MSHEdit: Enhanced Text-Driven Image Editing via Advanced Diffusion Model Architecture
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- To enhance fidelity in style transfer, we introduce an advanced HOS-DEIS module. Improvements to the DEIS index integrator—specifically through refined higher-order coefficient calculations and integrals—enable high-order stable solutions in the diffusion model’s inverse process. The incorporation of a logarithmic space coefficient remapping mechanism and a dynamic error-compensated integrator further boosts sampling efficiency and image detail reproduction, significantly reducing ambiguous style expression and overfitting typically encountered during style transfer.
- (2)
- For fine-grained structural editing, we propose a novel cross-scale residual window cross-attention module (MS-WRBA). By leveraging Pre-LayerNorm, dual-path multi-layer normalization, windowed attention computation, and cross-directional feature interaction, our approach substantially decreases the computational complexity of attention matrices while improving the model’s multi-scale contextual understanding. This results in more accurate localization of edited regions and improved edge fusion, yielding seamless integration between edited areas and background.
- (3)
- By integrating (1) and (2), we introduce MSHEdit, a training-free image editing framework based on a pre-trained text-conditioned diffusion model. The framework synergistically integrates the High-Order Stable Diffusion Sampler (HOS-DEIS) and the multi-scale window residual bridging attention mechanism (MS-WRBA), enabling high-quality and semantically consistent image editing without the need for additional training or fine-tuning. By incorporating high-order exponential integration and dynamic error compensation, the framework significantly improves numerical stability and sampling accuracy during the reverse diffusion process. Furthermore, the MS-WRBA module leverages localized windowed attention modeling and cross-scale feature fusion to enhance the precision of editing region localization and the naturalness of boundary transitions.
2. Related Work
2.1. Three Improvement Directions of the Diffusion Model Under Image Editing
2.2. Inversion Process of the Diffusion Model
2.3. Attention Mechanism in Semantic Editing
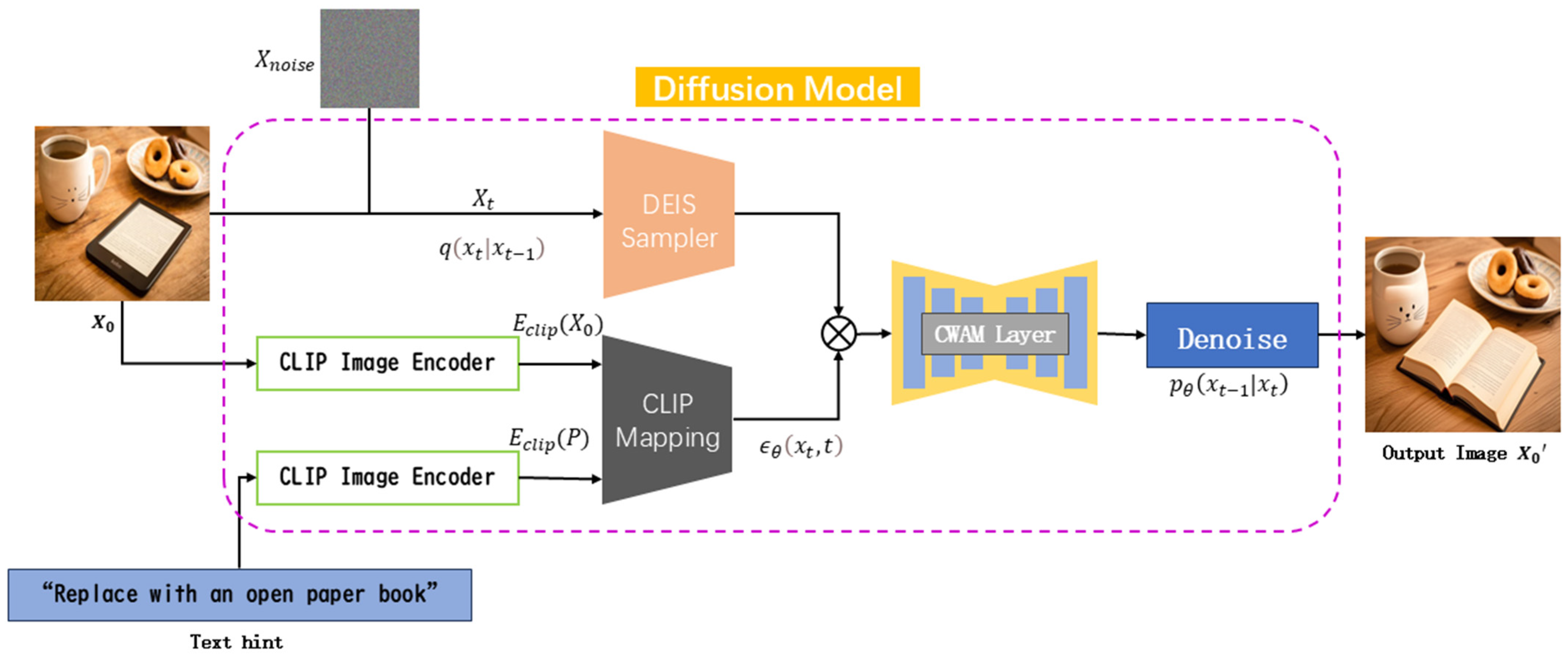
3. Methods
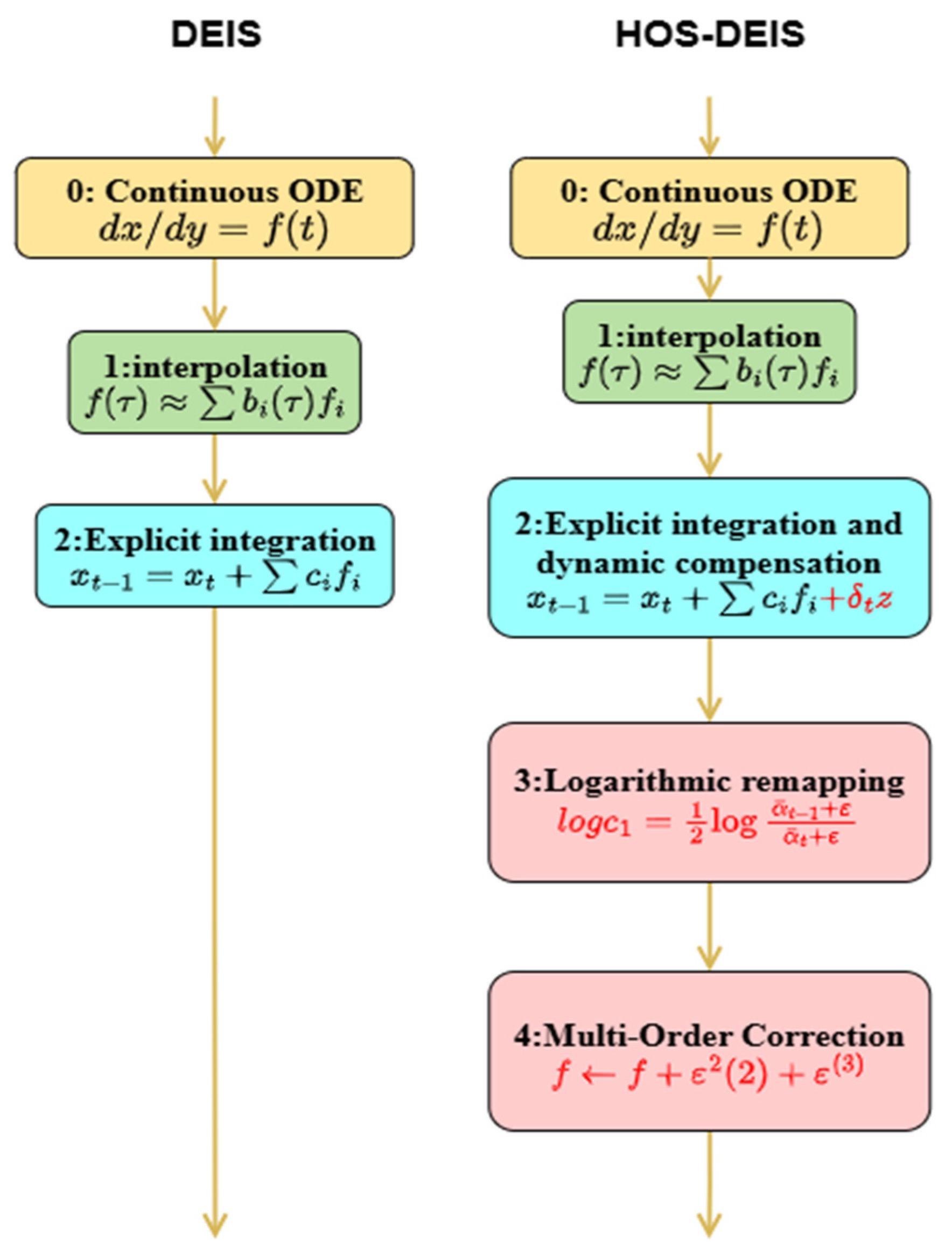
3.1. DEIS and HOS-DEIS Inversion Process
3.1.1. DEIS (Diffusion Exponential Integrator Sampler)
3.1.2. HOS-DEIS (High-Order Stable DEIS Solver)
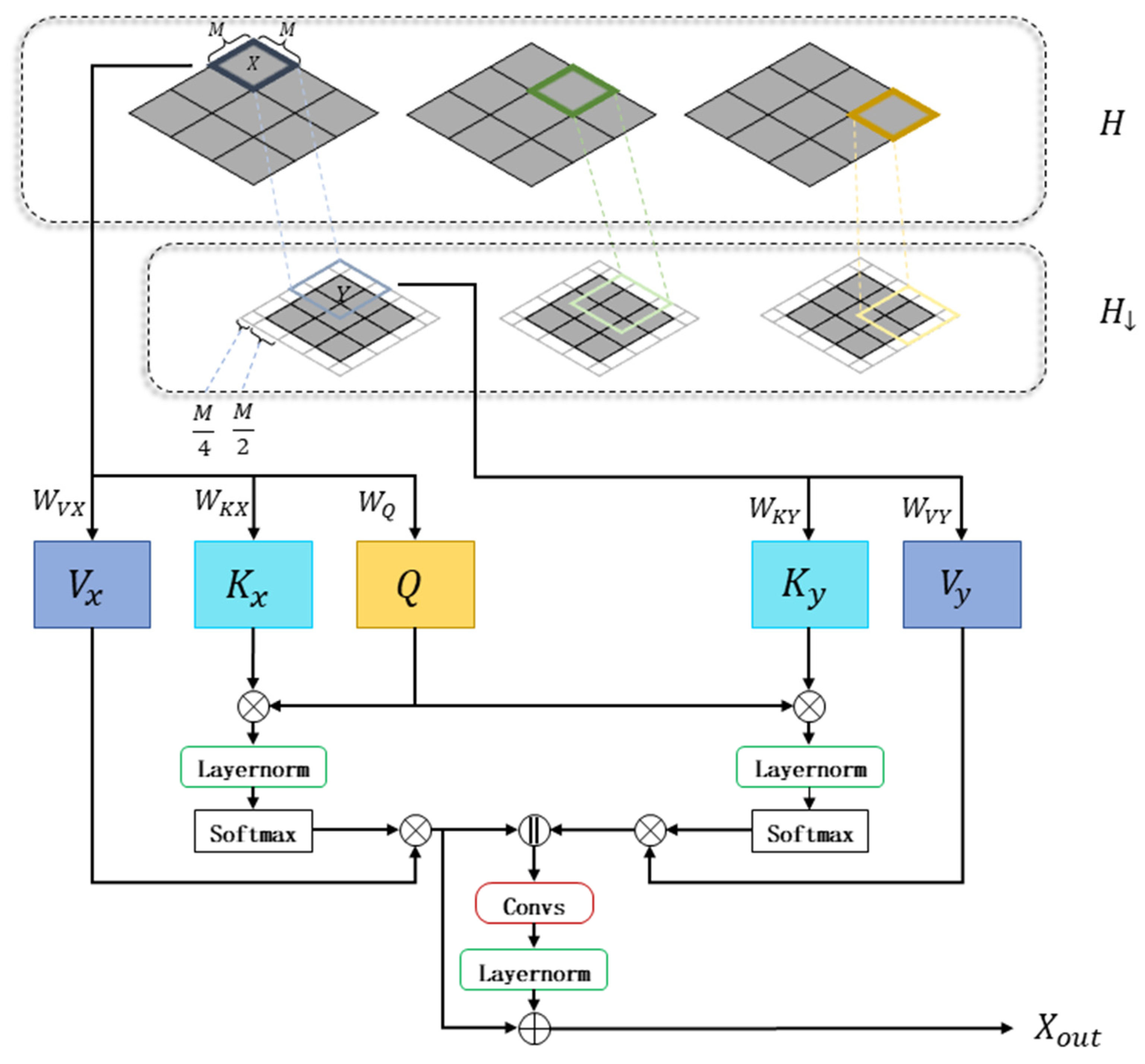
3.2. MS-WRBA (Multi-Scale Windowed Residual Bridge Attention)
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Settings
4.1.1. Task Description
4.1.2. Evaluation Indicators
4.1.3. Experimental Environment
4.1.4. Experimental Dataset
4.2. Qualitative Results
4.3. Quantitative Results
4.3.1. Performance Comparison
4.3.2. Discussion of Experimental Results
4.4. Ablation Experiment
4.5. Subjective Evaluation
4.6. Experimental Conclusions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Other Successful Results

Appendix A.2. Other Faild Results

References
- Sohl-Dickstein, J.; Weiss, E.; Maheswaranathan, N.; Ganguli, S. Deep unsupervised learning using nonequilibrium thermodynamics. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 7–9 July2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, J.; Jain, A.N.; Abbeel, P. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 33 (NeurIPS 2020), Online, 6–12 December 2020; Volume 33, pp. 6840–6851. [Google Scholar]
- Nichol, A.Q.; Dhariwal, P. Improved denoising diffusion probabilistic models. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, Online, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 8162–8171. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Meng, C.; Ermon, S. Denoising diffusion implicit models. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Vienna, Austria, 3–7 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Saharia, C.; Chan, W.; Saxena, S.; Li, L.; Whang, J.; Denton, E.; Ghasemipour, S.K.S.; Ayan, B.K.; Mahdavi, S.S.; Lopes, R.G.; et al. Photorealistic text-to-image diffusion models with deep language understanding. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.11487. [Google Scholar]
- Rombach, R.; Blattmann, A.; Lorenz, D.; Esser, P.; Ommer, B. High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 10684–10695. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, T.; Holynski, A.; Efros, A.A. InstructPix2Pix: Learning to Follow Image Editing Instructions. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.09800. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, N.; Li, Y.; Jampani, V.; Pritch, Y.; Rubinstein, M.; Aberman, K. Dreambooth: Fine tuning text-to-image diffusion models for subject-driven generation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 22500–22510. [Google Scholar]
- Kawar, B.; Zada, S.; Lang, O.; Tov, O.; Chang, H.; Dekel, T.; Mosseri, I.; Irani, M. Imagic: Text-based real image editing with diffusion models. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.09276. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Xie, J.; Lu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Tang, Y. In-context edit: Enabling instructional image editing with in-context generation in large scale diffusion transformer. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.20690. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, G.; Kwon, T.; Ye, J.C. DiffusionCLIP: Text-Guided Diffusion Models for Robust Image Manipulation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.02711. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Xing, W. Stylediffusion: Controllable disentangled style transfer via diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 7677–7689. [Google Scholar]
- Hertz, A.; Mokady, R.; Tenenbaum, J.; Aberman, K.; Pritch, Y.; Cohen-Or, D. Prompt-to-prompt image editing with cross attention control. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.01626. [Google Scholar]
- Parmar, G.; Singh, K.K.; Zhang, R. Zero-shot image-to-image translation. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH 2023 Conference Proceedings, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 6–10 August 2023; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ayoub, S.; Gulzar, Y.; Reegu, F.A.; Turaev, S. Generating image captions using bahdanau attention mechanism and transfer learning. Symmetry 2022, 14, 2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ul Qumar, S.M.; Azim, M.; Quadri, S.M.K.; Alkanan, M.; Mir, M.S.; Gulzar, Y. Deep neural architectures for Kashmiri-English machine translation. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 30014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünal, Z.; Gulzar, Y. Deep Learning Techniques for Image Clustering and Classification. In Modern Intelligent Techniques for Image Processing; IGI Global Scientific Publishing: Hershey, PA, USA, 2025; pp. 37–62. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y. Fast sampling of diffusion models with exponential integrator. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.13902. [Google Scholar]
- Mokady, R.; Hertz, A.; Aberman, K. Null-text inversion for editing real images using guided diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 6038–6047. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y.; Yan, M.; Lv, J.; Liu, J.; Xiong, W.; Zhang, H.; Cao, L.; Chen, S. Diffusion model-based image editing: A survey. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.17525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y. Personalized Image Generation with Deep Generative Models: A Decade Survey. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.13081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangkloy, P.; Lu, J.; Fang, C.; Yu, F.; Hays, J. Scribbler: Controlling deep image synthesis with sketch and color. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Avrahami, O.; Lischinski, D.; Fried, O. Blended diffusion for text-driven editing of natural images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 18208–18218. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Ren, Y.; Lin, Z.; Liu, L.; Ren, Y.; Lin, Z. Pseudo numerical methods for diffusion models on manifolds. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2202.09778. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Wang, C.; Cao, T.; Jia, K.; Huang, J. Towards understanding cross and self-attention in stable diffusion for text-guided image editing. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 7817–7826. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, S.; Chen, D.; Bao, J.; Wen, F.; Zhang, B.; Chen, D.; Yuan, L.; Guo, B. Vector quantized diffusion model for text-to-image synthesis. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 10696–10706. [Google Scholar]
- Ramesh, A.; Dhariwal, P.; Nichol, A.; Chu, C.; Chen, M. Hierarchical text-conditional image generation with clip latents. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.06125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.; Song, Y.; Song, J.; Wu, J.; Zhu, J.Y.; Ermon, S. Sdedit: Image synthesis and editing with stochastic differential equations. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.01073. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Ren, Z.; Pham, T. Instruction-Guided Editing Controls for Images and Multimedia: A Survey in LLM era. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.09955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esser, P.; Rombach, R.; Ommer, B. Taming transformers for high-resolution image synthesis. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 12873–12883. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Wang, Z. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lin, M.; Yan, S. Easyinv: Toward fast and better ddim inversion. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.05159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, W.; Zhu, X. INet: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 16591–16603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, H.R.; Sabir, M.F.; Bovik, A.C. A statistical evaluation of recent full reference image quality assessment algorithms. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2006, 15, 3440–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahdanau, D.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.0473. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Reit, J.U.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hessel, J.; Holtzman, A.; Forbes, M.; Le Bras, R.; Choi, Y. CLIPScore: A reference-free evaluation met ric for image captioning. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.08718. [Google Scholar]
- Tumanyan, N.; Bar-Tal, O.; Bagon, S.; Dekel, T. Splicing vit features for semantic appearance transfer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 10748–10757. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Hu, H.; Li, Y. Subject-driven text-to-image generation via apprenticeship learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 30286–30305. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Cui, Y.; Tang, H. Dreambench++: A human-aligned benchmark for personalized image generation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.16855. [Google Scholar]




| Time Period | Stage Category | Key Characteristics | Representative Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before 2020 | Early Era of Diffusion Models | Nonequilibrium thermodynamics-inspired generative theory proposed; image editing not yet addressed. | Deep Unsupervised Learning using Nonequilibrium Thermodynamics [1] |
| 2020–2021 | Development of Diffusion Probabilistic Models | DDPM and DDIM introduced with efficient sampling, laying the technical groundwork for later editing. | DDPM [2], DDIM [4] |
| 2022–present | Prosperous Era of Stable Diffusion-based Editing | Latent diffusion cuts computational cost; explosive growth of text-/instruction-/multi-condition editing frameworks; standardization underway. | Stable Diffusion [6], InstructPix2Pix [7], DreamBooth [8], MagicBrush, Imagic [9], ICEdit [10] |
| Order of Integration | Local Error | Global Error | Step Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 (DDIM) | 50–100 steps | ||
| Level 2 (DEIS) | 20–30 steps | ||
| Level 3 (HOS-DEIS) | 10–15 steps |
| Data Type | Number of Images | Number of Prompts | Proportion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Objects | 150 | 150 | 50% |
| Living subjects | 90 | 90 | 30% |
| Styles | 60 | 60 | 20% |
| Total | 300 | 300 | 100% |
| Method | Change the Color of the Clothes | Bicycle → Motorcycle | The Cat Wore Sunglasses | Image Style Replacement | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLIP Acc ↑ | BG LPIPS ↓ | Structure Dist ↓ | CLIP Acc ↑ | BG LPIPS ↓ | Structure Dist ↓ | CLIP Acc ↑ | Structure Dist ↓ | CLIP Acc ↑ | Structure Dist ↓ | |
| Prompt-to-Prompt | 18.4% | 0.342 | 0.095 | 66.0% | 0.327 | 0.085 | 34.0% | 0.082 | 30.8% | 0.079 |
| Pix2Pix | 92.2% | 0.261 | 0.082 | 77.2% | 0.273 | 0.087 | 69.6% | 0.081 | 52.4% | 0.082 |
| MagicQuill | 94.0% | 0.0667 | 0.057 | 87.9% | 0.269 | 0.069 | 71.2% | 0.028 | 74.3% | 0.063 |
| ICEdit | 96.0% | 0.045 | 0.048 | 93.5% | 0.243 | 0.065 | 74.9% | 0.027 | 77.5% | 0.054 |
| Ours (MSHEdit) | 86.4% | 0.044 | 0.044 | 92.8% | 0.241 | 0.063 | 74.6% | 0.025 | 77.6% | 0.052 |
| Method | Change the Color of the Clothes | Bicycle → Motorcycle | The Cat Wore Sunglasses | Image Style Replacement | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLIP Acc ↑ | BG LPIPS ↓ | Structure Dist ↓ | CLIP Acc ↑ | BG LPIPS ↓ | Structure Dist ↓ | CLIP Acc ↑ | Structure Dist ↓ | CLIP Acc ↑ | Structure Dist ↓ | |
| BL + DDIM | 85.3% | 0.183 | 0.123 | 72.0% | 0.279 | 0.087 | 37.6% | 0.085 | 32.4% | 0.082 |
| MS-WRBA + DDIM | 90.1% | 0.162 | 0.078 | 84.4% | 0.191 | 0.072 | 62.4% | 0.081 | 35.2% | 0.081 |
| BL + HOS-DEIS | 86.0% | 0.281 | 0.089 | 72.6% | 0.276 | 0.094 | 38.0% | 0.087 | 80.2% | 0.064 |
| HOS-DEIS + MS-WRBA | 86.4% | 0.044 | 0.044 | 92.8% | 0.241 | 0.063 | 74.6% | 0.025 | 77.6% | 0.052 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, M.; Yuan, J.; Xu, J.; Yan, W. MSHEdit: Enhanced Text-Driven Image Editing via Advanced Diffusion Model Architecture. Electronics 2025, 14, 3758. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14193758
Yang M, Yuan J, Xu J, Yan W. MSHEdit: Enhanced Text-Driven Image Editing via Advanced Diffusion Model Architecture. Electronics. 2025; 14(19):3758. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14193758
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Mingrui, Jian Yuan, Jiahui Xu, and Weishu Yan. 2025. "MSHEdit: Enhanced Text-Driven Image Editing via Advanced Diffusion Model Architecture" Electronics 14, no. 19: 3758. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14193758
APA StyleYang, M., Yuan, J., Xu, J., & Yan, W. (2025). MSHEdit: Enhanced Text-Driven Image Editing via Advanced Diffusion Model Architecture. Electronics, 14(19), 3758. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14193758






