Unified Spatiotemporal Detection for Isolated Sign Language Recognition Using YOLO-Act
Abstract
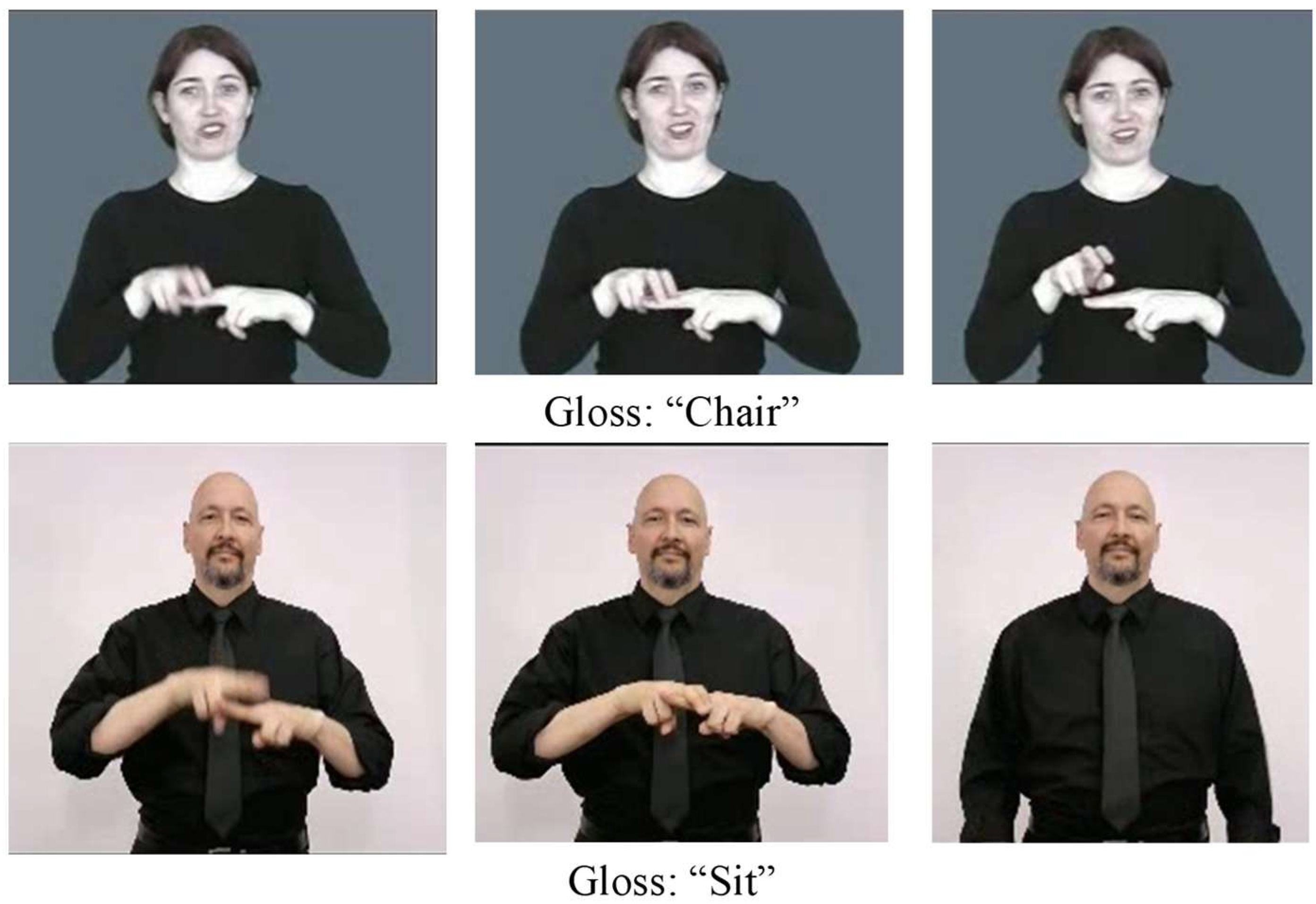
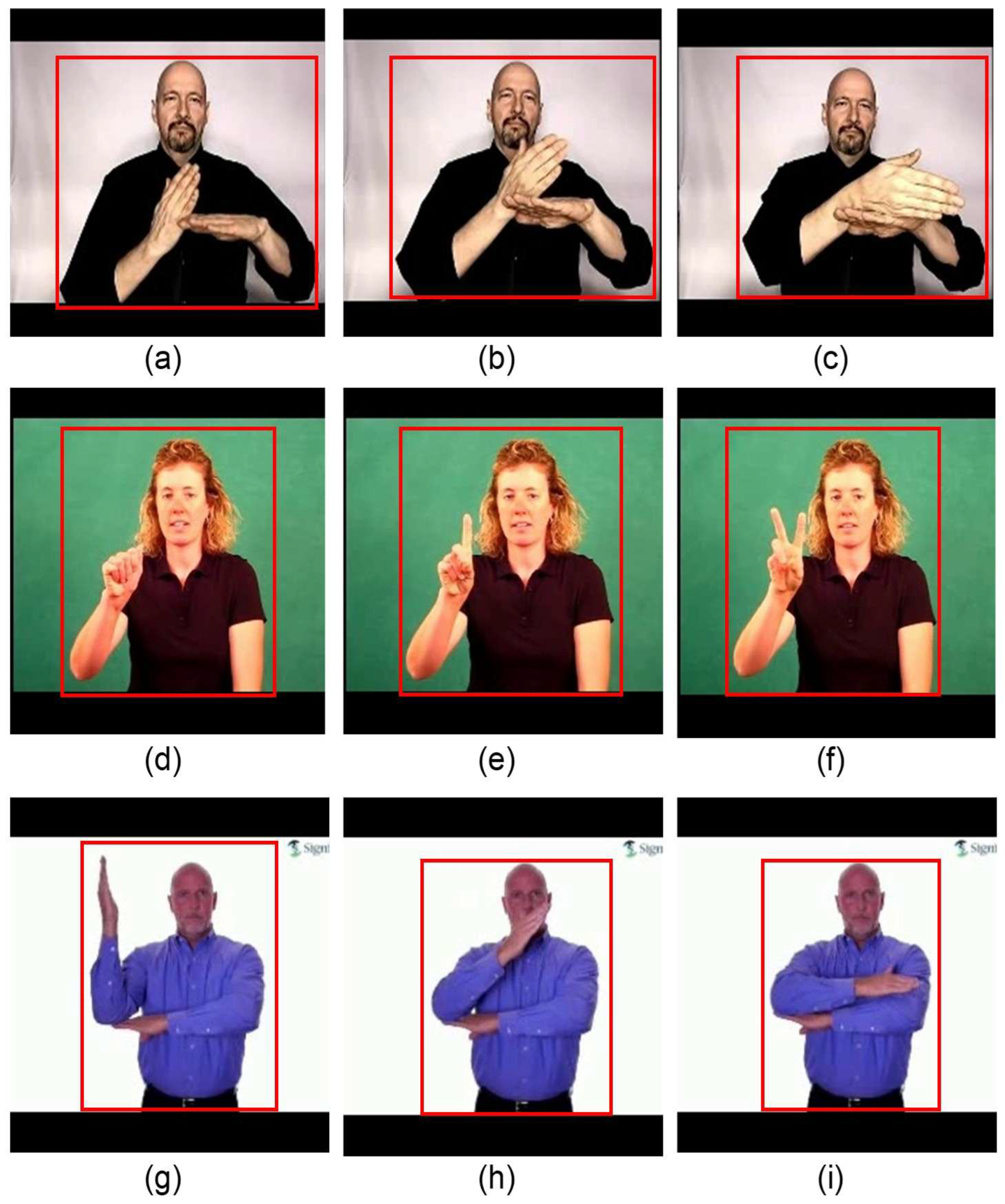
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Sign Language Recognition
2.1.1. RGB-Based Input Modality
2.1.2. Pose-Based Input Modality
2.2. CNN-Based Methods for Sign Language Recognition
2.3. SLR Based on Transformer
2.4. Discussion
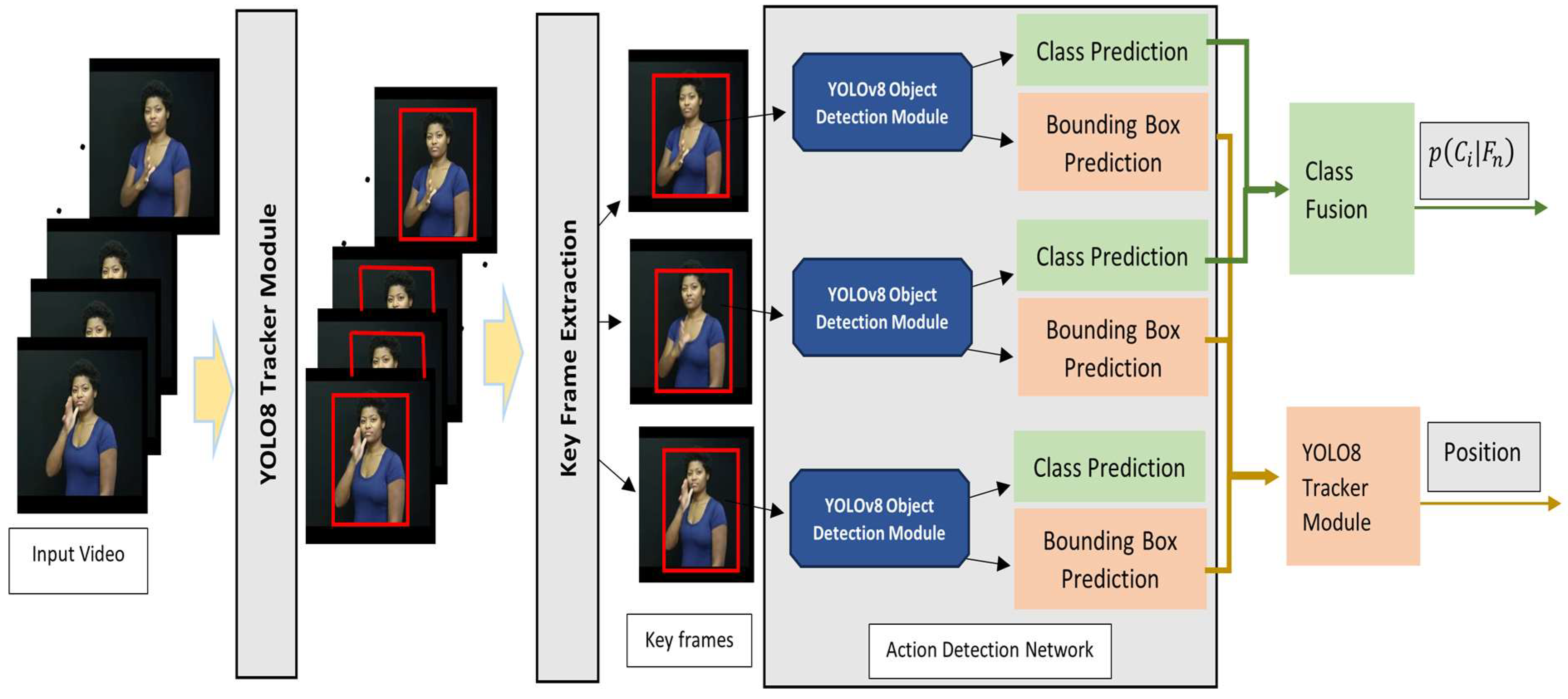
3. The YOLO-Act Model
3.1. Keyframe Extraction
3.2. Action Detection
3.3. Class Fusion
3.4. Actor Tracking
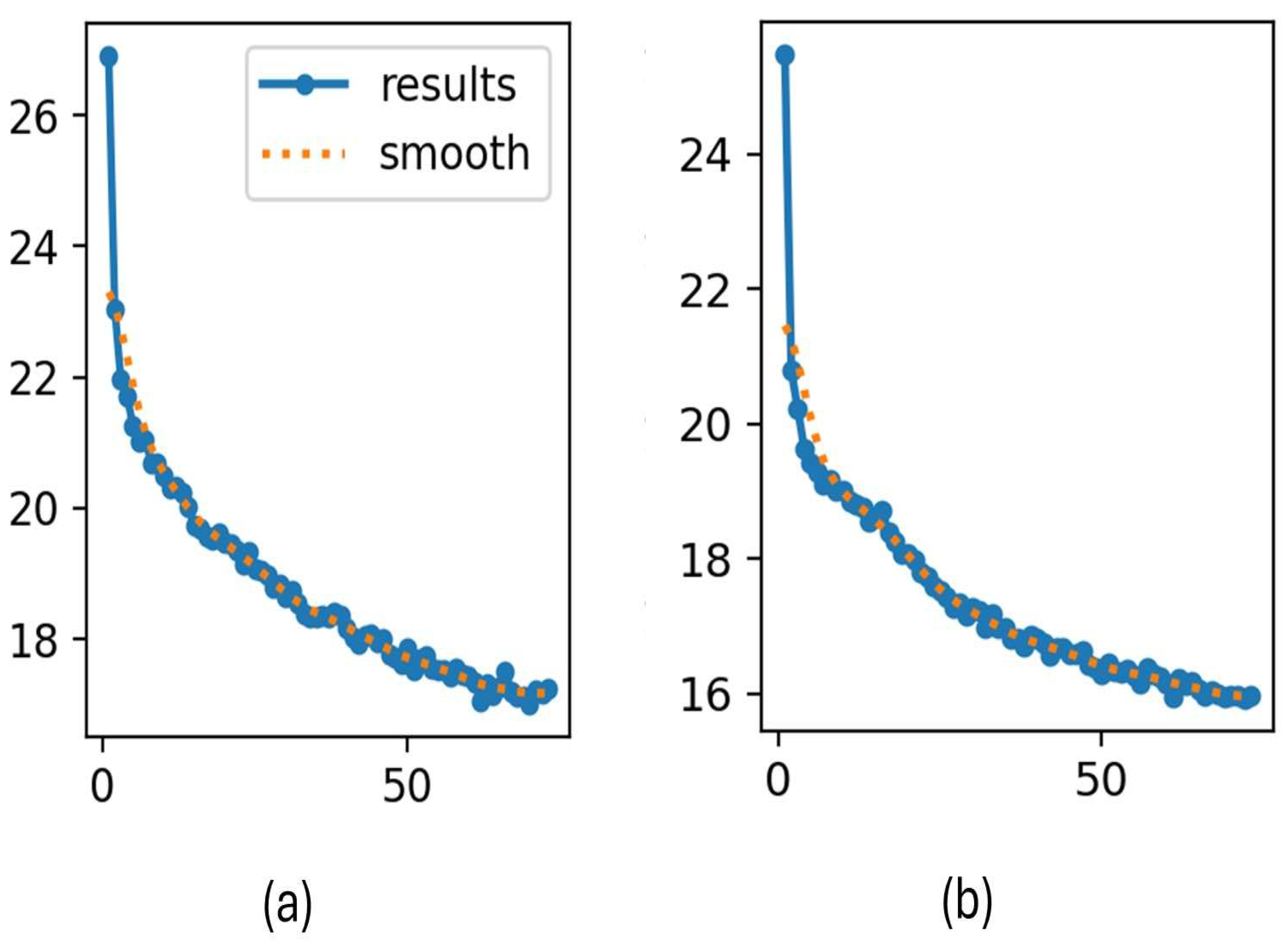
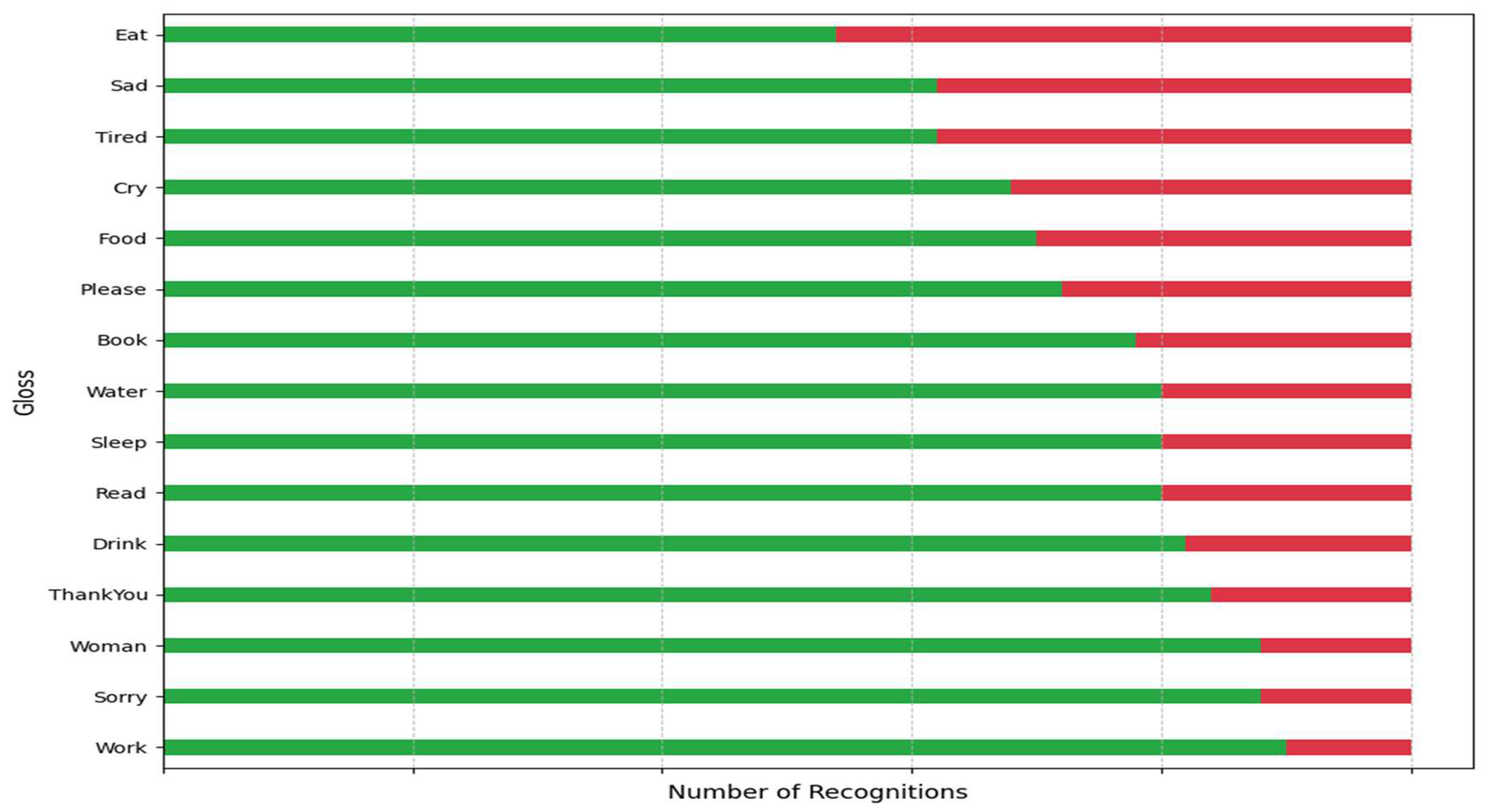
4. Experiments
4.1. Comparison with the State of the Arts
4.2. Ablation Study: Effect of Bounding Box Cropping
4.3. Ablation Study: Impact of Multi-Stage Supervision
4.4. Ablation Study: Number of Keyframes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adaloglou, N.; Chatzis, T.; Papastratis, I.; Stergioulas, A.; Papadopoulos, G.T.; Zacharopoulou, V.; Xydopoulos, G.J.; Atzakas, K.; Papazachariou, D.; Daras, P. A Comprehensive Study on Deep Learning-Based Methods for Sign Language Recognition. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022, 24, 1750–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, W.; Lillo-Martin, D.C. Sign Language and Linguistic Universals; Cambridge University Press: Cambridges, UK, 2006; ISBN 978-0-521-48248-6. [Google Scholar]
- Rastgoo, R.; Kiani, K.; Escalera, S. Sign Language Recognition: A Deep Survey. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 164, 113794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, A.; Zhao, Z.; Jin, W.; Zhang, M.; Zeng, X.; He, X. MLSLT: Towards Multilingual Sign Language Translation. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 5099–5109. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Lan, C.; Zeng, W.; Xing, J.; Xue, J.; Zheng, N. Semantics-Guided Neural Networks for Efficient Skeleton-Based Human Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 1109–1118. [Google Scholar]
- Molchanov, P.; Yang, X.; Gupta, S.; Kim, K.; Tyree, S.; Kautz, J. Online Detection and Classification of Dynamic Hand Gestures with Recurrent 3D Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4207–4215. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Zhou, W.; Li, H.; Li, W. Attention-Based 3D-CNNs for Large-Vocabulary Sign Language Recognition. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2019, 29, 2822–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Xiong, Y.; Lin, D. Spatial Temporal Graph Convolutional Networks for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Thirtieth Innovative Applications of Artificial Intelligence Conference and Eighth AAAI Symposium on Educational Advances in Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; Volume 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koller, O.; Forster, J.; Ney, H. Continuous Sign Language Recognition: Towards Large Vocabulary Statistical Recognition Systems Handling Multiple Signers. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2015, 141, 108–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelidis, G.D.; Singh, G.; Horaud, R. Continuous Gesture Recognition from Articulated Poses. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2014 Workshops; Agapito, L., Bronstein, M.M., Rother, C., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 8925, pp. 595–607. ISBN 978-3-319-16177-8. [Google Scholar]
- Alzahrani, N.; Bchir, O.; Ismail, M.M.B. YOLO-Act: Unified Spatiotemporal Detection of Human Actions Across Multi-Frame Sequences. Sensors 2025, 25, 3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Zhou, W.; Li, H. Hand-Model-Aware Sign Language Recognition. Assoc. Adv. Artif. Intell. 2021, 35, 1558–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koller, O.; Zargaran, S.; Ney, H.; Bowden, R. Deep Sign: Enabling Robust Statistical Continuous Sign Language Recognition via Hybrid CNN-HMMs. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2018, 126, 1311–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeni, L.; Bull, H.; Prajwal, K.R.; Albanie, S.; Varol, G.; Zisserman, A. Automatic Dense Annotation of Large-Vocabulary Sign Language Videos; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Z.; Mak, B. Stochastic Fine-Grained Labeling of Multi-State Sign Glosses for Continuous Sign Language Recognition. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2020; Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 12361, pp. 172–186. ISBN 978-3-030-58516-7. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Yu, X.; Xu, C.; Petersson, L.; Li, H. Transferring Cross-Domain Knowledge for Video Sign Language Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 6204–6213. [Google Scholar]
- Buehler, P.; Everingham, M.; Zisserman, A. Learning Sign Language by Watching TV (Using Weakly Aligned Subtitles). In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yasir, F.; Prasad, P.W.C.; Alsadoon, A.; Elchouemi, A. SIFT Based Approach on Bangla Sign Language Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 8th International Workshop on Computational Intelligence and Applications (IWCIA), Hiroshima, Japan, 6–7 November 2015; pp. 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Starner, T.E. Visual Recognition of American Sign Language Using Hidden Markov Models. Hidden Markov Models 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Starner, T.; Weaver, J.; Pentland, A. Real-Time American Sign Language Recognition Using Desk and Wearable Computer Based Video. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Machine Intell. 1998, 20, 1371–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, P.; NC, G.; Kumar, P.; Khapra, M. OpenHands: Making Sign Language Recognition Accessible with Pose-Based Pretrained Models across Languages. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.05877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Kalantidis, Y.; Li, J.; Yan, S.; Feng, J. Multi-Fiber Networks for Video Recognition. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2018; Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 11205, pp. 364–380. ISBN 978-3-030-01245-8. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Z.; Yao, T.; Mei, T. Learning Spatio-Temporal Representation with Pseudo-3D Residual Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 5534–5542. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Z.; Yao, T.; Ngo, C.-W.; Tian, X.; Mei, T. Learning Spatio-Temporal Representation with Local and Global Diffusion. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 12048–12057. [Google Scholar]
- Albanie, S.; Varol, G.; Momeni, L.; Afouras, T.; Chung, J.S.; Fox, N.; Zisserman, A. BSL-1K: Scaling up Co-Articulated Sign Language Recognition Using Mouthing Cues. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Zhong, Q.; Xie, D.; Pu, S. Co-Occurrence Feature Learning from Skeleton Data for Action Recognition and Detection with Hierarchical Aggregation. In Proceedings of the 27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 13–19 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, E.; Ginosar, S.; Darrell, T.; Joo, H. Body2Hands: Learning to Infer 3D Hands from Conversational Gesture Body Dynamics. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 11860–11869. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, K.; van Merrienboer, B.; Gulcehre, C.; Bahdanau, D.; Bougares, F.; Schwenk, H.; Bengio, Y. Learning Phrase Representations Using RNN Encoder-Decoder for Statistical Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Doha, Qatar, 25–29 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long Short-Term Memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Lan, C.; Xing, J.; Zeng, W.; Liu, J. An End-to-End Spatio-Temporal Attention Model for Human Action Recognition from Skeleton Data. Assoc. Adv. Artif. Intell. 2017, 31, 4263–4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Lan, C.; Xing, J.; Zeng, W.; Li, Y.; Shen, L.; Xie, X. Co-Occurrence Feature Learning for Skeleton Based Action Recognition Using Regularized Deep LSTM Networks. Assoc. Adv. Artif. Intell. 2016, 30, 3697–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, D.; Wang, W.; Wang, L. Hierarchical Recurrent Neural Network for Skeleton Based Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1110–1118. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, C.; Lan, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, W.; Lu, H.; Zhang, Y. Skeleton-Based Action Recognition with Gated Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2018, 29, 3247–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camgoz, N.C.; Hadfield, S.; Koller, O.; Ney, H.; Bowden, R. Neural Sign Language Translation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7784–7793. [Google Scholar]
- Min, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chai, X.; Chen, X. An Efficient PointLSTM for Point Clouds Based Gesture Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 5760–5769. [Google Scholar]
- Tunga, A.; Nuthalapati, S.V.; Wachs, J. Pose-Based Sign Language Recognition Using GCN and BERT. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision Workshops (WACVW), Waikola, HI, USA, 5–9 January 2021; pp. 31–40. [Google Scholar]
- Pigou, L.; Van Den Oord, A.; Dieleman, S.; Van Herreweghe, M.; Dambre, J. Beyond Temporal Pooling: Recurrence and Temporal Convolutions for Gesture Recognition in Video. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2018, 126, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molchanov, P.; Gupta, S.; Kim, K.; Kautz, J. Hand Gesture Recognition with 3D Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Pigou, L.; Kindermans, P.-J.; Le, N.D.-H.; Shao, L.; Dambre, J.; Odobez, J.-M. Deep Dynamic Neural Networks for Multimodal Gesture Segmentation and Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 38, 1583–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinidis, D.; Dimitropoulos, K.; Daras, P. Sign Language Recognition Based on Hand and Body Skeletal Data. In Proceedings of the 2018—3DTV-Conference: The True Vision—Capture, Transmission and Display of 3D Video (3DTV-CON), Helsinki, Finland, 3–5 June 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Daroya, R.; Peralta, D.; Naval, P. Alphabet Sign Language Image Classification Using Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the TENCON 2018—2018 IEEE Region 10 Conference, Jeju, Republic of Korea, 28–31 October 2018; pp. 646–650. [Google Scholar]
- Taskiran, M.; Killioglu, M.; Kahraman, N. A Real-Time System for Recognition of American Sign Language by Using Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 41st International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing (TSP), Athens, Greece, 4–6 July 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, R.; Wei, F.; Mak, B. Natural Language-Assisted Sign Language Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, H. SignBERT: Pre-Training of Hand-Model-Aware Representation for Sign Language Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 11067–11076. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, W.; Li, H. Signbert+: Hand-Model-Aware Self-Supervised Pre-Training for Sign Language Understanding. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 11221–11239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhao, W.; Hu, H.; Li, Z.; Li, H. Scaling up Multimodal Pre-Training for Sign Language Understanding. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2025, 47, 11753–11767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhou, B.; Huang, Y.; Wan, J.; Hu, Y.; Shi, H.; Liang, Y.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, D. C2 RL: Content and Context Representation Learning for Gloss-Free Sign Language Translation and Retrieval. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2025, 35, 8533–8544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, W.; Zhao, W.; Wu, K.; Hu, H.; Li, H. Uni-Sign: Toward Unified Sign Language un-Derstanding at Scale. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.15187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Hu, H.; Zhou, W.; Shi, J.; Li, H. BEST: BERT Pre-Training for Sign Language Recognition with Coupling Tokenization. Assoc. Adv. Artif. Intell. 2023, 37, 3597–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, R.; Wang, R.; Shu, C.; Li, J.; Wei, Z. Crack Detection in Civil Infrastructure Using Autonomous Robotic Systems: A Synergistic Review of Platforms, Cognition, and Autonomous Action. Sensors 2025, 25, 4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, C.; Xiong, B.; Li, X.; Sang, X.; Kong, Q. A Novel Intelligent Inspection Robot with Deep Stereo Vision for Three-Dimensional Concrete Damage Detection and Quantification. Struct. Health Monit. 2022, 21, 788–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, D.; He, S.; Tang, J. Divide-and-Conquer: Confluent Triple-Flow Network for RGB-T Salient Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2025, 47, 1958–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Opazo, C.R.; Yu, X.; Li, H. Word-Level Deep Sign Language Recognition from Video: A New Large-Scale Dataset and Methods Comparison. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Snowmass Village, CO, USA, 1–5 March 2020; pp. 1448–1458. [Google Scholar]
- Joze, H.R.V.; Koller, O. Ms-Asl: A Large-Scale Data Set and Benchmark for Understanding American Sign Language. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1812.01053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolya, D.; Zhou, C.; Xiao, F.; Lee, Y.J. YOLACT: Real-Time Instance Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 9156–9165. [Google Scholar]
- Jocher, G.; Chaurasia, A.; Qiu, J. YOLO by Ultralytics (Version 8.0.0). 2023. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics (accessed on 3 October 2024).
- Karpathy, A.; Toderici, G.; Shetty, S.; Leung, T.; Sukthankar, R.; Fei-Fei, L. Large-Scale Video Classification with Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Athitsos, V.; Neidle, C.; Sclaroff, S.; Nash, J.; Stefan, A.; Yuan, Q.; Thangali, A. The American Sign Language Lexicon Video Dataset. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Anchorage, AK, USA, 23–28 June 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zutalin, T. LabelImg (Free Software: MIT License). 2015. Available online: https://github.com/tzutalin/labelImg (accessed on 15 May 2025).





| Category | Reference | Input Modality | Architecture/Approach | Dataset | Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLR based on CNN | [6] | RGB | CNN with a recurrent extension | SKIG, ChaLearn2014 | Acc = 97.7%, 98.2% |
| [38] | RGB-D | 3D-CNN | VIVA | Acc = 77.5% | |
| [39] | RGB-D + Pose | 3D-CNN + Gaussian–Bernoulli DBN | ChaLearn LAP | Jaccard index = 0.81 | |
| [43] | RGB + Pose | S3D backbone + CNN-based keypoint encoding | MSASL1000, WLASL2000 | Acc = 72.56%, 61.05% | |
| [37] | RGB | CNNs spatial feature + LSTM/RNN temporal dynamics | ChaLearn LAP | Jaccard index = 0.906 | |
| SLR based on Transformer | [44] | Pose | Transformer encoder–decoder backbone | MSASL1000, WLASL2000 | Acc = 67.96%, 52.08% |
| [45] | Pose | Transformer encoder + hand-model-aware decoder | MSASL1000, WLASL2000 | Acc = 62.42%, 48.85% | |
| [46] | Pose | Transformer pre-training with (contrastive + masked modeling) | MSASL1000, WLASL2000 | Acc = 74.07%, 56.29% | |
| [48] | RGB + Pose | unified Transformer pre- with GCN-based pose encoder | MSASL1000, WLASL2000 | Acc = 78.16%, 63.52% | |
| [49] | Pose | BERT-style Transformer with GCN pose embedding | MSASL1000, WLASL2000 | Acc = 71.21%, 54.59% |
| Hyperparameters | Value |
|---|---|
| optimizer | AdamW |
| optimizer momentum | 0.937 |
| weight decay | 0.0005 |
| Learning rate schedule | Cosine Decay |
| warmup epochs | 5.0 |
| drop out | 0.1 |
| learning rate | 0.0001 |
| batch size | 16 |
| epochs | 150 early stopping at epoch 80 |
| Patience/early stopping | 15 |
| Method | Modality | MSASL100 | MSASL1000 | WLASL100 | WLASL2000 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pose | RGB | P-I | P-C | P-I | P-C | P-I | P-C | P-I | P-C | |
| ST-GCN [8] | ✔ | 50.78 | 51.62 | 34.40 | 32.53 | 50.78 | 51.62 | 34.40 | 32.53 | |
| SignBERT [44] | ✔ | 76.09 | 76.65 | 49.54 | 46.39 | 76.36 | 77.68 | 39.40 | 36.74 | |
| SignBERT+ [45] | ✔ | 84.94 | 85.23 | 62.42 | 60.15 | 79.84 | 80.72 | 48.85 | 46.37 | |
| MSLU [46] | ✔ | 91.54 | 91.75 | 74.07 | 71.81 | 88.76 | 89.25 | 56.29 | 53.29 | |
| BEST [49] | ✔ | 89.56 | 90.08 | 71.21 | 68.24 | 81.01 | 81.63 | 54.59 | 52.12 | |
| NLA-SLR [43] | ✔ | ✔ | 90.49 | 91.04 | 72.56 | 69.86 | 91.47 | 92.17 | 61.05 | 58.05 |
| Uni-Sign [48] | ✔ | ✔ | 93.79 | 94.02 | 78.16 | 76.97 | 92.25 | 92.67 | 63.52 | 61.32 |
| YOLO-Act (Ours) | ✔ | 95.04 | 95.49 | 81.41 | 79.13 | 93.77 | 94.32 | 67.07 | 64.59 | |
| Input Crop | P-I (%) | P-C (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Hand Bounding Box | 59.01 | 60.12 |
| Human Bounding Box | 93.77 | 94.32 |
| Δ (Human–Hand) = | +34.76 | +34.2 |
| Training Scheme | P-I (%) | P-C (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Stage-specific (Action1) | 12.87 | 11.60 |
| Stage-specific (Action2) | 17.26 | 15.64 |
| Stage-specific (Action3) | 15.76 | 14.09 |
| Fused multi-stage (Action1 + 2 + 3) | 67.07 | 64.59 |
| No of Frames | Extracted Key Frames |
|---|---|
| 2 |   Frame 0 - Frame 99 |
| 3 |    Frame 0 - Frame 49 - Frmae 99 |
| 5 |      Frame 0 - Frame 25 - Frmae 50 - Frame 75 - Frame 99 |
| 9 |      Frame 0 - Frame 12 - Frame 25 - Frame 37 - Frame 50     Frame 62 - Frame 75 - Frame 87 - Frame 99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alzahrani, N.; Bchir, O.; Ben Ismail, M.M. Unified Spatiotemporal Detection for Isolated Sign Language Recognition Using YOLO-Act. Electronics 2025, 14, 4589. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14234589
Alzahrani N, Bchir O, Ben Ismail MM. Unified Spatiotemporal Detection for Isolated Sign Language Recognition Using YOLO-Act. Electronics. 2025; 14(23):4589. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14234589
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlzahrani, Nada, Ouiem Bchir, and Mohamed Maher Ben Ismail. 2025. "Unified Spatiotemporal Detection for Isolated Sign Language Recognition Using YOLO-Act" Electronics 14, no. 23: 4589. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14234589
APA StyleAlzahrani, N., Bchir, O., & Ben Ismail, M. M. (2025). Unified Spatiotemporal Detection for Isolated Sign Language Recognition Using YOLO-Act. Electronics, 14(23), 4589. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14234589






