Prompt Self-Correction for SAM2 Zero-Shot Video Object Segmentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
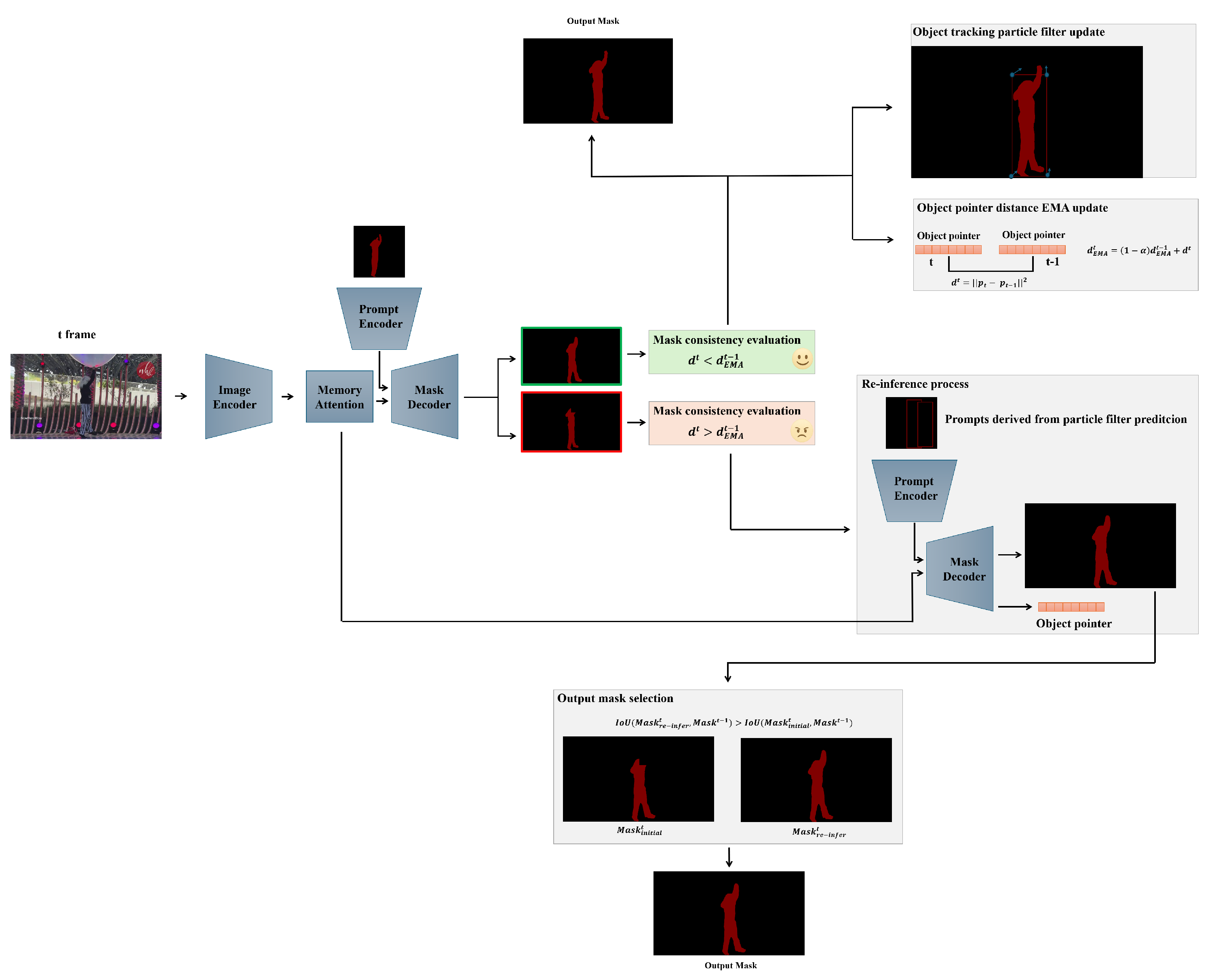
- We propose a mask consistency evaluation method that adaptively determines validity by thresholding the exponential moving average of the distance between the object pointers in consecutive frames (Section 3.1 and Section 3.2).
- We propose a SAM2-based framework that integrates a particle filter-based object tracker into the inference loop, updating it whenever the object score indicates presence. When the mask consistency evaluation triggers re inference, the framework uses the particle filter’s motion prediction to construct the prompt and re-query SAM2, thereby recovering valid masks (Section 3.3).
- Extensive experiments on DAVIS, the LVOS v2 train and validation splits and the YouTube-VOS validation set show that our framework yields small but consistent improvements over baseline SAM2 without using any learnable parameters (Section 4.3).
2. Related Works
2.1. Deep Learning-Based Video Object Segmentation
2.2. Filter-Based Object Tracking in Deep Learning
3. Methods
3.1. Object Pointer in SAM2
3.2. Mask Consistency Evaluation
3.3. Object Tracking and Re-Inference Based on Particle Filter
3.3.1. Object Tracking Using the Particle Filter
- Initialization ():
- Prediction:
- Update:
- Particle-filter confidence:
- Resampling: draw indices and set
- State estimate:
3.3.2. Re-Inference with Particle Filter Prediction-Based Prompt
| Algorithm 1 Prompt Self-Correction and Re-inference |
| Require: Base mask , previous mask , current pointer , previous pointer , object scores , particle set , EMA , threshold , frame index t Ensure: Final mask , updated particle set, updated , Hyper-parameters: warm-up N, smoothing , EMA threshold , warm-up threshold , object score cutoff , negatives K
|
4. Results
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Settings
4.3. Experiment Result Analysis
4.4. Ablation Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kirillov, A.; Mintun, E.; Ravi, N.; Mao, H.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L.; Xiao, T.; Whitehead, S.; Berg, A.; Lo, W.; et al. Segment Anything. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 4015–4026. [Google Scholar]
- Awais, M.; Raza, M.; Chen, W.; Wang, X.; Tao, D. Foundation Models Defining a New Era in Vision: A Survey and Outlook. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2025, 47, 2245–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, C.; Yin, B.; Liu, C.; Du, B.; Tao, D. Hi-SAM: Marrying Segment Anything Model for Hierarchical Text Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 47, 1431–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Li, K. EVF-SAM: Early Vision–Language Fusion for Text-Prompted Segment Anything Model. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.20076. [Google Scholar]
- Bucher, M.; Valada, A.; Navab, N.; Tombari, F. Zero-Shot Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Ravi, N.; Gabeur, V.; Hu, Y.; Hu, R.; Ryali, C.; Ma, T.; Khedr, H.; Rädle, R.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L.; et al. SAM 2: Segment Anything in Images and Videos. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.00714. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Sun, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X. SamRefiner: Taming Segment Anything Model for Universal Mask Refinement. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.06756. [Google Scholar]
- Shimaya, T.; Saiko, M. Sam-Correction: Fully Adaptive Label Noise Reduction for Medical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Athens, Greece, 27–30 May 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; Ning, K.; Shen, Q.; Zhou, S.; Yu, Z.; Wang, H. SAM-SP: Self-Prompting Makes SAM Great Again. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.12364. [Google Scholar]
- Caelles, S.; Maninis, K.K.; Pont-Tuset, J.; Leal-Taixé, L.; Cremers, D.; Van Gool, L. One-Shot Video Object Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An Image Is Worth 16 × 16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Karim, R.; Wildes, R.P. Understanding Video Transformers for Segmentation: A Survey of Application and Interpretability. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.12296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Wang, M.; Lin, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, Y. TransVOS: Video Object Segmentation with Transformers. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.00588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ning, J.; Cao, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Hu, H. Video Swin Transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 3202–3211. [Google Scholar]
- Jabbar, H.; Khan, R.Z. Methods to Avoid Over-Fitting and Under-Fitting in Supervised Machine Learning: A Comparative Study. Comp. Sci. Commun. Instrum. Devices 2015, 70, 978–981. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.; Oh, S.; Price, B.; Schwing, A.; Lee, J. Tracking Anything with Decoupled Video Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–3 October 2023; pp. 1316–1326. [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz, A.; Javed, O.; Shah, M. Object Tracking: A Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2006, 38, 13-es. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalman, R.E. A New Approach to Linear Filtering and Prediction Problems. Trans. ASME—J. Basic Eng. 1960, 82, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, N.J.; Salmond, D.J.; Smith, A.F.M. Novel Approach to Nonlinear/Non-Gaussian Bayesian State Estimation. IEE Proc. F—Radar Signal Process. 1993, 140, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep Learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1212.5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, D.; He, S.; Tang, J. Divide-and-Conquer: Confluent Triple-Flow Network for RGB-T Salient Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2025, 47, 1958–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bewley, A.; Ge, Z.; Ott, L.; Ramos, F.; Upcroft, B. Simple Online and Realtime Tracking. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 25–28 September 2016; pp. 3464–3468. [Google Scholar]
- Wojke, N.; Bewley, A.; Paulus, D. Simple Online and Realtime Tracking with a Deep Association Metric. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Beijing, China, 17–20 September 2017; pp. 3645–3649. [Google Scholar]
- Bertinetto, L.; Valmadre, J.; Henriques, J.; Vedaldi, A.; Torr, P. Fully Convolutional Siamese Networks for Object Tracking. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2016 Workshops, Amsterdam, The Netherland, 8–10 and 15–16 October 2016; pp. 850–865. [Google Scholar]
- Rafi, T.H.; Mahjabin, R.; Ghosh, E.; Ko, Y.-W.; Lee, J.-G. Domain Generalization for Semantic Segmentation: A Survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 57, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, D.; Dai, A.M.; Le, Q.V. HyperNetworks. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.09106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Borse, S.; Cai, H.; Wang, Y.; Bi, N.; Jiang, X.; Porikli, F. Perceptual Consistency in Video Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Varghese, S.; Bayzidi, Y.; Bär, A.; Kapoor, N.; Lahiri, S.; Schneider, J.D.; Schmidt, N.; Schlicht, P.; Hüger, F.; Fingscheidt, T. Unsupervised Temporal Consistency Metric for Video Segmentation in Highly-Automated Driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pont-Tuset, J.; Perazzi, F.; Caelles, S.; Arbeláez, P.; Sorkine-Hornung, A.; Van Gool, L. The 2017 DAVIS Challenge on Video Object Segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.00675. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, W.; Tan, C.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Guo, P.; Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Gao, S.; et al. LVOS: A Benchmark for Large-scale Long-term Video Object Segmentation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.19326. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Fan, Y.; Xu, N. The 4th Large-Scale Video Object Segmentation Challenge—Video Object Segmentation Track; Technical Report; CVPR: New Orleans, LO, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
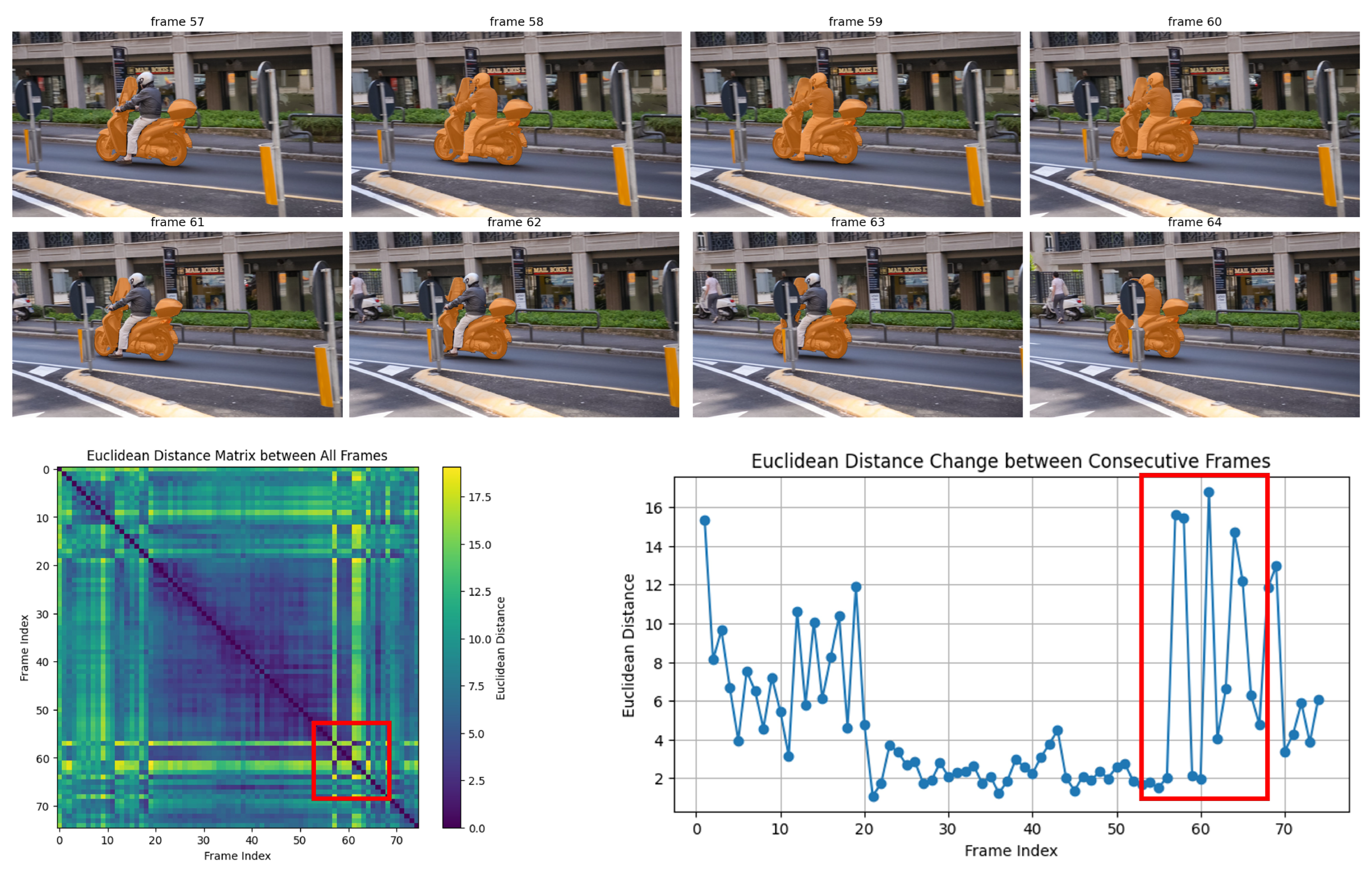


| DAVIS | LVOS v2 | YouTube-VOS | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | mIoU | fps | Train mIoU | Train fps | Val mIoU | Val fps | mIoU | fps | ||
| SAM2 | 90.25 | 27.78 | 92.08 | 18.33 | 68.47 | 18.12 | 82.66 | 15.36 | ||
| Ours | 90.35 | 26.84 | 92.21 | 16.90 | 68.52 | 17.00 | 82.68 | 15.13 | ||
| mIoU (%) | |
|---|---|
| Without EMA | 90.25 |
| 1.5 | 90.35 |
| 2.0 | 90.31 |
| 2.5 | 90.31 |
| Tracking Method | mIoU (%) |
|---|---|
| Without tracking | 90.25 |
| Kalman filter | 90.27 |
| Particle filter | 90.35 |
| Particles | mIoU | Avg fps |
|---|---|---|
| 20 | 90.33 | 27.43 |
| 40 | 90.35 | 26.84 |
| 60 | 90.32 | 26.39 |
| 128 | 90.29 | 26.35 |
| 256 | 90.30 | 23.82 |
| Object Score | mIoU |
|---|---|
| 0.0 | 0.9035 |
| 0.1 | 0.9034 |
| 0.2 | 0.9030 |
| 0.3 | 0.9030 |
| 0.4 | 0.9030 |
| 0.5 | 0.9030 |
| 0.6 | 0.9030 |
| Re-Inference Prompt Type | mIoU (%) |
|---|---|
| Without re-inference | 90.25 |
| 1 point (random) | 90.23 |
| 3 points (random) | 90.33 |
| 5 points (random) | 90.33 |
| 10 points (random) | 90.32 |
| Bounding box (without tracking) | 90.28 |
| Bounding box (with tracking) | 90.29 |
| Dual box + 1 negative point | 90.32 |
| Dual box + 3 negative points | 90.35 |
| Dual box + 5 negative points | 90.34 |
| Dual box + 10 negative points | 90.31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.; Bae, J.-H.; Vu, D.T.; Anh, L.H.; Rahman, Z.U.; Lee, H.; Yu, G.-H.; Kim, J.-Y. Prompt Self-Correction for SAM2 Zero-Shot Video Object Segmentation. Electronics 2025, 14, 3602. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14183602
Lee J, Bae J-H, Vu DT, Anh LH, Rahman ZU, Lee H, Yu G-H, Kim J-Y. Prompt Self-Correction for SAM2 Zero-Shot Video Object Segmentation. Electronics. 2025; 14(18):3602. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14183602
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jin, Ji-Hun Bae, Dang Thanh Vu, Le Hoang Anh, Zahid Ur Rahman, Heonzoo Lee, Gwang-Hyun Yu, and Jin-Young Kim. 2025. "Prompt Self-Correction for SAM2 Zero-Shot Video Object Segmentation" Electronics 14, no. 18: 3602. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14183602
APA StyleLee, J., Bae, J.-H., Vu, D. T., Anh, L. H., Rahman, Z. U., Lee, H., Yu, G.-H., & Kim, J.-Y. (2025). Prompt Self-Correction for SAM2 Zero-Shot Video Object Segmentation. Electronics, 14(18), 3602. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14183602






