Draughts: A Decentralized Jump-Based System for Interactive Anonymous Communication †
Abstract
1. Introduction
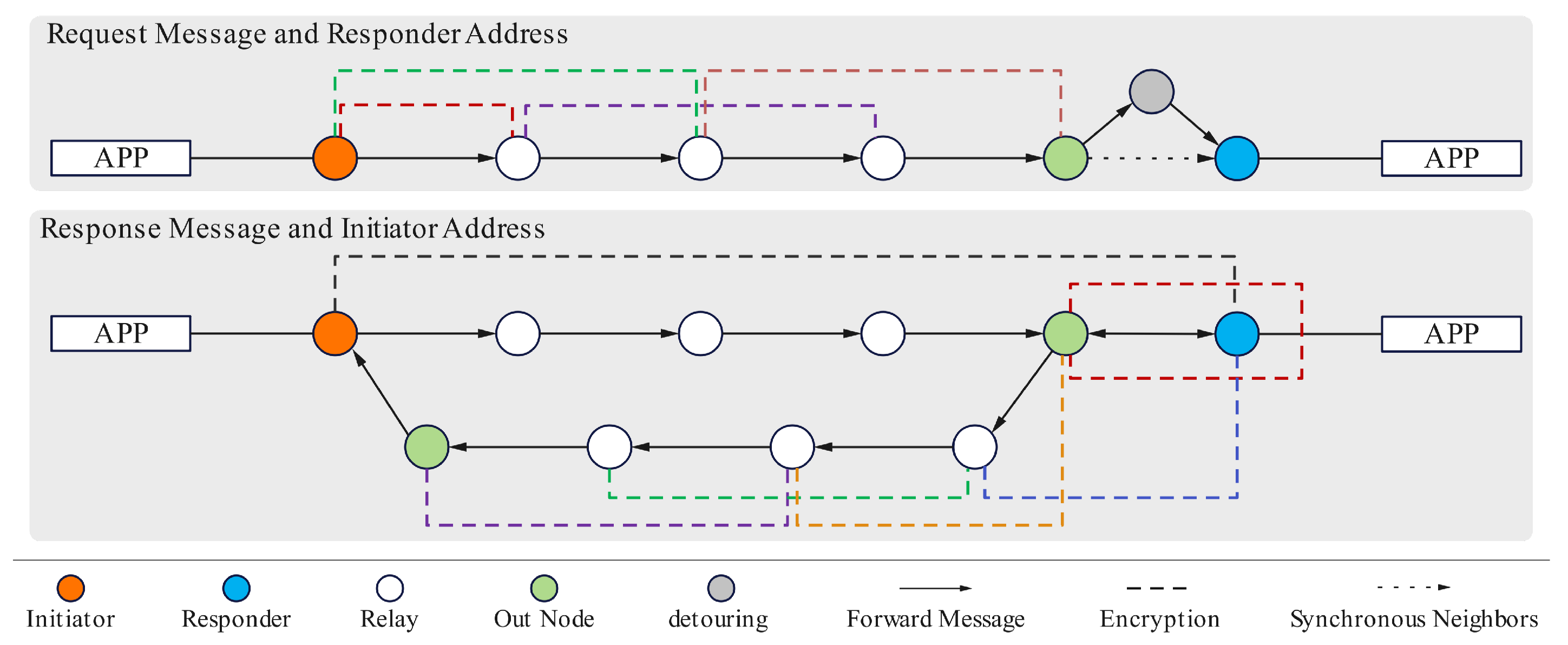
- Anonymous reply: Real-world applications often involve interactive processes—such as browsing, chatting, voting, and complaint submission—requiring initiators to receive responses without revealing their identities.
- Decentralization: Dependence on high-privilege directory servers or global network state introduces trust and scalability issues, as well as potential single points of failure.
- Resistance to traffic analysis: Advanced pattern-recognition techniques can exploit subtle correlations in traffic to de-anonymize users, particularly in systems with deterministic paths or insufficient cover.
- We propose Draughts, a jump-based anonymous communication design that eliminates global-state dependence by rethinking inter-node structures and extending commutative-encryption jump routing to support anonymous replies.
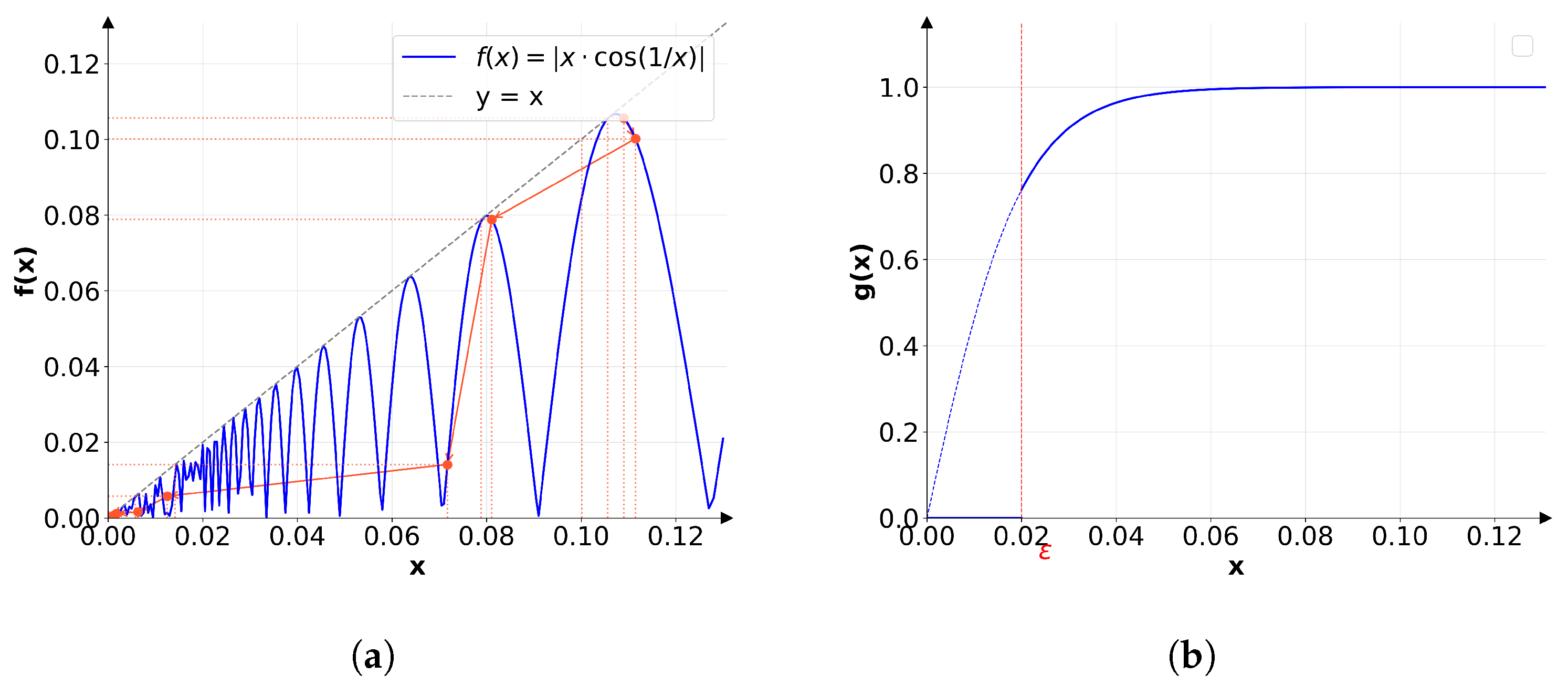
- We introduce a chaotic iterative path-length control (CIPLC), which ensures unpredictable hop counts while enabling fast convergence of the iterative process.
- We construct a predecessor attack model that estimates sender probability distributions and measure anonymity using normalized Shannon entropy, demonstrating Draughts’s resilience under local active attacks.
- We develop a traffic analysis attack model that predicts sender distributions from potential initiators and quantify anonymity via cross-entropy metrics, showing Draughts’s resistance to global passive attacks.
- We evaluate Draughts’s transmission performance by analyzing packet latency statistics, out-of-order (OOD) rates for flows of different sizes, and flow completion time (FCT), validating that Draughts achieves a balanced trade-off between anonymity and performance.
2. Related Work
2.1. Classification of Anonymous Network Paradigms
2.2. Jump Routing
2.3. Path-Length Control in Hop-by-Hop Routing
3. Draughts Design
3.1. Threat Model and Goals
3.1.1. Goals
- Decentralization achieved by avoiding reliance on a global view;
- Support for anonymous replies to enable anonymous interaction and feedback;
- Mitigation of receiver-side reordering to reduce communication cost.
3.1.2. Threat Model
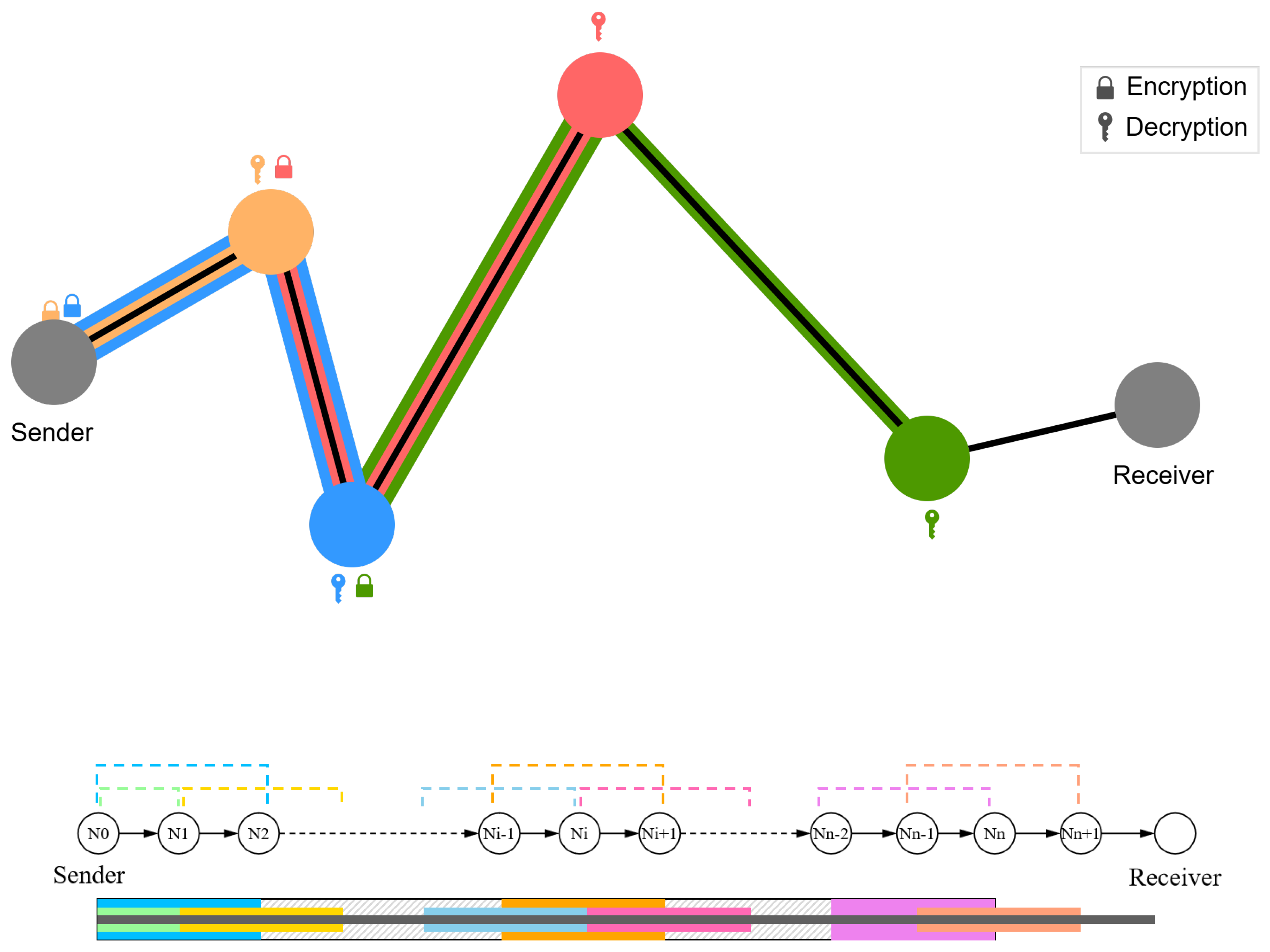
3.2. Draughts Architecture
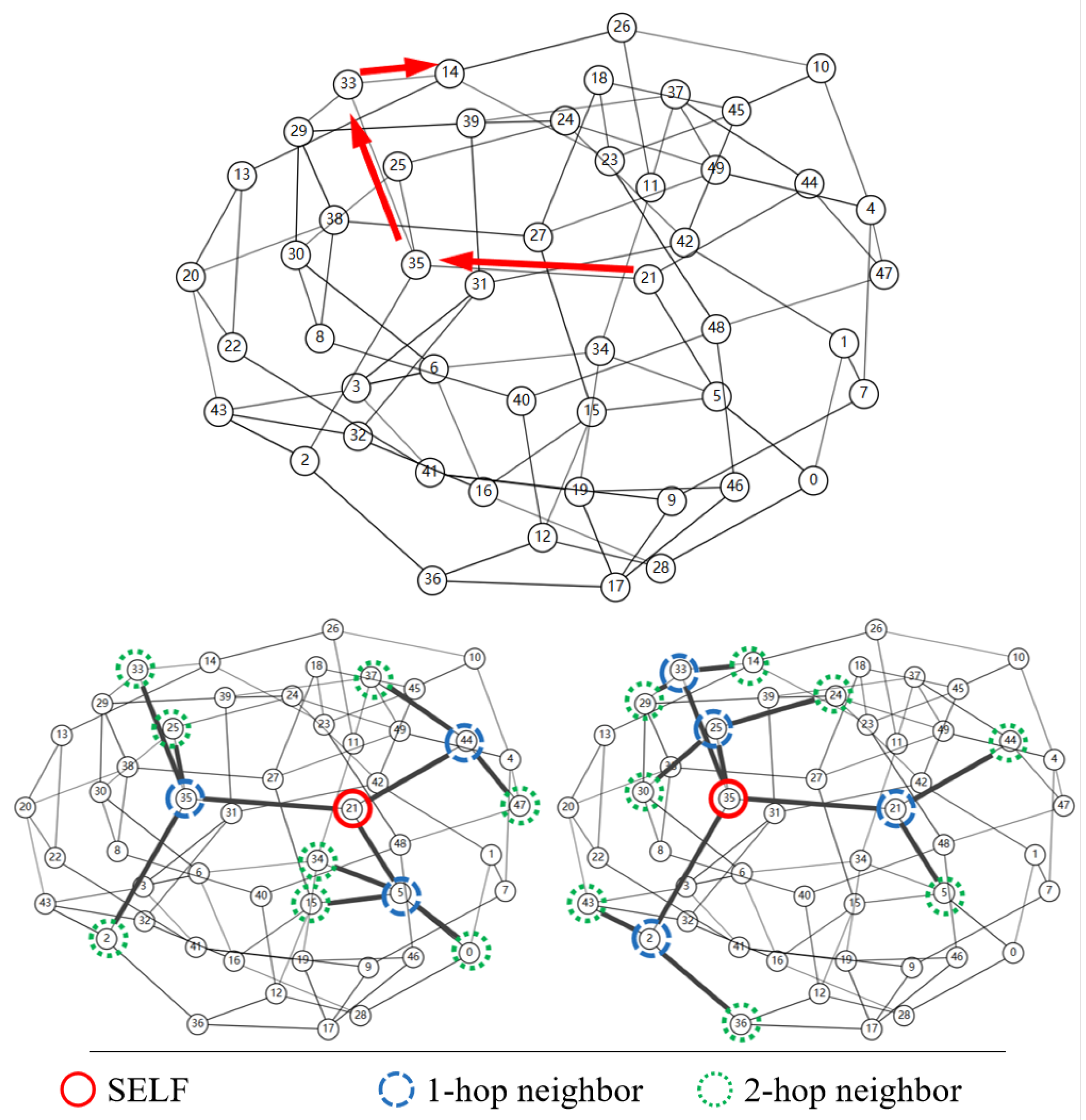
3.3. Draughts Routing
- CIPLC: Instead of using a fixed forwarding probability, each intermediate node calculates the forwarding probability using the forwarding parameter carried in the packet. This mechanism controls path length without revealing explicit hop counts, balancing anonymity and delivery efficiency (Section 3.4).
- Localized NNH selection: The NNH is chosen only from the direct neighbors of the NH rather than the global network. This reduces global search overhead while maintaining anonymity.
- Double encryption of initiator information: Initiator data is encrypted first with a temporary key established during initialization and then with a temporary key from the last hop. Upon decryption by the responder, it is re-encrypted for the return path, ensuring confidentiality throughout bidirectional anonymous communication.
- Last-hop neighbor synchronization: The last hop designates itself as the NNH, serving as the entry point for the response phase. Its neighbor data is synchronized to the receiver to enable proper response routing.
3.4. Chaotic Iterative Path-Length Control
3.5. Packet Format and Processing
| Algorithm 1 Draughts Intermediate Node Forwarding Process |
|
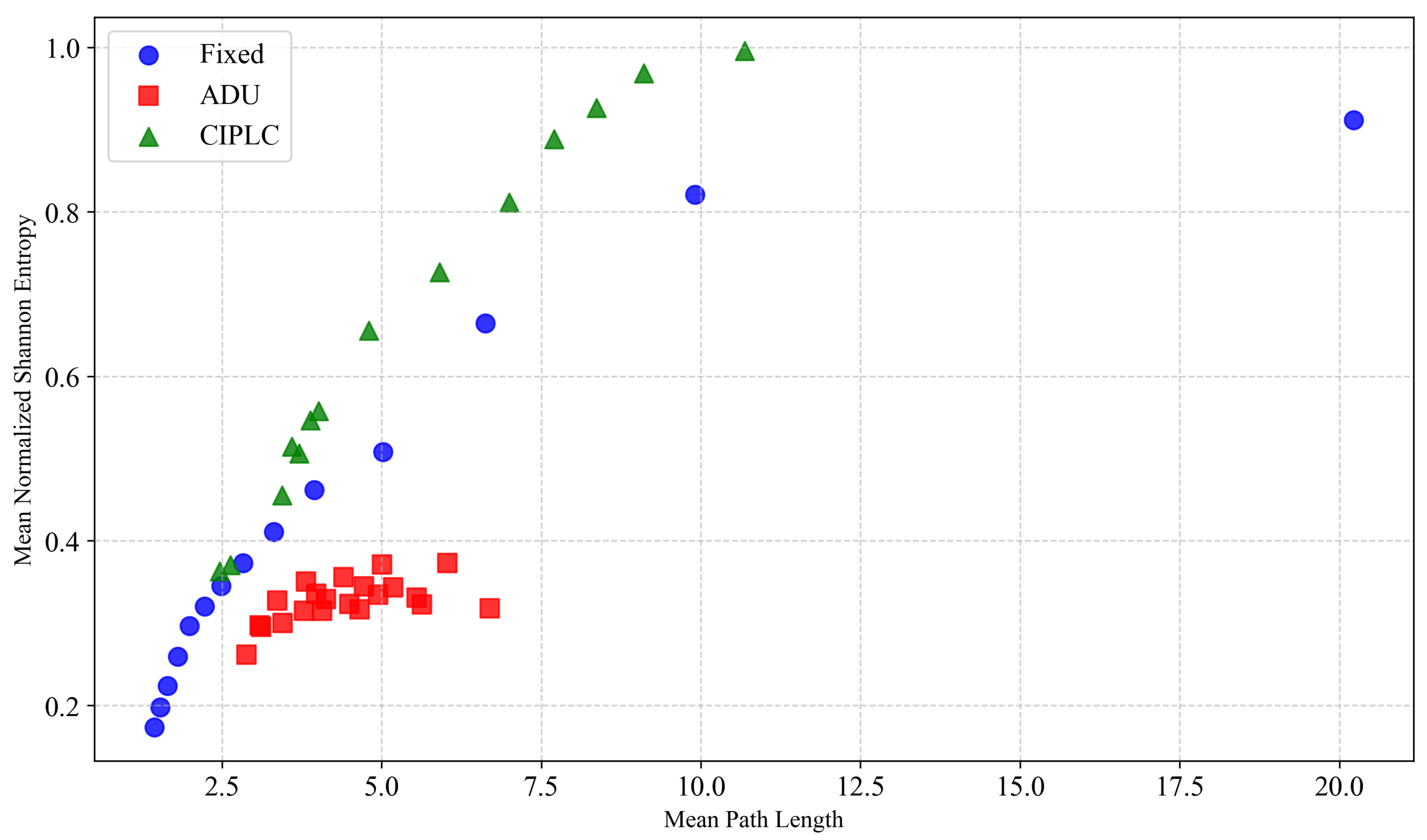
4. Anonymity Evaluation
4.1. Predecessor Attack
- Knowledge of the global network topology;
- Full knowledge of the path-length control algorithm (CIPLC) and its model parameters;
- Ability to observe the forwarding parameter x contained in each packet traversing a node under its control.
- Traditional fixed-probability decrement;
- ADU (Always-Down-or-Up) algorithm.
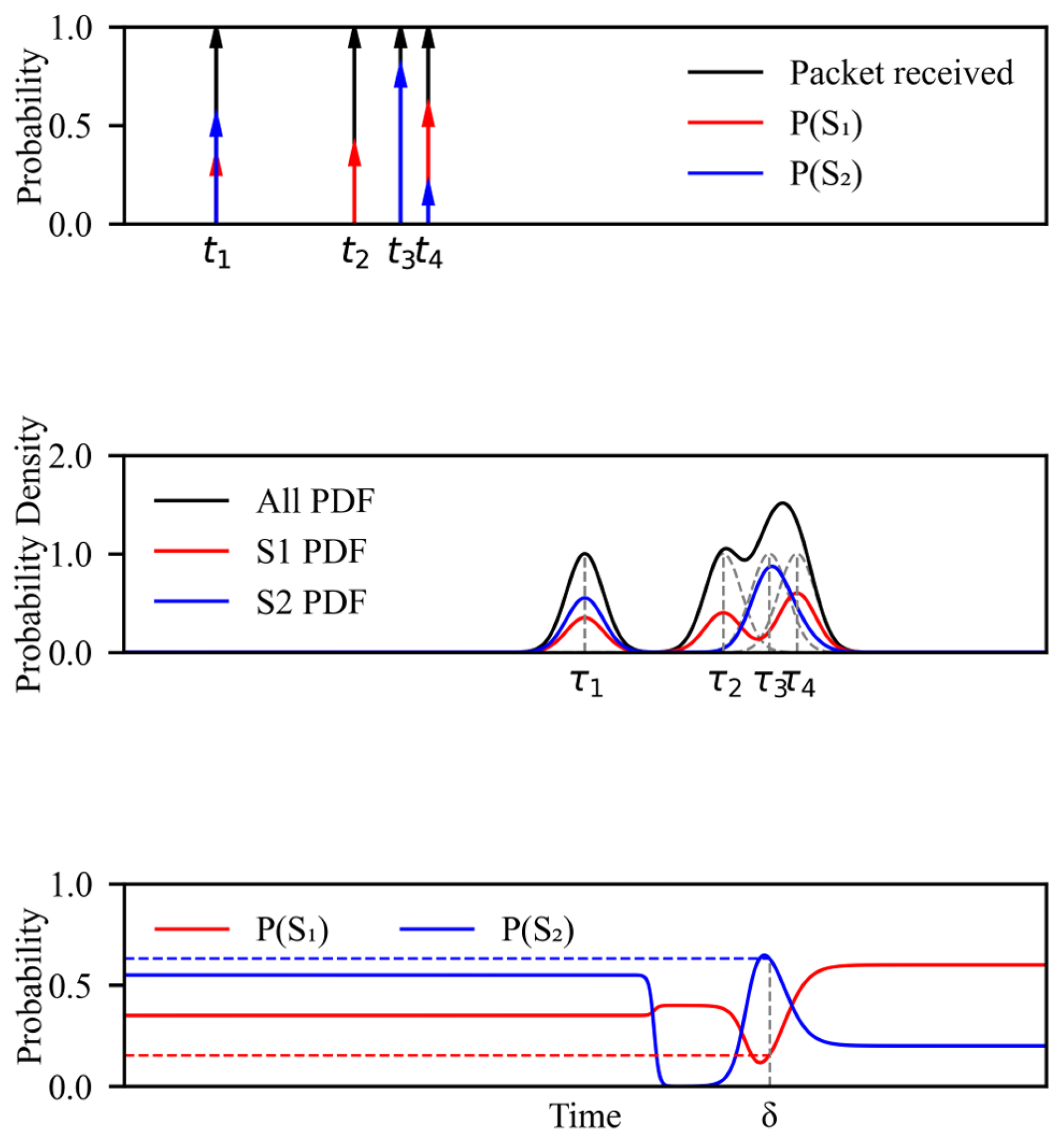
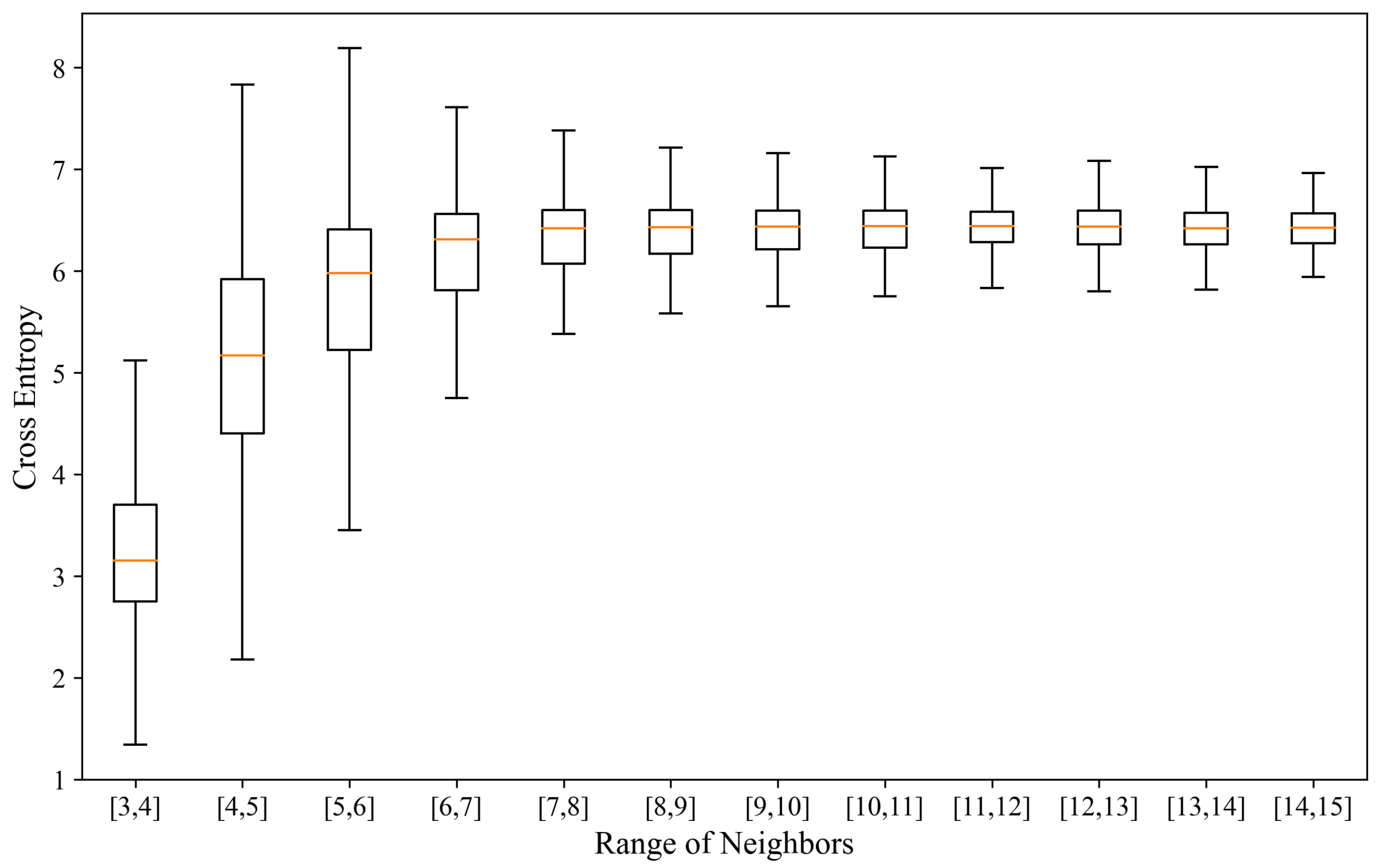
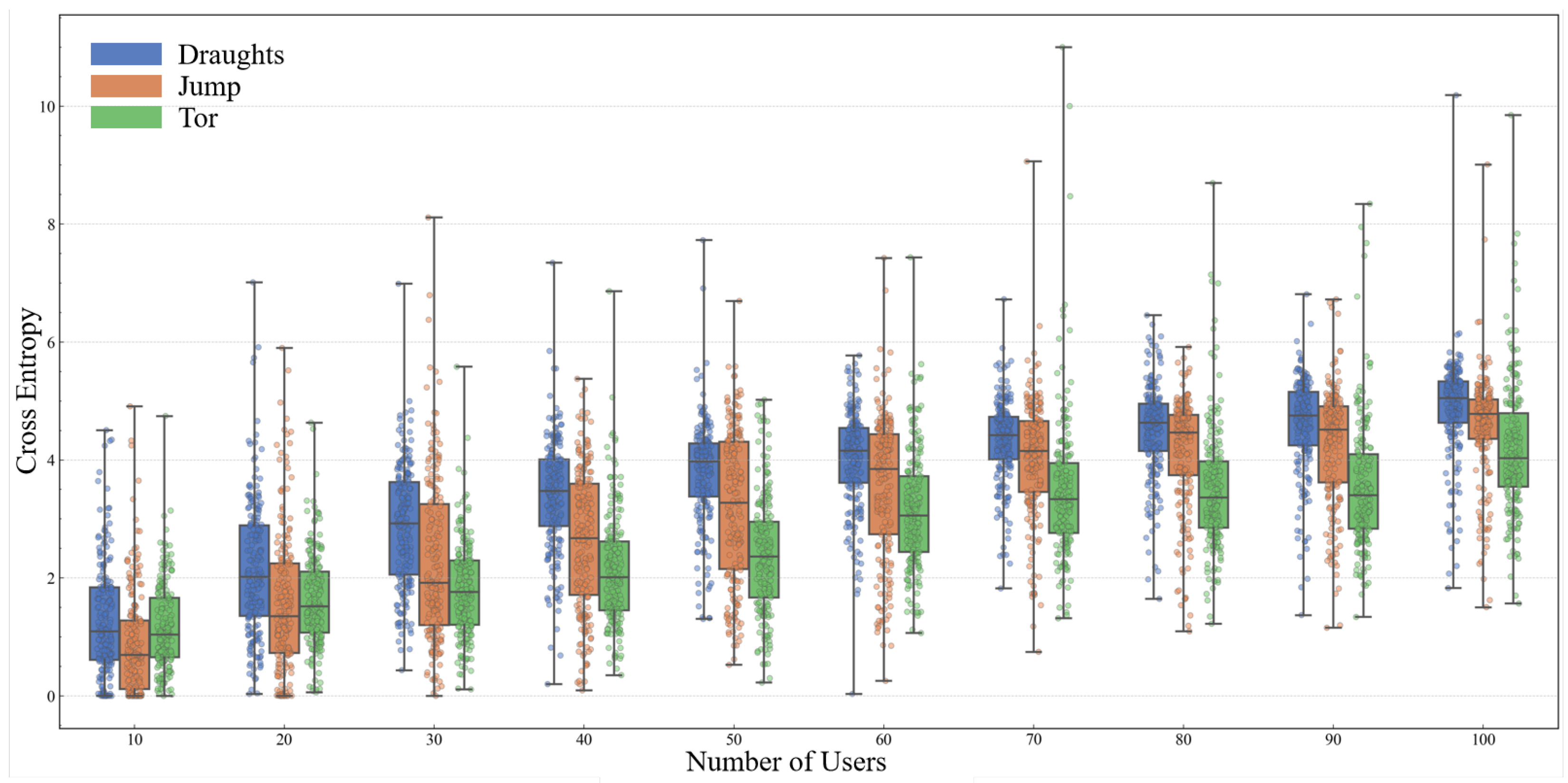
4.2. Traffic Analysis Attack
5. Performance Evaluation
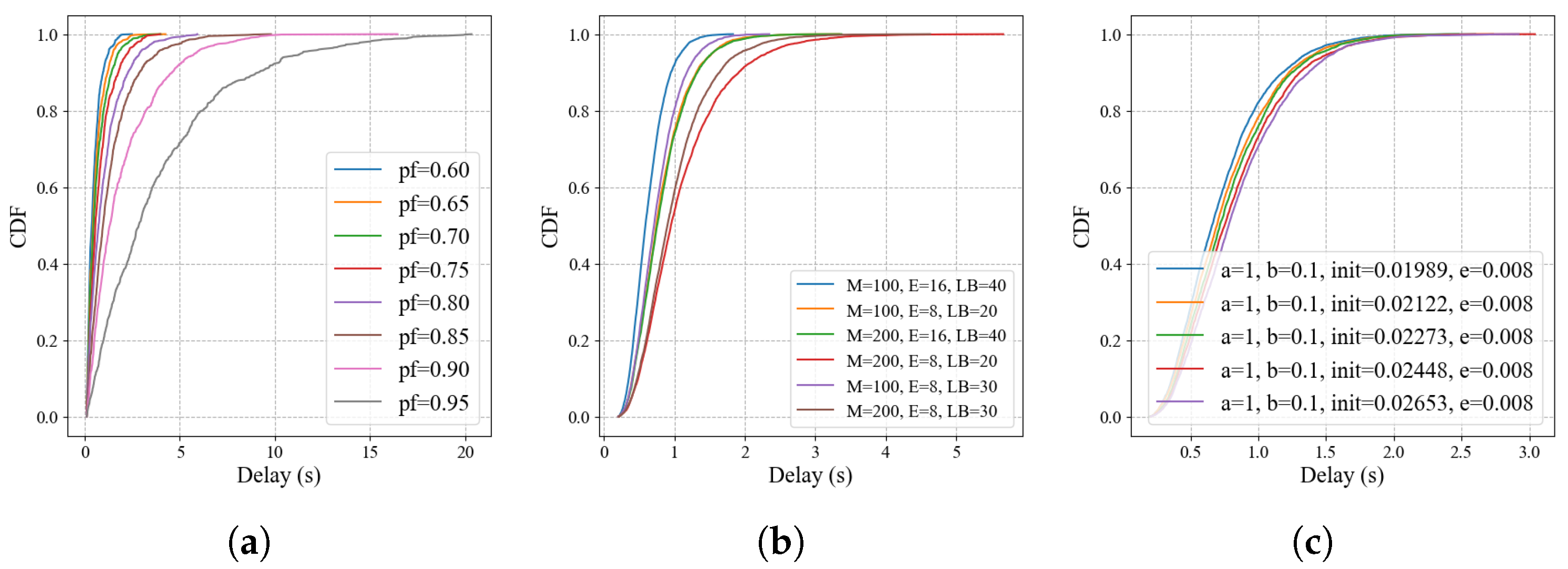
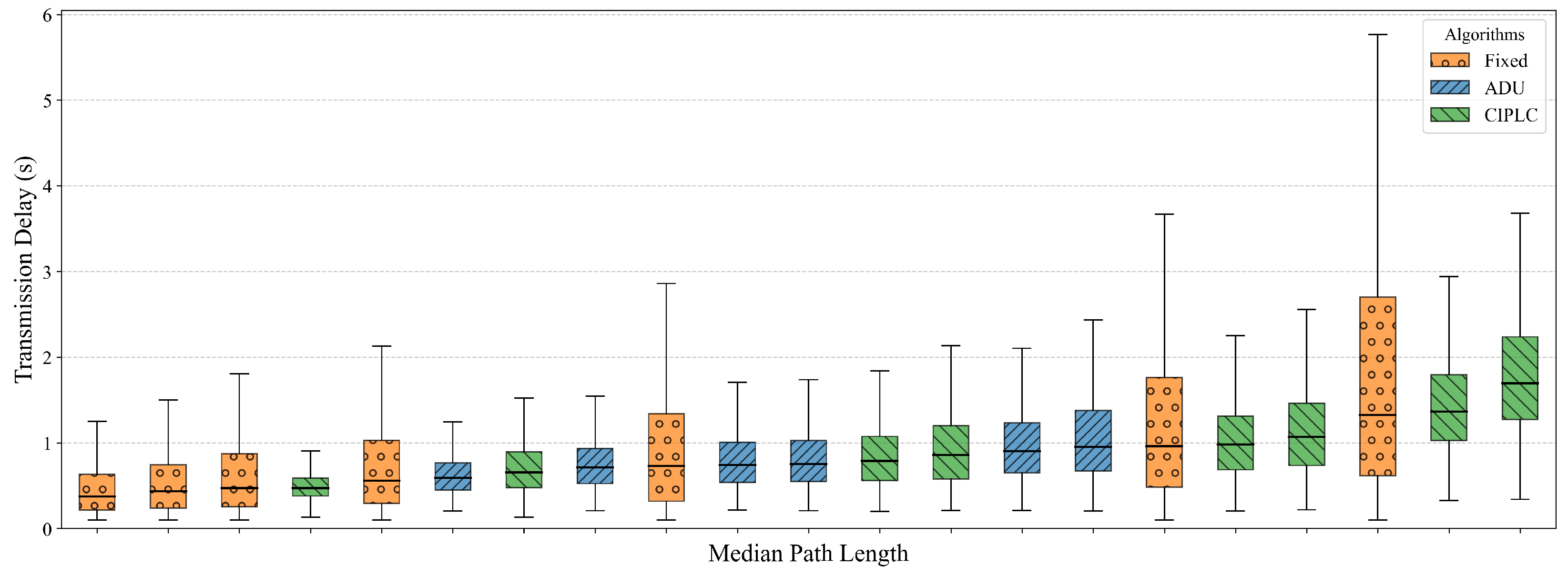
5.1. Transmission Delay Analysis
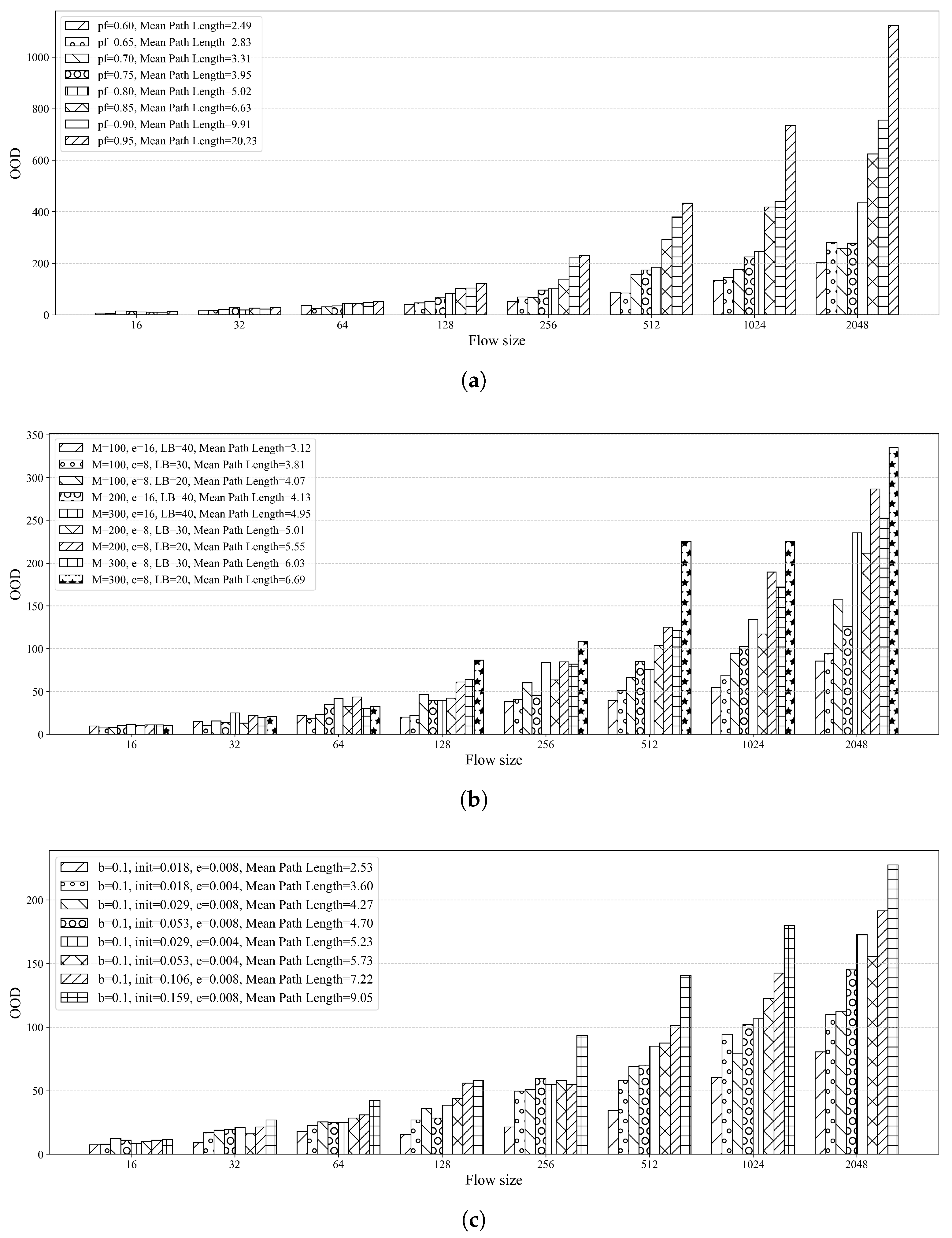
5.2. Out-of-Order Analysis
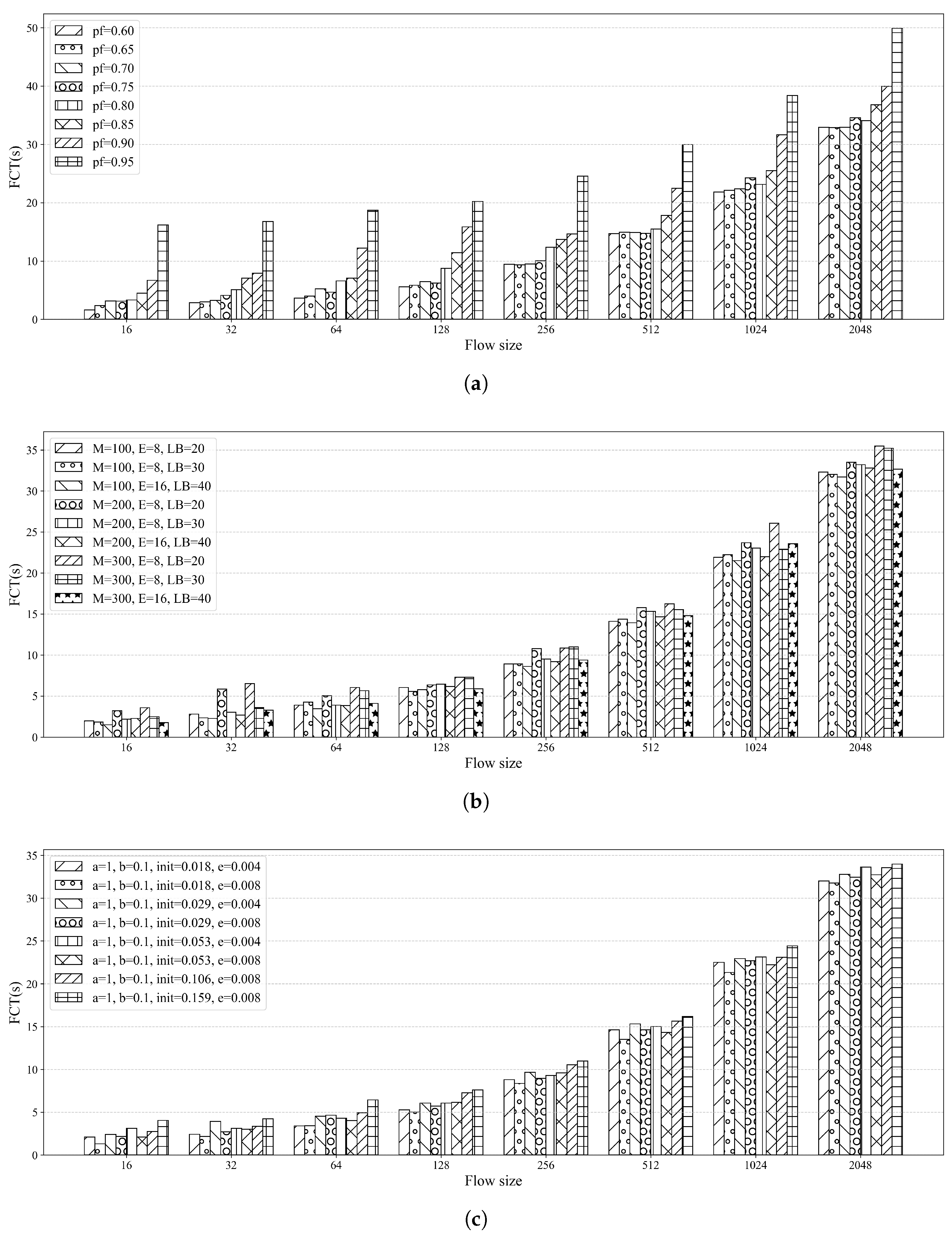
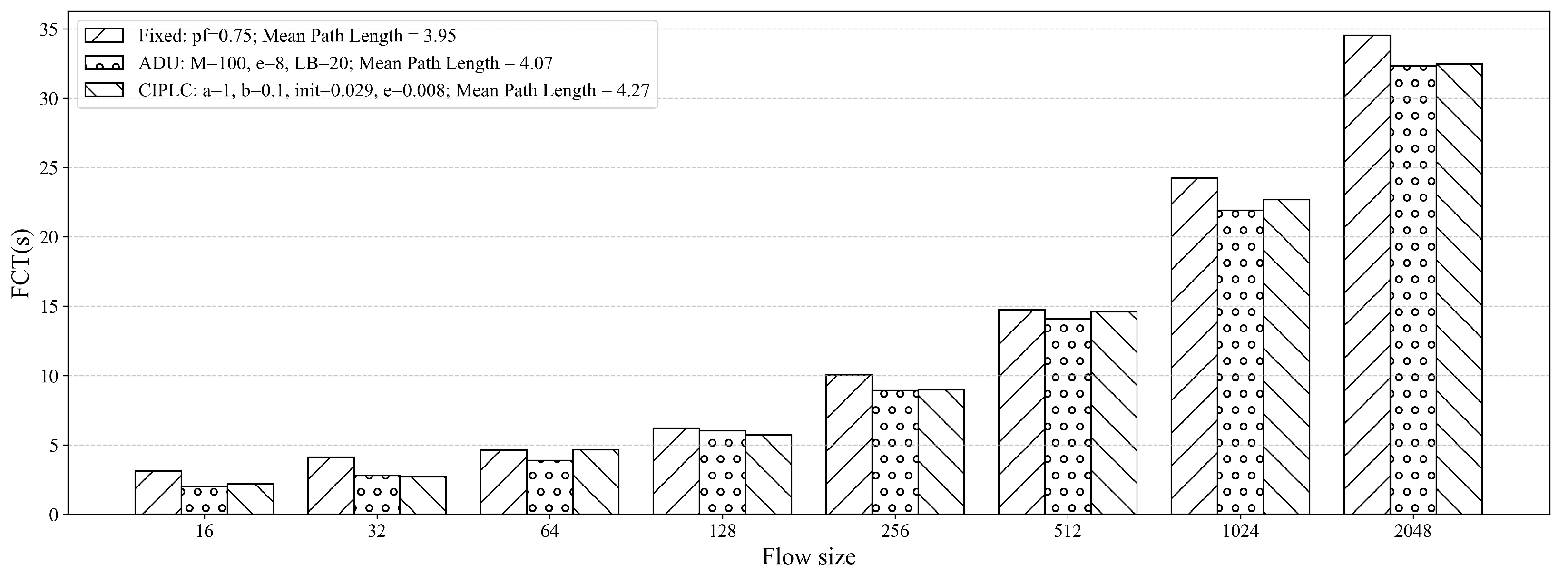
5.3. Flow Completion Time Analysis
5.4. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, P.; Shen, S.; Wan, Y.; Wu, Z.; Fang, Z.; Gao, X.Z. A survey of iot privacy security: Architecture, technology, challenges, and trends. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 34567–34591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACLU of Northern California. Metadata: Piecing Together a Privacy Solution. 2014. Available online: https://www.aclunc.org/publications/metadata-piecing-together-privacy-solution (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Cohn-Gordon, K.; Cremers, C.; Dowling, B.; Garratt, L.; Stebila, D. A formal security analysis of the signal messaging protocol. J. Cryptol. 2020, 33, 1914–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingledine, R.; Mathewson, N.; Syverson, P.F. Tor: The Second-Generation Onion Router. In Proceedings of the 13th USENIX Security Symposium, San Diego, CA, USA, 9–13 August 2004; USENIX Association: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Piotrowska, A.M.; Hayes, J.; Elahi, T.; Meiser, S.; Danezis, G. The loopix anonymity system. In Proceedings of the 26th Usenix Security Symposium (Usenix Security 17), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 16–18 August 2017; pp. 1199–1216. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz, C.; Halpin, H.; Kiayias, A. The Nym Network: The Next Generation of Privacy Infrastructure. Version 1.0. 2021. Available online: https://nym.com/nym-whitepaper.pdf (accessed on 2 August 2025).
- Platzer, F.; Schäfer, M.; Steinebach, M. Critical traffic analysis on the tor network. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Availability, Reliability and Security, Dublin, Ireland, 25–28 August 2020; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, M.; Ye, K.; Liu, X.; Zhu, L.; Kang, J.; Yu, S.; Li, Q.; Xu, K. Machine learning-powered encrypted network traffic analysis: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2022, 25, 791–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, D.; Dong, J.D.; Medeiros, P.; Castro, D.; Barradas, D.; Portela, B.; Vinagre, J.; Ferreira, B.; Christin, N.; Santos, N. Flow Correlation Attacks on Tor Onion Service Sessions with Sliding Subset Sum. In Proceedings of the Network and Distributed System Security (NDSS) Symposium, San Diego, CA, USA, 26 February–1 March 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Danezis, G.; Goldberg, I. Sphinx: A compact and provably secure mix format. In Proceedings of the 2009 30th IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, Oakland, CA, USA, 17–20 May 2009; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 269–282. [Google Scholar]
- Reiter, M.K.; Rubin, A.D. Crowds: Anonymity for web transactions. Acm Trans. Inf. Syst. Secur. (TISSEC) 1998, 1, 66–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y. Research on the Key Issues of Anonymous Communications. Ph.D. Thesis, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha, China, 2021. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Tso, R. A commutative encryption scheme based on ElGamal encryption. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Information Security and Intelligent Control, Yunlin, Taiwan, 14–16 August 2012; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 156–159. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, K.; Tso, R.; Chen, Y.C. One-time-commutative public key encryption. In Proceedings of the 2017 Computing Conference, London, UK, 18–20 July 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 814–818. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, T.; Schneider, K.; Walk, F. Out-of-Order Execution of Buffered Function Units in Exposed Data Path Architectures. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium Workshops (IPDPSW), Lake Buena Vista, FL, USA, 29 May–2 June 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 229–234. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; Moon, Y.; Hwang, J.; Park, K. Flexcp: A scalable multipath tcp proxy for cellular networks. Proc. ACM Netw. 2023, 1, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; You, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, J. Draughts: A Jump-Based Anonymous Communication System without Global Knowledge and with Built-In Anonymous Replies. In Proceedings of the IEEE Consumer Communications & Networking Conference (CCNC 2026), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 9–12 January 2026. [Google Scholar]
- Shirazi, F.; Simeonovski, M.; Asghar, M.R.; Backes, M.; Diaz, C. A survey on routing in anonymous communication protocols. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2018, 51, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Invisible Internet Project. I2P: The Invisible Internet Project. Available online: https://geti2p.net/ (accessed on 11 October 2025).
- Cuzzocrea, A.; Martinelli, F.; Mercaldo, F.; Vercelli, G. Tor traffic analysis and detection via machine learning techniques. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Boston, MA, USA, 11–14 December 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 4474–4480. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, R.; Juarez, M.; Gálvez, R.; Elahi, T.; Diaz, C. Inside Job: Applying Traffic Analysis to Measure Tor from Within. In Proceedings of the Network and Distributed System Security Symposium (NDSS), San Diego, CA, USA, 18–21 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Ye, D. Defending against Deep-Learning-Based Flow Correlation Attacks with Adversarial Examples. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2022, 2022, 2962318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjalawe, Y.; Fraihat, S.; Al-E’mari, S. Detection of obfuscated tor traffic based on bidirectional generative adversarial networks and vision transform. Comput. Secur. 2023, 135, 103512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLachlan, J.; Tran, A.; Hopper, N.; Kim, Y. Scalable onion routing with torsk. In Proceedings of the 16th ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Chicago, IL, USA, 9–13 November 2009; pp. 590–599. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Asoni, D.E.; Barrera, D.; Danezis, G.; Perrig, A. HORNET: High-speed onion routing at the network layer. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Denver, CO, USA, 12–16 October 2015; pp. 1441–1454. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, E.; Tschorsch, F. Poster: On Integrating Sphinx in IPFS. In Proceedings of the 2024 ACM on Internet Measurement Conference, Denver, CO, USA, 12–16 October 2024; pp. 753–754. [Google Scholar]
- Rahimi, M.; Kumar Sharma, P.; Diaz, C. LARMix: Latency-Aware Routing in Mix Networks. In Proceedings of the Network and Distributed System Security Symposium (NDSS), San Diego, CA, USA, 26 February–1 March 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Rahimi, M. Larmix++: Latency-Aware Routing in Mix Networks with Free Routes Topology. In Cryptology and Network Security; Kohlweiss, M., Di Pietro, R., Beresford, A., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2025; pp. 187–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, M. MOCHA: Mixnet Optimization Considering Honest Client Anonymity. In Proceedings of the ACM Workshop on Information Hiding and Multimedia Security, San Jose, CA, USA, 18–20 June 2025; pp. 98–107. [Google Scholar]
- Kocaoğullar, C.; Hugenroth, D.; Kleppmann, M.; Beresford, A.R. Pudding: Private user discovery in anonymity networks. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Francisco, CA, USA, 19–23 May 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 3203–3220. [Google Scholar]
- Corrigan-Gibbs, H.; Boneh, D.; Mazières, D. Riposte: An anonymous messaging system handling millions of users. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, San Jose, CA, USA, 17–21 May 2015; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 321–338. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, A.; Lazar, D.; Devadas, S.; Ford, B. Riffle: An Efficient Communication System with Strong Anonymity. Proc. Priv. Enhancing Technol. 2016, 2016, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Hooff, J.; Lazar, D.; Zaharia, M.; Zeldovich, N. Vuvuzela: Scalable private messaging resistant to traffic analysis. In Proceedings of the 25th Symposium on Operating Systems Principles, Monterey, CA, USA, 4–7 October 2015; pp. 137–152. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, T.; Jiang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, X.; Qi, J.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, F.; Luo, X.; Cui, H. Daenet: Making strong anonymity scale in a fully decentralized network. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2021, 19, 2286–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, I.; Domenic, K.; Memon, H.; Akhtar, R.; Yong, W.; Zhang, F. Rumor riding: An anonymity approach for decentralized peer to peer systems. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2014, 79, 647–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz-Gea, J.P.; Malgosa-Sanahuja, J.; Manzanares-Lopez, P.; Sanchez-Aarnoutse, J.C.; García-Haro, J. A low-variance random-walk procedure to provide anonymity in overlay networks. In Proceedings of the European Symposium on Research in Computer Security, Torremolinos, Spain, 6–8 October 2008; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 238–250. [Google Scholar]
- Danezis, G.; Diaz, C.; Käsper, E.; Troncoso, C. The wisdom of Crowds: Attacks and optimal constructions. In Proceedings of the European Symposium on Research in Computer Security, Saint-Malo, France, 21–23 September 2009; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 406–423. [Google Scholar]

| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| CUR | Current node |
| NH | Next hop node |
| NNH | Next-next hop node |
| PH | Previous hop node |
| PPH | Previous-previous hop node |
| SAddr | Sender address |
| RAddr | Receiver address |
| Unique identifier of node i |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, K.; You, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, J. Draughts: A Decentralized Jump-Based System for Interactive Anonymous Communication. Electronics 2025, 14, 4439. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14224439
Wang K, You J, Li Y, Chen J. Draughts: A Decentralized Jump-Based System for Interactive Anonymous Communication. Electronics. 2025; 14(22):4439. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14224439
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Kaiwen, Jiali You, Yang Li, and Jun Chen. 2025. "Draughts: A Decentralized Jump-Based System for Interactive Anonymous Communication" Electronics 14, no. 22: 4439. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14224439
APA StyleWang, K., You, J., Li, Y., & Chen, J. (2025). Draughts: A Decentralized Jump-Based System for Interactive Anonymous Communication. Electronics, 14(22), 4439. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14224439






