HGNN-AS: Enhancing Hypergraph Neural Network for Node Classification Accuracy with Attention and Self-Attention
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose the HGNN-AS model for enhancing the accuracy of node classification tasks on hypergraphs.
- We design two self-attention mechanisms using the hyperedge information and node information to learn richer information and obtain better representations.
- We apply the multihead attention mechanism to hypergraphs, which increases the stability of the model and prevents overfitting.
2. Related Work
2.1. Graph Neural Networks
2.2. Hypergraph Neural Networks
2.3. Self-Attention Mechanism
3. Methodology
3.1. HyperGAT for Node Classification
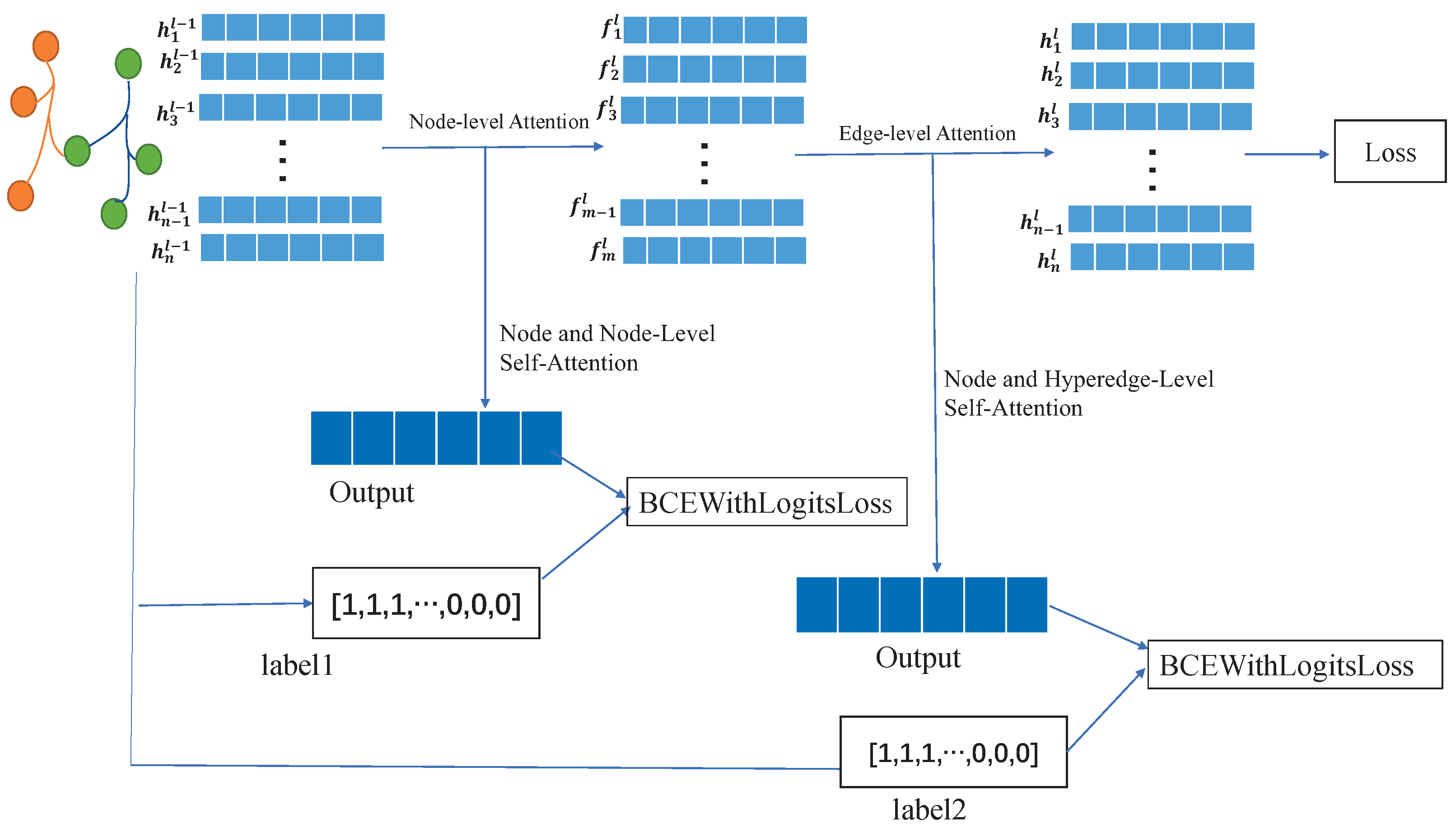
3.2. Hypergraph Neural Network with Attention and Self-Attention
3.2.1. Data Preprocessing and Building Hypergraphs
3.2.2. Node-Level Attention
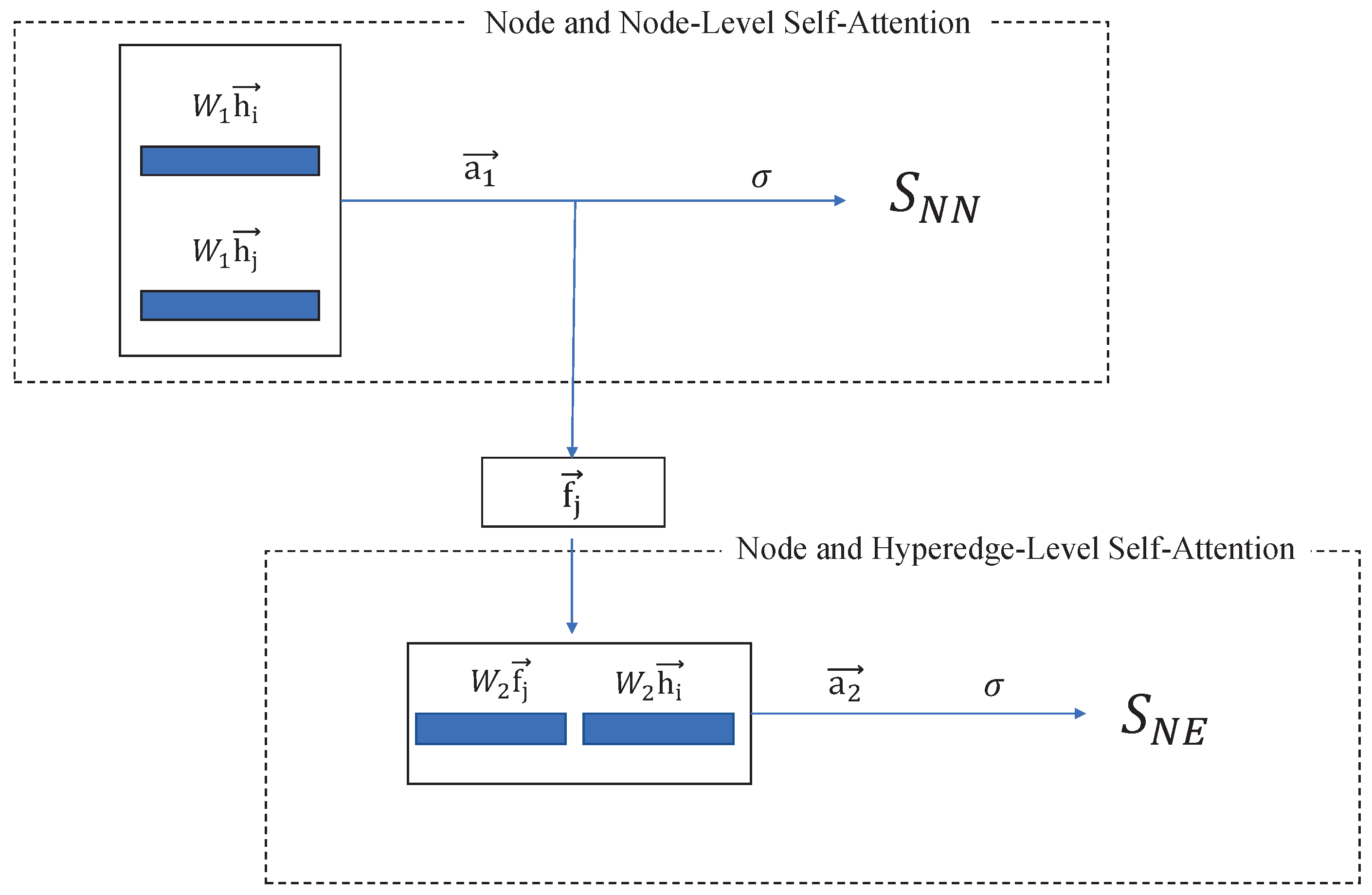
3.2.3. Node and Node-Level Self-Attention
3.2.4. Edge-Level Attention
3.2.5. Node and Hyperedge-Level Self-Attention
| Algorithm 1 Training process of the HGNN-AS model. |
|
3.2.6. Loss Function
4. Experiments
4.1. Citation Network Classification
Datasets
4.2. Experimental Settings
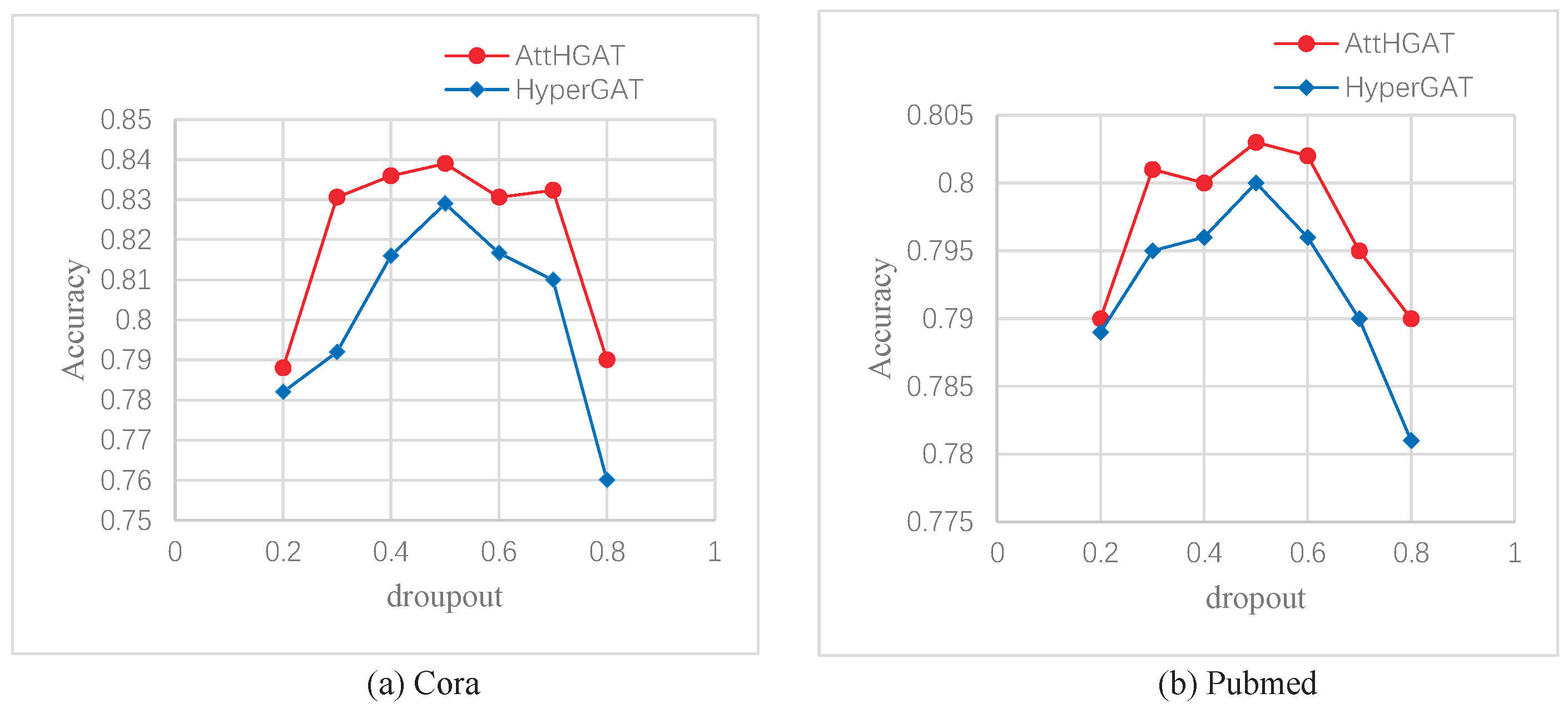
4.3. Results and Discussion
4.4. Visual Object Classification
4.4.1. Datasets
4.4.2. Experimental Settings
4.4.3. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lawson, S.; Donovan, D.; Lefevre, J. An application of node and edge nonlinear hypergraph centrality to a protein complex hypernetwork. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0311433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Ma, Z.; Zhao, W.; Li, L.; Gu, F. HRNN: Hypergraph recurrent neural network for network intrusion detection. J. Grid Comput. 2024, 22, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harit, A.; Sun, Z.; Yu, J.; Moubayed, N.A. Breaking down financial news impact: A novel AI approach with geometric hypergraphs. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2409.00438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; You, H.; Zhang, Z.; Ji, R.; Gao, Y. Hypergraph Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; pp. 3558–3565. [Google Scholar]
- Yadati, N.; Nimishakavi, M.; Yadav, P.; Nitin, V.; Louis, A.; Talukdar, P. HyperGCN: A new method of training graph convolutional networks on hypergraphs. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 32 (NeurIPS 2019), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, K.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Li, D.; Liu, H. Be More with Less: Hypergraph Attention Networks for Inductive Text Classification. In Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Online, 16–20 November 2020; pp. 4927–4936. [Google Scholar]
- Luong, M.T.; Pham, H.; Manning, C.D. Effective approaches to attention-based neural machine translation. In Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Lisbon, Portugal, 17–21 September 2015; pp. 1412–1421. [Google Scholar]
- Bahdanau, D.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.0473. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Velickovic, P.; Cucurull, G.; Casanova, A.; Romero, A.; Liò, P.; Bengio, Y. Graph attention networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.10903. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, W.; Chen, X.; Huang, S.; Xiong, G.; Yan, K.; Zhou, X. Federated learning edge network-based sentiment analysis combating global COVID-19. Comput. Commun. 2023, 204, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ping, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y. Dimensionality reduction in evolutionaryalgorithms-based featureselection for motor imagerybrain-computer interface. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2020, 52, 100597. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, Y.; Liu, W.; Yang, Q.; Mao, X.; Li, F. Trust based task offloading scheme in UAV-enhanced edge computing network. Peer-Peer Netw. Appl. 2021, 14, 3268–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Xian, M.; Zhou, X.; Wang, H.; Cheng, H.D. Multi-slice low-rank tensor decomposition based multi-atlas segmentation: Application to automatic pathological liver CT segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 73, 102152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Kou, G.; Zhou, X.; Peng, Y.; Sheng, H.; Alsaadi, F.E. Time-dependent vehicle routing problem with time windows of city logistics with a congestion avoidance approach. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2020, 188, 104813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, F.; Li, S.; Dai, H.; Hu, C.; Dou, W.; Ni, Q. k-anonymity based schema for location privacy preservation. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Comput. 2017, 4, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; He, A.; Wen, Y.; Liu, G.; Chronopoulos, A.T. Optimal trading mechanism based on differential privacy protection and Stackelberg game in big data market. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2023, 16, 3550–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xihua, L.; Chen, X. D-intuitionistichesitant fuzzy sets and their application in multiple attributedecision making. Cogn. Comput. 2018, 10, 496–505. [Google Scholar]
- Donghai, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, A. The new similarity measureand distance measure betweenhesitant fuzzy linguisticterm sets and their applicationin multi-criteria decisionmaking. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 37, 995–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Xu, G.; Xu, X.; Jiang, H.; Tian, Z.; Ma, T. Multicenter hierarchical federated learningwithfault-tolerance mechanismsforresilient edge computingnetworks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 36, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Du, Z.; Chen, X.; Cai, C. Confidence consensus-based model for large-scale group decision making: A novel approach to managing non-cooperative behaviors. Inf. Sci. 2019, 477, 410–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Cai, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, X.; Zeng, H. The optimization of reverse logistics cost based on value flow analysis—A case study on automobile recycling company in China. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2018, 34, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gori, M.; Monfardini, G.; Scarselli, F. A new model for learning in graph domains. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Montreal, QC, Canada, 31 July–4 August 2005; pp. 729–734. [Google Scholar]
- Scarselli, F.; Gori, M.; Tsoi, A.C.; Hagenbuchner, M.; Monfardini, G. The graph neural network model. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2009, 20, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipf, T.N.; Welling, M. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 24–26 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Defferrard, M.; Bresson, X.; Vandergheynst, P. Convolutional neural networks on graphs with fast localized spectral filtering. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 3844–3852. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, C.; Ma, Q. Dual graph convolutional networks for graph-based semi-supervised classification. In Proceedings of the 2018 World Wide Web Conference, International World Wide Web Conferences Steering Committee, Lyon, France, 23–27 April 2018; pp. 499–508. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, F.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, S.; Wang, L.; Tan, T. Hierarchical graph convolutional networks for semi-supervised node classification. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.06667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Liu, W.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y. Two-order graph convolutional networks for semi-supervised classification. IET Image Process. 2019, 13, 2763–2771. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, M.; Kou, G.; Dong, Y.; Chiclana, F.; Herrera-Viedma, E. Bounded confidence evolution of opinions and actions in social networks. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 52, 7017–7028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Chen, H.; Wang, D.; Shoaib, J.; Yu, P.; Xu, G. Click-through rate prediction with multi-modal hypergraphs. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Virtual, 1–5 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Park, J.; Park, J. A hypergraph convolutional neural network for molecular properties prediction using functional group. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.01028. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Bhuiyan, M.Z.A.; Yang, X.; Wang, T.; Xu, X.; Hayajneh, T.; Khan, F. AntiConcealer: Reliable detection of adversary concealed behaviors in EdgeAI-assisted IoT. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 9, 22184–22193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Yemei, Q.; Shen, Z. Correlation-split and Recombination-sort Interaction Networks for airquality forecasting. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 145, 110544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berge, C. Graphs and Hypergraphs. In North-Holland Mathematical Library; North-Holland: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.; Huang, J.; Schölkopf, B. Learning with hypergraphs: Clustering, classification, and embedding. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 4–7 December 2006; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007; pp. 1601–1608. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Lin, H.; Gao, Y. Dynamic hypergraph structure learning. In Proceedings of the 27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 13–19 July 2018; AAAI Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; pp. 3162–3169. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, N.; Chen, Y.; Zou, C.; Wan, H.; Zhao, X.; Gao, Y. Hypergraph label propagation network. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; AAAI Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2020; Volume 34, pp. 6885–6892. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Sawin, W.; Bengio, Y. HNHN: Hypergraph Networks with Hyperedge Neurons. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.12278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Zhang, F.; Torr, P.H. Hypergraph convolution and hypergraph attention. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 110, 107637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duta, I.; Cassarà, G.; Silvestri, F.; Lió, P. Sheaf hypergraph networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 12087–12099. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.; Sarkar, S.; Lausen, L.; Srinivasan, B.; Zha, S.; Huang, R.; Karypis, G. Hytrel: Hypergraph-enhanced tabular data representation learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 32173–32193. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, W.; Mao, Z.; Yi, S.; Qin, Y.; Gu, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Luo, X.; Zhang, M. Hypergraph-enhanced dual semi-supervised graph classification. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.04773. [Google Scholar]
- Mnih, V.; Heess, N.; Graves, A.; Kavukcuoglu, K. Recurrent models of visual attention. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.6247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rush, A.M.; Chopra, S.; Weston, J. A neural attention model for abstractive sentence summarization. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1509.00685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnih, V.; Heess, N.; Graves, A. Recurrent models of visual attention. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014; pp. 2204–2212. [Google Scholar]
- Ba, J.; Mnih, V.; Kavukcuoglu, K. Multiple object recognition with visual attention. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.7755. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, E.; Rappaport, L.A.; Kemper, K.J. Complementary and alternative therapies in childhood attention and hyperactivity problems. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. 2003, 24, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Ba, J.; Kiros, R.; Cho, K.; Courville, A.; Salakhudinov, R.; Zemel, R.; Bengio, Y. Show, attend and tell: Neural image caption generation with visual attention. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 2048–2057. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; Oh, A. How to Find Your Friendly Neighborhood: Graph Attention Design with Self-Supervision. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.04879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cao, X.; Dong, W. Factors affecting customer intention to adopt a mobile chronic disease management service: Differentiating age effect from experiential distance perspective. J. Organ. End User Comput. (JOEUC) 2022, 34, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cai, J.; Zhao, R.; Li, C.; He, C.; He, D. Optimizing anchor node deployment for fingerprint localization with low-cost and coarse-grained communication chips. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 15297–15311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Dou, W.; Hu, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, J. A context-aware service evaluation approach over big data for cloud applications. IEEE Trans. Cloud Comput. 2015, 8, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Liu, A.; Mao, X.; Li, F. An intelligent charging scheme maximizing the utility for rechargeable network in smart city. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2021, 77, 101457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-S.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.-J.; Chin, K.S.; Tsui, K.L. Fostering linguistic decision-making under uncertainty: A proportional interval type-2 hesitant fuzzy TOPSIS approach based on Hamacher aggregation operators and andness optimization models. Inf. Sci. 2019, 500, 229–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.; Van Merriënboer, B.; Gulcehre, C.; Bahdanau, D.; Bougares, F.; Schwenk, H.; Bengio, Y. Learning Phrase Representations using RNN Encoder-Decoder for Statistical Machine Translation. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.; Namata, G.; Bilgic, M.; Getoor, L.; Galligher, B.; Eliassi-Rad, T. Collective classification in network data. AI Mag. 2008, 29, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Cohen, W.W.; Salakhutdinov, R. Revisiting Semi-Supervised Learning with Graph Embeddings. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, NY, USA, 19–24 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R. Dropout:A Simple Way to Prevent Neural Networks from Overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1929–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Song, S.; Khosla, A.; Yu, F.; Zhang, L.; Tang, X.; Xiao, J. 3D shapenets: A deep representation for volumetric shapes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1912–1920. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Tian, X.; Shen, Y.; Ouhyoung, M. On visual similarity based 3D model retrieval. In Computer Graphics Forum; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; Volume 22, pp. 223–232. [Google Scholar]
- Su, H.; Maji, S.; Kalogerakis, E.; Learned-Miller, E. Multi-view convolutional neural networks for 3D shape recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 945–953. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Ji, R.; Gao, Y. Gvcnn: Group-view convolutional neural networks for 3D shape recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 264–272. [Google Scholar]


| Dataset | Cora | Pubmed |
|---|---|---|
| Node | 2708 | 19,717 |
| Edge | 5429 | 44,338 |
| Feature | 1433 | 500 |
| Class | 7 | 3 |
| Method | Cora Acc (%) | 95% CI | Pubmed Acc (%) | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GCN [25] | 81.5 | 81.0–82.0 | 79.0 | 78.5–79.5 |
| GAT [10] | 83.0 | 82.5–83.5 | 79.0 | 78.5–79.5 |
| HGNN [4] | 81.6 | 81.2–82.0 | 80.1 | 79.8–80.4 |
| HyperGAT [58] | 82.9 | 82.4–83.4 | 80.0 | 79.6–80.4 |
| HGNN-AS | 83.9 | 83.2–84.3 | 80.3 | 80.0–80.6 |
| Dataset | ModelNet40 | NTU |
|---|---|---|
| Objects | 12,311 | 2012 |
| MVCNN Feature | 4096 | 4096 |
| GVCNN Feature | 2048 | 2048 |
| Training node | 9843 | 1639 |
| Testing node | 2468 | 373 |
| Classes | 40 | 67 |
| Experimental Parameter | Setting |
|---|---|
| Attention head | 2 |
| Feature dimension | 128 |
| Optimizer | Adam optimizer |
| Learning rate | 0.001 |
| Dropout rate | 0.3 |
| Epochs | 1000 |
| Datasets | Feature | Structure | GCN [25] | HGNN [4] | HyperGAT [58] | HGNN-AS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NTU | MVCNN | MVCNN | 86.7% | 91.0% | 90.2% | 91.1% |
| GVCNN | GVCNN | 91.8% | 92.6% | 92.4% | 93.0% | |
| MVCNN | BOTH | 92.3% | 96.6% | 96.4% | 96.7% | |
| GVCNN | BOTH | 92.8% | 96.6% | 96.7% | 97.0% | |
| BOTH | BOTH | 94.4% | 96.7% | 96.7% | 97.0% | |
| Model-Net40 | MVCNN | MVCNN | 71.3% | 75.6% | 76.9% | 77.4% |
| GVCNN | GVCNN | 78.8% | 82.5% | 82.3% | 82.6% | |
| MVCNN | BOTH | 73.2% | 83.6% | 82.8% | 83.7% | |
| GVCNN | BOTH | 75.9% | 84.2% | 83.9% | 84.2% | |
| BOTH | BOTH | 76.1% | 84.2% | 84.0% | 84.2% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Huang, L.; Liu, R.; He, D.; Chen, M.; Wu, Q. HGNN-AS: Enhancing Hypergraph Neural Network for Node Classification Accuracy with Attention and Self-Attention. Electronics 2025, 14, 4282. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14214282
Li C, Huang L, Liu R, He D, Chen M, Wu Q. HGNN-AS: Enhancing Hypergraph Neural Network for Node Classification Accuracy with Attention and Self-Attention. Electronics. 2025; 14(21):4282. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14214282
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chuang, Lanfang Huang, Ruihai Liu, Dian He, Minghui Chen, and Qian Wu. 2025. "HGNN-AS: Enhancing Hypergraph Neural Network for Node Classification Accuracy with Attention and Self-Attention" Electronics 14, no. 21: 4282. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14214282
APA StyleLi, C., Huang, L., Liu, R., He, D., Chen, M., & Wu, Q. (2025). HGNN-AS: Enhancing Hypergraph Neural Network for Node Classification Accuracy with Attention and Self-Attention. Electronics, 14(21), 4282. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14214282





