A High-Accuracy Normalization Unit Using Multi-Bit Random Variables
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
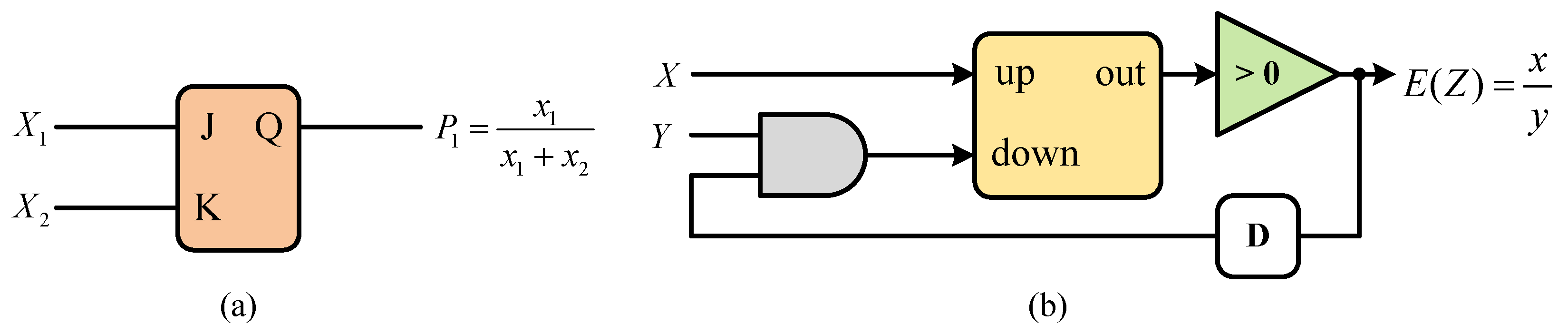
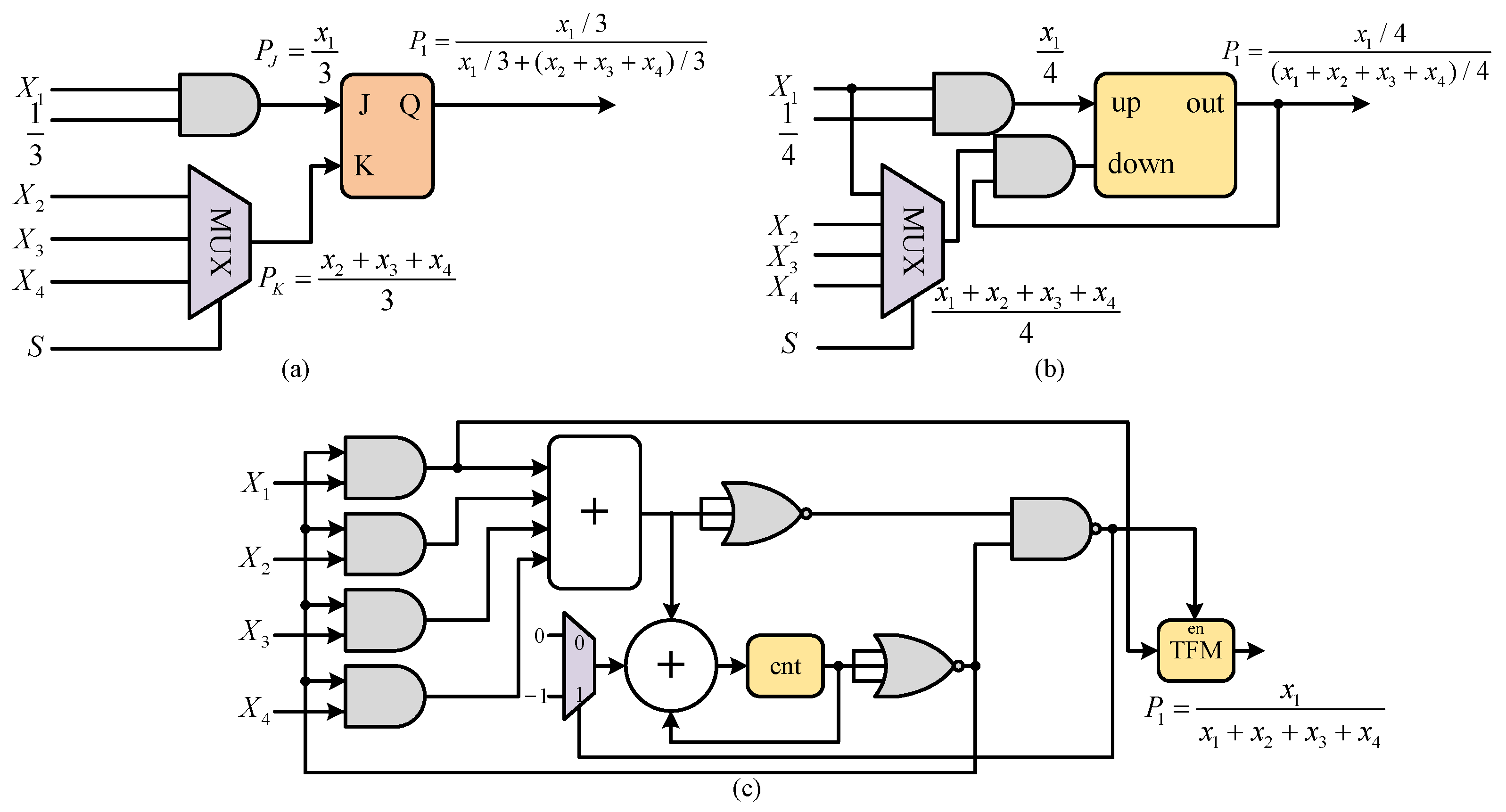
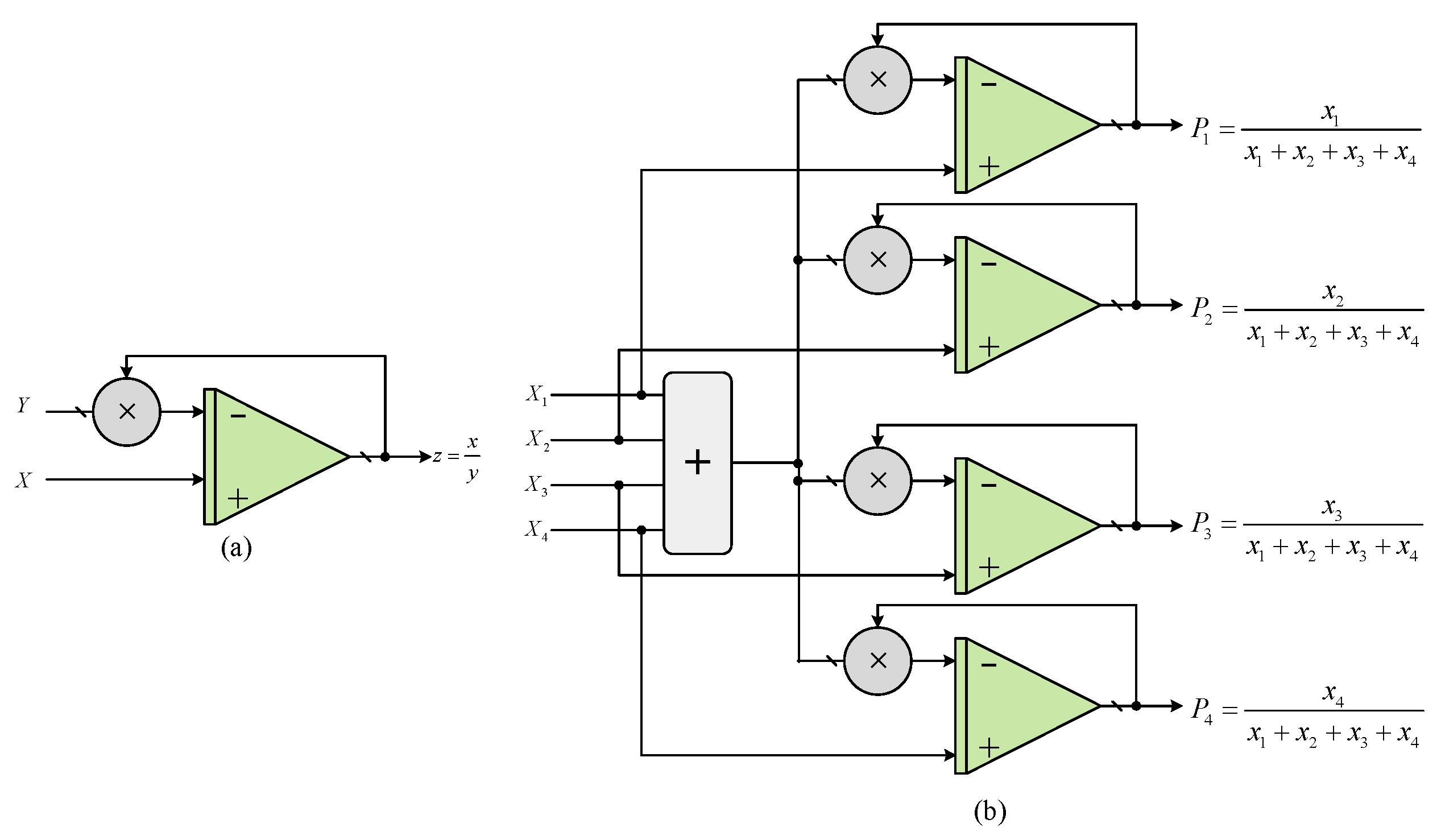
2.1. Existing Stochastic Normalization Units
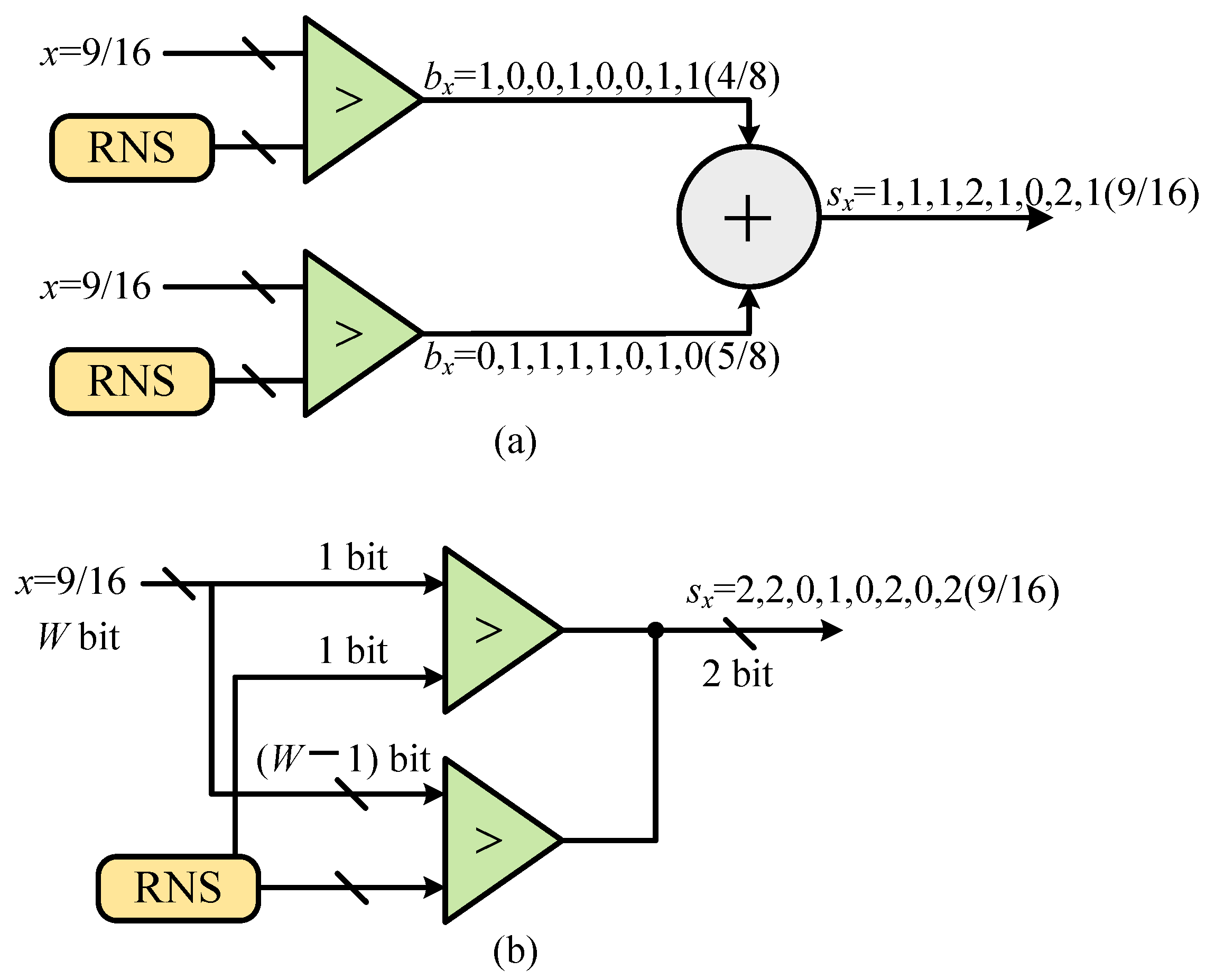
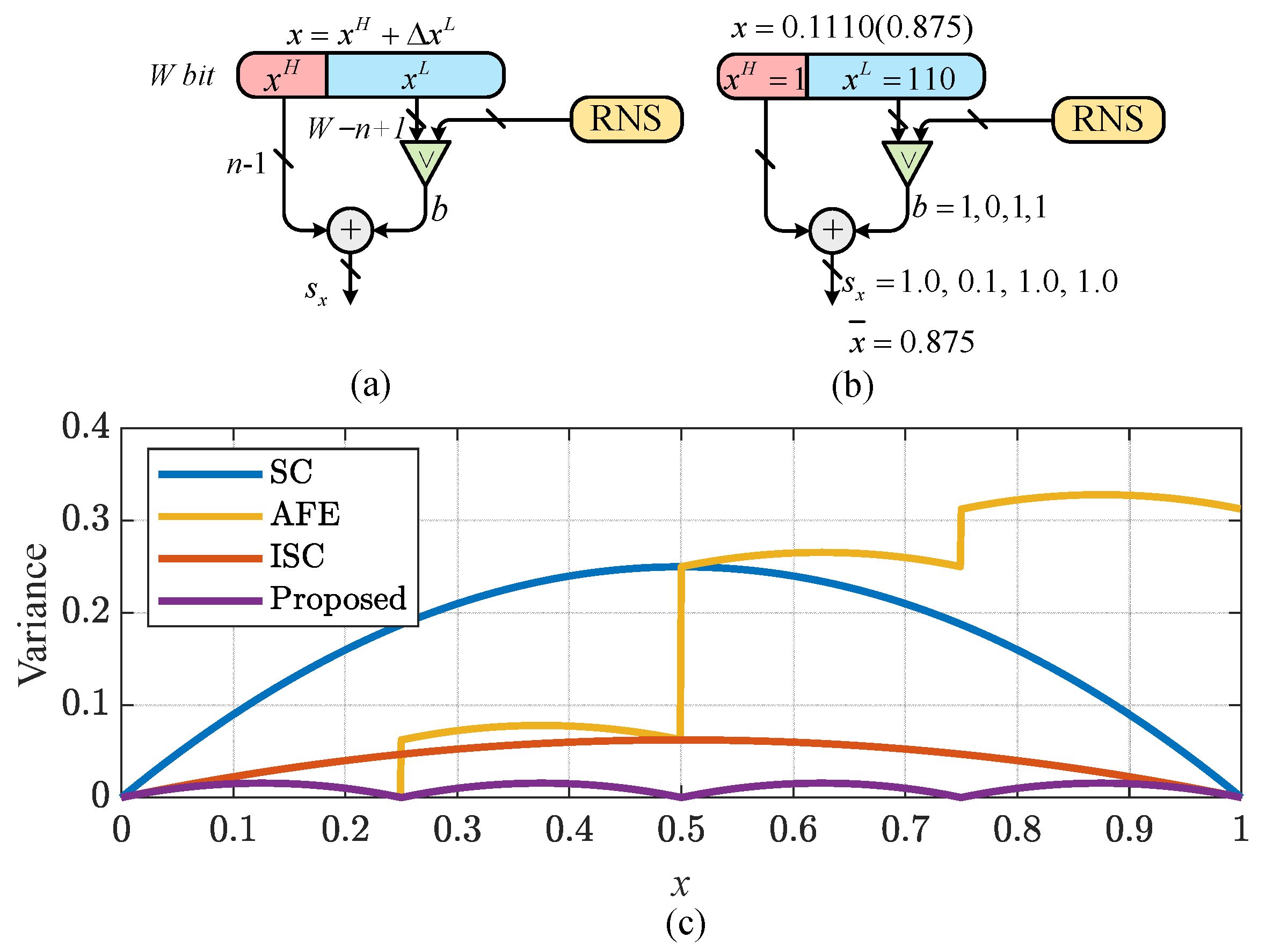
2.2. Multi-Bit Random Variables
3. Joint Normalization Unit for Multi-Bit Random Variable
3.1. High-Precision Multi-Bit Random Variable Generation
3.2. Normalization Unit for Multi-Bit Random Variable
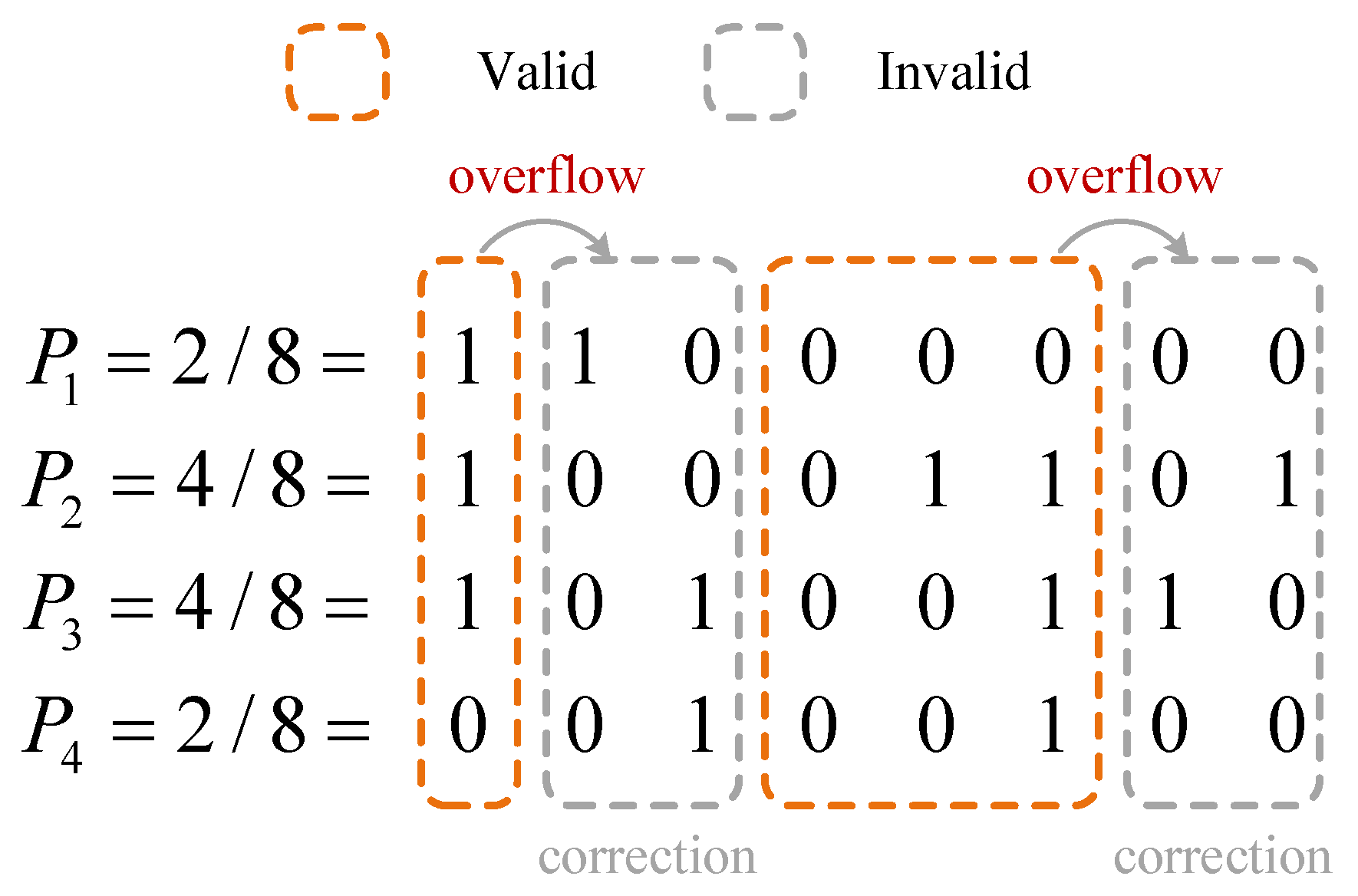
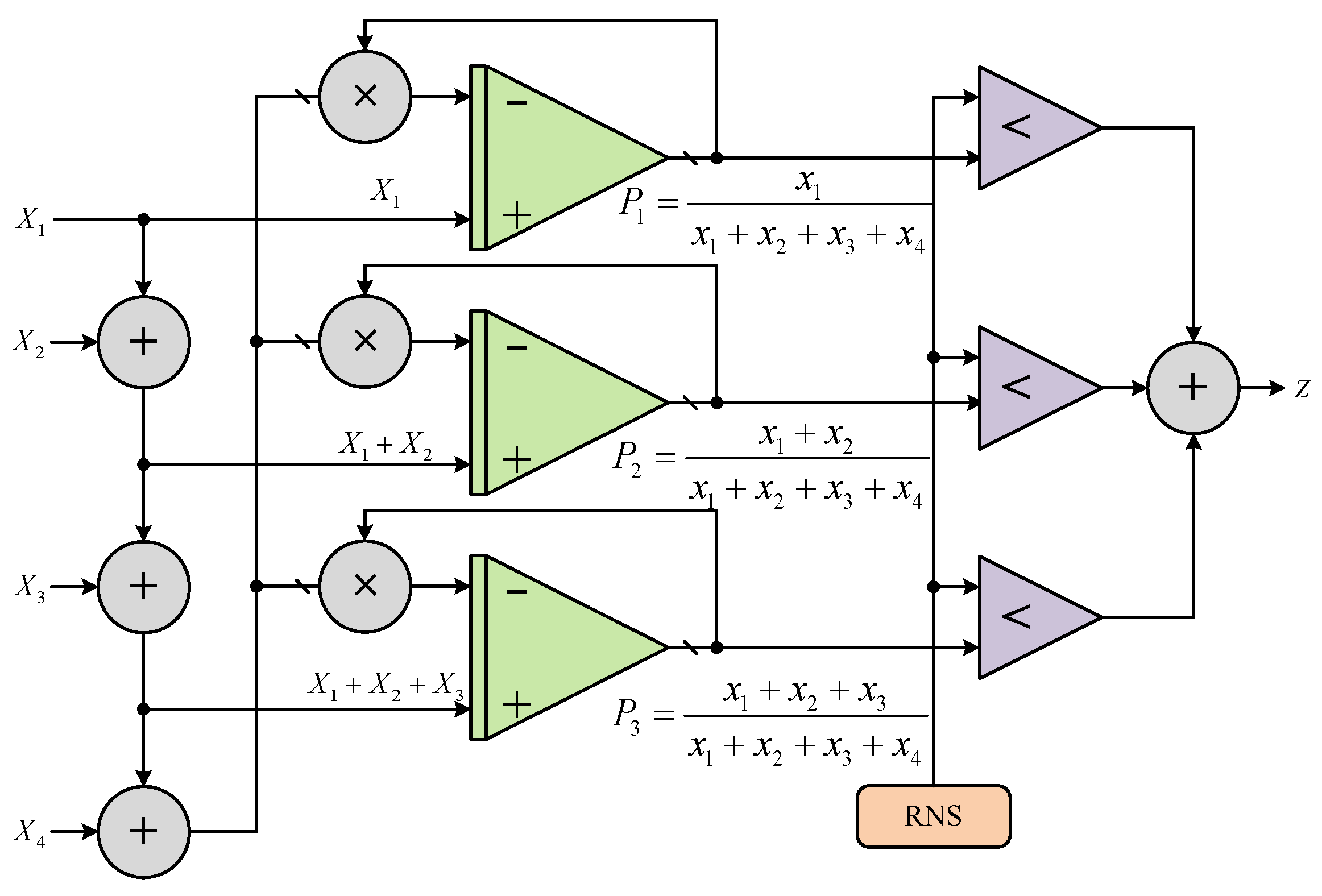
3.3. Constant Sum of Normalized Probabilities
3.4. Re-Randomize According to Normalized Probabilities
4. Performance Simulation and Complexity Analysis
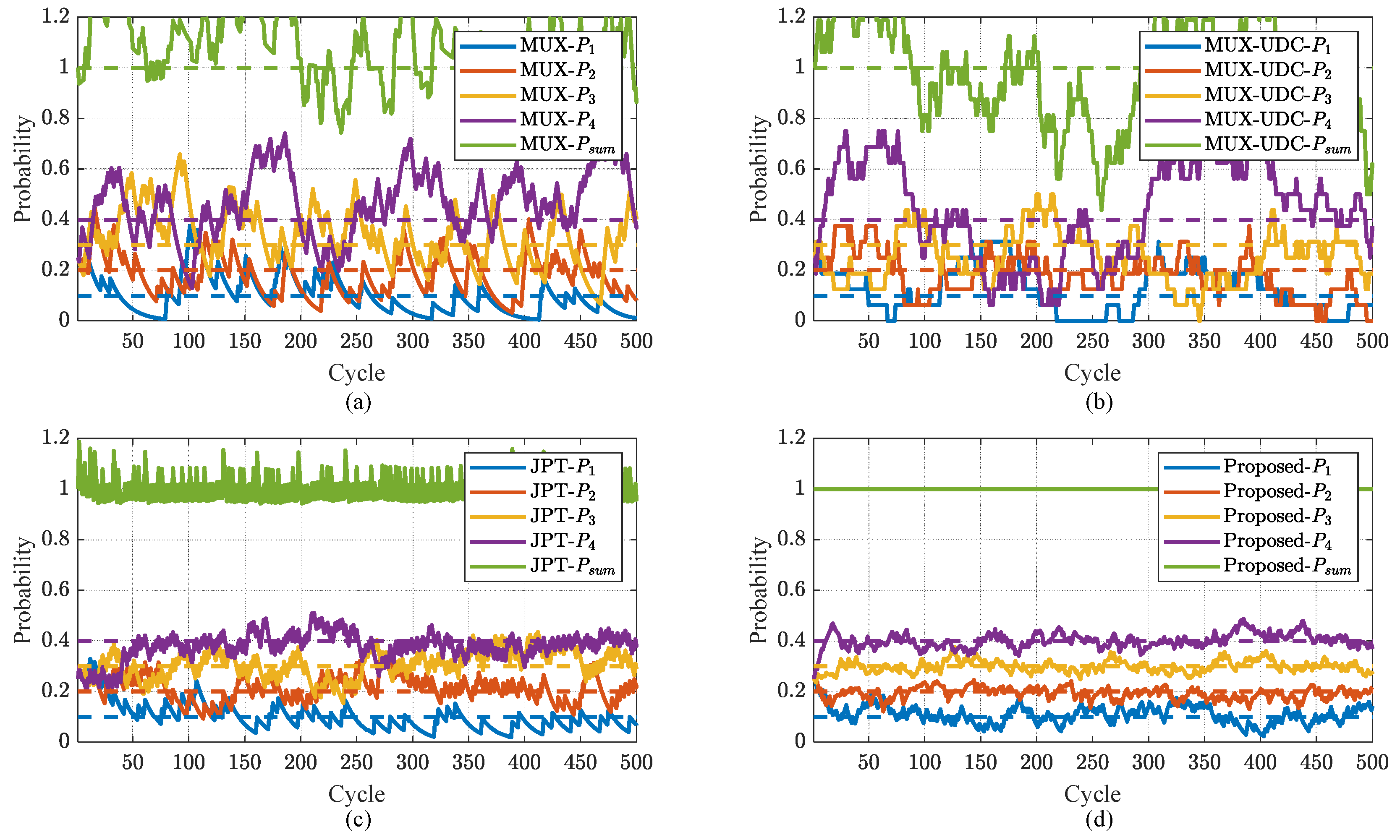
4.1. Performance Simulation
4.2. Hardware Implementation
4.3. Application Verification
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gaines, B.R. Stochastic computing. In Proceedings of the Spring Joint Computer Conference, Atlantic City, NJ, USA, 18–20 April 1967; pp. 149–156. [Google Scholar]
- Alaghi, A.; Qian, W.; Hayes, J.P. The promise and challenge of stochastic computing. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2017, 37, 1515–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joe, H.; Kim, Y. Novel stochastic computing for energy-efficient image processors. Electronics 2019, 8, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, W.J.; Gaudet, V.C.; Milner, A. Stochastic implementation of LDPC decoders. In Proceedings of the 2005 39th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 30 October–2 November 2005; pp. 713–717. [Google Scholar]
- Tehrani, S.S.; Naderi, A.; Kamendje, G.A.; Mannor, S.; Gross, W.J. Tracking forecast memories in stochastic decoders. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Taipei, Taiwan, 19–24 April 2009; pp. 561–564. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkis, G.; Hemati, S.; Mannor, S.; Gross, W.J. Stochastic decoding of LDPC codes over GF (q). IEEE Trans. Commun. 2013, 61, 939–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Hu, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, H. A fast converging normalization unit for stochastic computing. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2017, 65, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, H.; Hu, J.; Sobelman, G.E. An intra-iterative interference cancellation detector for large-scale MIMO communications based on convex optimization. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2016, 63, 2062–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Hu, J.; Chen, J.; Lu, H. A low complexity sparse code multiple access detector based on stochastic computing. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2017, 65, 769–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasser, C.F.; Roca, M.; Rossello, J.L. Optimal stochastic computing randomization. Electronics 2021, 10, 2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jeong, W.S.; Jeong, Y.; Lee, S.E. Parallel stochastic computing architecture for computationally intensive applications. Electronics 2023, 12, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardakani, A.; Leduc-Primeau, F.; Onizawa, N.; Hanyu, T.; Gross, W.J. VLSI implementation of deep neural network using integral stochastic computing. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2017, 25, 2688–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, H. Stochastic computing using amplitude and frequency encoding. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2022, 30, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, W.J.; Gaudet, V.C. Stochastic Computing: Techniques and Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Temenos, N.; Sotiriadis, P.P. Deterministic finite state machines for stochastic division in unipolar format. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Virtual, 12–14 October 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Canals, V.; Morro, A.; Rosselló, J.L. Stochastic-based pattern-recognition analysis. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2010, 31, 2353–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Perez-Andrade, I.; Zhong, S.; Maunder, R.G.; Al-Hashimi, B.M.; Hanzo, L. Stochastic computing improves the timing-error tolerance and latency of turbo decoders: Design guidelines and tradeoffs. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 1008–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Song, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, R.; Wang, R. Parallel convolutional neural network (CNN) accelerators based on stochastic computing. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Workshop on Signal Processing Systems (SiPS), Nanjing, China, 20–23 October 2019; pp. 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Dai, Y.; Han, K.; Wang, J.; Hu, J. An efficient bicubic interpolation implementation for real-time image processing using hybrid computing. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2022, 19, 1211–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikopour, H.; Baligh, H. Sparse code multiple access. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 24th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), London, UK, 8–11 September 2013; pp. 332–336. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, C.W.; Calderbank, A.R. Multiuser detection of Alamouti signals. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2009, 57, 2080–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K. Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access Using Guessing Random Additive Noise Decoding Aided Macrosymbols. Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, C.; Xu, S.; You, X. Efficient stochastic detector for large-scale MIMO. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Shanghai, China, 20–25 March 2016; pp. 6550–6554. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Hu, J.; Sobelman, G.E. Stochastic iterative MIMO detection system: Algorithm and hardware design. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2017, 62, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ji, H.; Tan, X.; Zhang, C. Stochastic Belief Propagation-Based Iterative Detection and Decoding for MIMO Systems. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2025, 33, 2324–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Geng, L.; Cao, Z.; Cao, M.; Li, S.; Li, W.; Fu, G. Adaptive Sparse Softmax: An Effective and Efficient Softmax Variant. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2025, 33, 3148–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


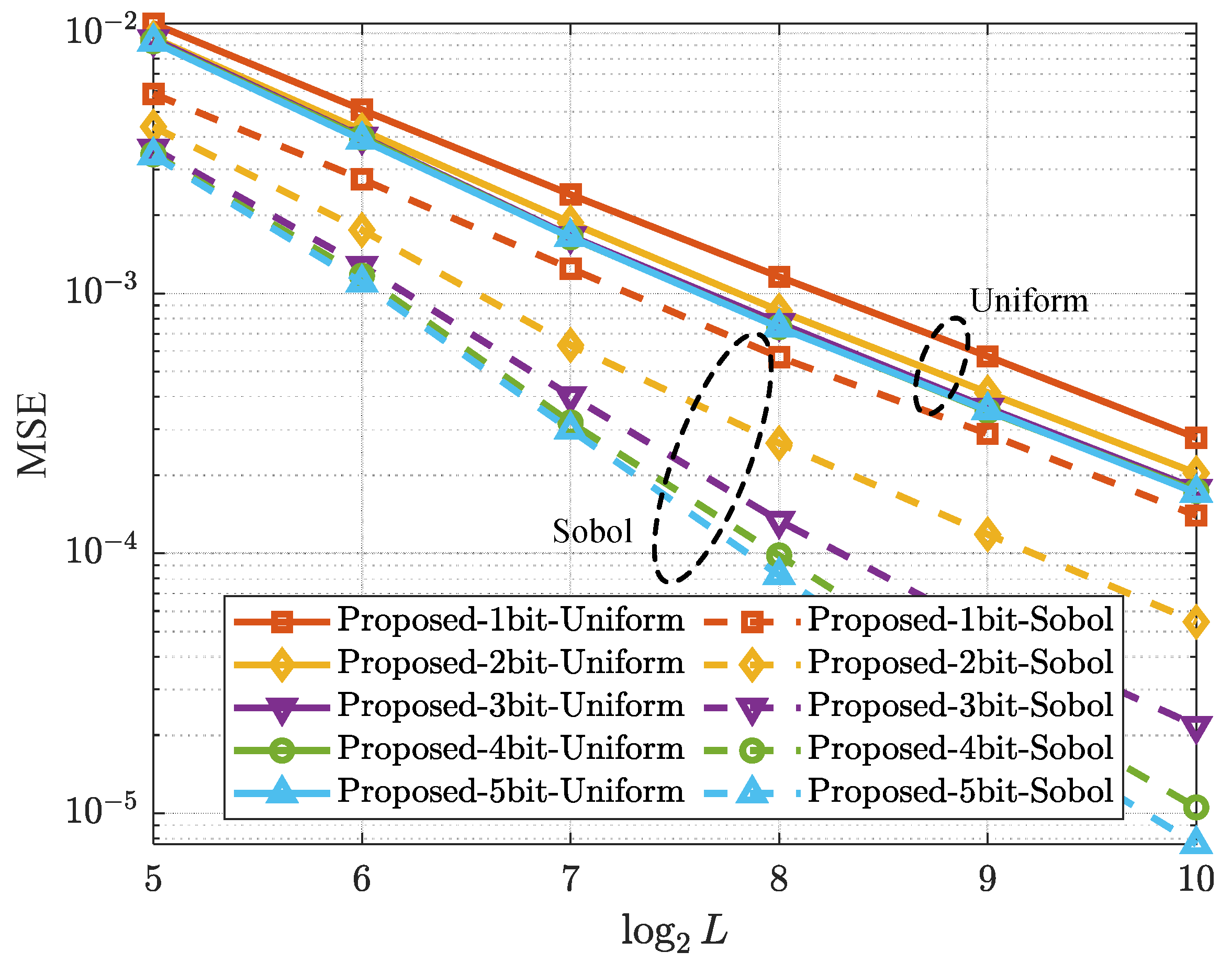
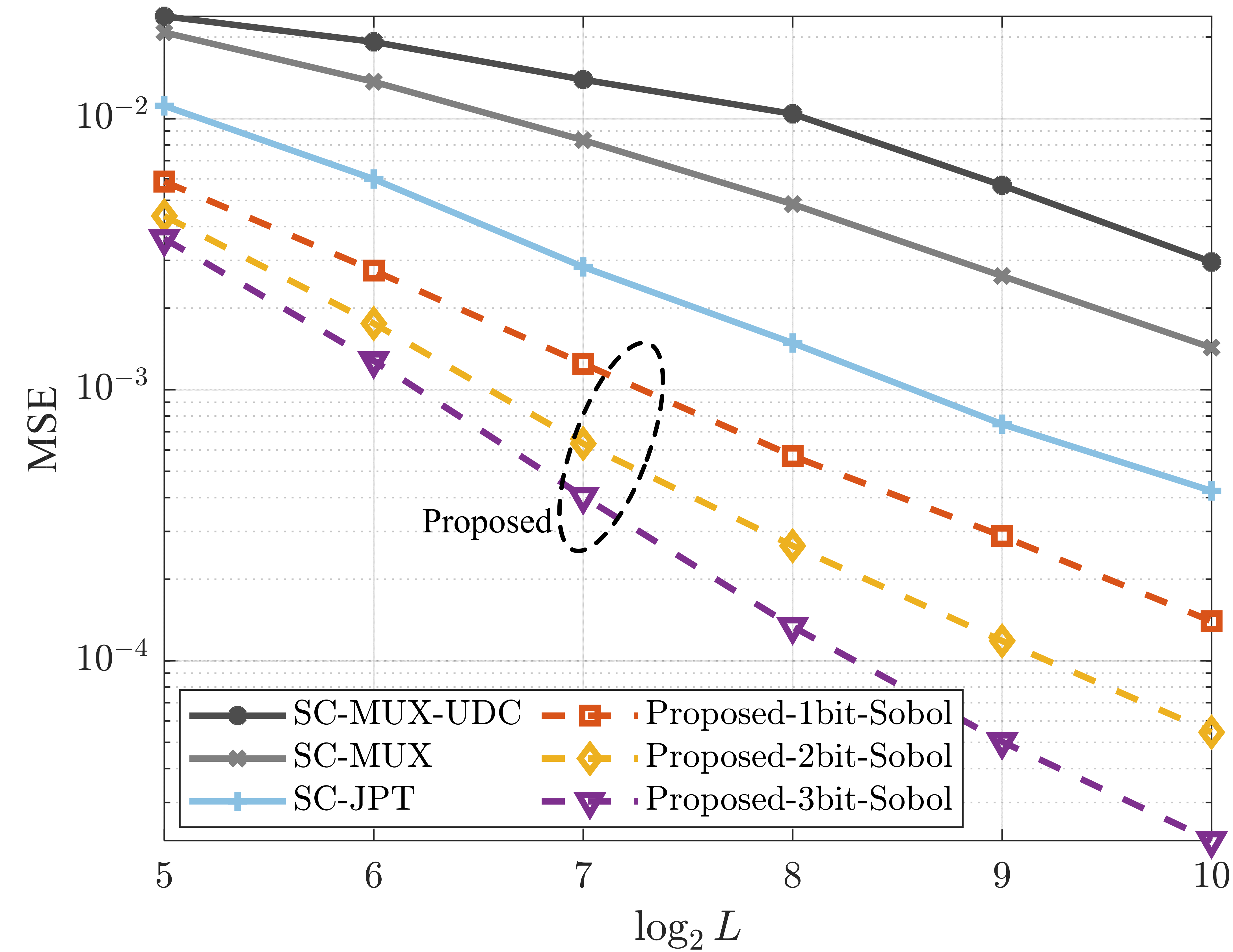
| Structure | Proposed | |||
| Technology | 65 nm | |||
| Bit Width | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Area () | 1336.32 | 1754.64 | 2156.04 | 2528.28 |
| Frequency (MHz) | 500 | 500 | 500 | 500 |
| MSE | ||||
| MSE Convergence Cycle | 128 | 80 | 64 | 64 |
| Throughput (MS/s) | 3.9 | 6.3 | 7.8 | 7.8 |
| TAR (MS/(s · )) | ||||
| Structure | Proposed | JPT [7] | MUX [17] | MUX-UDC [16] |
| Technology | 65 nm | 65 nm | 65 nm | 65 nm |
| Bit width | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Area () | 2156.04 | 1133.64 | 1002.24 | 743.40 |
| Frequency (MHz) | 500 | 500 | 500 | 1000 |
| MSE | ||||
| Cycle | 64 | 256 | 1024 | 2048 |
| Throughput (MS/s) | 7.8 | 2.0 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| TAR (MS/(s · )) | ||||
| TAR Ratio | 2.10 | 1.00 | 0.28 | 0.38 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Han, K.; Hu, J. A High-Accuracy Normalization Unit Using Multi-Bit Random Variables. Electronics 2025, 14, 4042. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14204042
Zhu Y, Han K, Hu J. A High-Accuracy Normalization Unit Using Multi-Bit Random Variables. Electronics. 2025; 14(20):4042. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14204042
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yubin, Kaining Han, and Jianhao Hu. 2025. "A High-Accuracy Normalization Unit Using Multi-Bit Random Variables" Electronics 14, no. 20: 4042. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14204042
APA StyleZhu, Y., Han, K., & Hu, J. (2025). A High-Accuracy Normalization Unit Using Multi-Bit Random Variables. Electronics, 14(20), 4042. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14204042