Modern Approaches to Software Vulnerability Detection: A Survey of Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Large Language Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Reviews
3. Background
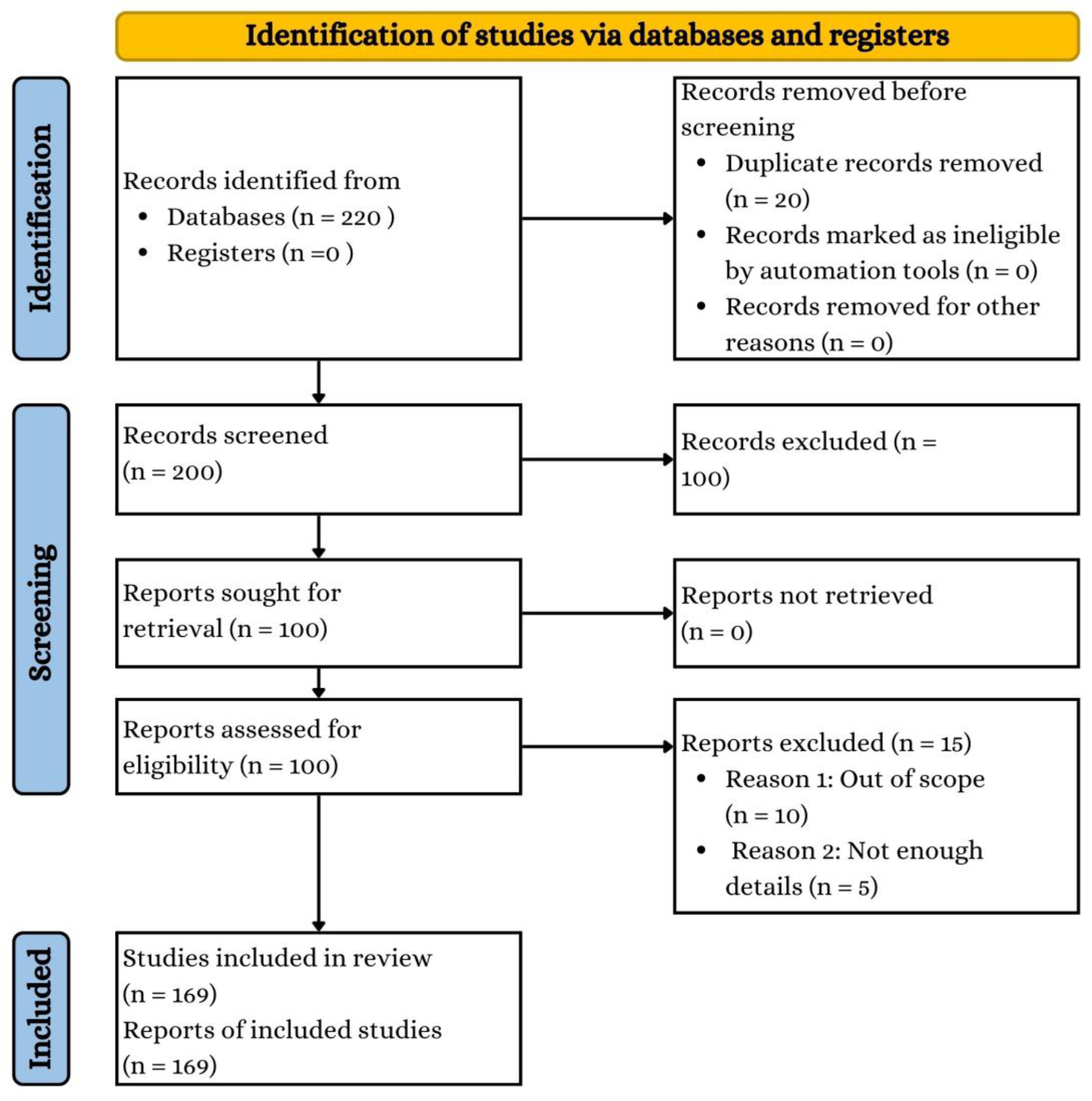
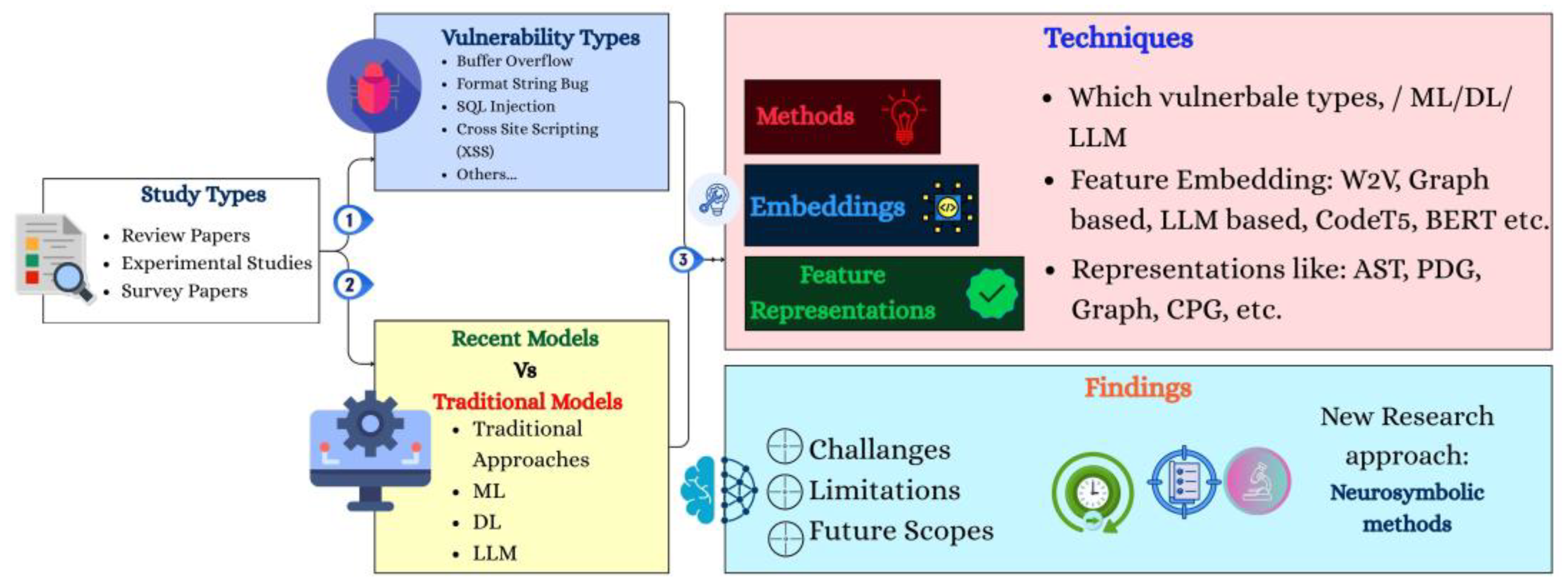
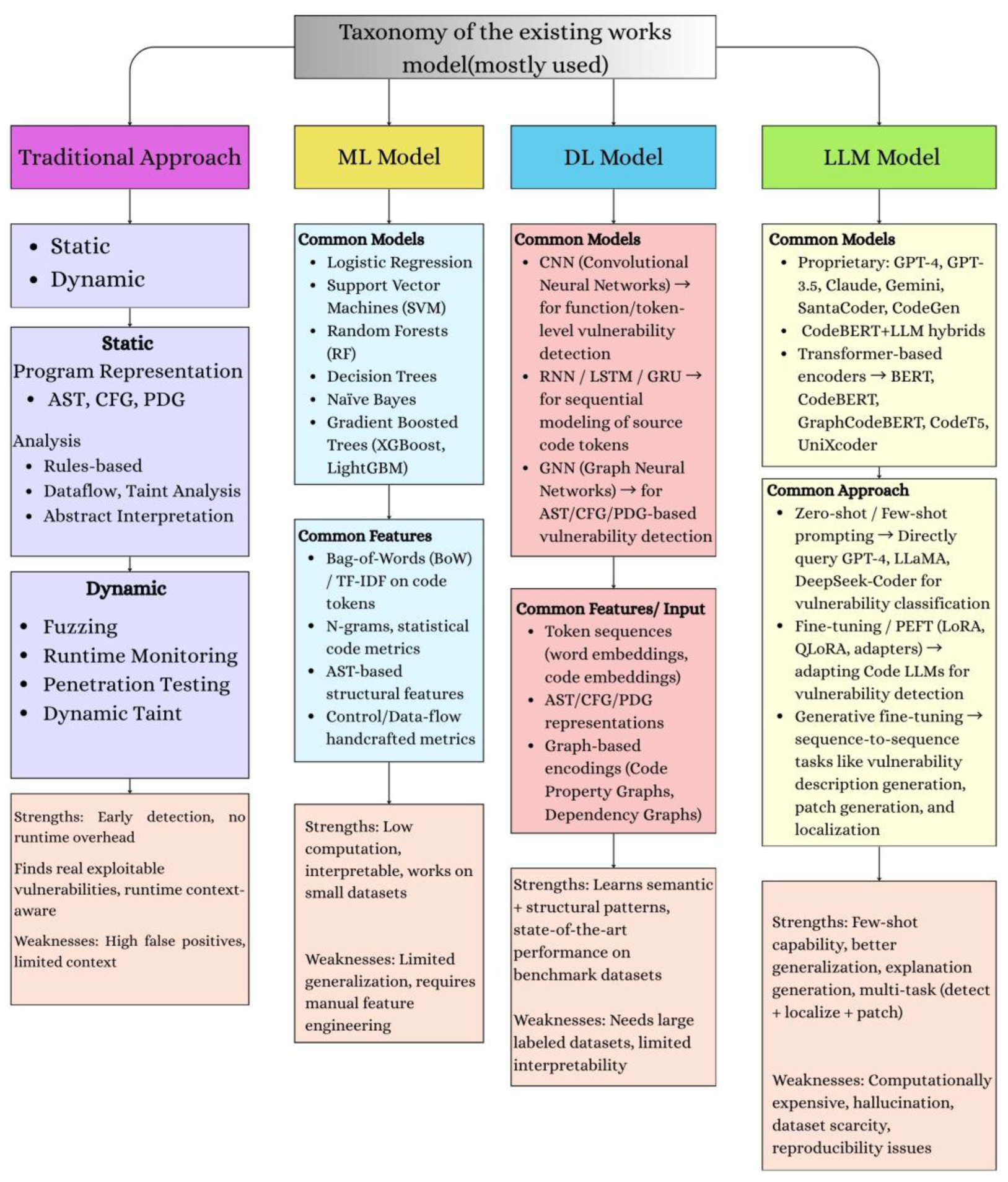
3.1. Methodology
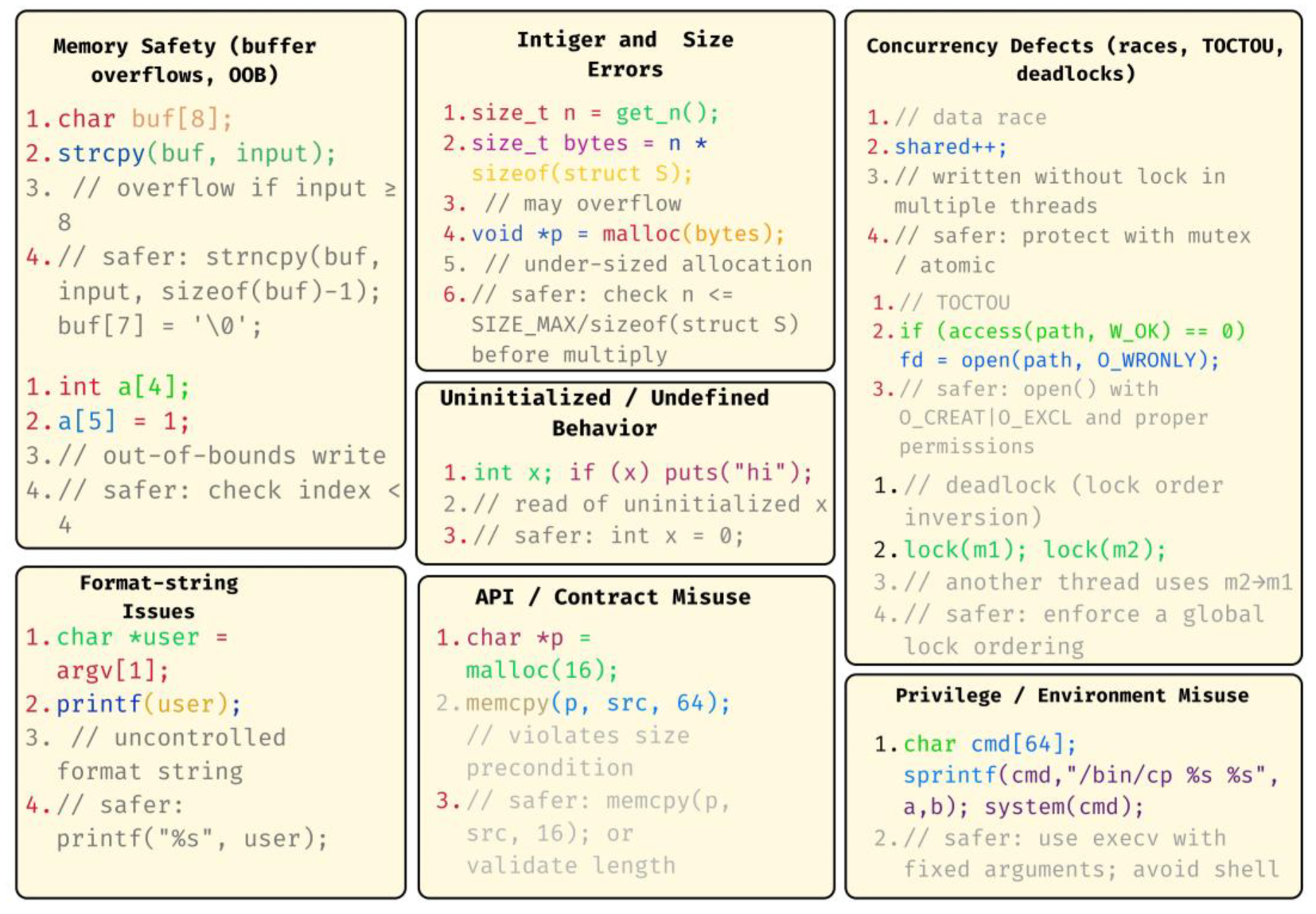
3.2. Vulnerability Types
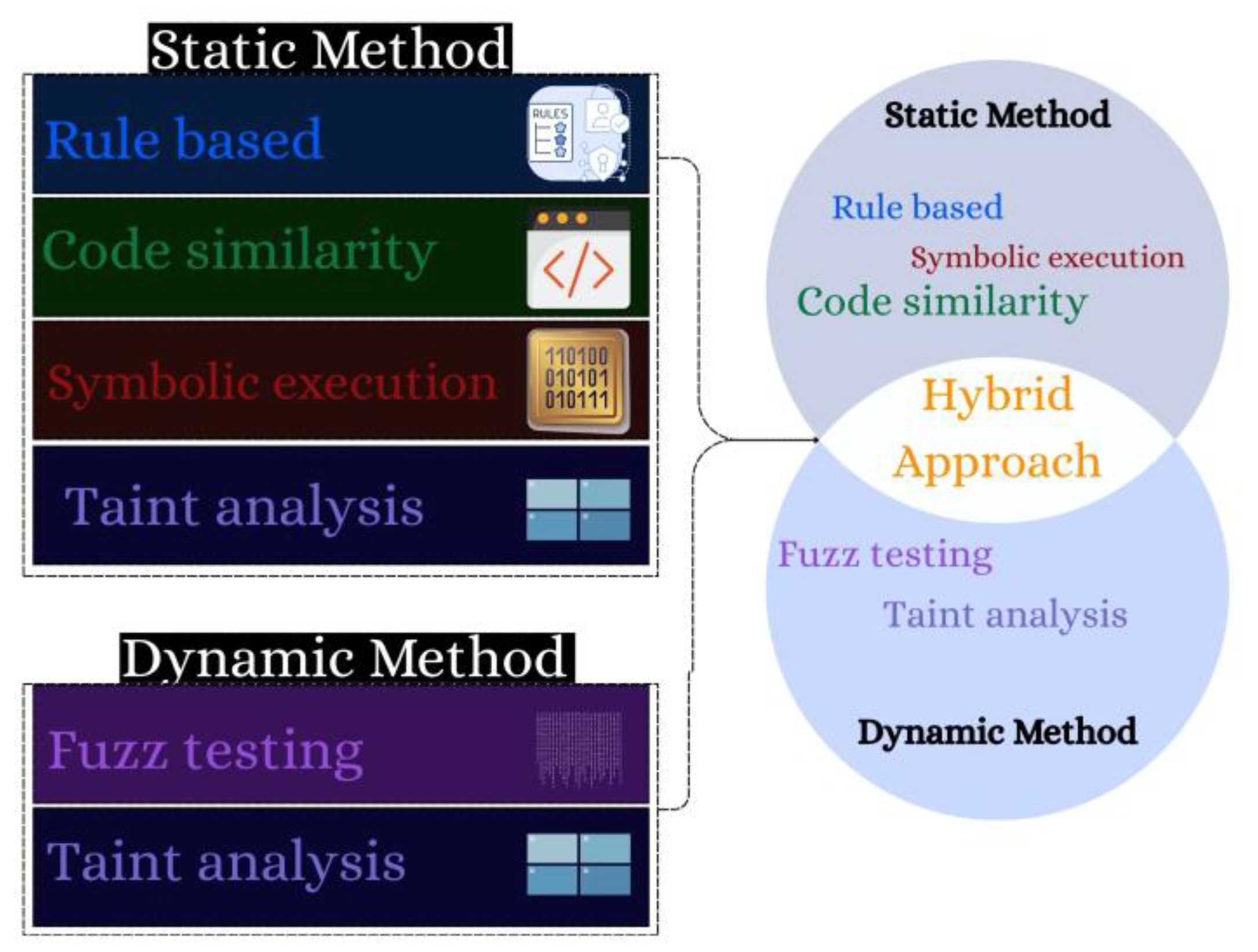
3.3. Traditional Methods
3.3.1. Static Analysis
3.3.2. Dynamic Approach
3.4. Code Based Detection
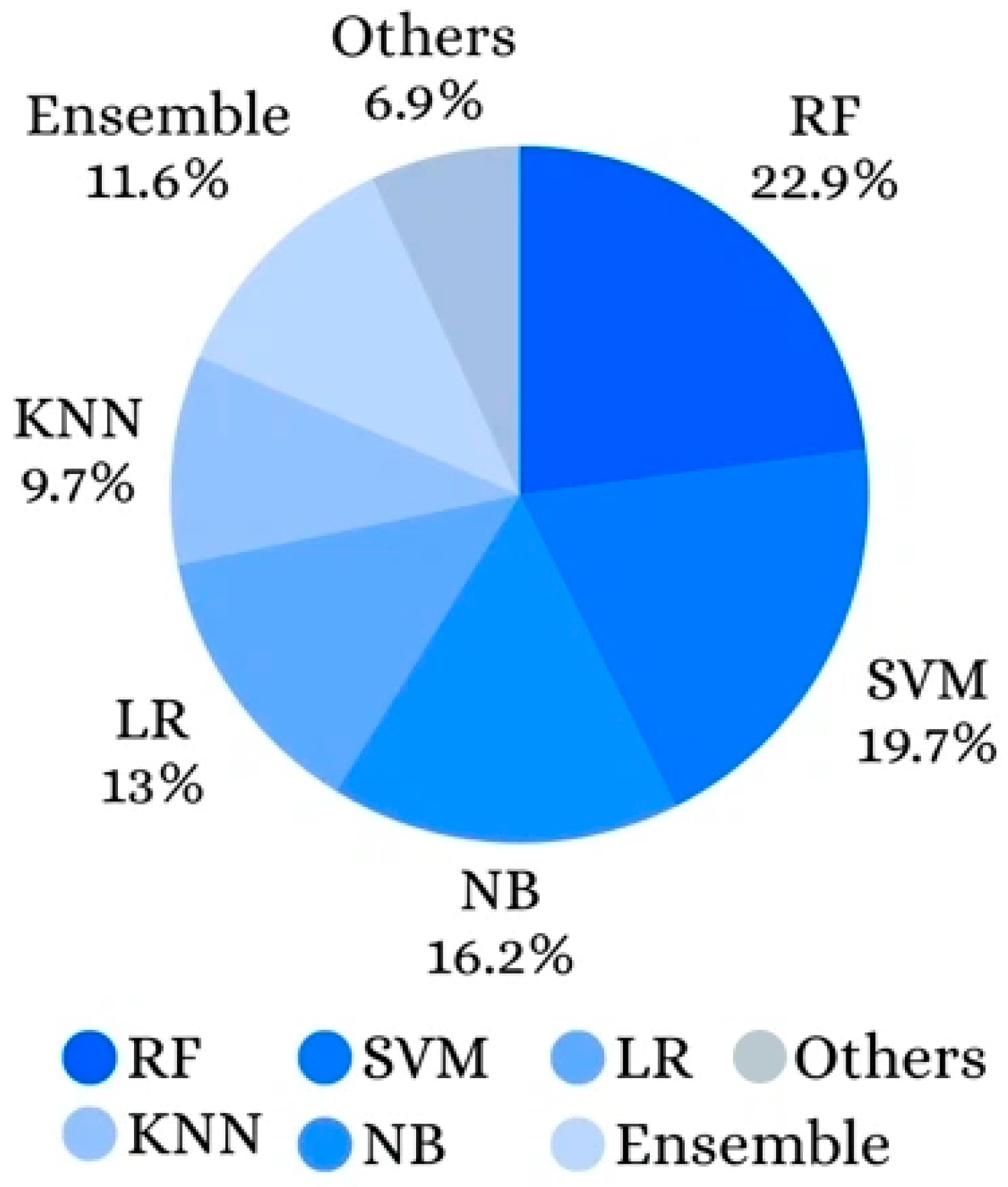
3.4.1. ML Based Methods
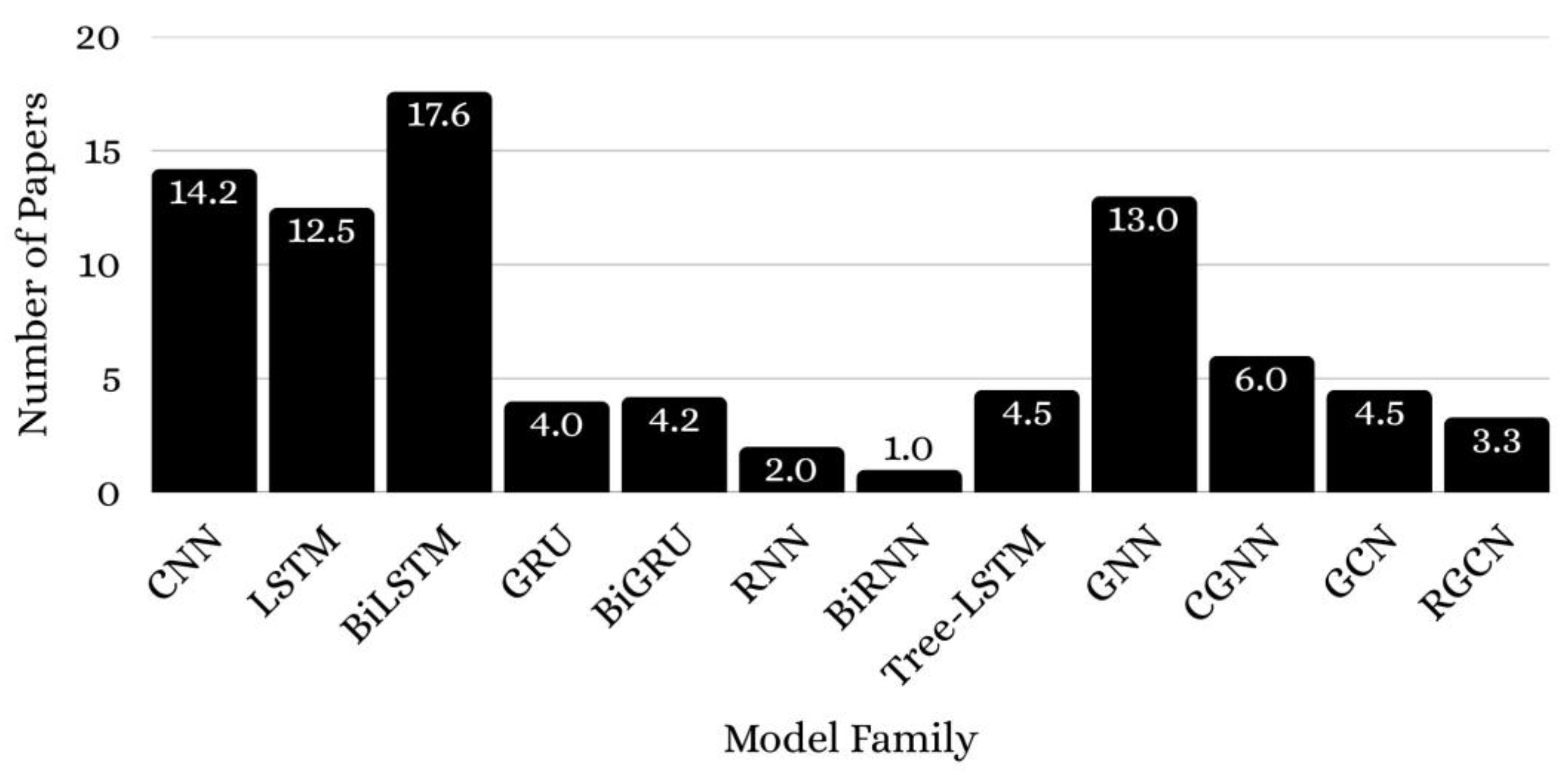
3.4.2. DL Based Methods
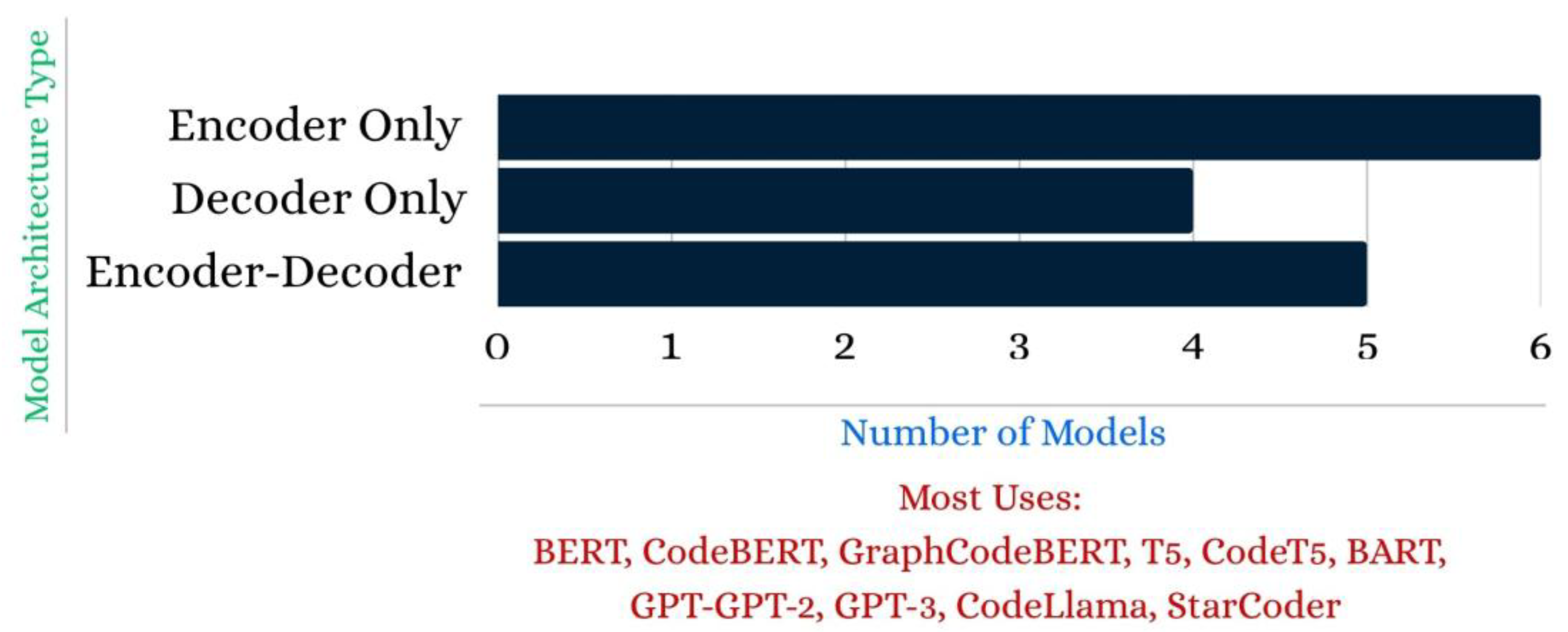
3.4.3. Large Language Models (LLMs)
3.5. Feature Representation
3.5.1. Graph Based Feature Representation
3.5.2. Text Based Feature Representation
3.6. Prompt Engineering Techniques
3.7. Fine Tuning
3.8. Evaluation Metrics
4. Insights, and Challenges
4.1. Limited Scope
4.2. Generalization Across Languages and Domains
4.3. Limited Vulnerability Type Coverage
4.4. Limited Availability
4.5. Reproducibility and Benchmarking Gaps
4.6. Lack of Interpretability
4.7. Real-World Performances
4.8. LLM Hallucination and Overfitting Issues
4.9. Bias in LLM-Based Vulnerability Detection
4.10. GPU and Resource Limitations
5. Future Directions
5.1. Data-Centric Development
5.2. Neuro-Symbolic and Hybrid Approaches
5.3. Efficient and Resource-Aware Fine-Tuning
5.4. Cross-Language and Multi-Modal Vulnerability Detection
5.5. Explainability and Trustworthy AI
5.6. Fairness, Bias, and Robust Evaluation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wen, S.F.; Kowalski, S. A case study: Heartbleed vulnerability management and swedish municipalities. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Human Aspects of Information Security, Privacy, and Trust, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 9–14 July 2017; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 414–431. [Google Scholar]
- Shetty, R.; Choo, K.K.R.; Kaufman, R. Shellshock vulnerability exploitation and mitigation: A demonstration. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Applications and Techniques in Cyber Security and Intelligence, Ningbo, China, 31 January–31 December 2017; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 338–350. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Li, C.; Wang, D.; Wen, S.; Zhang, J.; Nepal, S.; Xiang, Y.; Ren, K. Android HIV: A study of repackaging malware for evading machine-learning detection. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2019, 15, 987–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Equifax Had Patch 2 Months Before Hack and Didn’t Install It, Security Group Says. Available online: https://www.contrastsecurity.com/security-influencers/still-making-headlines-struts-2-and-the-equifax-breach (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Zhu, T.; Li, G.; Zhou, W.; Yu, P.S. Differentially private data publishing and analysis: A survey. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2017, 29, 1619–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Xiong, P.; Li, G.; Zhou, W.; Yu, P.S. Differentially private model publishing in cyber physical systems. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 108, 1297–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Wen, S.; Han, Q.L.; Zhang, J.; Xiang, Y. Software vulnerability detection using deep neural networks: A survey. Proc. IEEE 2020, 108, 1825–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engler, D.; Chen, D.Y.; Hallem, S.; Chou, A.; Chelf, B. Bugs as deviant behavior: A general approach to inferring errors in systems code. ACM SIGOPS Oper. Syst. Rev. 2001, 35, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, D.A. Flawfinder. 2016. Available online: https://dwheeler.com/flawfinder/ (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Woo, S.; Lee, H.; Oh, H. Vuddy: A scalable approach for vulnerable code clone discovery. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Jose, CA, USA, 22–26 May 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 595–614. [Google Scholar]
- Cadar, C.; Dunbar, D.; Engler, D.R. Klee: Unassisted and automatic generation of high-coverage tests for complex systems programs. In Proceedings of the OSDI, San Diego, CA, USA, 8–10 December 2008; Volume 8, pp. 209–224. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, D.A.; Engler, D. {Under-Constrained} symbolic execution: Correctness checking for real code. In Proceedings of the 24th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 15), Austin, TX, USA, 10–12 August 2015; pp. 49–64. [Google Scholar]
- Thanassis, H.A.; Kil, C.S.; David, B. Aeg: Automatic exploit generation. In Proceedings of the Network and Distributed System Security Symposium, San Diego, CA, USA, 6–9 February 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Zou, D.; Xu, S.; Ou, X.; Jin, H.; Wang, S.; Deng, Z.; Zhong, Y. Vuldeepecker: A deep learning-based system for vulnerability detection. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.01681. [Google Scholar]
- Sabottke, C.; Suciu, O.; Dumitraș, T. Vulnerability disclosure in the age of social media: Exploiting twitter for predicting {Real-World} exploits. In Proceedings of the 24th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 15), Austin, TX, USA, 10–12 August 2015; pp. 1041–1056. [Google Scholar]
- Sutton, M.; Greene, A.; Amini, P. Fuzzing: Brute Force Vulnerability Discovery; Pearson Education: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Newsome, J.; Song, D.X. Dynamic taint analysis for automatic detection, analysis, and signaturegeneration of exploits on commodity software. In Proceedings of the Network and Distributed System Security (NDSS) Symposium, San Diego, CA, USA, 3–4 February 2005; Volume 5, pp. 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Portokalidis, G.; Slowinska, A.; Bos, H. Argos: An emulator for fingerprinting zero-day attacks for advertised honeypots with automatic signature generation. ACM SIGOPS Oper. Syst. Rev. 2006, 40, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulter, R.; Han, Q.L.; Pan, L.; Zhang, J.; Xiang, Y. Data-driven cyber security in perspective—Intelligent traffic analysis. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019, 50, 3081–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffarian, S.M.; Shahriari, H.R. Software vulnerability analysis and discovery using machine-learning and data-mining techniques: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2017, 50, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; De Vel, O.; Han, Q.L.; Zhang, J.; Xiang, Y. Detecting and preventing cyber insider threats: A survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018, 20, 1397–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Zhang, J.; Rimba, P.; Gao, S.; Zhang, L.Y.; Xiang, Y. Data-driven cybersecurity incident prediction: A survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018, 21, 1744–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.; Zulkernine, M. Mitigating program security vulnerabilities: Approaches and challenges. ACM Comput. Surv. 2012, 44, 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra, R. A systematic review of machine learning techniques for software fault prediction. Appl. Soft Comput. 2015, 27, 504–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Shi, L.; Cai, Z.; Li, M. Software vulnerability discovery techniques: A survey. In Proceedings of the 2012 Fourth International Conference on Multimedia Information Networking and Security, Nanjing, China, 2–4 November 2012; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 152–156. [Google Scholar]
- Jie, G.; Xiao-Hui, K.; Qiang, L. Survey on software vulnerability analysis method based on machine learning. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE First International Conference on Data Science in Cyberspace (DSC), Changsha, China, 13–16 June 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 642–647. [Google Scholar]
- Allamanis, M.; Barr, E.T.; Devanbu, P.; Sutton, C. A survey of machine learning for big code and naturalness. ACM Comput. Surv. 2018, 51, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimmi, S.; Okhravi, H.; Rahimi, M. AI-Based Software Vulnerability Detection: A Systematic Literature Review. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2506.10280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, H.; Nasir, M.H.N.M.; Ab Razak, M.F.; Firdaus, A.; Anuar, N.B. The rise of software vulnerability: Taxonomy of software vulnerabilities detection and machine learning approaches. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2021, 179, 103009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiri Harzevili, N.; Boaye Belle, A.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Jiang, Z.M.; Nagappan, N. A systematic literature review on automated software vulnerability detection using machine learning. ACM Comput. Surv. 2024, 57, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, P.; Lin, G.; Pan, L.; Tai, Y.; Zhang, J. Software vulnerability analysis and discovery using deep learning techniques: A survey. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 197158–197172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomio, F.; Iannone, E.; De Lucia, A.; Palomba, F.; Lenarduzzi, V. Just-in-time software vulnerability detection: Are we there yet? J. Syst. Softw. 2022, 188, 111283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, B.; Chen, W.; Zhang, X. A survey of exploitation and detection methods of XSS vulnerabilities. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 182004–182016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Krishna, R.; Ding, Y.; Ray, B. Deep learning based vulnerability detection: Are we there yet? IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng. 2021, 48, 3280–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Semasaba, A.O.A.; Wu, X.; Agyemang, S.A.; Liu, T.; Ge, Y. Representation vs. Model: What matters most for source code vulnerability detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Software Analysis, Evolution and Reengineering (SANER), Honolulu, HI, USA, 9–12 March 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 647–653. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Zhu, K.; Yu, L.; Huang, H.; Lu, Y. Yama: Precise Opcode-Based Data Flow Analysis for Detecting PHP Applications Vulnerabilities. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2025, 20, 7748–7763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Dai, T.; Zhou, Z.; Tang, Y.; He, J. Artemis: Toward Accurate Detection of Server-Side Request Forgeries through LLM-Assisted Inter-Procedural Path-Sensitive Taint Analysis. Proc. ACM Program. Lang 2025, 9, 1349–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Real World Example. Available online: https://www.invokesec.com/2025/01/13/a-real-world-example-of-blind-sqli/ (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- SQL Injection. Available online: https://www.radware.com/cyberpedia/application-security/sql-injection/ (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Vulnerability Reports. Available online: https://www.edgescan.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/2023-Vulnerability-Statistics-Report.pdf (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Vulnerable XSS. Available online: https://www.acunetix.com/blog/articles/33-websites-webapps-vulnerable-xss/ (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Buffer Overflow. Available online: https://www.invicti.com/blog/web-security/2024-cwe-top-25-list-xss-sqli-buffer-overflows/ (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Security Patches. Available online: https://www.wired.com/story/apple-google-moveit-security-patches-june-2023-critical-update/ (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Top 10 OWASP. Available online: https://owasp.org/Top10/ (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- IEEE. IEEE Standard Glossary of Software Engineering Terminology; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Chess, B.; McGraw, G. Static analysis for security. IEEE Secur. Priv. 2004, 2, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, M.D. Static and dynamic analysis: Synergy and duality. In Proceedings of the WODA 2003: ICSE Workshop on Dynamic Analysis, Portland, OR, USA, 3–10 May 2003; pp. 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ayewah, N.; Pugh, W.; Hovemeyer, D.; Morgenthaler, J.D.; Penix, J. Using static analysis to find bugs. IEEE Softw. 2008, 25, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harzevili, N.S.; Shin, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Nagappan, N. Automatic static vulnerability detection for machine learning libraries: Are we there yet? In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 34th International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering (ISSRE), Florence, Italy, 9–12 October 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 795–806. [Google Scholar]
- Akram, J.; Luo, P. SQVDT: A scalable quantitative vulnerability detection technique for source code security assessment. Softw. Pract. Exp. 2021, 51, 294–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, B.; Huang, H.H. VGRAPH: A robust vulnerable code clone detection system using code property triplets. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy (EuroS&P), Genoa, Italy, 7–11 September 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 53–69. [Google Scholar]
- Rahaman, S.; Xiao, Y.; Afrose, S.; Shaon, F.; Tian, K.; Frantz, M.; Kantarcioglu, M.; Yao, D. Cryptoguard: High precision detection of cryptographic vulnerabilities in massive-sized java projects. In Proceedings of the 2019 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, London, UK, 11–15 November 2019; pp. 2455–2472. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, B.P.; Fredriksen, L.; So, B. An empirical study of the reliability of UNIX utilities. Commun. ACM 1990, 33, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehlert, P. Violating Assumptions with Fuzzing. IEEE Secur. Priv. 2005, 3, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzi, A.; Martignoni, L.; Monga, M.; Paleari, R. A smart fuzzer for x86 executables. In Proceedings of the Third International Workshop on Software Engineering for Secure Systems (SESS’07: ICSE Workshops 2007), Minneapolis, MN, USA, 20–26 May 2007; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2007; p. 7. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, W.; Son, B.; Heo, K. Tracer: Signature-based static analysis for detecting recurring vulnerabilities. In Proceedings of the 2022 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 7–11 November 2022; pp. 1695–1708. [Google Scholar]
- Zagane, M.; Abdi, M.K.; Alenezi, M. A new approach to locate software vulnerabilities using code metrics. Int. J. Softw. Innov. (IJSI) 2020, 8, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimi, S.; Ebrahimzadeh, M.; Kharrazi, M. Improving real-world vulnerability characterization with vulnerable slices. In Proceedings of the 16th ACM International Conference on Predictive Models and Data Analytics in Software Engineering, Virtual, 8–9 November 2020; pp. 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Kosker, Y.; Turhan, B.; Bener, A. An expert system for determining candidate software classes for refactoring. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 10000–10003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Sureka, A. Application of LSSVM and SMOTE on seven open source projects for predicting refactoring at class level. In Proceedings of the 2017 24th Asia-Pacific Software Engineering Conference (APSEC), Nanjing, China, 4–8 December 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 90–99. [Google Scholar]
- Nyamawe, A.S.; Liu, H.; Niu, N.; Umer, Q.; Niu, Z. Automated recommendation of software refactorings based on feature requests. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 27th International Requirements Engineering Conference (RE), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 23–27 September 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 187–198. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, D.; Huang, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X. FTCLNet: Convolutional LSTM with Fourier transform for vulnerability detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 19th International Conference on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications (TrustCom), Guangzhou, China, 29 December 2020–1 January 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 539–546. [Google Scholar]
- Dam, H.K.; Tran, T.; Pham, T.; Ng, S.W.; Grundy, J.; Ghose, A. Automatic feature learning for predicting vulnerable software components. IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng. 2018, 47, 67–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.; Kim, H.K. AutoVAS: An automated vulnerability analysis system with a deep learning approach. Comput. Secur. 2021, 106, 102308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccente, N.; Dehlinger, J.; Deng, L.; Chakraborty, S.; Xiong, Y. Project achilles: A prototype tool for static method-level vulnerability detection of java source code using a recurrent neural network. In Proceedings of the 2019 34th IEEE/ACM International Conference on Automated Software Engineering Workshop (ASEW), San Diego, CA, USA, 11–15 November 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 114–121. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaomeng, W.; Tao, Z.; Runpu, W.; Wei, X.; Changyu, H. CPGVA: Code property graph based vulnerability analysis by deep learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 10th International Conference on Advanced Infocomm Technology (ICAIT), Stockholm, Sweden, 12–15 August 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 184–188. [Google Scholar]
- Ziems, N.; Wu, S. Security vulnerability detection using deep learning natural language processing. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2021-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 10–13 May 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.; Ma, Z.; Cao, B.; Zhu, E. VDDA: An effective software vulnerability detection model based on deep learning and attention mechanism. In Proceedings of the 2023 26th International Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work in Design (CSCWD), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 24–26 May 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 474–479. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Z. Hlt: A hierarchical vulnerability detection model based on transformer. In Proceedings of the 2022 4th International Conference on Data Intelligence and Security (ICDIS), Shenzhen, China, 24–26 August 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Du, G.; Chen, L.; Wu, T.; Zheng, X.; Cui, N.; Shi, G. Cross domain on snippets: BiLSTM-TextCNN based vulnerability detection with domain adaptation. In Proceedings of the 2023 26th International Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work in Design (CSCWD), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 24–26 May 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 1896–1901. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.; Fang, Y.; Huang, C.; Ou, H.; Lin, C.; Guo, Y. HyVulDect: A hybrid semantic vulnerability mining system based on graph neural network. Comput. Secur. 2022, 121, 102823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zou, D.; Xu, S.; Jin, H.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Z. Sysevr: A framework for using deep learning to detect software vulnerabilities. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2021, 19, 2244–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zou, D.; Xu, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Jin, H. Vuldeelocator: A deep learning-based fine-grained vulnerability detector. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2021, 19, 2821–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Fu, X.; Sun, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y. Efficient vulnerability detection based on abstract syntax tree and deep learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2020-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–9 July 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 722–727. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, S.; Sun, X.; Bo, L.; Wu, R.; Li, B.; Tao, C. MVD: Memory-related vulnerability detection based on flow-sensitive graph neural networks. In Proceedings of the 44th International Conference on Software Engineering, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 21–29 May 2022; pp. 1456–1468. [Google Scholar]
- De Kraker, W.; Vranken, H.; Hommmersom, A. GLICE: Combining graph neural networks and program slicing to improve software vulnerability detection. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy Workshops (EuroS&PW), Delft, The Netherlands, 3–7 July 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, X.; Wu, J.; Du, M.; Luo, T.; Yang, M.; Wu, Y. MultiCode: A Unified Code Analysis Framework based on Multi-type and Multi-granularity Semantic Learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering Workshops (ISSREW), Wuhan, China, 25–28 October 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 359–364. [Google Scholar]
- Hin, D.; Kan, A.; Chen, H.; Babar, M.A. Linevd: Statement-level vulnerability detection using graph neural networks. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Mining Software Repositories, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 23–24 May 2022; pp. 596–607. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Li, C.; Li, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wen, Y. ACGVD: Vulnerability detection based on comprehensive graph via graph neural network with attention. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information and Communications Security, Chongqing, China, 19–21 November 2021; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 243–259. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Xu, W.; Xu, D. Compact abstract graphs for detecting code vulnerability with GNN models. In Proceedings of the 38th Annual Computer Security Applications Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 5–9 December 2022; pp. 497–507. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, V.A.; Nguyen, D.Q.; Nguyen, V.; Le, T.; Tran, Q.H.; Phung, D. Regvd: Revisiting graph neural networks for vulnerability detection. In Proceedings of the ACM/IEEE 44th International Conference on Software Engineering: Companion Proceedings, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 21–29 May 2022; pp. 178–182. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, S.; Fang, Z.; Yang, K. HGVul: A Code Vulnerability Detection Method Based on Heterogeneous Source-Level Intermediate Representation. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2022, 2022, 1919907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, C.B. Semantic-based vulnerability detection by functional connectivity of gated graph sequence neural networks. Soft Comput. 2023, 27, 5703–5719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ye, G.; Tang, Z.; Tan, S.H.; Huang, S.; Fang, D.; Feng, Y.; Bian, L.; Wang, Z. Combining graph-based learning with automated data collection for code vulnerability detection. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2020, 16, 1943–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Liu, S.; Xiao, Y.; Li, Z.; Sun, J.; Lin, S.W. Learning program semantics for vulnerability detection via vulnerability-specific inter-procedural slicing. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM Joint European Software Engineering Conference and Symposium on the Foundations of Software Engineering, San Francisco, CA, USA, 3–9 December 2023; pp. 1371–1383. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Chen, L.; Du, G.; Zhu, C.; Cui, N.; Shi, G. Inductive vulnerability detection via gated graph neural network. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 25th International Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work in Design (CSCWD), Hangzhou, China, 4–6 May 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 519–524. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Ruan, O.; Zhang, J. Tensor-based gated graph neural network for automatic vulnerability detection in source code. Softw. Test. Verif. Reliab. 2024, 34, e1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Jiang, Y.; Su, X. Vu1SPG: Vulnerability detection based on slice property graph representation learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 32nd International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering (ISSRE), Wuhan, China, 25–28 October 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 457–467. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Tang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S. SedSVD: Statement-level software vulnerability detection based on Relational Graph Convolutional Network with subgraph embedding. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2023, 158, 107168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Wang, H.; Hua, J.; Zhang, M.; Xu, G.; Yi, L.; Sui, Y. Static detection of control-flow-related vulnerabilities using graph embedding. In Proceedings of the 2019 24th International Conference on Engineering of Complex Computer Systems (ICECCS), Guangzhou, China, 10–13 November 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J. Introduction to Convolutional Neural Networks; National Key Lab for Novel Software Technology, Nanjing University: Nanjing, China, 2017; Volume 5, p. 495. [Google Scholar]
- Bilgin, Z.; Ersoy, M.A.; Soykan, E.U.; Tomur, E.; Çomak, P.; Karaçay, L. Vulnerability prediction from source code using machine learning. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 150672–150684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, L.; Xin, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y. Automated vulnerability detection in source code using minimum intermediate representation learning. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y. An Effective Software Vulnerability Detection Method Based on Devised Deep-Learning Model to Fix the Vague Separation. In Proceedings of the 2022 3rd International Symposium on Big Data and Artificial Intelligence, Singapore, 9–10 December 2022; pp. 90–95. [Google Scholar]
- Mim, R.S.; Khatun, A.; Ahammed, T.; Sakib, K. Impact of Centrality on Automated Vulnerability Detection Using Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology for Sustainable Development (ICICT4SD), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 21–23 September 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 331–335. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, B.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Su, P. CEVulDet: A code edge representation learnable vulnerability detector. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Gold Coast, Australia, 18–23 June 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, R.; Kim, L.; Hamilton, L.; Lazovich, T.; Harer, J.; Ozdemir, O.; Ellingwood, P.; McConley, M. Automated vulnerability detection in source code using deep representation learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 17th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), Orlando, FL, USA, 17–20 December 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 757–762. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.; Hu, Q.; Hu, Y.; Kuang, W.; Chen, J. SEVulDet: A semantics-enhanced learnable vulnerability detector. In Proceedings of the 2022 52nd Annual IEEE/IFIP International Conference on Dependable Systems and Networks (DSN), Baltimore, MD, USA, 27–30 June 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 150–162. [Google Scholar]
- Xuan, C.D. A new approach to software vulnerability detection based on CPG analysis. Cogent Eng. 2023, 10, 2221962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.X.; Zhou, K.; Li, J.; Tang, T.; Wang, X.; Hou, Y.; Min, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Dong, Z.; et al. A survey of large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.18223. [Google Scholar]
- Ashish, V. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, I. [Google Scholar]
- Bommasani, R. On the opportunities and risks of foundation models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.07258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, J.; McCandlish, S.; Henighan, T.; Brown, T.B.; Chess, B.; Child, R.; Gray, S.; Radford, A.; Wu, J.; Amodei, D. Scaling laws for neural language models. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2001.08361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Liu, Z.; Liao, W.; Huang, X.; Cao, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Xu, S.; Zeng, F.; Liu, W.; et al. Auggpt: Leveraging chatgpt for text data augmentation. IEEE Trans. Big Data 2025, 11, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Luo, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, J.; Wu, X. Unifying large language models and knowledge graphs: A roadmap. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2024, 36, 3580–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; Volume 1 (long and short papers), pp. 4171–4186. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.; Guo, D.; Tang, D.; Duan, N.; Feng, X.; Gong, M.; Shou, L.; Qin, B.; Liu, T.; Jiang, D.; et al. Codebert: A pre-trained model for programming and natural languages. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.08155. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.; Ren, S.; Lu, S.; Feng, Z.; Tang, D.; Liu, S.; Zhou, L.; Duan, N.; Svyatkovskiy, A.; Fu, S.; et al. Graphcodebert: Pre-training code representations with data flow. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.08366. [Google Scholar]
- Kanade, A.; Maniatis, P.; Balakrishnan, G.; Shi, K. Learning and evaluating contextual embedding of source code. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Virtual, 13–18 July 2020; pp. 5110–5121. [Google Scholar]
- Hanif, H.; Maffeis, S. VulBERTa: Simplified source code pre-training for vulnerability detection. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Padua, Italy, 18–23 July 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Xu, B.; Han, D.; Yang, Z.; He, J.; Lo, D. CCBERT: Self-supervised code change representation learning. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Software Maintenance and Evolution (ICSME), Bogotá, Colombia, 1–6 October 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 182–193. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Wu, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Huang, J. Leveraging Deep Learning Models for Cross-function Null Pointer Risks Detection. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Artificial Intelligence Testing (AITest), Athens, Greece, 17–20 July 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 107–113. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Choi, J.; Ahmed, M.E.; Nepal, S.; Kim, H. VulDeBERT: A vulnerability detection system using bert. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering Workshops (ISSREW), Charlotte, NC, USA, 31 October–3 November 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Chen, L.; Du, G.; Zhu, C.; Cui, N.; Shi, G. CDNM: Clustering-based data normalization method for automated vulnerability detection. Comput. J. 2024, 67, 1538–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, V.L.A.; Phat, C.T.; Van Nguyen, K.; The Duy, P.; Pham, V.H. Xgv-bert: Leveraging contextualized language model and graph neural network for efficient software vulnerability detection. J. Supercomput. 2025, 81, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, W.U.; Chakraborty, S.; Ray, B.; Chang, K.W. Unified pre-training for program understanding and generation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.06333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffel, C.; Shazeer, N.; Roberts, A.; Lee, K.; Narang, S.; Matena, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, P.J. Exploring the limits of transfer learning with a unified text-to-text transformer. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2020, 21, 1–67. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Joty, S.; Hoi, S.C. Codet5: Identifier-aware unified pre-trained encoder-decoder models for code understanding and generation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.00859. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.; Lu, S.; Duan, N.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Yin, J. Unixcoder: Unified cross-modal pre-training for code representation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.03850. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, S.; Ahmed, T.; Ding, Y.; Devanbu, P.T.; Ray, B. NatGen: Generative pre-training by “naturalizing” source code. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM Joint European Software Engineering Conference and Symposium on the Foundations of Software Engineering, Singapore, 14–18 November 2022; pp. 18–30. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Wu, J.; Child, R.; Luan, D.; Amodei, D.; Sutskever, I. Language models are unsupervised multitask learners. OpenAI Blog 2019, 1, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Agarwal, S. Language models are few-shot learners. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.14165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenAI 2022. GPT-3.5. Available online: https://platform.openai.com/docs/models (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- Achiam, J.; Adler, S.; Agarwal, S.; Ahmad, L.; Akkaya, I.; Aleman, F.L.; Almeida, D.; Altenschmidt, J.; Altman, S.; Anadkat, S.; et al. Gpt-4 technical report. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.08774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Guo, D.; Ren, S.; Huang, J.; Svyatkovskiy, A.; Blanco, A.; Clement, C.; Drain, D.; Jiang, D.; Tang, D.; et al. Codexglue: A machine learning benchmark dataset for code understanding and generation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.04664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Tworek, J.; Jun, H.; Yuan, Q.; Pinto, H.P.D.O.; Kaplan, J.; Edwards, H.; Burda, Y.; Joseph, N.; Brockman, G.; et al. Evaluating large language models trained on code. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.03374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.F.; Alon, U.; Neubig, G.; Hellendoorn, V.J. A systematic evaluation of large language models of code. In Proceedings of the 6th ACM SIGPLAN International Symposium on Machine Programming, San Diego, CA, USA, 13 June 2022; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Fried, D.; Aghajanyan, A.; Lin, J.; Wang, S.; Wallace, E.; Shi, F.; Zhong, R.; Yih, W.T.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Lewis, M. Incoder: A generative model for code infilling and synthesis. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.05999. [Google Scholar]
- Nijkamp, E.; Pang, B.; Hayashi, H.; Tu, L.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Savarese, S.; Xiong, C. Codegen: An open large language model for code with multi-turn program synthesis. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.13474. [Google Scholar]
- Roziere, B.; Gehring, J.; Gloeckle, F.; Sootla, S.; Gat, I.; Tan, X.E.; Adi, Y.; Liu, J.; Sauvestre, R.; Remez, T.; et al. Code llama: Open foundation models for code. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.12950. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Allal, L.B.; Zi, Y.; Muennighoff, N.; Kocetkov, D.; Mou, C.; Marone, M.; Akiki, C.; Li, J.; Chim, J.; et al. Starcoder: May the source be with you! arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.06161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, T.; Lo, D. Large language model for vulnerability detection: Emerging results and future directions. In Proceedings of the 2024 ACM/IEEE 44th International Conference on Software Engineering: New Ideas and Emerging Results, Lisbon, Portugal, 14–20 April 2024; pp. 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, S.; Sun, X.; Bo, L.; Wei, Y.; Li, B. Bgnn4vd: Constructing bidirectional graph neural-network for vulnerability detection. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2021, 136, 106576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, T.; Tan, L. Automatically learning semantic features for defect prediction. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Software Engineering, Austin, TX, USA, 14–22 May 2016; pp. 297–308. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, J.D.A.; Lourenço, N.; Vieira, M. On the Use of Deep Graph CNN to Detect Vulnerable C Functions. In Proceedings of the 11th Latin-American Symposium on Dependable Computing, Fortaleza, Brazil, 21–24 November 2022; pp. 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Dam, H.K.; Tran, T.; Pham, T.; Ng, S.W.; Grundy, J.; Ghose, A. Automatic feature learning for vulnerability prediction. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1708.02368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gear, J.; Xu, Y.; Foo, E.; Gauravaram, P.; Jadidi, Z.; Simpson, L. Software Vulnerability Detection Using Informed Code Graph Pruning. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 135626–135644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Nguyen, T.N. Vulnerability detection with fine-grained interpretations. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM Joint Meeting on European Software Engineering Conference and Symposium on the Foundations of Software Engineering, Athens, Greece, 23–28 August 2021; pp. 292–303. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yadavally, A.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Nguyen, T.N. Commit-level, neural vulnerability detection and assessment. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM Joint European Software Engineering Conference and Symposium on the Foundations of Software Engineering, San Francisco, CA, USA, 3–9 December 2023; pp. 1024–1036. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Bi, Y.; Guo, H.; Sun, W.; Li, J. ISVSF: Intelligent vulnerability detection against Java via sentence-level pattern exploring. IEEE Syst. J. 2021, 16, 1032–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Mou, L.; Li, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jin, Z. Building program vector representations for deep learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Science, Engineering and Management, Chongqing, China, 28–30 October 2015; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 547–553. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.J.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, C.; Lim, S.H.; Park, K.W. Learning binary code with deep learning to detect software weakness. In Proceedings of the KSII the 9th International Conference on Internet (ICONI) 2017 Symposium, Vientiane, Laos, 17–20 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mikolov, T.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.; Dean, J. Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1301.3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TMikolov, I.; Sutskever, K.; Chen, C.; Corrado, G.S.; Dean, J. Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 5–10 December 2013; pp. 3111–3119. [Google Scholar]
- Black, P.E.; Black, P.E. Juliet 1.3 Test Suite: Changes From 1.2; US Department of Commerce, National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Alenezi, M.; Zagane, M.; Javed, Y. Efficient deep features learning for vulnerability detection using character n-gram embedding. Jordanian J. Comput. Inf. Technol. (JJCIT) 2021, 7, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Liu, Y.; Ding, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Hao, Z.; Zhu, H. An enhanced vulnerability detection in software using a heterogeneous encoding ensemble. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications (ISCC), Gammarth, Tunisia, 9–12 July 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 1214–1220. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, F. BBregLocator: A vulnerability detection system based on bounding box regression. In Proceedings of the 2021 51st Annual IEEE/IFIP International Conference on Dependable Systems and Networks Workshops (DSN-W), Taipei, Taiwan, 21–24 June 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, Y. Vulnerability detection with feature fusion and learnable edge-type embedding graph neural network. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2025, 181, 107686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wu, D.; Xue, Y.; Liu, H.; Ma, W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y. Llm4vuln: A unified evaluation framework for decoupling and enhancing llms’ vulnerability reasoning. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.16185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Q.; Havaldar, S.; Stein, A.; Zhang, L.; Rao, D.; Wong, E.; Apidianaki, M.; Callison-Burch, C. Faithful chain-of-thought reasoning. In Proceedings of the 13th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing and the 3rd Conference of the Asia-Pacific Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics (IJCNLP-AACL 2023), Nusa Dua, Bali, Indonesia, 1–4 November 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kojima, T.; Gu, S.S.; Reid, M.; Matsuo, Y.; Iwasawa, Y. Large language models are zero-shot reasoners. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 22199–22213. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, C. How far have we gone in vulnerability detection using large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.12420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Duan, J.; Xu, K.; Cai, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Y. A survey on large language model (llm) security and privacy: The good, the bad, and the ugly. High-Confid. Comput. 2024, 4, 100211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Cao, S.; Sun, X.; Lo, D. Large language model for vulnerability detection and repair: Literature review and the road ahead. ACM Trans. Softw. Eng. Methodol. 2025, 34, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Fu, Y.; Ibrahim, O.; Sitawarin, C.; Chen, X.; Alomair, B.; Wagner, D.; Ray, B.; Chen, Y. Vulnerability detection with code language models: How far are we? arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.18624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Patsakis, C.; Hu, Q.; Tang, Q.; Casino, F. Outside the comfort zone: Analysing llm capabilities in software vulnerability detection. In Proceedings of the European Symposium on Research in Computer Security, Bydgoszcz, Poland, 16–20 September 2024; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 271–289. [Google Scholar]
- Haurogné, J.; Basheer, N.; Islam, S. Advanced Vulnerability Detection Using Llm with Transparency Obligation Practice Towards Trustworthy Ai. Mach. Learn. Appl. 2024, 18, 100598. [Google Scholar]
- Purba, M.D.; Ghosh, A.; Radford, B.J.; Chu, B. Software vulnerability detection using large language models. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 34th International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering Workshops (ISSREW), Florence, Italy, 9–12 October 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 112–119. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, A.Z.; Le Goues, C.; Martins, R.; Hellendoorn, V. Large language models for test-free fault localization. In Proceedings of the 46th IEEE/ACM International Conference on Software Engineering, Lisbon, Portugal, 14–20 April 2024; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Du, X.; Wen, M.; Zhu, J.; Xie, Z.; Ji, B.; Liu, H.; Shi, X.; Jin, H. Generalization-enhanced code vulnerability detection via multi-task instruction fine-tuning. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.03718. [Google Scholar]
- Boi, B.; Esposito, C.; Lee, S. Smart contract vulnerability detection: The role of large language model (llm). ACM SIGAPP Appl. Comput. Rev. 2024, 24, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Ni, C.; Wang, S. Multitask-based evaluation of open-source llm on software vulnerability. IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng. 2024, 50, 3071–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, L. Analysis and comparison of classification metrics. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.05355. [Google Scholar]
- Muntean, M.; Militaru, F.D. Metrics for evaluating classification algorithms. In Education, Research and Business Technologies: Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Informatics in Economy (IE 2022), Bucharest, Romania, 26–27 May 2022; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 307–317. [Google Scholar]
- Leiter, C.; Lertvittayakumjorn, P.; Fomicheva, M.; Zhao, W.; Gao, Y.; Eger, S. Towards explainable evaluation metrics for natural language generation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.11131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
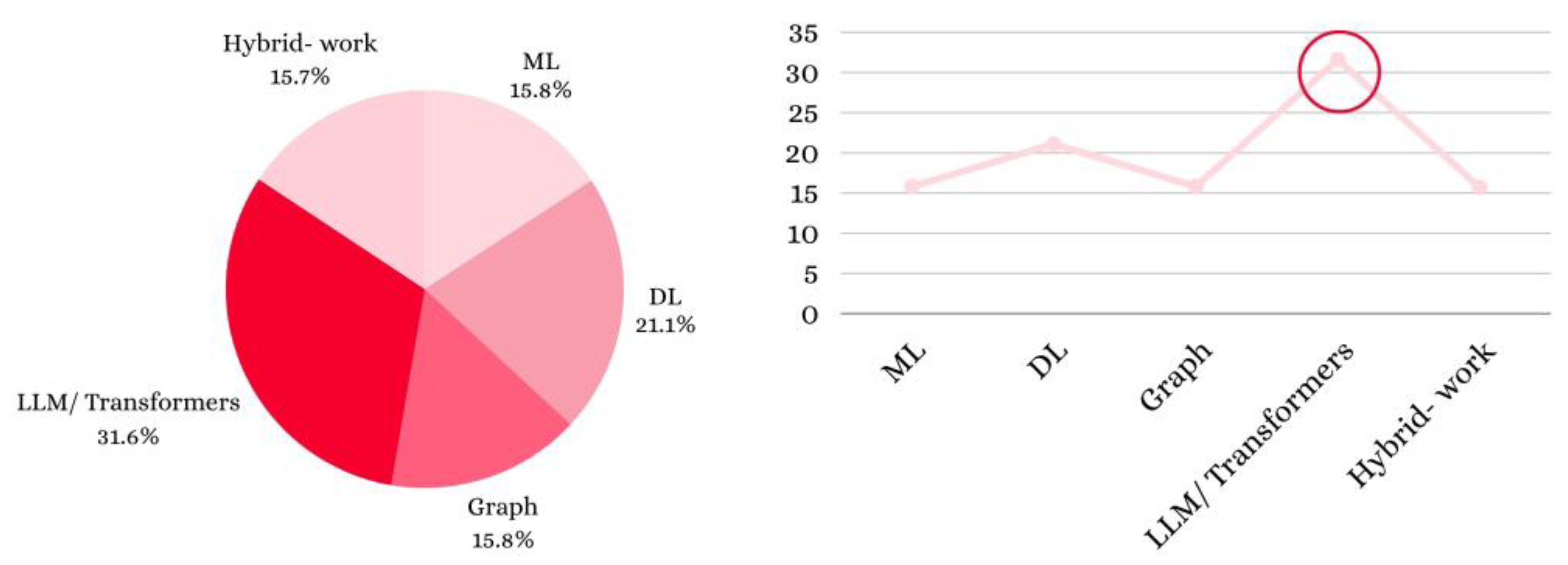
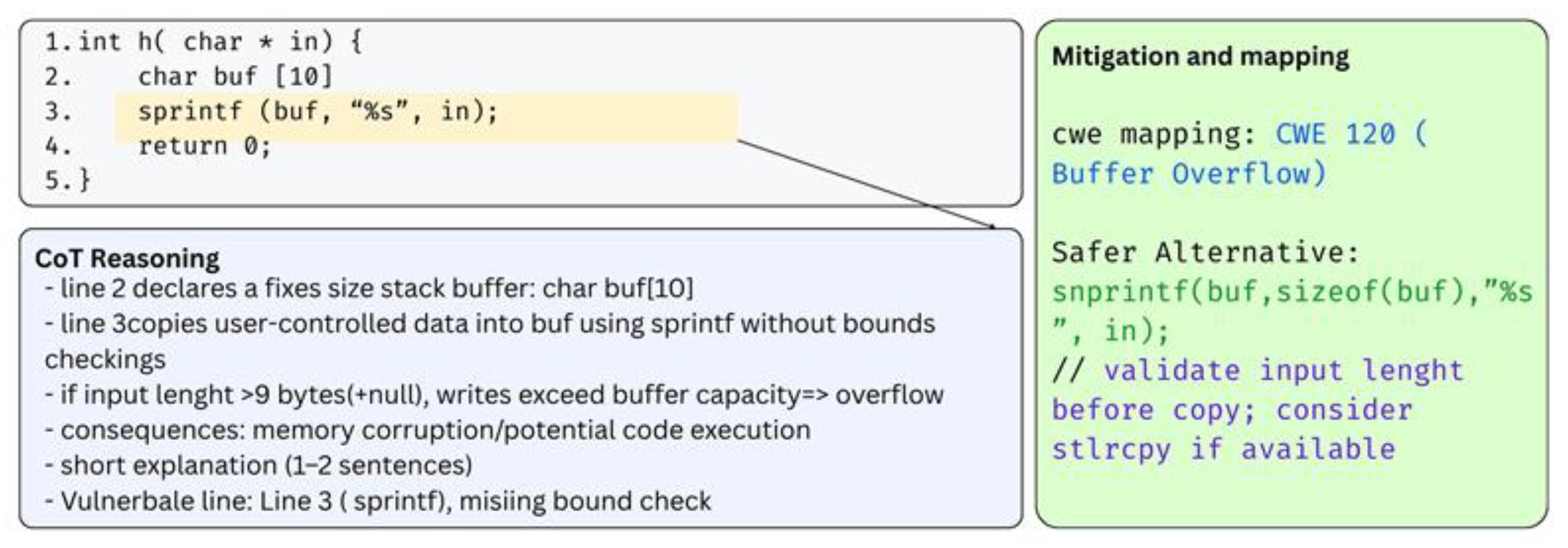
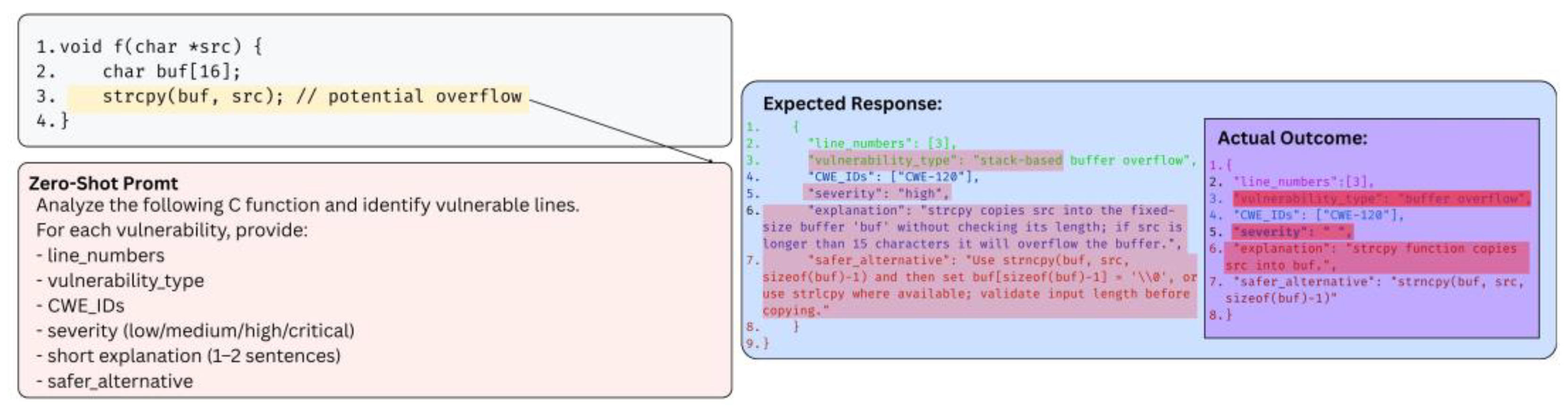

| Published Paper | Published Date | Contributions |
|---|---|---|
| Shahriar et al. [24] | 2012 | Vulnerability detection experiments employing various code analysis approaches. |
| Malhotra et al. [25] | 2015 | Programming defects identification methods using ML strategies, |
| Liu et al. [26] | 2012 | A comprehensive summary of finding vulnerabilities analysis. |
| Ghaffarian et al. [21] | 2017 | Presented fundamental labeling for work in the software vulnerabilities detection area. |
| Uddin et al. [29] | 2025 | Deep learning models with code representation, and implementation. |
| Lomio et al. [33] | 2022 | The study explored the extent to which Machine Learning has been adopted as an assistive tool for developers in vulnerability detection. By leveraging statistical models and pattern-recognition algorithms, ML enables automated identification of code anomalies, thereby reducing developers’ reliance on manual inspection and traditional static analysis methods |
| Hanif et al. [30] | 2021 | Designed two alternative taxonomies for software vulnerability detection, one representing research interests and the other highlighting methodological methods. |
| Harzevili et al. [31] | 2024 | Explored ML-based methods to analyze publication trends, dataset usage, feature representations, and model architectures, while also identifying the most frequently studied vulnerability types. |
| Zeng et al. [32] | 2020 | Highlighted and critically analyzed four seminal papers in the field, emphasizing their transformative impact on the direction of software vulnerability detection research. |
| Liu et al. [34] | 2019 | Provided a comprehensive discussion on the classification of Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks, highlighting their types and implications. |
| Chakraborty et al. [35] | 2022 | Conducted a survey to evaluate the effectiveness of existing deep learning–based vulnerability detection methods when applied to real-world datasets. |
| Zheng et al. [36] | 2021 | In their study, the authors examined how various ML strategies affect the performance of source-code vulnerability detection. By comparing multiple approaches including feature-engineering based models, attention mechanisms, and transfer learning—they evaluated the relative contribution of each strategy toward identifying vulnerable code segments. |
| Zhao et al. [37] | 2025 | Provided Yama tools for PHP vulnerabilities identification, where experimental findings on 24 real-world applications (10M LOC) demonstrate a 99.1% detection accuracy and the identification of 38 zero-day vulnerabilities, higher than 9 modern static analyzers. |
| Ji et al. [38] | 2025 | Evaluated on 250 PHP applications, it achieved a 90.2% reduction in false positives and discovered 35 new SSRF vulnerabilities (24 CVEs). The framework highlights the potential of combining large language models with program analysis for vulnerability detection |
| Vulnerability Type | Most Common/Dangerous | Real-World Impact & Statistics | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| SQL Injection (SQLi) | Massive data exposure through unsanitized query inputs. Widely exploited across industries. | 2023 ResumeLooters campaign hit 65+ websites, stealing over 2M records. Equifax 2017 breach traced to SQLi. | [39,40] |
| Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) | Found in nearly one-third of web apps; enables session theft and phishing via injected scripts. | XSS present in 19.1% of web apps with medium severity in 2023 reporting. | [41,42] |
| Buffer Overflow | Continues to dominate the 2024 CWE Top 25 due to memory corruption risks in unmanaged languages. | The SQL Slammer worm (2003) exploited such a bug to cause global outages within minutes. | [43] |
| SSRF (Server-Side Request Forgery) | Prolific in cloud environments; attackers exploit internal service access. | Ranked significant in the 2023 Vulnerability Report; cloud metadata targeting is notable. | [41] |
| Path Traversal | Allows attackers to access restricted files via malformed path input. | Jira CVE-2019-11581 enabled path traversal to expose sensitive files. | [40,43] |
| Insecure Deserialization | Deserialized untrusted data can execute arbitrary code; critical risk in Python/Java ecosystems. | Apache Commons Collections exploit (2015) is a prime example used in high-profile breaches. | [44] |
| XML External Entity (XXE) | Misconfigured XML parsers allow file disclosure or SSRF. | Still recurring in enterprise environments due to insecure defaults and legacy systems. | [45] |
| OS Command Injection | Injected shell commands compromise host; extremely powerful if exploited. | Log4Shell (2021) indirectly leveraged command injection vectors; Shellshock (2014) is another critical case. | [44] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shaon, M.S.H.; Akter, M.S. Modern Approaches to Software Vulnerability Detection: A Survey of Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Large Language Models. Electronics 2025, 14, 4449. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14224449
Shaon MSH, Akter MS. Modern Approaches to Software Vulnerability Detection: A Survey of Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Large Language Models. Electronics. 2025; 14(22):4449. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14224449
Chicago/Turabian StyleShaon, Md. Shazzad Hossain, and Mst Shapna Akter. 2025. "Modern Approaches to Software Vulnerability Detection: A Survey of Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Large Language Models" Electronics 14, no. 22: 4449. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14224449
APA StyleShaon, M. S. H., & Akter, M. S. (2025). Modern Approaches to Software Vulnerability Detection: A Survey of Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Large Language Models. Electronics, 14(22), 4449. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14224449






