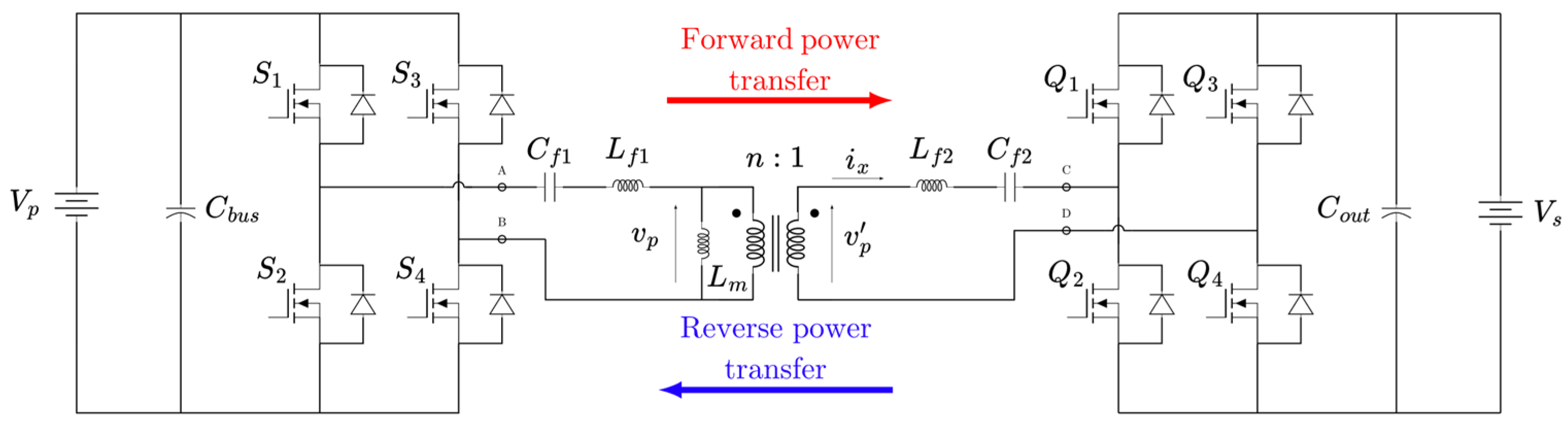
Figure 1.
Series resonant CLLC Dual-Active Bridge topology.
Figure 1.
Series resonant CLLC Dual-Active Bridge topology.
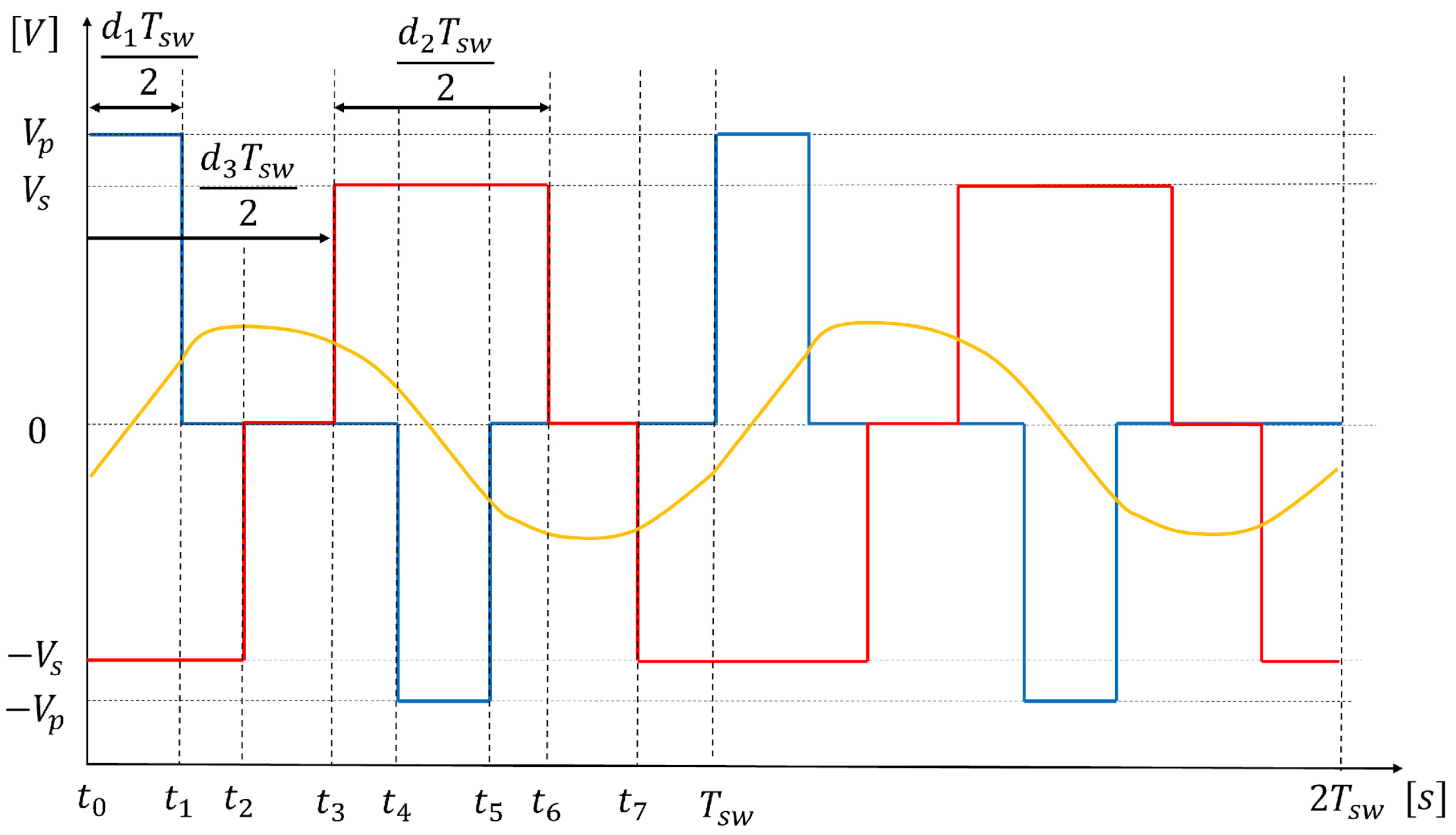
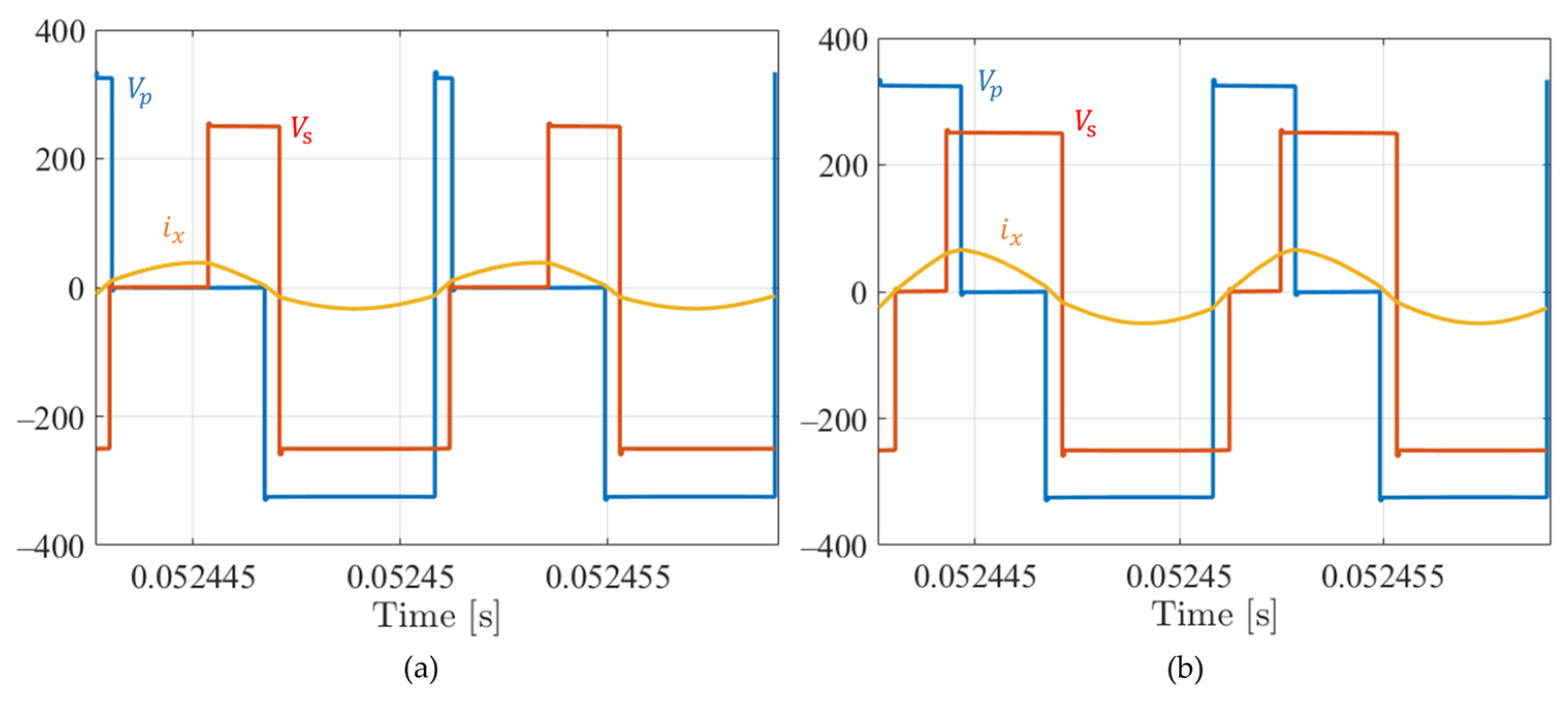
Figure 2.
TPS modulation applied to a resonant DAB, mode 2. Primary full-bridge FB1, output voltage (blue), secondary full-bridge FB2, output voltage (red), and resonant tank or inductor current seen by the transformer primary circuit (yellow).
Figure 2.
TPS modulation applied to a resonant DAB, mode 2. Primary full-bridge FB1, output voltage (blue), secondary full-bridge FB2, output voltage (red), and resonant tank or inductor current seen by the transformer primary circuit (yellow).
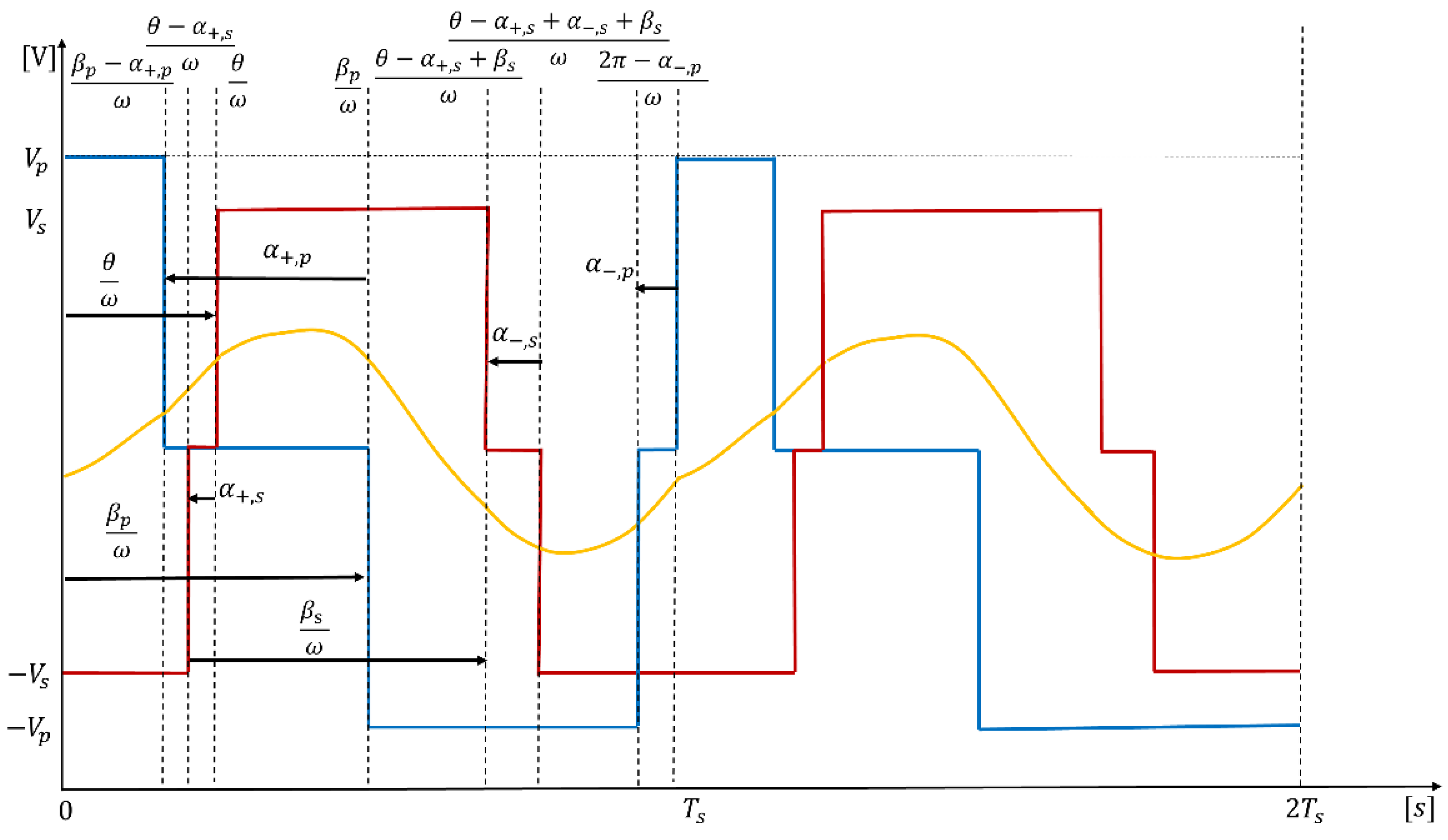
Figure 3.
General conceptualization of the Double AVC modulation: FB1 output voltage (blue), FB2 output voltage (red), and tank current (yellow).
Figure 3.
General conceptualization of the Double AVC modulation: FB1 output voltage (blue), FB2 output voltage (red), and tank current (yellow).
Figure 4.
Modulation mode 1: .
Figure 4.
Modulation mode 1: .
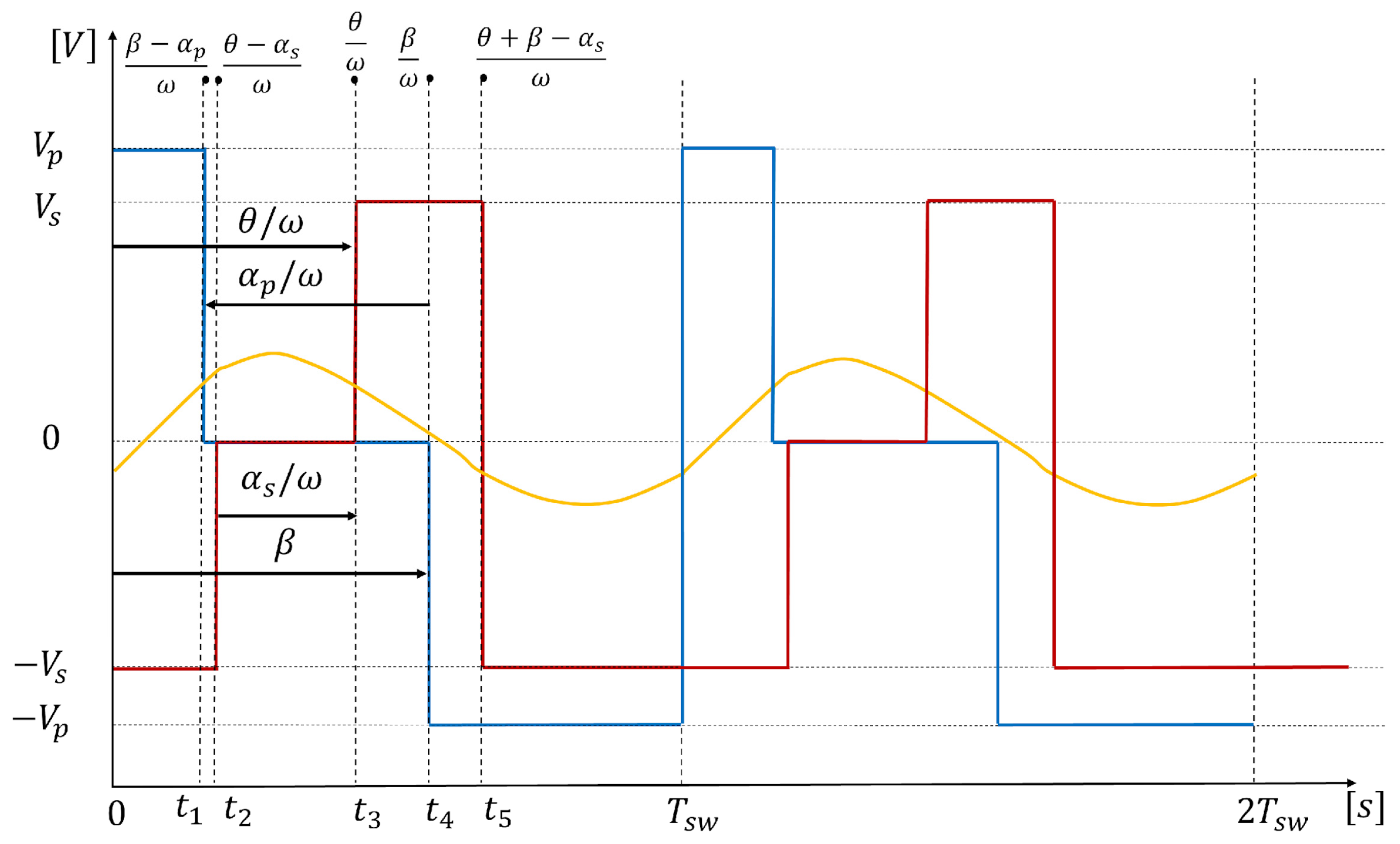
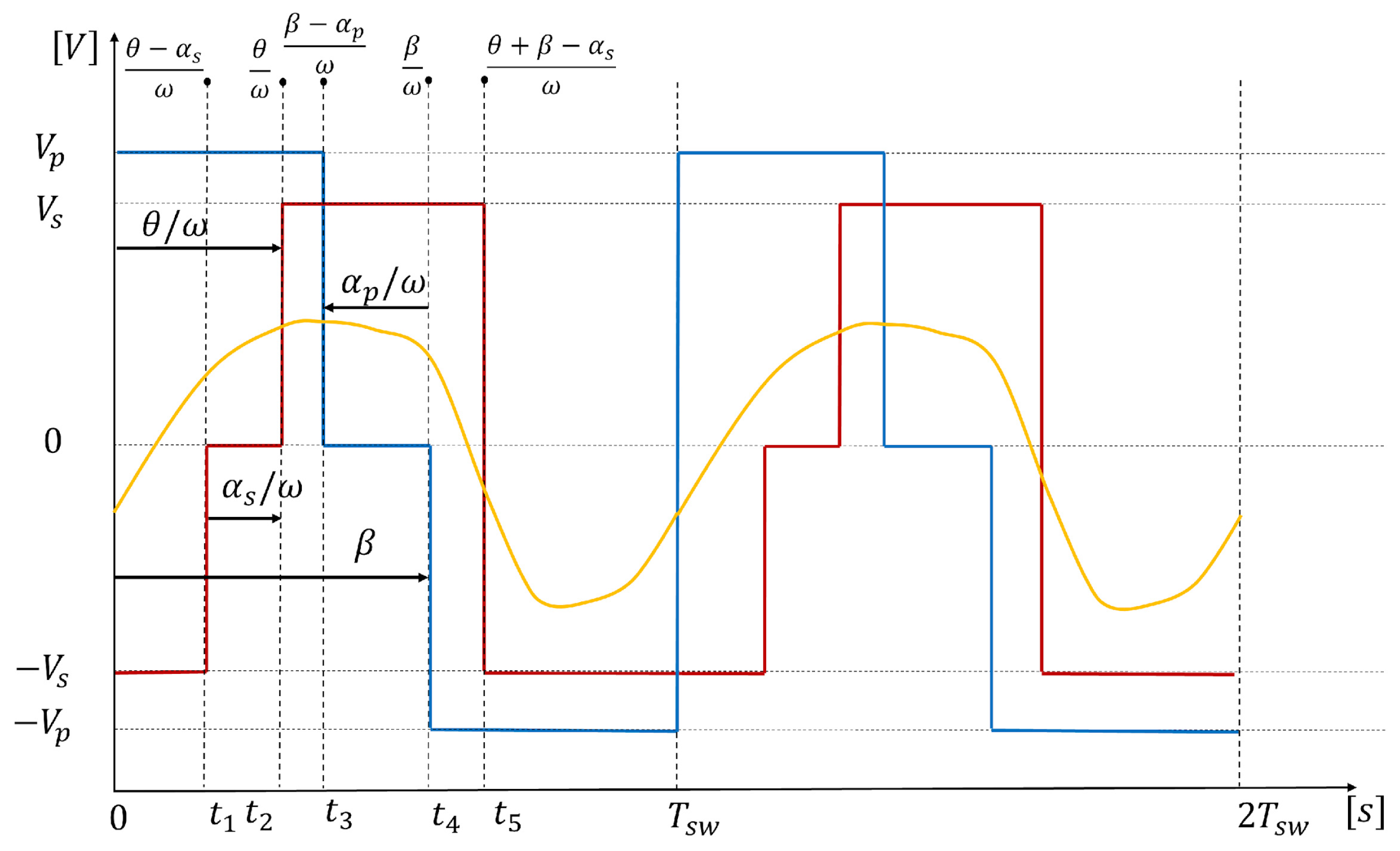
Figure 5.
Modulation mode 2: .
Figure 5.
Modulation mode 2: .
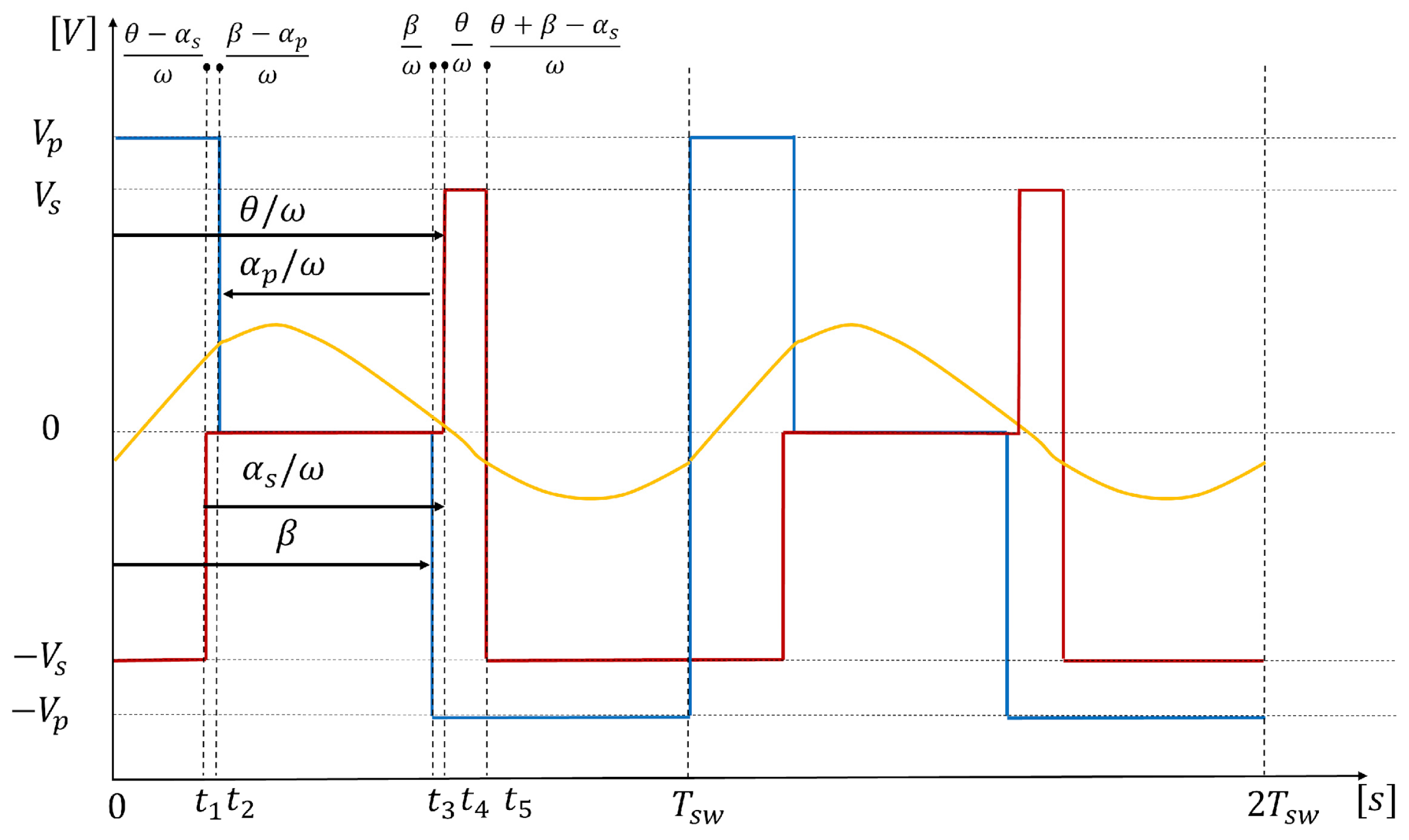
Figure 6.
Modulation mode 3: .
Figure 6.
Modulation mode 3: .
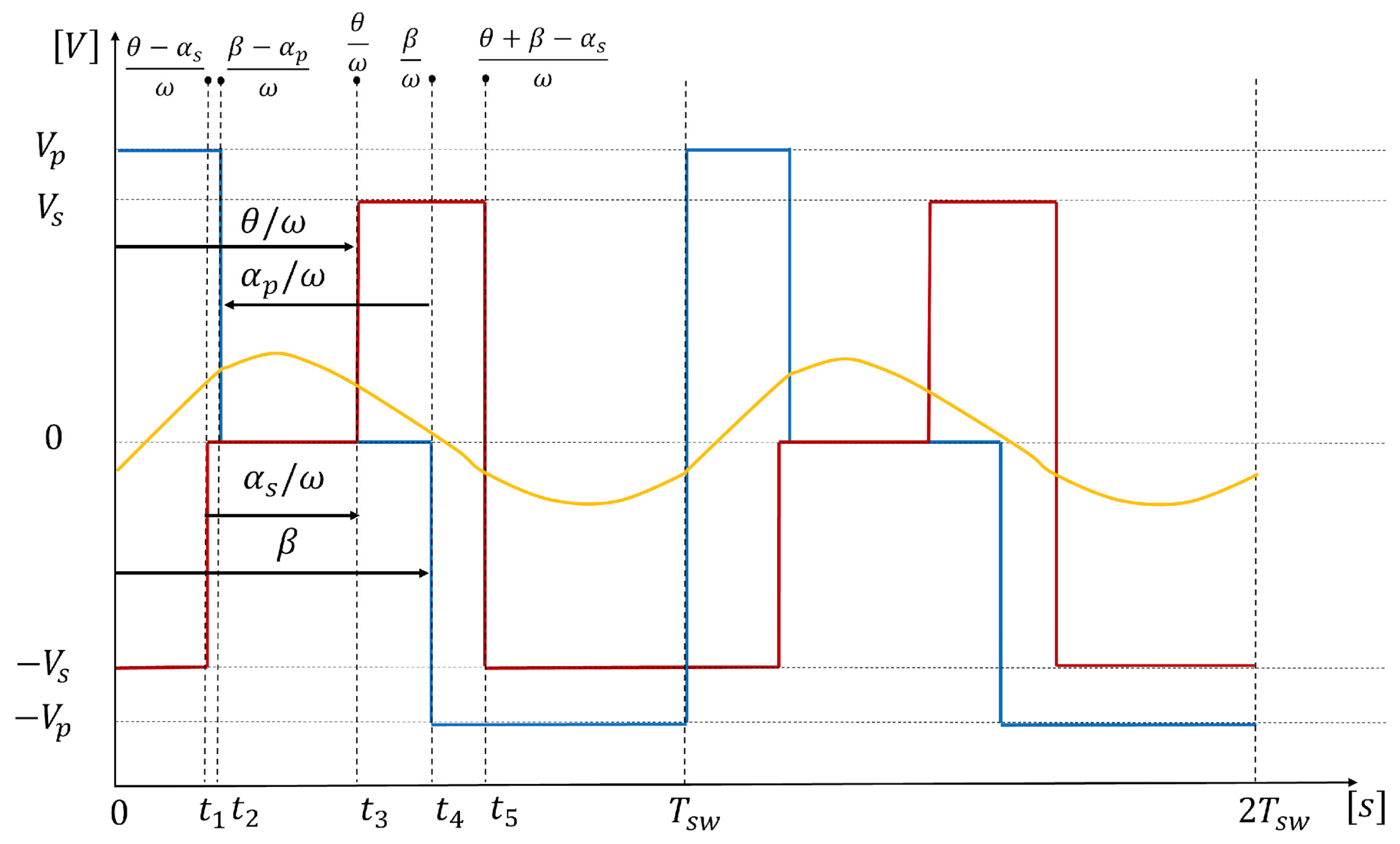
Figure 7.
Modulation mode 4: .
Figure 7.
Modulation mode 4: .
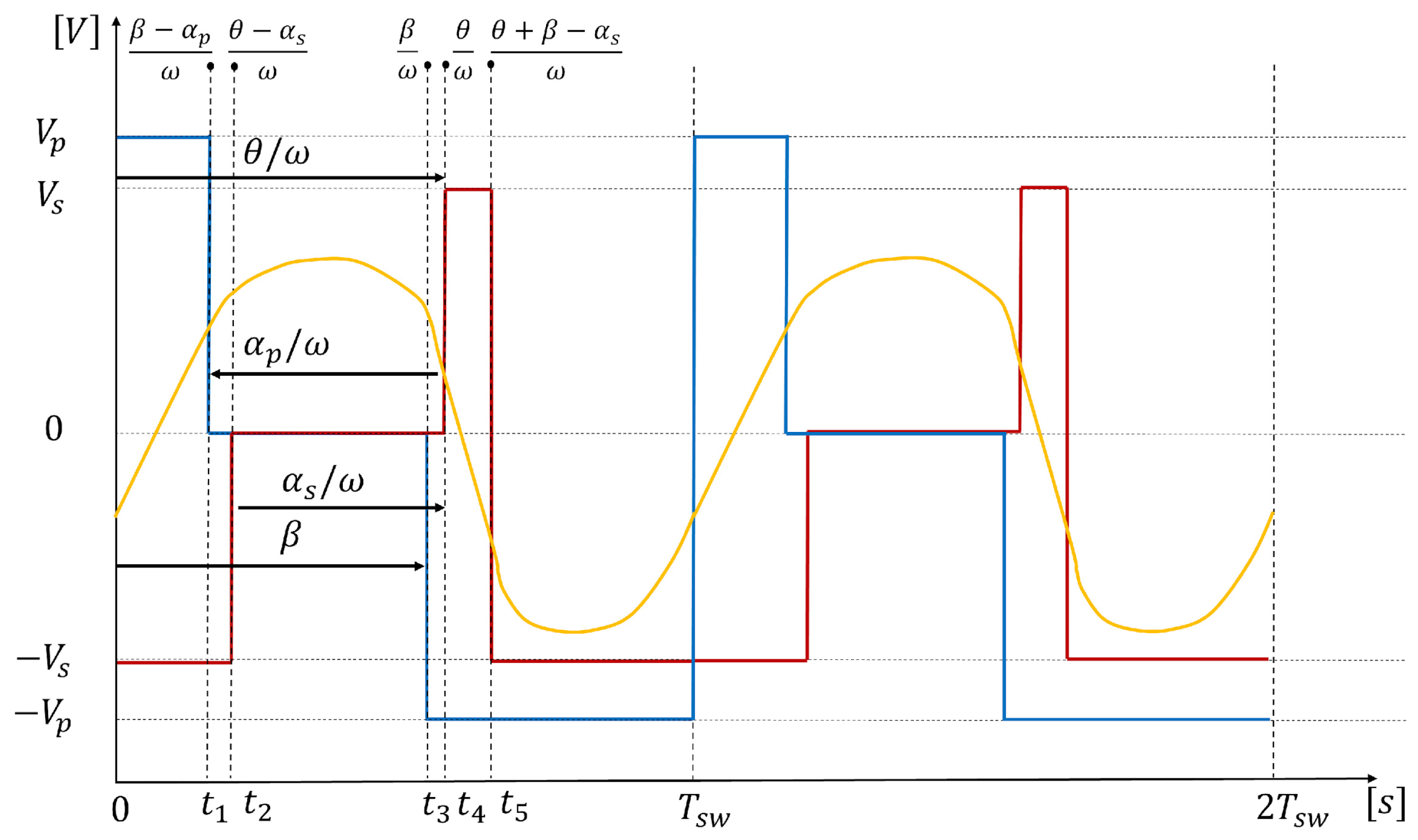
Figure 8.
Modulation mode 5: . Primary full-bridge, FB1, output voltage (blue), secondary full-bridge, FB2, output voltage (red) and resonant tank or inductor current seen by the transformer primary circuit (yellow).
Figure 8.
Modulation mode 5: . Primary full-bridge, FB1, output voltage (blue), secondary full-bridge, FB2, output voltage (red) and resonant tank or inductor current seen by the transformer primary circuit (yellow).
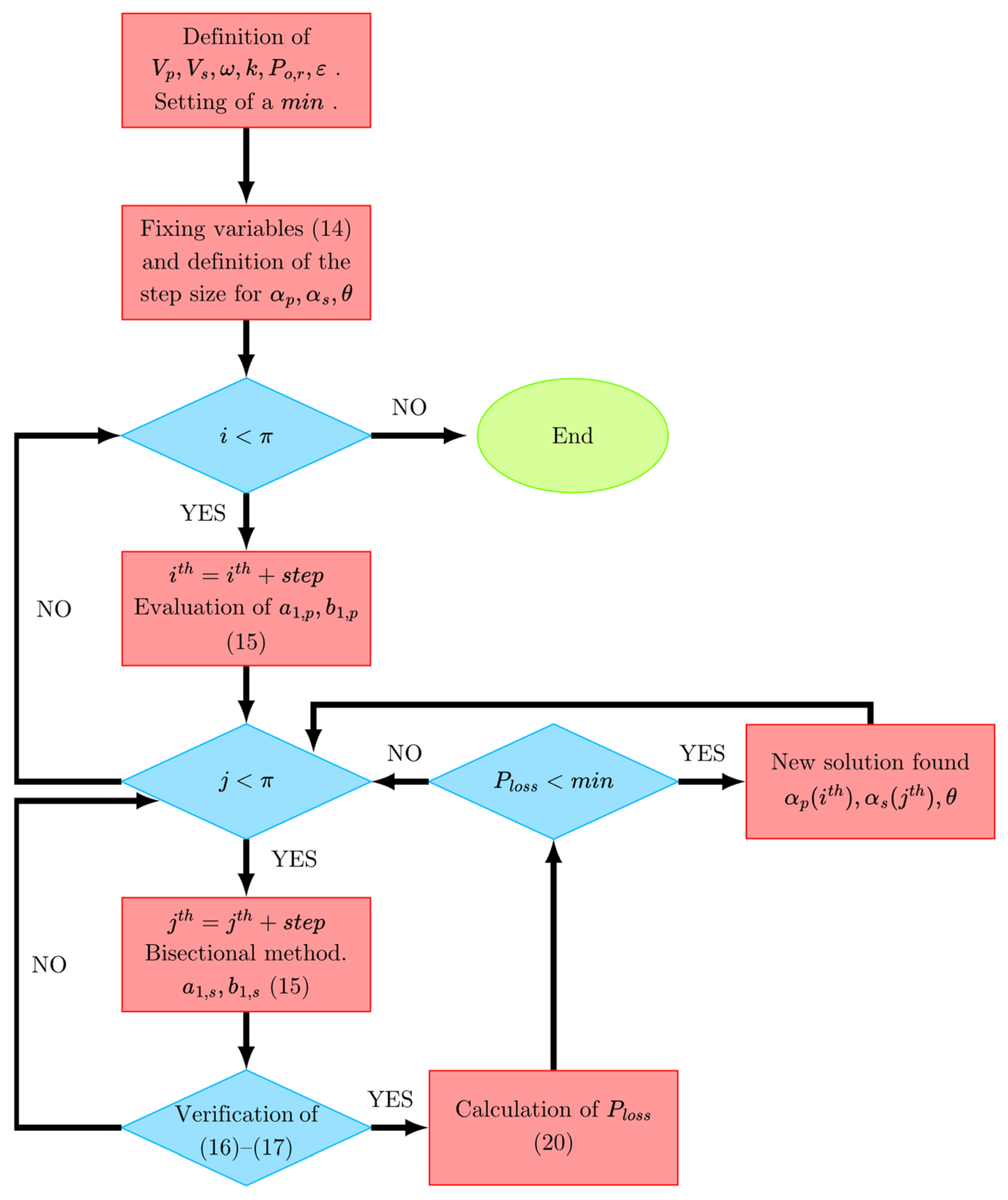
Figure 9.
Optimal operation point algorithm.
Figure 9.
Optimal operation point algorithm.
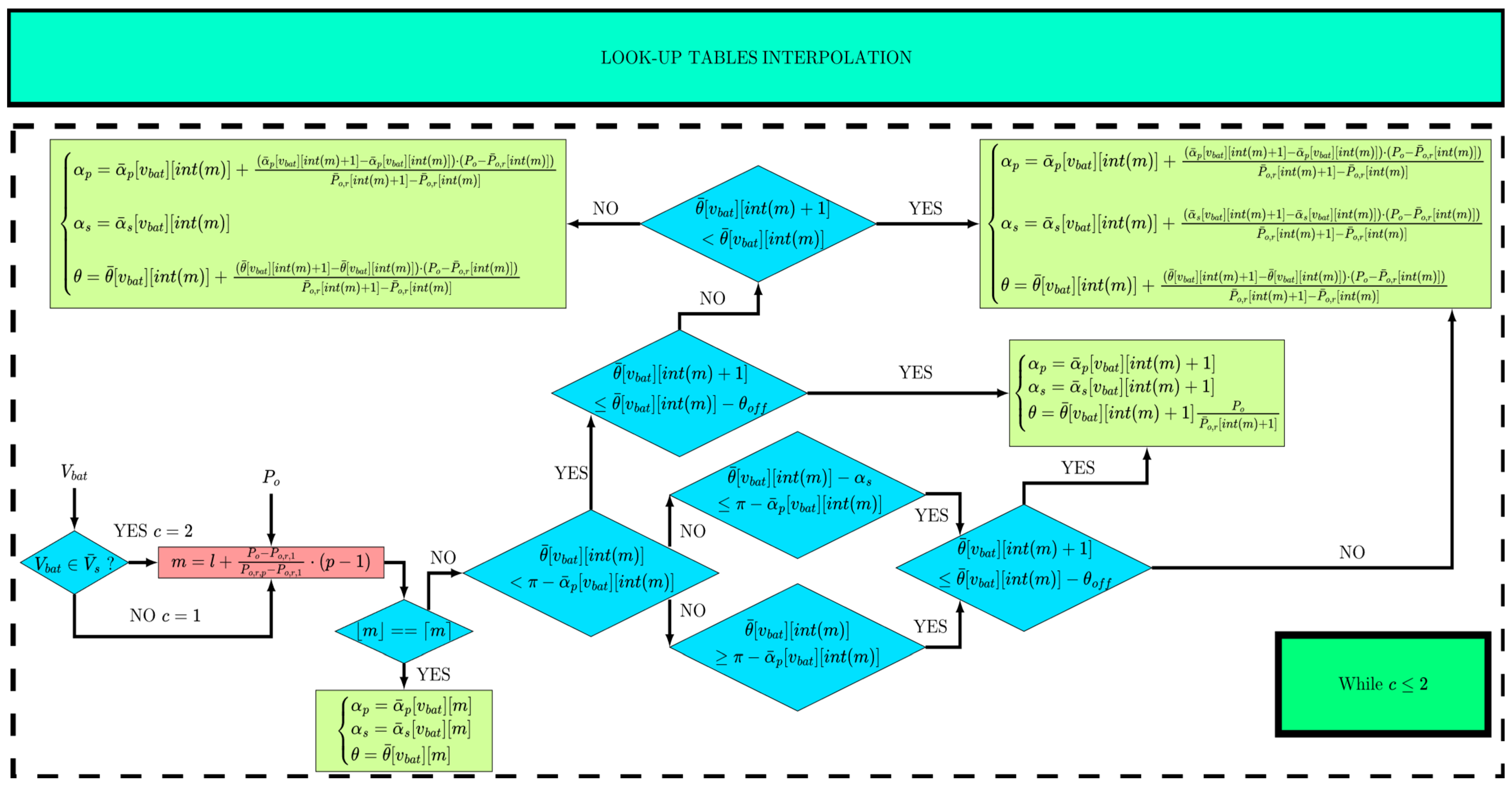
Figure 10.
Control and interpolation strategy between optimal points.
Figure 10.
Control and interpolation strategy between optimal points.
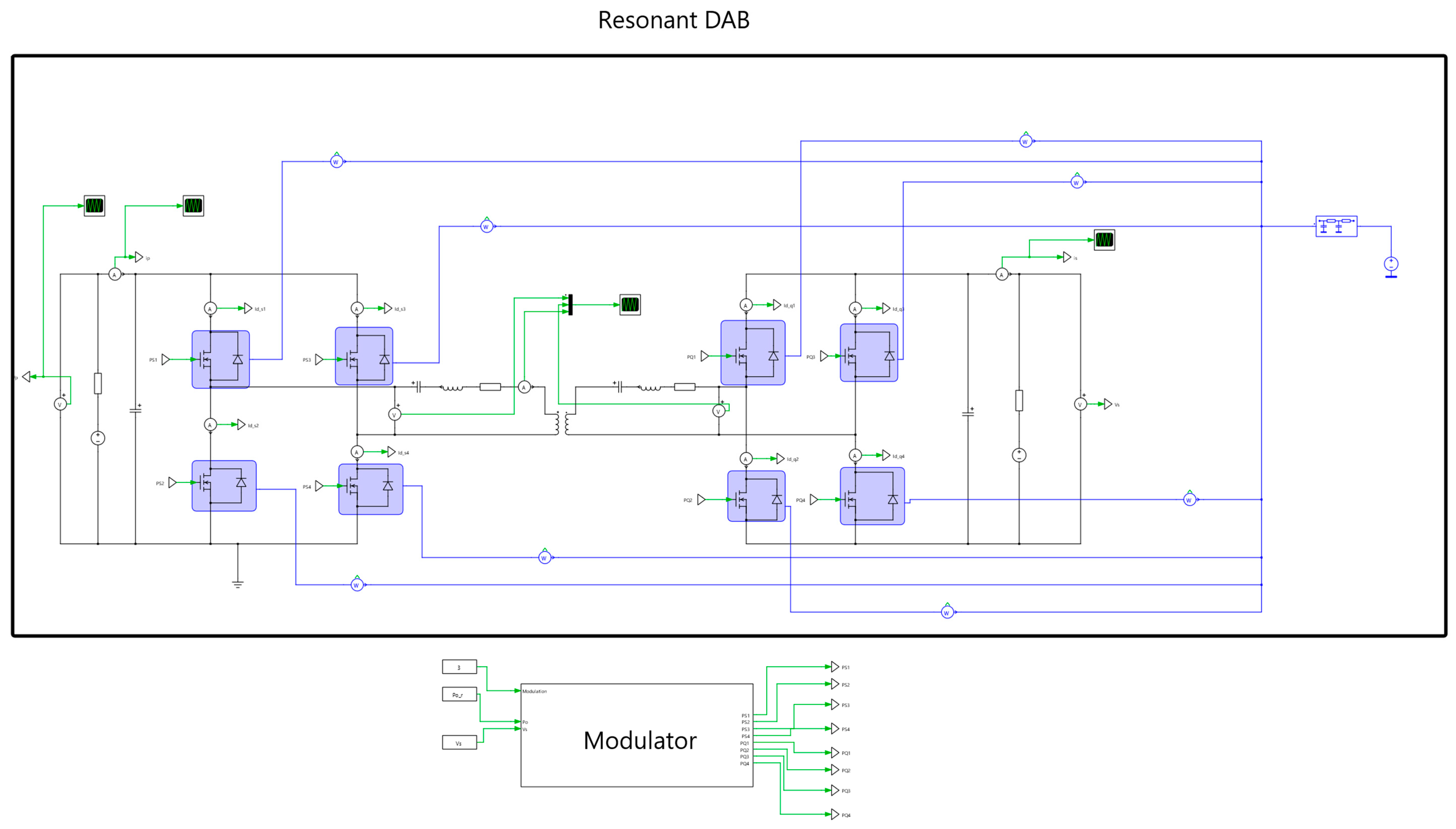
Figure 11.
CLLC Resonant DAB schematic in PLECS.
Figure 11.
CLLC Resonant DAB schematic in PLECS.
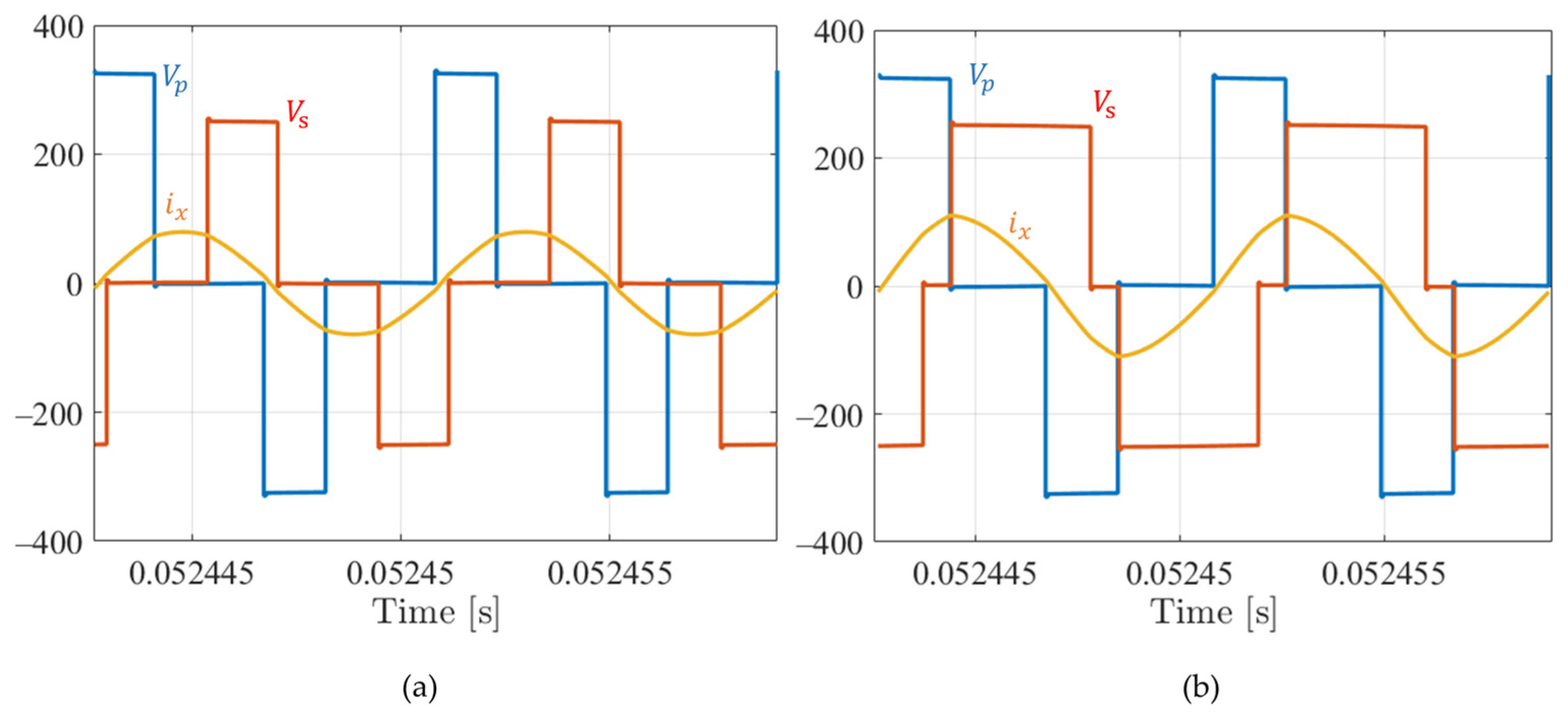
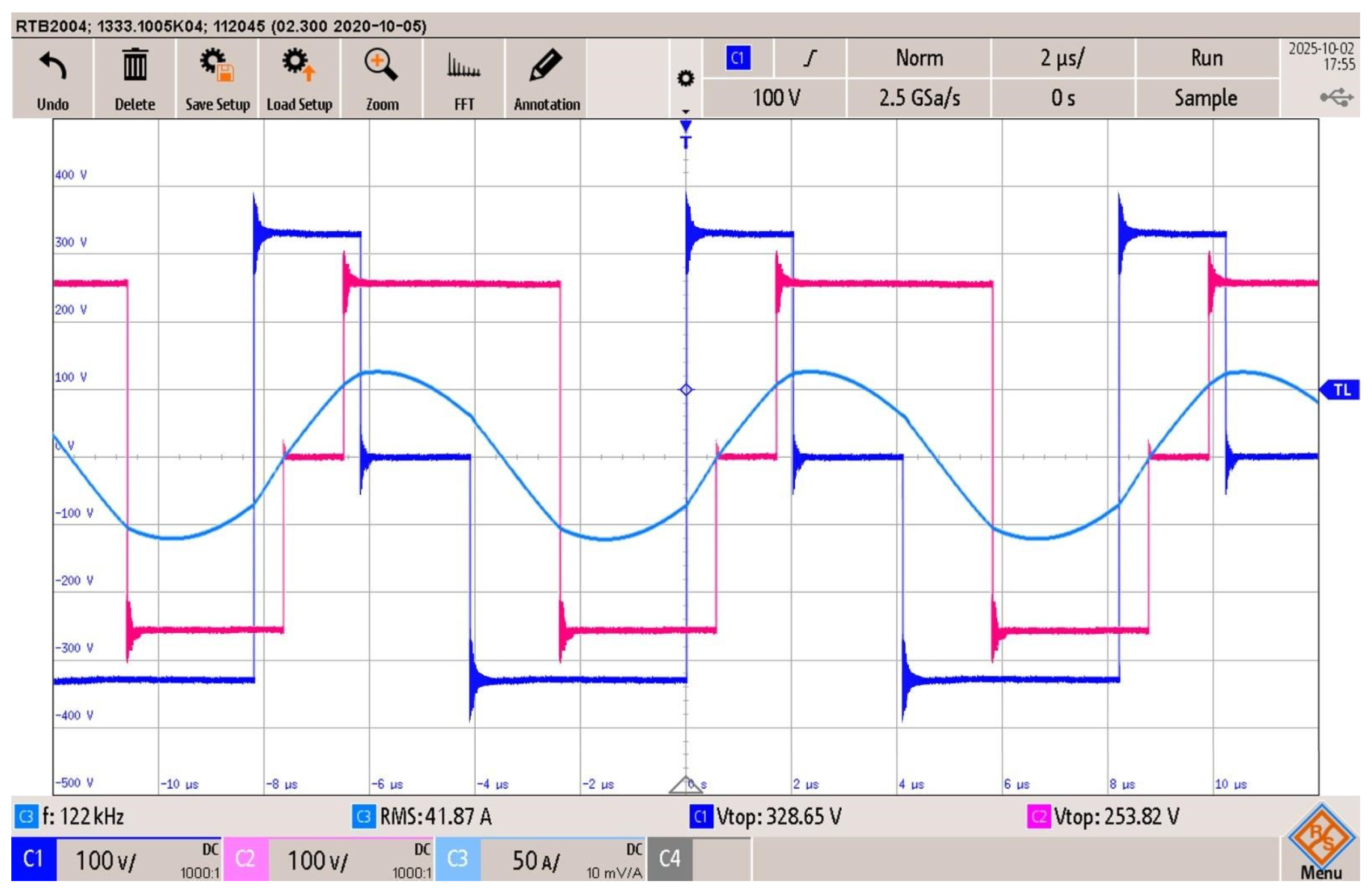
Figure 12.
Double AVC modulation. Battery charging (250 V) from the grid: (a) at 4 kW and (b) at 8 kW. FB1 output voltage (blue), FB2 output voltage (red), and current in the resonant tank (yellow, Arms and Arms).
Figure 12.
Double AVC modulation. Battery charging (250 V) from the grid: (a) at 4 kW and (b) at 8 kW. FB1 output voltage (blue), FB2 output voltage (red), and current in the resonant tank (yellow, Arms and Arms).
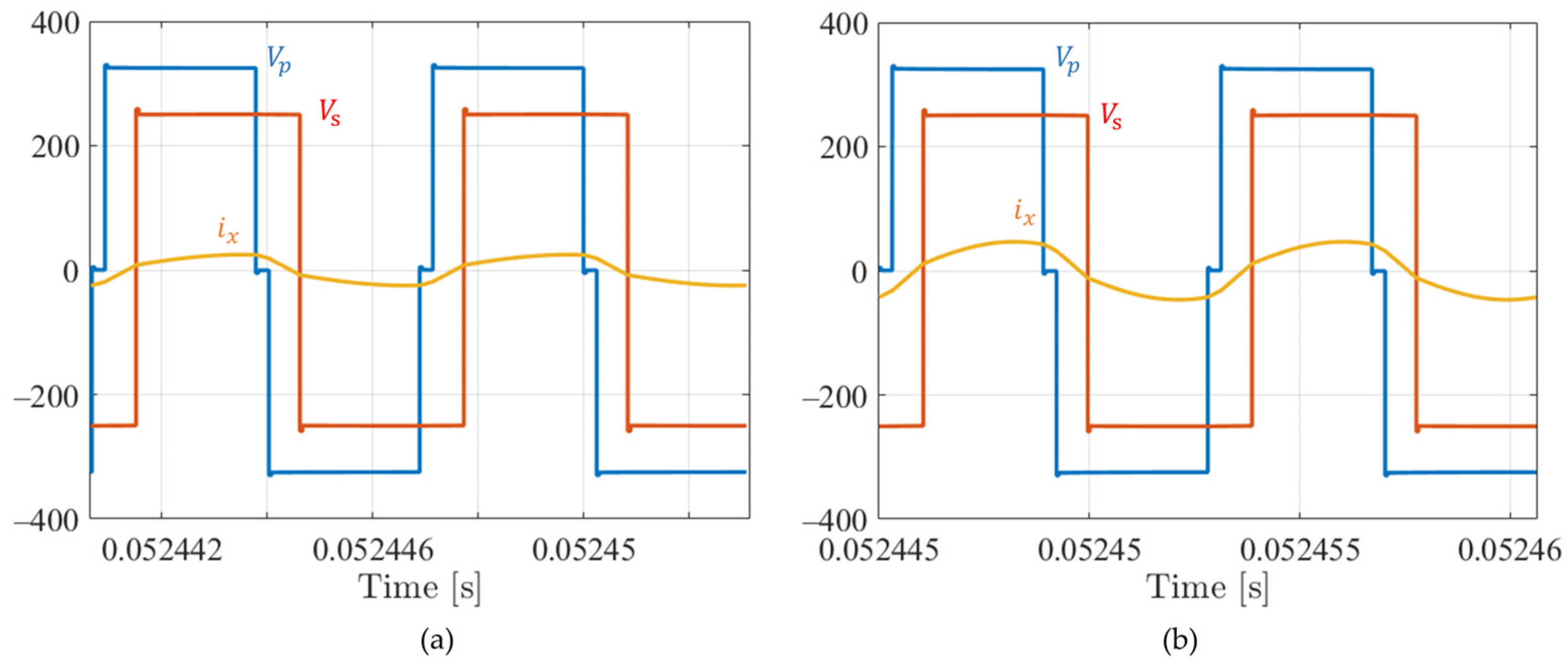
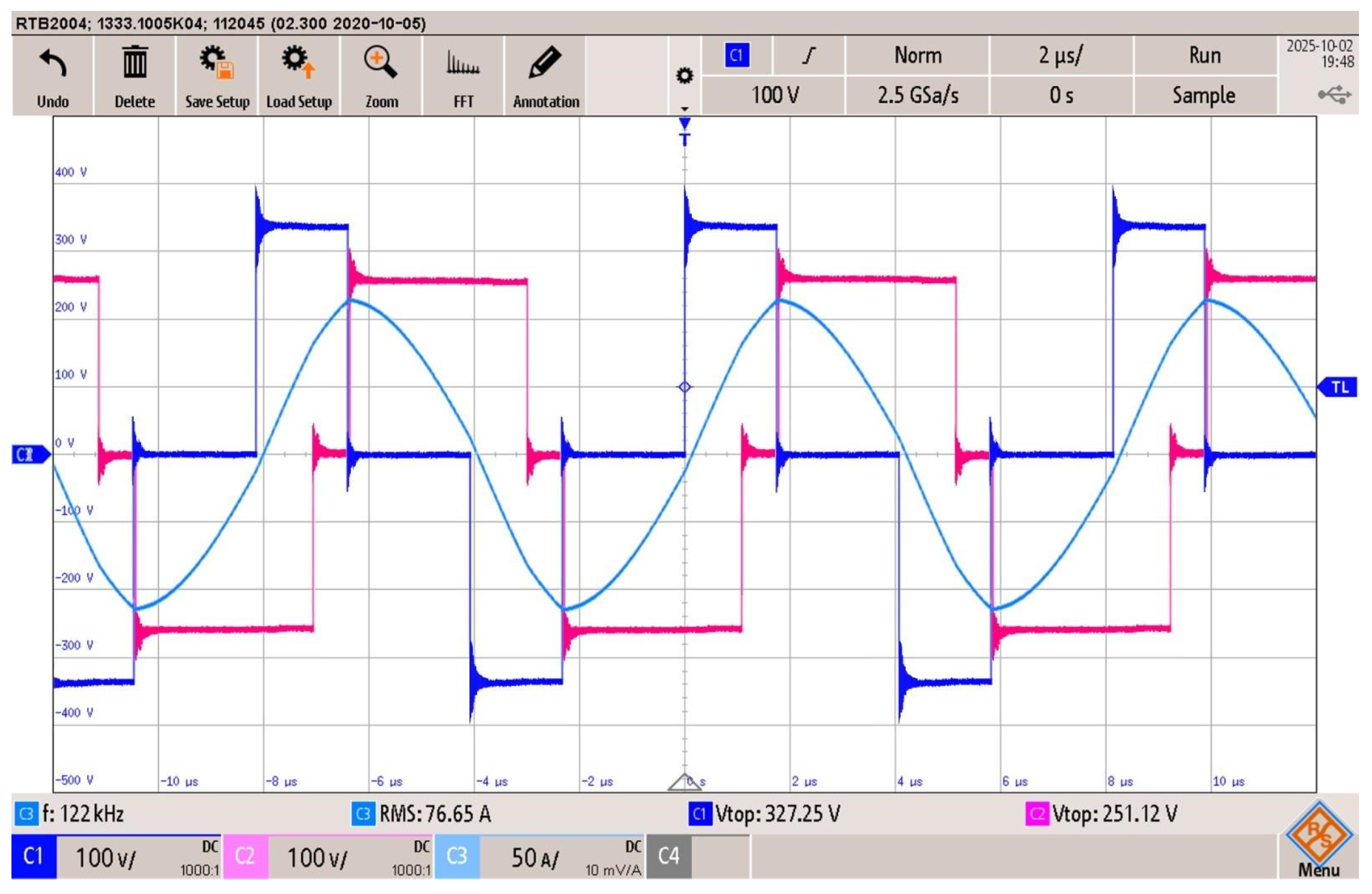
Figure 13.
TPS modulation. Battery charging (250 V) from the grid: (a) at 4 kW and (b) at 8 kW. FB1 output voltage (blue), FB2 output voltage (red), and current in the resonant tank (yellow, Arms and Arms).
Figure 13.
TPS modulation. Battery charging (250 V) from the grid: (a) at 4 kW and (b) at 8 kW. FB1 output voltage (blue), FB2 output voltage (red), and current in the resonant tank (yellow, Arms and Arms).
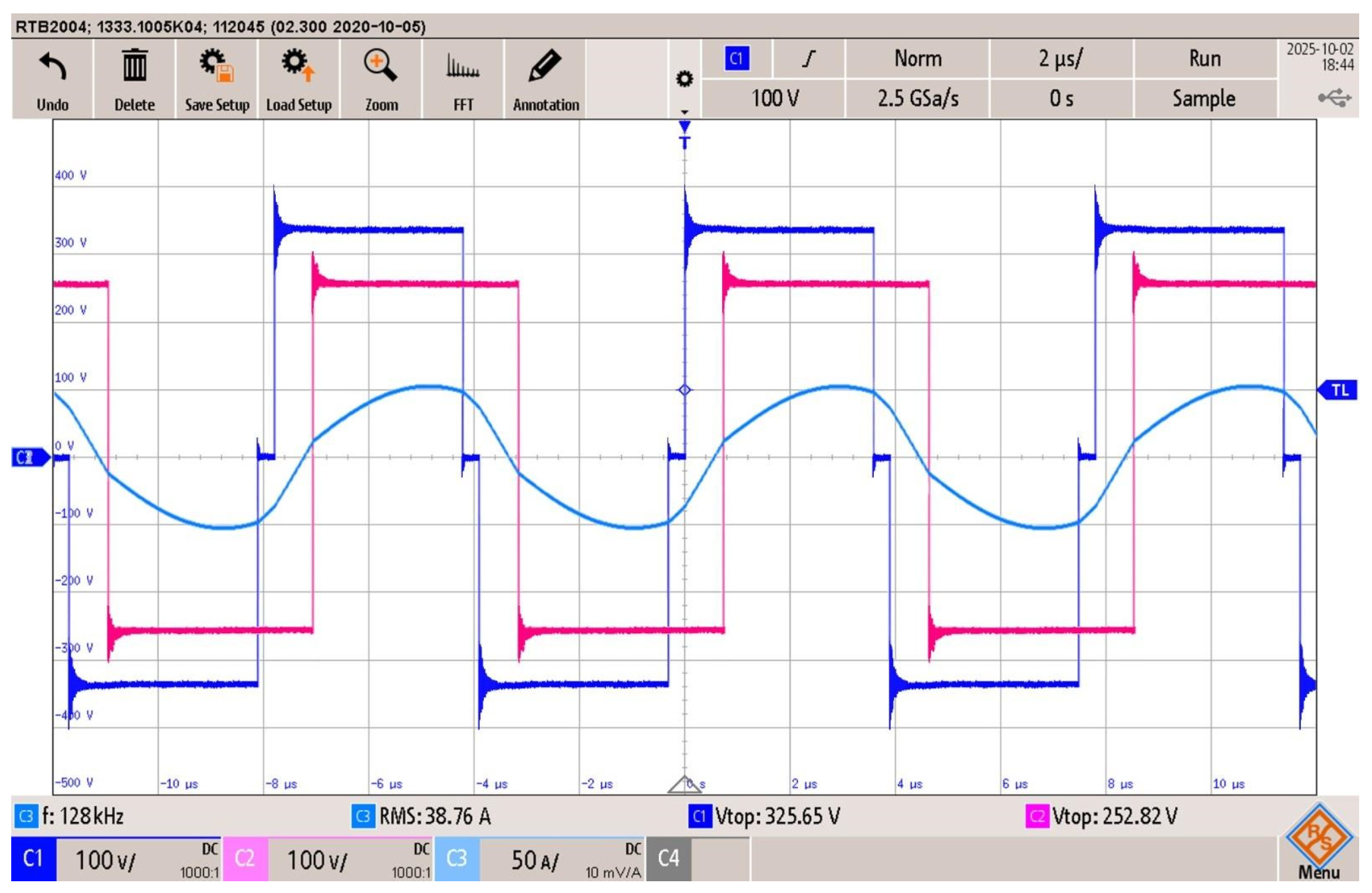
Figure 14.
4DOF modulation. Battery charging (250 V) from the grid: (a) at 4 kW and (b) at 8 kW. FB1 output voltage (blue), FB2 output voltage (red), and current in the resonant tank (yellow, Arms and Arms).
Figure 14.
4DOF modulation. Battery charging (250 V) from the grid: (a) at 4 kW and (b) at 8 kW. FB1 output voltage (blue), FB2 output voltage (red), and current in the resonant tank (yellow, Arms and Arms).
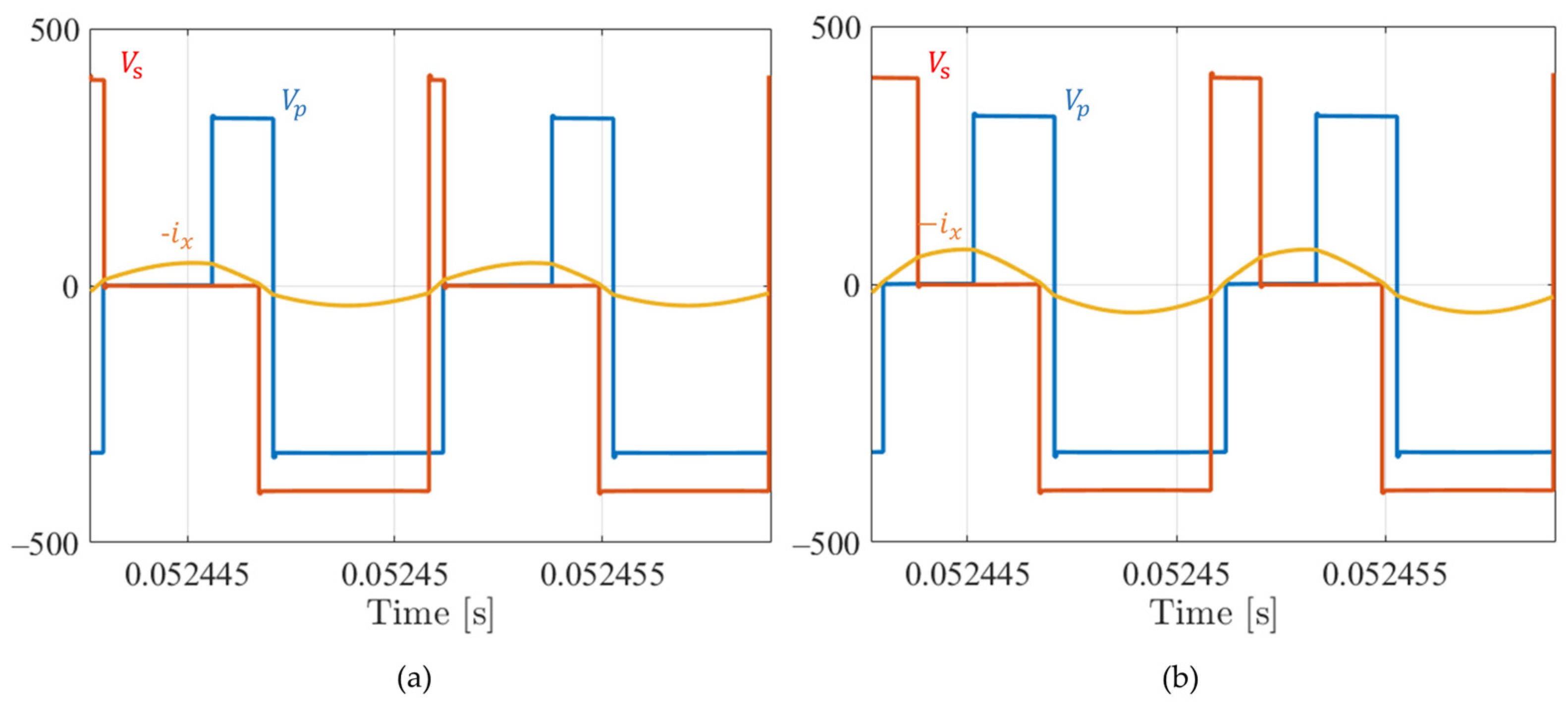
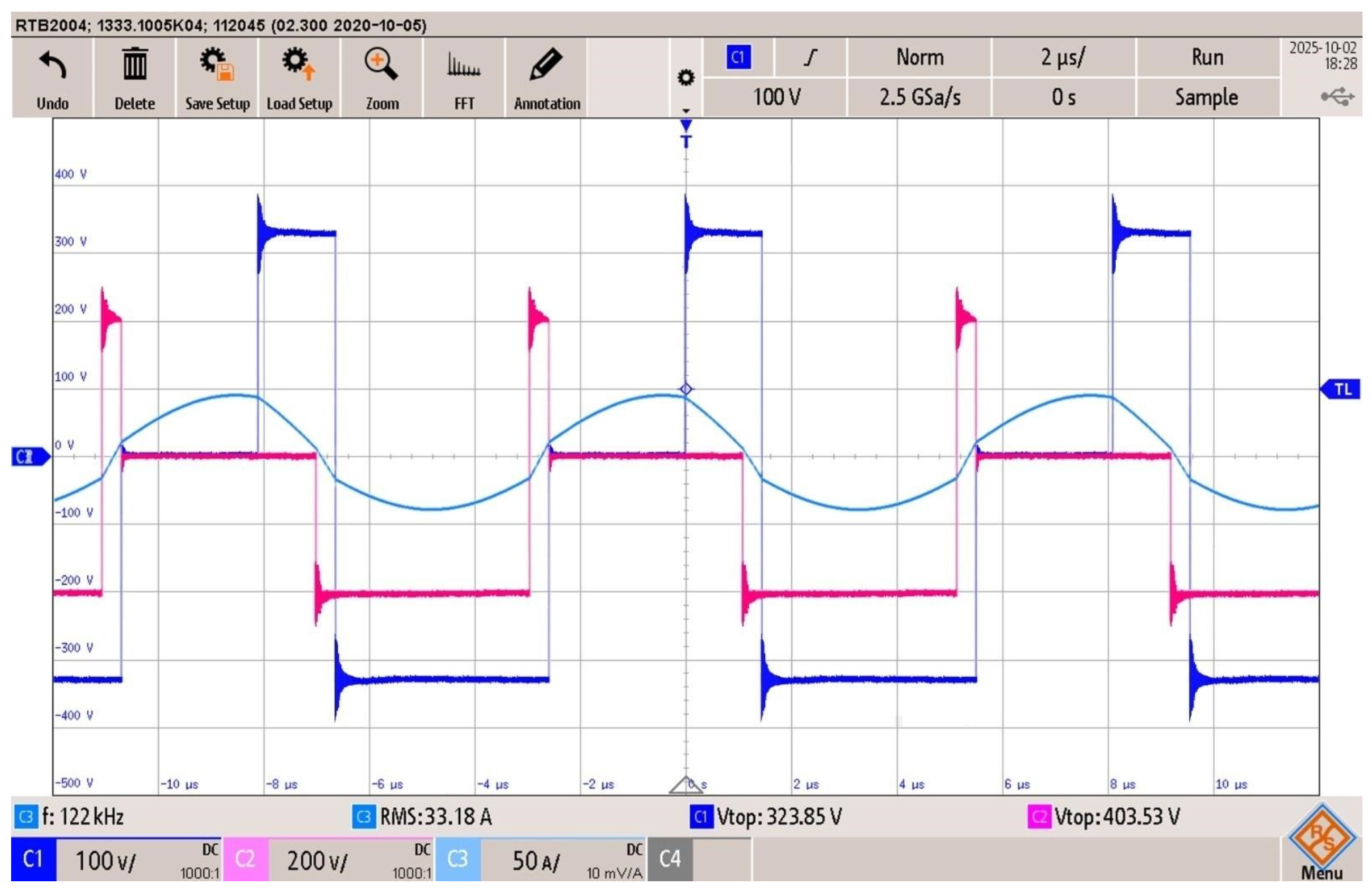
Figure 15.
Double AVC modulation. Battery discharging (400 V): (a) at 5.4 kW and (b) 8.5 kW. FB1 output voltage (blue), FB2 output voltage (red), and current in the resonant tank (yellow, Arms and Arms).
Figure 15.
Double AVC modulation. Battery discharging (400 V): (a) at 5.4 kW and (b) 8.5 kW. FB1 output voltage (blue), FB2 output voltage (red), and current in the resonant tank (yellow, Arms and Arms).
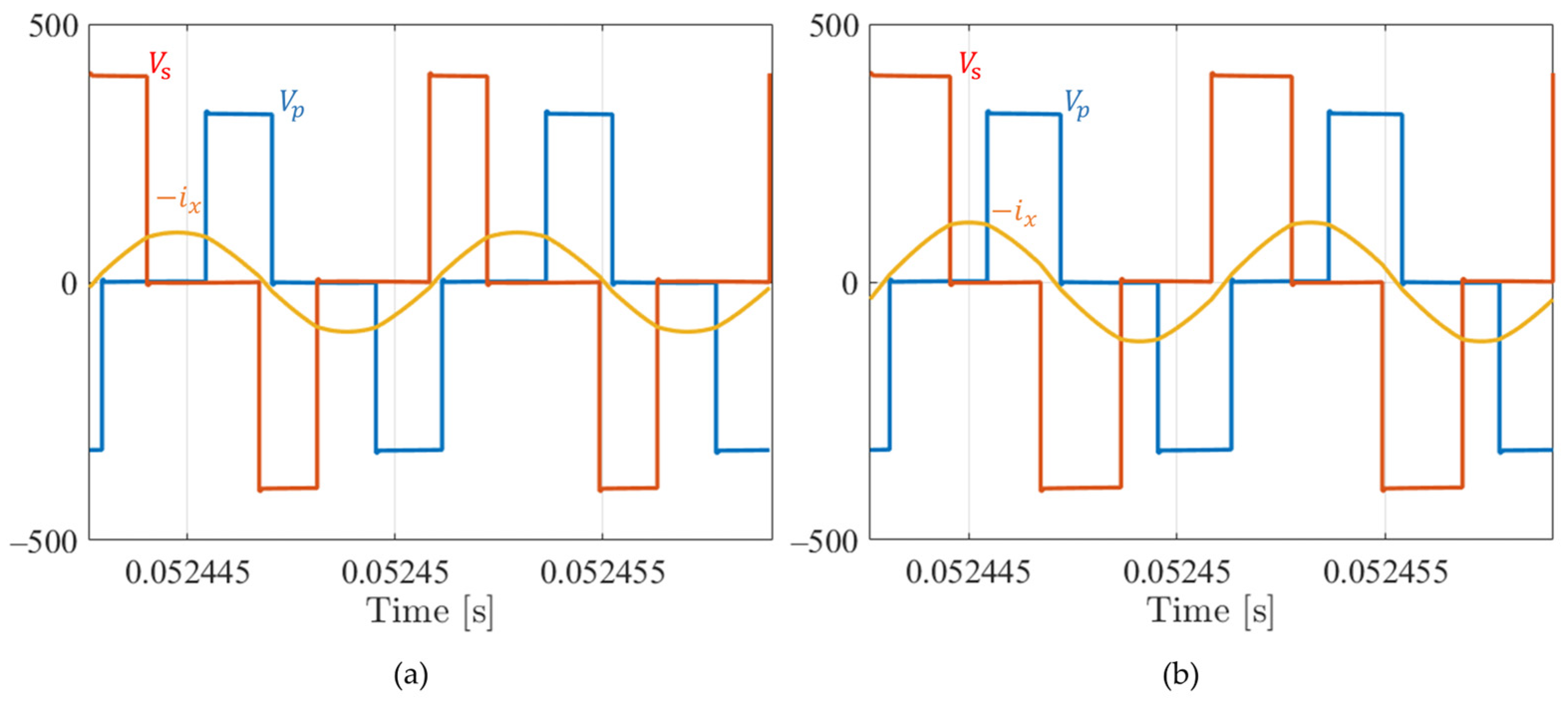
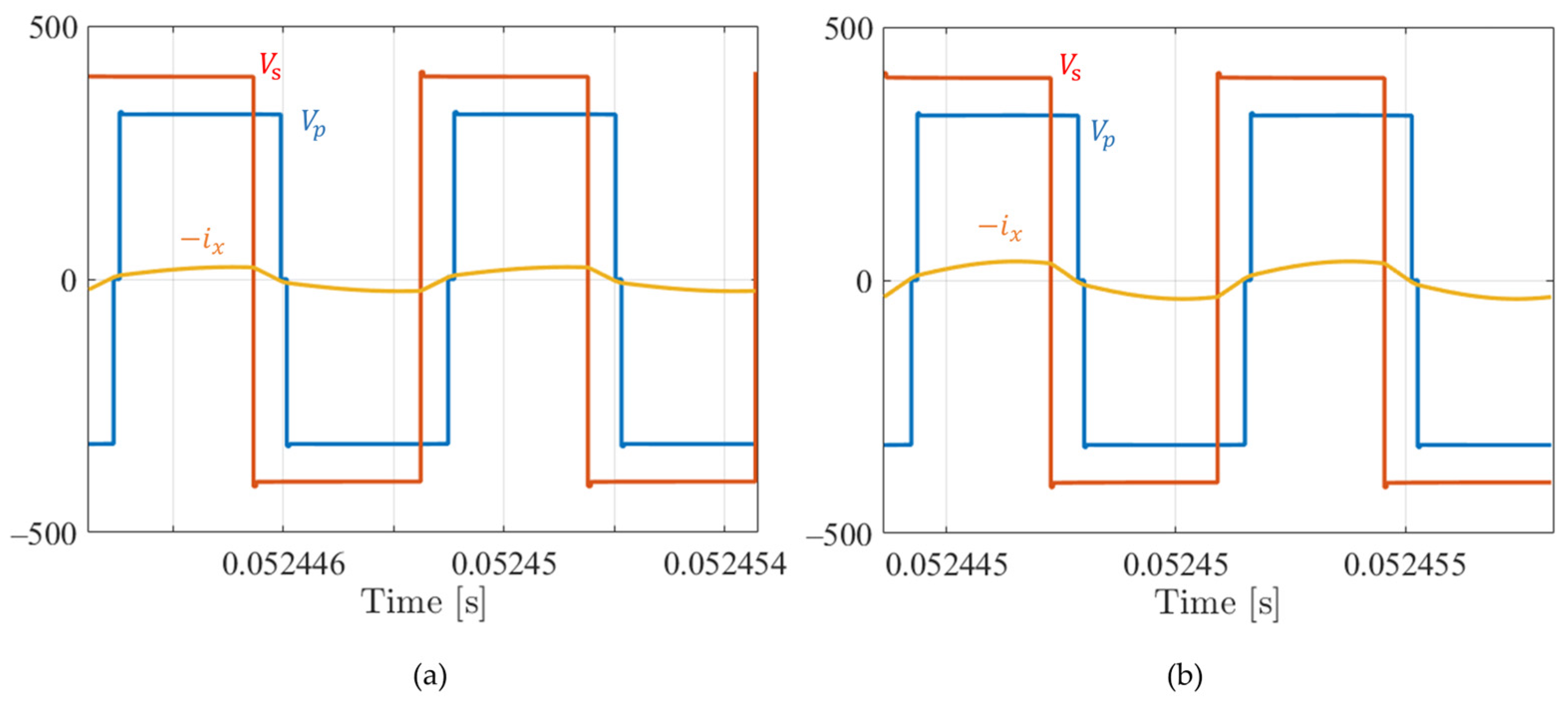
Figure 16.
TPS modulation. Battery discharging (400 V): (a) at 5.4 kW and (b) 8.5 kW. FB1 output voltage (blue), FB2 output voltage (red), and current in the resonant tank (yellow, Arms and Arms).
Figure 16.
TPS modulation. Battery discharging (400 V): (a) at 5.4 kW and (b) 8.5 kW. FB1 output voltage (blue), FB2 output voltage (red), and current in the resonant tank (yellow, Arms and Arms).
Figure 17.
4DOF modulation. Battery discharging (400 V): (a) at 5.4 kW and (b) 8.5 kW. FB1 output voltage (blue), FB2 output voltage (red), and current in the resonant tank (yellow, Arms and Arms).
Figure 17.
4DOF modulation. Battery discharging (400 V): (a) at 5.4 kW and (b) 8.5 kW. FB1 output voltage (blue), FB2 output voltage (red), and current in the resonant tank (yellow, Arms and Arms).
Figure 18.
HIL simulation of the Resonant DAB CLLC converter.
Figure 18.
HIL simulation of the Resonant DAB CLLC converter.
Figure 19.
Battery charge: transition from 12 kW to 4 kW power (modulation transition). FB1 output voltage (blue), FB2 output voltage (pink), current in the resonant tank (yellow), and output power (green). Scales are 1:100 for the output voltages and current and 1:2000 for the average output power.
Figure 19.
Battery charge: transition from 12 kW to 4 kW power (modulation transition). FB1 output voltage (blue), FB2 output voltage (pink), current in the resonant tank (yellow), and output power (green). Scales are 1:100 for the output voltages and current and 1:2000 for the average output power.
Figure 20.
Battery charge: transition from 12 kW to 4 kW power (output power transition). FB1 output voltage (blue), FB2 output voltage (pink), current in the resonant tank (yellow), and output power (green). Scales are 1:100 for the output voltages and current and 1:2000 for the average output power.
Figure 20.
Battery charge: transition from 12 kW to 4 kW power (output power transition). FB1 output voltage (blue), FB2 output voltage (pink), current in the resonant tank (yellow), and output power (green). Scales are 1:100 for the output voltages and current and 1:2000 for the average output power.
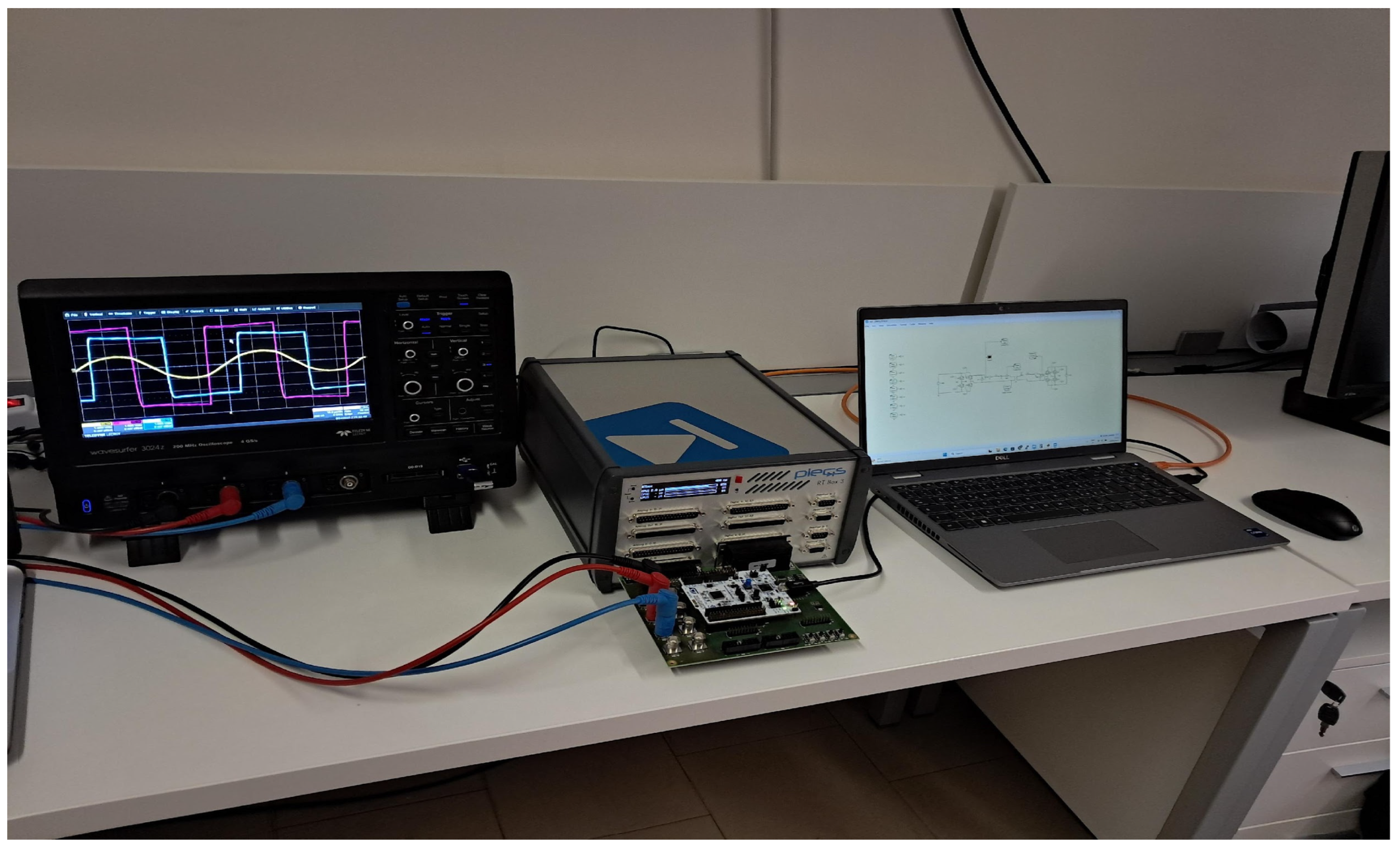
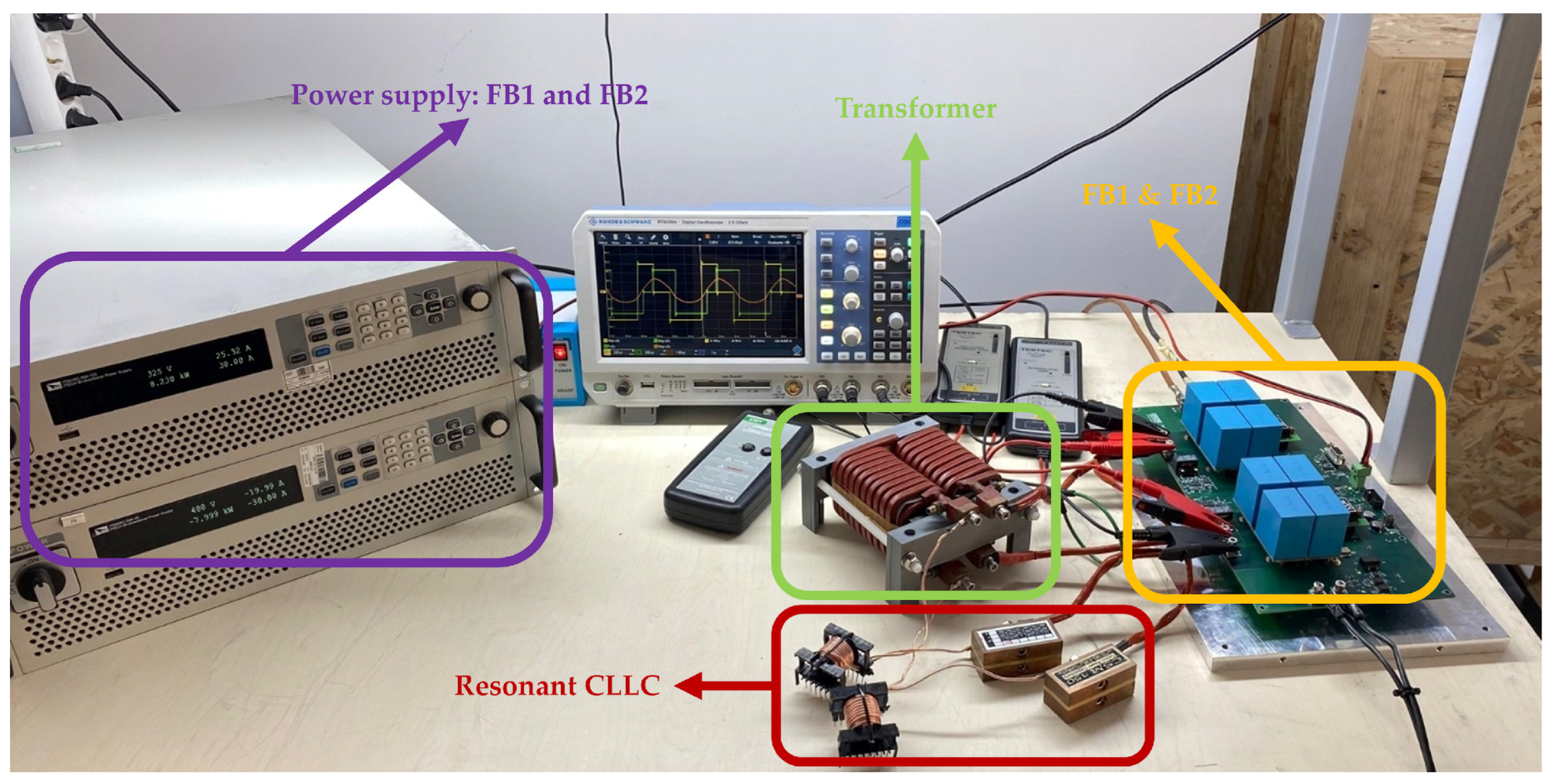
Figure 21.
Experimental setup: full-bridges, resonant capacitors, transformer, additional resonant inductors, and two bidirectional power supplies. Control board is under the converter.
Figure 21.
Experimental setup: full-bridges, resonant capacitors, transformer, additional resonant inductors, and two bidirectional power supplies. Control board is under the converter.
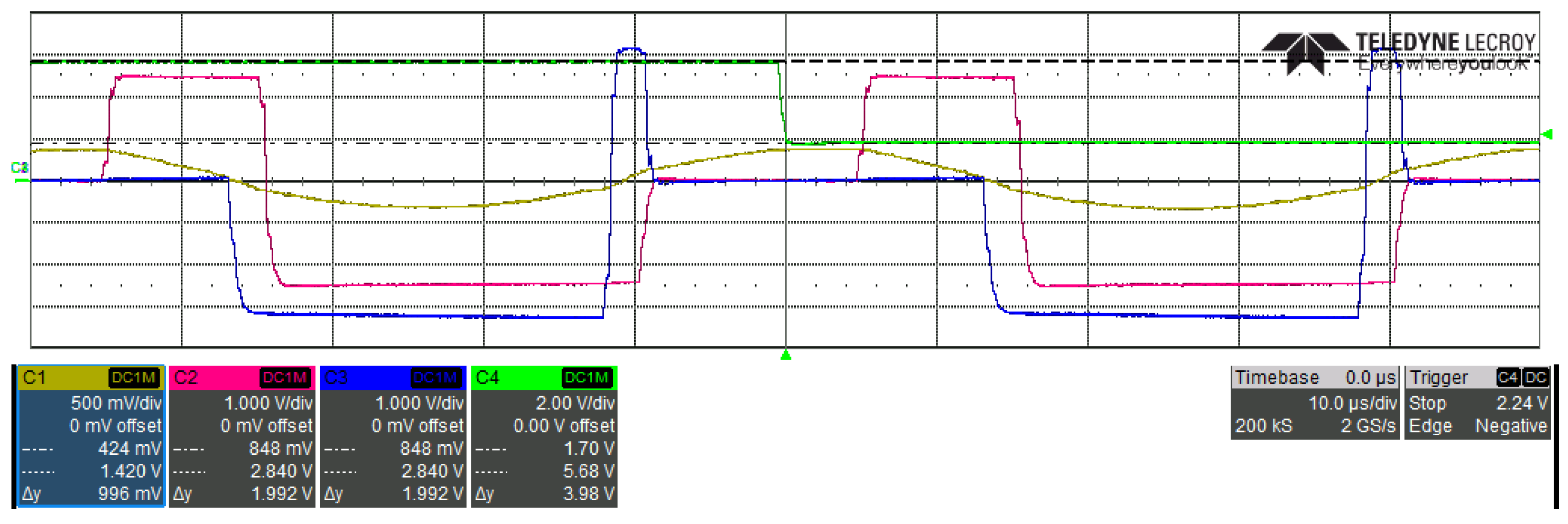
Figure 22.
Double AVC modulation, battery charge at 8 kW: FB1 output voltage (blue trace), FB2 output voltage (pink trace), and resonant tank current (light blue), .
Figure 22.
Double AVC modulation, battery charge at 8 kW: FB1 output voltage (blue trace), FB2 output voltage (pink trace), and resonant tank current (light blue), .
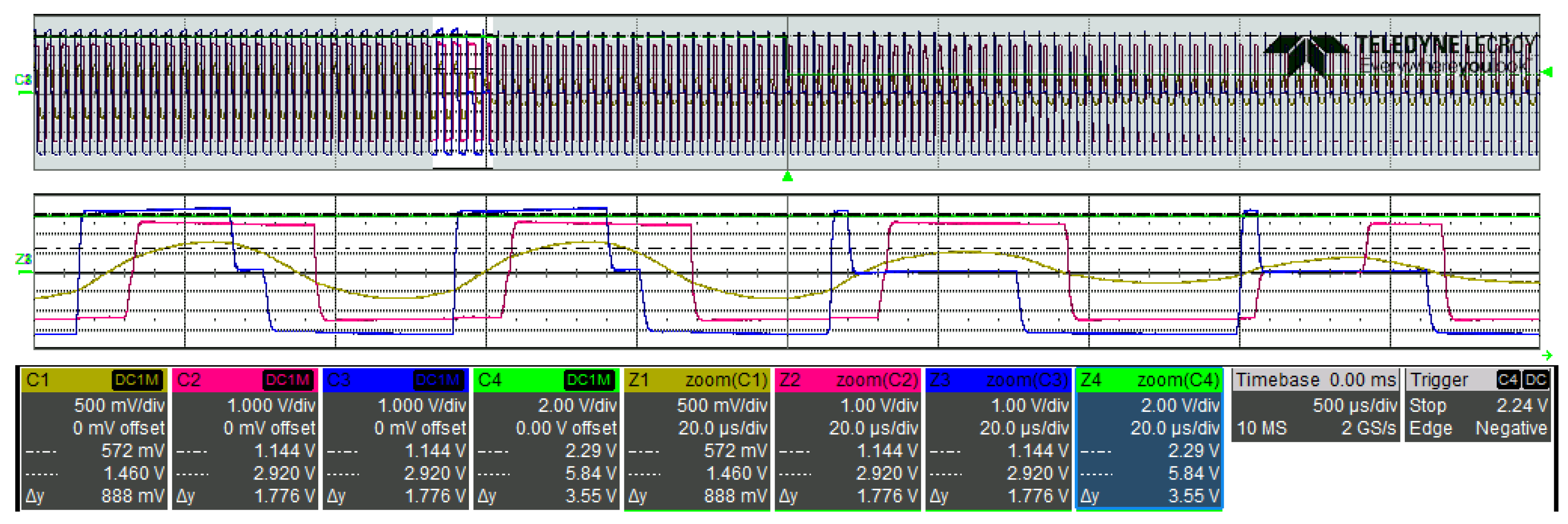
Figure 23.
TPS modulation, battery charge at 8 kW: FB1 output voltage (blue trace), FB2 output voltage (pink trace), and resonant tank current (light blue), .
Figure 23.
TPS modulation, battery charge at 8 kW: FB1 output voltage (blue trace), FB2 output voltage (pink trace), and resonant tank current (light blue), .
Figure 24.
4DOF modulation, battery charge at 8 kW: FB1 output voltage (blue trace), FB2 output voltage (pink trace), and resonant tank current (light blue), .
Figure 24.
4DOF modulation, battery charge at 8 kW: FB1 output voltage (blue trace), FB2 output voltage (pink trace), and resonant tank current (light blue), .
Figure 25.
Double AVC modulation, battery discharge at 5.5 kW: FB1 output voltage (blue trace), FB2 output voltage (pink trace), and resonant tank current (light blue), .
Figure 25.
Double AVC modulation, battery discharge at 5.5 kW: FB1 output voltage (blue trace), FB2 output voltage (pink trace), and resonant tank current (light blue), .
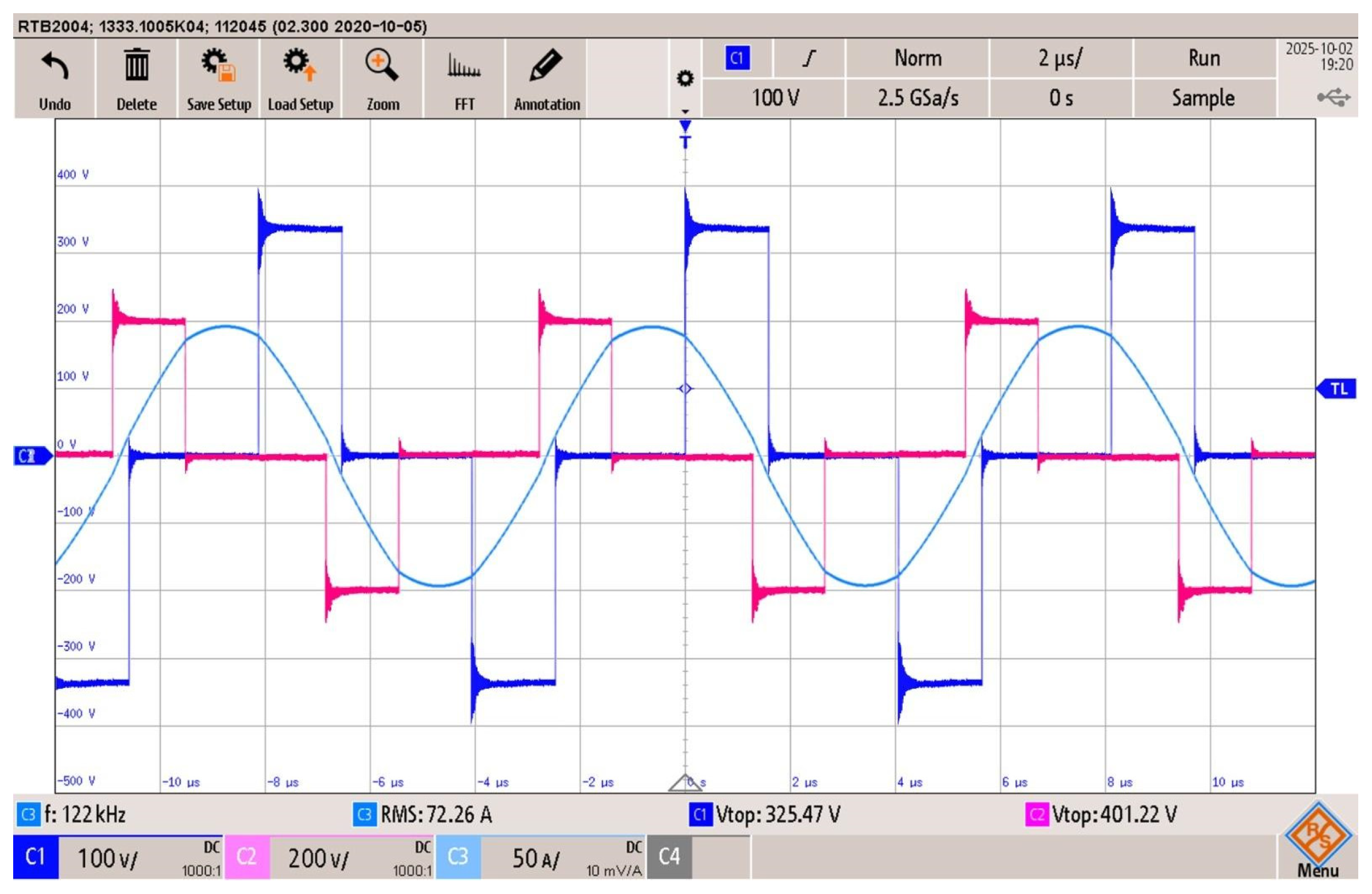
Figure 26.
TPS modulation, battery discharge at 5.5 kW: FB1 output voltage (blue trace), FB2 output voltage (pink trace), and resonant tank current (light blue), .
Figure 26.
TPS modulation, battery discharge at 5.5 kW: FB1 output voltage (blue trace), FB2 output voltage (pink trace), and resonant tank current (light blue), .
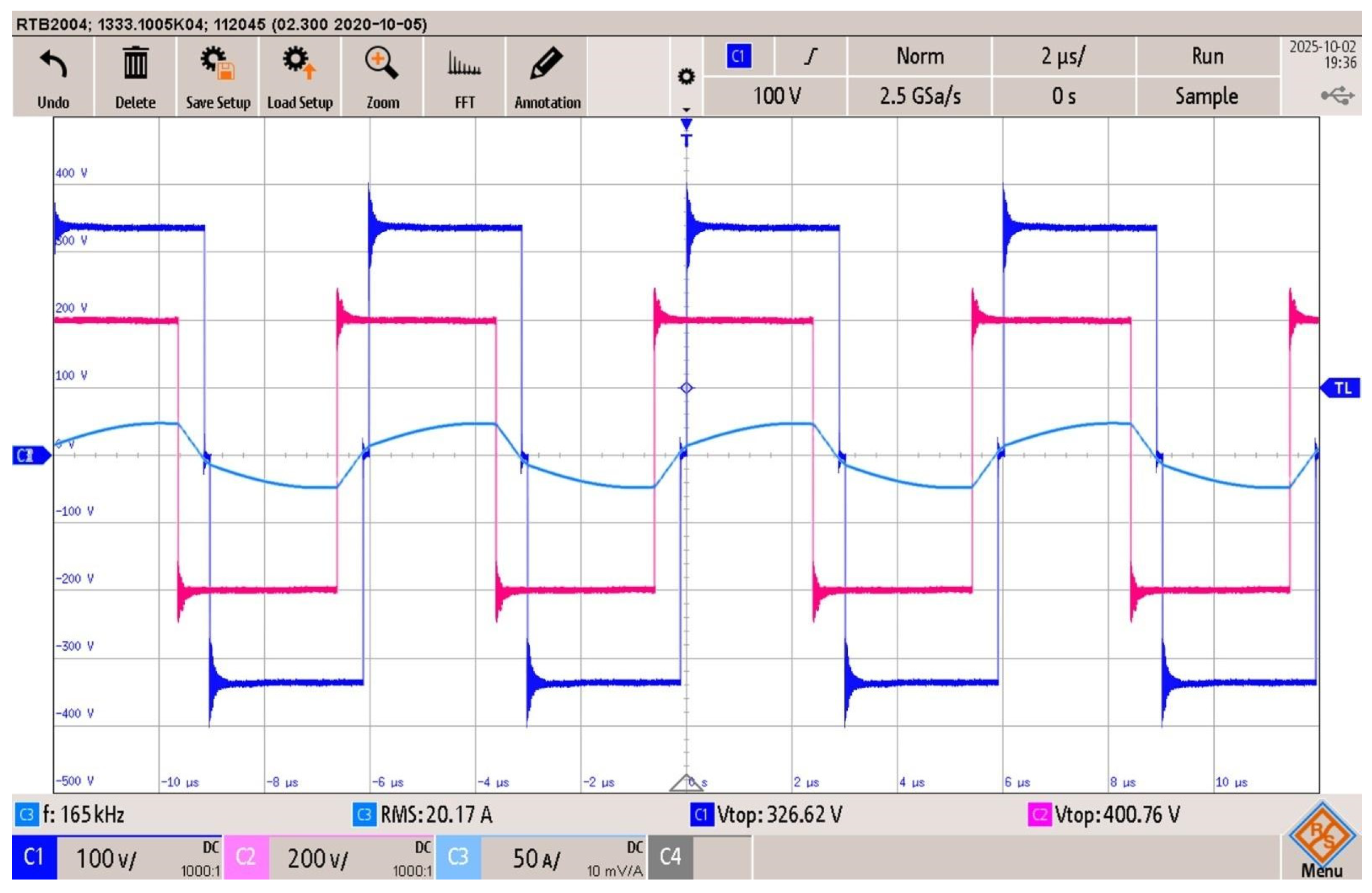
Figure 27.
4DOF modulation, battery discharge at 5.5 kW: FB1 output voltage (blue trace), FB2 output voltage (pink trace), and resonant tank current (light blue), .
Figure 27.
4DOF modulation, battery discharge at 5.5 kW: FB1 output voltage (blue trace), FB2 output voltage (pink trace), and resonant tank current (light blue), .
Table 1.
TPS modulation modes.
Table 1.
TPS modulation modes.
| Mode | | | | | |
|---|
| 1 | 0 | | | | |
| 2 | 0 | | | | |
| 3 | 0 | | | | |
| 4 | 0 | | | | |
| 5 | 0 | | | | |
| 6 | 0 | | | | |
Table 2.
Double AVC modulation modes.
Table 2.
Double AVC modulation modes.
| Mode | | | | | | |
|---|
| 1 | 0 | | | | | |
| 2 | 0 | | | | | |
| 3 | 0 | | | | | |
| 4 | 0 | | | | | |
| 5 | 0 | | | | | |
Table 3.
Possible sequences of AVC modulation.
Table 3.
Possible sequences of AVC modulation.
| Sequence | | | | | | | | |
|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 5 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 6 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 7 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 8 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 9 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 10 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 11 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 12 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 13 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 14 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 15 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 16 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
Table 4.
Association between modes and sequences.
Table 4.
Association between modes and sequences.
| Mode | Seq. 1 | Seq. 2 | Seq. 3 | Seq. 4 | Seq. 5 | Seq. 6 |
|---|
| 1 | 1 | 5 | 7 | 11 | 16 | 13 |
| 2 | 1 | 5 | 7 | 14 | 16 | 13 |
| 3 | 1 | 2 | 7 | 11 | 16 | 13 |
| 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 | 14 | 16 | 13 |
| 5 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 11 | 16 | 13 |
Table 5.
CLLC Resonant DAB converter parameters.
Table 5.
CLLC Resonant DAB converter parameters.
| Parameter | Symbol | Value |
|---|
| Rectified primary voltage | | V |
| Battery voltage range | | V |
| Output power range | | kW |
| Transformer ratio | | 1 |
| Magnetizing inductance | | mH |
| Resonant inductance | | µH |
| Resonant capacitor | | nF |
| Resonant frequency | | kHz |
| Fixed switching frequency | | kHz |
Table 6.
Main parameters of the experimental tests.
Table 6.
Main parameters of the experimental tests.
| Parameter | Symbol | Part Number | Value |
|---|
| Rectified primary voltage | | / | V |
| Battery voltage range | | / | V |
| Output power range | | / | kW |
| Transformer ratio | | / | 1 |
| Magnetizing inductance | | / | mH |
| Leakage inductance | | / | µH |
| Resonant additional inductance | | / | µH |
| Resonant capacitor | | CSM 150 | nF |
| Resonant frequency | | / | kHz |
| 2 parallel SiC MOSFETs | / | C3M0040120K | / |
| SoC FPGA | / | Zynq 7000 | / |
| Fixed switching frequency (AVC and TPS) | | / | kHz |
| Variable switching frequency (4DOF) | | / | kHz |
Table 7.
Comparison of the three modulation techniques.
Table 7.
Comparison of the three modulation techniques.
| Modulation Technique Feature | TPS | 4DOF | Double AVC |
|---|
| Symmetry | Yes | Yes | No |
| Switching frequency [kHz] | 122 (fixed) | 113.5–165 (variable) | 122 (fixed) |
| Control | Easy | Hard | Easy |
| EMI/EMC | Low | High | Low |
| Sim. [Arms] | 74.87 (+8 kW) | 35.11 (+8 kW) | 41.2 (+8 kW) |
| 70.0 (−5.5 kW) | 18.22 (−5.5 kW) | 31.8 (−5.5 kW) |
| Sim. [%] | 92.65 (+8 kW) | 97.4 (+8 kW) | 97.1 (+8 kW) |
| 89.65 (−5.5 kW) | 96.8 (−5.5 kW) | 96.6 (−5.5 kW) |
| Exp. | 76.65 (+8 kW) | 38.76 (+8 kW) | 41.87 (+8 kW) |
| 72.26 (−5.5 kW) | 20.17 (−5.5 kW) | 33.18 (−5.5 kW) |
| Exp. [%] | 91.5 (+8 kW) | 97.2 (+8 kW) | 96.3 (+8 kW) |
| 87.7 (−5.5 kW) | 97.4 (−5.5 kW) | 96.8 (−5.5 kW) |