LF-Net: A Lightweight Architecture for State-of-Charge Estimation of Lithium-Ion Batteries by Decomposing Global Trend and Local Fluctuations
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Motivation
1.2. Literature Review and Research Gaps
2. Proposed Method
2.1. Linear Module
2.2. Fluctuation Module
2.3. Differential Feature Extraction Module
2.4. Local Enhancer Module
2.5. Fusion and Output
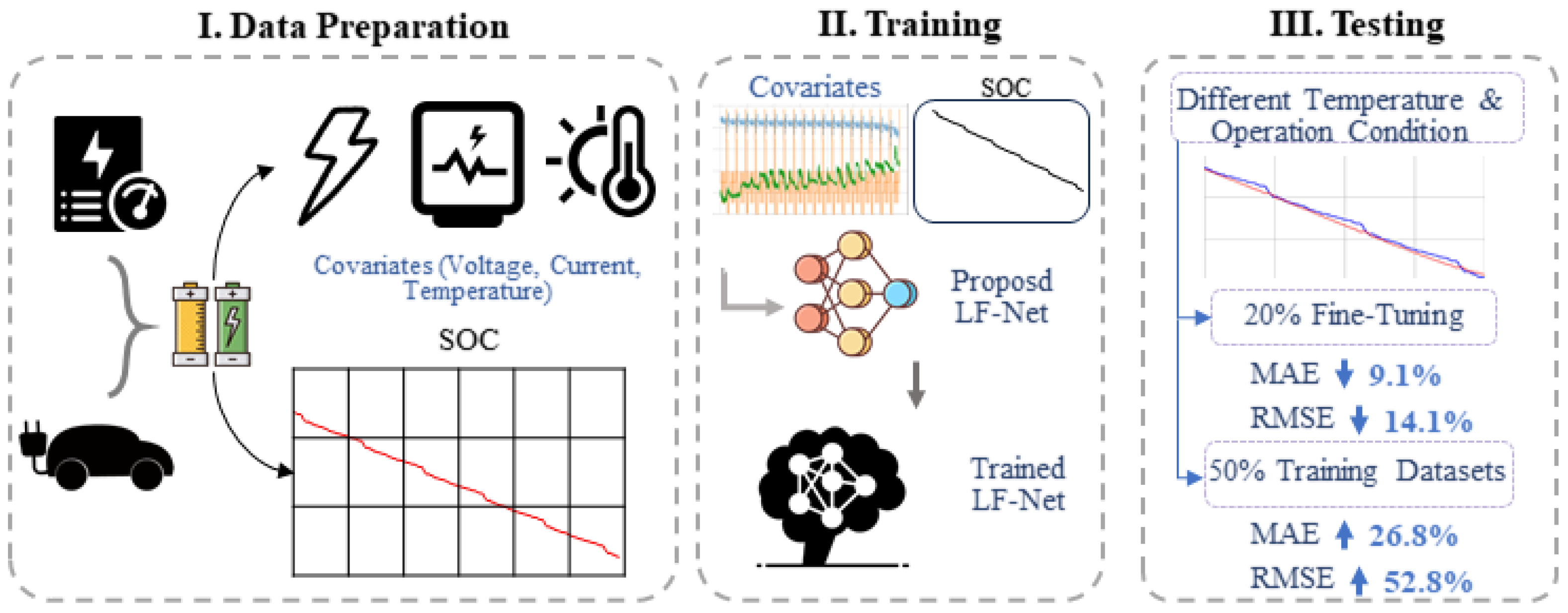
3. Experimental Approval
3.1. Datasets
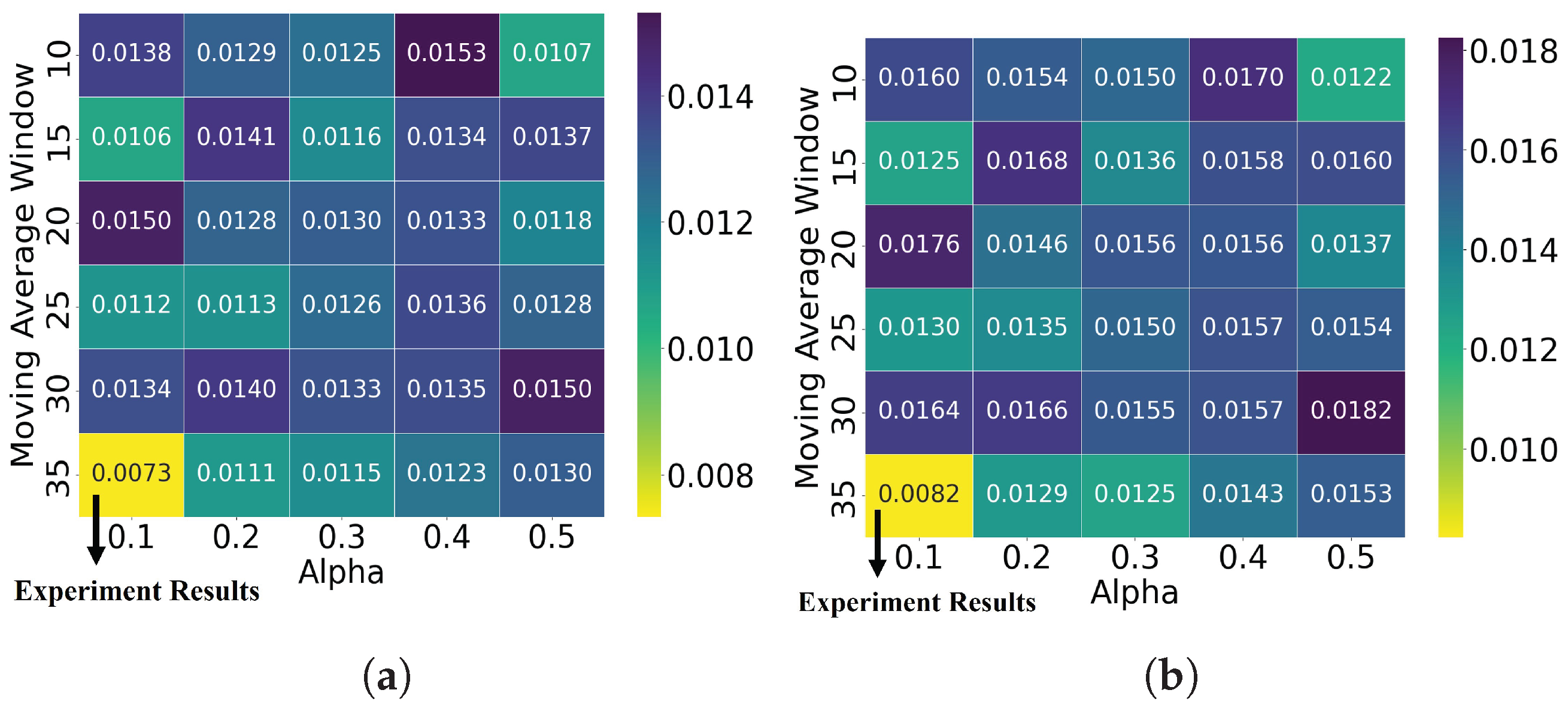
3.2. Experimental Approval Settings
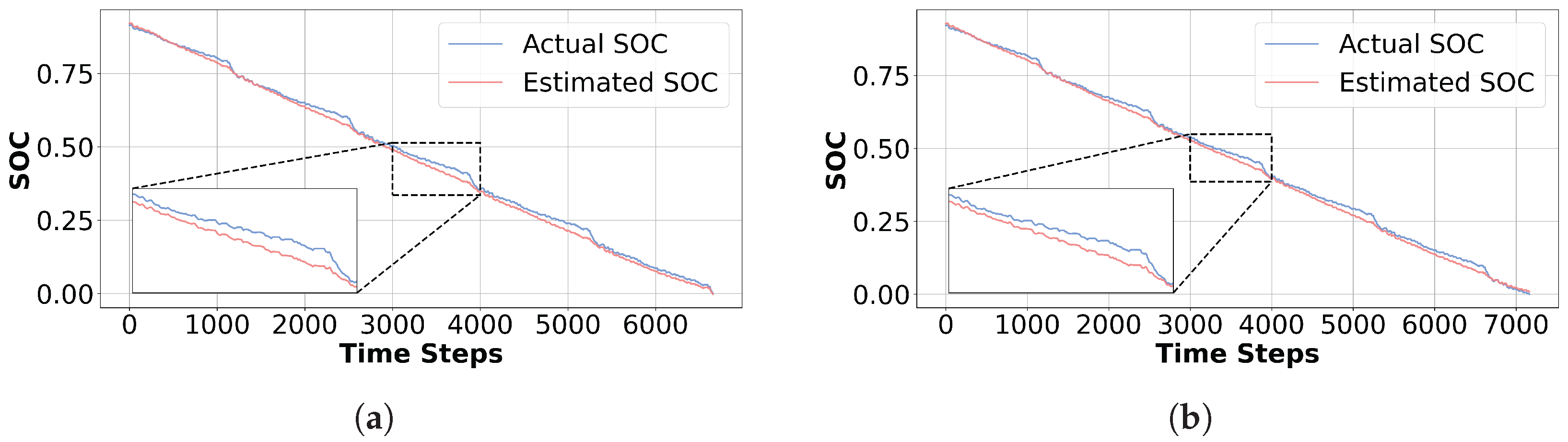
3.3. Experimental Approval Results
3.3.1. Ablation Experiments
3.3.2. Verification Experiments
4. Discussion
4.1. Results of This Study
4.2. Practical and General Deployment Across Chemistries and Physical Implications
4.3. Structural Disbalancing in Parallel-Connected Cells
4.4. Local Fluctuation Capture
- (i)
- Derivative-aware auxiliary loss, which encourages matching the rate of change shown in Equation (19):
- (ii)
- Context-conditioned fusion weighting (Equation (3)), which increases the contribution of fluctuation-sensitive pathways under rapid dynamics, e.g., with .
- (iii)
- Increasing the local window l and reinforcing a small-kernel convolutional branch to focus on short-horizon patterns.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SOC | State of Charge |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| RMSE | Root-Mean-Square Error |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| GRU | Gated Recurrent Unit |
| BMS | Battery Management System |
| EV | Electric Vehicle |
| LiFePO4 | Lithium Iron Phosphate |
| FUDS | Full Urban Driving Schedule |
| DST | Dynamic Stress Test |
| US06 | Supplemental Federal Test Procedure |
References
- Saw, L.H.; Ye, Y.; Tay, A.A. Integration issues of lithium-ion battery into electric vehicles battery pack. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 113, 1032–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.G.; Liu, T.; Wang, C.Y. Thermally modulated lithium iron phosphate batteries for mass-market electric vehicles. Nat. Energy 2021, 6, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.; Neiber, R.R.; Park, J.; Ali Soomro, R.; Greene, G.W.; Ali Mazari, S.; Young Seo, H.; Hong Lee, J.; Shon, M.; Wook Chang, D.; et al. Recent progress in sustainable recycling of LiFePO4-type lithium-ion batteries: Strategies for highly selective lithium recovery. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 133993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannan, M.; Lipu, M.; Hussain, A.; Mohamed, A. A review of lithium-ion battery state of charge estimation and management system in electric vehicle applications: Challenges and recommendations. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 78, 834–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manas, M.; Yadav, R.; Dubey, R.K. Designing a battery Management system for electric vehicles: A congregated approach. J. Energy Storage 2023, 74, 109439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, G. Simulation and experiment of thermal energy management with phase change material for ageing LiFePO4 power battery. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 3408–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Li, C.; Schneider, E.W.; Harris, S.J. Chemistry, Impedance, and Morphology Evolution in Solid Electrolyte Interphase Films during Formation in Lithium Ion Batteries. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Tran, T.N.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, G. Electrolyte decomposition and solid electrolyte interphase revealed by mass spectrometry. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 399, 139362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Chen, C.; Shen, W.; Sun, F.; Xiong, R. Deep Learning Framework for Lithium-ion Battery State of Charge Estimation: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives. Energy Storage Mater. 2023, 61, 102883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Guan, T.; Cheng, X.; Zuo, P.; Gao, Y.; Du, C.; Yin, G. Accelerated aging and degradation mechanism of LiFePO4/graphite batteries cycled at high discharge rates. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 25695–25703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snihir, I.; Rey, W.; Verbitskiy, E.; Belfadhel-Ayeb, A.; Notten, P.H. Battery open-circuit voltage estimation by a method of statistical analysis. J. Power Sources 2006, 159, 1484–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhang, C. An extended Kalman filter design for state-of-charge estimation based on variational approach. Batteries 2023, 9, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Lu, J.; Amine, K.; Pan, F. Depolarization effect to enhance the performance of lithium ions batteries. Nano Energy 2017, 33, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhao, C.Z.; Huang, J.Q.; Zhang, Q. The timescale identification decoupling complicated kinetic processes in lithium batteries. Joule 2022, 6, 1172–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, R.; Badr, M.M.; Shalash, O.; Othman, A.A.; Hamdan, E.; Hamad, M.S.; Abdel-Khalik, A.S.; Ahmed, S.; Imam, S.M. A data-driven digital twin of electric vehicle li-ion battery state-of-charge estimation enabled by driving behavior application programming interfaces. Batteries 2023, 9, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ancary, M.; Lassioui, A.; El Fadil, H.; El Asri, Y.; Hasni, A.; Yahya, A.; Chiheb, M. Hybrid Efficient Fast Charging Strategy for WPT Systems: Memetic-Optimized Control with Pulsed/Multi-Stage Current Modes and Neural Network SOC Estimation. World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long Short-Term Memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, M.; Wang, D.; Qiu, J. A GRU-RNN based momentum optimized algorithm for SOC estimation. J. Power Sources 2020, 459, 228051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Tang, W.; Li, C.; Mak, S.L.; Li, C.; Lee, C. Joint state of charge (SOC) and state of health (SOH) estimation for lithium-ion batteries packs of electric vehicles based on NSSR-LSTM neural network. Energies 2023, 16, 5313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Fallah, S.; Kharbach, J.; Vanagas, J.; Vilkelytė, Ž.; Tolvaišienė, S.; Gudžius, S.; Kalvaitis, A.; Lehmam, O.; Masrour, R.; Hammouch, Z.; et al. Advanced state of charge estimation using deep neural network, gated recurrent unit, and long short-term memory models for lithium-Ion batteries under aging and temperature conditions. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6648. [Google Scholar]
- Sutanto, E.; Astawa, P.E.; Fahmi, F.; Hamid, M.I.; Yazid, M.; Shalannanda, W.; Aziz, M. Lithium-ion battery state-of-charge estimation from the voltage discharge profile using gradient vector and support vector machine. Energies 2023, 16, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.u.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is All you Need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Guyon, I., Luxburg, U.V., Bengio, S., Wallach, H., Fergus, R., Vishwanathan, S., Garnett, R., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, S.; Peng, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Xiong, H.; Zhang, W. Informer: Beyond Efficient Transformer for Long Sequence Time-Series Forecasting. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.07436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Hu, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wang, J.; Long, M. TimesNet: Temporal 2D-Variation Modeling for General Time Series Analysis. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2210.02186. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, W.; Xie, X.; Yi, Y.; Qi, C.; Huang, Y.; Feng, M.; Zheng, T. The LiFePO4 battery lifespan SoC estimation using Ham-Informer and internal pressure. J. Energy Storage 2024, 88, 111474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Long, M. Autoformer: Decomposition Transformers with Auto-Correlation for Long-Term Series Forecasting. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.13008. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Yao, L.; Chen, L.; Cai, D.; He, X.; Liu, W. CrossFormer: A Versatile Vision Transformer Based on Cross-scale Attention. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.00154. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Ma, Z.; Wen, Q.; Wang, X.; Sun, L.; Jin, R. FEDformer: Frequency Enhanced Decomposed Transformer for Long-term Series Forecasting. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.12740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitaev, N.; Kaiser, L.; Levskaya, A. Reformer: The Efficient Transformer. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2001.04451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, B.; Ark, S.O.; Loeff, N.; Pfister, T. Temporal Fusion Transformers for interpretable multi-horizon time series forecasting. Int. J. Forecast. 2021, 37, 1748–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, A.; Chen, M.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Q. Are Transformers effective for time series forecasting? Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2023, 37, 11121–11128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battery Data|Center for Advanced Life Cycle Engineering. 2025. Available online: https://calce.umd.edu/ (accessed on 30 April 2025).
- How, D.N.T.; Hannan, M.A.; Lipu, M.S.H.; Sahari, K.S.M.; Ker, P.J.; Muttaqi, K.M. State-of-Charge Estimation of Li-Ion Battery in Electric Vehicles: A Deep Neural Network Approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 5565–5574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Zhu, X.; Zheng, H.; Bo, Z.; Lu, J. Deployment strategies for Li-rich cathode materials in batteries. Nat. Energy 2025, 10, 789–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, W.; Pecht, M.; Liu, T. Management of imbalances in parallel-connected lithium-ion battery packs. J. Energy Storage 2019, 24, 100781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


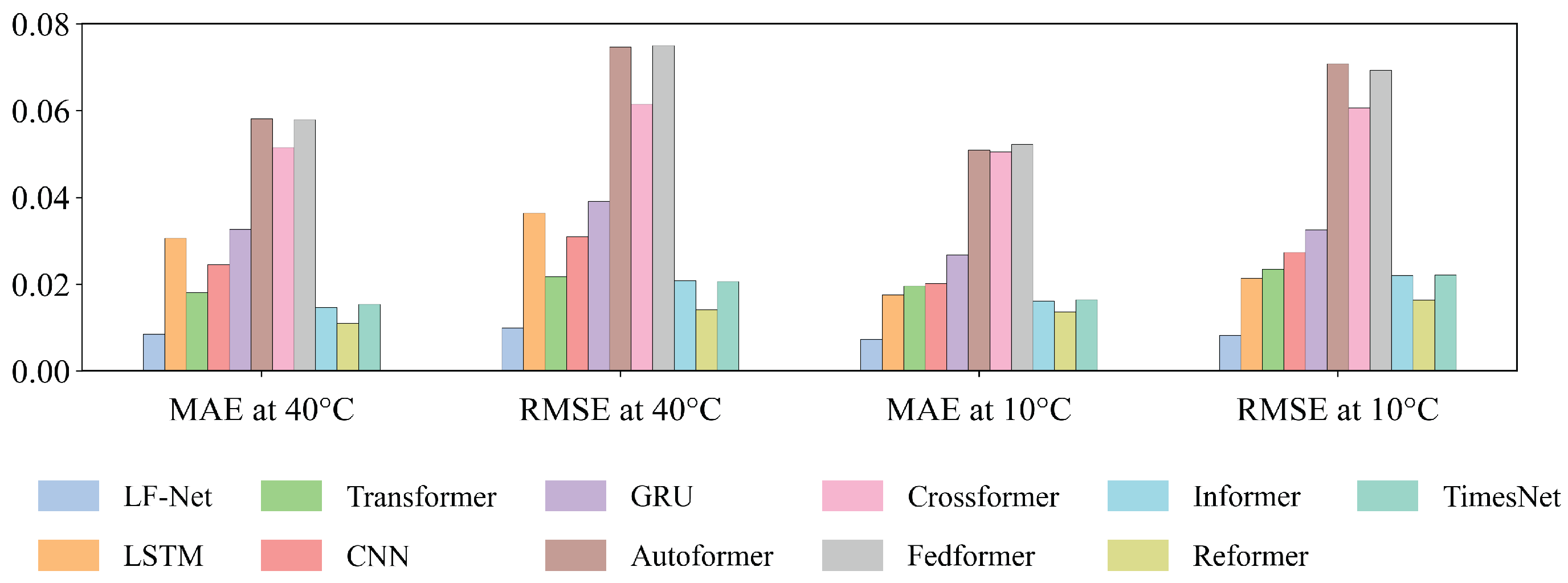
| Type | LF-Net | LSTM [18] | Trans-Former [23] | CNN [17] | GRU [19] | Auto-Former [27] | Cross-Former [28] | Fed-Former [29] | Ham-Informer [26] | Re-Former [30] | TimesNet [25] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE at 40 °C | 0.0085 | 0.0306 | 0.0181 | 0.0246 | 0.0327 | 0.0582 | 0.0515 | 0.0580 | 0.0147 | 0.0110 | 0.0154 |
| RMSE at 40 °C | 0.0099 | 0.0364 | 0.0218 | 0.0310 | 0.0391 | 0.0747 | 0.0615 | 0.0751 | 0.0208 | 0.0141 | 0.0206 |
| MAE at 10 °C | 0.0073 | 0.0176 | 0.0196 | 0.0202 | 0.0268 | 0.0510 | 0.0505 | 0.0523 | 0.0162 | 0.0136 | 0.0164 |
| RMSE at 10 °C | 0.0082 | 0.0214 | 0.0234 | 0.0274 | 0.0326 | 0.0709 | 0.0607 | 0.0694 | 0.0220 | 0.0163 | 0.0221 |
| Type | LF-Net | LSTM [18] | Trans-Former [23] | CNN [17] | GRU [19] | Auto-Former [27] | Cross-Former [28] | Fed-Former [29] | Ham-Informer [26] | Re-Former [30] | TimesNet [25] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | 15,925 | 5,263,873 | 152,385 | 1,621,441 | 3,948,033 | 1,259,009 | 945,584 | 494,337 | 1,657,345 | 663,553 | 4,689,474 |
| Setting | Data Proportion | Selection Method | Epochs | Fine-Tuning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50% continuous subsets | 50% per dataset | Continuous 25% datasets: front 50% 25% datasets: back 50% 50% datasets: random contiguous 50% | 150 | No |
| Light fine-tuning (20% datasets) | 20% per dataset (additional datasets) | Continuous Random contiguous 20% | 150 | Yes |
| (a) Training on 50% Continuous Subsets | (b) Light Fine-Tuning | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Single-Cell) | (20% Continuous Segments from DST/US06 at 10 °C and 40 °C) | ||||
| Metric | Full-Data Training | Continuous Subset (50%) | Metric | No Fine-Tuning | Light Fine-Tuning (20%) |
| MAE at 40 °C | 0.0085 | 0.0105 | MAE at 40 °C | 0.0085 | 0.0080 |
| RMSE at 40 °C | 0.0099 | 0.0125 | RMSE at 40 °C | 0.0099 | 0.0088 |
| MAE at 10 °C | 0.0073 | 0.0095 | MAE at 10 °C | 0.0073 | 0.0064 |
| RMSE at 10 °C | 0.0082 | 0.0147 | RMSE at 10 °C | 0.0082 | 0.0068 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, R.; Dai, X.; Zhang, J.; He, K.; Lin, F.; Ma, H. LF-Net: A Lightweight Architecture for State-of-Charge Estimation of Lithium-Ion Batteries by Decomposing Global Trend and Local Fluctuations. Electronics 2025, 14, 3643. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14183643
Zhou R, Dai X, Zhang J, He K, Lin F, Ma H. LF-Net: A Lightweight Architecture for State-of-Charge Estimation of Lithium-Ion Batteries by Decomposing Global Trend and Local Fluctuations. Electronics. 2025; 14(18):3643. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14183643
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Ruidi, Xilin Dai, Jinhao Zhang, Keyi He, Fanfan Lin, and Hao Ma. 2025. "LF-Net: A Lightweight Architecture for State-of-Charge Estimation of Lithium-Ion Batteries by Decomposing Global Trend and Local Fluctuations" Electronics 14, no. 18: 3643. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14183643
APA StyleZhou, R., Dai, X., Zhang, J., He, K., Lin, F., & Ma, H. (2025). LF-Net: A Lightweight Architecture for State-of-Charge Estimation of Lithium-Ion Batteries by Decomposing Global Trend and Local Fluctuations. Electronics, 14(18), 3643. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14183643







