Reconfigurable Intelligence Surface Assisted Multiuser Downlink Communication with User Scheduling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. RIS-Assisted Multiuser Scheduling System
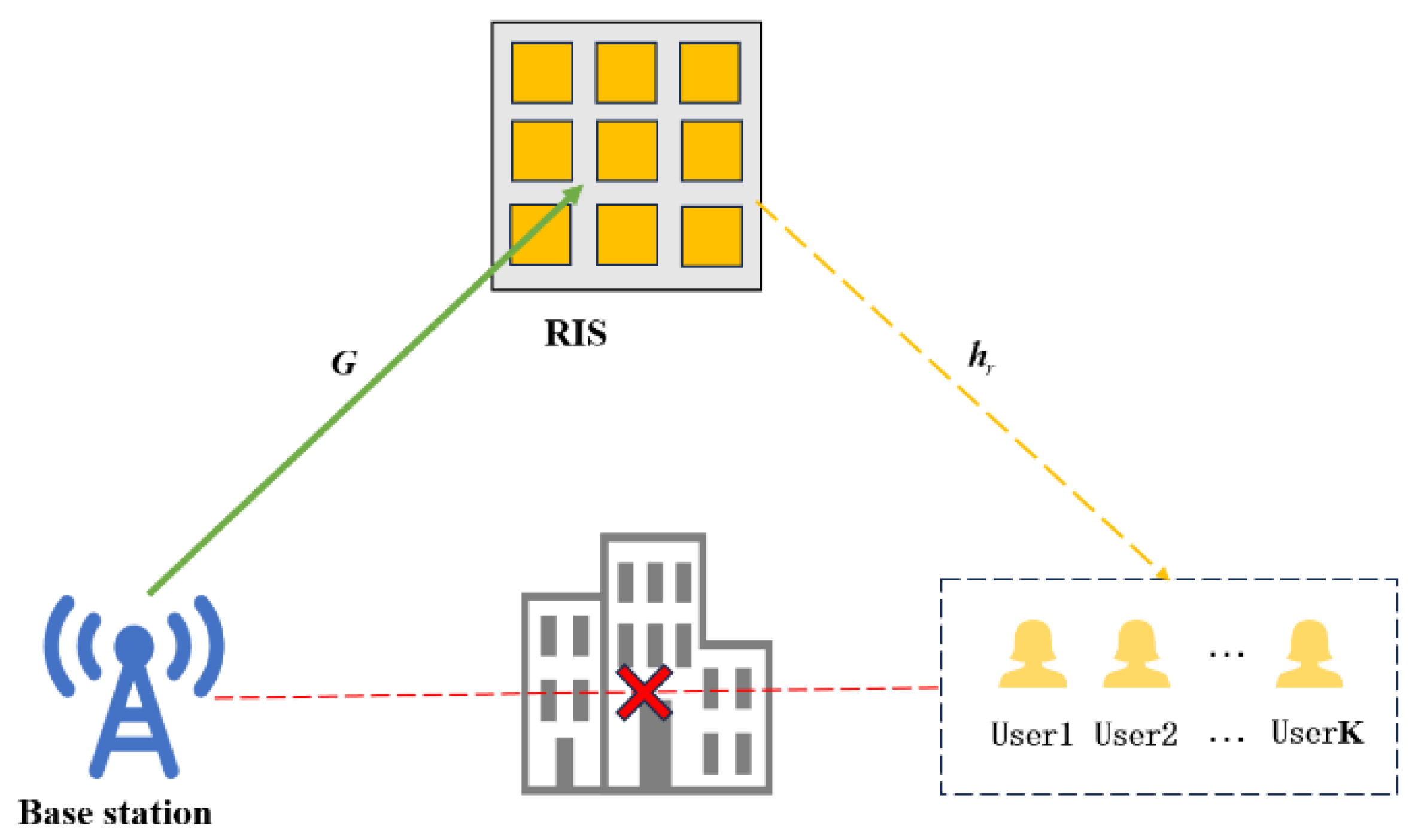
2.1. System Model
2.2. Joint Optimization Design
| Algorithm 1 Multiuser Scheduling and Discrete Phase Shift Design Algorithm |
| 1: Input: |
| 2: Output: |
| 3: Initialize the auxiliary angle , and set ; |
| 4: Calculate the fitness according to the formula ; |
| 5: While: |
| 6: Update the velocity of the auxiliary angle ; |
| 7: Update the positions of the auxiliary angle and the phase shift ; |
| 8: Calculate the fitness and update the individual best fitness fpbest, the individual best position , global best fitness fgbest, and global best position ; |
| 9: |
| 10: Until: ; |
| 11: Return the current global best position . |
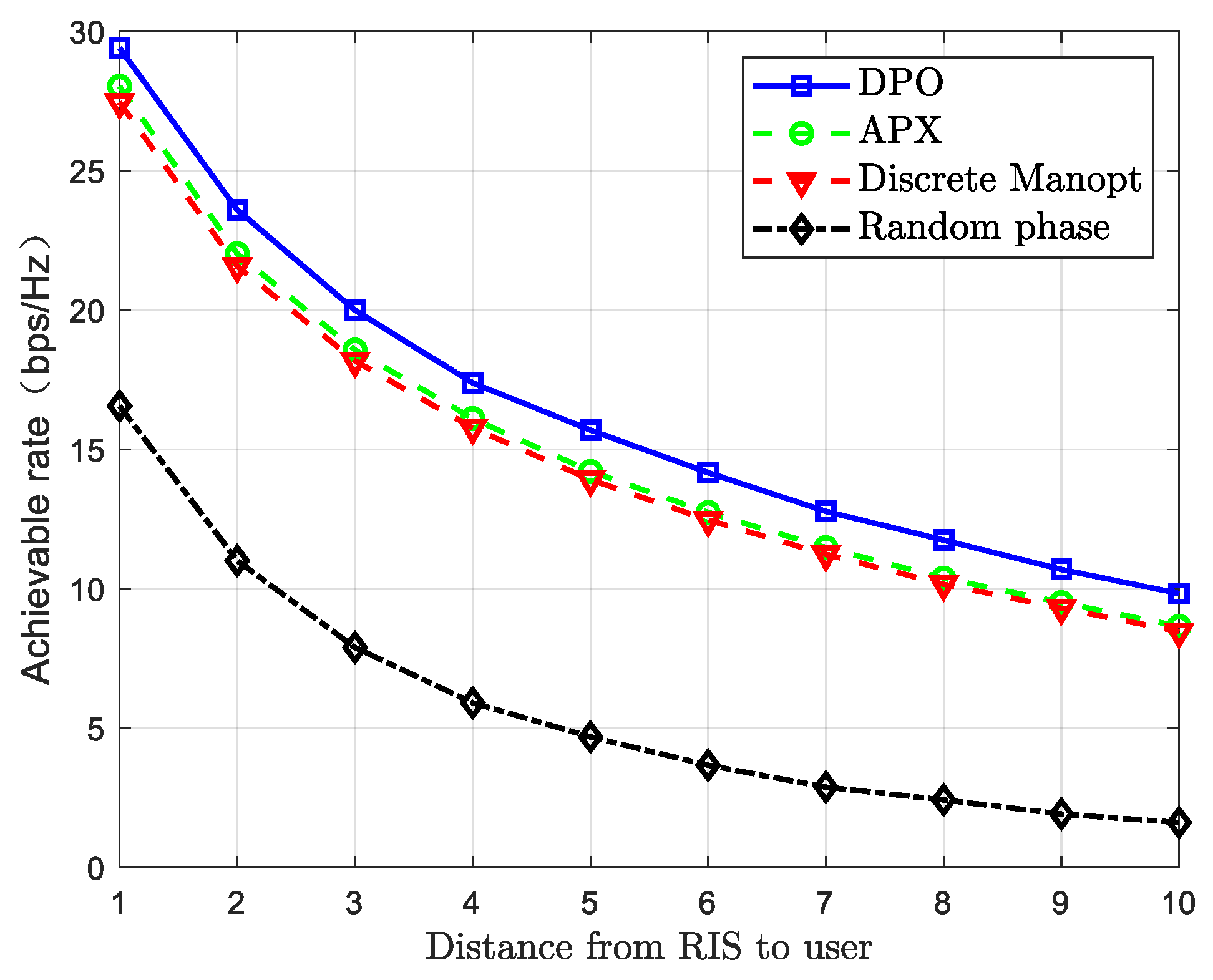
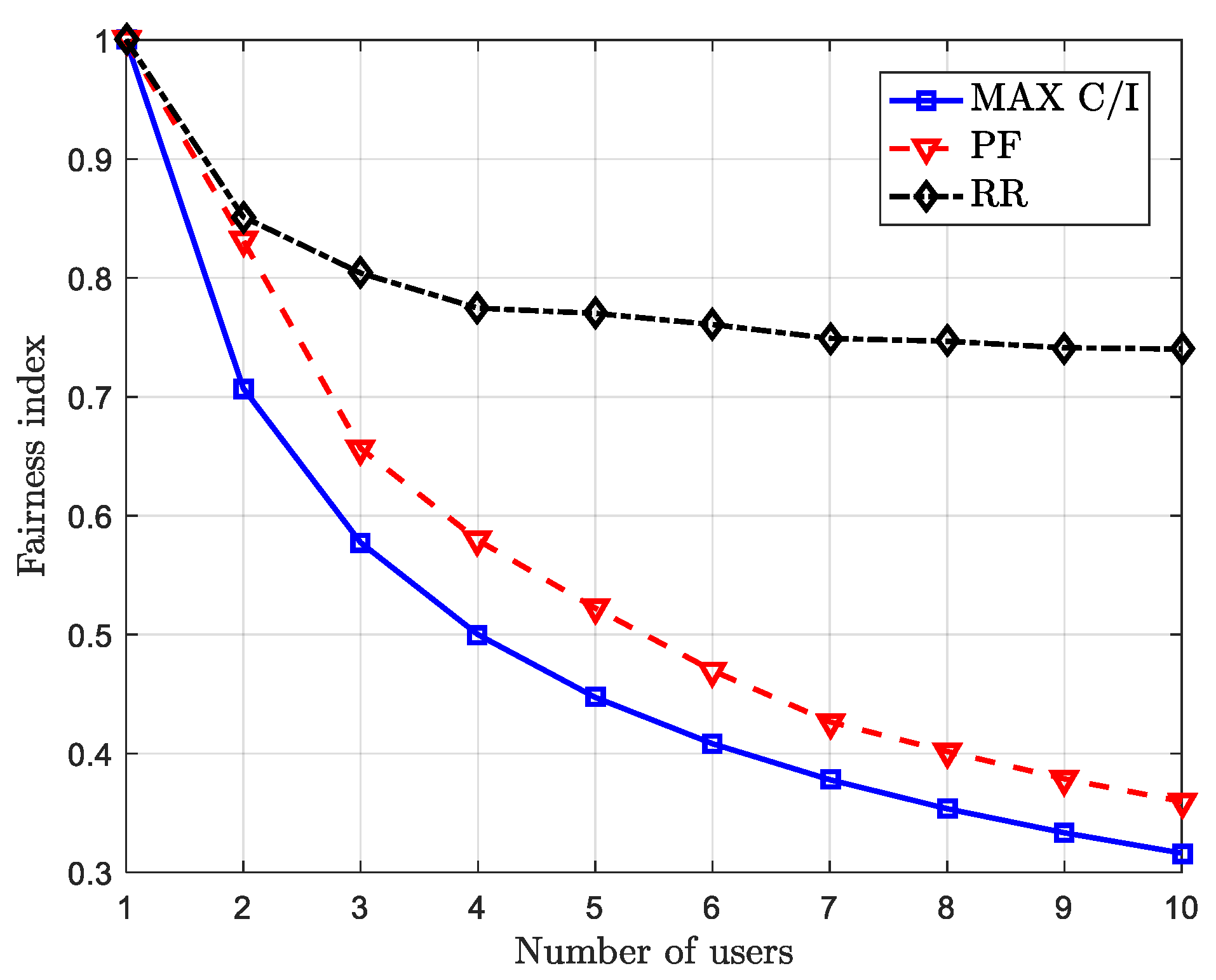
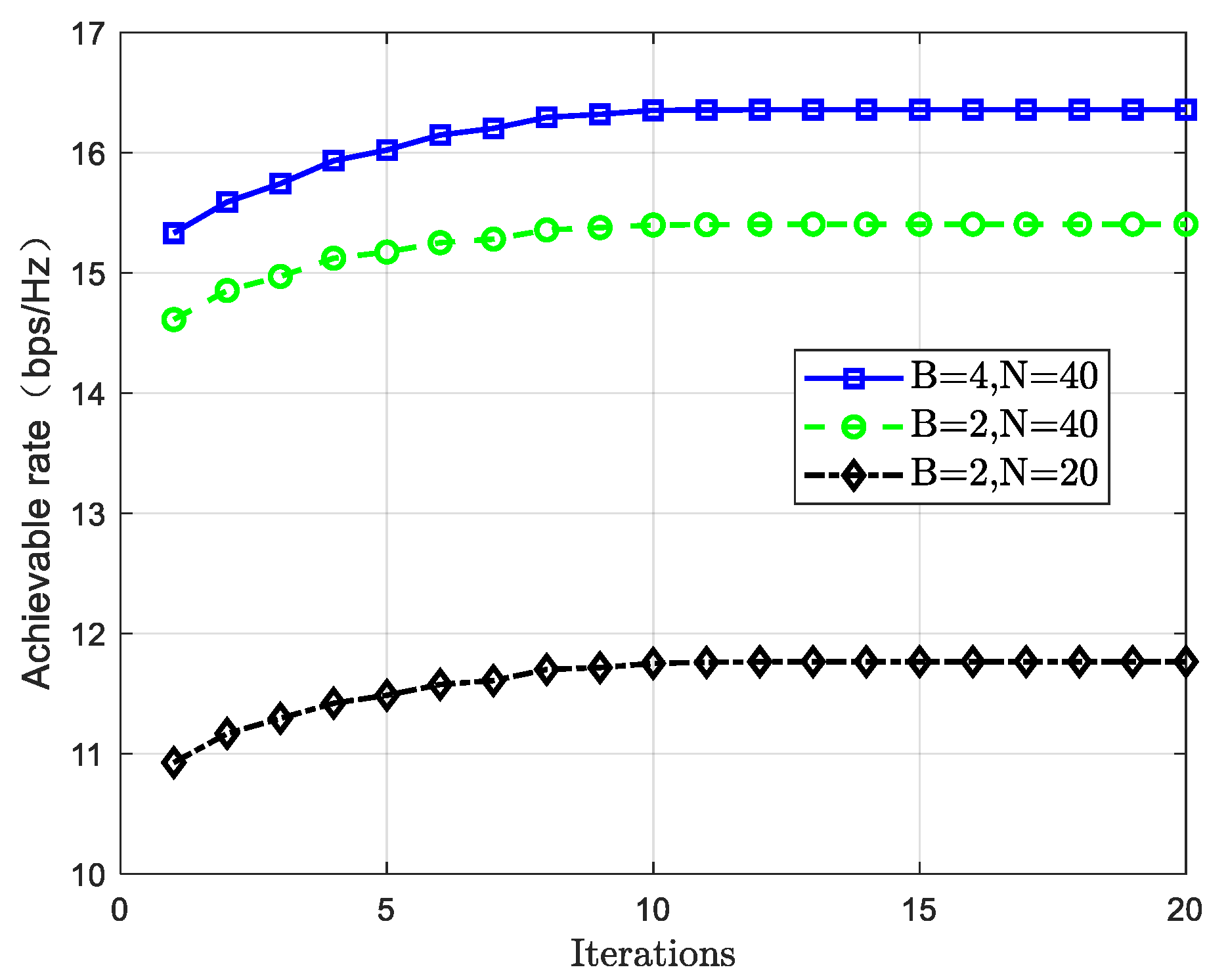
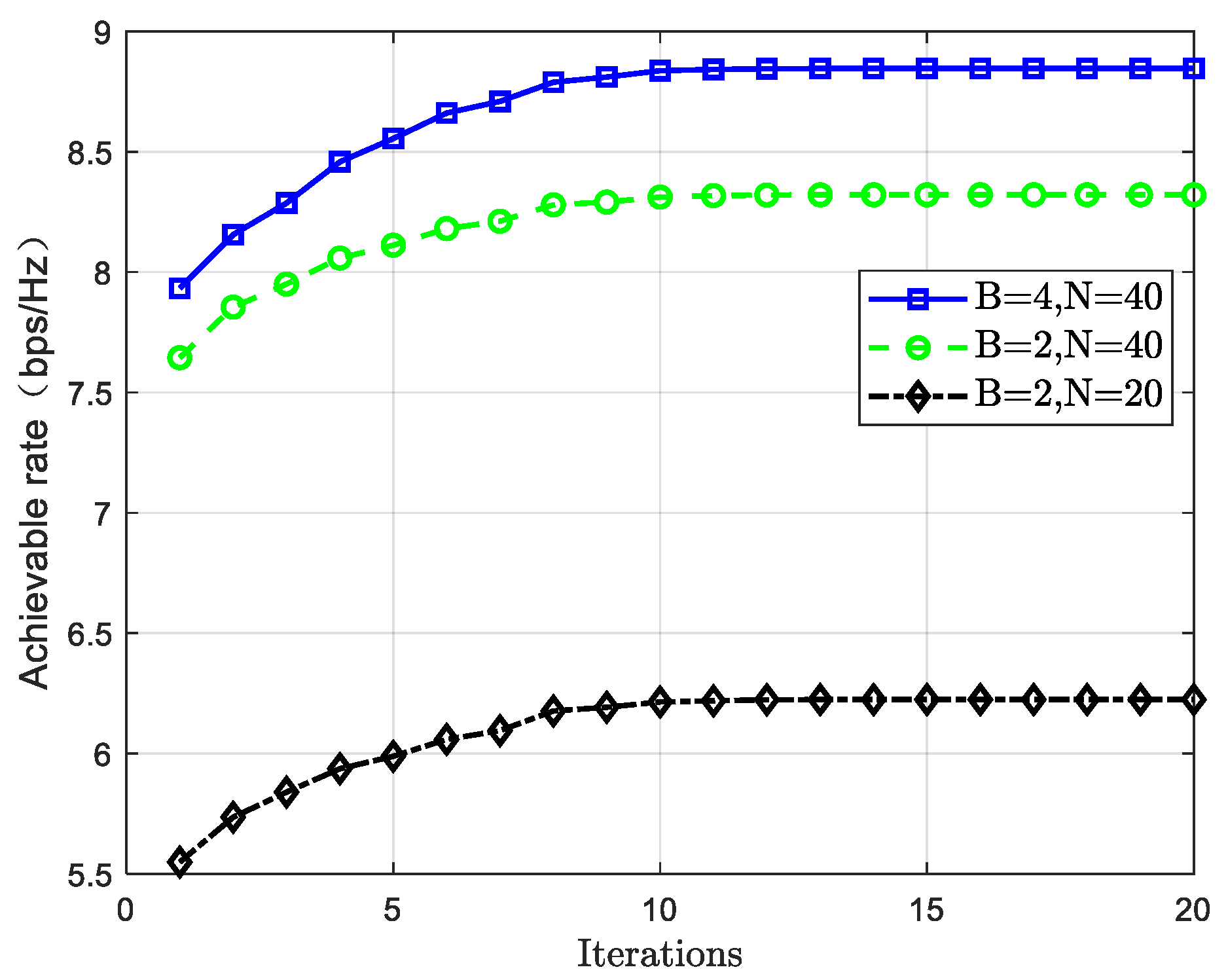
2.3. Joint Optimization Design Parameter Settings and Simulation Results Analysis
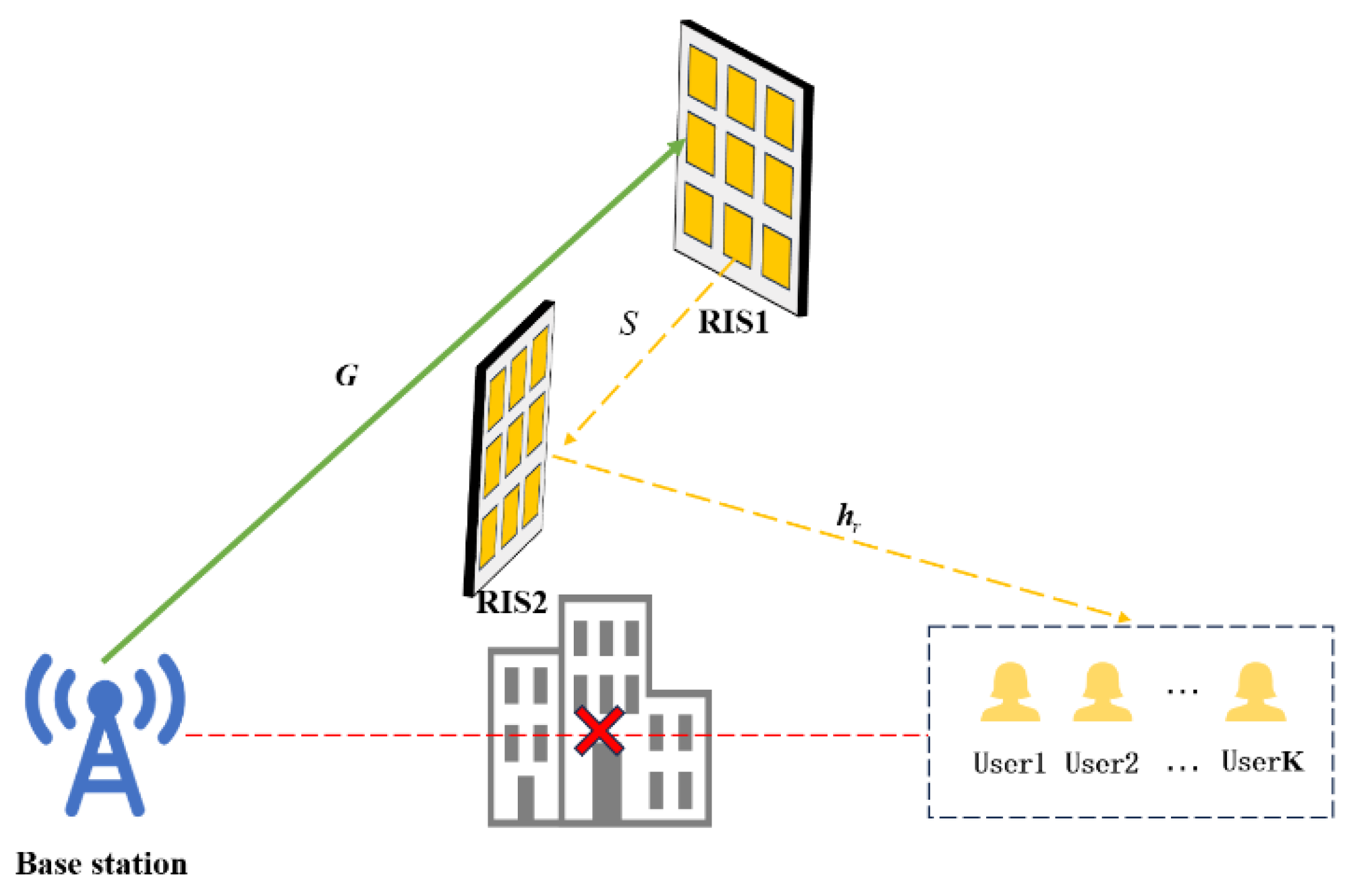
3. Multiuser Scheduling System Assisted by Double RISs
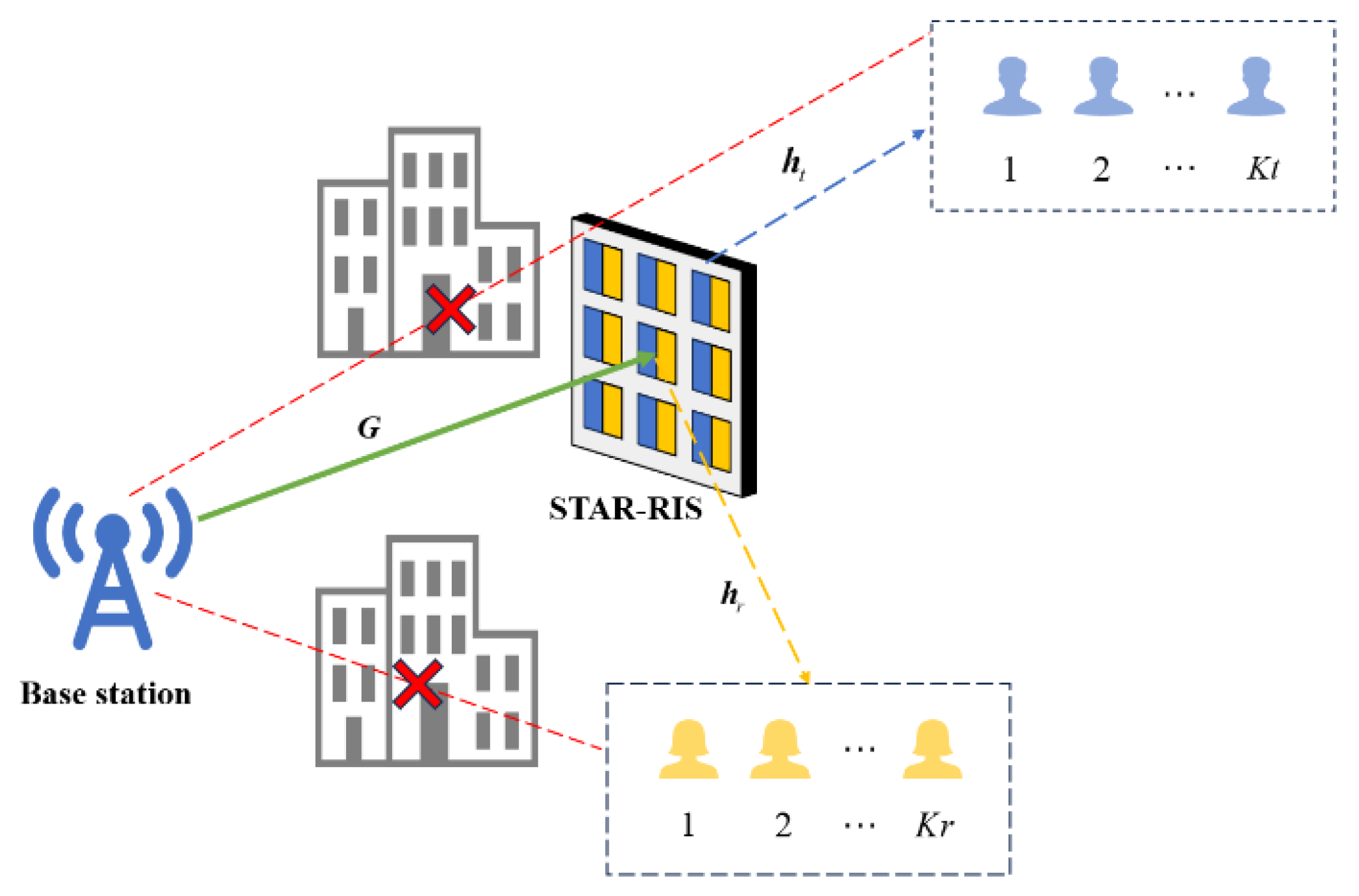
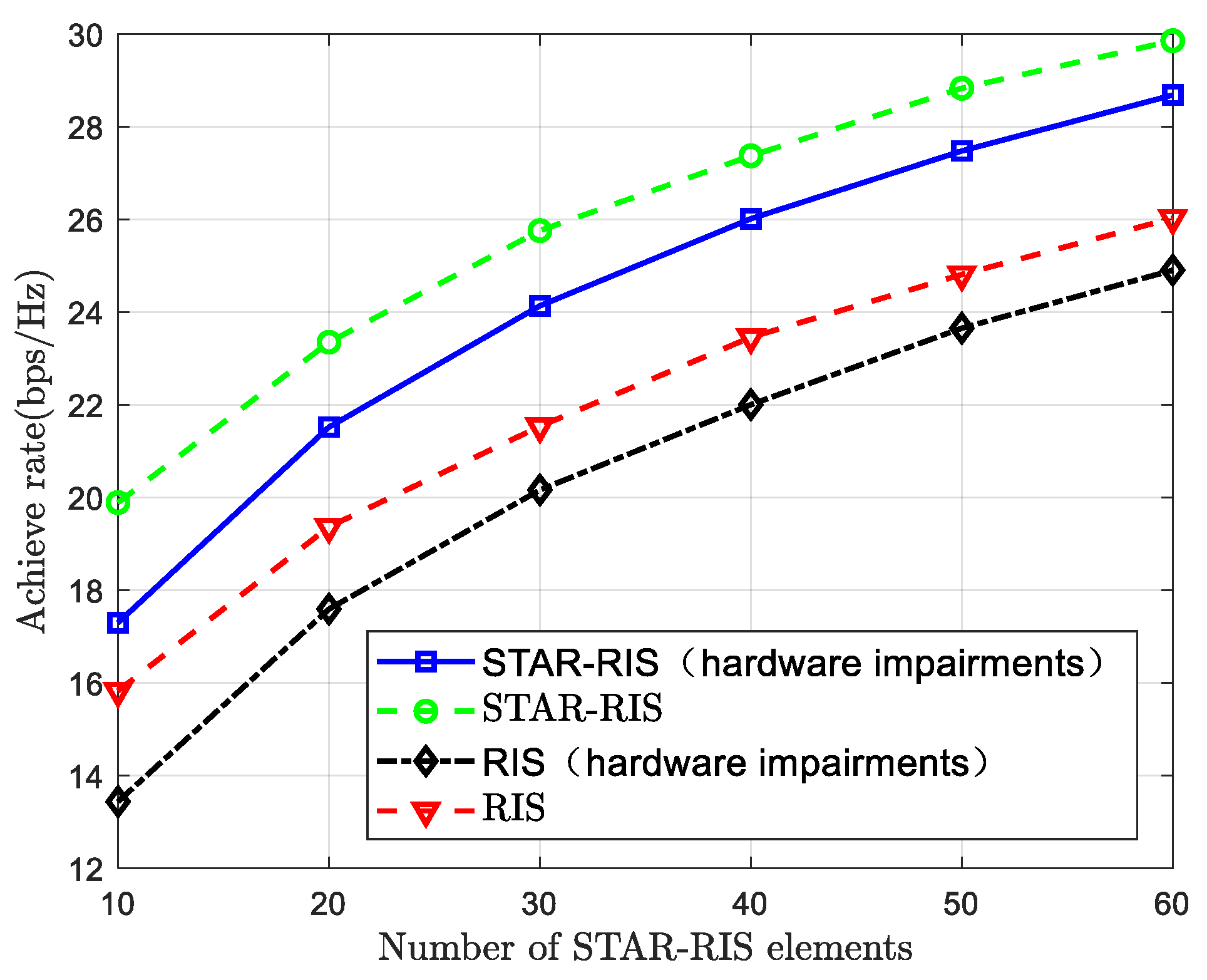
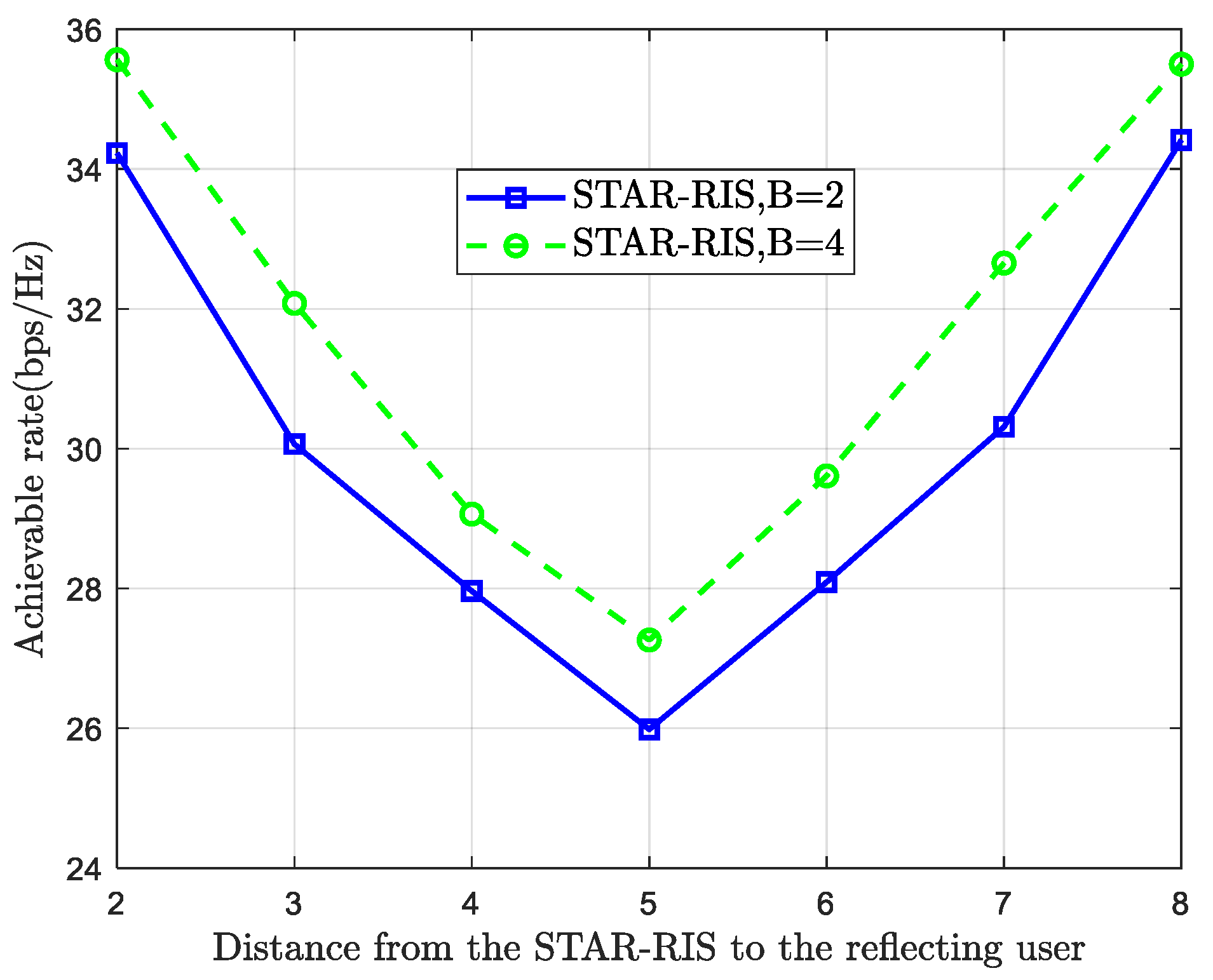
4. Multiuser Scheduling System Assisted by STAR-RIS
4.1. System Model and Problem Formulation
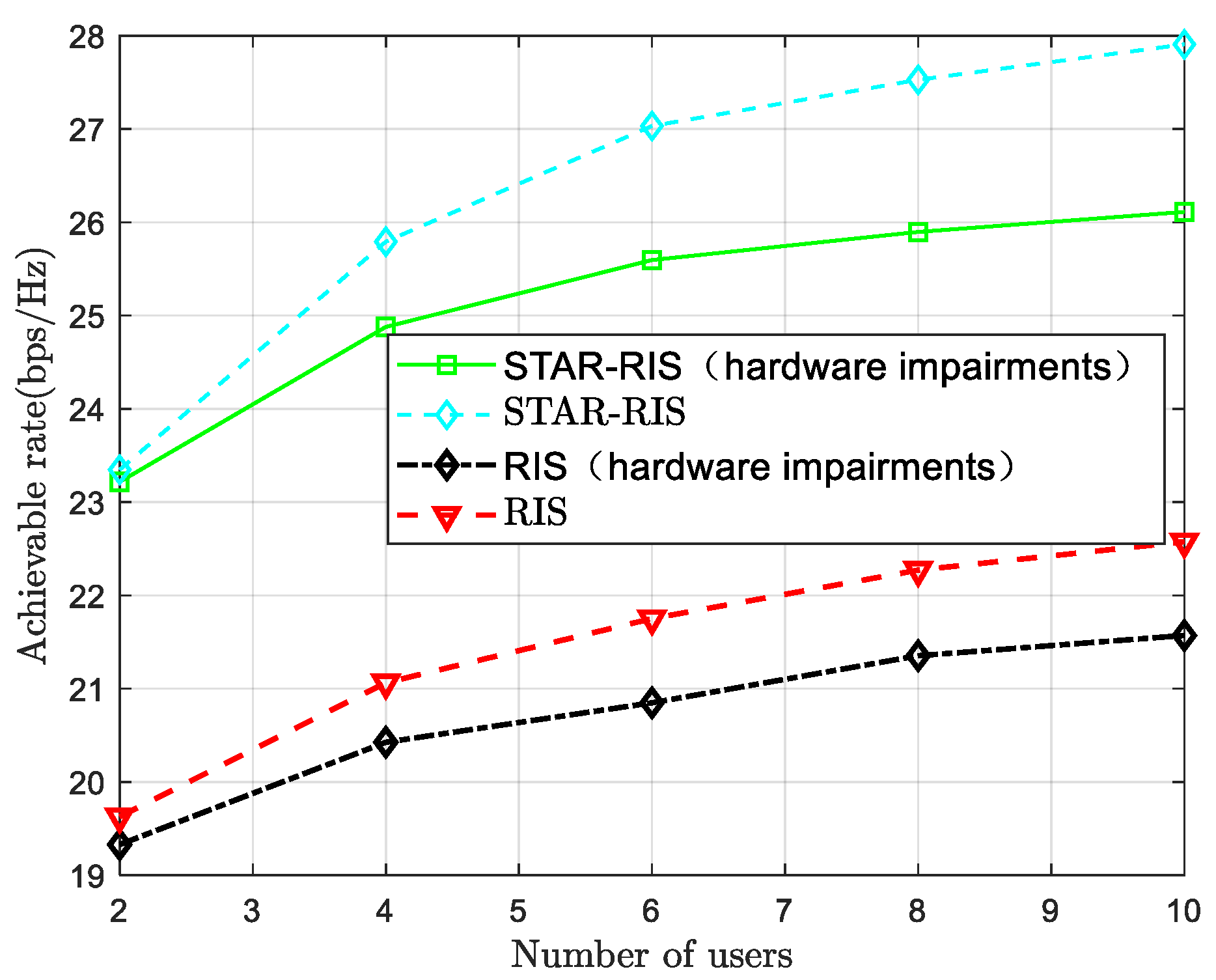
4.2. Phase and Amplitude Design Based on Alternating Optimization
| Algorithm 2 Alternate optimization algorithm steps |
| 1: Initialization: Initialize the amplitude of the STAR-RIS transmission/reflection coefficients ; set the iteration index , and the convergence tolerance ; 2: Repeat: 3: Given and , solve problem using the DPO algorithm to obtain and ; 4: Given and , solve problem using the Lagrange multiplier-based method to obtain and ; 5: Update ; 6: Update r = r + 1; 7: Repeat until . |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 6G | The sixth generation |
| RIS | Reconfigurable intelligent surface |
| STAR-RIS | Simultaneously transmitting and reflecting a reconfigurable intelligent surface |
| DPO | Discrete phase optimization |
| PSO | Particle swarm optimization |
| AO | Alternating optimization |
| BS | Base station |
| CSI | Channel state information |
| MRT | Maximum ratio transmission |
| NLOS | Non-line-of-sight |
| RR | Round-robin |
| PF | Proportional fair |
| KKT | Karush–Kuhn–Tucker |
References
- Nguyen, D.C.; Ding, M.; Pathirana, P.N.; Seneviratne, A.; Li, J.; Niyato, D.; Dobre, O.; Poor, H.V. 6G internet of things: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 9, 359–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, S.; Amin, O.; Shihada, B.; Alouini, M.S. What should 6G be? Nat. Electron. 2020, 3, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Jia, X.; Chi, K.; Liu, X. DDPG-based Joint Time and Energy Management in Ambient Backscatter-assisted Hybrid Underlay CRNs. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2023, 1, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElMossallamy, M.A.; Zhang, H.; Song, L.; Seddik, K.G.; Han, Z.; Li, G.Y. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for wireless communications: Principles, challenges, and opportunities. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2020, 6, 990–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, R. Towards smart and reconfigurable environment: Intelligent reflecting surface aided wireless network. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2019, 58, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tödtling, F.; Trippl, M.; Desch, V. New directions for RIS studies and policies in the face of grand societal challenges. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2022, 30, 2139–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Liu, Y.; Guo, L.; Lin, J.; Schober, R. Simultaneously transmitting and reflecting (STAR) RIS aided wireless communications. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2022, 21, 3083–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Chu, Z.; Chen, G.; Xiao, P.; Xiao, Y.; Wu, X.; Hao, W. STAR-RIS assisted wireless powered IoT networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 10644–10658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Liu, Y.; Mu, X.; Gu, X.; Dobre, O.A. Coverage characterization of STAR-RIS networks: NOMA and OMA. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2021, 25, 3036–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; He, B.; Lv, L.; Chen, J. Security enhancement for coupled phase-shift STAR-RIS networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 8210–8215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feres, C.; Ding, Z. An unsupervised learning paradigm for user scheduling in large scale multi-antenna systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2022, 22, 2932–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denis, J.; Assaad, M. Improving cell-free massive MIMO networks performance: A user scheduling approach. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2021, 20, 7360–7374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiang, T.; Yu, W. Learning based user scheduling in reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted multiuser downlink. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2022, 16, 1026–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, J. Dynamic aerial reconfigurable intelligent surface aided multi-cell multi-user communications. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2024, 23, 16453–16465. [Google Scholar]
- Azar, Y.; Wong, G.N.; Wang, K.; Mayzus, R.; Schulz, J.K.; Zhao, H.; Gutierrez, F.; Hwang, D.; Rappaport, T.S. 28 GHz propagation measurements for outdoor cellular communications using steerable beam antennas in New York city. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Communications, Budapest, Hungary, 9–13 June 2013; pp. 5143–5147. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, K.; Ren, S.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; Luo, Z. Configuring intelligent reflecting surface with performance guarantees: Optimal beamforming. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2022, 16, 967–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bounal, N.; Mishra, B.; Absil, P.; Sepulchre, R. Manopt, a matlab toolbox for optimization on manifolds. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1455–1459. [Google Scholar]
- Adian, F.R.; Abdul, M.; Riri, F.S. A discrimination index based on Jain’s fairness index to differentiate researchers with identical H-index values. J. Data Inf. Sci. 2020, 5, 5–18. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, X.; Wang, R.; Wu, J.; Liu, E. Achievable rate analysis and phase shift optimization on intelligent reflecting surface with hardware impairments. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2021, 20, 5514–5530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameter | Symbol | Valid Values |
|---|---|---|
| Number of RIS elements | N | 10–60 |
| Discrete phase shift bits | B | 1–4 |
| Number of users | K | 1–10 |
| Learning factor | c1, c2 | 1, 1 |
| Population size | M | 100 |
| Inertia weight | 0.9, 0.1 | |
| User region radius | r | 1–10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, Z.; Rui, X. Reconfigurable Intelligence Surface Assisted Multiuser Downlink Communication with User Scheduling. Electronics 2025, 14, 4253. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14214253
Dai Z, Rui X. Reconfigurable Intelligence Surface Assisted Multiuser Downlink Communication with User Scheduling. Electronics. 2025; 14(21):4253. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14214253
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Zhengjun, and Xianyi Rui. 2025. "Reconfigurable Intelligence Surface Assisted Multiuser Downlink Communication with User Scheduling" Electronics 14, no. 21: 4253. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14214253
APA StyleDai, Z., & Rui, X. (2025). Reconfigurable Intelligence Surface Assisted Multiuser Downlink Communication with User Scheduling. Electronics, 14(21), 4253. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14214253






