Abstract
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies into islanded microgrids has increased their vulnerability to cyberattacks, particularly those targeting critical components such as power converters within an islanded AC microgrid. This study investigates the impact of False Data Injection (FDI) and Denial of Service (DoS) attacks on various power converters, including DC–DC boost converters, DC–AC converters, battery inverters, and DC–DC buck–boost converters, modeled in MATLAB/Simulink. A dataset of healthy and compromised operational parameters, including voltage and current, was generated under simulated attack conditions. To enhance system resilience, a deep learning-based detection and classification framework was proposed. After evaluating various deep learning models, including Deep Neural Networks (DNNs), Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs), Support Vector Machines (SVMs), Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), and Feedforward Neural Networks (FNNs), the final system integrates an FNN for rapid attack detection and an LSTM model for accurate classification. Real-time simulation validation demonstrated a detection accuracy of 95% and a classification accuracy of 92%, with minimal computational overhead and fast response times. These findings emphasize the importance of implementing intelligent and efficient cybersecurity measures to ensure the secure and reliable operation of islanded microgrids against evolving cyberattacks.
1. Introduction
Islanded microgrids have emerged as highly effective solutions for ensuring reliable power supply, reducing energy losses, and minimizing maintenance requirements in remote or isolated locations without access to standard electrical grids. By enabling localized generation and distribution, microgrids significantly reduce transmission and distribution losses, address global energy challenges, and promote the integration of renewable energy sources. This approach contributes to cutting carbon emissions, lowering operational costs, and reducing large-scale land use associated with conventional grid infrastructure. Consequently, islanded microgrids are increasingly deployed in critical sectors, such as hospitals and private enterprises, where continuous and stable power supply is essential. Their role in enhancing energy efficiency and supporting sustainable development underscores their growing importance in the global energy landscape [1].
However, the growing adoption of the IoT in the control and security management of islanded microgrids has increased their vulnerability to cyberattacks during operation [1,2]. In particular, power converters, which are pivotal in maintaining stability and power quality within microgrids, have become prime targets for malicious intrusions. Cyberattacks targeting these converters can cause severe operational disruptions, leading to system instability, considerable economic losses, and reduced reliability. Given that islanded microgrids often serve critical applications, such as defense installations, healthcare facilities, and other high-security environments, such disruptions can have profound consequences, affecting energy management, demand response, and economic dispatch, ultimately resulting in energy waste and substantial recovery costs [3].
Historically, critical energy infrastructure has been a frequent target of cyberattacks, exposing significant vulnerabilities and raising concerns about power system resilience worldwide. Recent high-profile incidents exemplify this threat landscape. The May 2021 Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack disrupted fuel supplies across the eastern United States, illustrating the susceptibility of critical infrastructure to cyber extortion [4]. In 2010, malware identified by Kaspersky Labs (Woburn, MA, USA) [5] showcased a sophisticated architecture capable of targeting industrial control systems, human–machine interfaces, electrical devices, and SCADA systems, thereby posing significant threats to power infrastructures. The 2020 Mumbai power outage investigation revealed Trojan horse malware infiltration within the city’s electrical grid, causing extensive service disruption. In December 2015, Ukraine’s power grid was severely impacted by the Black Energy malware, which incapacitated control center operations and left thousands without electricity [6]. These cyber incidents are accompanied by notable operational failures, such as Austria’s 2013 network congestion due to software faults, Switzerland’s information overload in 2005, and the 2003 North American blackout caused by a status estimator malfunction [6]. Collectively, these events highlight the persistent risks posed by both cyber and technical failures, resulting in widespread outages, service disruptions, and potential damage to critical infrastructure [7].
Cyberattacks on islanded microgrid data are generally classified into three categories: attacks targeting data availability, data integrity, and data confidentiality [8]. Attacks on data availability aim to disrupt legitimate access to networks or data-sharing systems, often through overwhelming traffic such as DoS attacks [9,10,11]. Data integrity attacks involve unauthorized modification or manipulation of information within the system, with FDI attacks being a prominent example. Attacks on data confidentiality focus on unauthorized access to sensitive information [12].
The effective classification of cybersecurity attacks plays a vital role in proactive mitigation strategies. As attack methods continue to evolve and diversify, categorizing these threats enables a deeper understanding of their characteristics, which is essential for establishing strong defensive measures [13]. Traditional security systems often struggle to detect novel or sophisticated attacks; however, advanced classification techniques have proven successful in uncovering hidden patterns, thereby improving detection accuracy [14]. Furthermore, a standardized framework for attack categorization facilitates the optimal allocation of cybersecurity resources by prioritizing threats based on their type and severity [15].
Considering the increasing cyber vulnerabilities of islanded microgrids, this study develops a deep neural network-based framework to detect and classify cyber attacks targeting power converters within islanded microgrids [16]. An islanded microgrid model was created in MATLAB/Simulink R2022b, incorporating essential components, such as DC–DC boost converters, DC–AC converters, DC–DC buck–boost converters, and battery inverters. A cyberattack model was simulated by mathematically representing various attack scenarios. Operational data reflecting both normal and compromised conditions, including input and output voltages and currents were generated and collected. These datasets were employed to train deep learning models to effectively detect and classify cyberattacks. Multiple deep learning architectures were evaluated, with LSTM networks and FNN emerging as the most effective for classification and detection of cyberattacks, respectively. A summary of the performance of these different deep learning models is presented in the accompanying Table 1.
The research expands the current understanding of microgrid cyberattacks by concentrating on the classification of FDI and DoS attacks within an islanded AC microgrid environment. Unlike previous studies, which primarily focus on localizing attacks within the microgrid, this work includes a comprehensive set of power converters [17]. Prior research has largely emphasized grid-connected or DC microgrids, leaving islanded AC microgrids, particularly those integrated with battery inverter systems, less explored [18,19]. The methodology employs a two-stage deep learning framework: an FNN for rapid attack detection and an LSTM network for precise classification [18,20,21]. The FNN model’s relatively simple architecture, with only four trainable layers, achieves a detection accuracy of 95%, reducing computational overhead. The LSTM model, capable of capturing long-term dependencies and mitigating the vanishing gradient problem common in recurrent neural networks, attains a classification accuracy of 92%. This combined approach offers an effective balance of computational efficiency and high accuracy, making it suitable for real-time security applications in microgrids.
The microgrid in this study was modeled following the configuration from the University of Moratuwa (UoM) microgrid. Cyberattack scenarios were simulated by introducing malicious signals to the controllers of various power converters. Voltage and current measurements at both inputs and outputs were collected under normal and attack conditions and used to train FNN and LSTM networks for efficient detection and classification [18,21]. The FNN model’s simplicity and computational efficiency make it well suited for real-time deployment on hardware platforms such as Raspberry Pi, while the LSTM network’s capability to analyze sequential data enables accurate identification of cyberattack types based on their behavioral patterns. The remainder of this paper is organized as follows: Section 2 describes the islanded microgrid model and its components. Section 3 discusses various cyberattacks in microgrids and their impact. Section 4 presents the experimental setup and evaluation of the proposed deep learning system for attack detection and classification. Finally, Section 5 concludes the paper and suggests directions for future work.

Table 1.
Summary of cyberattack detection methods in microgrid systems.
Table 1.
Summary of cyberattack detection methods in microgrid systems.
| Paper Reference | Detection Type | Accuracy (%) | Model Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Koduru et al. [22] | Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack | 98.00 | Deep Neural Network (DNN) |
| Koduru et al. [22] | False Data Injection (FDI) attack | 90.00 | Deep Neural Network (DNN) |
| Hybrid ML Approach in DC Microgrids [23] | False Data Injection (FDI) attack | >96.5 | Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) |
| Hybrid ML Approach in DC Microgrids [23] | False Data Injection (FDI) attack | >96.0 | Logistic Regression |
| Dehghani et al. [24] | FDI on control signals, communication networks | >97 | Wavelet transform + Deep auto-encoder |
| Ye et al. [25] | FDI into smart metering and central controller unit | 97.00 | Modified prediction interval-based LSTM |
| Hakim and Karegar [26] | FDI into substation measurements and sensors | 95.53 | Cross wavelet transform + SVM |
| Mohiuddin et al. [27] | FDI into output voltage and power measurements | 91.00 | Deep learning using rectified linear unit |
2. Islanded Microgrid
The MATLAB/Simulink model of the microgrid was developed based on the UoM microgrid, with particular emphasis on their load profiles. The model incorporates various load sections, including a new administration building with a power demand of 100 kW, a canteen requiring 50 kW, and the Sumanadasa building, which has a load requirement of 200 kW. Figure 1 illustrates the basic microgrid model, showing the load distribution and the conceptual framework used for the MATLAB design and simulation of the system’s behavior and control.
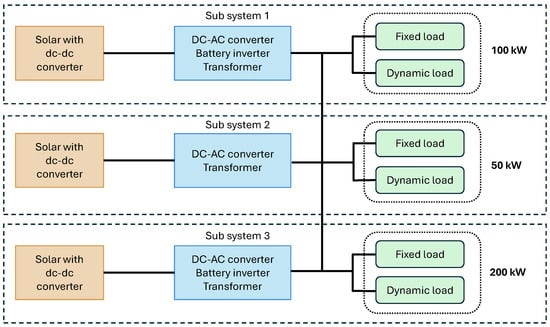
Figure 1.
Microgrid model with loads.
2.1. Solar PV with Solar Inverter
The proposed islanded PV system employs a two-stage power conversion architecture, comprising a DC–DC boost converter followed by a standalone DC–AC inverter. The DC–DC converter adopts a high-gain step-up topology to raise the variable PV array voltage to a regulated DC link voltage, allowing the use of low-voltage PV modules and ensuring stable operation under varying irradiance and temperature conditions.
A Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) algorithm is implemented within the converter control using a MATLAB function. The Perturb and Observe (P&O) method is chosen for its simplicity, low computational requirements, and reliable steady-state tracking capability. The inverter stage is based on a voltage-source inverter (VSI) topology, which converts the regulated DC voltage into a stable AC output for local loads. In islanded mode, the inverter maintains both output voltage and frequency within prescribed limits, independent of any external grid connection.
The control strategy employs a dual-loop structure: an inner current control loop for fast dynamic response and an outer voltage control loop for regulating the load-side voltage. The voltage loop ensures stable RMS voltage under varying load conditions, while the current loop provides overcurrent protection and improves transient performance. Additionally, the power management scheme coordinates the operation of the PV array, energy storage system, and local load to maintain supply–demand balance during islanded operation. Table 2 illustrates the design parameters of the three solar PV arrays.

Table 2.
Parameters of three PV arrays.
Each PV inverter has a central AC output, which connects to the PV AC combiner panels and then feeds into the building’s power system. All inverters communicate with the DHYBRID Universal Power Platform via an RS-485 communication line, which helps prevent battery overcharging. Since communication is involved, there is a high possibility of cyberattacks on the solar inverter. The MATLAB design of the solar PV system includes a DC–DC boost converter with MPPT control, the PV array, and measurement units, as shown in Figure 2. Figure 3 presents the schematic of the DC–AC converter with its controller, filter, and measurement devices. An EMI (Electro Magnetic Interference) filter for reducing higher-order harmonic frequencies from the inverter output is shown in Figure 4. Figure 5 depicts the PI-based control structure with d–q axis-oriented cascade control for the three-phase voltage source PWM rectifier.
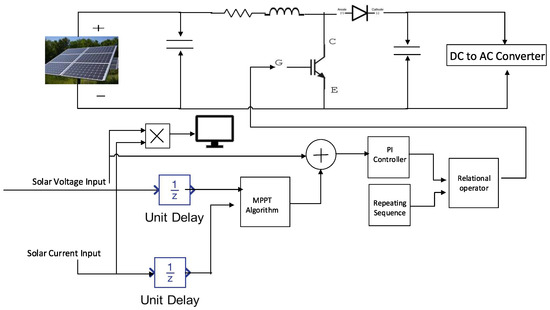
Figure 2.
Schematic of the solar PV system comprising a DC–DC boost converter with MPPT control, PV array, and measurement units.
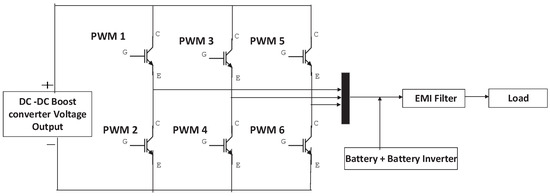
Figure 3.
Schematic of the DC–AC converter with controller, filter, and measurement devices.
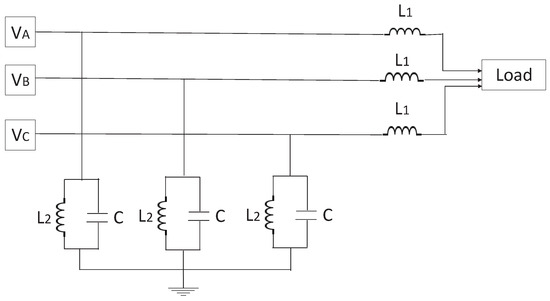
Figure 4.
EMI filter for reducing higher-order harmonic frequencies from the DC–AC inverter output.
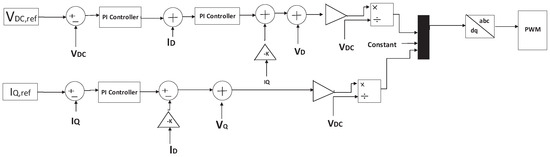
Figure 5.
PI-based control structure with d–q axis-oriented cascade control of three-phase voltage source PWM rectifier.
2.1.1. DC–DC Boost Converter and Inverter Control Equations
The DC–DC boost converter steps up the input voltage to a higher output voltage , which is then used as input to a DC–AC inverter. The main components include an inductor with series resistance , a diode D, an IGBT switch, a parallel output capacitor , and a load .
- Steady-State Output Voltage
- Load and Inductor Currents
- Inductor Current Ripple
- Output Voltage Ripple
2.1.2. DC–AC Converter System Parameters
The DC–AC converter (VSI) converts the DC output of the boost converter into a three-phase AC voltage. Key parameters include:
- Inverter inductance L and resistance R (AC-side filter)
- DC-link voltage (from the boost converter)
- AC-side voltages and currents
Control variables include d–q axis reference currents and modulation indices for PWM. A PLL measures grid angle and frequency .
- Reference Currents
- Outer DC-Voltage PI Controller
- Current PI Controllers
- Voltage Commands with Decoupling
- PWM Generation
2.1.3. EMI Filter Design: − () Branch
The EMI filter branch consists of a series inductor and a parallel LC tank (), designed to suppress high-frequency noise from power electronic converters.
- Series inductor : Acts as a line choke, blocking high-frequency harmonics.
- Shunt capacitor C: Diverts high-frequency components to ground.
- Parallel inductor : Forms a resonant LC tank with C, high impedance at fundamental frequency, enhancing filtering near resonance.
- Series Inductor Impedance
- Parallel LC Tank Impedance
- Total Input Impedance
- Component Selection
2.2. Battery Bank with Battery Inverter
The battery bank consists of parallel strings, each containing series-connected modules. This setup provides a total resultant capacity of 470 Ah to the battery inverter. A battery inverter converts DC power to AC to supply the load and converts AC to DC for battery charging using a bi-directional power converter. This system enables both active and reactive power management. In off-grid mode, the battery inverter acts as a virtual synchronous generator to regulate AC voltage and frequency through droop control. Voltage regulation is managed based on the reactive power demand within the system.
Figure 6 illustrates the use of a universal bridge to perform both AC–DC and DC–AC conversions. This configuration enables efficient interfacing between the microgrid and the battery inverter system. The universal bridge facilitates bidirectional power flow, supporting both charging and discharging operations of the battery. Figure 7 shows the battery storage system, which includes a controller, the battery itself, a DC–DC buck–boost converter, and measurement units. The controller manages the battery’s charging and discharging processes to maintain optimal performance. The buck–boost converter adjusts the voltage levels as needed to ensure efficient energy flow between the battery and the microgrid. These converters use parameters such as state of charge (SOC), battery system current, AC supply parameters, and DC parameters as inputs to the controller. The system communicates with the Battery Management System (BMS), which is highly vulnerable to cyberattacks.
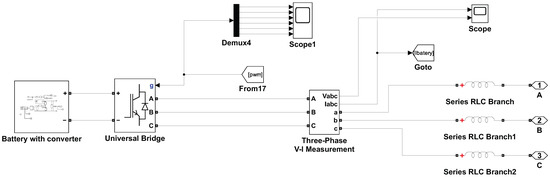
Figure 6.
AC–DC and DC–AC conversion using a universal bridge for interfacing with the battery inverter system.
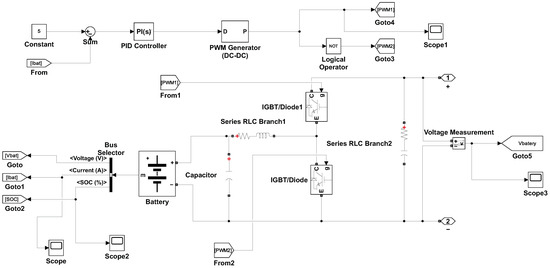
Figure 7.
The battery storage system comprising a controller, battery, DC–DC buck–boost converter, and measurement units.
3. Cyberattacks in Microgrid
A cyberattack refers to a deliberate action by a person or group to steal or expose confidential data while attempting to breach security or damage networks and computers. Based on their impact on different security properties, cyberattacks are categorized as affecting availability, integrity, and confidentiality. Historically, there have been many cyberattacks on power systems. However, islanded microgrids are more vulnerable compared to traditional power systems.
3.1. Attacks on Data Integrity
These attacks can corrupt measurements or command signals within the communication network, leading to malfunctions in the microgrid and affecting its control systems. Examples of attacks on data integrity include rogue software and malware and the FDI attack. FDI attacks are among the most challenging threats to microgrids, with impacts on modern power grids that can be severe and unacceptable.
- If , this attack manipulates the real measurement by
- If , this attack replaces the real measurement by
- If , there is no attack in the controller.
The manipulation in Equation (15) is derived from the paper [5]. represents the input from the sensors to the controllers, while denotes the manipulated output obtained after the cyberattack. Based on this manipulation, we can categorize the FDI attack into three distinct cases.
- FDI Case 1:
- FDI Case 2:
- FDI Case 3:
3.2. Attacks on Data Availability
The cybersecurity system must ensure timely and accessible data, which is essential for controlling power electronics converters in smart microgrids, particularly in islanded mode and during transient events. Attacks aimed at obstructing or delaying data communications are known as attacks on data availability, commonly referred to as Denial of Service (DoS) attacks. The DoS attack model is defined as in Equation (15). Attackers can employ DoS attacks to target communication links, while False Data Injection (FDI) attacks compromise the data exchanged between the controller and sensors.
3.3. Attacks on Data Confidentiality
Cyberattacks that breach confidentiality enable hackers to eavesdrop on the communication network, gaining access to sensitive information about customers and the microgrid operation and control strategies. While these attacks may not immediately disrupt microgrid operations, they pose significant privacy and security risks. In our project, we employ False Data Injection (FDI) attacks in three distinct cases, along with Denial of Service (DoS) attacks, which have more impact on microgrids and attackers commonly willing to use these types.
3.4. Cyberattack Model Design
In the MATLAB design, we used a step input U(t) along with a delayed step input to simulate an attack over a specific period. The rationale for limiting the duration of the attack is rooted in safety considerations. If the attack persists beyond the system’s safety thresholds, protection mechanisms such as circuit breakers would be triggered in a real-world scenario. Therefore, to realistically simulate a transient disturbance without initiating a system shutdown, the attack duration was kept brief. Figure 8 shows the model that was designed based on Equation (15).
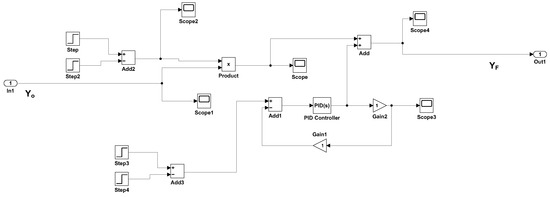
Figure 8.
Cyberattack model.
We independently varied the parameters using the corresponding Equation (15). This experimental design enables us to isolate and observe the effects of manipulating each parameter individually during the attack window. Figure 9 is an example of how the attack model is integrated with the microgrid solar inverter.
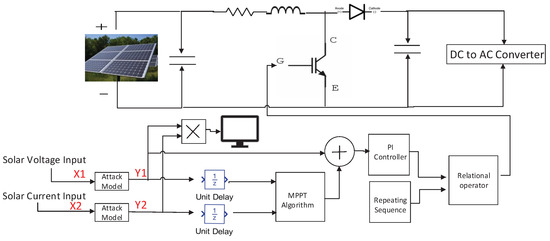
Figure 9.
Solar inverter with DC–DC boost converter with attack in MATLAB.
3.5. Cyberattack Results
The graphical representation illustrates the effects of a cyberattack on different power converters, quantifying the extent to which each converter is impacted. It demonstrates how such attacks influence the operational behavior of the microgrid. Figure 10, Figure 11, Figure 12 and Figure 13 show examples of the results of cyberattacks that occurred in power converters.
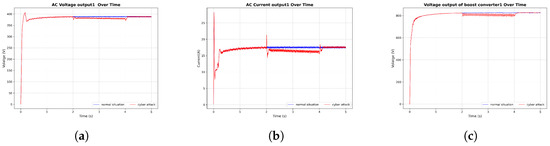
Figure 10.
FDI attack in solar inverter. (a) AC voltage output, (b) AC current output, (c) DC boost converter voltage output.
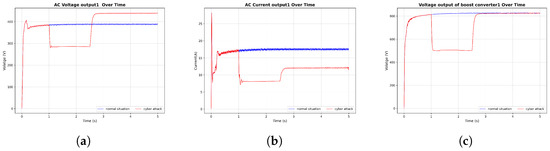
Figure 11.
DoS attack in the solar inverter. (a) AC voltage output, (b) AC current output, (c) DC boost converter voltage output.
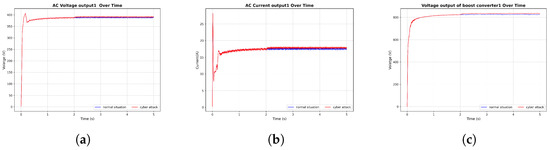
Figure 12.
FDI attack in the battery inverter. (a) AC voltage output, (b) AC current output, (c) DC boost converter voltage output.
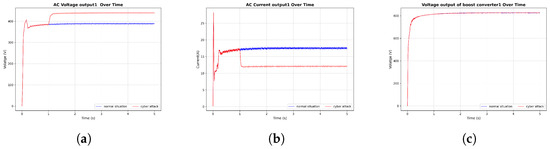
Figure 13.
DoS attack in each DC-DC boost converter. (a) AC voltage output, (b) AC current output, (c) DC boost converter voltage output.
In these graphs, the attacks are introduced after 1 s of simulation time. Notably, in Figure 10, following the termination of a cyberattack at 4 s, the system response of the solar inverter under FDI attack returns to normal operating conditions. However, in other cases, the system does not regain stability after the attack. These observations underscore the necessity of implementing cybersecurity measures to ensure microgrid stability and resilience against such disturbances.
4. Experiment and Evaluation
The proposed data-driven evaluation method is directly applied to the islanded microgrid MATLAB model output. Cyberattacks are applied at specific time intervals, recording and labeling the output data. Based on the labeled data, data processing methods are applied. Subsequently, data-driven methods are trained. With respect to evaluation of methods, precision, F1-score, recall, accuracy, MSE (mean squared error), MAE (mean absolute error), and validation processing methods are applied based on the labeled data loss.
FNNs are typically less complex than other deep learning architectures. Due to their simpler structure, they enable quick processing along with brief training periods. The quick computational capabilities of FNNs make them suitable for applications requiring quick performance, together with restricted computational resources.
LSTMs are highly effective for cyberattack detection because they analyze sequential patterns and track variations in data during operations. The LSTM network captures long-term patterns while retaining essential information, enabling it to detect changes effectively. LSTMs are also highly capable of handling diverse sequences and supporting real-time monitoring, making them effective in detecting cyber threats across a variety of data types, including system events and network.
4.1. Data Pre-Processing
The basic step is data analysis to understand the relationships between variables and how the data are distributed. Handling missing values, and detecting and removing outliers are managed by data cleaning. The data transformation process consists of normalization, duplicate removal and encoding of categories, and discretization procedures. Feature engineering is used to select relevant features and create new features from existing ones to identify patterns. The process of data integration unites information across multiple sources, while data reduction works to simplify the collected data.
In data processing, the input data window size is (10, 9). Each window is assigned a label based on the maximum frequency of outputs within those 10 rows. Ten rows and nine features are combined into a matrix. To address this, the FNN and LSTM models were designed to accept two-dimensional input with a window size of 10 rows and 9 features. The process involves sliding the window from the 1st to the 10th row, then from the 2nd to the 11th row, and so on. Below Table 3 explains the hyperparameters used for our four models.

Table 3.
Deep learning model hyperparameters for classification and detection.
4.2. FNN Model for Detection
Implementing a hyperparameter tuning process for an FNN model using a grid search technique, the model has three hidden layers with 128, 64, and 32 neurons, respectively, activated by ReLU. The input layer accepts 2D input, and the output layer uses the sigmoid activation function. We identified the best configuration that included dropout rates through a grid search process to boost performance. Early stopping is also used to measure validation loss, with a threshold value of 0.01. It monitors 10 epochs and waits for 10 epochs to check the change in validation loss. If the change is not significant, training stops. The validation performance deterioration triggers this method to stop training processes while keeping the optimal network weights for the prevention of overfitting. The defined epoch count is 50, and the batch size is 20. The model is trained using the training dataset.
In tests, the FNN detection model demonstrated solid performance through the binary cross-entropy result of 0.278 and the mean squared error of 0.0408. The model showed reliable binary classification results with 95.32% accuracy and 93.3% precision alongside 95% recall because of its optimal false positive and negative ratio. Figure 14 and Figure 15 show how accuracy and loss change with each epoch during training for a given scenario.
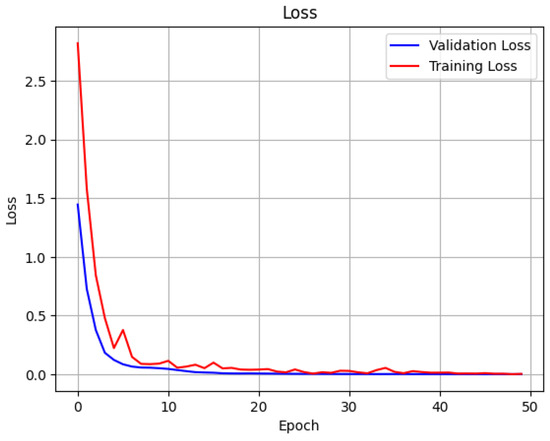
Figure 14.
Loss curve of training and validation loss of FNN model for detection.
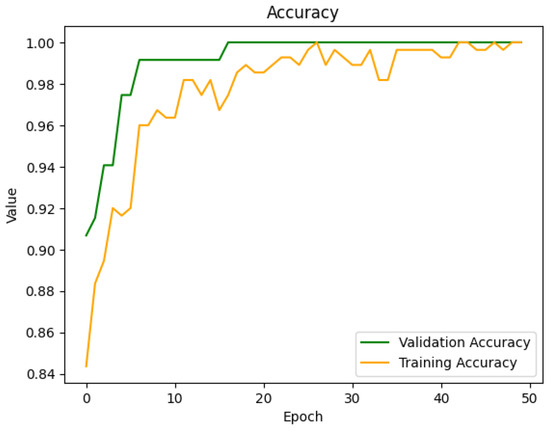
Figure 15.
Accuracy curve of training and validation of FNN model for detection.
4.3. LSTM Model for Detection
The LSTM model consists of four LSTM layers, each with 50 units of neurons, which process sequential data by maintaining 50-dimensional hidden states. The model generalizes and prevents overfitting with a dropout rate of 0.2 implemented after each LSTM layer. During dropout operations, a random partition of neurons is deactivated to prevent the model from depending on particular features. The final classification step depends on a dense layer with sigmoid activation to generate a binary output, which determines the data class. The detection model utilizing LSTM produced exceptional outcomes through its measurement of 0.171 binary cross-entropy value and 0.030 mean square error. The 96.6% accurate model revealed 99.0% precision, and 93.0% recall, establishing highly successful detection with very low error rates. The learning curves for accuracy and loss with the attack data are illustrated in Figure 16 and Figure 17.
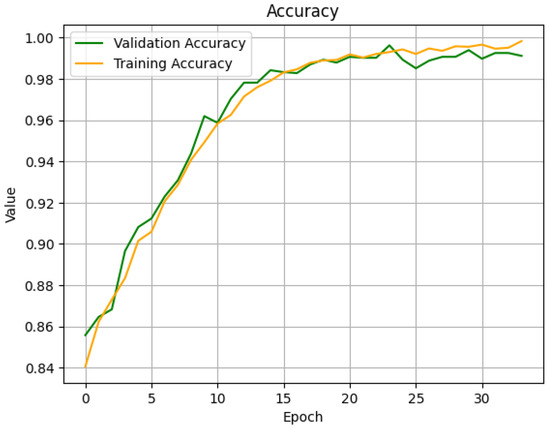
Figure 16.
Accuracy curve of training and validation of LSTM model for detection.
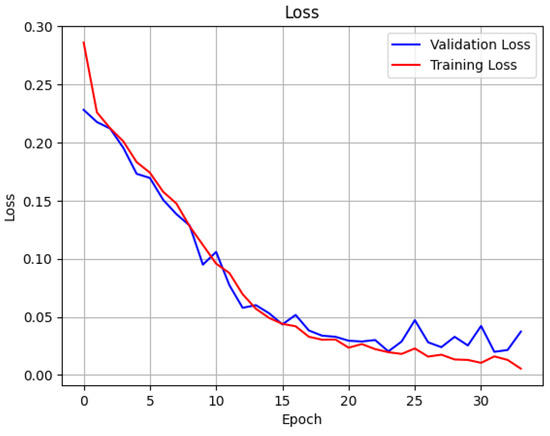
Figure 17.
Loss curve of training and validation loss of the LSTM model for detection.
4.4. FNN Model for Classification
The grid search algorithm was used to identify the number of neurons in each hidden layer. It provides the best parameters for each dataset. The aim is to identify the optimal set of parameters that exhibit good performance when presented with various inputs. Based on the results of the grid search, the number of neurons in the hidden layers, in order from the input layer, is 128, 64, 64, and 32. This configuration gives a higher performance compared to other parameter sets during training. Figure 18 and Figure 19 illustrate the learning curves for accuracy and loss using the attack data. For its classification model, the FNN showed performance through a cross-entropy of 0.378 and mean squared error of 0.0456, together with mean absolute error of 0.0836. An evaluation of the model exhibited balanced classification performance through 90.1% accuracy, as well as precision and recall, while maintaining an F1-score of 0.925.
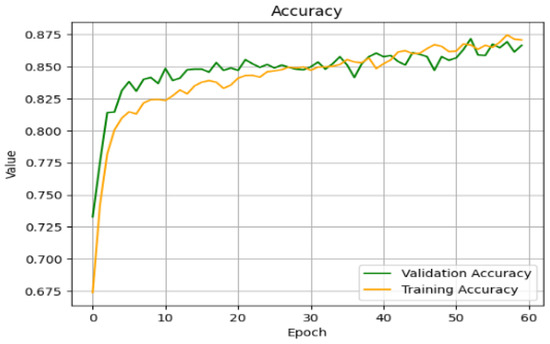
Figure 18.
Accuracy curve of training and validation of FNN model for classification.
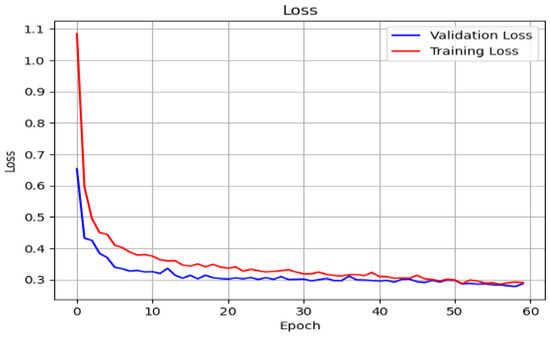
Figure 19.
Loss curve of training and validation of FNN model for classification.
4.5. LSTM Model for Classification
This LSTM model is designed for multi-class classification tasks on sequential data. The model is made up of six stacked LSTM layers, each containing 50 units. The first five LSTM layers maintain sequence return functionality to process the full temporal data patterns, while the final LSTM layer produces a fixed-length vector summary of the sequence. After each LSTM layer, the model applies a dropout layer with a dropout of 0.2 to increase generalization and decrease overfitting effects. The application of batch normalization directly follows each LSTM layer to stabilize and accelerate the training process. The first LSTM layer also incorporates L2 regularization to constrain the model’s complexity. The final output layer has three neurons while employing softmax activation to generate probability estimates of the three target classes. This architecture uses a balance between depth features and regularization and stability, which makes it an ideal fit for the classification of sequences. The performance of the LSTM classification model was exceptional, as it recorded a Brier score of 0.0346, along with 92% accuracy. The model reached a cross-entropy value of 0.1742 along with a loss of 0.1929 and MAE 0.0721, precision 93.34%, recall 92.19%, and PRC 0.9825. The learning curves for accuracy and loss with the attack data are illustrated in Figure 20 and Figure 21.
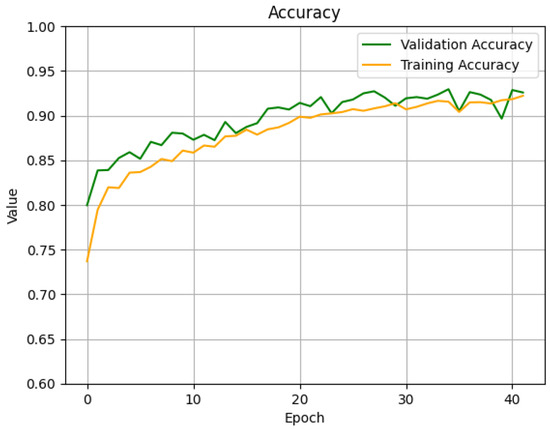
Figure 20.
Accuracy curve of training and validation of LSTM model for classification.
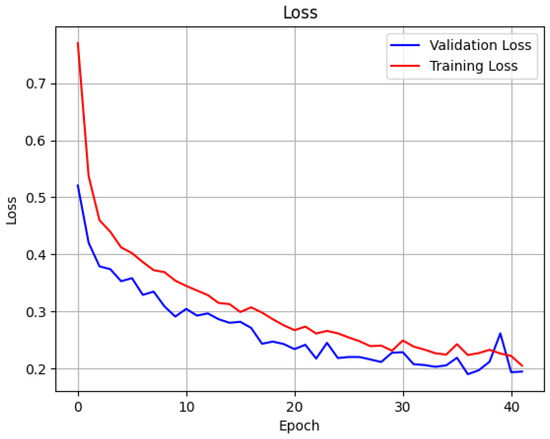
Figure 21.
Loss curve of training and validation of LSTM model for classification.
4.6. Final Combined Model
An FNN model was preferred over an LSTM model for the initial detection phase due to the complexity and time-consuming nature of LSTM models. However, the LSTM model was selected for classification purposes due to its high accuracy. To reduce resource usage, the system is designed such that the LSTM model is activated only if the FNN model detects an attack. Otherwise, the LSTM remains idle. Figure 22 illustrates the final model developed. The system enables complete allocation of computational resources to every model so that it can perform its processing tasks.
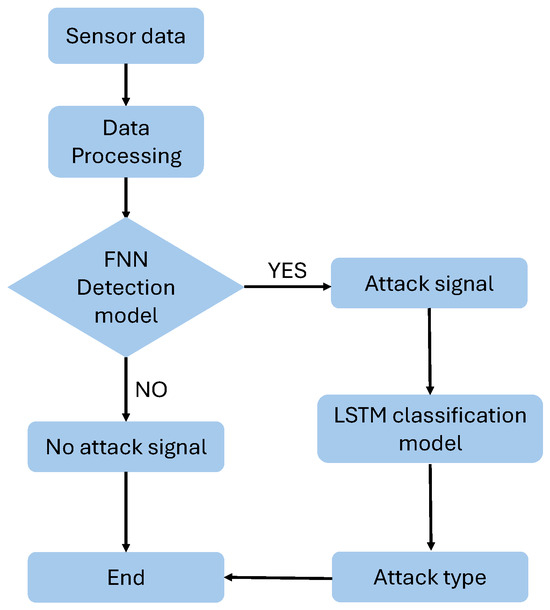
Figure 22.
Overall combined model.
5. Conclusions
Due to the evolution of the power sector with the integration of IoT technologies, islanded microgrids have become increasingly vulnerable to cyberattacks. Such attacks, particularly when targeting power converters, can cause severe system damage, making recovery highly challenging and underscoring the importance of reliable cybersecurity mechanisms. This study investigated the impact of cyberattacks on power converters in an islanded microgrid, along with the development of deep learning-based detection and classification models. Numerous experiments were conducted, and the resulting datasets were used to train models capable of identifying high-impact attacks. Results indicated that DoS attack had a relatively lower impact compared to three cases of FDI attack scenarios. Among the converters tested, solar inverters were the most vulnerable, while battery inverters showed the least susceptibility.
For attack detection, the FNN achieved an accuracy of 95.33%, while the LSTM achieved 96.60%. In classification tasks, the FNN attained 90.10% accuracy, and the LSTM reached 92.85%. A combined architecture was developed, consisting of an FNN-based detection model followed by an LSTM-based classification model to minimize resource usage and enable quick detection. The classification process using the LSTM model is initiated only after the FNN model detects an attack. The FNN model was chosen for detection due to its simplicity and faster response time compared to the LSTM, which is essential for rapid detection. The LSTM model excels in classification tasks as it is well suited for managing sequential data, achieving higher accuracy rates. Future work on this project will include hardware implementation and a comparison of the models with other built-in models.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.E., J.S. and K.K.; methodology, N.E.; software, N.E. and K.K.; validation, J.S. and K.K.; formal analysis, N.E., J.S. and K.K.; investigation, L.V.; resources, S.K., L.V. and C.W.; data curation, K.K. and J.S.; writing—original draft preparation, N.E.; writing—review and editing, K.K., J.S. and L.V.; visualization, K.K.; supervision, S.K., L.V. and C.W.; funding acquisition, C.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data used in this study were generated using a MATLAB simulation model developed by the authors. The model outputs were validated using historical data from the microgrid laboratory at the University of Moratuwa. These datasets are not publicly available but can be obtained from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Microgrid Laboratory of the University of Moratuwa for providing the data and technical details that were essential for validating the simulation model used in this study. We also thank the laboratory staff for their continuous support and assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AC | Alternating Current |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Networks |
| BMS | Battery Management System |
| DC | Direct Current |
| DNN | Deep Neural Networks |
| DoS | Denial of Service |
| EMI | Electromagnetic Interference |
| FDI | False Data Injection |
| FNN | Feedforward Neural Network |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| MPPT | Maximum Power Point Tracking |
| SCADA | Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition |
| SOC | State of Charge |
| SVM | Support Vector Machines |
| UoM | University of Moratuwa |
| VSI | Voltage Source Inverter |
References
- Wang, Y.; Deng, C.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Z. A Cyber-Resilient Control Approach for Islanded Microgrids under Hybrid Attacks. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2023, 147, 108889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canaan, B.; Colicchio, B.; Abdeslam, D.O. Microgrid Cyber-Security: Review and Challenges toward Resilience. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ye, J.; Guo, L.; Li, F.; Song, W. Vulnerability Assessments for Power-Electronics-Based Smart Grids. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Detroit, MI, USA, 11–15 October 2020; pp. 1702–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohee, A. Cyber War: The Hidden Side of the Russian-Ukrainian Crisis. SocArXiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stănculescu, M.; Deleanu, S.; Andrei, P.C.; Andrei, H. A Case Study of an Industrial Power Plant under Cyberattack: Simulation and Analysis. Energies 2021, 14, 2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beg, O.A.; Khan, A.A.; Rehman, W.U.; Hassan, A. A Review of AI-Based Cyber-Attack Detection and Mitigation in Microgrids. Energies 2023, 16, 7644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wei, Q.; Xie, Y. Research on Cascading Failures of Power Grid. In Advances in Technology and Engineering; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejabatkhah, F.; Li, Y.R.; Liang, H.; Ahrabi, R. Cyber-Security of Smart Microgrids: A Survey. Energies 2020, 14, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Sun, Q.; Wang, R.; Dong, C. Vulnerability Analysis of Secondary Control System When Microgrid Suffering from Sequential Denial-of-Service Attacks. IET Energy Syst. Integr. 2021, 4, 12026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Song, K.; Li, T.; Zhang, N. An Optimal DoS Attack Strategy Disturbing the Distributed Economic Dispatch of Microgrid. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2021, 2021, 5539829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Sun, Q.; Han, R.R.; Ma, D. Consensus-Based Secondary Frequency Control under Denial-of-Service Attacks of Distributed Generations for Microgrids. J. Frankl. Inst. 2019, 358, 2343–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ye, J.; Guo, L. Model-Based Cyber-Attack Detection for Voltage Source Converters in Island Microgrids. In Proceedings of the IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 10–14 October 2021; pp. 1413–1418. [Google Scholar]
- Hussien, A. Classification of Cybersecurity Attacks Using Machine Learning: A Comparative Study of Random Forest, Logistic Regression, and Neural Networks. 2025. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/391234103_Classification_of_Cybersecurity_Attacks_Using_Machine_Learning_A_Comparative_Study_of_Random_Forest_Logistic_Regression_and_Neural_Networks (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Avci, İ.; Koca, M. Cybersecurity Attack Detection Model, Using Machine Learning Techniques. Acta Polytech. Hung. 2023, 20, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doris, L.; Shad, R. Cyber Attack Prediction Using Machine Learning Algorithms. J. Cybersecur. 2024. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/385444981_CYBER_ATTACK_PREDICTION_USING_MACHINE_LEARNING_ALGORITHMS (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Hajira, A.B.; Gokulraj, S. Cyber Attacks Classification Using Supervised Machine Learning Techniques. J. Sens. IoT Health Sci. 2025, 3, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, A.; Mahmood, A.N.; Pickering, M. Modeling and Performance Evaluation of Stealthy False Data Injection Attacks on Smart Grid in the Presence of Corrupted Measurements. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 2017, 83, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barua, A.; Al Faruque, M.A. Hall Spoofing: A Non-Invasive DoS Attack on Grid-Tied Solar Inverter. In SEC’20: Proceedings of the 29th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 20), Online, 12–14 August 2020; USENIX Association: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2020; pp. 1273–1290. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Li, F.; Zhang, J.; Ye, J.; Song, W.; Mantooth, A. Data-Driven Cyberattack Detection for Photovoltaic (PV) Systems through Analyzing Micro-PMU Data. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Detroit, MI, USA, 11–15 October 2020; pp. 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohiuddin, S.M.; Qi, J. Attack Resilient Distributed Control for AC Microgrids with Distributed Robust State Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Texas Power and Energy Conference (TPEC), College Station, TX, USA, 2–5 February 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Houdt, G.; Mosquera, C.; Nápoles, G. A Review on the Long Short-Term Memory Model. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2020, 53, 5929–5955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koduru, S.; Machina, V.S.P.; Madichetty, S. Cyber Attacks in Cyber-Physical Microgrid Systems: A Comprehensive Review. Energies 2023, 16, 4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souri, N.; Mehrizi-Sani, A. Hybrid Machine Learning Approach for Cyberattack Mitigation in DC Microgrids. In Proceedings of the IECON 2024—50th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Chicago, IL, USA, 3–6 November 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, M.; Kavousi-Fard, A.; Dabbaghjamanesh, M.; Avatefipour, O. Deep learning based method for false data injection attack detection in AC smart islands. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2020, 14, 5756–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Yang, H.; Zheng, M. Using modified prediction interval-based machine learning model to mitigate data attack in microgrid. Int. J. Elec. Power Energy Syst. 2021, 129, 106847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, M.S.S.; Karegar, H.K. Detection of False Data Injection Attacks Using Cross Wavelet Transform and Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 11th Smart Grid Conference (SGC), Tabriz, Iran, 7–9 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mohiuddin, S.M.; Qi, J.; Fung, S.; Huang, Y.; Tang, Y. Deep learning based multi-label attack detection for distributed control of AC microgrids. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Control, and Computing Technologies for Smart Grids (SmartGridComm), Aachen, Germany, 25–28 October 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).