDML
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stojmenovic, I.; Wen, S.; Huang, X.; Luan, H. An overview of Fog computing and its security issues. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2016, 28, 2991–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Liu, W.; Huang, Z.; Yu, F.R. Task Decomposition and Hierarchical Scheduling for Collaborative Cloud-Edge-End Computing. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2024, 17, 4368–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Gleerup, T.; Tan, J.; Wang, Y. A security enhanced android unlock scheme based on pinch-to-zoom for smart devices. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2023, 70, 3985–3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azab, A.; Khasawneh, M.; Alrabaee, S.; Choo, K.K.R.; Sarsour, M. Network traffic classification: Techniques, datasets, and challenges. Digit. Commun. Netw. 2024, 10, 676–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Ma, W.; Han, Q.; Zhou, W.; Zhu, X.; Wen, S.; Xiang, Y. Exploring DeepSeek: A Survey on Advances, Applications, Challenges and Future Directions. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2025, 12, 872–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahaei, H.; Afifi, F.; Asemi, A.; Zaki, F.; Anuar, N.B. The rise of traffic classification in IoT networks: A survey. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2020, 154, 102538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujlow, T.; Carela-Español, V.; Barlet-Ros, P. Independent comparison of popular DPI tools for traffic classification. Comput. Netw. 2015, 76, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Armitage, G. A survey of techniques for internet traffic classification using machine learning. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2008, 10, 56–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Wei, Z.; Luo, J. ICS Anomaly Detection based on Sensor Patterns and Actuator Rules in Spatiotemporal Dependency. IEEE Trans. Ind. Informantics 2024, 20, 10647–10656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wen, Z.; Wu, Z.; Hu, S.; Wang, N.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; He, B. A survey on federated learning systems: Vision, hype and reality for data privacy and protection. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2021, 35, 3347–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Fu, M.; Ye, Y.; Wang, P. Network traffic classification based on federated semi-supervised learning. J. Syst. Archit. 2024, 149, 103091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, C.; Wang, D.; Wen, S.; Zhang, J.; Nepal, S.; Xiang, Y.; Ren, K. Android HIV: A study of repackaging malware for evading machine-learning detection. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2019, 15, 987–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, S.D.; Wu, D.; Hu, X.; Wang, Y. ARDST: An Adversarial-Resilient Deep Symbolic Tree for Adversarial Learning. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2024, 2024, 2767008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Sun, R.; Xue, M.; Ma, W.; Wen, S.; Nepal, S.; Yang, X. Hardening LLM Fine-Tuning: From Differentially Private Data Selection to Trustworthy Model Quantization. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2025, 20, 7211–7226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, W.; Wei, G.; Yang, L.T. Internet Traffic Classification Using Constrained Clustering. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2014, 25, 2932–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Sun, R.; Xue, M.; Wen, S.; Camtepe, S.; Nepal, S.; Xiang, Y. Leakage-Resilient and Carbon-Neutral Aggregation Featuring the Federated AI-Enabled Critical Infrastructure. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2025, 22, 3661–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roughan, M.; Sen, S.; Spatscheck, O.; Duffield, N. Class-of-service mapping for QoS: A statistical signature-based approach to IP traffic classification. In Proceedings of the 4th ACM SIGCOMM Conference on Internet Measurement, Taormina Sicily, Italy, 25–27 October 2004; pp. 135–148. [Google Scholar]
- Finsterbusch, M.; Richter, C.; Rocha, E.; Muller, J.A.; Hanssgen, K. A survey of payload-based traffic classification approaches. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2013, 16, 1135–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumano, Y.; Ata, S.; Nakamura, N.; Nakahira, Y.; Oka, I. Towards real-time processing for application identification of encrypted traffic. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Computing, Networking and Communications (ICNC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 3–6 February 2014; pp. 136–140. [Google Scholar]
- Okada, Y.; Ata, S.; Nakamura, N.; Nakahira, Y.; Oka, I. Application identification from encrypted traffic based on characteristic changes by encryption. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Workshop Technical Committee on Communications Quality and Reliability (CQR), Naples, FL, USA, 10–12 May 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Yanai, R.; Langberg, M.; Peleg, D.; Roditty, L. Realtime classification for encrypted traffic. In Proceedings of the Experimental Algorithms: 9th International Symposium, SEA 2010, Ischia Island, Naples, Italy, 20–22 May 2010; Proceedings 9. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 373–385. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Zhu, M.; Zeng, X.; Ye, X.; Sheng, Y. Malware traffic classification using convolutional neural network for representation learning. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Information Networking (ICOIN), Da Nang, Vietnam, 11–13 January 2017; pp. 712–717. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Xie, Y.; Bai, H.; Yu, B.; Li, W.; Gao, Y. A survey on federated learning. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2021, 216, 106775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Liang, Z.; He, M.; Peng, Y.; Xue, H.; Wang, Y. A federated semi-supervised learning approach for network traffic classification. Int. J. Netw. Manag. 2023, 33, e2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakopoulou, E.; Tillman, B.; Markopoulou, A. A Federated Learning approach for mobile packet classification. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.13113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, K.; Yang, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z. On the convergence of fedavg on non-iid data. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.02189. [Google Scholar]
- Mun, H.; Lee, Y. Internet traffic classification with federated learning. Electronics 2020, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, D. Feat: A federated approach for privacy-preserving network traffic classification in heterogeneous environments. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 10, 1274–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiang, T.; Hospedales, T.M.; Lu, H. Deep mutual learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 4320–4328. [Google Scholar]
- Gou, J.; Yu, B.; Maybank, S.J.; Tao, D. Knowledge distillation: A survey. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 1789–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukman, A.; Yang, C.K. Improving Deep Mutual Learning via Knowledge Distillation. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, P.; Yan, D.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z. Deep knowledge distillation: A self-mutual learning framework for traffic prediction. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 252, 124138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lang, B. Machine learning and deep learning methods for intrusion detection systems: A survey. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper-Gil, G.; Lashkari, A.H.; Mamun, M.S.I.; Ghorbani, A.A. Characterization of encrypted and vpn traffic using time-related. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy (ICISSP), Rome, Italy, 19–21 February 2016; pp. 407–414. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Lille, France, 7–9 July 2015; pp. 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- De Boer, P.T.; Kroese, D.P.; Mannor, S.; Rubinstein, R.Y. A tutorial on the cross-entropy method. Ann. Oper. Res. 2005, 134, 19–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottou, L. Stochastic gradient descent tricks. In Neural Networks: Tricks of the Trade, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 421–436. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Zhu, M.; Wang, J.; Zeng, X.; Yang, Z. End-to-end encrypted traffic classification with one-dimensional convolution neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Intelligence and Security Informatics (ISI), Beijing, China, 22–24 July 2017; pp. 43–48. [Google Scholar]

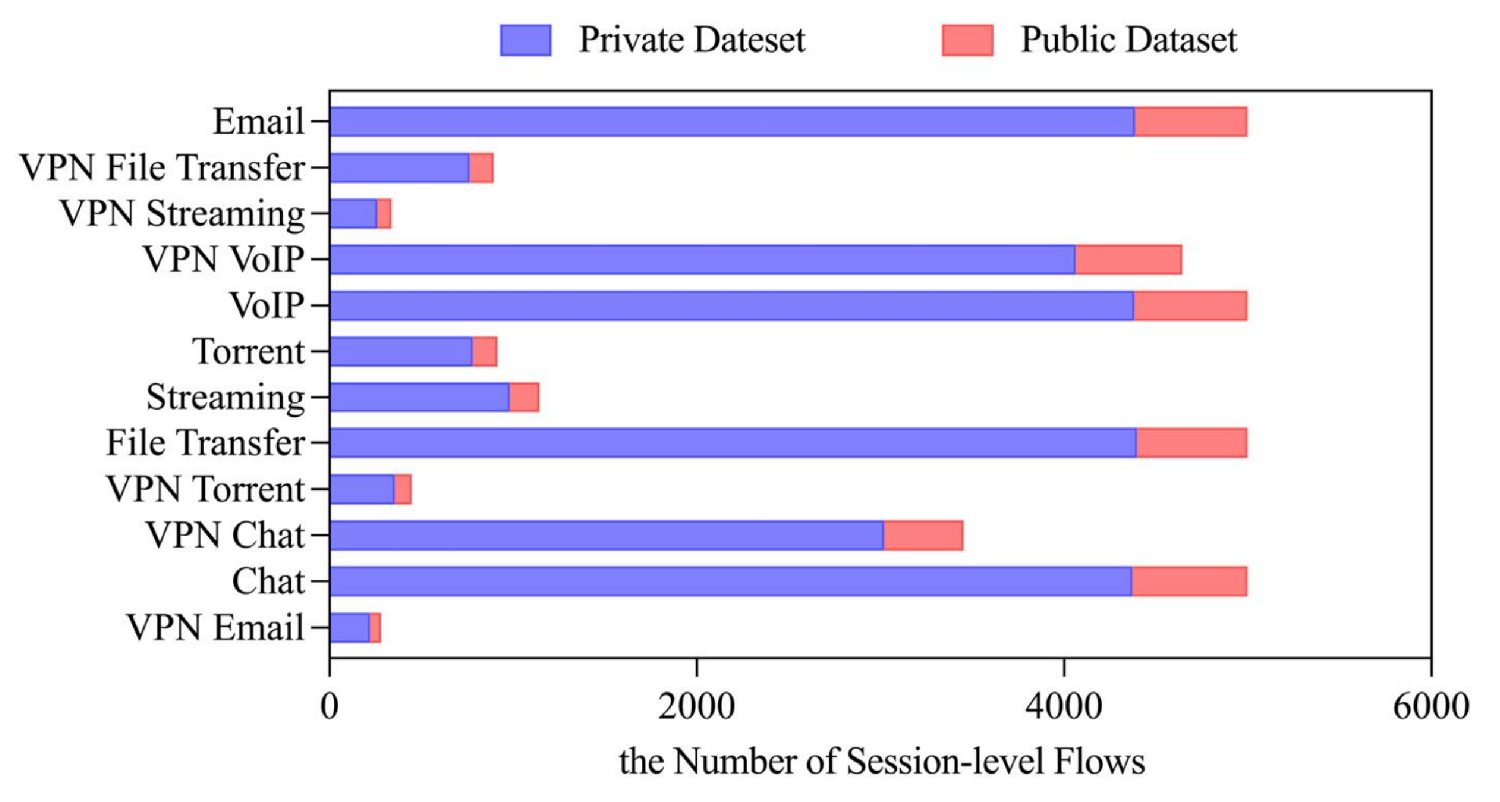



| Traffic Service Type | Application | File Size |
|---|---|---|
| Chat | AIM, ICQ, Skype, Facebook, Hangouts | 29.5MB |
| VPN Chat | 27.6 MB | |
| Email, Gmail | 13 MB | |
| VPN Email | 7.8 MB | |
| File Transfer | Skype, SFTP, FTPS, SCP | 17.3 GB |
| VPN File Transfer | 279 MB | |
| Streaming | Vimeo, Youtube, Netflix, Spotify | 1.53 GB |
| VPN Streaming | 1.37 GB | |
| Torrent | uTorrent, Bittorrent | 96.8 MB |
| VPN Torrent | 358 MB | |
| VoIP | Facebook, Skype, Hangouts, VoIPbuster | 4.48 GB |
| VPN VoIP | 360 MB |
| Layer | Operation | Input Size | Filter Size | Stride | Output Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Conv1d + BN | 784 × 1 | 4 × 1 | 2 | 391 × 32 |
| 2 | MaxPool | 391 × 32 | 3 × 1 | 3 | 130 × 32 |
| 3 | Conv1d + BN | 130 × 32 | 3 × 1 | 2 | 64 × 64 |
| 4 | MaxPool | 64 × 64 | 3 × 1 | 3 | 21 × 64 |
| 5 | Linear | 21 × 64 | - | - | 256 |
| 6 | Linear | 256 | - | - | 12 |
| 7 | Softmax | 12 | - | - | 12 |
| Predicted Value (Positive) | Predicted Value (Negative) | |
|---|---|---|
| True Value (Positive) | TP (True Positives) | FN (False Negatives) |
| True Value (Negative) | FP (False Positives) | TN (True Negatives) |
| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN-without-BN | 0.951 | 0.953 | 0.952 | 0.951 |
| BN-CNN | 0.958 | 0.960 | 0.957 | 0.959 |
| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C4.5 | 0.807 | 0.810 | 0.808 | 0.807 |
| KNN | 0.735 | 0.746 | 0.737 | 0.738 |
| DP-CNN | 0.941 | 0.944 | 0.937 | 0.940 |
| CNN-LSTM | 0.920 | 0.922 | 0.920 | 0.921 |
| BN-CNN | 0.958 | 0.960 | 0.957 | 0.959 |
| Method | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Centralized | 0.958 | 0.960 | 0.957 | 0.959 |
| FedAvg | 0.944 | 0.942 | 0.948 | 0.944 |
| FLDML | 0.948 | 0.946 | 0.952 | 0.949 |
| Heterogeneity Level Configuration | Algorithm | Evaluation Index | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision | Recall | F1 | ||
| m = 2 | FedAvg | 0.867 | 0.864 | 0.865 |
| FLDML | 0.886 | 0.887 | 0.887 | |
| m = 5 | FedAvg | 0.918 | 0.921 | 0.920 |
| FLDML | 0.942 | 0.944 | 0.942 | |
| m = 8 | FedAvg | 0.936 | 0.939 | 0.938 |
| FLDML | 0.940 | 0.944 | 0.942 | |
| m = 10 | FedAvg | 0.939 | 0.936 | 0.939 |
| FLDML | 0.943 | 0.945 | 0.943 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, H.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y. Federated Distributed Network Traffic Classification Based on Deep Mutual Learning. Electronics 2025, 14, 4928. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14244928
Xue H, Hu Y, Wang Y. Federated Distributed Network Traffic Classification Based on Deep Mutual Learning. Electronics. 2025; 14(24):4928. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14244928
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Hanxiao, Yuyong Hu, and Yu Wang. 2025. "Federated Distributed Network Traffic Classification Based on Deep Mutual Learning" Electronics 14, no. 24: 4928. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14244928
APA StyleXue, H., Hu, Y., & Wang, Y. (2025). Federated Distributed Network Traffic Classification Based on Deep Mutual Learning. Electronics, 14(24), 4928. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14244928







