An Automatic Brain Cortex Segmentation Technique Based on Dynamic Recalibration and Region Awareness
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A novel dual-module design (DRB + RAB) is proposed to enhance feature discrimination and structural awareness for accurate cortical segmentation.
- A lightweight, multi-plane segmentation strategy is employed to strike a balance between segmentation performance and computational efficiency.
- The training framework demonstrates strong generalization and robustness in small-sample scenarios.
- The proposed method offers a scalable and practical solution for clinical applications such as disease localization and neurosurgical navigation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Datasets
2.2. Data Preprocessing
- (1)
- Skull stripping: brain and non-brain tissues were separated using grayscale thresholding and edge detection techniques to remove the skull, resulting in clean images for further brain analysis.
- (2)
- Normalization: A non-rigid registration algorithm was employed to align all brain images to a common standard space. This step mitigates individual variability and enables cross-subject comparison of brain structures.
- (3)
- Tissue segmentation: brain tissues (gray matter, white matter, and cerebrospinal fluid) were labeled using a Bayesian classification approach based on the Expectation-Maximization (EM) algorithm, ensuring efficiency and accuracy in subsequent segmentation processes.
- (4)
- White matter segmentation: a gradient-based watershed algorithm combined with morphological operations was applied to precisely segment white matter, providing fine-grained structural information for brain parcellation.
- (5)
- Cortical extraction: the cerebral cortex was extracted using algorithms based on gradient and geometric morphology, allowing accurate differentiation between cortical and subcortical structures.
- (6)
- Spherical registration: a spherical registration algorithm was used to map the cortical surface onto a standard spherical template, thereby reducing morphological differences across individuals.
- (7)
- Label annotation: finally, automatic labeling was performed using the DKT (Desikan–Killiany–Tourville) atlas to generate the training labels required for the model.
2.3. Methods
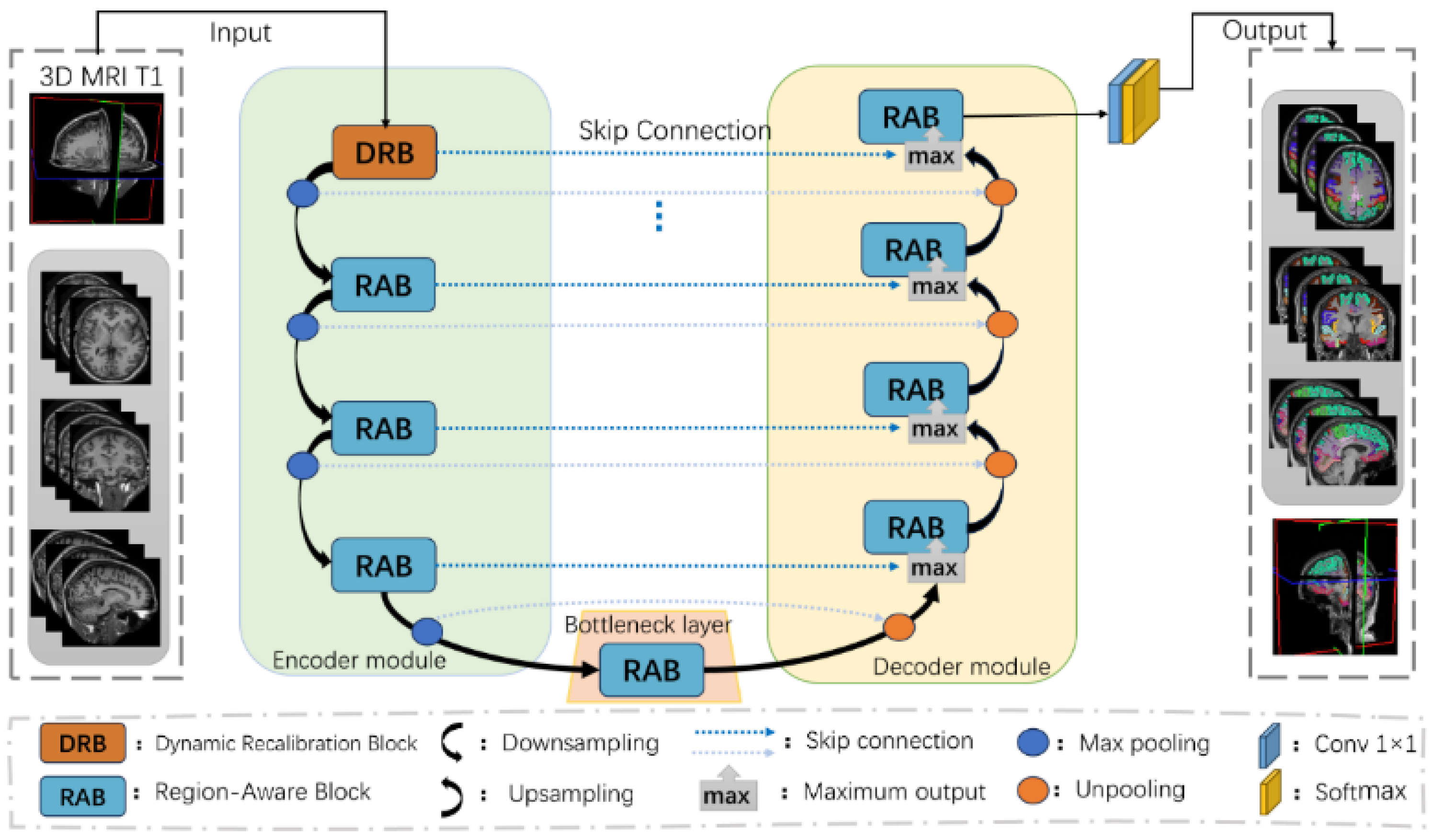
2.3.1. Cortical Structural Network Architecture
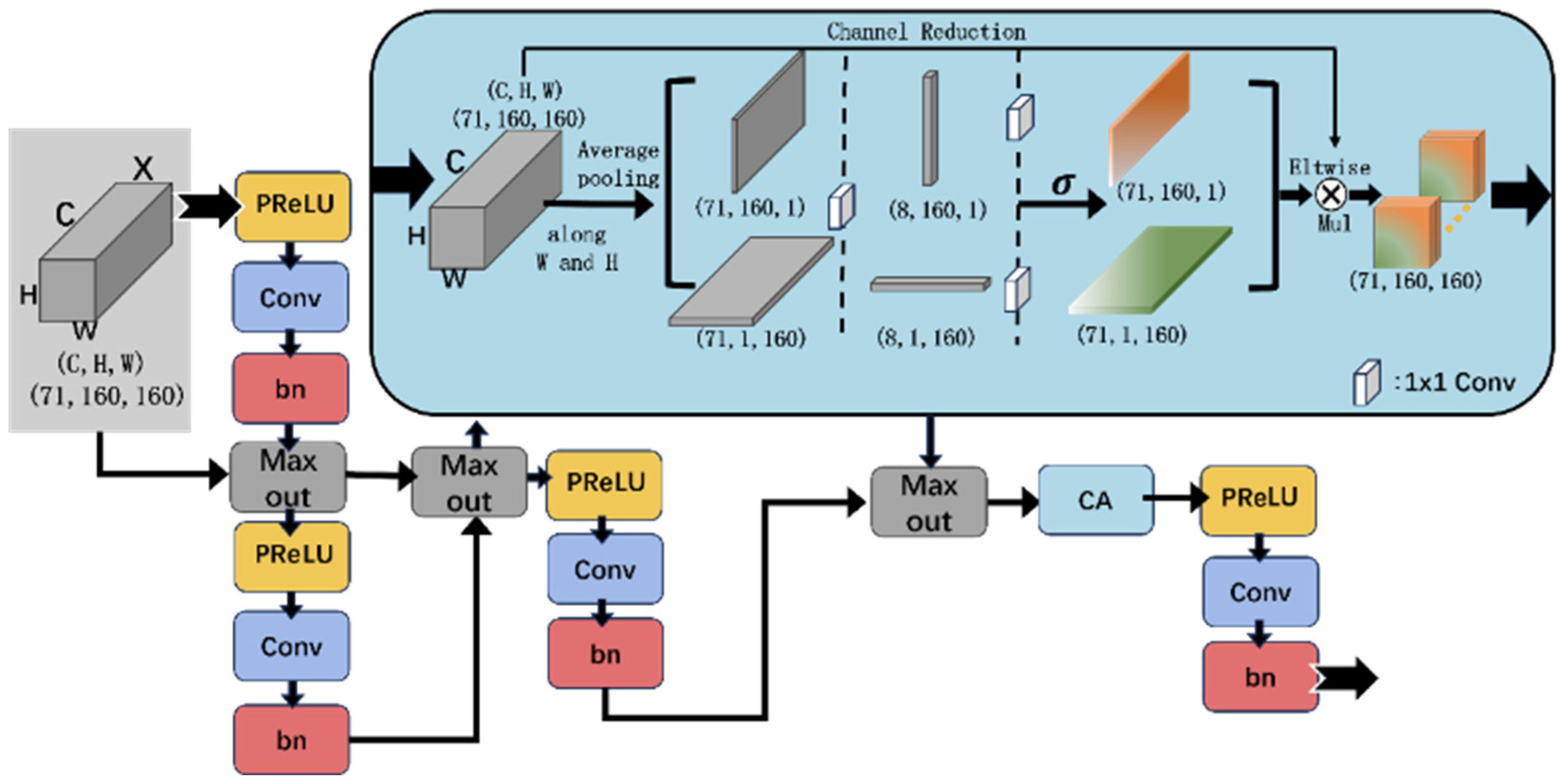
2.3.2. Dynamic Recalibration Block (DRB)
2.3.3. Region-Aware Block (RAB)
2.4. Loss Function
2.5. Evaluation Metrics
2.6. Experimental Setup
3. Experimental Results
3.1. Determination of the Number of RAB Modules
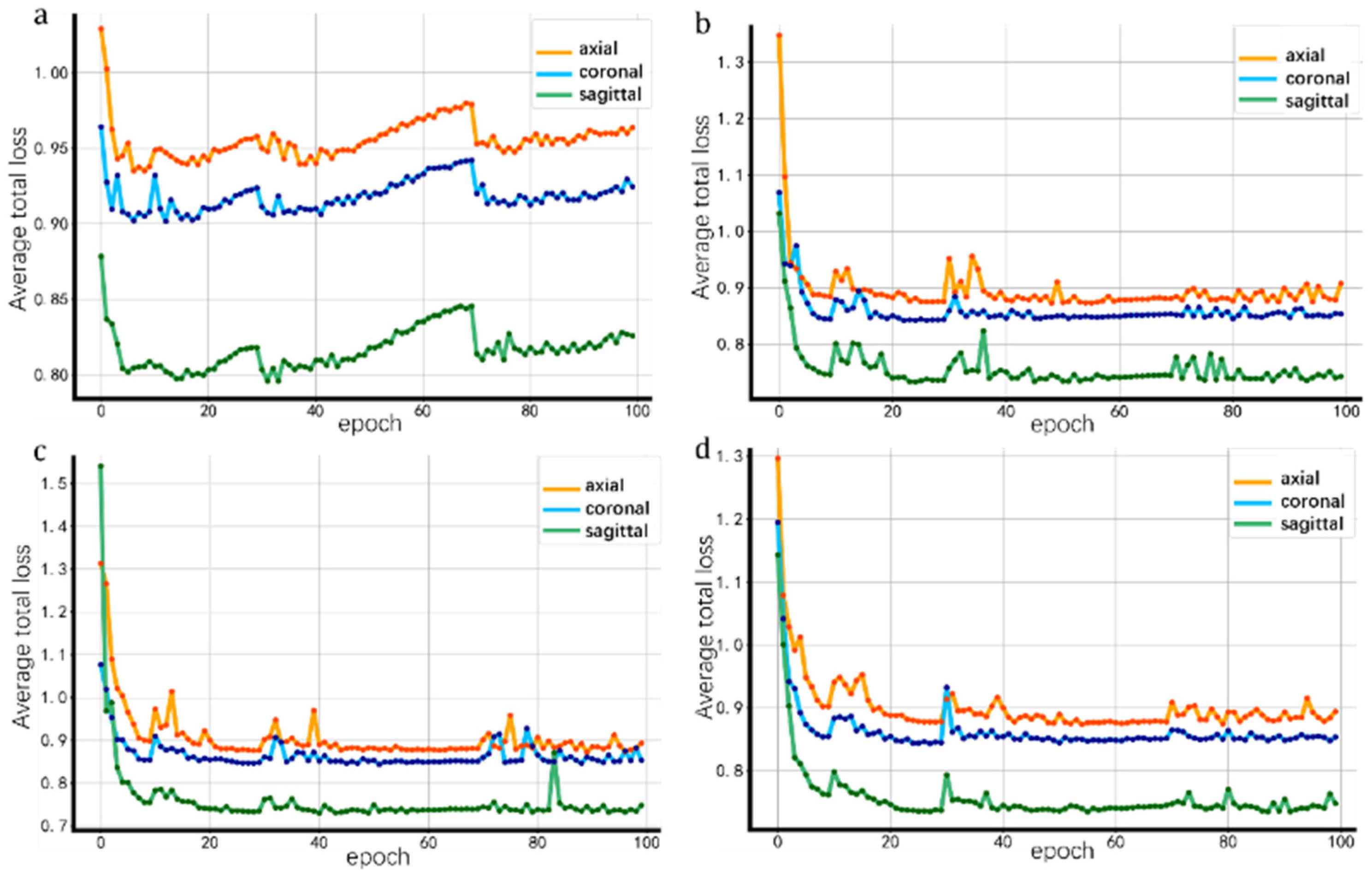
3.2. Model Convergence Results
3.2.1. Impact of Different Slice Orientations on Loss
3.2.2. Impact of Different Modules on Loss
3.3. Segmentation Accuracy Results
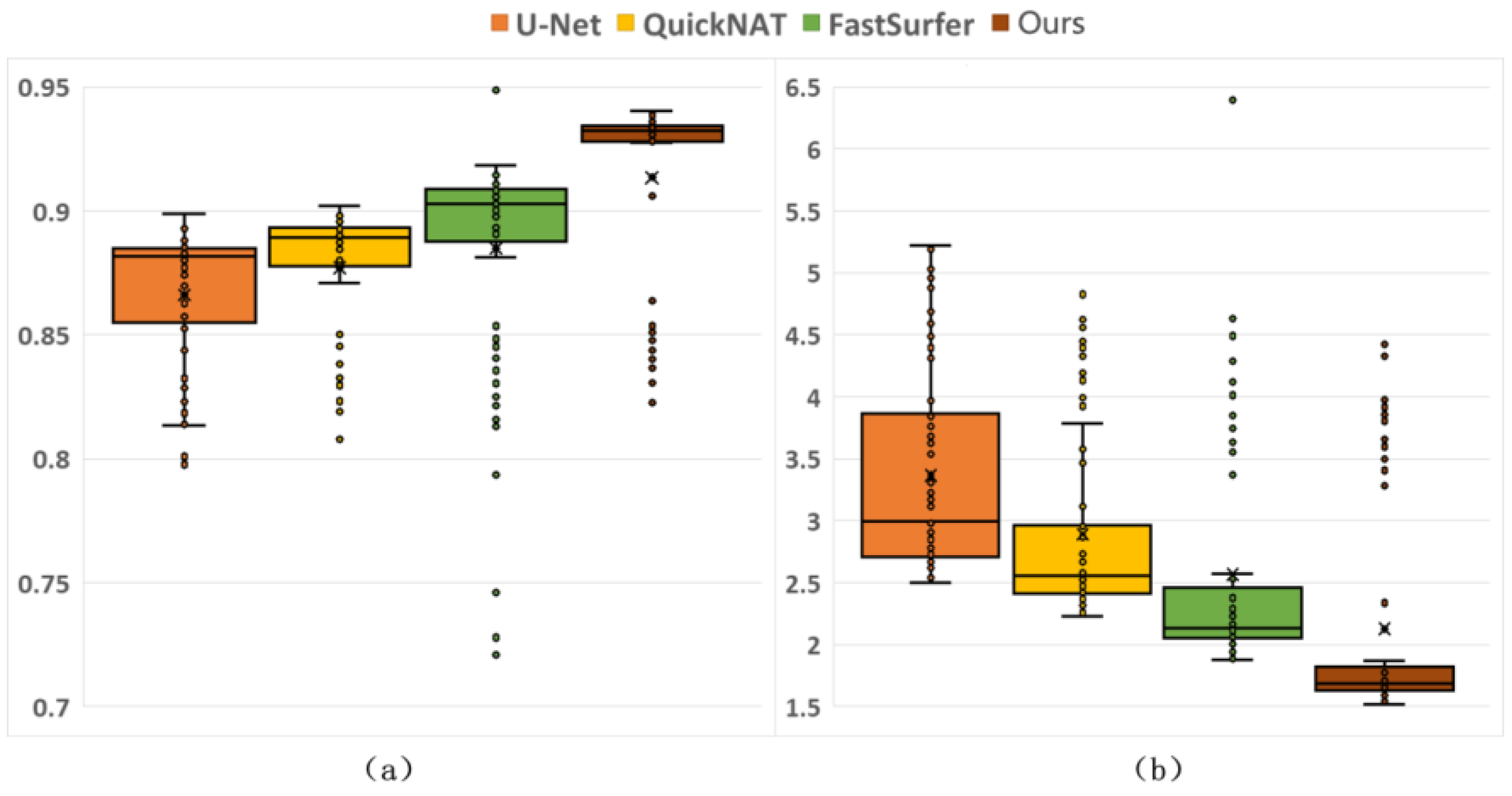
3.3.1. Comparative Results from Different Methods
| Method | Dice (%) | Hausdorff Distance (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| U-Net [32] | 86.62 ± 2.81 * | 3.3657 ± 0.8257 * |
| QuickNAT [25] | 87.70 ± 2.67 * | 2.8918 ± 0.7307 * |
| FastSurfer [27] | 88.48 ± 4.38 * | 2.5700 ± 0.8962 * |
| DRA-Net | 91.35 ± 3.76 | 2.1279 ± 0.8888 |
3.3.2. Generalization Results
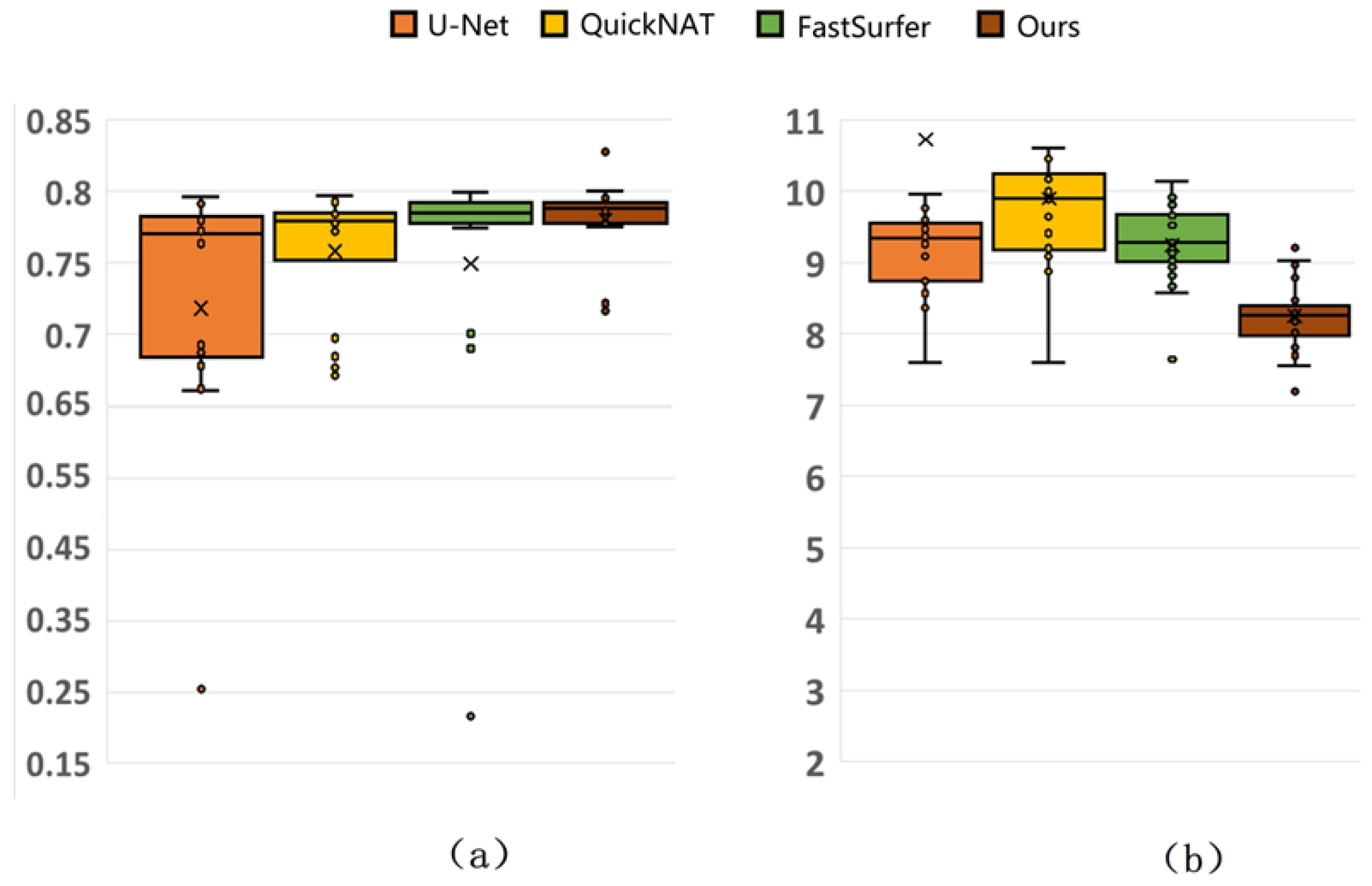
3.3.3. Comparison with Mainstream Methods
| Method | Dice (%) | Hausdorff Distance (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net [32] | CNN | 71.83 ± 12.88 | 10.728 ± 7.1801 |
| QuickNAT [25] | CNN | 75.84 ± 4.42 | 9.8983 ± 1.3562 |
| FastSurfer [27] | CNN | 74.92 ± 12.01 | 9.2437 ± 0.5632 |
| FreeSurfer [20] | Atlas-based | 74.75 ± 5.83 | 8.9852 ± 0.4936 |
| FSL [14] | Atlas-based | 64.3 ± 0.29 | — |
| JLF [36] | Atlas-based | 74.6 ± 0.90 | — |
| F-CNN [34] | CNN | 57.9 ± 0.24 | — |
| Naive U-Net [37] | CNN | 60.6 ± 0.60 | — |
| SLANT-8 [35] | Transformer | 69.9 ± 1.40 | — |
| SLANT-27 [35] | Transformer | 76.6 ± 0.80 | — |
| SLANT-27 FT [35] | Transformer | 75.9 ± 1.70 | — |
| DRA-Net | CNN | 77.99 ± 2.83 | 8.2571 ± 0.5009 |
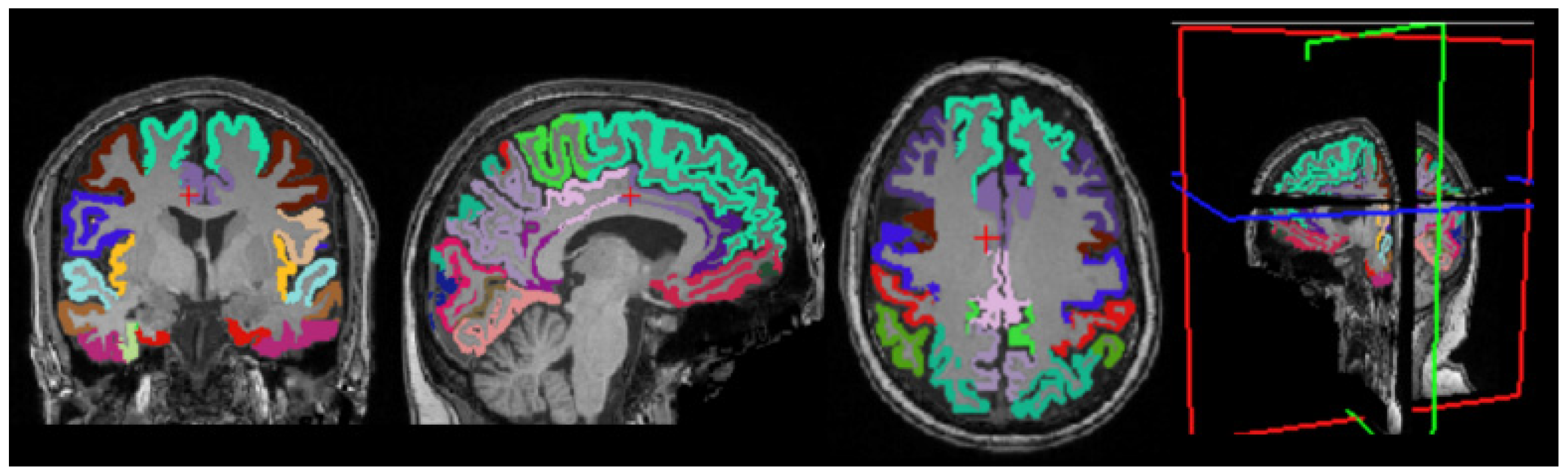
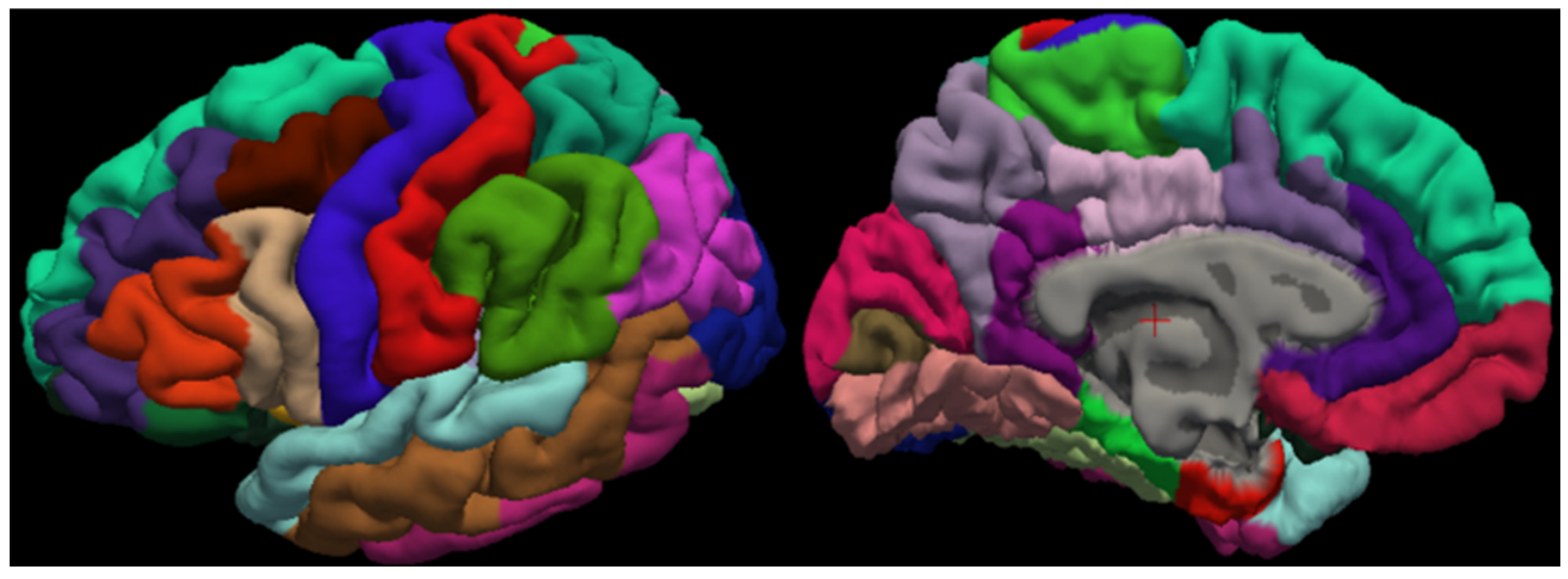
3.4. Cortical Structure Segmentation Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Advantages of the Proposed Method
4.2. Analysis of DRB and RAB
4.3. Analysis of Segmentation Performance
4.4. Limitation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, J.; Sui, S.F.; Liu, Z. Brain structure and structural basis of neurodegenerative diseases. Biophys. Rep. 2022, 8, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carew, T.J.; Magsamen, S.H. Neuroscience and Education: An Ideal Partnership for Producing Evidence-Based Solutions to Guide 21st Century Learning. Neuron 2010, 67, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeYoe, E.A.; Bandettini, P.; Neitz, J.; Miller, D.; Winans, P. Functional magnetic resonance imaging (FMRI) of the human brain. J. Neurosci. Methods 1994, 54, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjanar, R.; Dixit, U.D. Advanced Fusion of 3D U-Net-LSTM Models for Accurate Brain Tumor Segmentation. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2024, 15, 488–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siraisi, N.G. Vesalius and Human Diversity in De humani corporis fabrica. J. Warbg. Court. Inst. 1994, 57, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Zhang, R.; Hu, C.; Guo, B. GMDNet: Grouped Encoder-Mixer-Decoder Architecture Based on the Role of Modalities for Brain Tumor MRI Image Segmentation. Electronics 2025, 14, 1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiani, D.; Nascimento, A.M.; Pereira, L.K. Cortical brain functions–the brodmann legacy in the 21st century. Arq. Bras. De. Neurocir. Braz. Neurosurg. 2020, 39, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporns, O.; Tononi, G.; Kötter, R. The human connectome: A structural description of the human brain. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2005, 1, e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajita, R. Galen and his contribution to anatomy: A review. J. Evol. Med. Dent. Sci. 2015, 4, 4509–4517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loukas, M.; Pennell, C.; Groat, C.; Tubbs, R.S.; Cohen-Gadol, A.A. Korbinian Brodmann (1868–1918) and his contributions to mapping the cerebral cortex. Neurosurgery 2011, 68, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, J.L.; Woldorff, M.G.; Parsons, L.M.; Liotti, M.; Freitas, C.S.; Rainey, L.; Kochunov, P.V.; Nickerson, D.; Mikiten, S.A.; Fox, P.T. Automated Talairach atlas labels for functional brain mapping. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2000, 10, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, A.; Nowinski, W.L.; Nguyen, B.T.; Bryan, R.N. Three-dimensional Talairach-Tournoux brain atlas. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 1995: Image Display, San Diego, CA, USA, 26–28 February 1995; pp. 583–592. [Google Scholar]
- Friston, K.J. Statistical parametric mapping. In Neuroscience Databases: A Practical Guide; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2003; pp. 237–250. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson, M.; Beckmann, C.F.; Behrens, T.E.; Woolrich, M.W.; Smith, S.M. Fsl. Neuroimage 2012, 62, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, R.W. AFNI: Software for analysis and visualization of functional magnetic resonance neuroimages. Comput. Biomed. Res. 1996, 29, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboudi, F.; Drissi, C.; Kraiem, T. A Hybrid Model for Ischemic Stroke Brain Segmentation from MRI Images using CBAM and ResNet50-UNet. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2024, 15, 950–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzourio-Mazoyer, N.; Landeau, B.; Papathanassiou, D.; Crivello, F.; Etard, O.; Delcroix, N.; Mazoyer, B.; Joliot, M. Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. Neuroimage 2002, 15, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Morgan, P.S.; Ashburner, J.; Smith, J.; Rorden, C. The first step for neuroimaging data analysis: DICOM to NIfTI conversion. J. Neurosci. Methods 2016, 264, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desikan, R.S.; Ségonne, F.; Fischl, B.; Quinn, B.T.; Dickerson, B.C.; Blacker, D.; Buckner, R.L.; Dale, A.M.; Maguire, R.P.; Hyman, B.T. An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 968–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischl, B. FreeSurfer. Neuroimage 2012, 62, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahnke, R.; Yotter, R.A.; Gaser, C. Cortical thickness and central surface estimation. Neuroimage 2013, 65, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destrieux, C.; Fischl, B.; Dale, A.; Halgren, E. Automatic parcellation of human cortical gyri and sulci using standard anatomical nomenclature. Neuroimage 2010, 53, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, R.; Majumdar, A.; Sivaswamy, J. BrainSegNet: A convolutional neural network architecture for automated segmentation of human brain structures. J. Med. Imaging 2017, 4, 024003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachinger, C.; Reuter, M.; Klein, T. DeepNAT: Deep convolutional neural network for segmenting neuroanatomy. NeuroImage 2018, 170, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, A.G.; Conjeti, S.; Navab, N.; Wachinger, C.; Initiative, A.s.D.N. QuickNAT: A fully convolutional network for quick and accurate segmentation of neuroanatomy. NeuroImage 2019, 186, 713–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coupé, P.; Mansencal, B.; Clément, M.; Giraud, R.; de Senneville, B.D.; Ta, V.-T.; Lepetit, V.; Manjon, J.V. AssemblyNet: A large ensemble of CNNs for 3D whole brain MRI segmentation. NeuroImage 2020, 219, 117026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henschel, L.; Conjeti, S.; Estrada, S.; Diers, K.; Fischl, B.; Reuter, M. Fastsurfer-a fast and accurate deep learning based neuroimaging pipeline. NeuroImage 2020, 219, 117012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, A.; Tourville, J. 101 labeled brain images and a consistent human cortical labeling protocol. Front. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11534–11542. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Warde-Farley, D.; Mirza, M.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Maxout networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Atlanta, GA, USA, 17–19 June 2013; pp. 1319–1327. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, M.; Kim, H.; Han, B.; Xu, N.; Lee, K.M. Channel attention is all you need for video frame interpolation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; pp. 10663–10671. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Fu, H.; Luk, W.; Yu, T.; Wang, S.; Feng, B.; Ma, Y.; Yang, G. F-CNN: An FPGA-based framework for training convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 27Th International Conference on Application-Specific Systems, Architectures and Processors (ASAP), London, UK, 6–8 July 2016; pp. 107–114. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, Y.; Xu, Z.; Aboud, K.; Parvathaneni, P.; Bao, S.; Bermudez, C.; Resnick, S.M.; Cutting, L.E.; Landman, B.A. Spatially localized atlas network tiles enables 3D whole brain segmentation from limited data. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2018: 21st International Conference, Granada, Spain, 16–20 September 2018; pp. 698–705. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Yushkevich, P.A. Multi-atlas segmentation with joint label fusion and corrective learning—An open source implementation. Front. Neuroinform. 2013, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çiçek, Ö.; Abdulkadir, A.; Lienkamp, S.S.; Brox, T.; Ronneberger, O. 3D U-Net: Learning dense volumetric segmentation from sparse annotation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2016: 19th International Conference, Athens, Greece, 17–21 October 2016; pp. 424–432. [Google Scholar]
- Khedir, M.; Amara, K.; Dif, N.; Kerdjidj, O.; Atalla, S.; Ramzan, N. BrainAR: Automated Brain Tumor Diagnosis with Deep Learning and 3D Augmented Reality Visualization. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 128639–128653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, H. Dual attention network for scene segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3146–3154. [Google Scholar]
- Hayat, M.; Aramvith, S.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Ahmad, N. Attention ghostunet++: Enhanced segmentation of adipose tissue and liver in ct images. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.11491. [Google Scholar]



| Experiment | Dataset Name | Sample Size | Age Range (Years) | Mean Age ± SD (Years) | Male/ Female | Left-/Right-Handed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training and Validation | NKI-RS | 22 | 20–40 | 26 ± 5.2 | 12/10 | 1/21 |
| NKI-TRT | 20 | 19–60 | 31.4 ± 11.1 | 14/6 | 3/15 | |
| MMRR | 21 | 22–61 | 31.8 ± 9.2 | 11/10 | 3/18 | |
| HLN | 12 | 23–39 | 27.8 ± 4.6 | 6/6 | 0/12 | |
| Colin27 | 1 | 33 | 33 | 1/0 | 0/1 | |
| Twins | 2 | 41 | — | 0/2 | 0/2 | |
| Independent Test | OASIS-TRT | 20 | 19–34 | 23.4 ± 3.9 | 8/12 | 0/20 |
| Number of Layers | MIoU | Recall | Precision | Loss Total | Time (h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.66 ± 0.07 | 0.79 ± 0.06 | 0.79 ± 0.04 | 0.90 ± 0.07 | 38.14 |
| 2 | 0.73 ± 0.03 | 0.85 ± 0.02 | 0.83 ± 0.03 | 0.85 ± 0.03 | 41.02 |
| 3 | 0.72 ± 0.05 | 0.84 ± 0.05 | 0.83 ± 0.03 | 0.84 ± 0.06 | 41.55 |
| 4 | 0.73 ± 0.03 | 0.85 ± 0.02 | 0.83 ± 0.02 | 0.83 ± 0.03 | 42.01 |
| 5 | 0.73 ± 0.04 | 0.85 ± 0.03 | 0.83 ± 0.03 | 0.83 ± 0.03 | 42.43 |
| 6 | 0.74 ± 0.04 | 0.85 ± 0.02 | 0.84 ± 0.03 | 0.83 ± 0.03 | 46.94 |
| View (Plane) | Mean Loss | Loss Volatility |
|---|---|---|
| Axial | 0.9018 | 0.0027 |
| Coronal | 0.8630 | 0.0017 |
| Sagittal | 0.7574 | 0.0015 |
| ROI | Dice (%) | Hausdorff Distance (mm) | ROI | Dice (%) | Hausdorff Distance (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Insula | 87.64 ± 3.40 | 4.7818 ± 1.6534 | Posterior cingulate | 78.83 ± 5.43 | 6.7194 ± 2.1258 |
| Superior frontal | 84.72 ± 4.16 | 13.4316 ± 3.0392 | Postcentral | 78.76 ± 6.21 | 12.6653 ± 3.5746 |
| Precentral | 84.62 ± 4.31 | 9.5087 ± 1.0761 | Inferior temporal | 78.71 ± 3.50 | 10.5309 ± 4.2501 |
| Superior temporal | 83.50 ± 4.03 | 12.6089 ± 5.8031 | Middle frontal | 77.56 ± 4.78 | 11.8840 ± 2.4110 |
| Precuneus | 83.00 ± 3.56 | 8.9933 ± 2.6247 | Fusiform | 76.43 ± 4.88 | 10.7908 ± 3.2435 |
| Middle temporal | 81.27 ± 4.71 | 11.8217 ± 3.5855 | Orbitofrontal | 75.01 ± 3.84 | 9.1331 ± 1.0612 |
| Parietal | 79.67 ± 4.83 | 11.6662 ± 1.9720 | Anterior cingulate | 74.78 ± 5.42 | 7.2973 ± 2.2701 |
| Paracentral | 79.58 ± 4.25 | 9.0082 ± 2.7561 | Cuneus | 74.74 ± 4.72 | 9.7077 ± 2.4501 |
| Lingual | 79.57 ± 4.70 | 7.5641 ± 2.4250 | Inferior frontal | 71.79 ± 6.32 | 9.9689 ± 2.2038 |
| Parahippocampal | 79.29 ± 5.90 | 4.2071 ± 1.2654 | Entorhinal | 68.46 ± 6.65 | 6.1400 ± 1.0972 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nan, J.; Fan, G.; Zhang, K.; Zhai, S.; Jin, X.; Li, D.; Yu, C. An Automatic Brain Cortex Segmentation Technique Based on Dynamic Recalibration and Region Awareness. Electronics 2025, 14, 3631. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14183631
Nan J, Fan G, Zhang K, Zhai S, Jin X, Li D, Yu C. An Automatic Brain Cortex Segmentation Technique Based on Dynamic Recalibration and Region Awareness. Electronics. 2025; 14(18):3631. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14183631
Chicago/Turabian StyleNan, Jiaofen, Gaodeng Fan, Kaifan Zhang, Shuyao Zhai, Xueqi Jin, Duan Li, and Chunlai Yu. 2025. "An Automatic Brain Cortex Segmentation Technique Based on Dynamic Recalibration and Region Awareness" Electronics 14, no. 18: 3631. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14183631
APA StyleNan, J., Fan, G., Zhang, K., Zhai, S., Jin, X., Li, D., & Yu, C. (2025). An Automatic Brain Cortex Segmentation Technique Based on Dynamic Recalibration and Region Awareness. Electronics, 14(18), 3631. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14183631






