Real-Time Lightweight Vehicle Object Detection via Layer-Adaptive Model Pruning
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Background and Motivation
- We design a Mixed Local Channel Attention (MLCA) mechanism that integrates local structural features with global contextual semantics, thereby enhancing small-object representation under multi-scale variations.
- We construct a Task-Aligned Dynamic Detection Head (TADDH) that employs Deformable Convolutional Networks v2 (DCNv2) to achieve adaptive spatial alignment and facilitate cross-task feature interaction between classification and regression.
- We propose a Layer-Adaptive Magnitude-based Pruning (LAMP) strategy that performs global channel ranking and adaptive structural compression, effectively balancing model efficiency and accuracy preservation.
- The proposed YOLOv8n-ALM achieves a 65.3% reduction in parameters and a 29.6% decrease in computational load, while improving mAP@0.5 by 2.2%, thereby validating its effectiveness for real-time deployment.
- Real-vehicle experiments conducted on the PIX-Hooke autonomous driving platform demonstrate strong robustness, stability, and engineering feasibility under complex driving conditions.
- For a detailed comparative analysis of representative methods, please refer to Section 1.2 and Table 1.
1.2. Related Works and Research Gaps
2. Development and Improvement of Forward Vehicle Detection Model
2.1. Network Architecture
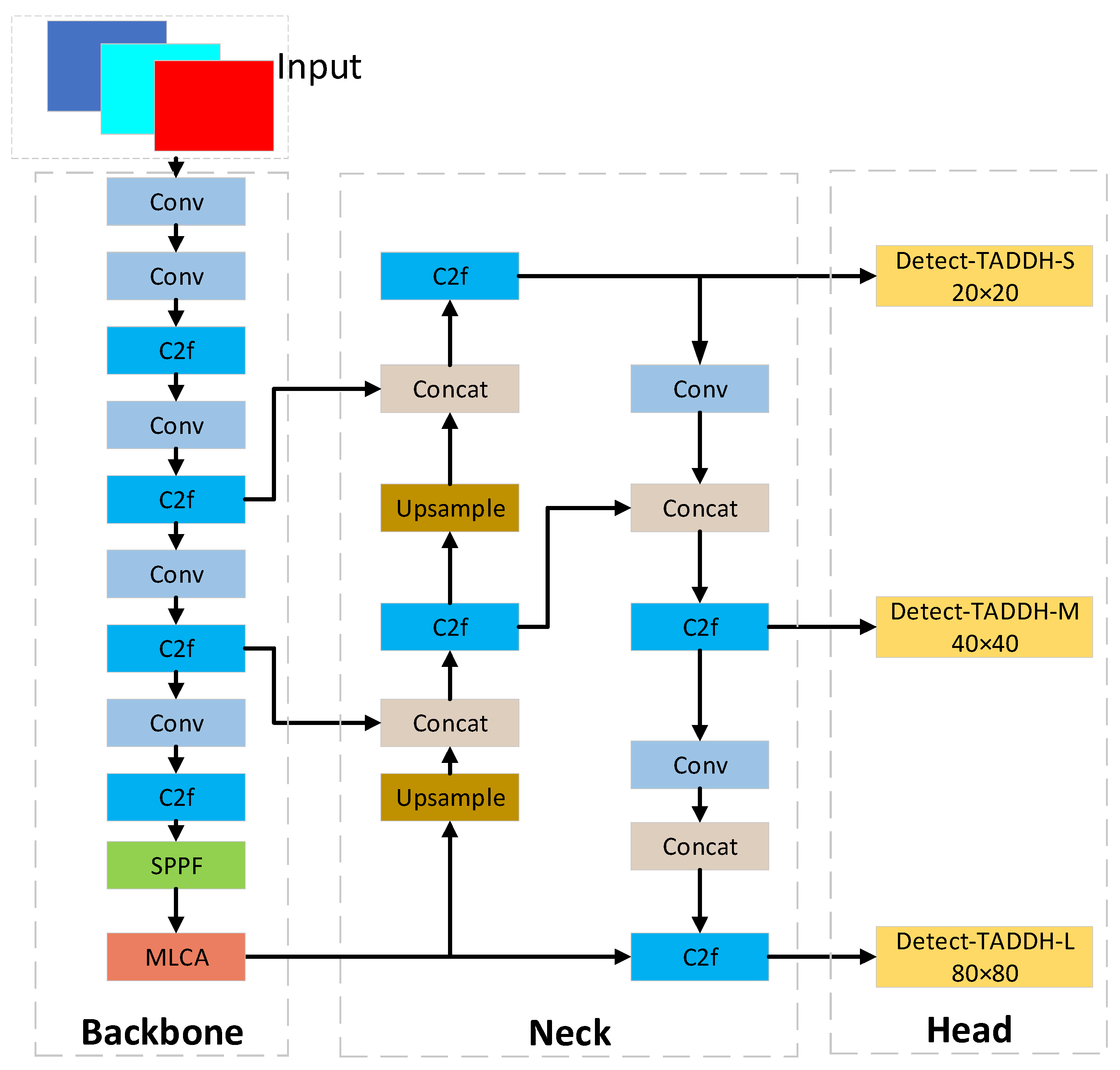
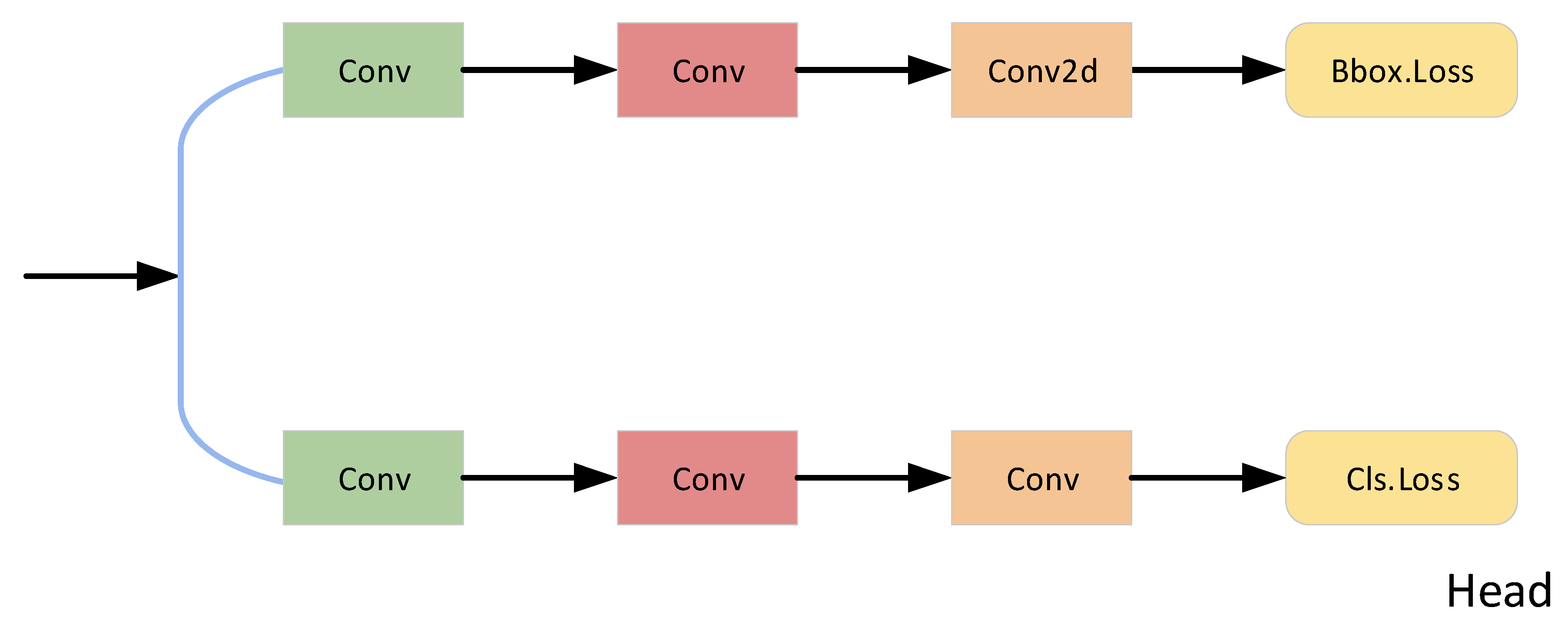
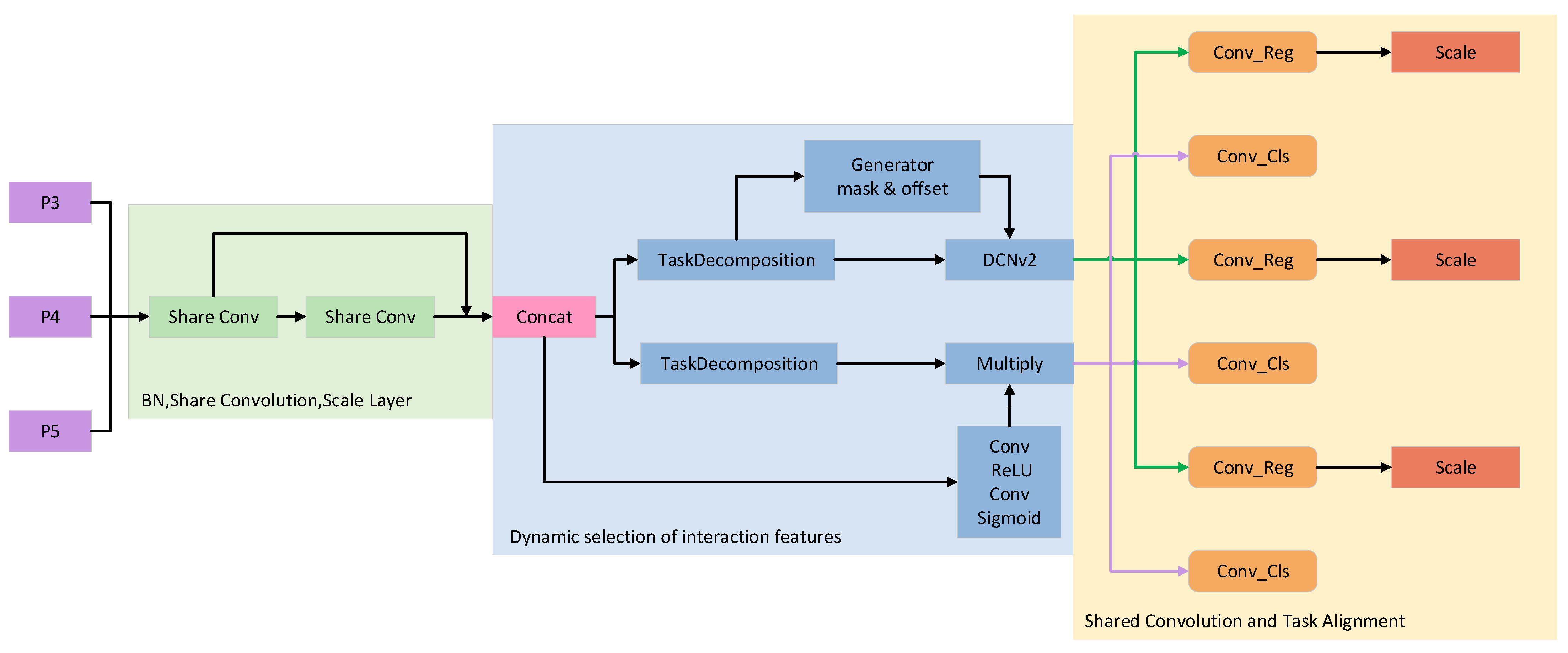
2.2. Task-Aligned Dynamic Detection Head
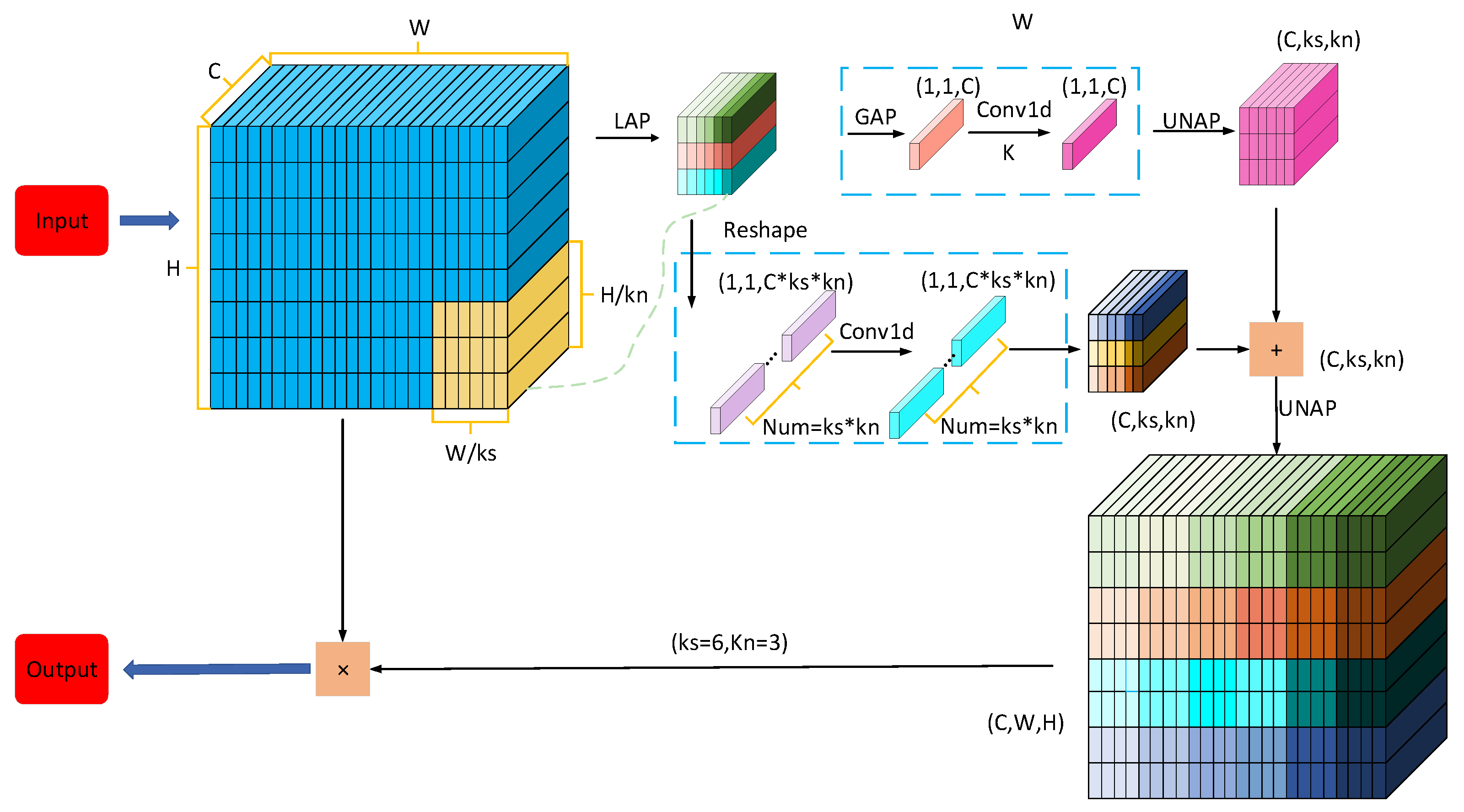
2.3. Mixed Local Channel Attention
2.4. Pruning Operation
3. Dataset and Evaluation Metrics
3.1. Data Augmentation
3.2. Evaluation Criteria for Network Models
4. Experiments and Results Analysis
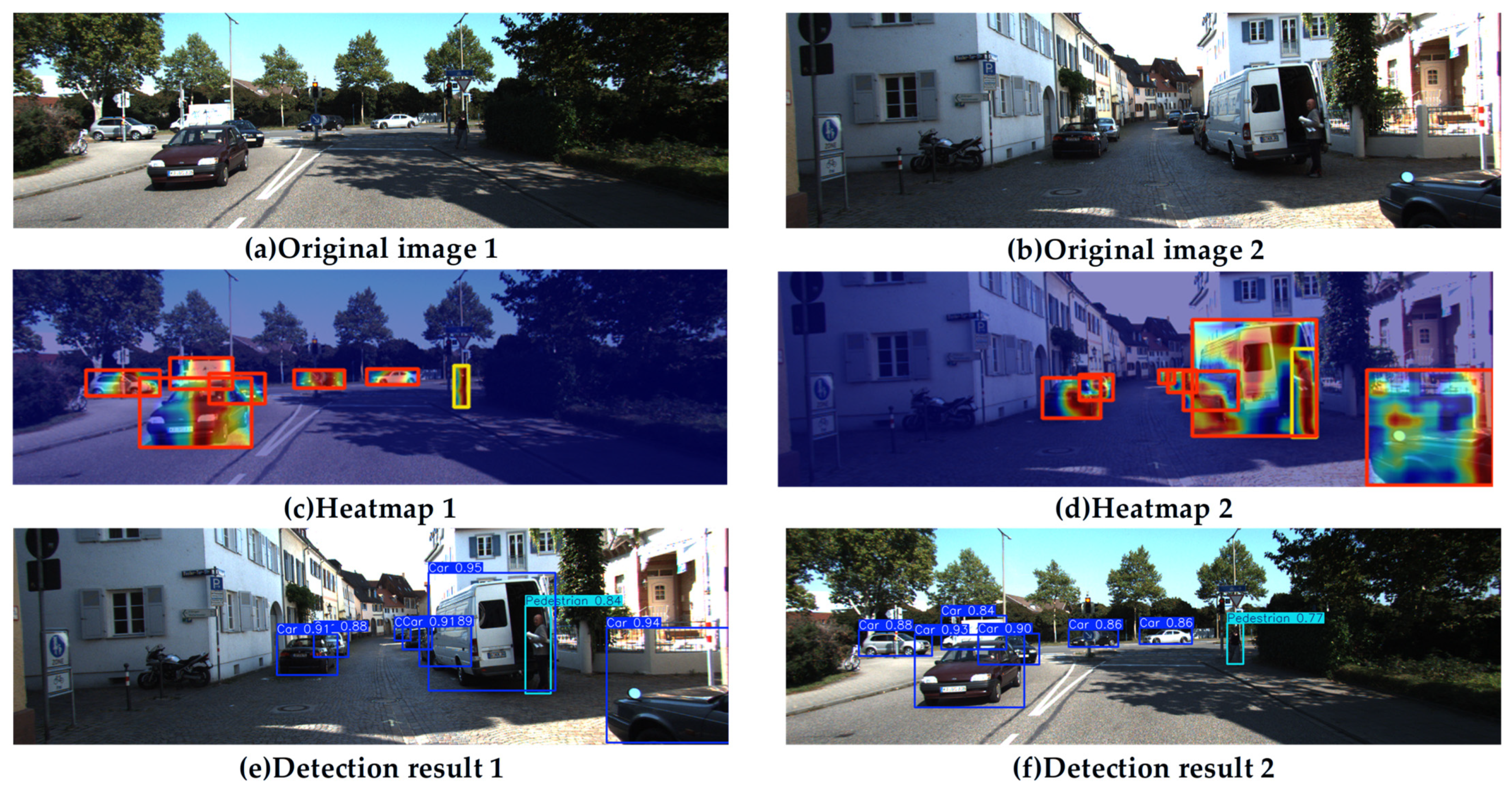
4.1. Attention Mechanism Comparison Experiment
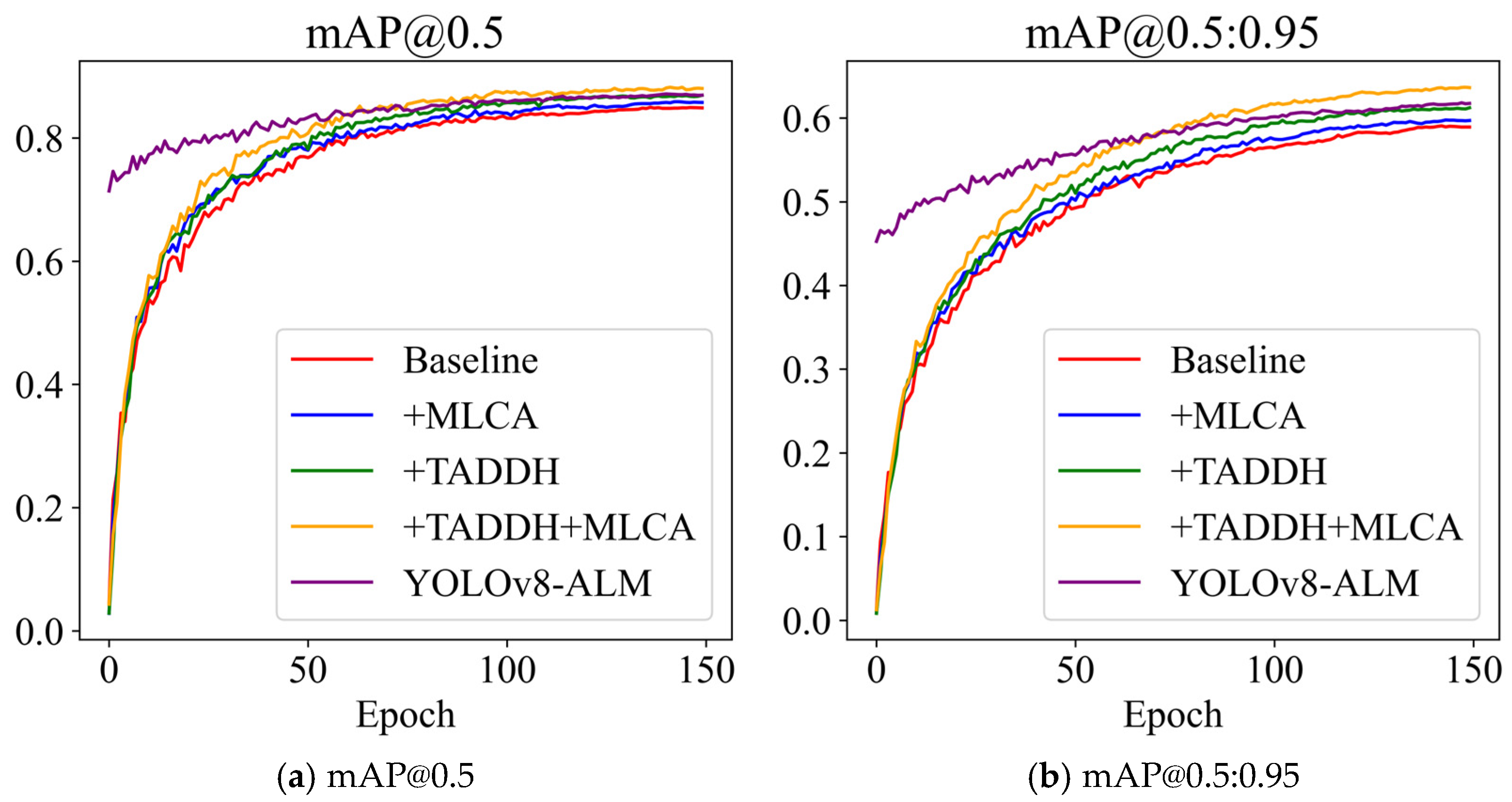
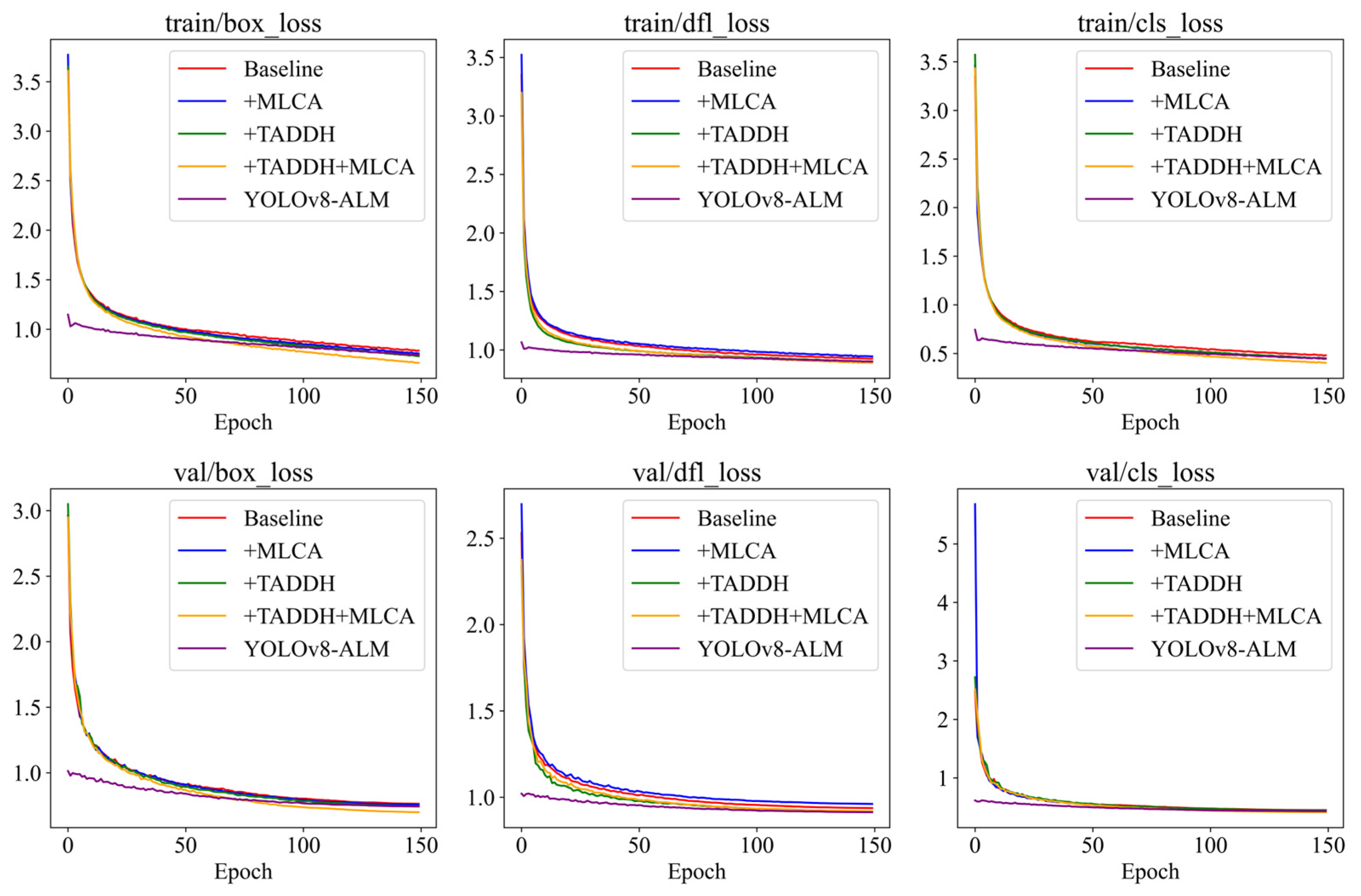
4.2. Ablation Experiment
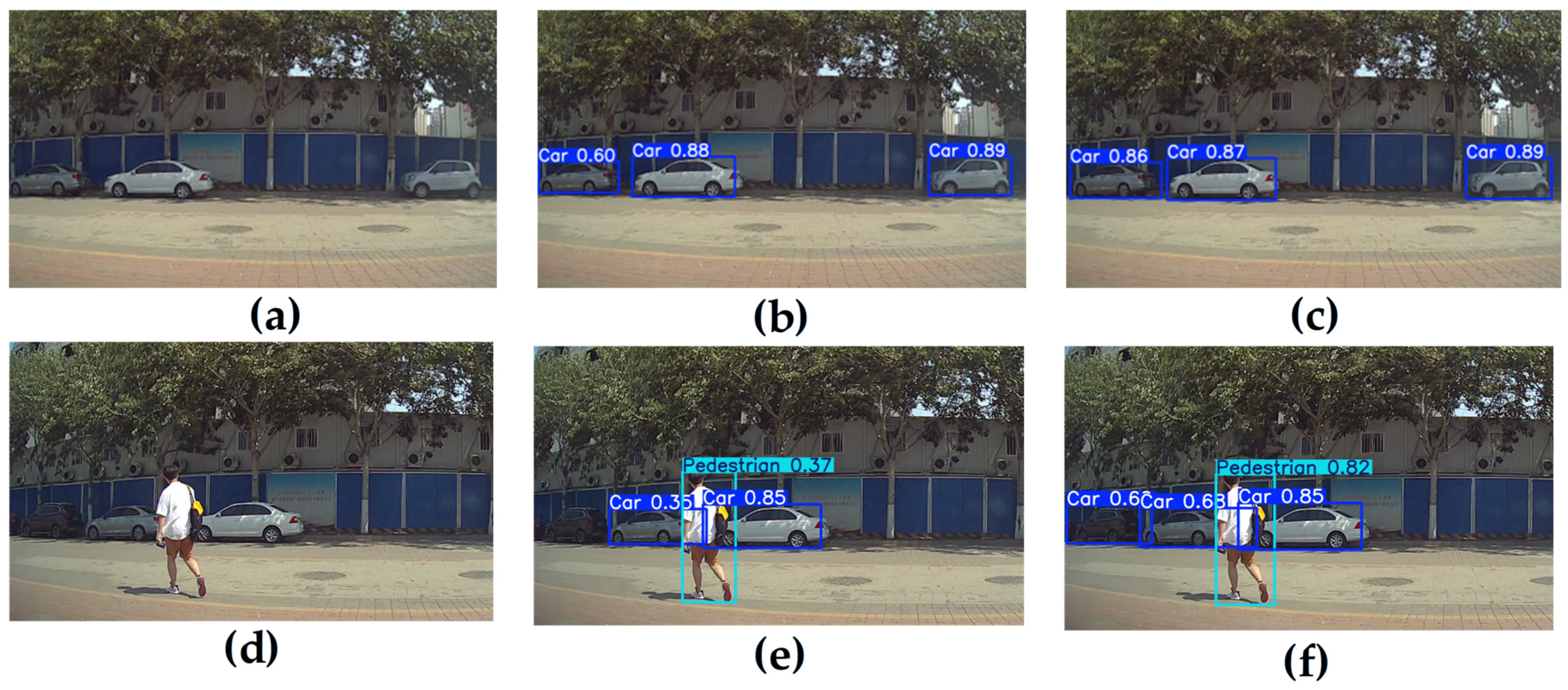
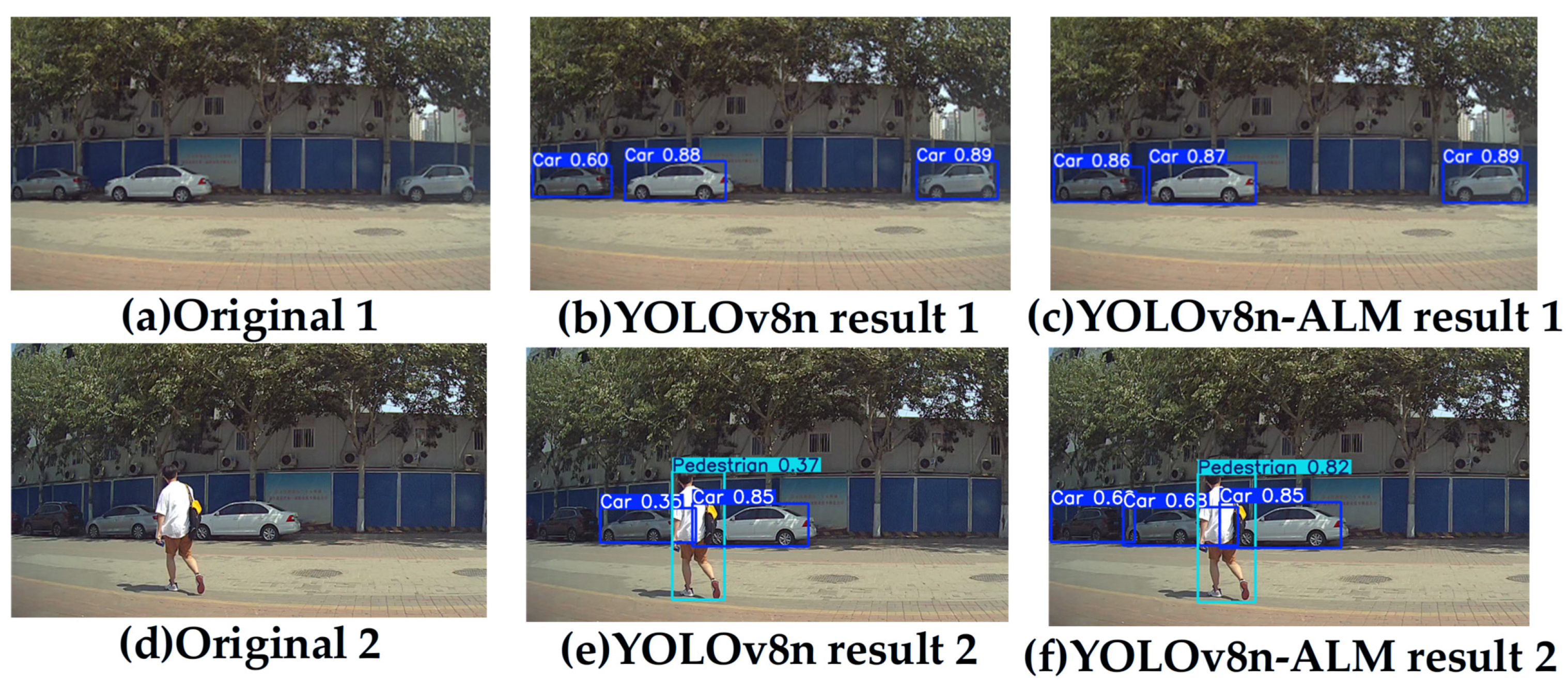
4.3. Comparison Experiment
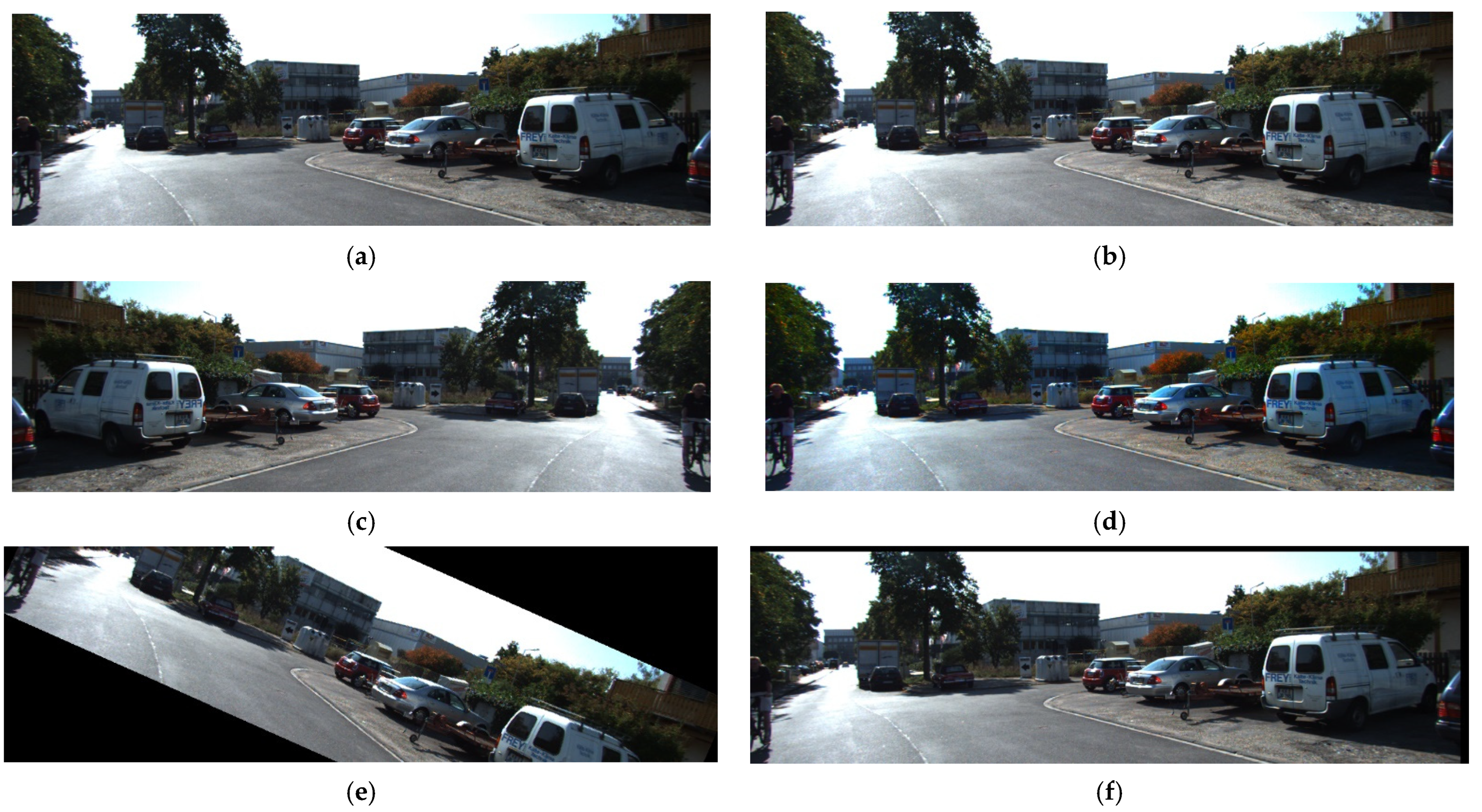
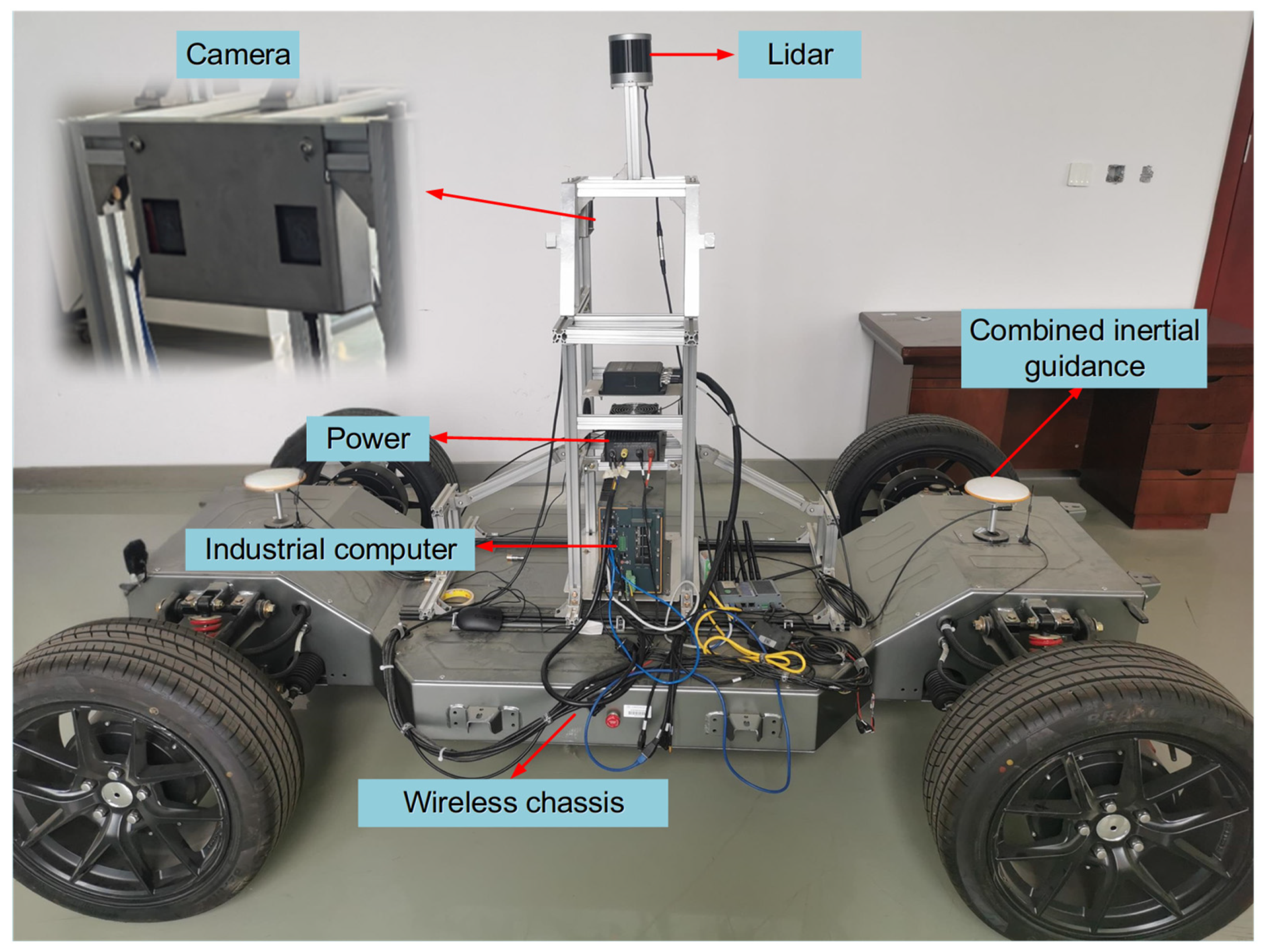
4.4. Real-World Onboard Vehicle Video Detection Experiments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MLCA | Mixed Local Channel Attention |
| TADDH | Task-Aligned Dynamic Detection Head |
| LAMP | Layer-Adaptive Magnitude-based Pruning |
| DCNv2 | Deformable Convolutional Networks v2 |
| UNAP | Unified Non-Autoregressive Parsing |
| GAP | Global Average Pooling |
| KITTI | Karlsruhe Institute of Technology and Toyota Technological Institute Dataset |
| YOLOv8-ALM | YOLOv8-Attention-Lightweight-Multihead |
References
- Pang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Li, X.; Pan, J. Efficient HOG human detection. Signal Process. 2011, 91, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Yang, Y.; Tian, Q. SIFT meets CNN: A decade survey of instance retrieval. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 1224–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Liao, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; He, X.; Wu, X. Haar wavelet downsampling: A simple but effective downsampling module for semantic segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 143, 109819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurani, A.; Doshi, P.; Vakharia, A.; Shah, M. A comprehensive comparative study of artificial neural networks (ANN) and support vector machines (SVM) on stock forecasting. Ann. Data Sci. 2023, 10, 183–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Zhou, Y.; Bao, F.; Chen, J.; Li, C.; Zhu, J. Dpm-solver++: Fast solver for guided sampling of diffusion probabilistic models. Mach. Intell. Res. 2025, 22, 730–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhao, M.; Shi, P.; Ren, R.; He, X.; Wei, X.; Yang, H. Crack detection and comparison study based on faster R-CNN and mask R-CNN. Sensors 2022, 22, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Ren, H.; Cai, S.; Zhang, X. An improved, faster R-CNN algorithm for assisted detection of lung nodules. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 153, 106470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, E.; El-Rashidy, N. Mask R-CNN models. Nile J. Commun. Comput. Sci. 2022, 3, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Meng, L.; Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; Wu, D. CSP-Net: Common spatial pattern empowered neural networks for EEG-based motor imagery classification. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2024, 305, 112668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yao, Q.; Fan, X.; Gong, M.; Ma, W.; Miao, Q. PANet: A point-attention based multi-scale feature fusion network for point cloud registration. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Huang, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Z. NWPU-captions dataset and MLCA-net for remote sensing image captioning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Ding, Z.Y.; Jiang, M.N.; Xu, W.K.; Lv, M. LBT-YOLO: A Lightweight Road Targeting Algorithm Based on Task-Aligned Dynamic Detection Heads (April 2024); IEEE Access: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Vysogorets, A.; Kempe, J. Connectivity matters: Neural network pruning through the lens of effective sparsity. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2023, 24, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, M.; Huang, L.; Tang, B.-H. ASFF-YOLOv5: Multielement Detection Method for Road Traffic in UAV Images Based on Multiscale Feature Fusion. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Dong, J.; Nie, W.; Ye, Z. A Lightweight YOLOv5 Optimization of Coordinate Attention. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jani, M.; Fayyad, J.; Al-Younes, Y.; Najjaran, H. Model compression methods for YOLOv5: A review. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.11904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, K.; Yu, Z. Channel-pruned YOLOv5-based deep learning approach for rapid and accurate outdoor obstacles detection. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.13699. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Dong, Z.; Gao, M. Improved YOLOv5 network for real-time multi-scale traffic sign detection. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 7853–7865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shen, T.; Xu, D. Object detection in remote sensing images based on an improved YOLOv8 algorithm. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2024, 61, 1028001. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Zhou, X.; Yang, F.; Zhou, M.; Wang, H. PIMnet: A quality enhancement network for compressed videos with prior information modulation. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2023, 117, 117005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, N.A.; Cruz, L.A.D.S.; Lopes, F. Impact of LiDAR point cloud compression on 3D object detection evaluated on the KITTI dataset. EURASIP J. Image Video Process. 2024, 2024, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, D.; Zhu, L. CAF-RCNN: Multimodal 3D object detection with cross-attention. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2023, 44, 6131–6146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Du, W.; Deng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, W. Ship target detection in SAR images based on SimAM attention YOLOv8. IET Commun. 2024, 18, 1428–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Shi, Z.; Karungaru, S.; Lv, S.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J. Classification of typical pests and diseases of rice based on the ECA attention mechanism. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.V.; Horng, S.J.; Vu, D.T.; Chen, H.; Li, T. LAWNet: A lightweight attention-based deep learning model for wrist vein verification in smartphones using RGB images. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yu, Y.; Tang, Z. FDM-RTDETR: A Multi-scale Small Target Detection Algorithm; IEEE Access: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Wu, S.; Gou, L.; Yu, H.; Lin, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Li, M.; Li, X. SCD: A stacked carton dataset for detection and segmentation. Sensors 2022, 22, 3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safa’a, S.S.; Mabrouk, T.F.; Tarabishi, R.A. An improved energy-efficient head election protocol for clustering techniques of wireless sensor networks (June 2020). Egypt. Inform. J. 2021, 22, 439–445. [Google Scholar]






| Reference | Model | Main Idea | Research Gap |
|---|---|---|---|
| [14] | YOLOv5 + ASFF + Multi-scale Attention | Enhanced small-object fusion across scales | Increased computational load; difficult real-time deployment |
| [15] | YOLOv5 + Coordinate Attention | Improves spatial-channel feature representation | Weak task alignment between classification and regression |
| [16] | YOLOv5 + FPGM Pruning | Lightweight pruning for model compression | Fixed pruning ratio; reduced adaptability |
| [17] | YOLOv5 + BiFPN | Facilitates efficient multi-scale feature aggregation | Insufficient response to dense small targets |
| [18] | LBT-YOLO + TADDH | Task-aligned detection head for better cls-reg consistency | Lacks an adaptive attention and pruning mechanism |
| This work | YOLOv8n-ALM | Integrates mixed attention, dynamic alignment, and adaptive pruning | Addresses the above gaps under a unified framework |
| Category | Environmental Conditions |
|---|---|
| CPU | Inter Core i9-9900KF |
| GPU | NVIDIA RTX 3080 |
| CUDA version | 12.0 |
| Python | 3.9.12 |
| Pytorch | 2.0.0 |
| mmcv | 2.2.0 |
| MMDetection | 3.3.0 |
| Operating system | Ubuntu22.04 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Epochs | 150 |
| Batch Size | 32 |
| Image Size | 640 × 640 |
| Optimizer | SGD |
| Weight Decay | 0.0005 |
| Pruning Method | LAMP |
| Pruning Type | Global pruning |
| Model | P (%) | R (%) | mAP@0.5 (%) | mAP@0.5–0.95 (%) | Params/M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic | 86.0 | 77.6 | 84.8 | 59.0 | 3.00 |
| +CAFM | 88.3 | 76.2 | 84.8 | 58.7 | 3.35 |
| +SimAM | 90.3 | 75.8 | 85.1 | 58.6 | 3.00 |
| +ECA | 87.5 | 78.1 | 85.4 | 58.9 | 3.00 |
| +MPCA | 85.8 | 77.0 | 84.1 | 58.8 | 3.33 |
| +MLCA | 88.9 | 76.4 | 85.9 | 59.7 | 3.00 |
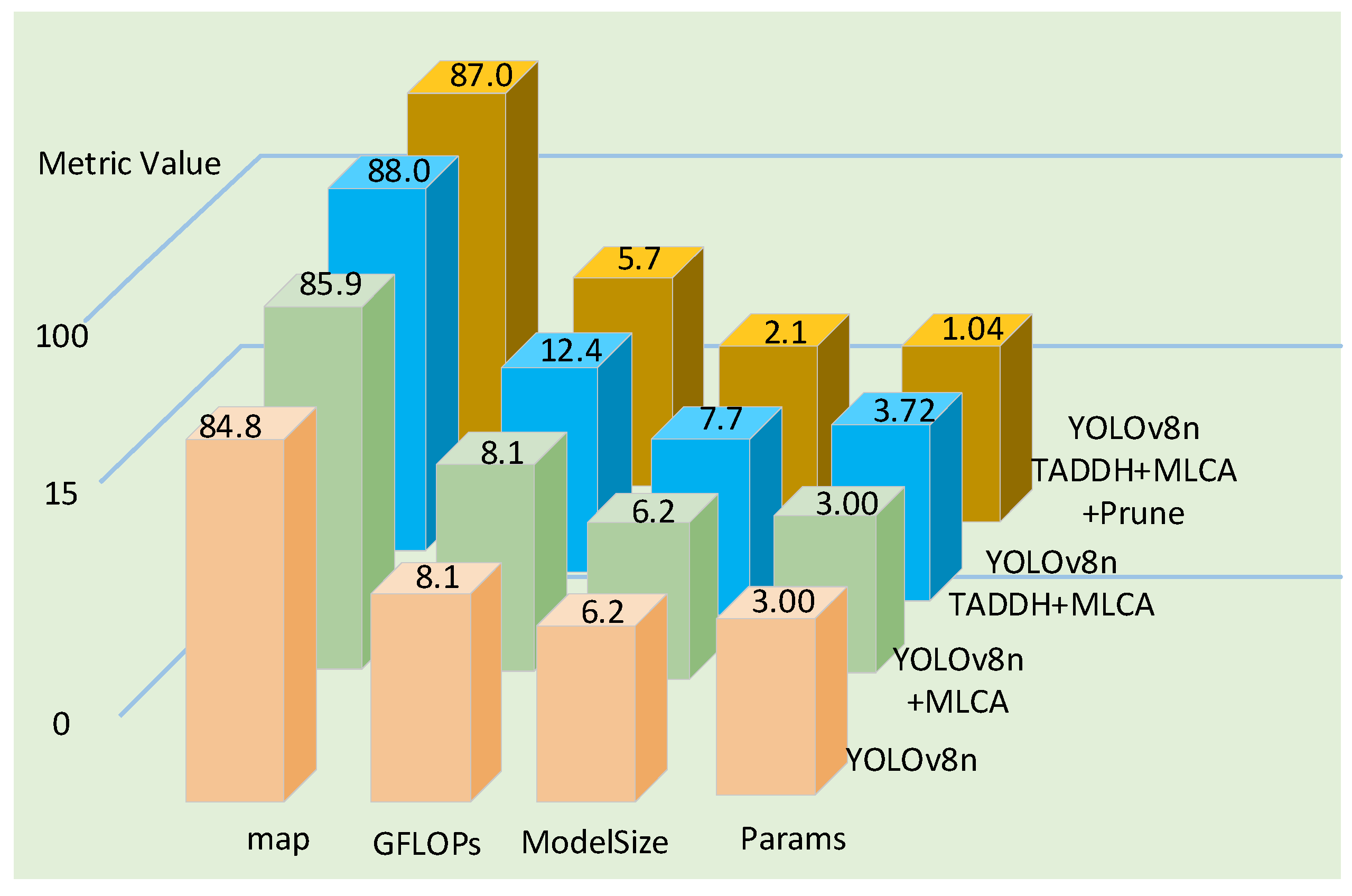
| YOLOv8n | MLCA | TADDH | Prune | ModelSize/MB | GFLOPs | Params | P (%) | R (%) | mAP@0.5 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ✓ | 6.2 | 8.1 | 3.00 | 86.0 | 77.6 | 84.8 | |||
| ✓ | ✓ | 6.2 | 8.1 | 3.00 | 88.9 | 76.4 | 85.9 | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 7.7 | 12.4 | 3.72 | 91.5 | 79.4 | 88.0 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 2.1 | 5.7 | 1.04 | 91.8 | 77.7 | 87.0 |
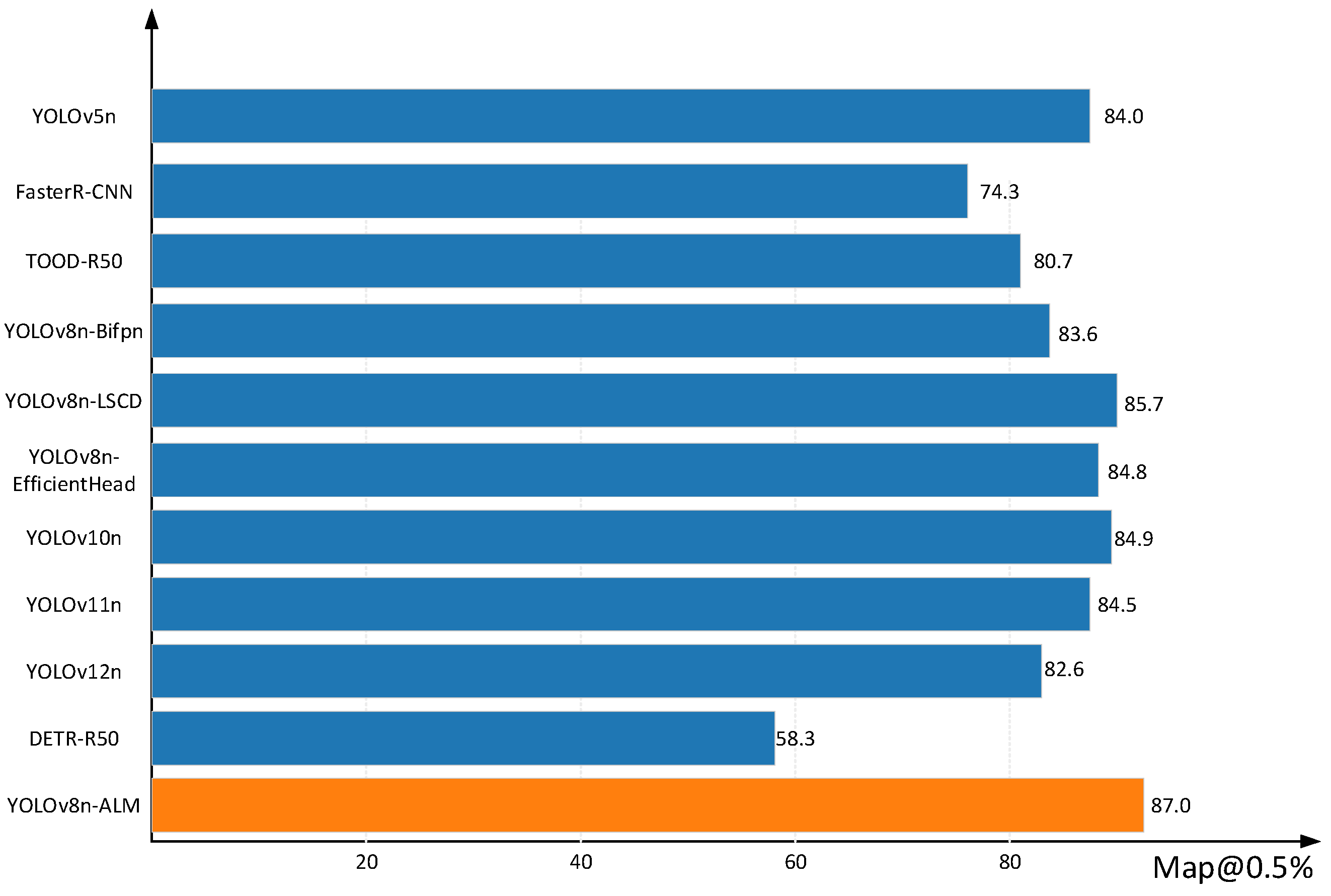
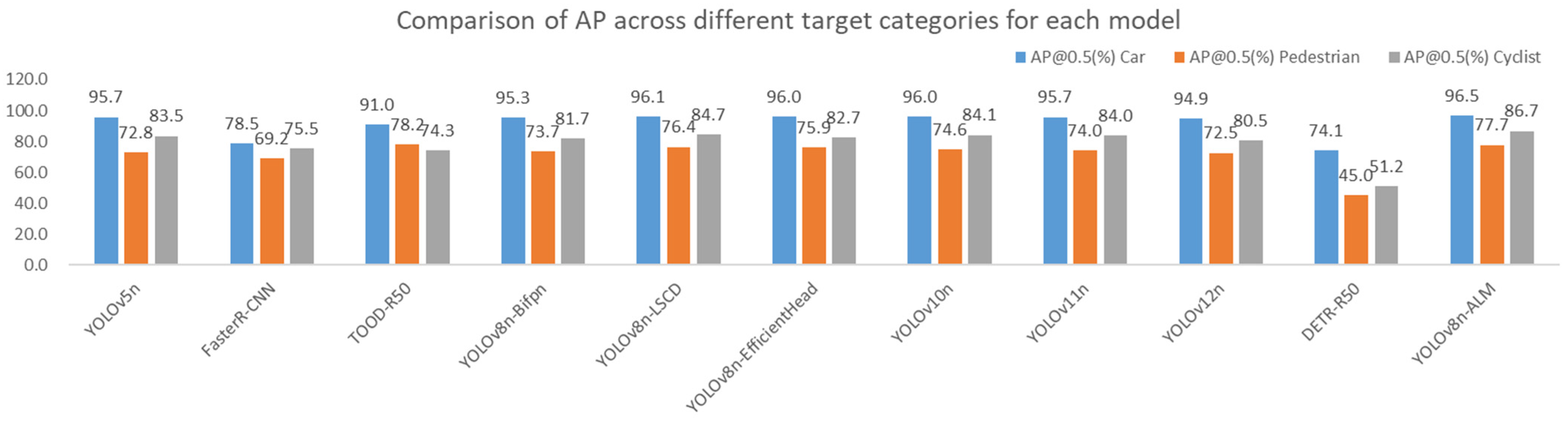
| Model | AP@0.5 (%) | mAP@0.5 (%) | GFLOPs | Params | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Car | Pedestrian | Cyclist | ||||
| YOLOv5n | 95.7 | 72.8 | 83.5 | 84.0 | 7.10 | 2.50 |
| FasterR-CNN | 78.5 | 69.2 | 75.5 | 74.3 | 236 | 70.12 |
| TOOD-R50 | 91.0 | 78.2 | 74.3 | 80.7 | 199 | 32.10 |
| YOLOv8n-Bifpn | 95.3 | 73.7 | 81.7 | 83.6 | 7.10 | 1.99 |
| YOLOv8n-LSCD | 96.1 | 76.4 | 84.7 | 85.7 | 6.5 | 2.36 |
| YOLOv8n- EfficientHead | 96.0 | 75.9 | 82.7 | 84.8 | 8.1 | 3.83 |
| YOLOv10n | 96.0 | 74.6 | 84.1 | 84.9 | 6.5 | 2.26 |
| YOLOv11n | 95.7 | 74.0 | 84.0 | 84.5 | 6.3 | 2.58 |
| YOLOv12n | 94.9 | 72.5 | 80.5 | 82.6 | 5.8 | 2.50 |
| DETR-R50 | 74.1 | 45.0 | 51.2 | 58.3 | 39.0 | 84.1 |
| YOLOv8n-ALM | 96.5 | 77.7 | 86.7 | 87.0 | 5.7 | 1.04 |
| Model | Latency-E2E Mean (ms) | P95 (ms) | Model-Only Mean (ms) | Pre (ms) | Infer (ms) | Post (ms) | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8n | 29.98 | 35.60 | 10.68 | 1.26 | 8.63 | 0.80 | 33.36 |
| YOLOv8n-ALM | 27.36 | 33.38 | 6.98 | 1.30 | 4.73 | 0.86 | 36.55 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Du, F.; Kang, W.; Wang, C.; Li, G. Real-Time Lightweight Vehicle Object Detection via Layer-Adaptive Model Pruning. Electronics 2025, 14, 4149. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14214149
Zhang Y, Zhang J, Du F, Kang W, Wang C, Li G. Real-Time Lightweight Vehicle Object Detection via Layer-Adaptive Model Pruning. Electronics. 2025; 14(21):4149. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14214149
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yu, Junhui Zhang, Feng Du, Wenjie Kang, Cen Wang, and Guofei Li. 2025. "Real-Time Lightweight Vehicle Object Detection via Layer-Adaptive Model Pruning" Electronics 14, no. 21: 4149. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14214149
APA StyleZhang, Y., Zhang, J., Du, F., Kang, W., Wang, C., & Li, G. (2025). Real-Time Lightweight Vehicle Object Detection via Layer-Adaptive Model Pruning. Electronics, 14(21), 4149. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14214149





