A Nonlinear Volterra Filtering Hybrid Image-Denoising Method Based on the Improved Bat Algorithm for Optimizing Kernel Parameters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Volterra Series Model
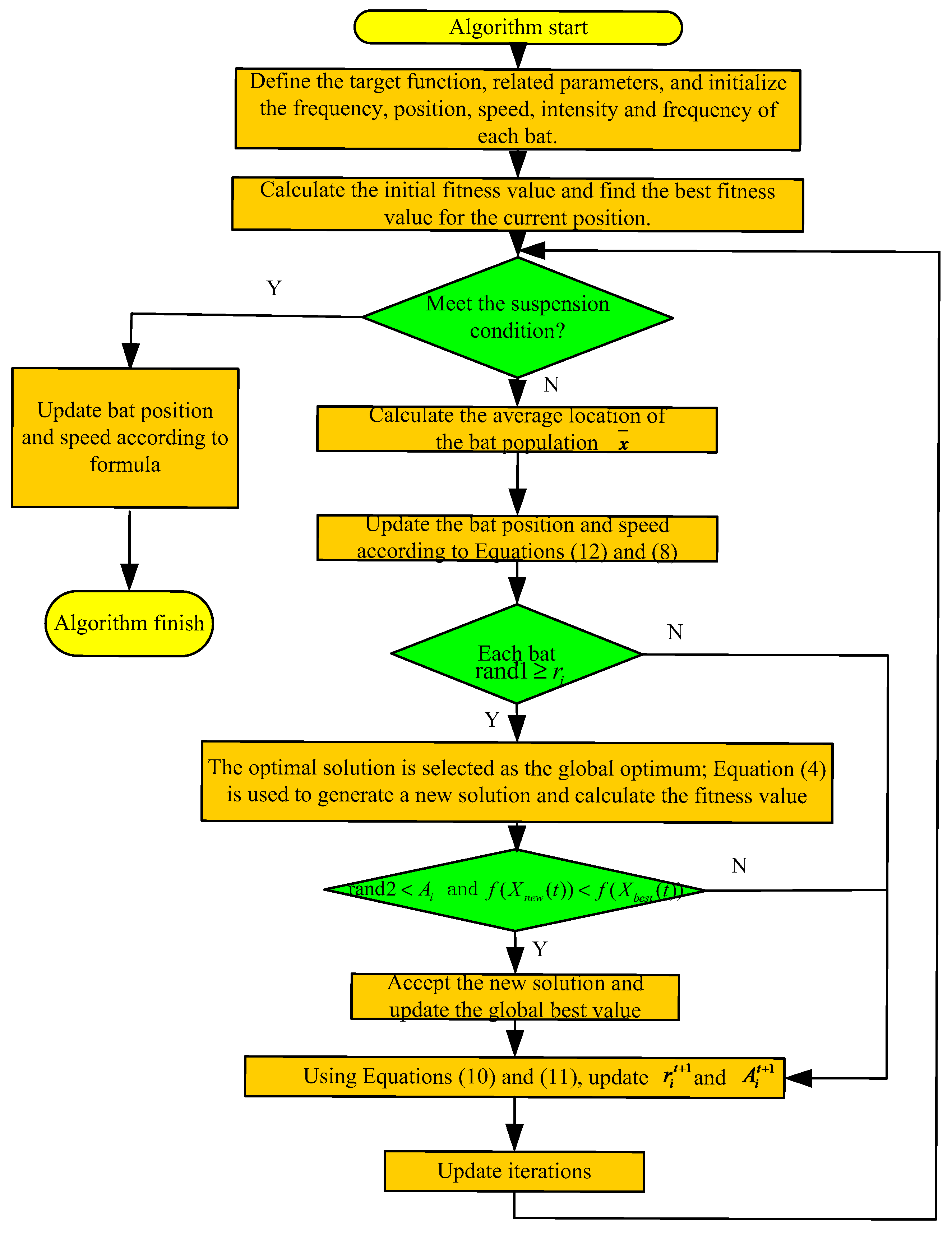
3. Bat Algorithm with Velocity Weight Perturbation
3.1. Bat Algorithm
3.2. Bat Algorithm with Velocity Weight
3.3. Kernel Parameters Optimized Based on VWDBA
4. Bat Algorithm with Velocity Weight Perturbation
4.1. Kernel Parameter Optimization Based on VWDBA
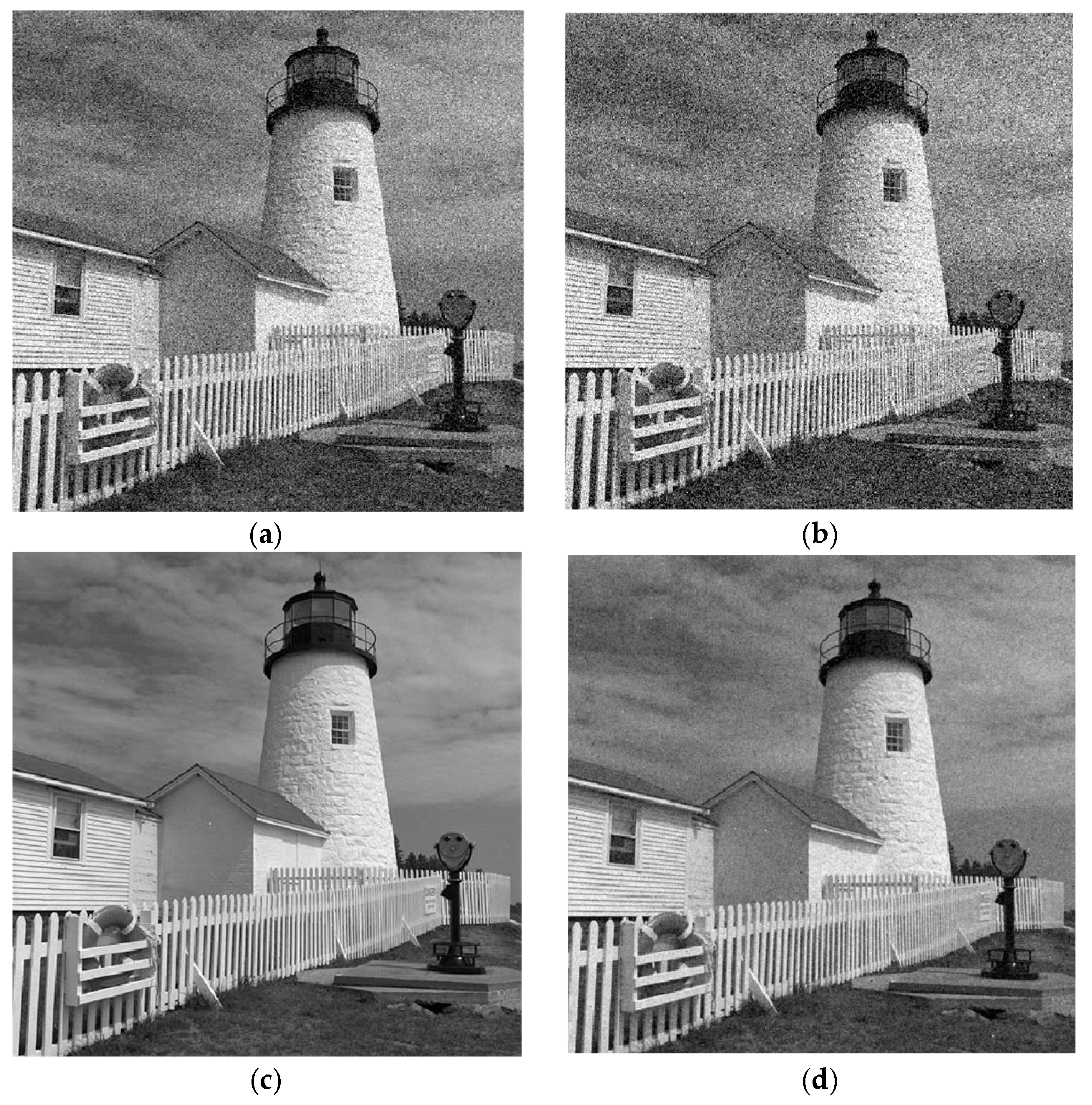
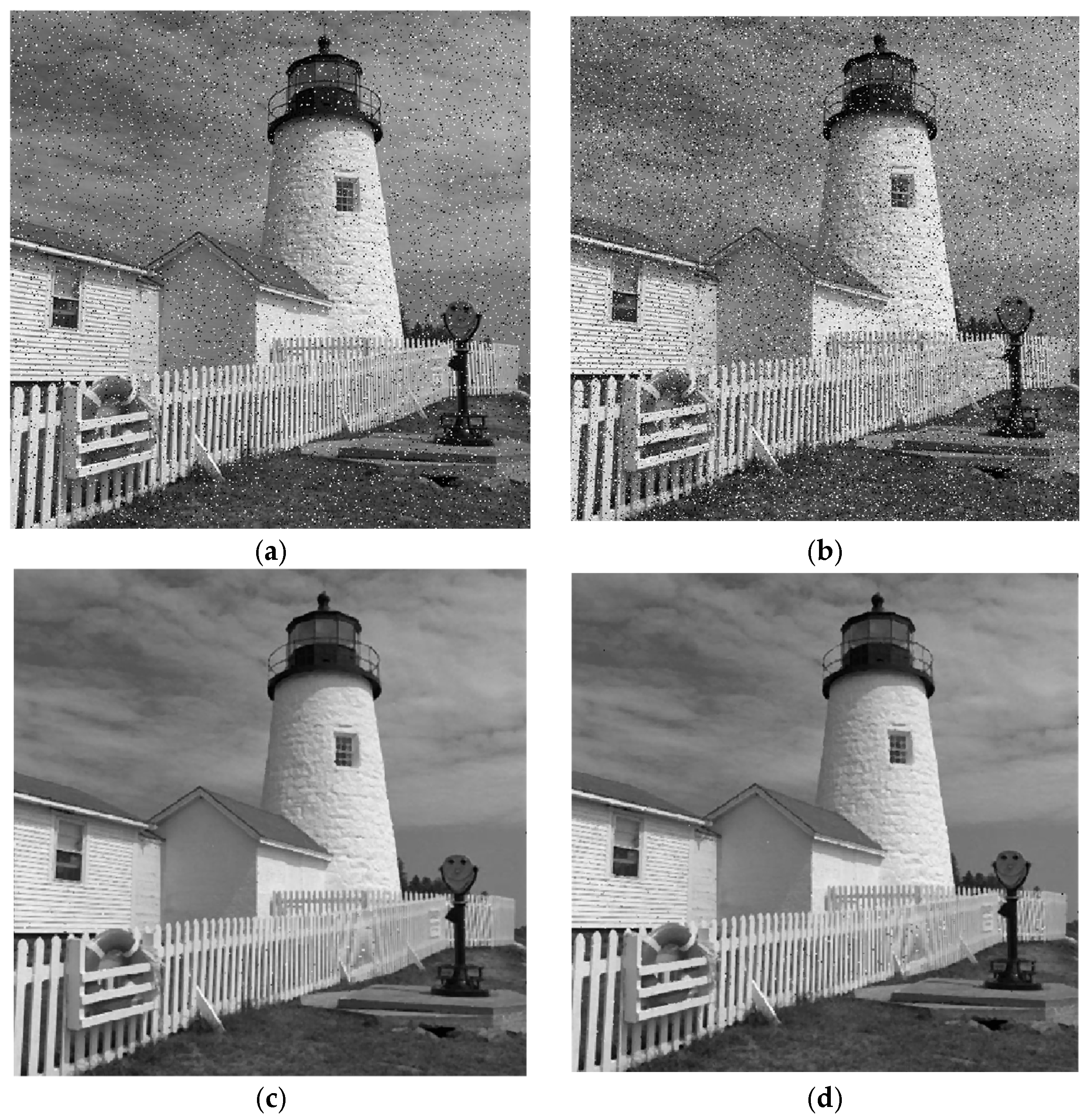
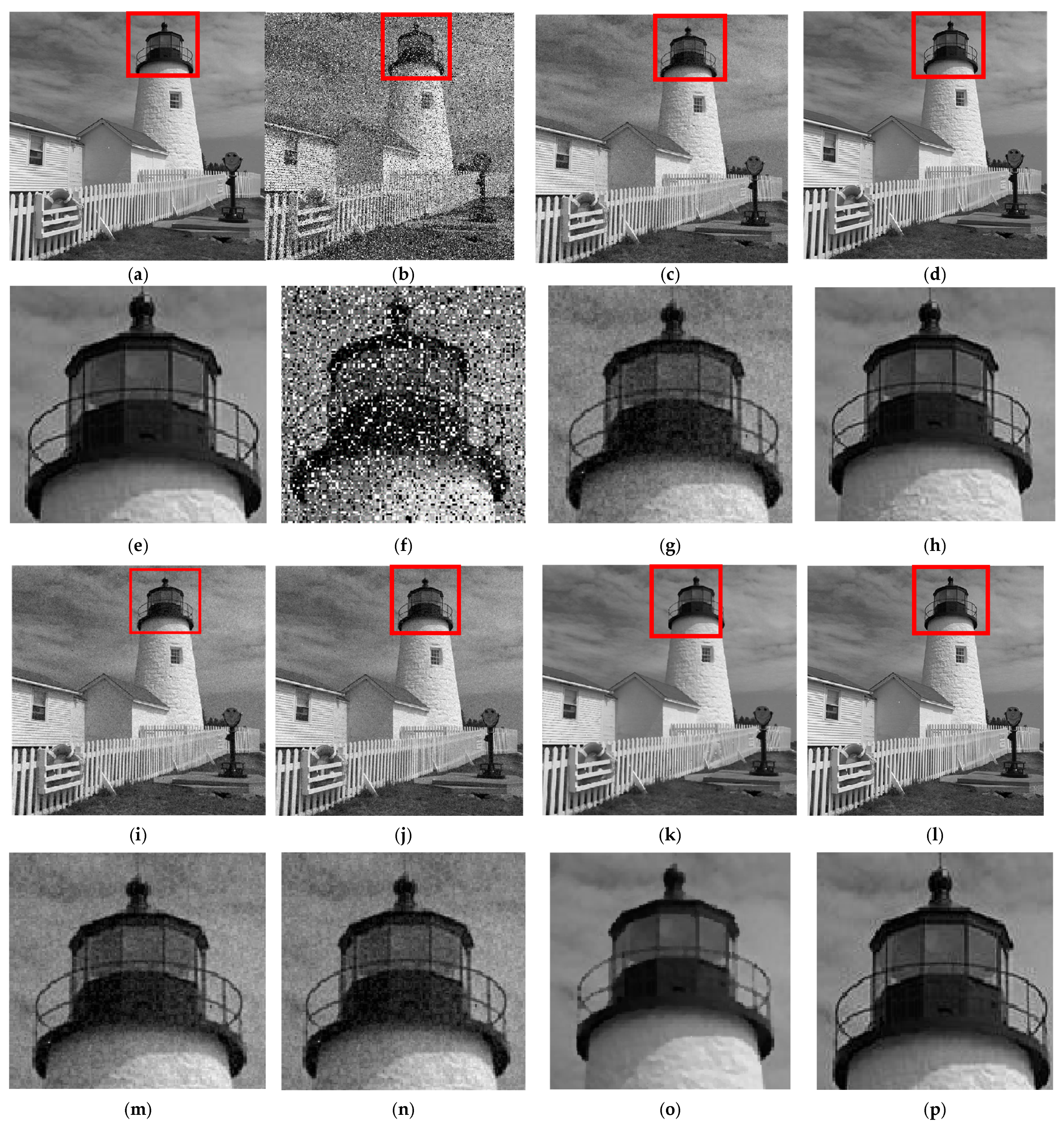
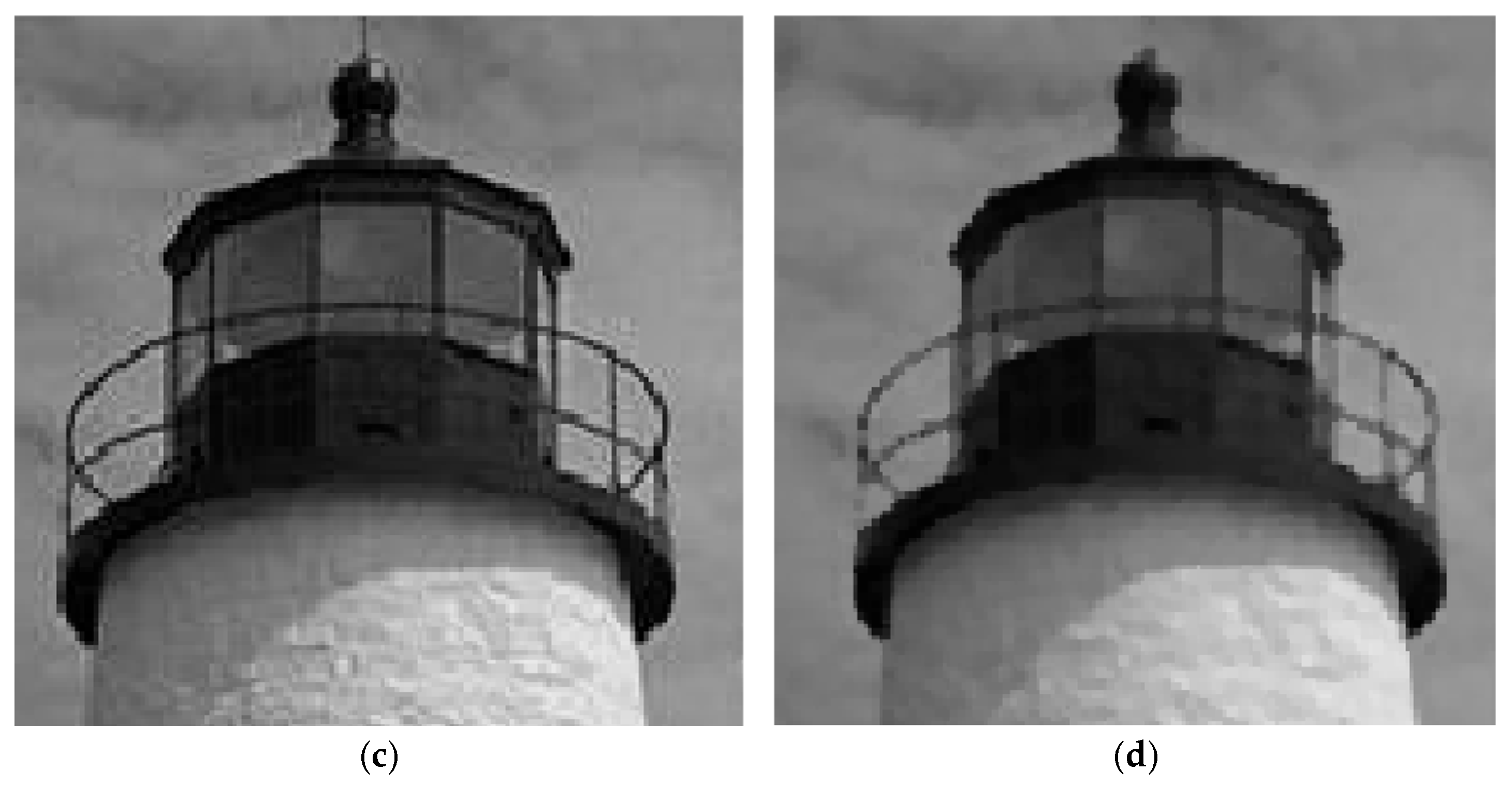
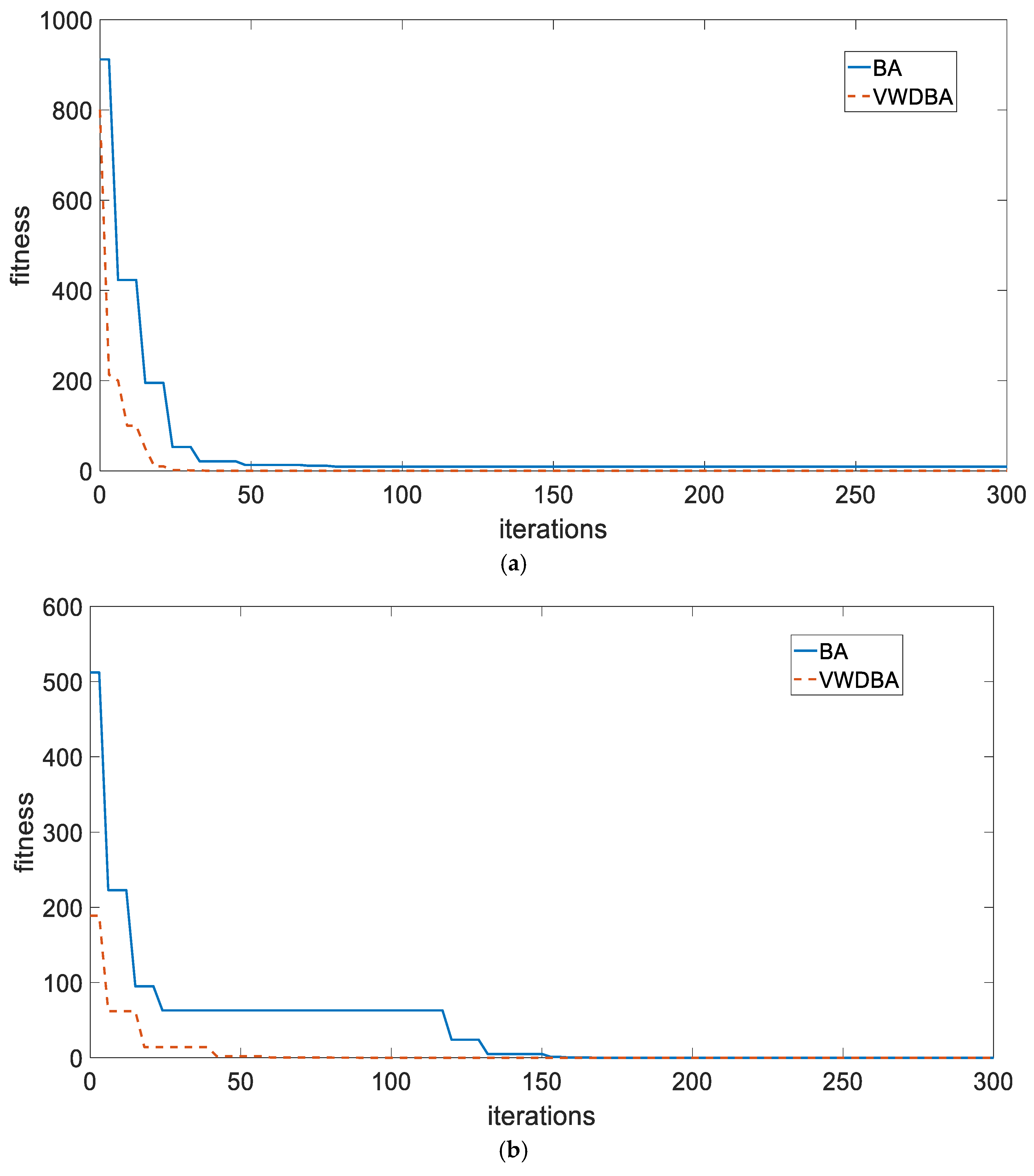
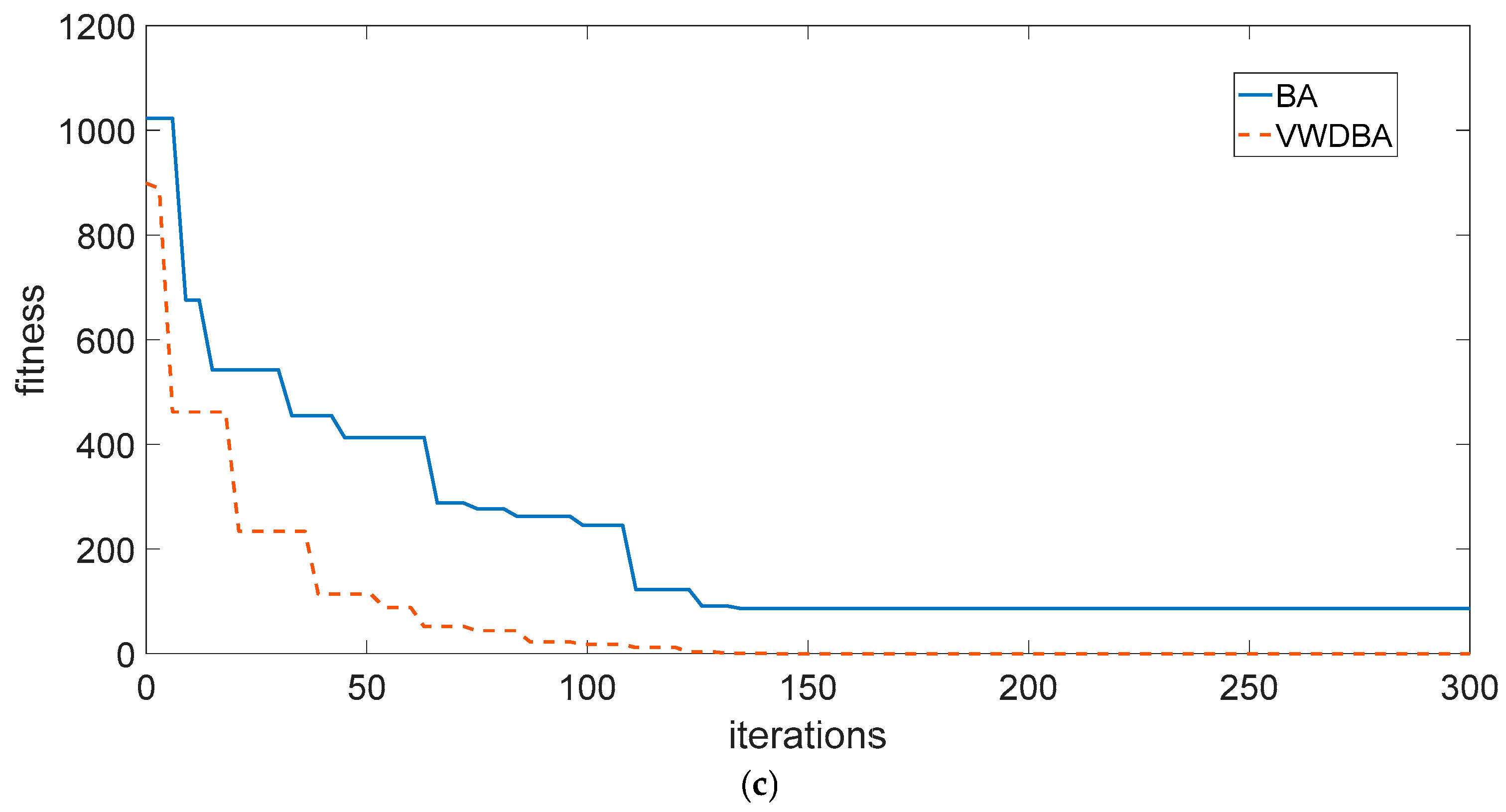
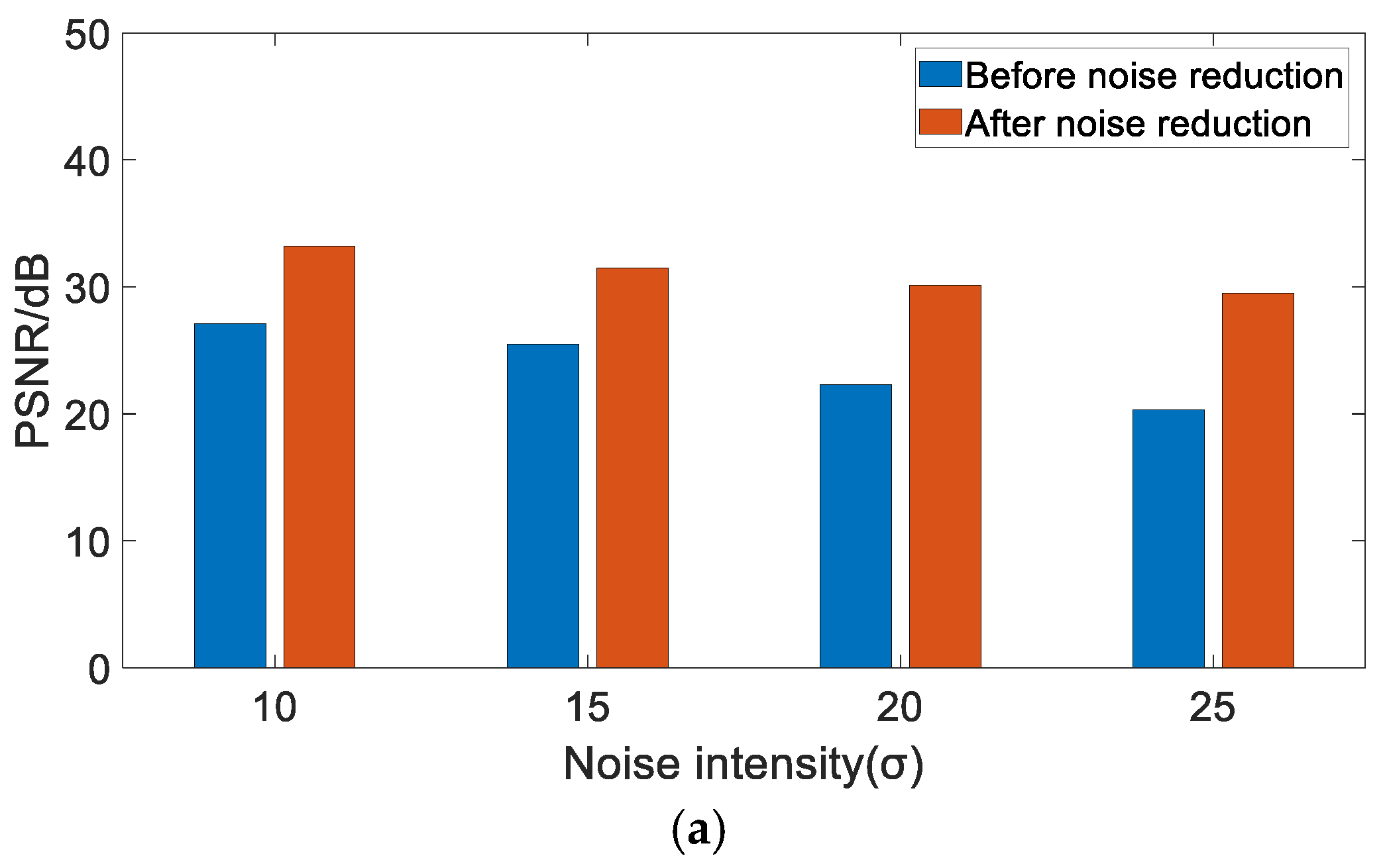
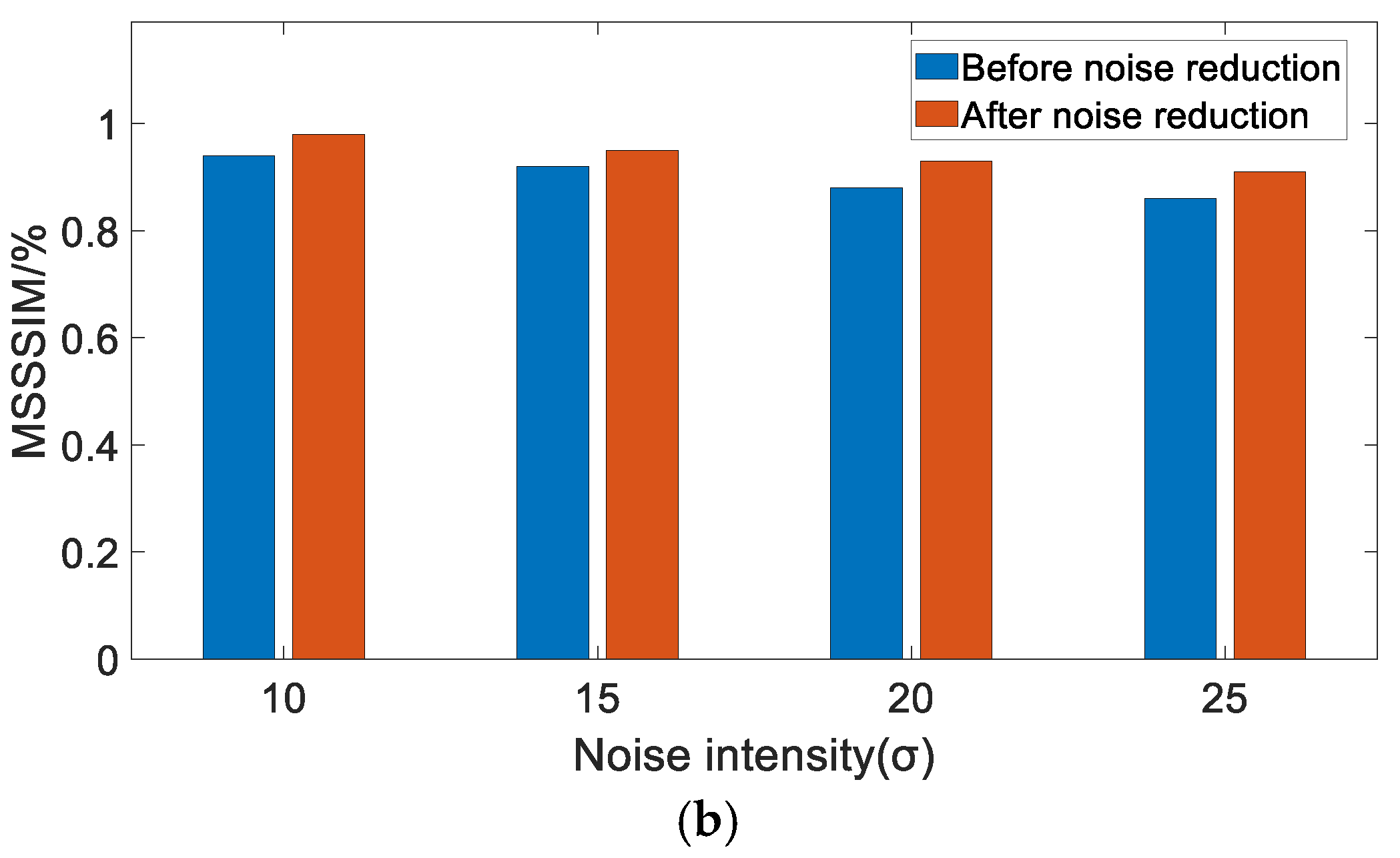
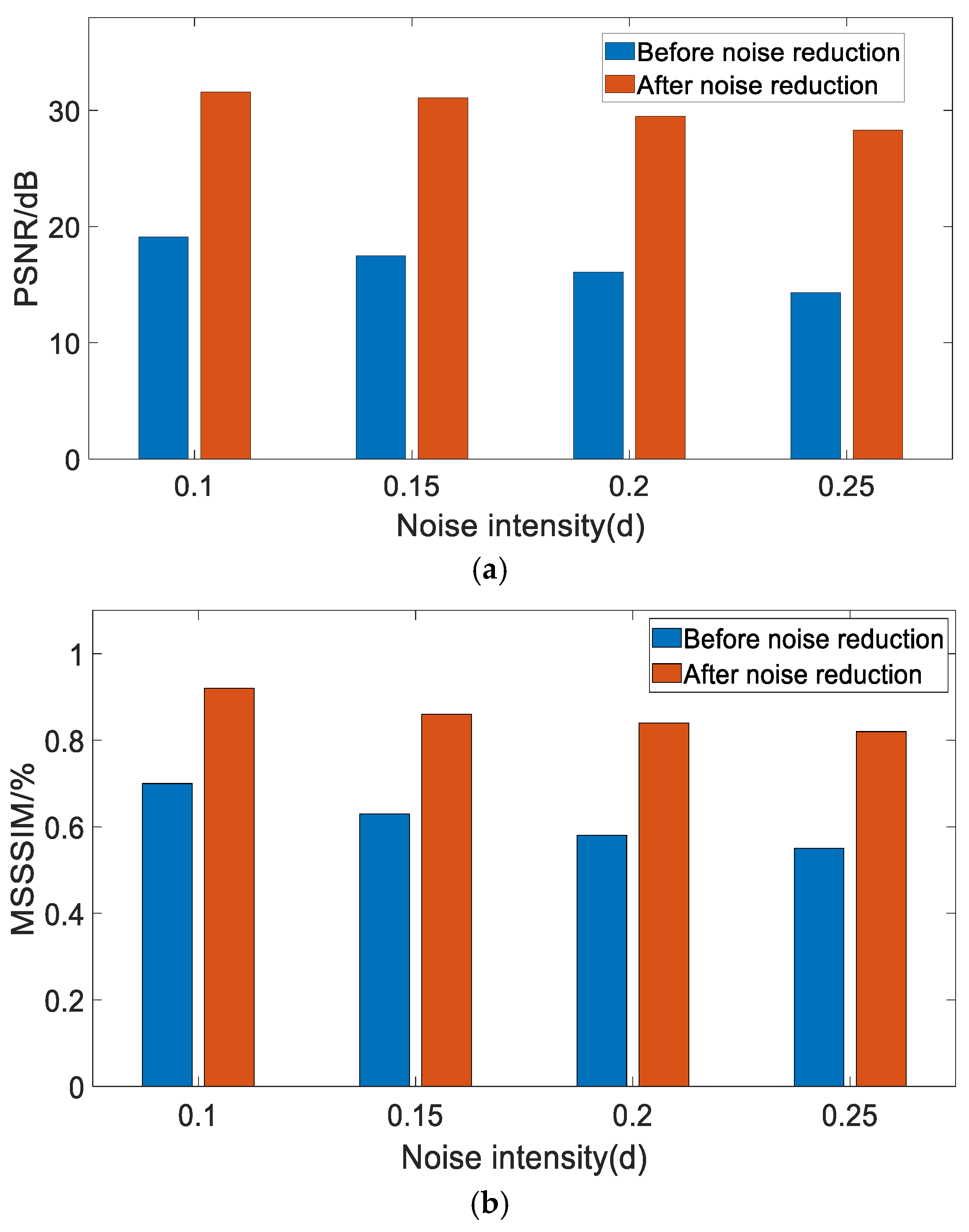
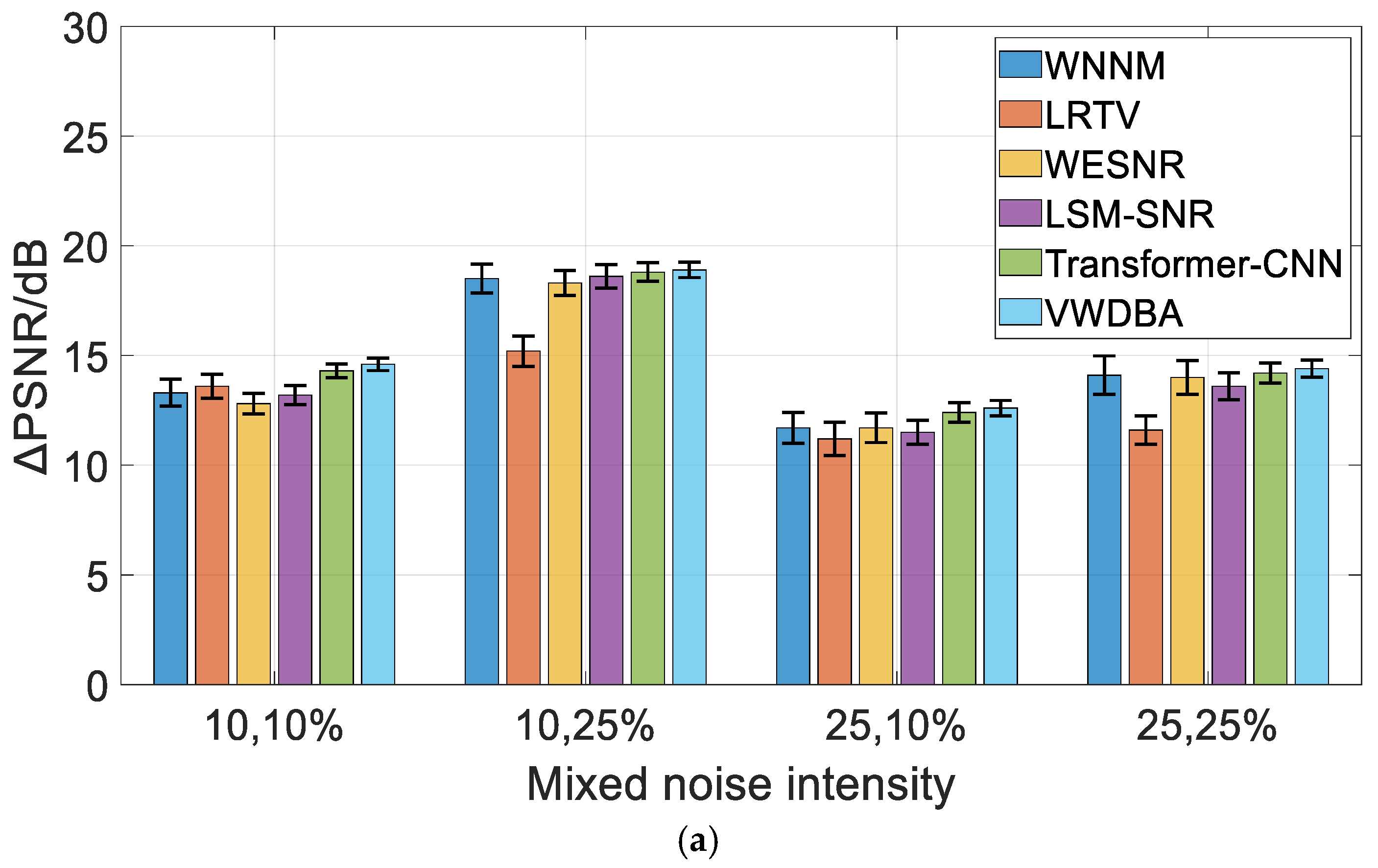
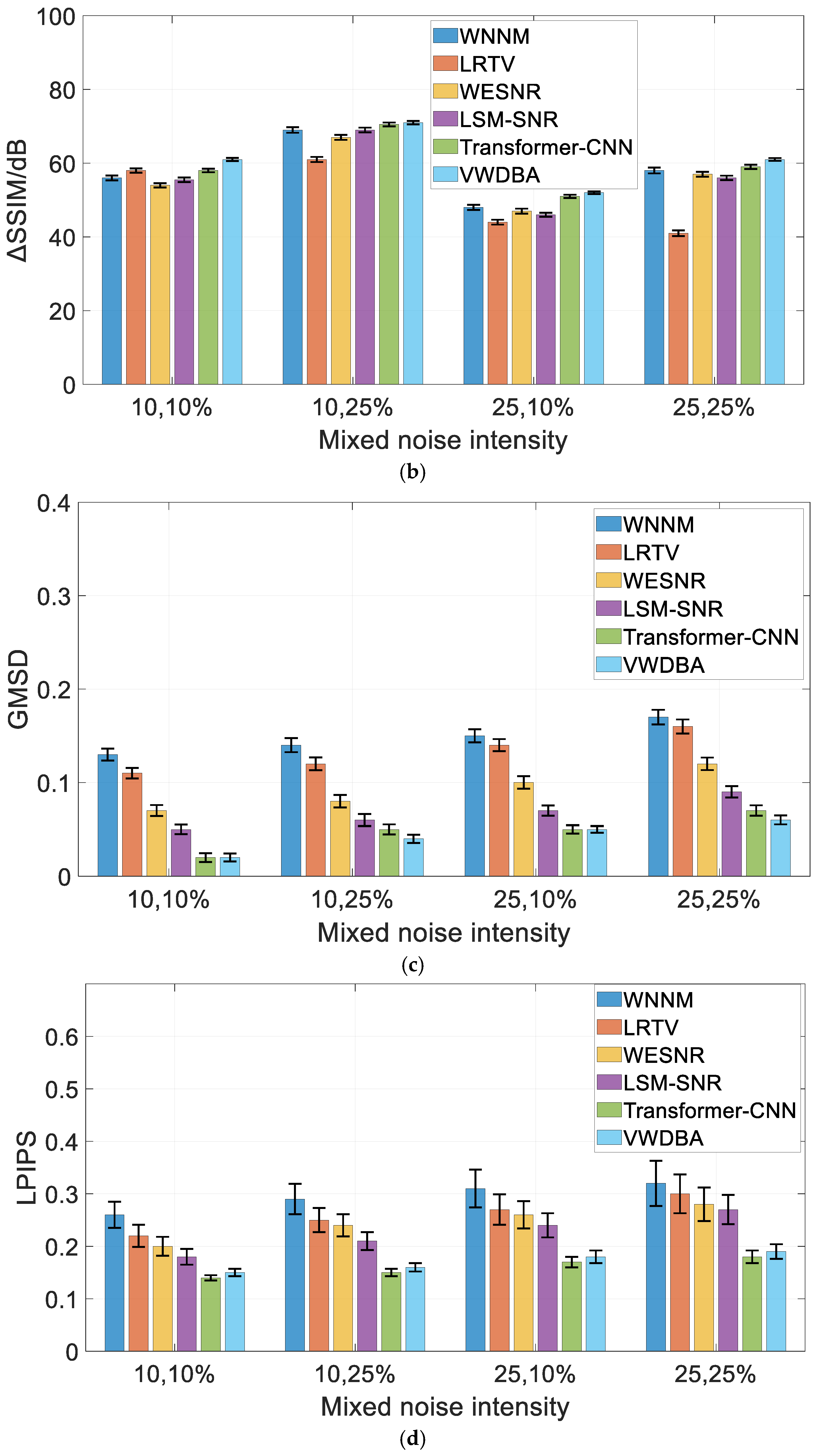
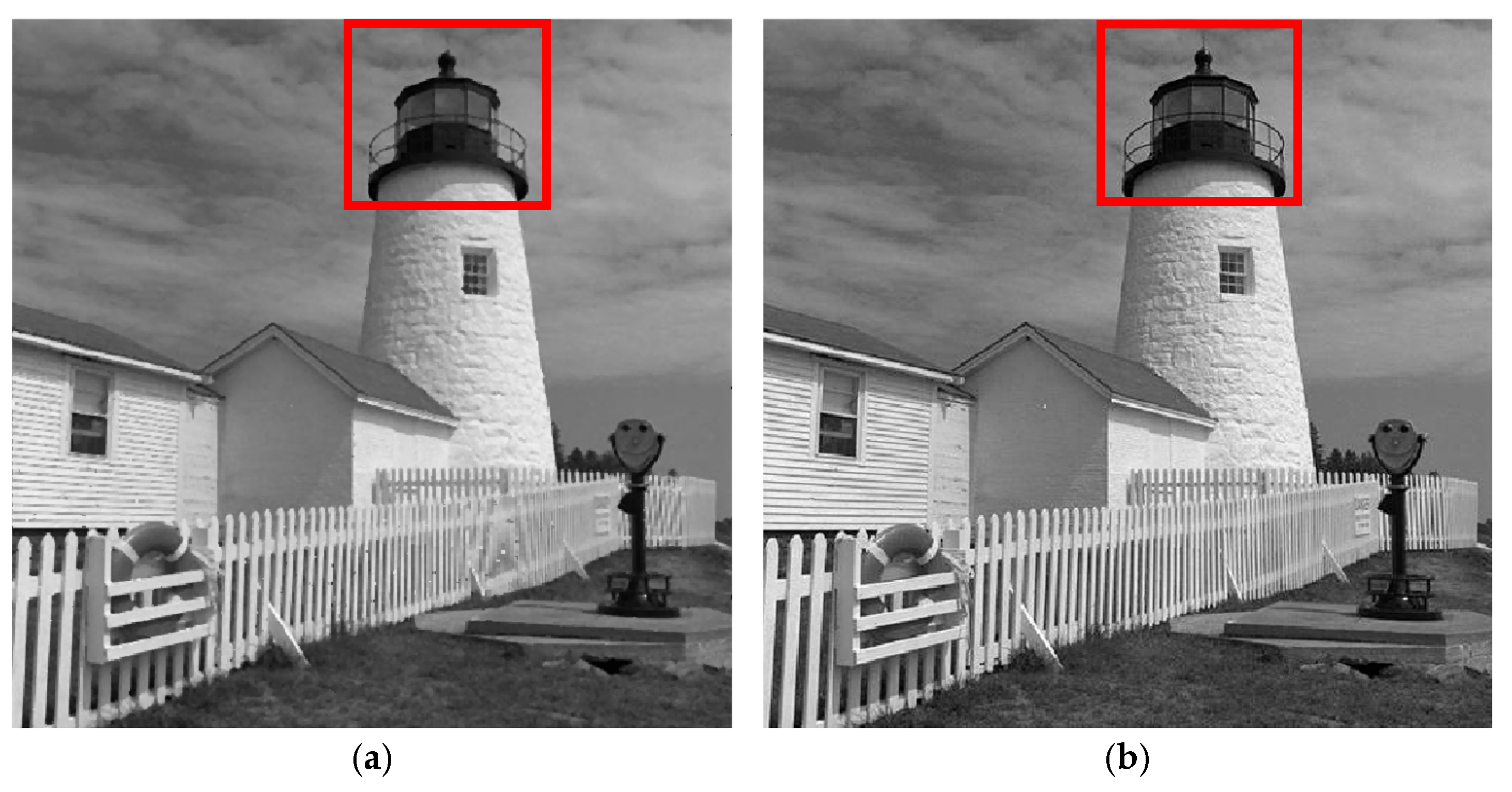
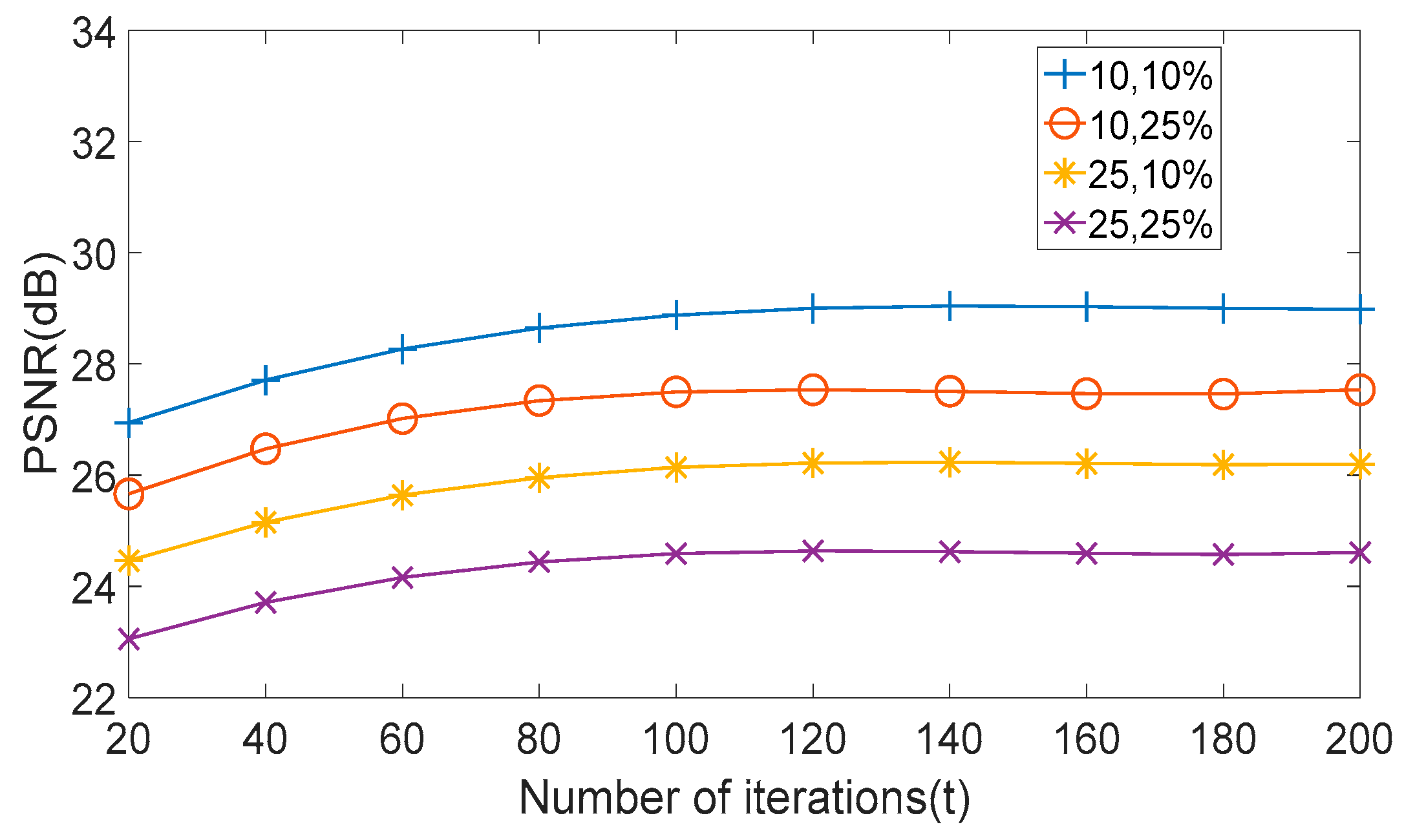
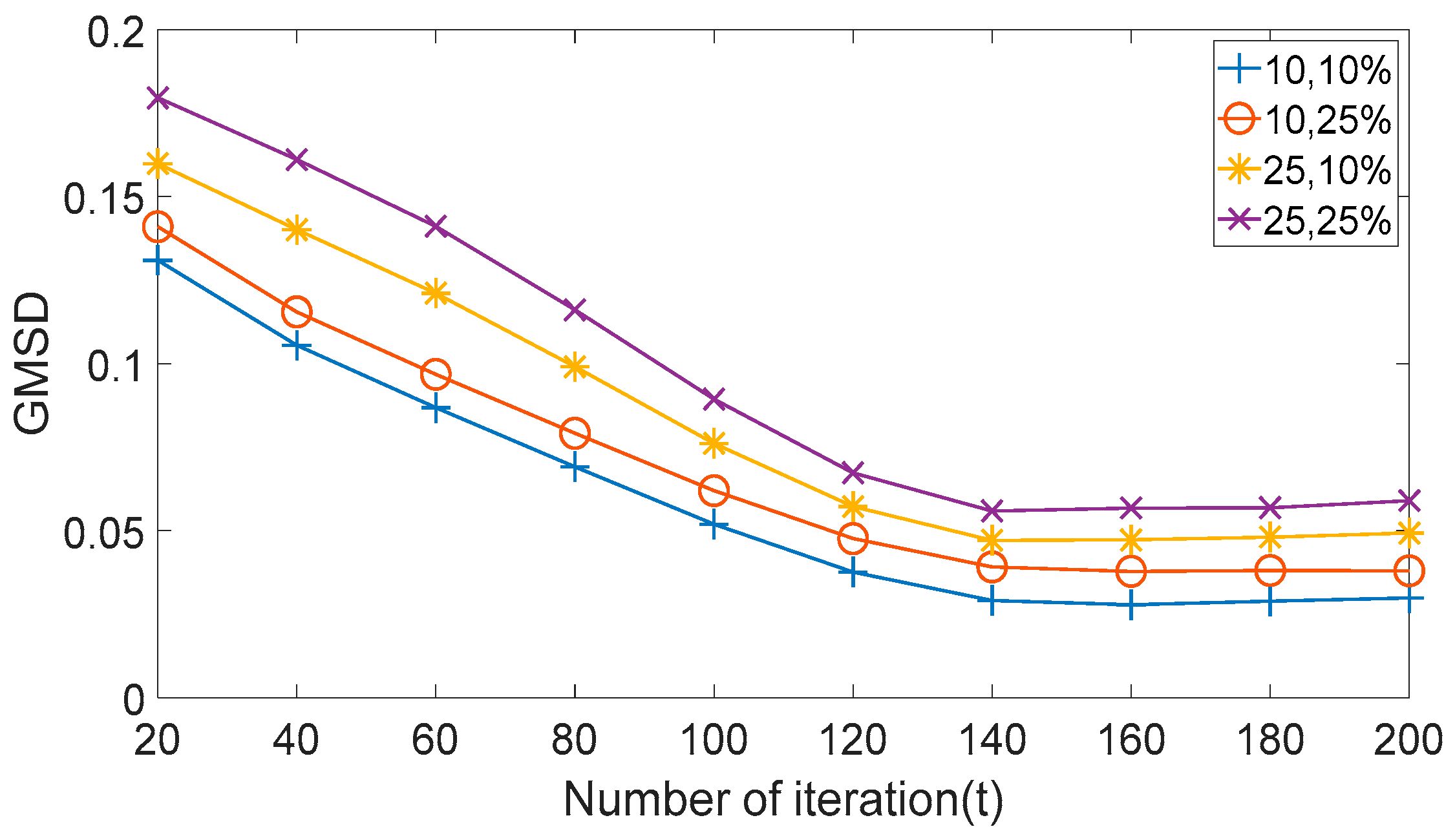
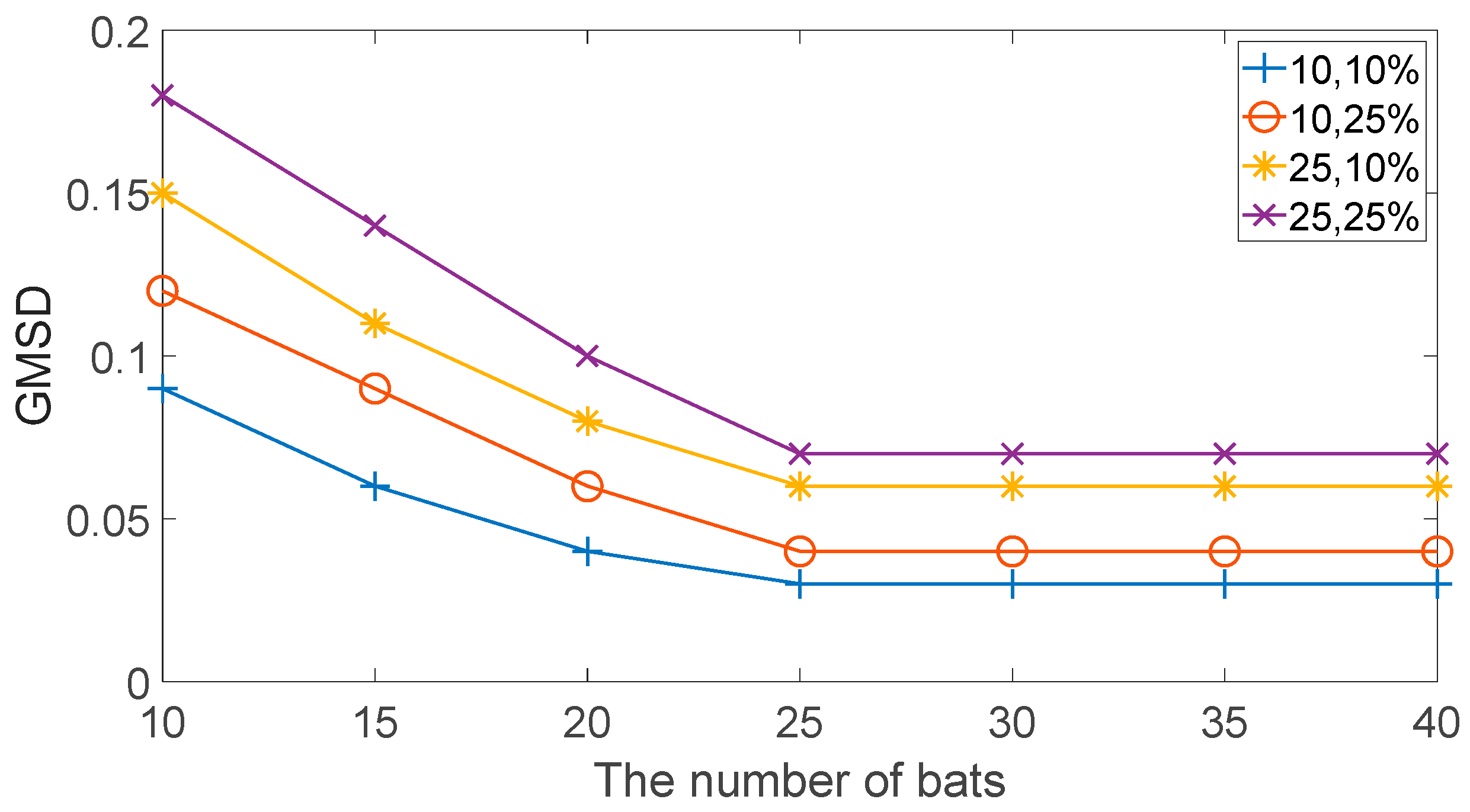
4.2. Analysis of Experimental Results
- (1)
- Results of Experiment 1:
- (2)
- Results of Experiment 2:
- (3)
- Results of Experiment 3:
- (4)
- Results of Experiment 4:
- (5)
- Results of Experiment 5:
5. Results
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Variable Name | Variable Definition |
|---|---|
| input of the Volterra model | |
| output of the Volterra model | |
| the n-th-order time-domain kernel of the nonlinear Volterra filter model | |
| the discrete time-domain model of the output signal | |
| N | the highest order |
| k | the order of the Volterra series |
| the error of truncation | |
| the memory length | |
| the n-th-order time-domain kernel function of Volterra | |
| any of the permutations of | |
| the weight coefficient when the time-domain kernel is symmetric | |
| t | the iteration number |
| the bat’s position vector at time t | |
| the bat’s flight speed vector at time t | |
| the best position among the bats in the current population | |
| the pulse rate used by a bat when searching for prey | |
| ε | follows a random distribution in the interval [0, 1] |
| the average loudness of the bat population at time t | |
| the maximum pulse rate of a bat | |
| represents the pulse rate of a bat at time | |
| the pulse rate increase coefficient | |
| represents the sound intensity of the bat at time t | |
| the pulse sound intensity decay coefficient, | |
| a random variable that follows a normal distribution in [0, 1]. | |
| input matrix | |
| the mean square error (MSE) for calculating the predicted and ideal outputs | |
| the ideal signal | |
| the kernel-parameter vector optimized by d-th iteration of the algorithm |
References
- Wu, L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Tang, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y. Focus+Context semantic representation in scene segmentation. Acta Electron. Sin. 2021, 49, 596–604. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.P.; Lin, Z.Y.; Zhang, G.Z.; Chen, X.; Li, F. A low-light image enhancement algorithm using the hybrid strategy of deep learning and image fusion. Acta Electron. Sin. 2021, 49, 72–76. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.H.; Yu, X.D.; Zhao, S.M.; Wang, L. Ghost Imaging Denoising Based on Mean Filtering. Acta Opt. Sin. 2022, 42, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Shahdoosti, H.R.; Khayat, O. Image denoising using sparse representation classification and non-subsampled shear-let transform. Signal Image Video Process. 2016, 10, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharon, M.; Elad, M.; Bruckstein, A. K-SVD: An algorithm for designing overcomplete dictionaries for sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2006, 54, 4311–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.F.; Candes, E.J.; Shen, Z.W. A singular value thresholding algorithm for matrix completion. SIAM J. Optim. 2010, 20, 1956–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.H.; Xie, Q.; Meng, D.Y.; Zuo, W.; Feng, X.; Zhang, L. Weighted nuclear norm minimization and its applications to low level vision. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2017, 121, 183–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, X.; Yu, L.; Liao, X.; Lai, Z.; Cheng, H.; Liao, D. Extraction of asymptotic edges of microcracks in silicon nitride bearings based on adaptive nonlocal mean filtering and iterative tracking algorithm. Measurement 2025, 242, 116215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, T.Z.; Ye, W.H. Improved Adaptive Kalman-Median Filter for Line-Scan X-ray Transmission Image. Sensors 2022, 22, 4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faragallah, S.O.; Ibrahem, M.H. Adaptive switching weighted median filter framework for suppressing salt-and-pepper noise. AEUE Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2016, 70, 1034–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.X.; Zhu, G.P.; Zhu, Z.B. A TV-log nonconvex approach for image deblurring with impulsive noise. Signal Process. 2020, 174, 107631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Zhang, H.Y.; Zhang, L.P.; Shen, H. Total variation regularized low-rank matrix factorization for hyperspectral image restoration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.J.; Xie, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yee, L.; Meng, D. Enhanced 3DTV regularization and its applications on HSI denoising and compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 7889–7903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Dong, W.S.; Xie, X.M.; Shi, G.; Bai, X. Mixed noise removal via Laplacian scale mixture modeling and nonlocal low-rank approximation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 3171–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Wang, C.; Xiao, S.; Li, H.; Zhao, X.; Guo, F.; Shi, L.; Zhou, X. Magnetic resonance image denoising for Rician noise using a novel hybrid transformer-CNN network (HTC-net) and self-supervised pretraining. Med. Phys. 2024, 52, 1643–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S. A hybrid SMOTE and Trans-CWGAN for data imbalance in real operational AHU AFDD: A case study of an auditorium building. Energy Build. 2025, 348, 116447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Lin, C.C. Identification of nonlinear systems by the genetic programming based Volterra filter. IET Signal Process. 2009, 3, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Shen, P.; Guan, X.; Liu, X.; Massari, C.; Wang, Z.; Feng, M.; Wang, Q.; Lu, Y.; et al. Regional-scale intelligent optimization and topography impact in restoring global precipitation data gaps. Commun. Earth Environ. 2025, 6, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, H.P.; Li, N.Z.; Chen, Z.W. Cancellation of mechanical vibration signal noise based on Volterra filter. J. Lanzhou Jiaotong Univ. 2015, 34, 130–135. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.Z.; Wei, X.J.; Ding, W.C.; Lu, K.K. Removing mixed noise in locomotive wheel speed signal with a nonlinear Volterra filter. J. Lanzhou Univ. 2017, 53, 280–286. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.Z.; Feng, X.Y. Volterra series identification method based on adaptive quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization combined with the chaotic strategy. J. Lanzhou Univ. 2014, 50, 128–134. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Li, Z.Z.; Zhang, H.T.; Wang, D.; Yuan, Y. Nonlinear Volterra filter method for mixed noise reduction in rotate-speed with kernel parameters optimized based on Bat algorithm. J. Nonlinear Convex Anal. 2022, 23, 1895–1911. [Google Scholar]
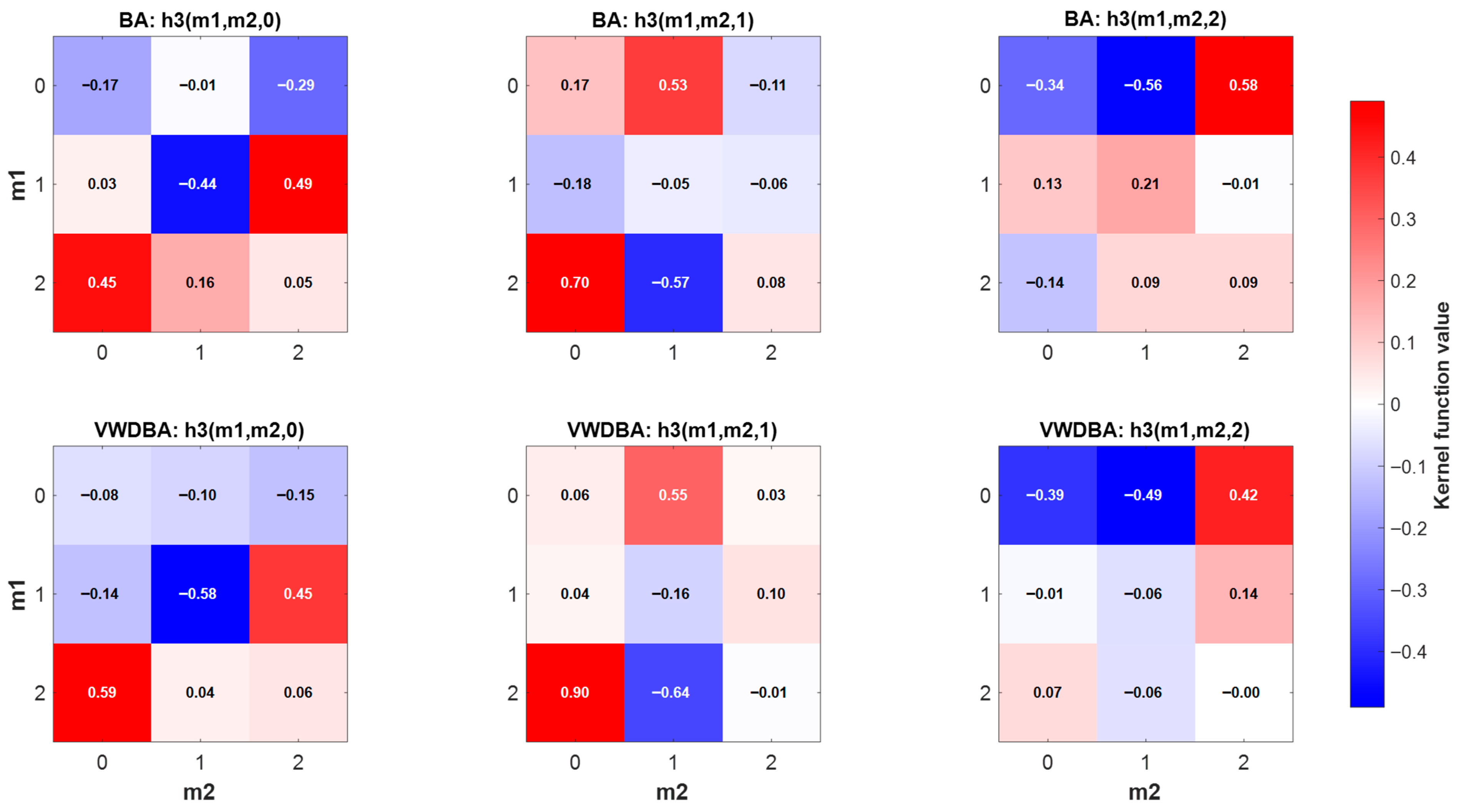







| Function Name | Function Expression | Search Space | Theoretical Optimal Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Griewank | |||
| Rastrigrin | |||
| Schwefel |
| 1.20 × 10−1 | 4.05 × 10−3 | −1.58 × 10−4 | |||
| 4.01 × 10−1 | −2.21 × 10−3 | 8.62 × 10−5 | |||
| −2.18 × 10−1 | −2.08 × 10−3 | −7.14 × 10−4 | |||
| 1.23 × 10−1 | −1.24 × 10−3 | 9.66 × 10−5 | |||
| 2.24 × 10−1 | 2.11 × 10−3 | 1.74 × 10−4 | |||
| 2.51 × 10−1 | 3.49 × 10−3 | −2.15 × 10−4 | |||
| 2.44 × 10−3 | 2.46 × 10−3 | 3.42 × 10−4 | |||
| 1.84 × 10−3 | 2.42 × 10−3 | −6.77 × 10−4 |
| Algorithm | Computational Complexity | Key Bottlenecks |
|---|---|---|
| WNNM | t × B × (m × n × r + r3) | t: Number of iterations (typically 10–20); B: Number of patch groups (thousands); m, n: Patch size (e.g., 8 × 8); r: Rank of the patch group |
| LRTV | t × (B × r3+ N log N) | t: Number of ADMM iterations; B: Number of non-local patch groups; r: Rank for low-rank approximation; N: Number of pixels |
| WESNR | t × (B × L2+ N × L) | t: Number of iterations; B: Number of patch groups; L: Number of dictionary atoms; N: Number of pixels |
| LSM-NLR | t × B × (m × n × r + r3) | I: Number of iterations; B: Number of patch groups |
| Transformer-CNN | t × (H × W × C2+ H × W2× C)) | t: Number of layers; H, W: Feature map size (256 × 256); C: Number of channels |
| VWDBA-Volterra | T × P × N × K | T: Number of iterations (typically 50–200) P: Population size; N: Number of pixels (256 × 256 = 65,536); K: Volterra kernel size |
| Algorithm | Estimated Computational Time (s) | Hardware Dependency and Time Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| WNNM | 243.5 | CPU: Massive SVD computations are the main bottleneck. Even for a size of 256 × 256, thousands of patch groups need processing. |
| LRTV | 123.4 | CPU: ADMM iteration convergence requires time, alternating between low-rank and TV optimizations. |
| WESNR | 56.8 | CPU: Hybrid model but optimized, typically more efficient than pure WNNM. |
| LSM-NLR | 34.5 | CPU: Specifically designed for mixed noise, employing more efficient robust estimation, typically faster than WNNM. |
| Transformer-CNN | 26 h | GPU: highly recommended. Training: Requires extensive data and time for parameter training. |
| VWDBA-Volterra | 14.6 | CPU: Time depends directly on population size × iterations. Adaptive inertia weight may accelerate convergence. Volterra filtering itself is computationally efficient. |
| Kernel Parameters | Optimized Results | Kernel Parameters | Optimized Results | Kernel Parameters | Optimized Results | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t = 60 | t = 120 | t = 60 | t = 120 | t = 60 | t = 120 | |||
| 1.25 × 10−1 | 1.18 × 10−1 | 4.98 × 10−3 | 5.36 × 10−3 | −2.41 × 10−3 | −2.31 × 10−4 | |||
| 3.98 × 10−1 | 3.04 × 10−1 | −1.25 × 10−3 | −1.56 × 10−3 | 1.34 × 10−5 | 8.72 × 10−5 | |||
| −2.15 × 10−1 | −2.16 × 10−1 | 2.55 × 10−3 | −2.72 × 10−3 | 3.43 × 10−3 | −6.36 × 10−5 | |||
| 1.77 × 10−1 | 1.65 × 10−1 | −2.46 × 10−3 | −2.42 × 10−3 | 1.19 × 10−4 | 8.89 × 10−5 | |||
| 2.24 × 10−1 | 2.16 × 10−1 | 3.66 × 10−3 | 4.21 × 10−3 | 9.63 × 10−5 | 2.31 × 10−4 | |||
| 2.66 × 10−1 | 2.42 × 10−1 | 4.51 × 10−3 | 5.41 × 10−3 | −8.23 × 10−5 | −1.26 × 10−4 | |||
| 1.42 × 10−3 | 2.63 × 10−3 | 4.78 × 10−3 | 9.64 × 10−4 | −1.33 × 10−4 | 1.56 × 10−5 | |||
| 2.38 × 10−3 | 2.66 × 10−3 | 8.92 × 10−4 | 1.34 × 10−3 | −8.29 × 10−5 | −5.32 × 10−5 | |||
| Kernel Parameters | Optimized Results | Kernel Parameters | Optimized Results | Kernel Parameters | Optimized Results | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 30 | 15 | 30 | 15 | 30 | |||
| 1.25 × 10−1 | 1.22 × 10−1 | 4.23 × 10−3 | 4.13 × 10−3 | −1.23 × 10−3 | −1.78 × 10−4 | |||
| 4.01 × 10−1 | 3.99 × 10−1 | −3.25 × 10−3 | −2.34 × 10−3 | 1.55 × 10−5 | 9.32 × 10−5 | |||
| −2.23 × 10−1 | −2.15 × 10−1 | −5.31 × 10−3 | −3.01 × 10−3 | 6.13 × 10−3 | −7.35 × 10−4 | |||
| 1.45 × 10−1 | 1.33 × 10−1 | −4.68 × 10−3 | −1.2 × 10−3 | 2.23 × 10−4 | 9.66 × 10−5 | |||
| 2.52 × 10−1 | 2.12 × 10−1 | 4.78 × 10−3 | 2.35 × 10−3 | −6.37 × 10−5 | 1.22 × 10−4 | |||
| 2.44 × 10−1 | 2.52 × 10−1 | 2.51 × 10−3 | 3.41 × 10−3 | −2.24 × 10−4 | −2.15 × 10−4 | |||
| 1.82 × 10−3 | 1.75 × 10−3 | 4.95 × 10−3 | 2.33 × 10−3 | −3.32 × 10−4 | 4.55 × 10−4 | |||
| 2.17 × 10−3 | 1.96 × 10−3 | 4.91 × 10−3 | 2.15 × 10−3 | −3.66 × 10−4 | −6.82 × 10−4 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, W.; Yu, C.-B.; Liu, H.-J.; Hu, Y. A Nonlinear Volterra Filtering Hybrid Image-Denoising Method Based on the Improved Bat Algorithm for Optimizing Kernel Parameters. Electronics 2025, 14, 4076. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14204076
Zhao W, Yu C-B, Liu H-J, Hu Y. A Nonlinear Volterra Filtering Hybrid Image-Denoising Method Based on the Improved Bat Algorithm for Optimizing Kernel Parameters. Electronics. 2025; 14(20):4076. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14204076
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Wei, Chang-Bai Yu, Hai-Jun Liu, and Yue Hu. 2025. "A Nonlinear Volterra Filtering Hybrid Image-Denoising Method Based on the Improved Bat Algorithm for Optimizing Kernel Parameters" Electronics 14, no. 20: 4076. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14204076
APA StyleZhao, W., Yu, C.-B., Liu, H.-J., & Hu, Y. (2025). A Nonlinear Volterra Filtering Hybrid Image-Denoising Method Based on the Improved Bat Algorithm for Optimizing Kernel Parameters. Electronics, 14(20), 4076. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14204076





