Actuator Selection and Control of an Array of Electromagnetic Soft Actuators
Abstract
1. Introduction
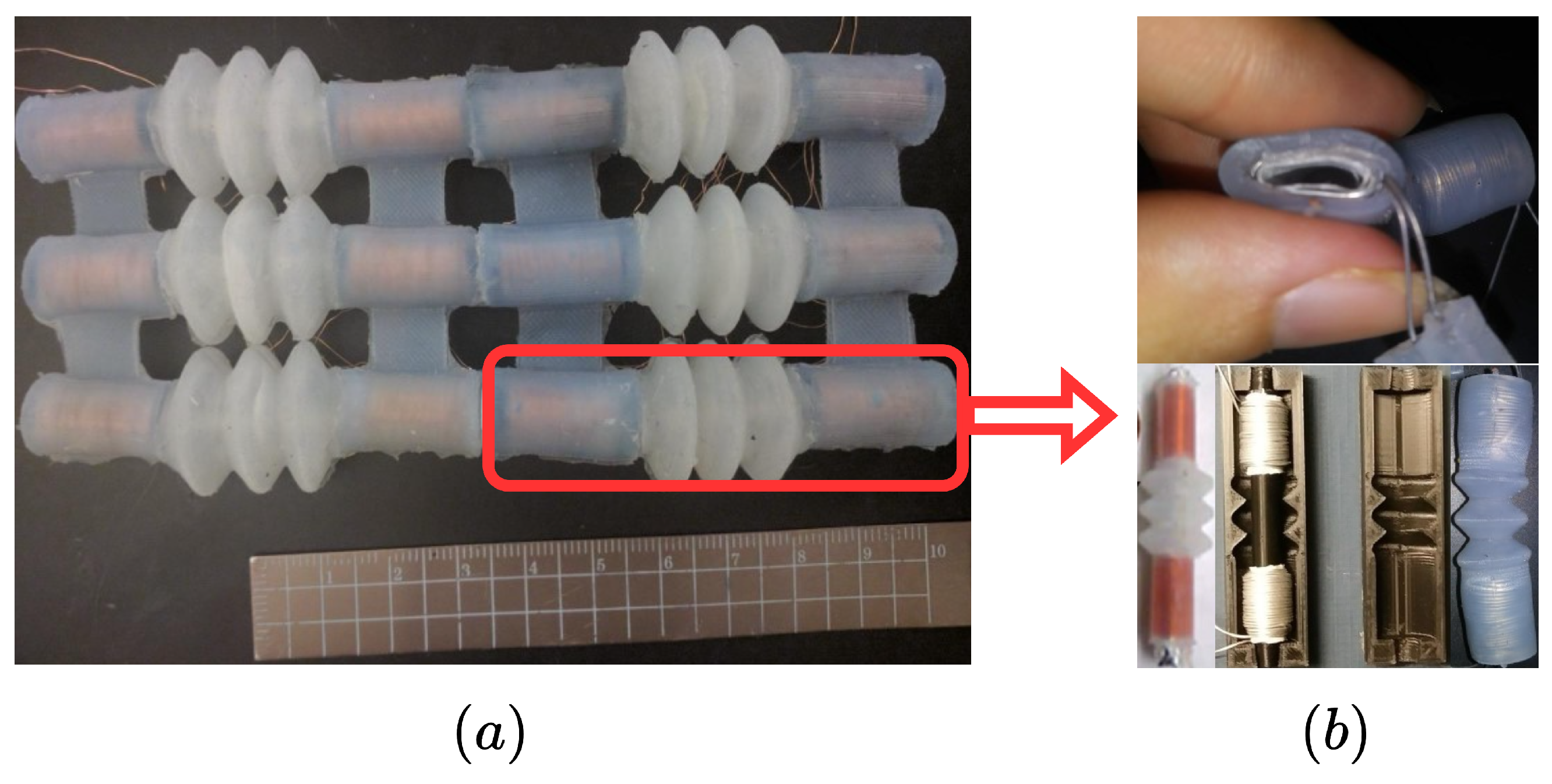
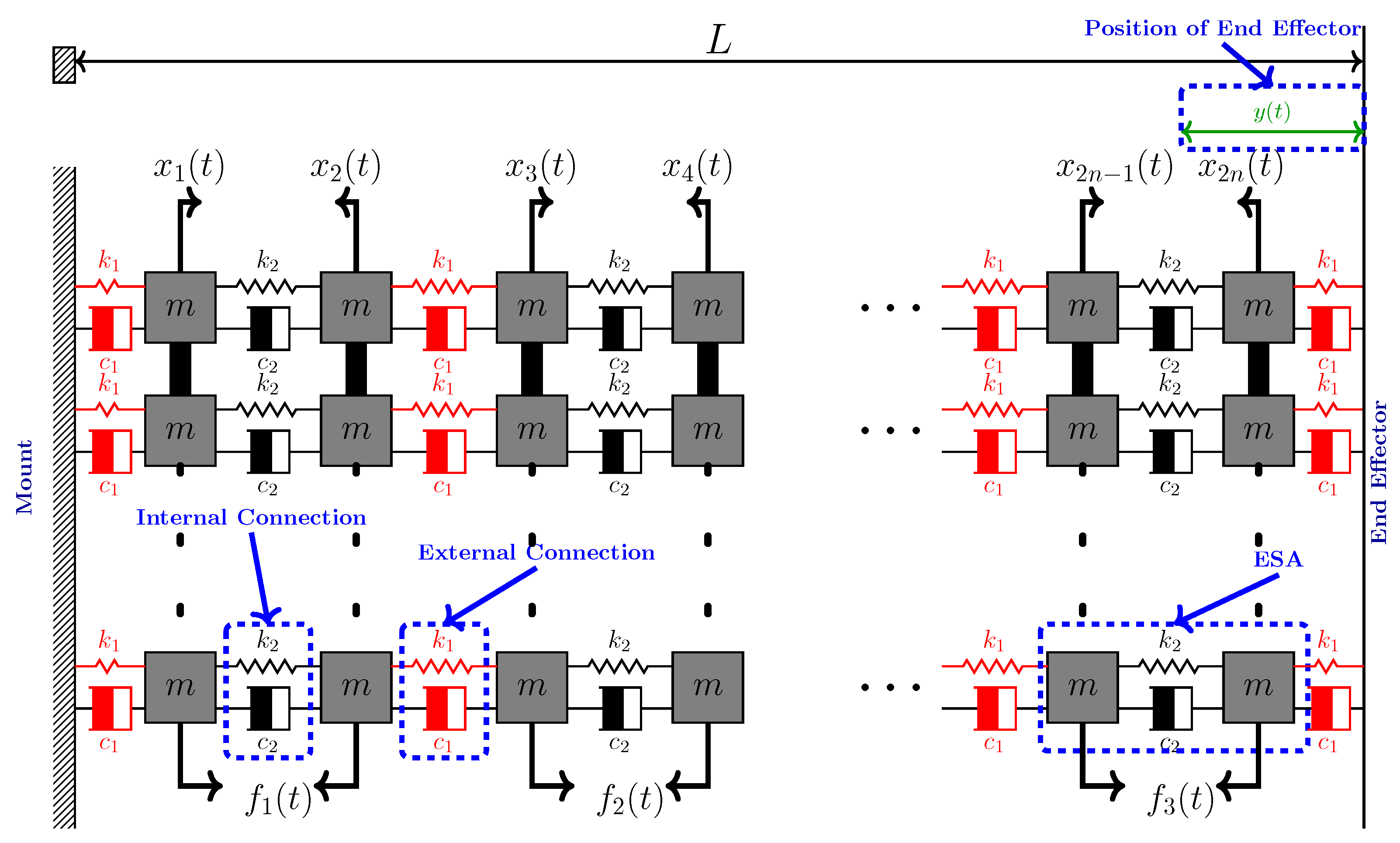
2. System Description and Problem Formulation
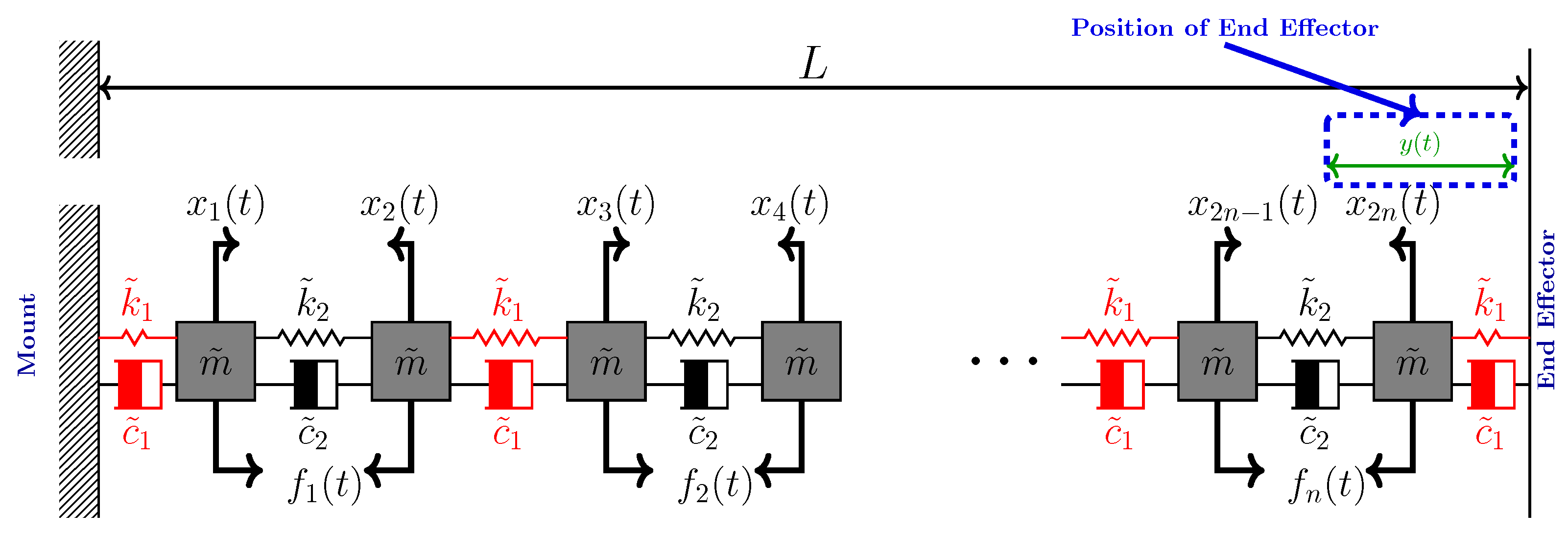
2.1. Mathematical Modeling and Control-Oriented Formulation
2.2. Problem Formulation
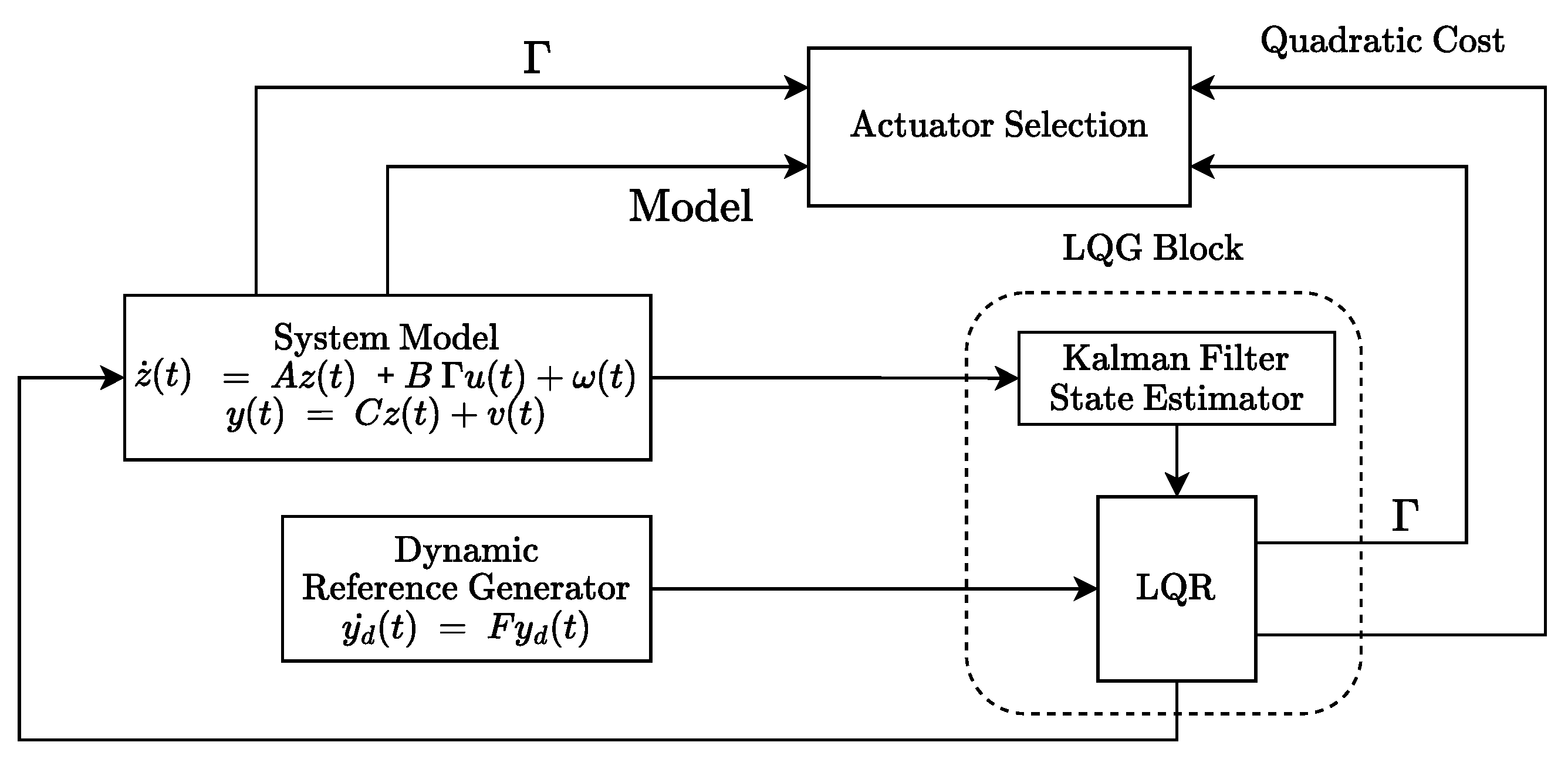
3. Main Results
3.1. Kalman-Bucy Filter Design
3.2. Reference Tracking Control Design
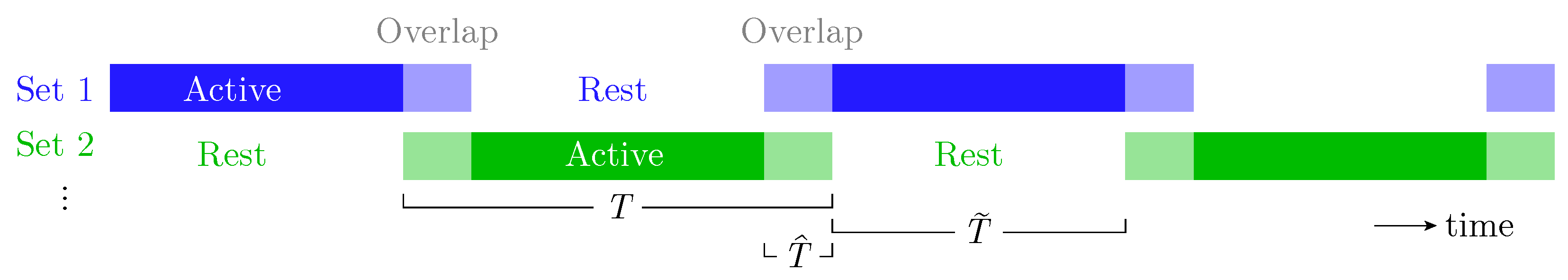
3.3. Actuator Selection Strategy
| Algorithm 1 Two-Phase Actuator Selection and Tracking |
| Inputs: System matrices ; weighting matrices ; noise covariance ; regularization parameter ; actuator set ; actuation interval T; resting time ; overlap time Outputs: Optimal actuator count , actuator selections , and control effort Phase 1: Determining the Optimal Number of Actuators. for each actuator count to do Initialize actuator mask vector while do for each actuator such that do Set trial vector , then set Compute Form augmented matrix (26) Solve ARE (27) to obtain matrix P Compute control gain matrix for the current actuator subset Evaluate cost using (25) end for Choose the actuator with the lowest cost Add actuator to the current set by setting end while Save the total cost and the corresponding actuator set end for Select optimal actuator count: Phase 2: Switching Strategy with Smooth Transitions Initialize rest timer vector ; each actuator starts fully rested, with representing the required rest time between activations if then Raise error: overlap duration too long for given actuation and rest times end if for each switching interval do Solve optimization problem in Equation (28) to determine actuator set Generate time-varying selection matrix that enables simultaneous activation of current and new actuator sets during the overlap interval Compute control effort using Update actuator usage: Reset rest timers: Increment rest timers: end for |
4. Simulation Setup and Results
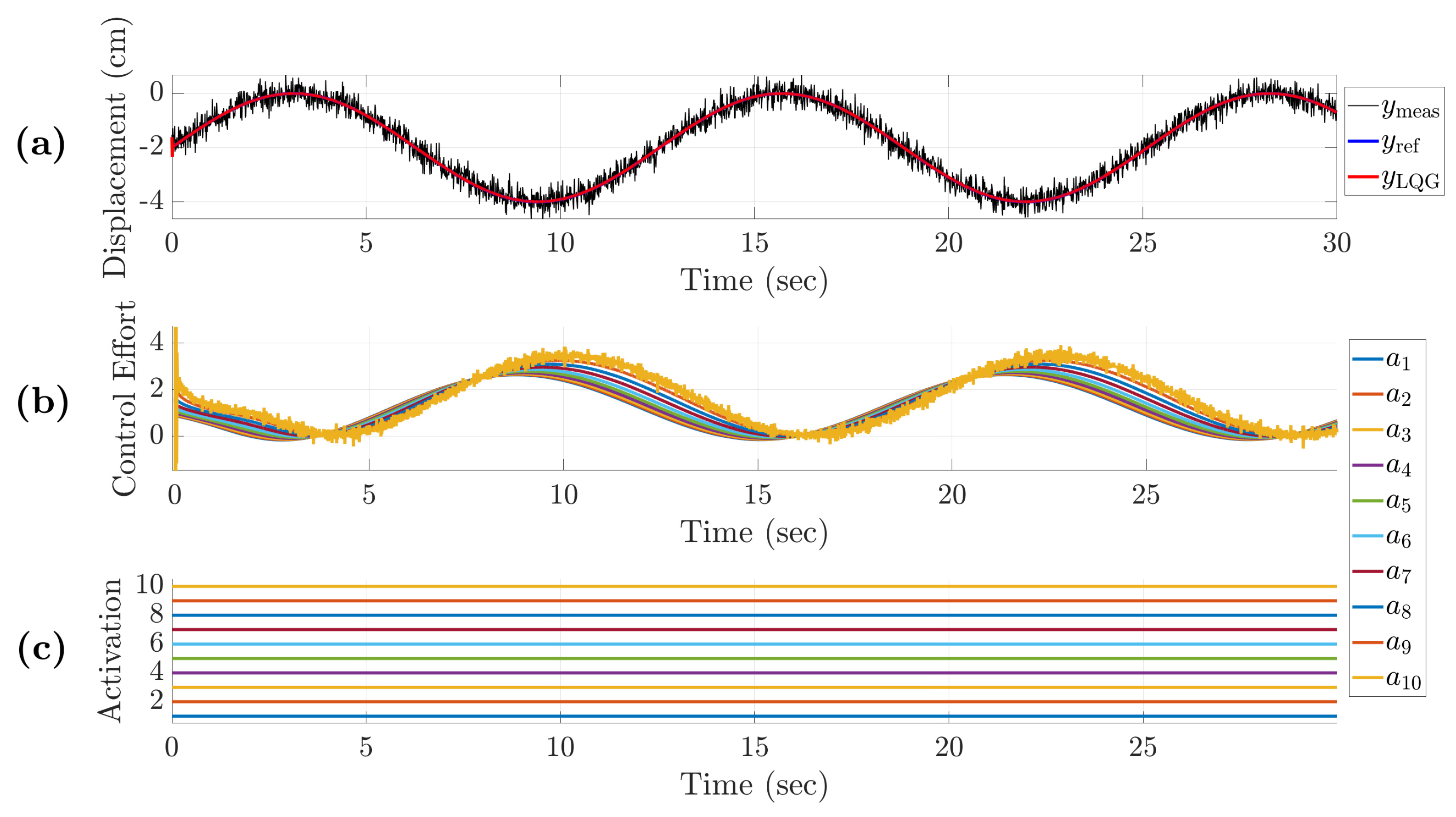
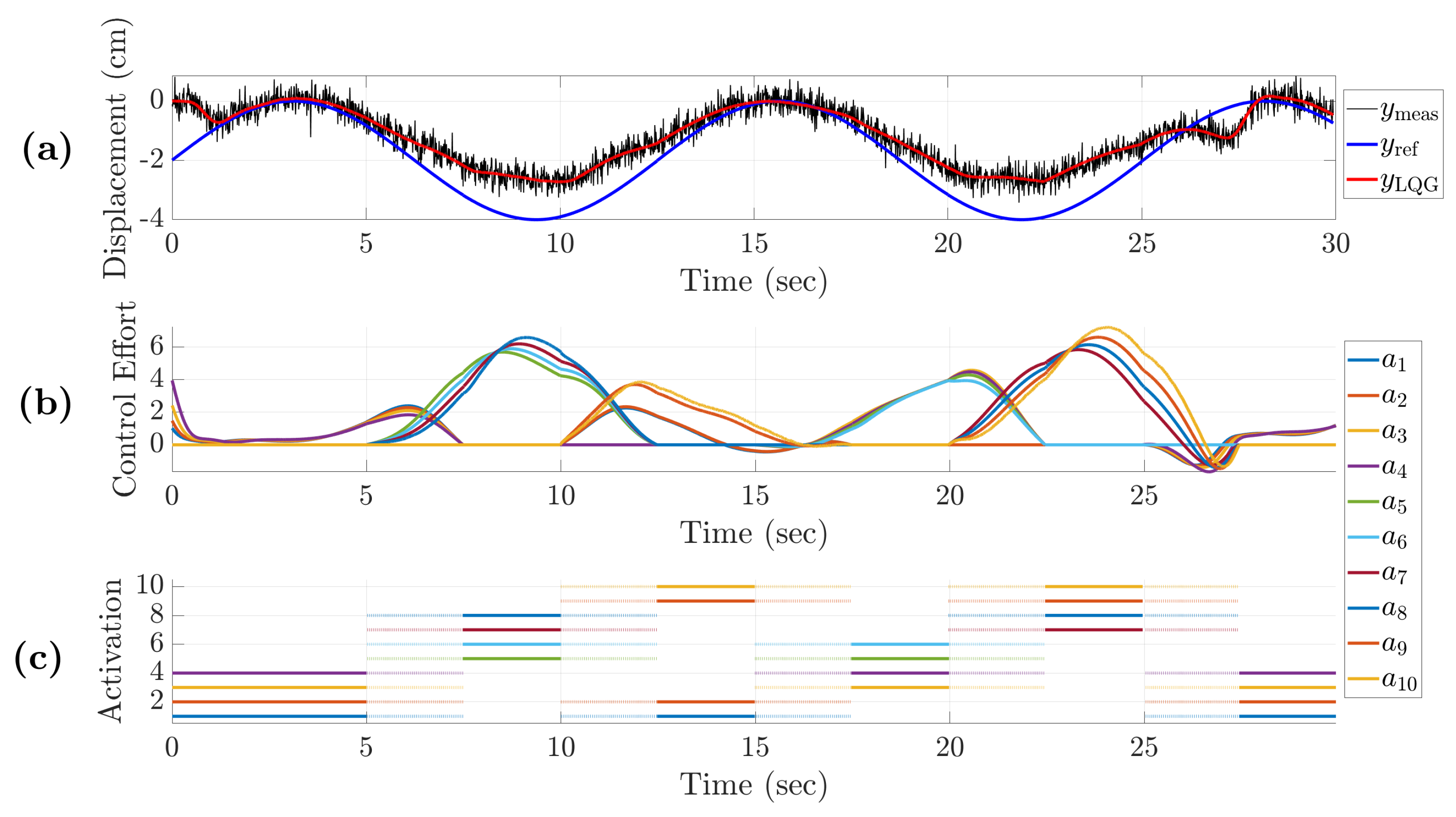
4.1. Scenario 1: Switching Configuration with and Without Overlap Interval
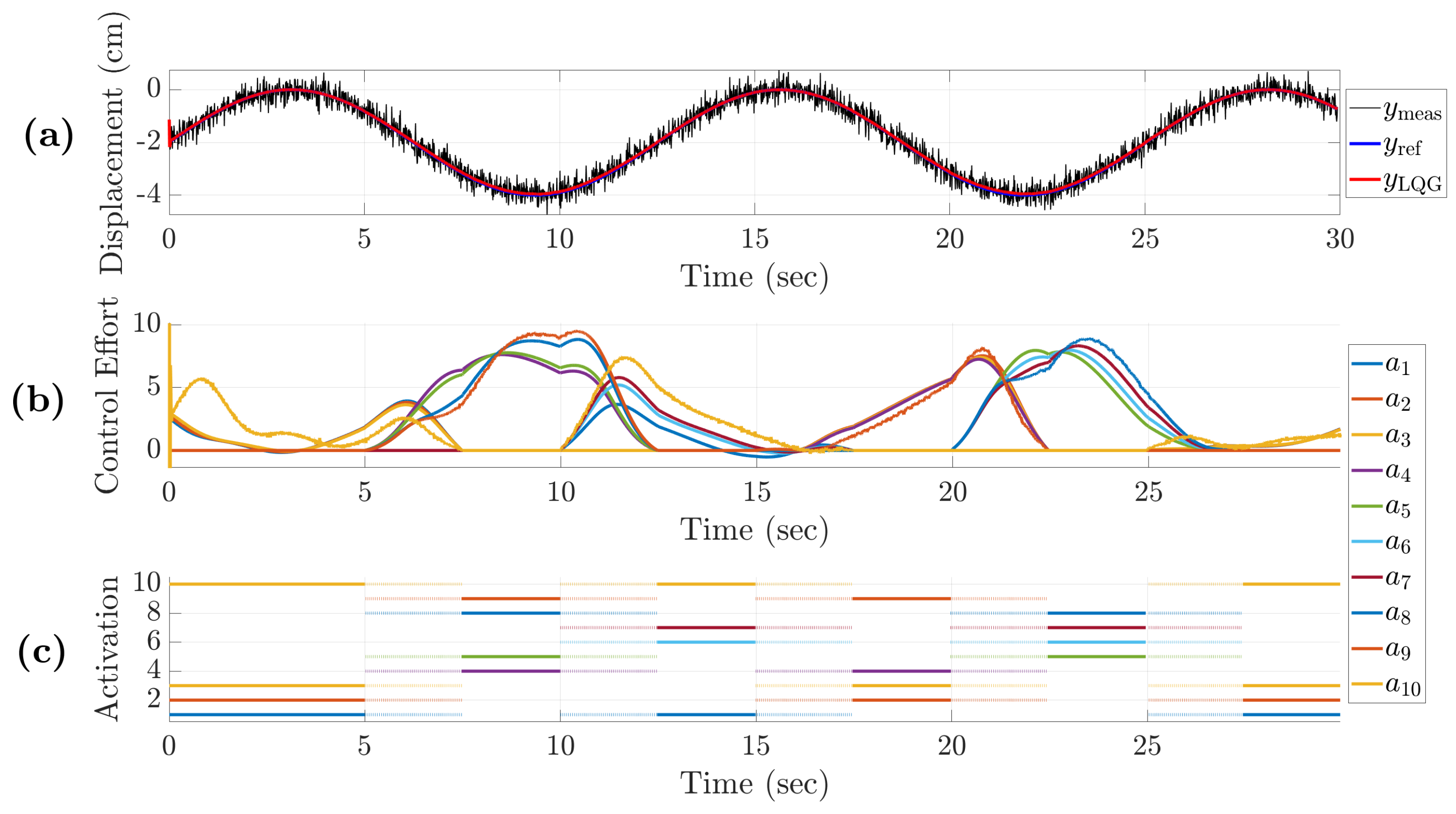
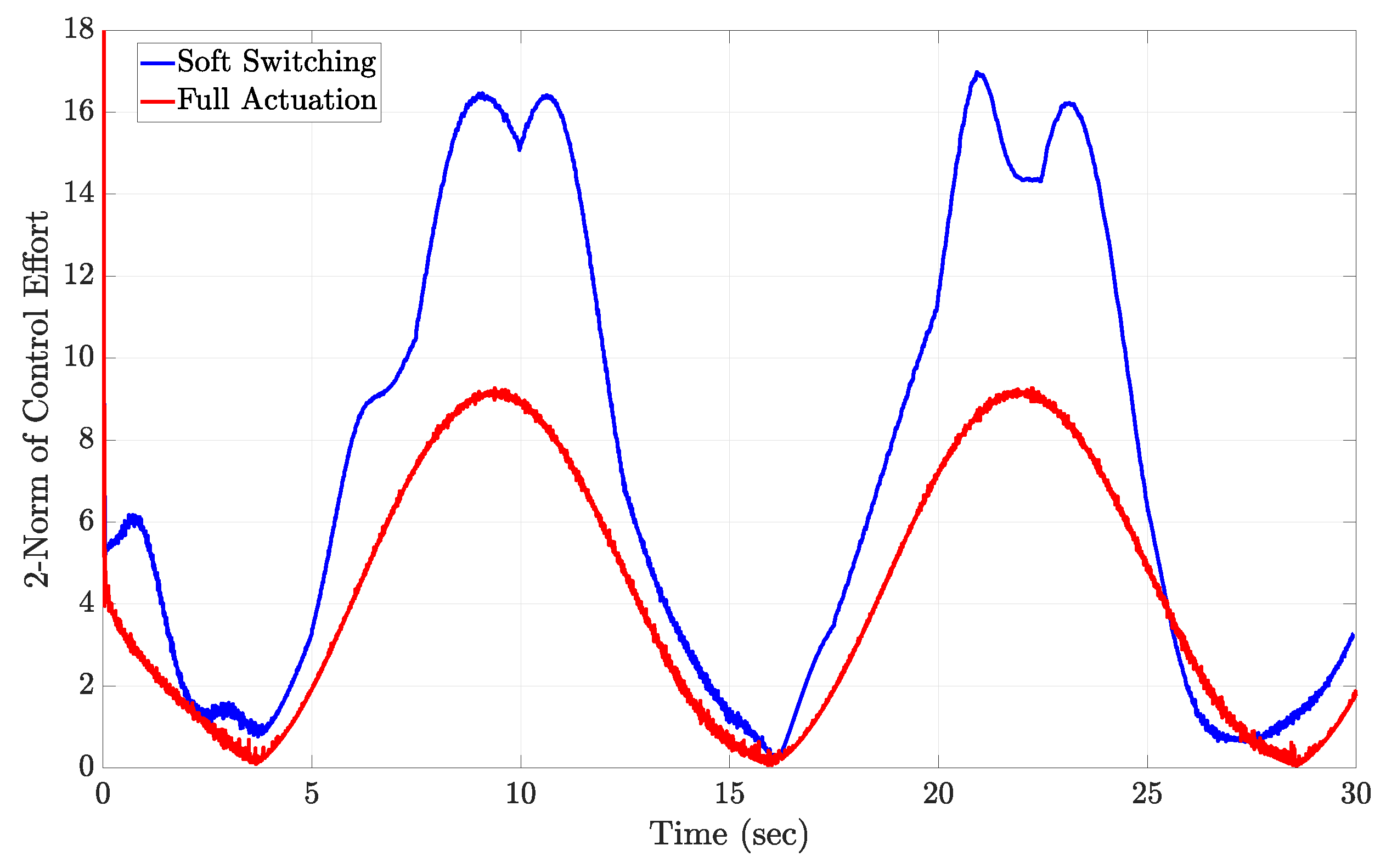
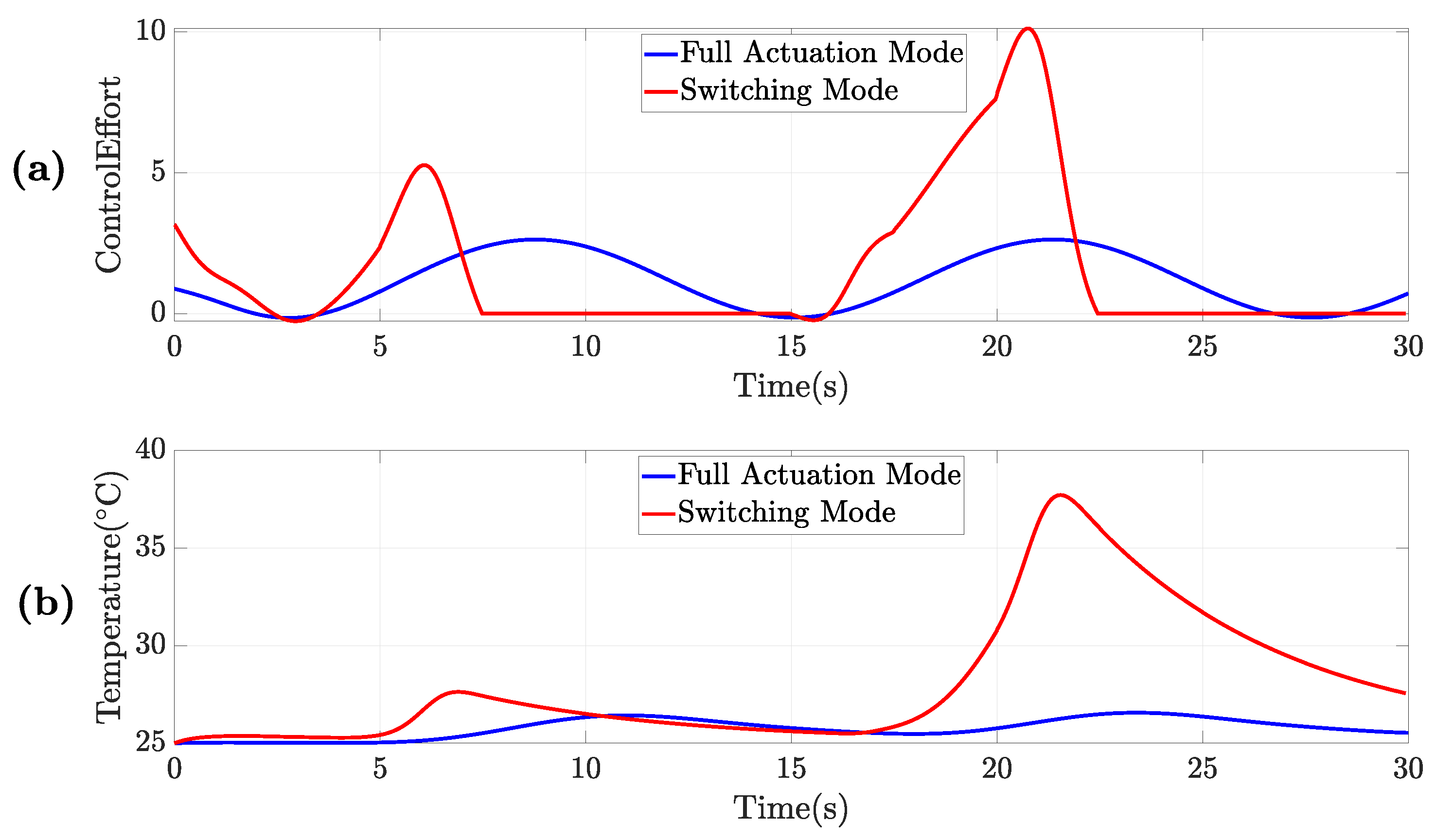
4.2. Scenario 2: Switching Strategy for Tracking and Thermal Management
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Appiah, C.; Arndt, C.; Siemsen, K.; Heitmann, A.; Staubitz, A.; Selhuber-Unkel, C. Living materials herald a new era in soft robotics. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1807747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, N.; Nugroho, S.; Taha, A.F.; Gatsis, N.; Gao, W.; Jafari, A. Dynamic actuator selection and robust state-feedback control of networked soft actuators. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 21–25 May 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 2857–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milana, E. Soft robotics for infrastructure protection. Front. Robot. 2022, 9, 1026891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- der Maur, P.A.; Djambazi, B.; Haberthür, Y.; Hörmann, P.; Kübler, A.; Lustenberger, M.; Sigrist, S.; Vigen, O.; Förster, J.; Achermann, F.; et al. Roboa: Construction and evaluation of a steerable vine robot for search and rescue applications. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 4th International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft), New Haven, CT, USA, 12–16 April 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, P.; Deshpande, A.D. Series elastic actuators for small-scale robotic applications. J. Mech. Robot. 2017, 9, 031016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Dong, E.; Xu, M.; Liu, C.; Alici, G.; Jie, Y. Soft and smart modular structures actuated by shape memory alloy (SMA) wires as tentacles of soft robots. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 085026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrikopoulos, G.; Nikolakopoulos, G.; Manesis, S. A survey on applications of pneumatic artificial muscles. In Proceedings of the 2011 19th Mediterranean Conference on Control & Automation (MED), Corfu, Greece, 20–23 June 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 1439–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosu, V.; Rodriguez-Guerrero, C.; Grosu, S.; Vanderborght, B.; Lefeber, D. Design of smart modular variable stiffness actuators for robotic-assistive devices. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2017, 22, 1777–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borboni, A.; Faglia, R.; Palpacelli, M. Shape memory actuator with slider and slot layout and single fan cooling. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE/ASME 10th International Conference on Mechatronic and Embedded Systems and Applications (MESA), Senigallia, Italy, 10–12 September 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Y.; Cheng, L.K.; Stommel, M.; Xu, W. Technical requirements and conceptualization of a soft pneumatic actuator inspired by human gastric motility. In Proceedings of the 2016 23rd International Conference on Mechatronics and Machine Vision in Practice (M2VIP), Nanjing, China, 28–30 November 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfaghari, A.; Aminian, E.; Saffari, H. Numerical investigation on entropy generation in the dropwise condensation inside an inclined pipe. Heat Transf. 2022, 51, 551–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfaghari, H.; Momeni, H.; Karimi, H. Multilevel Inverter Real-Time Simulation and Optimization Through Hybrid GA/PSO Algorithm. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.13817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.L.; Wood, R.J. Smart pneumatic artificial muscle actuator with embedded microfluidic sensing. In Proceedings of the SENSORS, 2013 IEEE, Baltimore, MD, USA, 3–6 November 2013; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, R.; Laschi, C. Soft robotics for human health. Device 2024, 2, 100432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, G.; Choi, Y.; Jeon, B.; Choi, I.; Song, S.; Park, Y.L. Soft Electromagnetic Artificial Muscles Using High-Density Liquid-Metal Solenoid Coils and Bistable Stretchable Magnetic Housings. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 34, 2302895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfaghari, H.; Ebrahimi, N.; Ji, Y.; Pitkow, X.; Davoodi, M. Integrated Analytical Modeling and Numerical Simulation Framework for Design Optimization of Electromagnetic Soft Actuators. Actuators 2025, 14, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, N.; Schimpf, P.; Jafari, A. Design optimization of a solenoid-based electromagnetic soft actuator with permanent magnet core. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 284, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.W.; Lee, S.Y. Design of a solenoid actuator with a magnetic plunger for miniaturized segment robots. Appl. Sci. 2015, 5, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyatt, P.; Wingate, D.; Killpack, M.D. Model-based control of soft actuators using learned non-linear discrete-time models. Front. Robot. 2019, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rus, D.; Tolley, M.T. Design, fabrication and control of soft robots. Nature 2015, 521, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruder, D.; Gillespie, B.; Remy, C.D.; Vasudevan, R. Modeling and control of soft robots using the koopman operator and model predictive control. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.02827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chortos, A. Control strategies for soft robot systems. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2022, 4, 2100165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, A.F.; Gatsis, N.; Summers, T.; Nugroho, S.A. Time-varying sensor and actuator selection for uncertain cyber-physical systems. IEEE Trans. Control Netw. Syst. 2018, 6, 750–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, A.; Mohammadi, H.; Dhingra, N.K.; Georgiou, T.T.; Jovanović, M.R. Proximal algorithms for large-scale statistical modeling and sensor/actuator selection. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2019, 65, 3441–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modares, H.; Lewis, F.L. Linear quadratic tracking control of partially-unknown continuous-time systems using reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2014, 59, 3051–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milam, M.B. Real-Time Optimal Trajectory Generation for Constrained Dynamical Systems; California Institute of Technology: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2003; Available online: https://ezproxy.memphis.edu:3443/login?url=https://www.proquest.com/dissertations-theses/real-time-optimal-trajectory-generation/docview/305343031/se-2?accountid=14582 (accessed on 10 September 2025).
- Lavretsky, E.; Wise, K.A. Output Feedback Control. In Robust and Adaptive Control: With Aerospace Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 161–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavretsky, E. Adaptive output feedback design using asymptotic properties of LQG/LTR controllers. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2011, 57, 1587–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athans, M. The role and use of the stochastic linear-quadratic-Gaussian problem in control system design. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1971, 16, 529–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George Thuruthel, T.; Renda, F.; Iida, F. First-order dynamic modeling and control of soft robots. Front. Robot. AI 2020, 7, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zolfaghari, H.; Karimi, H.; Ramezani, A.; Davoodi, M. Minimizing voltage ripple of a DC microgrid via a particle-swarm-optimization-based fuzzy controller. Algorithms 2024, 17, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, T.H.; Lygeros, J. Optimal sensor and actuator placement in complex dynamical networks. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2014, 47, 3784–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, T. Actuator placement in networks using optimal control performance metrics. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 55th Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 12–14 December 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 2703–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, N.; Guda, T.; Alamaniotis, M.; Miserlis, D.; Jafari, A. Design optimization of a novel networked electromagnetic soft actuators system based on branch and bound algorithm. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 119324–119335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, F.L.; Xie, L.; Popa, D. Optimal and Robust Estimation: With an Introduction to Stochastic Control Theory; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkka, S. On unscented Kalman filtering for state estimation of continuous-time nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2007, 52, 1631–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, A.N.; Del Moral, P. On the mathematical theory of ensemble (linear-Gaussian) Kalman–Bucy filtering. Math. Control Signals Syst. 2023, 35, 835–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hespanha, J.P. Lecture notes on lqr/lqg controller design. Knowl. Creat. Diffus. Util. 2005. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/6945404/Undergraduate_Lecture_Notes_on_LQG_LQR_controller_design (accessed on 10 September 2025).
- Smooth-On Inc. Ecoflex Series Technical Bulletin, 2017. Available online: https://www.smooth-on.com/tb/files/ECOFLEX_SERIES_TB.pdf (accessed on 14 September 2017).



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zolfaghari, H.; Ebrahimi, N.; Pitkow, X.; Davoodi, M. Actuator Selection and Control of an Array of Electromagnetic Soft Actuators. Electronics 2025, 14, 3682. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14183682
Zolfaghari H, Ebrahimi N, Pitkow X, Davoodi M. Actuator Selection and Control of an Array of Electromagnetic Soft Actuators. Electronics. 2025; 14(18):3682. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14183682
Chicago/Turabian StyleZolfaghari, Hussein, Nafiseh Ebrahimi, Xaq Pitkow, and Mohammadreza Davoodi. 2025. "Actuator Selection and Control of an Array of Electromagnetic Soft Actuators" Electronics 14, no. 18: 3682. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14183682
APA StyleZolfaghari, H., Ebrahimi, N., Pitkow, X., & Davoodi, M. (2025). Actuator Selection and Control of an Array of Electromagnetic Soft Actuators. Electronics, 14(18), 3682. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14183682






