Analysis of the Impact of Conductive Fabrics Parameters on Textronic UHF RFID Transponder Antennas
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Digital Product Passport
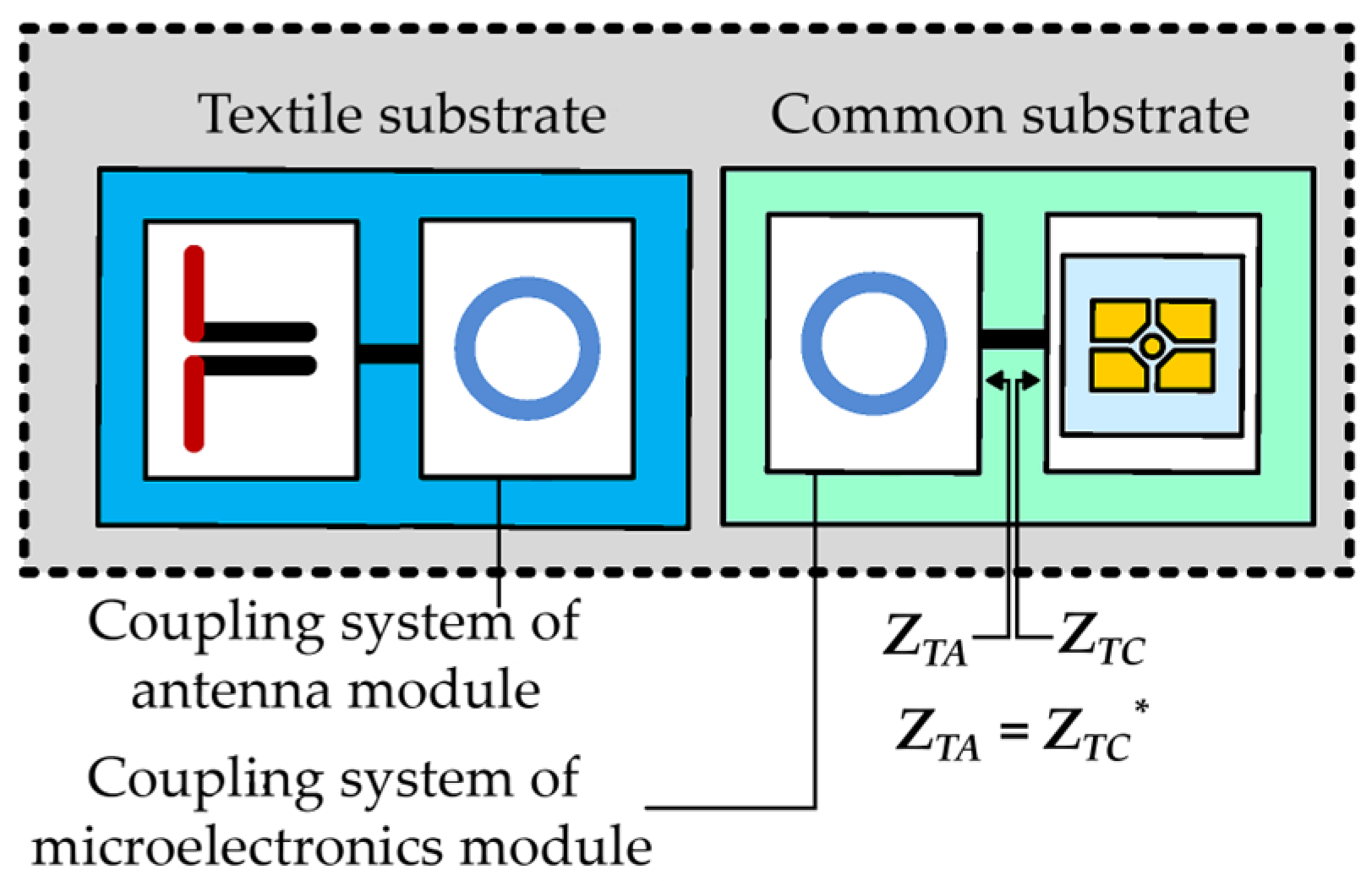
1.2. Textronix RFID Transponder Antenna
1.3. Aim of the Research
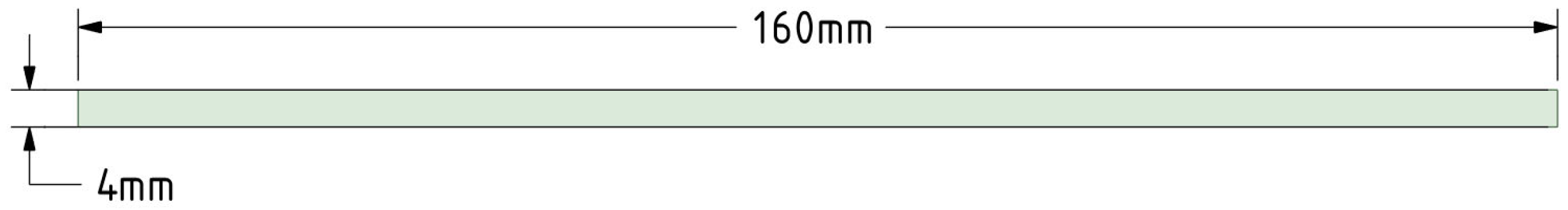
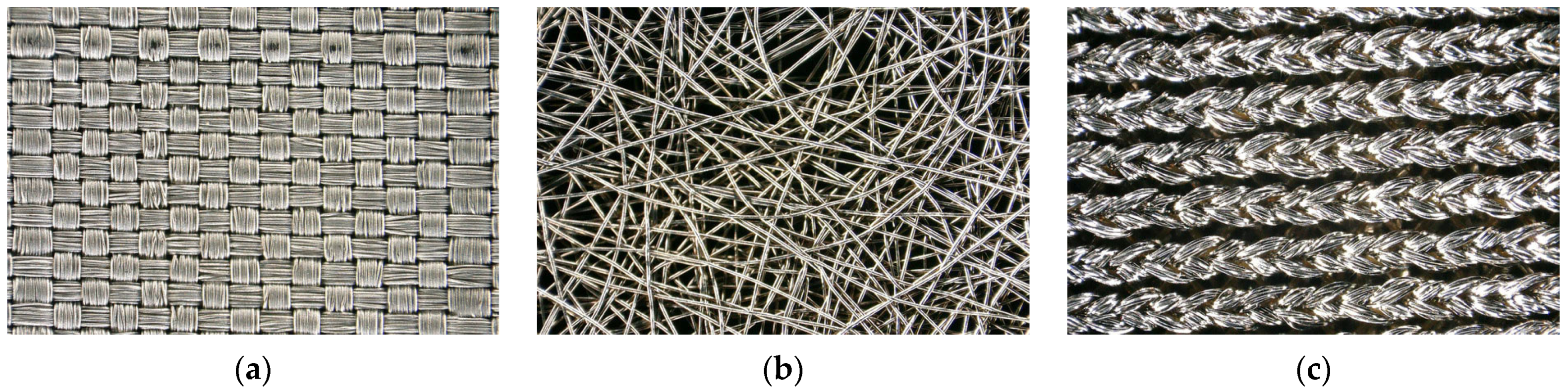
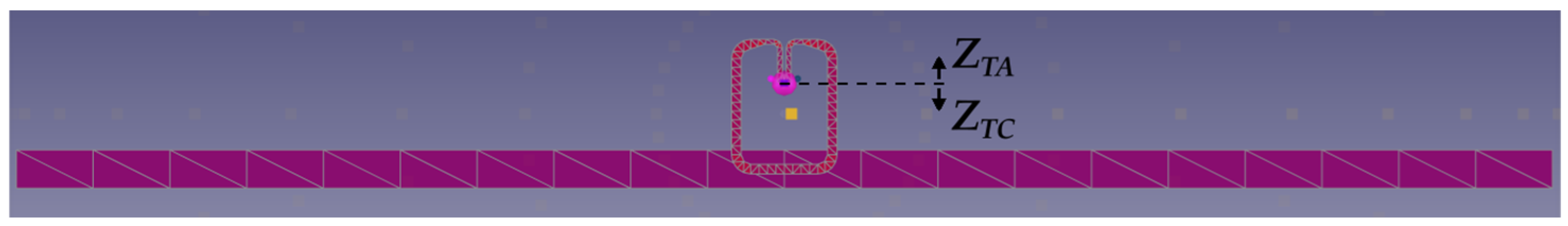
2. Materials and Methods
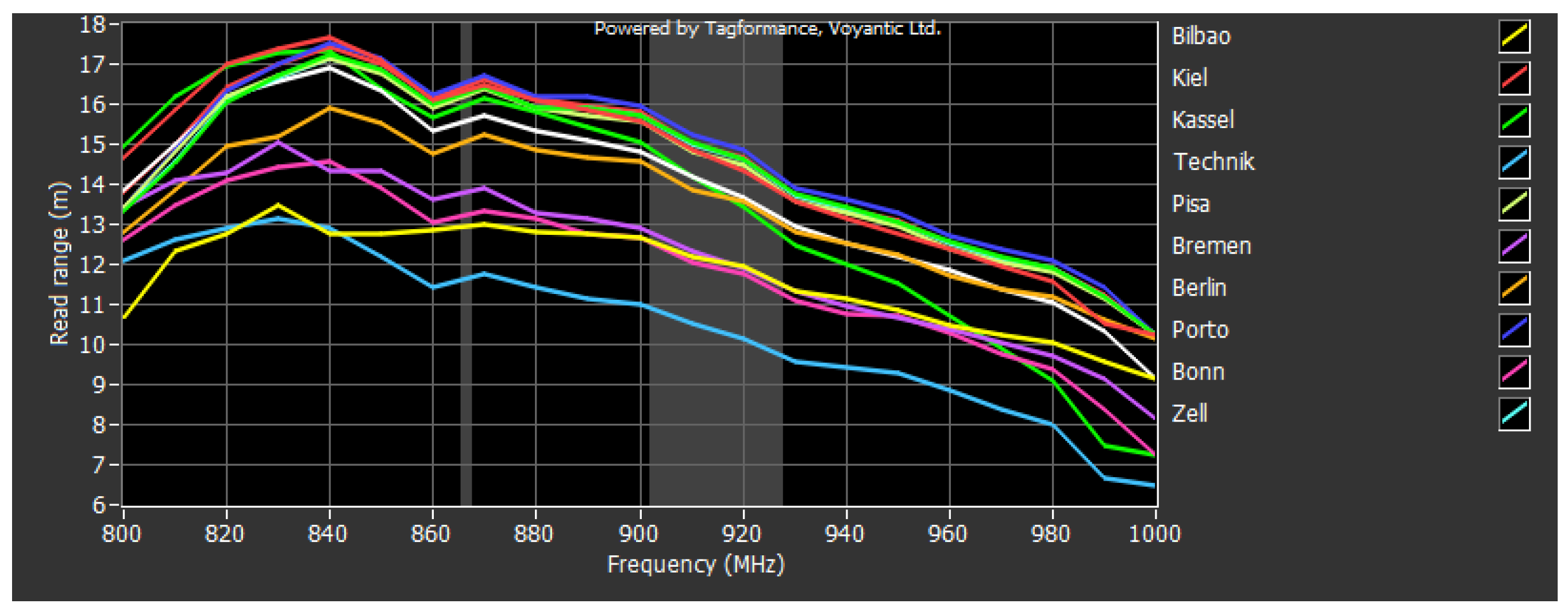
3. Results
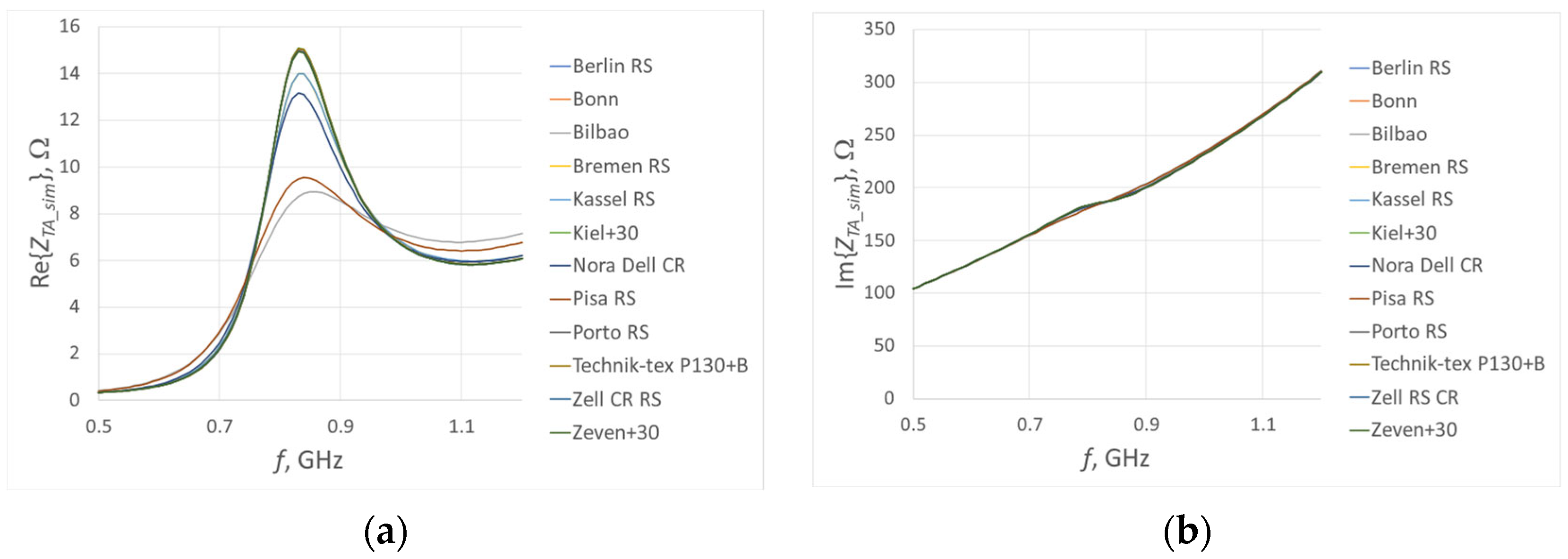
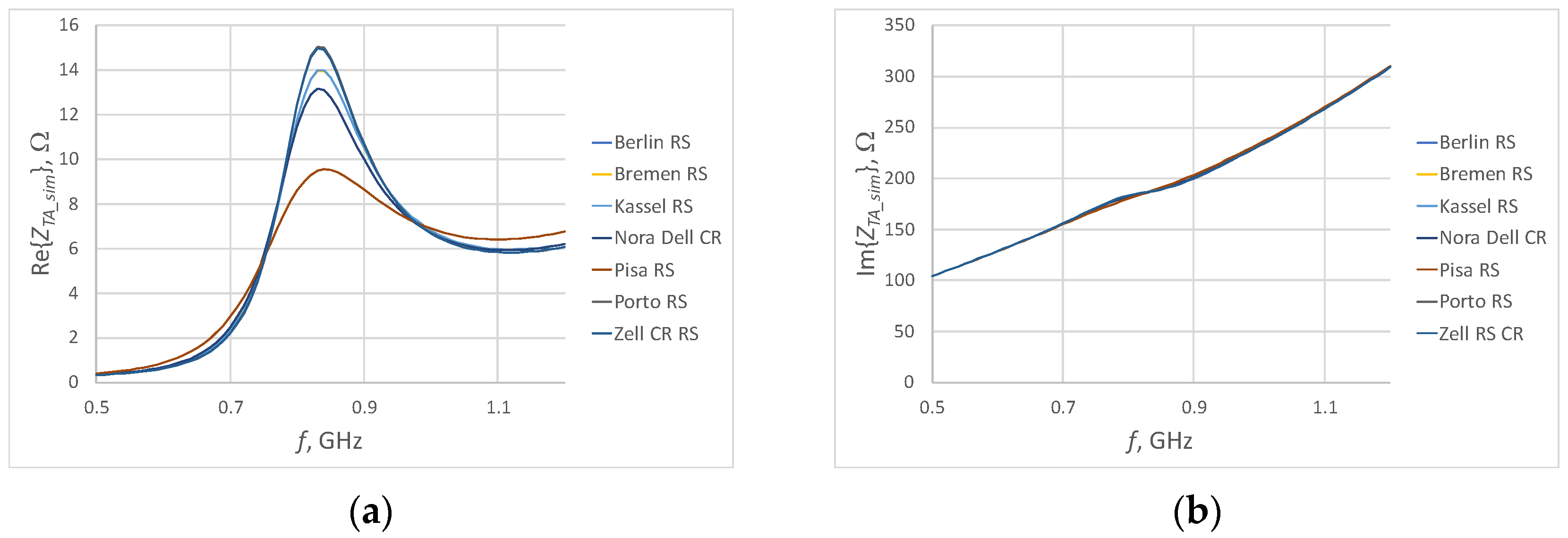
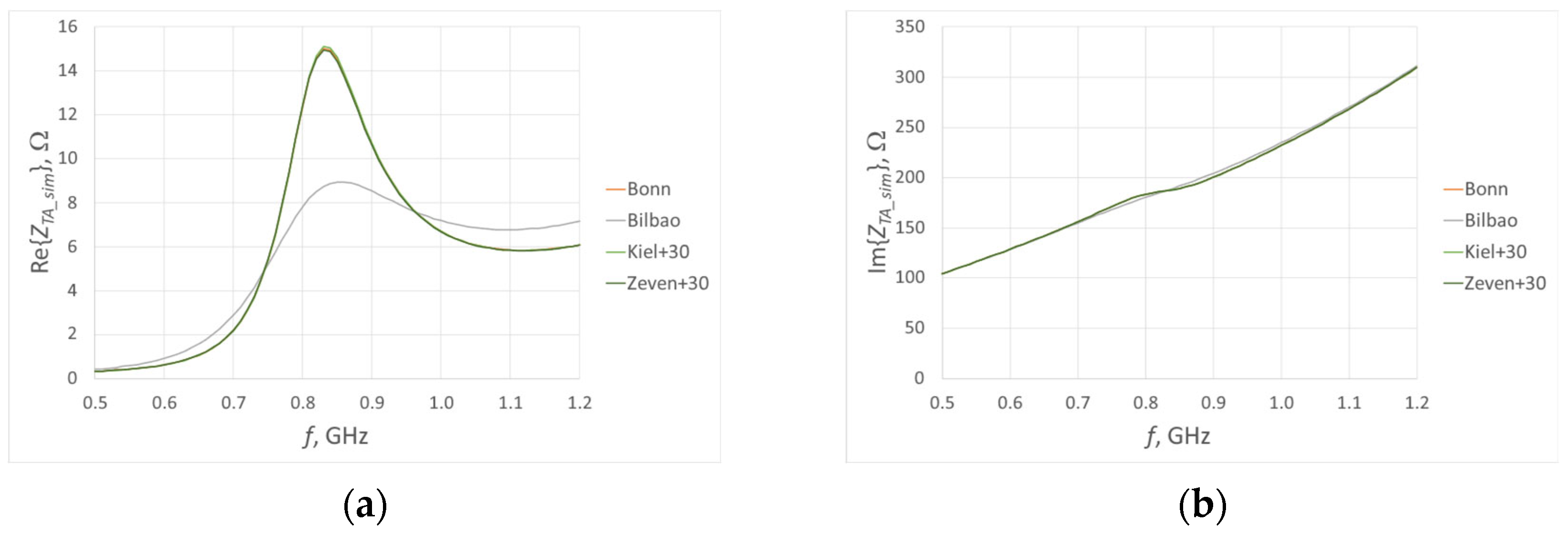
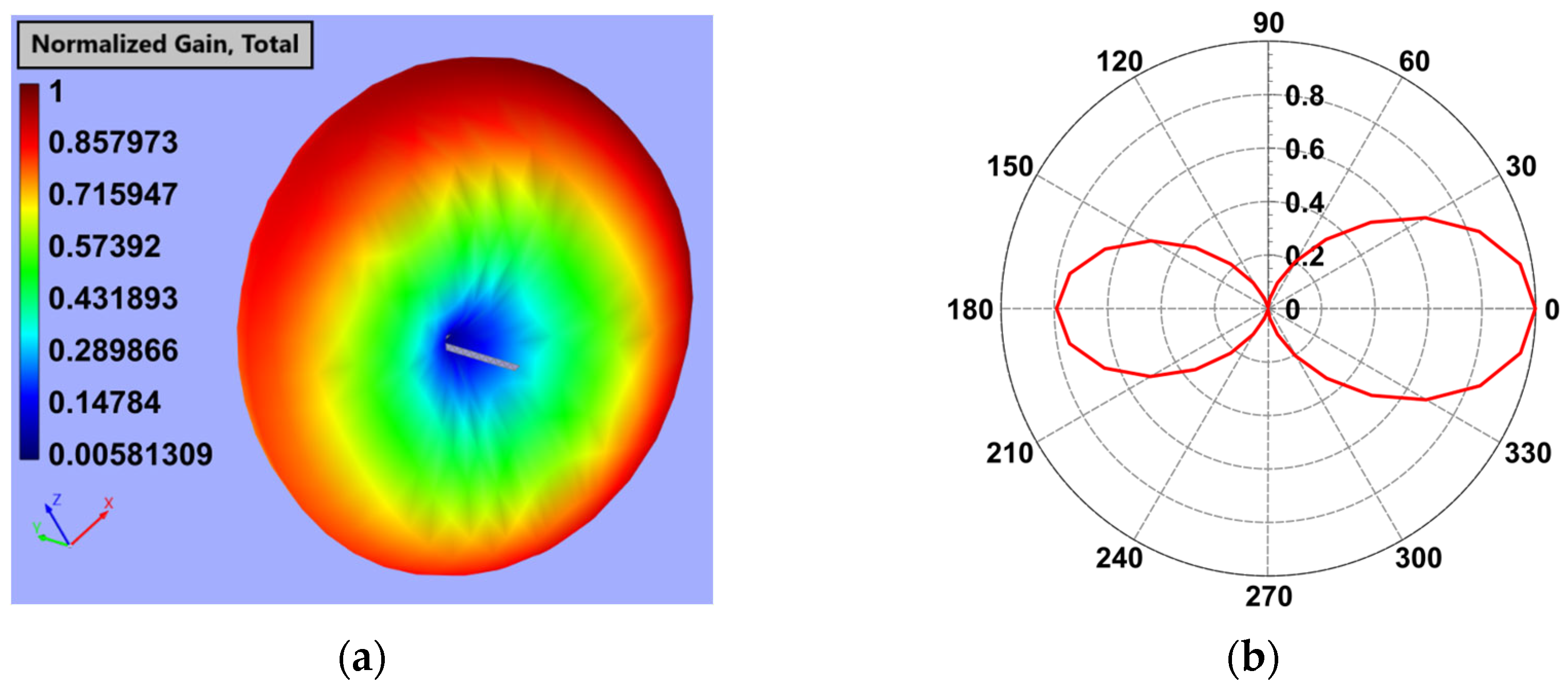
3.1. Simulation Studies
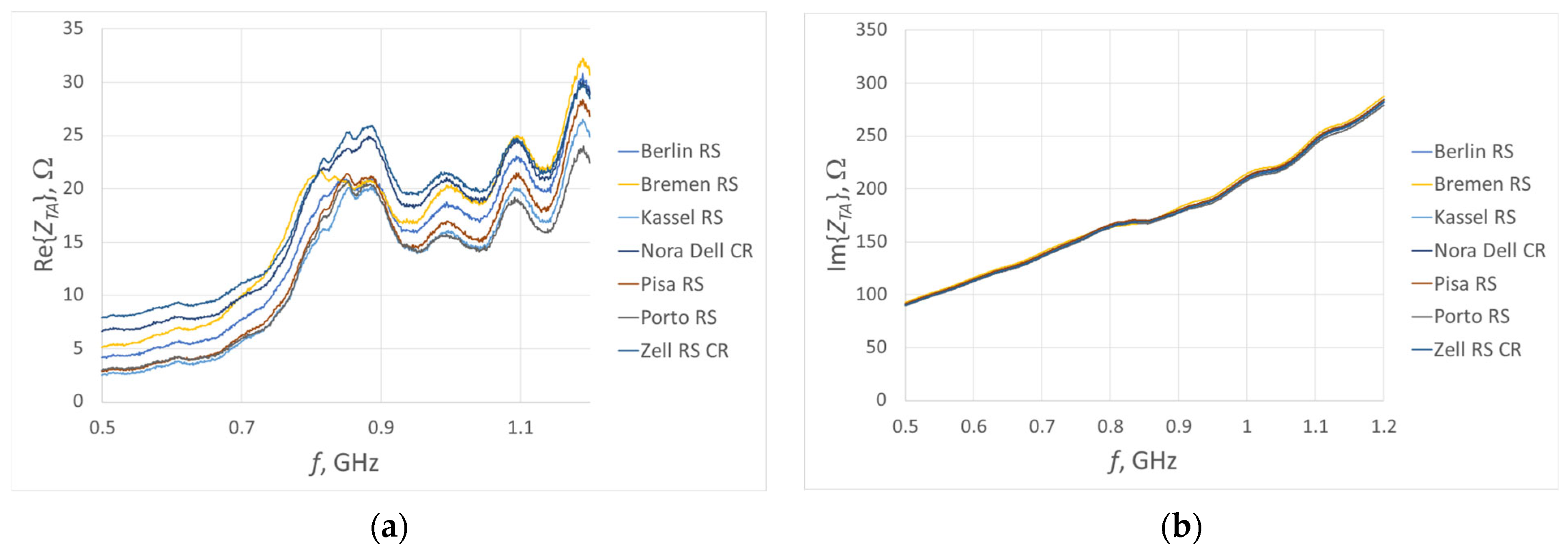
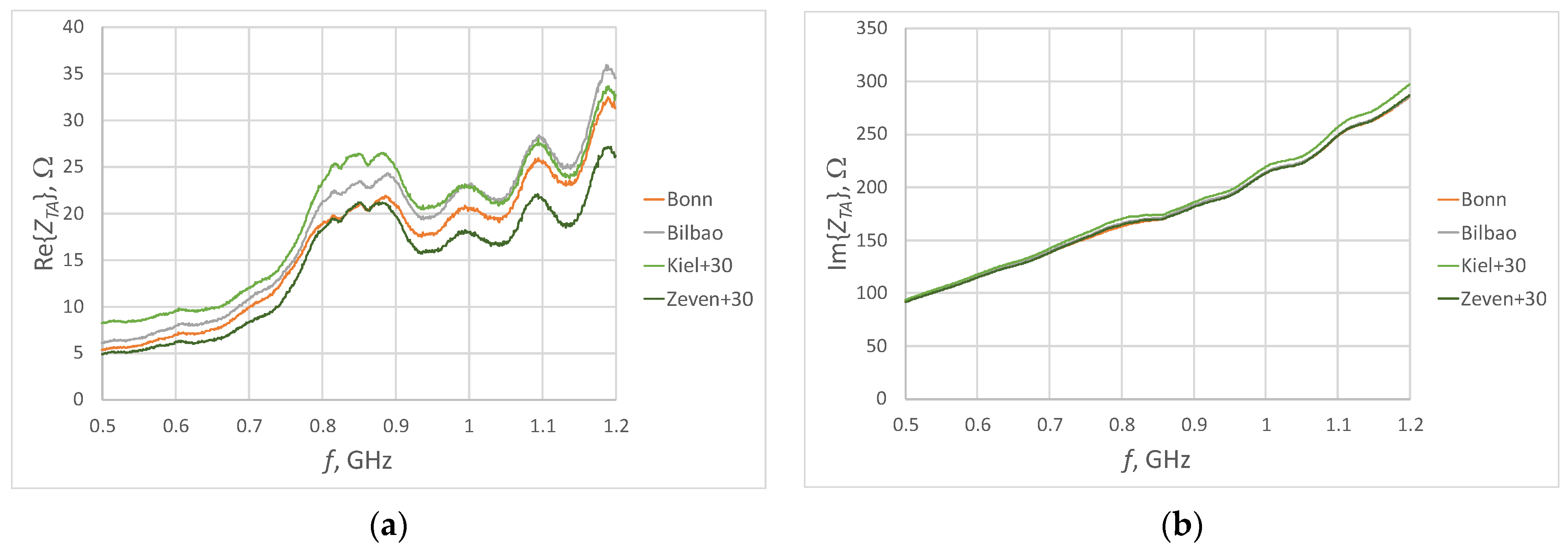
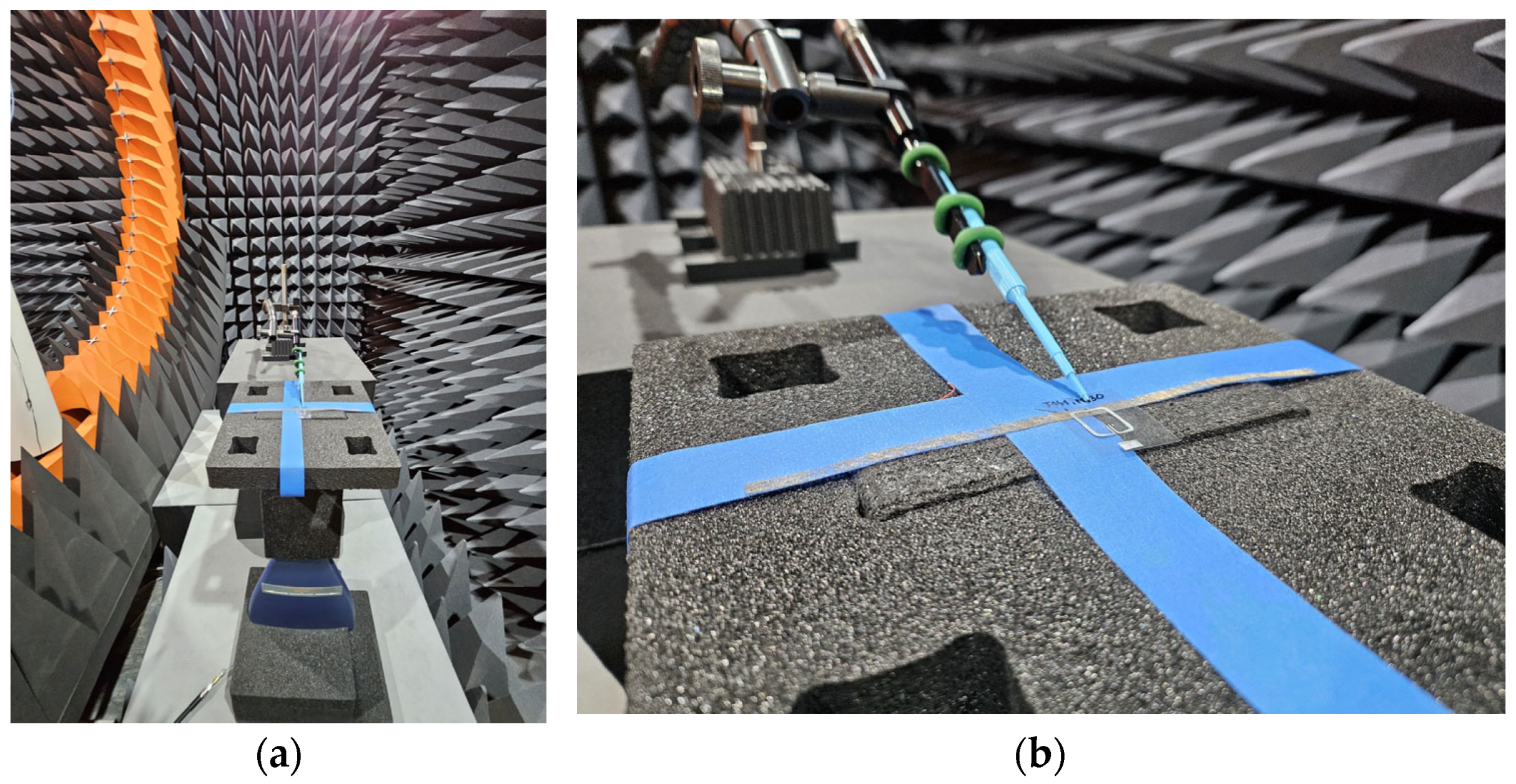
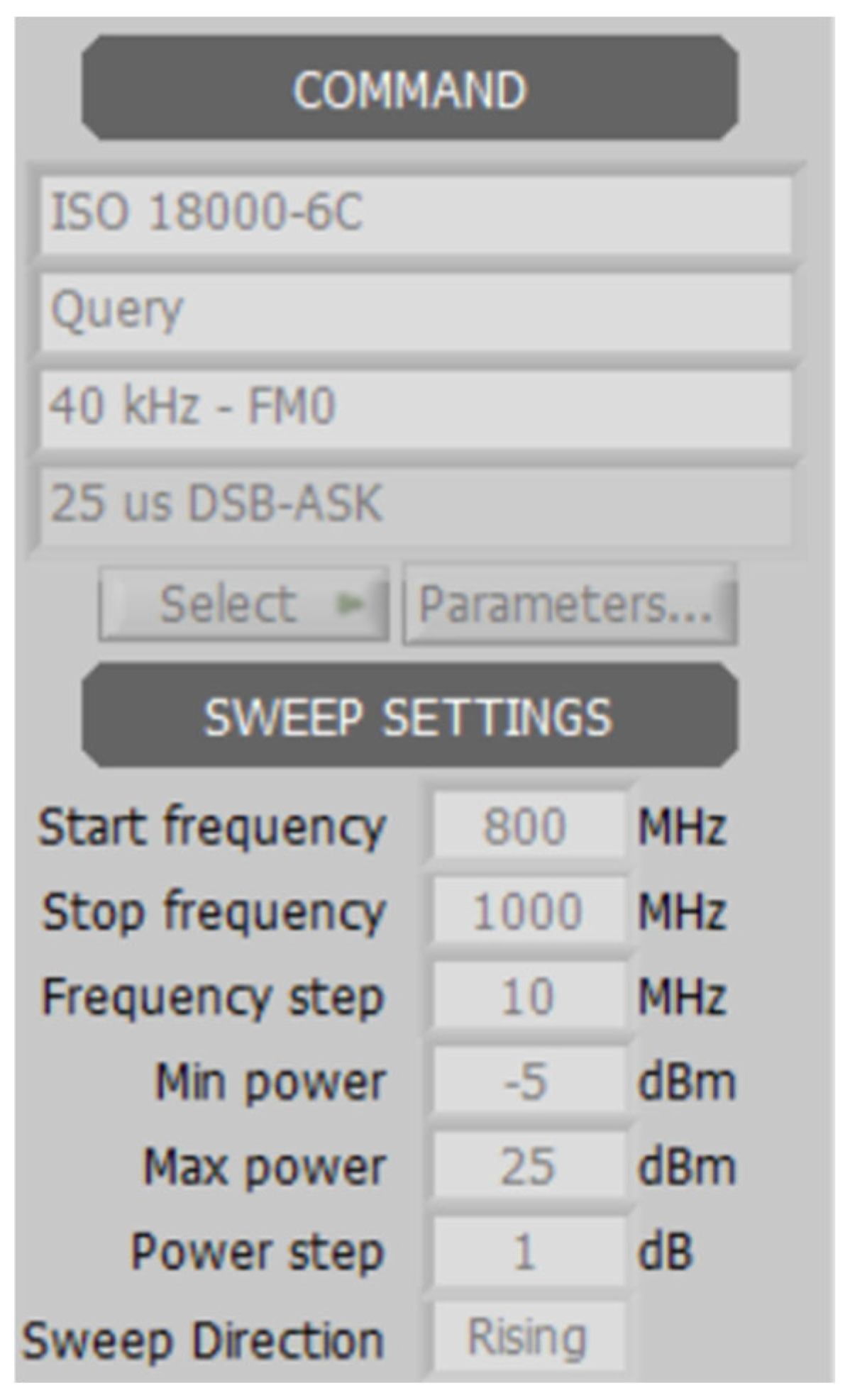
3.2. Experimental Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cruz, E.F.; Silva, P.; Serra, S.; Rodrigues, R.; Alves, M.; Oliveira, J.; da Cruz, A.M. Machine Learning-Based Data Quality Assessment for the Textile and Clothing Digital Product Passport. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pracucci, A.; Giovanardi, M. Design of a Sensor-Based Digital Product Passport for Low-Tech Manufacturing: Traceability and Environmental Monitoring in Bio-Block Production. Sensors 2025, 25, 5653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.J.; Han, C.H.; Park, K.J.; Moon, J.S.; Um, J. A Blockchain-Based Digital Product Passport System Providing a Federated Learning Environment for Collaboration Between Recycling Centers and Manufacturers to Enable Recycling Automation. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plociennik, C.; Pourjafarian, M.; Saleh, S.; Hagedorn, T.; Lopes, A.d.C.P.; Vogelgesang, M.; Baehr, J.; Kellerer, B.; Jansen, M.; Berg, H.; et al. Requirements for a Digital Product Passport to Boost the Circular Economy. In Proceedings-Series of the Gesellschaft fur Informatik (GI), Proceedings of the Lecture Notes in Informatics (LNI), Hamburg, Germany, 26–30 September 2022; Gesellschaft für Informatik: Bonn, Germany, 2022; Volume P-326. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, The Council, The European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions A New Circular Economy Action Plan For a Cleaner and More Competitive Europe. Brussels, 11.03.2020. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/resource.html?uri=cellar:9903b325-6388-11ea-b735-01aa75ed71a1.0017.02/DOC_1&format=PDF (accessed on 31 August 2025).
- Tolcha, Y.K.; Park, G.; Kim, D. Building Digital Product Passports: EPCIS 2.0 Meets Knowledge Graphs. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE International Conference on RFID (RFID), Atlanta, GA, USA, 22–24 April 2025; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Nowacki, S.; Sisik, G.M.; Angelopoulos, C.M. Digital Product Passports: Use Cases Framework and Technical Architecture Using DLT and Smart Contracts. In Proceedings of the 2023 19th International Conference on Distributed Computing in Smart Systems and the Internet of Things (DCOSS-IoT), Pafos, Cyprus, 19–21 June 2023; pp. 373–380. [Google Scholar]
- Kapoor, M.; Deshpande, P.; Kausley, S.; Rai, B. Digital Passport for Fresh Food Traceability. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE Applied Sensing Conference (APSCON), Hyderabad, India, 20–22 January 2025; pp. 363–366. [Google Scholar]
- Maló, P.; Almeida, B.; Mateus, M.; Querido, F.; Inácio, D.; Teixeira, T.; Di Orio, G.; Marques, F. From Static Records to Smart Passports: Evolving Digital Product Passports Toward Product-Service System Integration. In Proceedings of the 2025 21st International Conference on Distributed Computing in Smart Systems and the Internet of Things (DCOSS-IoT), Lucca, Italy, 9–11 June 2025; pp. 1087–1094. [Google Scholar]
- Abedi, F.; Saari, U.A.; Hakola, L. Implementation and Adoption of Digital Product Passports: A Systematic Literature Review. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Engineering, Technology, and Innovation (ICE/ITMC), Funchal, Portugal, 24–28 June 2024; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Raut, S.; Roldan, M.L.; Villarreal, P.; Caliusco, M.L.; Colombo, A.W. An Orchestration Engine Approach for Building Digital Product Passports in the Dairy Value Chain. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE 8th International Conference on Industrial Cyber-Physical Systems (ICPS), Emden, Germany, 12–15 May 2025; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Papile, F.; Del Curto, B. Textile Materials Information for Digital Product Passport Implementation in the Textile and Clothing Ecosystem: A Review on the Role of Raw Fibers in a Substantial Transition. Sustainability 2025, 17, 8804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidon, M.N.; Farnana, T.D.; Hasan, I.H.; Sali, A.; Isa, M.M. Printing of Passive RFID Tag Antennas on Flexible Substrates for Long Read Distance Applications: Materials and Techniques. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2024, 9, 100778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douhi, S.; Labihi, S.; Eddiai, A.; Lakrit, S.; El Achaby, M.; Al-Gburi, A.J.A. Design, Characterization, and Electromagnetic Performance of a Flexible Wideband RF Antenna Using Composite Materials. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2025, 10, 100847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zheng, C.; Tao, Q.; Hu, J. A Review of the Structure, Performance, Fabrication, and Impacts of Application Conditions on Wearable Textile GNSS Antennas. Textiles 2025, 5, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simorangkir, R.B.V.B.; Le, D.; Björninen, T.; Sayem, A.S.M.; Zhadobov, M.; Sauleau, R. Washing Durability of PDMS-Conductive Fabric Composite: Realizing Washable UHF RFID Tags. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2019, 18, 2572–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Gharbi, M.; Abounasr, J.; Fernández-García, R.; Gil, I. Study of Wash-Induced Performance Variability in Embroidered Antenna Sensors for Physiological Monitoring. Electronics 2025, 14, 2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toivonen, M.; Björninen, T.; Sydänheimo, L.; Ukkonen, L.; Rahmat-Samii, Y. Impact of Moisture and Washing on the Performance of Embroidered UHF RFID Tags. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2013, 12, 1590–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraru, A.; Ursachi, C.; Helerea, E. A New Washable UHF RFID Tag: Design, Fabrication, and Assessment. Sensors 2020, 20, 3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankowski-Mihułowicz, P.; Węglarski, M.; Chamera, M.; Pyt, P. Textronic UHF RFID Transponder. Sensors 2021, 21, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharif, A.; Ali, M.Z.; Arshad, K.; Assaleh, K.; Imran, M.A.; Abbasi, Q.H. Knitted Antenna Design for UHF RFID and Wearable IoT Applications. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation and USNC-URSI Radio Science Meeting (AP-S/URSI), Denver, CO, USA, 10–15 July 2022; pp. 123–124. [Google Scholar]
- Angelaki, C.; Bakogianni, S.; Tsolis, A.; Alexandridis, A.A. Embroidered Textile Patch Antennas: Design and Implementation Methodology. In Proceedings of the 2022 30th Telecommunications Forum (TELFOR), Belgrade, Serbia, 15–16 November 2022; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Bakogianni, S.; Tsolis, A.; Angelaki, C.; Alexandridis, A.A. On the Development of Embroidered Reconfigurable Dipole Antennas: A Textile Approach to Mechanical Reconfiguration. Electronics 2024, 13, 3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonefačić, D.; Bartolić, J. Embroidered Textile Antennas: Influence of Moisture in Communication and Sensor Applications. Sensors 2021, 21, 3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nizioł, M.; Jankowski-Mihułowicz, P.; Węglarski, M. The Influence of the Washing Process on the Impedance of Textronic Radio Frequency Identification Transponder Antennas. Materials 2023, 16, 4639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nizioł, M.; Jankowski-Mihułowicz, P.; Węglarski, M. Effect of Embroidery Style on the Bandwidth of Textronic RFID UHF Transponder Antenna. Sensors 2025, 25, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikulić, D.; Šopp, E.; Bonefačić, D.; Šipuš, Z. Textile Slotted Waveguide Antennas for Body-Centric Applications. Sensors 2022, 22, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, M.P.; Green, R.B. Wearable E-Textile Antenna Design for Continuous Monitoring Systems. Textiles 2025, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajin, M.A.S.; Levitt, A.S.; Liu, Y.; Amanatides, C.E.; Schauer, C.L.; Dion, G.; Dandekar, K.R. Extraction of Knitted RFID Antenna Design Parameter from Transmission Line Measurements. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation and North American Radio Science Meeting, Montreal, QC, Canada, 5–10 July 2020; pp. 1551–1552. [Google Scholar]
- Hoeye, S.V.; Fernández, M.; Alonso, L.; Antuña, C.V.; Ghekiere, P.; Casas, J.A. A Novel Surface-Independent Textile Fully Woven UHF RFID Tag. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2022, 70, 10156–10165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavrakis, A.K.; Stojanović, G.M.; Ioannidou, M.P. A Novel Approach towards Fabrication of Textile Antennas for Wearable Applications. In Proceedings of the 2024 23rd International Symposium INFOTEH-JAHORINA (INFOTEH), East Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina, 20–22 March 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Stavrakis, A.K.; Ioannidou, M.; Stojanović, G.M. A Novel, Fluidically Reconfigurable Patch Antenna Utilizing Conductive Fabrics. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Smart Systems and Technologies (SST), Osijek, Croatia, 16–18 October 2024; pp. 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Avireni, B.; Chu, Y.; Kepros, E.; Ghosh, S.K.; Chahal, P. Conductive Fabric Based RFID Wearable Textile Antennas for Product Authentication and Quality Control. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 74th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), Denver, CO, USA, 28–31 May 2024; pp. 1746–1751. [Google Scholar]
- Hasni, U.; Piper, M.E.; Lundquist, J.; Topsakal, E. Screen-Printed Fabric Antennas for Wearable Applications. IEEE Open J. Antennas Propag. 2021, 2, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shieldex Online Product Catalog. Available online: https://www.shieldex.de/en/products_categories/fabrics (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- EPC Radio-Frequency Identity Protocols Generation-2 UHF RFID Standard; Specification for RFID Air Interface Protocol for Communications at 860 MHz–960 MHz, Ver. 2.1. GS1 EPCglobal Inc.: Nashville, TN, USA, 2018.

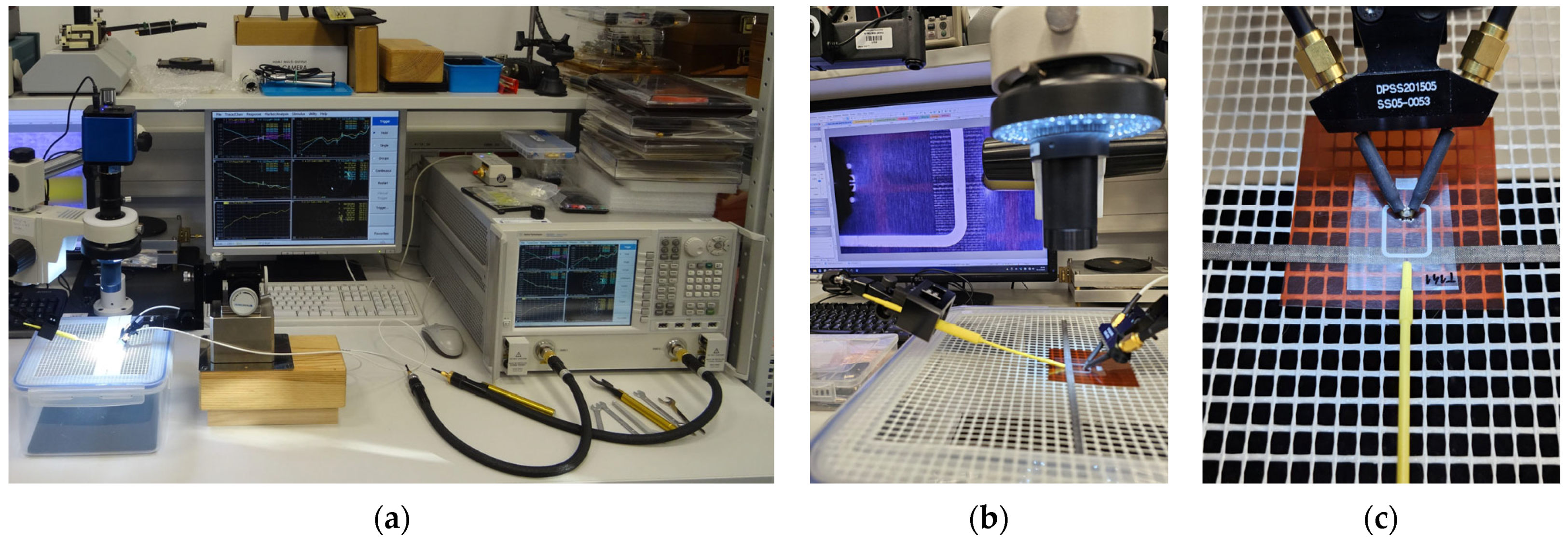
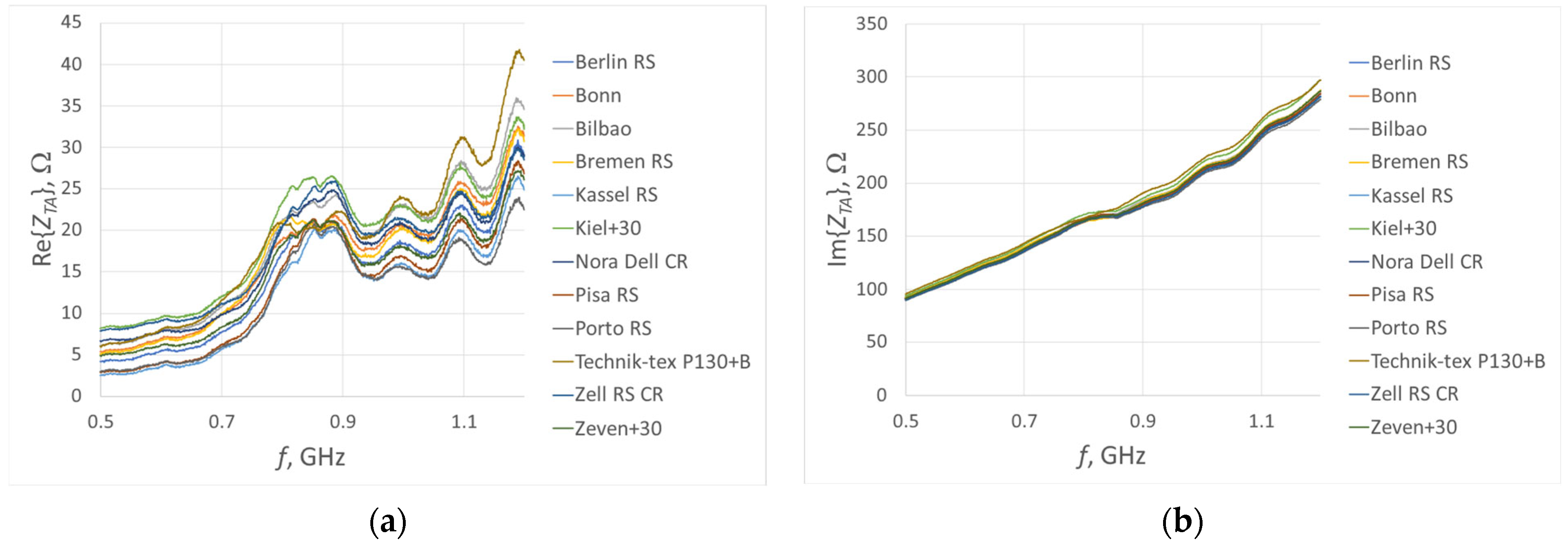
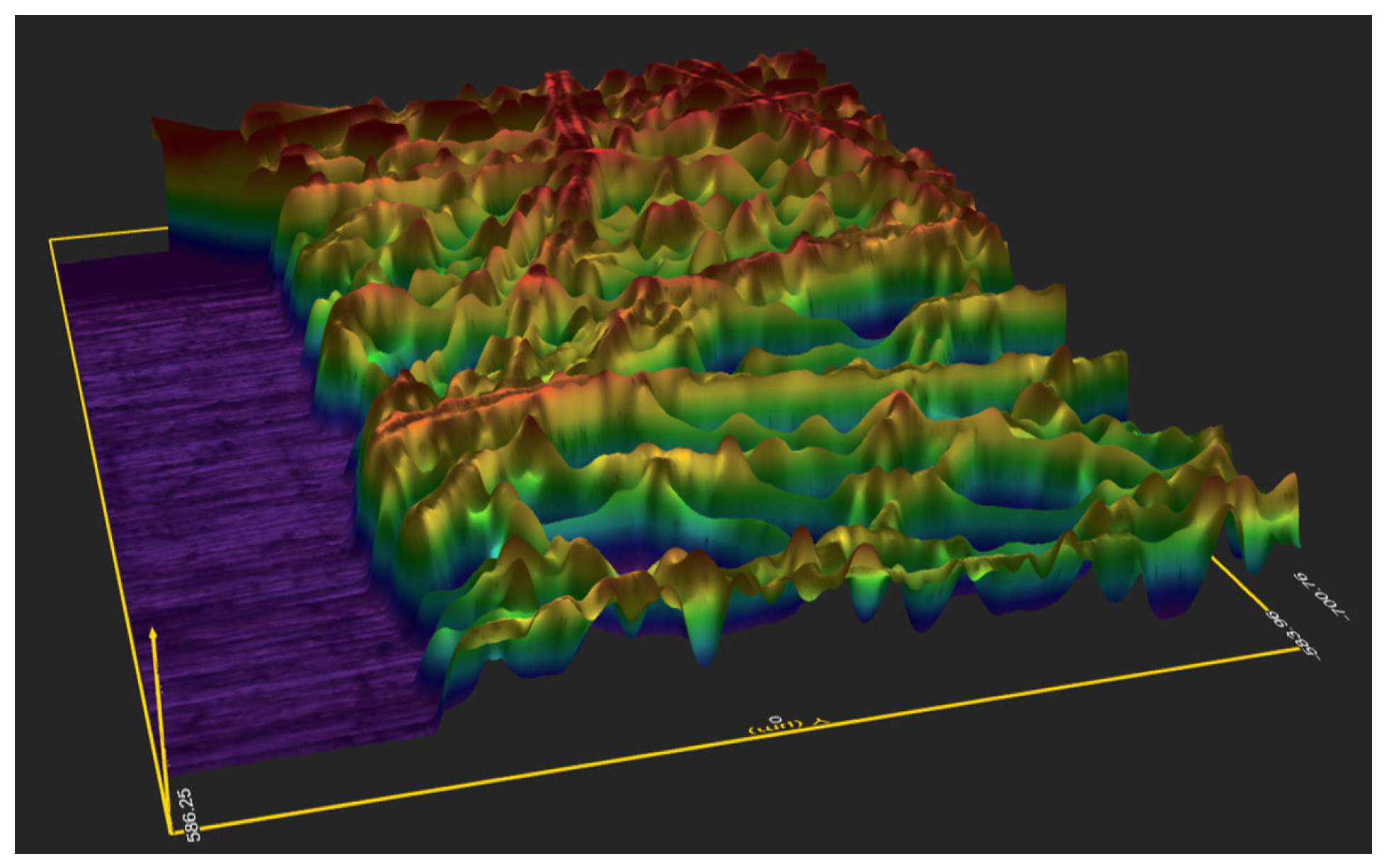
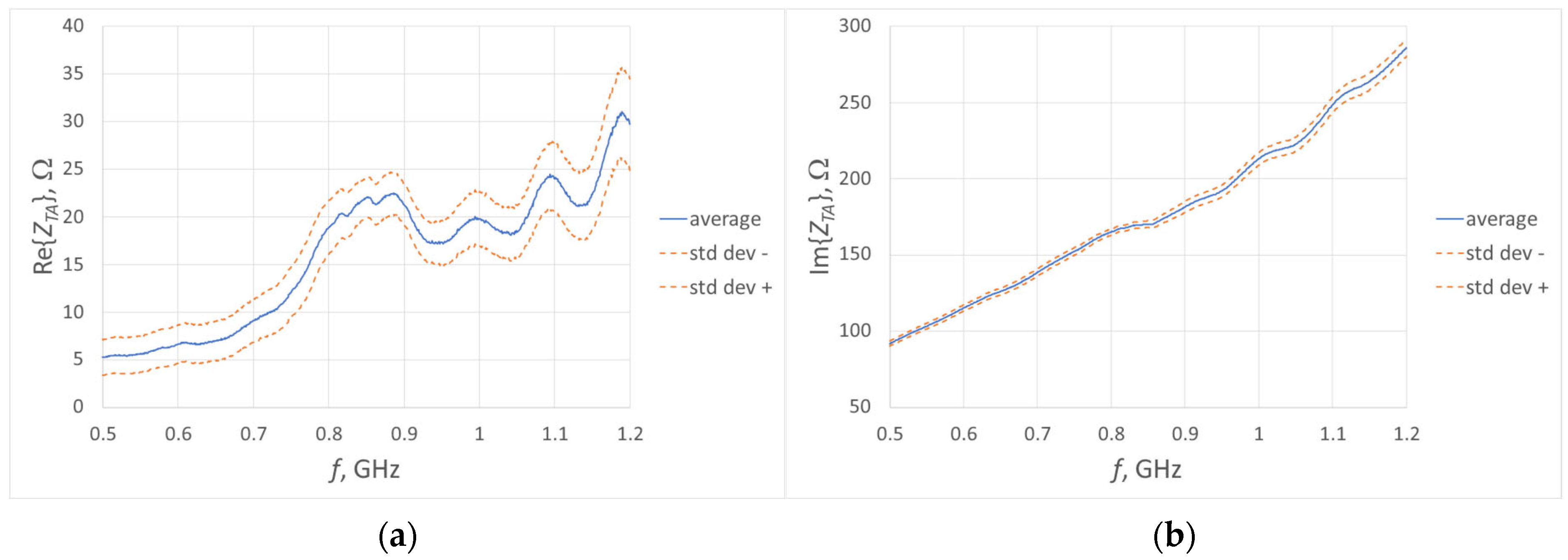
| Reference | Antenna Type | Material | Frequency | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Authors’ ongoing research | Dipole | Various conductive fabrics (Shieldex®, Bremen, Germany) | 860–960 MHz | DPP for textiles, wearable applications |
| [27] | Waveguide | Shieldex® Nora Dell conductive fabric, Shieldex® 117/17 HCB conductive yarn | 5.8 GHz | Wearable applications |
| [28] | Microstrip slot antenna | Various conductive fabrics (i.e., from Xtreme Sight Line, Henderson, NV, USA; Suzhou Amradield Co., Ltd., Suzhou, China) | 2.4, 5.8 GHz | Medical monitoring system |
| [29] | Bellyband antenna | Knitted conductive fabric made from silver-coated nylon yarn | 913 MHz | IoT-based healthcare system |
| [30] | Patch antenna | Woven conductive fabric | 865–868 MHz | Various applications based on textile antennas |
| [31] | Patch antenna | Shieldex® Kiel-SK-96 | 2.4 GHz | Wearable applications |
| [32] | Patch antenna | Shieldex® Zell RS | 3.4–6 GHz | IoT wearable applications |
| [33] | Bowtie antenna | Conductive fabrics (copper-coated brass and steel) | 915 MHz | Supply chain management |
| [34] | Coplanar keyhole; RFID tag meander antenna | Conductive ink on nonconductive fabric | 2.4, 5.8 GHz; 915 MHz | Health monitoring sensors; motion tracking |
| Fabric Model | Fabric Type | Percentage Share of Conductive Additives | Thickness, mm | Electrical Surface Resistivity, Ω/□ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Berlin RS | Woven | 14% Ag | 0.10 ± 12% | <0.3 |
| Bilbao | Non-woven | 16% Ag | 0.10 ± 20% | <2.5 |
| Bonn | Non-woven | 17% Ag | 0.25 ± 30% | <0.5 |
| Bremen RS | Woven | 18% Ag | 0.09 ± 12% | <0.3 |
| Kassel RS | Woven | 2% Ag + 50% Cu | 0.11 ± 10% | <0.03 |
| Kiel + 30 | Non-woven | 48% Cu | 0.32 ± 15% | <0.02 |
| Nora Dell CR | Woven | 7% Ag + 48% Cu + 3.5% Ni | 0.125 ± 15% | <0.009 |
| Pisa RS | Woven | 61% Cu + 4% Ni | 0.09 ± 12% | <0.05 |
| Porto RS | Woven | 65% Cu + 4% Sn | 0.10 ± 12% | <0.02 |
| Technik-tex P130 + B | Knitted | 26,5% Ag | 0.55 ± 15% | <2 |
| Zell RS CR | Woven | 10% Ag + 34% Cu + 4% Sn | 0.12 ± 15% | <0.02 |
| Zeven + 30 | Non-woven | 42% Cu + 16% Sn | 0.32 ± 20% | <0.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nizioł, M.; Jankowski-Mihułowicz, P.; Węglarski, M. Analysis of the Impact of Conductive Fabrics Parameters on Textronic UHF RFID Transponder Antennas. Electronics 2025, 14, 4552. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14234552
Nizioł M, Jankowski-Mihułowicz P, Węglarski M. Analysis of the Impact of Conductive Fabrics Parameters on Textronic UHF RFID Transponder Antennas. Electronics. 2025; 14(23):4552. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14234552
Chicago/Turabian StyleNizioł, Magdalena, Piotr Jankowski-Mihułowicz, and Mariusz Węglarski. 2025. "Analysis of the Impact of Conductive Fabrics Parameters on Textronic UHF RFID Transponder Antennas" Electronics 14, no. 23: 4552. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14234552
APA StyleNizioł, M., Jankowski-Mihułowicz, P., & Węglarski, M. (2025). Analysis of the Impact of Conductive Fabrics Parameters on Textronic UHF RFID Transponder Antennas. Electronics, 14(23), 4552. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14234552









