Frequency-Aware Multi-Rate Resampling with Multi-Band Deep Supervision for Modular Speech Denoising
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Wave-U-Net and the Focus on Temporal Modeling
2.2. Comparison with Sub-Band and Hybrid Approaches
2.3. Spectral Information Loss from Downsampling
2.4. Recent Advancements (2022–2025)
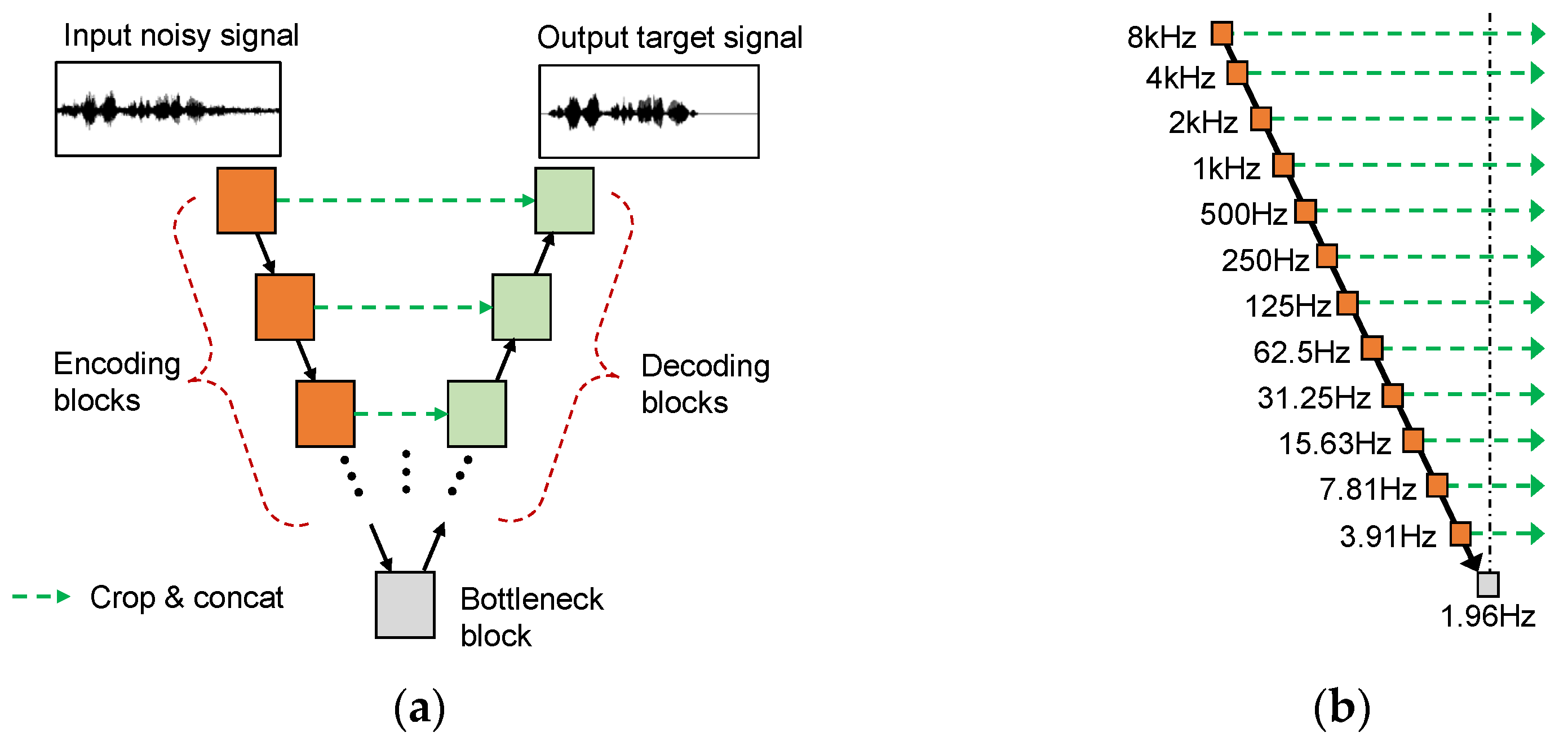
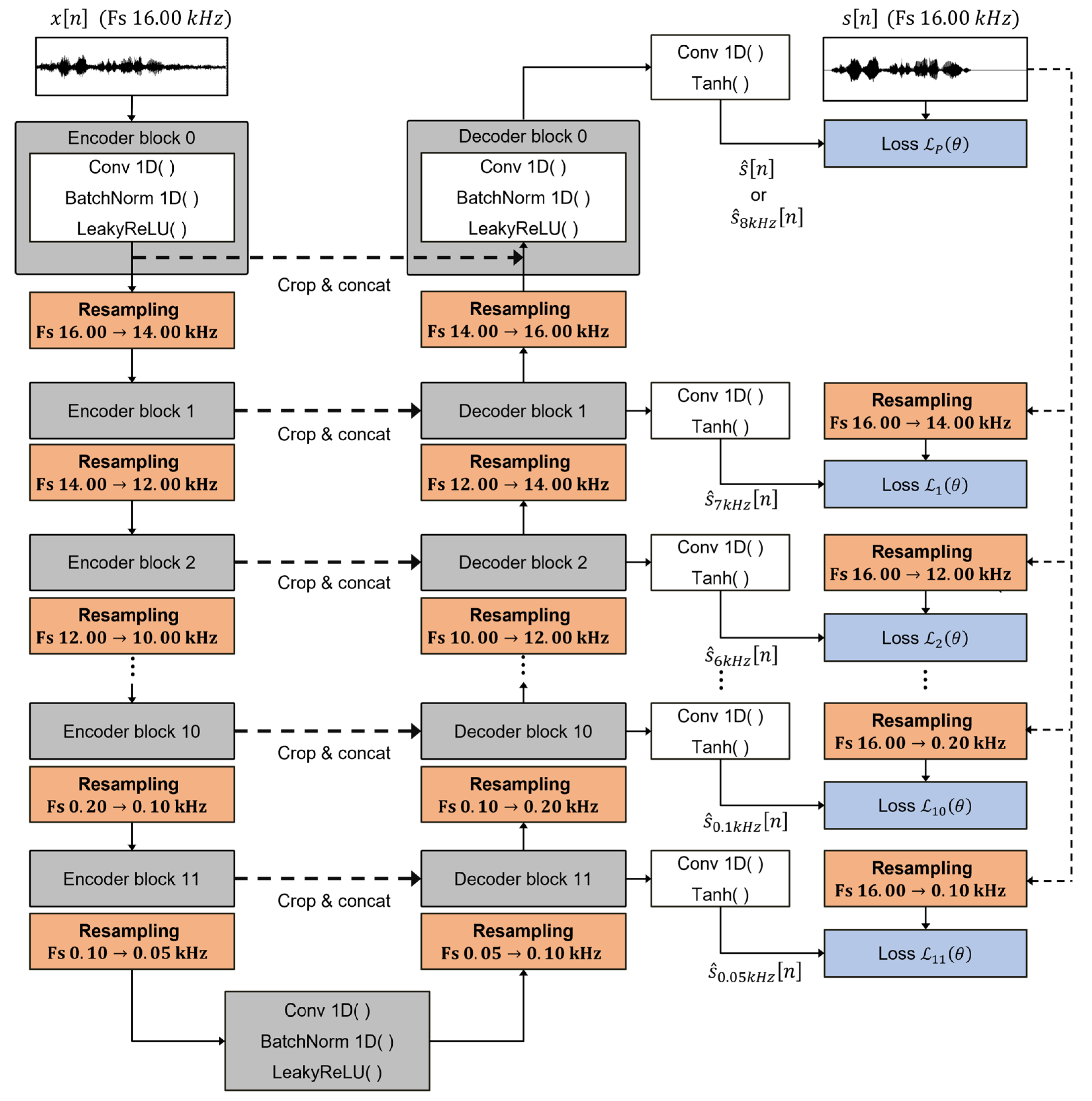
3. Proposed Model Architecture
3.1. Design Principle and Overall Structure
3.2. Multi-Rate Resampling Module
3.3. Multi-Band Deep Supervision
3.4. Analysis of the Proposed Framework
4. Experimental Setup
4.1. Experimental Design, Datasets, and Metrics
4.2. Implementation Details
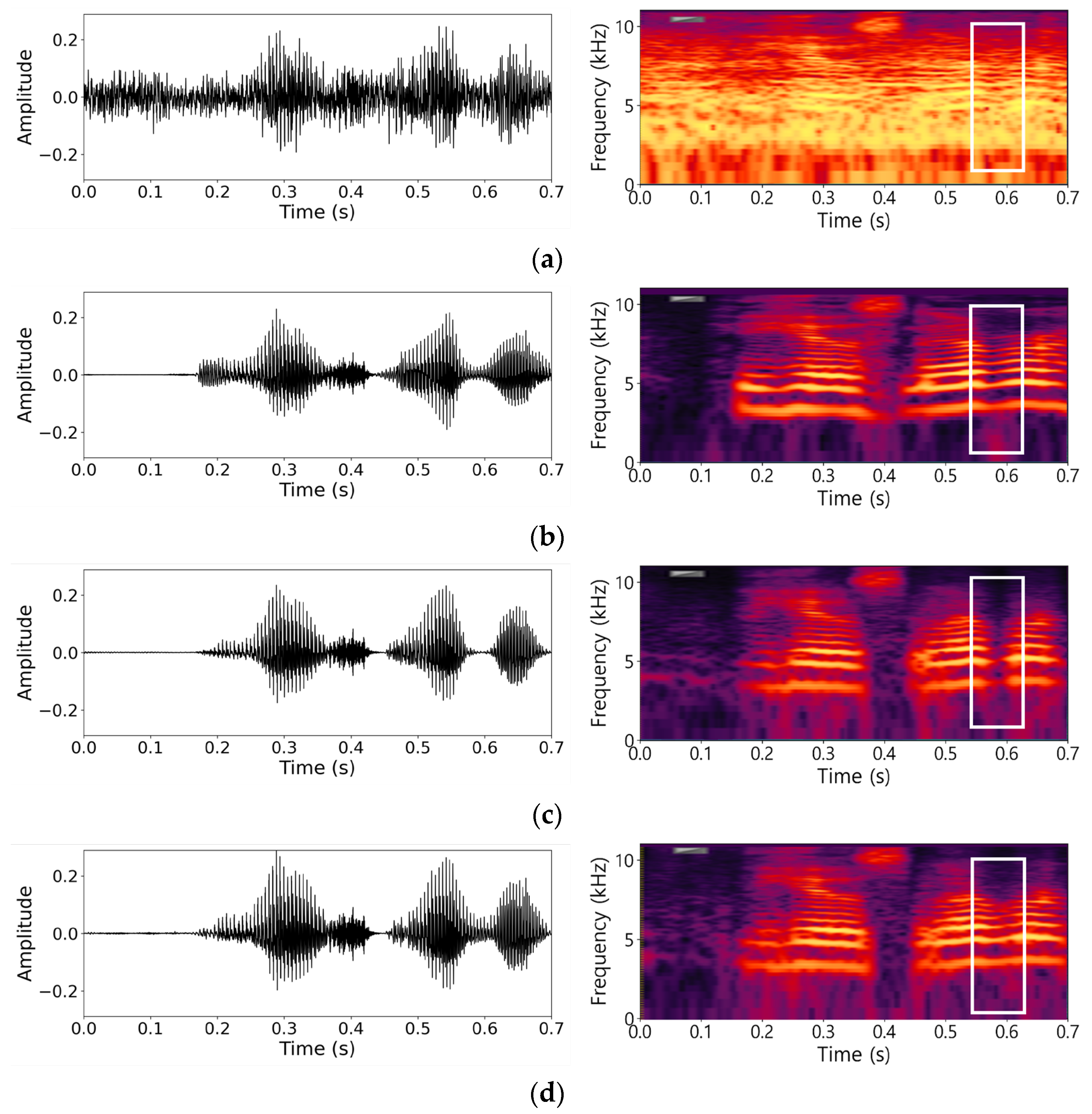
5. Results and Discussion
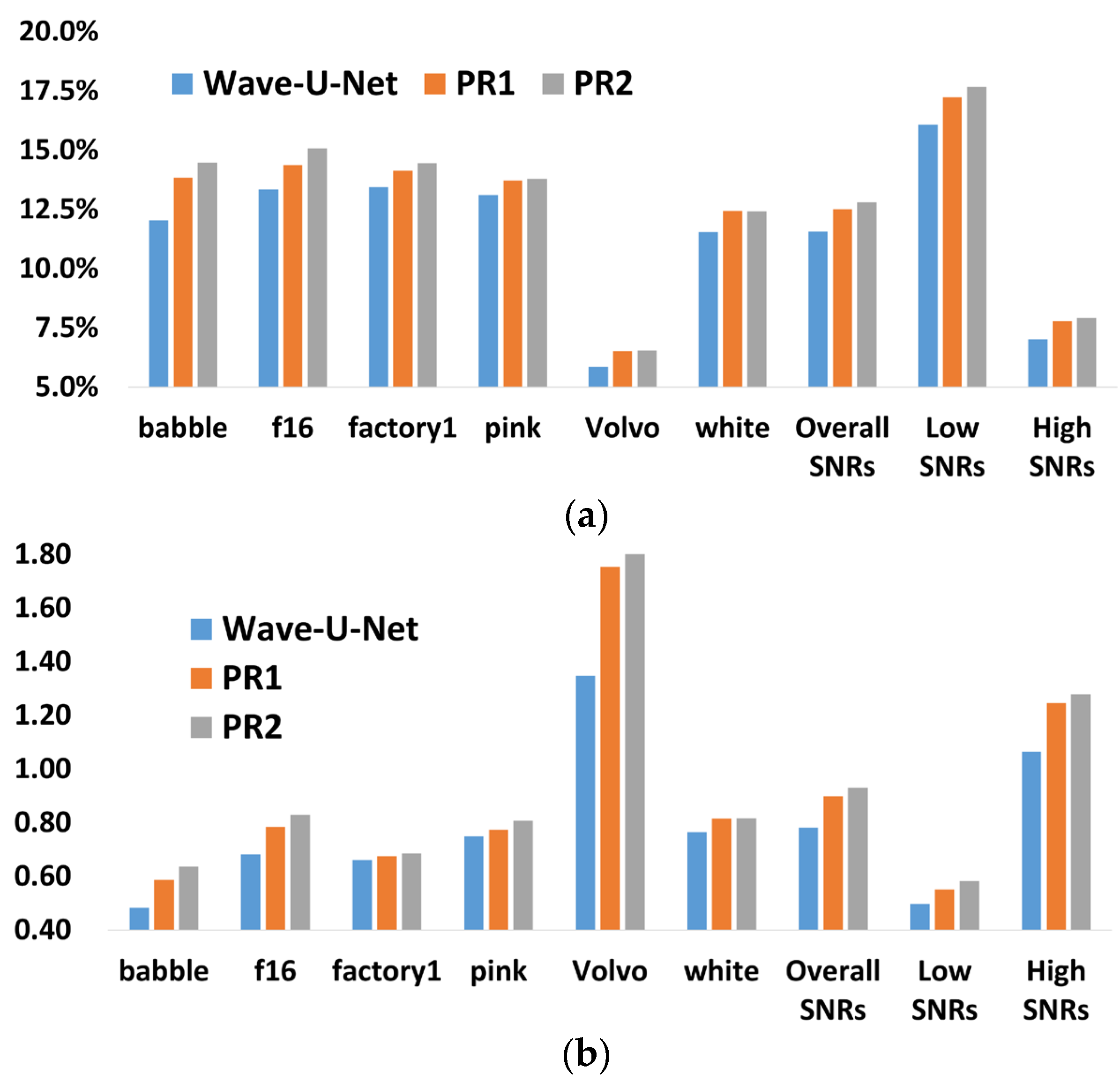
5.1. Performance Analysis of Proposed Methods
5.1.1. Effect of Principled Resampling with Anti-Aliasing
5.1.2. Effect of Multi-Band Deep Supervision
5.2. Further Analysis and Robustness
6. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boll, S.F. Suppression of Acoustic Noise in Speech Using Spectral Subtraction. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1979, 27, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalart, P.; Vieira, J. Speech Enhancement Based on a Priori SNR Estimation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Atlanta, GA, USA, 9 May 1996; pp. 629–632. [Google Scholar]
- Ephraim, Y.; Malah, D. Speech Enhancement Using a Minimum Mean-Square Error Short-Time Spectral Amplitude Estimator. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1984, 32, 1109–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Chen, J. Supervised Speech Separation Based on Deep Learning: An Overview. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2018, 26, 1702–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.S.; Kim, J.H.; Huh, J.; Kim, A.; Ha, J.W.; Lee, K. Phase-Aware Speech Enhancement with Deep Complex U-Net. In Proceedings of the ICLR 2019, New Orleans, LA, USA, 6–9 May 2019; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Stoller, D.; Ewert, S.; Dixon, S. Wave-U-Net: A Multiscale Neural Network for End-to-End Audio Source Separation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.03185. [Google Scholar]
- Macartney, C.; Weyde, T. Improved Speech Enhancement with the Wave-U-Net. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.11307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Défossez, A.; Synnaeve, G.; Adi, Y. Real-Time Speech Enhancement in the Waveform Domain. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2020, Shanghai, China, 25–29 October 2020; pp. 3291–3295. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, Z.; Ping, W.; Dantrey, A.; Catanzaro, B. Speech Denoising in the Waveform Domain with Self-Attention. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2202.07790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Watanabe, S.; Richard, A.; Yu, C.; Tsao, Y. Conditional Diffusion Probabilistic Model for Speech Enhancement. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022, Singapore, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 7402–7406. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Cornell, S.; Choi, S.; Lee, Y.; Kim, B.-Y.; Watanabe, S. TF-GridNet: Integrating Full- and Sub-Band Modeling for Speech Separation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.12433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Chen, H.; Luo, Y.; Gu, R.; Weng, C. High Fidelity Speech Enhancement with Band-split RNN. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2023, Dublin, Ireland, 20–24 August 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Défossez, A. Hybrid Spectrogram and Waveform Source Separation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.03600. [Google Scholar]
- Schröter, H.; Escalante-B, A.N.; Rosenkranz, T.; Maier, A. DeepFilterNet: A Low-Complexity Speech Enhancement Framework for Full-Band Audio Based on Deep Filtering. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022, Singapore, 22–27 May 2022; pp. 7492–7496. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, H.; Aazami, A.; Gopal, V.; Naderi, B.; Braun, S.; Cutler, R.; Ju, A.; Zohourian, M.; Tang, M.; Gamper, H.; et al. ICASSP 2023 Deep Noise Suppression Challenge. IEEE Open J. Signal Process 2024, 5, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, P.; Tan, Z.; Østergaard, J.; Jensen, J.; Alstrøm, T.S.; May, T. Investigating the Design Space of Diffusion Models for Speech Enhancement. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process 2024, 32, 4486–4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröter, H.; Rosenkranz, T.; Escalante-B, A.N.; Maier, A. DeepFilterNet: Perceptually Motivated Real-Time Speech Enhancement. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.08227. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Mesgarani, N. Conv-TasNet: Surpassing Ideal Time–Frequency Magnitude Masking for Speech Separation. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2019, 27, 1256–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the MICCAI 2015, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Crochiere, R.E.; Rabiner, L.R. Multirate Digital Signal Processing; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, X.; Su, X.; Horaud, R.; Li, X. FullSubNet: A Full-Band and Sub-Band Fusion Model for Real-Time Single-Channel Speech Enhancement. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021, Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 6633–6637. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Rao, W.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yu, T.; Shang, S.; Meng, H. Speech Enhancement with Fullband-Subband Cross-Attention Network. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2022, Incheon, Republic of Korea, 18–22 September 2022; pp. 976–980. [Google Scholar]
- Westhausen, N.L.; Meyer, B.T. Dual-Signal Transformation LSTM Network for Real-Time Noise Suppression. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2020, Shanghai, China, 25–29 October 2020; pp. 2477–2481. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C.E. Communication in the Presence of Noise. Proc. IRE 1949, 37, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ITU-T Rec. P.862; Perceptual Evaluation of Speech Quality (PESQ), An Objective Method for End-to-End Speech Quality Assessment of Narrowband Telephone Networks and Speech Codecs. International Telecommunication Union–Telecommunication Standardization Sector: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001.
- Taal, C.H.; Hendriks, R.C.; Heusdens, R.; Jensen, J. A Short-Time Objective Intelligibility Measure for Time–Frequency Weighted Noisy Speech. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2010, Dallas, TX, USA, 14–19 March 2010; pp. 4214–4217. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.Y.; Xie, S.; Gallagher, P.; Zhang, Z.; Tu, Z. Deeply-Supervised Nets. In Proceedings of the Eighteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, San Diego, CA, USA, 9–12 May 2015; pp. 562–570. [Google Scholar]
- ANSI S3.5-1997; Methods for Calculation of the Speech Intelligibility Index. ANSI: New York, NY, USA, 1997.
- Roux, J.L.; Wisdom, S.; Erdogan, H.; Hershey, J.R. SDR—Half-Baked or Well Done? In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019, Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 626–630. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.L.; Yang, Y.B. SA-Net: Shuffle Attention for Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021, Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 2235–2239. [Google Scholar]
- Garofolo, J.S.; Lamel, L.F.; Fisher, W.M.; Fiscus, J.G.; Pallett, D.S.; Dahlgren, N.L.; Zue, V. DARPA TIMIT Acoustic-Phonetic Continuous Speech Corpus CD-ROM. NIST Speech Disc 1–1.1; NIST: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Varga, A.; Steeneken, H.J.M. Assessment for Automatic Speech Recognition: II. NOISEX-92: A Database and an Experiment to Study the Effect of Additive Noise on Speech Recognition Systems. Speech Commun. 1993, 12, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, C.K.A.; Gopal, V.; Cutler, R.; Beyrami, E.; Cheng, R.; Dubey, H.; Matusevych, S.; Aichner, R.; Aazami, A.; Braun, S.; et al. The Interspeech 2020 Deep Noise Suppression Challenge: Datasets, Subjective Testing Framework, and Challenge Results. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2020, Shanghai, China, 25–29 October 2020; pp. 2492–2496. [Google Scholar]
| Encoder–Decoder Level | Conventional Fs | Conventional Effective Band | Proposed Fs | Proposed Effective Band |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 16.00 | 8.00 | 16.00 | 8.00 |
| 1 | 8.00 | 4.00 | 14.00 | 7.00 |
| 2 | 4.00 | 2.00 | 12.00 | 6.00 |
| 3 | 2.00 | 1.00 | 10.00 | 5.00 |
| 4 | 1.00 | 0.50 | 8.00 | 4.00 |
| 5 | 0.50 | 0.25 | 6.00 | 3.00 |
| 6 | 0.25 | 0.125 | 4.00 | 2.00 |
| 7 | 0.125 | 0.0625 | 2.00 | 1.00 |
| 8 | 0.0625 | 0.0313 | 1.50 | 0.75 |
| 9 | 0.0313 | 0.0156 | 1.00 | 0.50 |
| 10 | 0.0200 | 0.0100 | 0.50 | 0.25 |
| 11 | 0.0100 | 0.0050 | 0.20 | 0.10 |
| Model | Parameters (M) | GFLOPs | RTF |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline Wave-U-Net | 10.13 | 4.92 | 0.0042 |
| Proposed (PR1) | 10.13 | 38.28 | 0.0048 |
| Proposed (PR2) | 10.13 | 38.18 | 0.0142 |
| Proposed (PR3) | 10.13 | 38.18 | 0.0142 |
| Hyperparameter | Setting |
|---|---|
| Optimizer | Adam |
| Learning Rate | 5 × 10−4 (fixed) |
| Adam Betas | (0.9, 0.999) |
| Batch Size | 32 |
| Max Epochs | 1200 |
| Early Stopping Patience | 300 |
| Encoder Kernel Size | 15 |
| Decoder Kernel Size | 5 |
| Activation Function | LeakyReLU (slope = 0.1) |
| Final Activation Function | Tanh |
| Encoder Channels | 24, 48,..., 288 |
| Methods | Noise Conditions | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Babble | F16 | Factory | Pink | Volvo | White | |
| PR2 | 0.720 (0.960) | 0.761 (0.964) | 0.734 (0.955) | 0.752 (0.957) | 0.977 (0.994) | 0.789 (0.955) |
| PR3 | 0.719 (0.962) | 0.767 (0.966) | 0.730 (0.958) | 0.752 (0.959) | 0.977 (0.994) | 0.796 (0.956) |
| Methods | Noise Conditions | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Babble | F16 | Factory | Pink | Volvo | White | |
| PR2 | 1.301 (2.642) | 1.444 (2.718) | 1.327 (2.529) | 1.382 (2.604) | 3.257 (4.112) | 1.405 (2.513) |
| PR3 | 1.335 (2.674) | 1.477 (2.752) | 1.351 (2.610) | 1.418 (2.656) | 3.231 (4.150) | 1.443 (2.612) |
| Model | Description | STOI | PESQ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Original Wave-U-Net | 0.882 | 2.25 |
| Model A | Baseline + Attention Module (Temporal) | 0.915 | 2.58 |
| Model B | Baseline + Proposed Module (Frequency-Aware) | 0.911 | 2.65 |
| Model C | Baseline + Attention + Proposed (Combined) | 0.926 | 2.77 |
| Noise Type | Model | STOI | PESQ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Typing Noise | Baseline | 0.78 | 1.85 |
| Model B | 0.82 | 2.01 | |
| Siren Noise | Baseline | 0.75 | 1.79 |
| Model B | 0.79 | 1.95 |
| Model | ∆STOI (Avg.) | ∆PESQ (Avg.) |
|---|---|---|
| Baseline (Wave-U-Net) | 0.116 | 0.78 |
| PR1 | 0.125 | 0.90 |
| PR2 | 0.128 | 0.93 |
| PR3 | 0.129 | 0.97 |
| CleanUNet | 0.120 | 0.92 |
| Conv-TasNet | 0.113 | 0.73 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.M. Frequency-Aware Multi-Rate Resampling with Multi-Band Deep Supervision for Modular Speech Denoising. Electronics 2025, 14, 4523. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14224523
Kim SM. Frequency-Aware Multi-Rate Resampling with Multi-Band Deep Supervision for Modular Speech Denoising. Electronics. 2025; 14(22):4523. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14224523
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Seon Man. 2025. "Frequency-Aware Multi-Rate Resampling with Multi-Band Deep Supervision for Modular Speech Denoising" Electronics 14, no. 22: 4523. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14224523
APA StyleKim, S. M. (2025). Frequency-Aware Multi-Rate Resampling with Multi-Band Deep Supervision for Modular Speech Denoising. Electronics, 14(22), 4523. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14224523






