YOLO-HDEW: An Efficient PCB Defect Detection Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
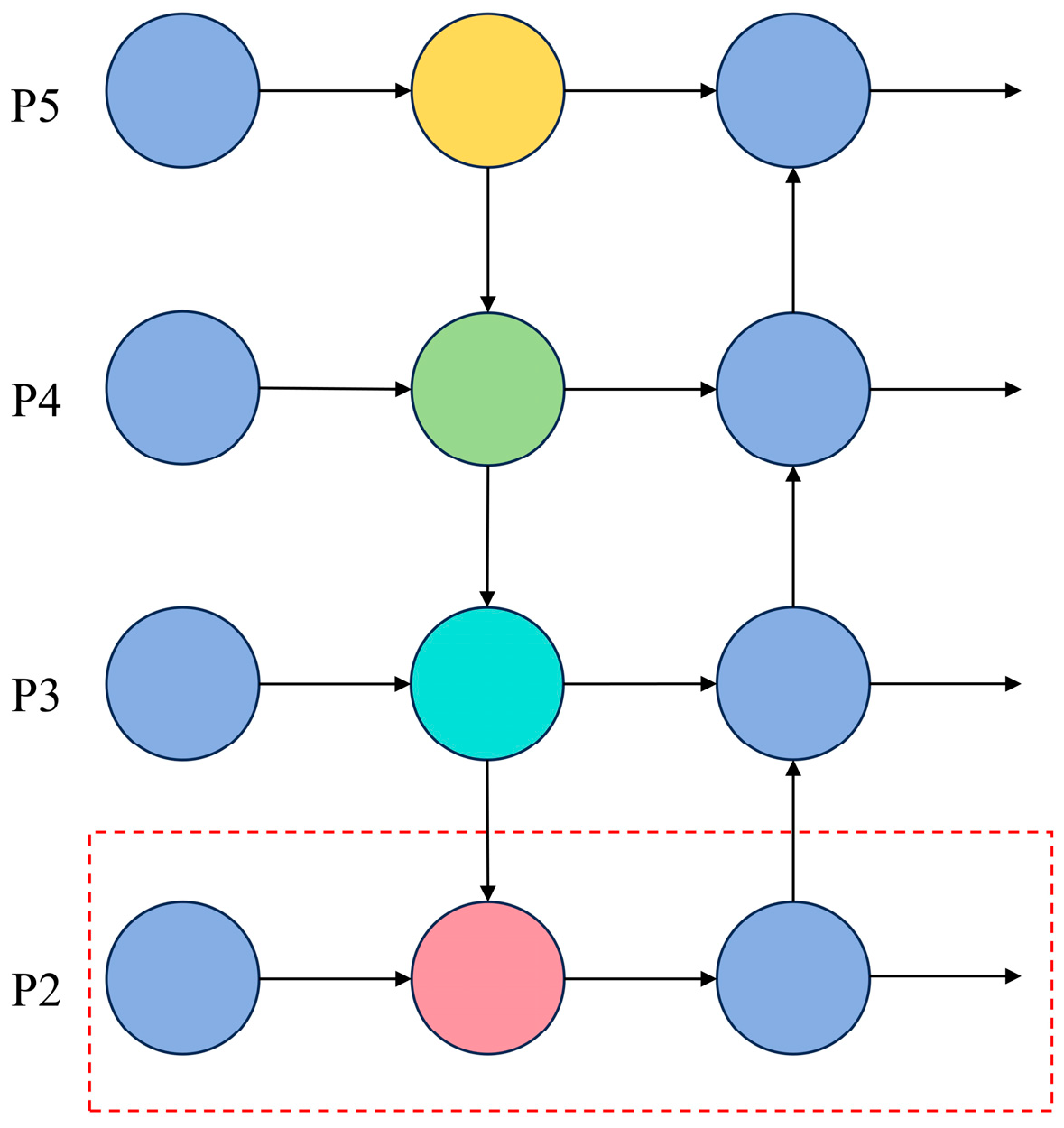
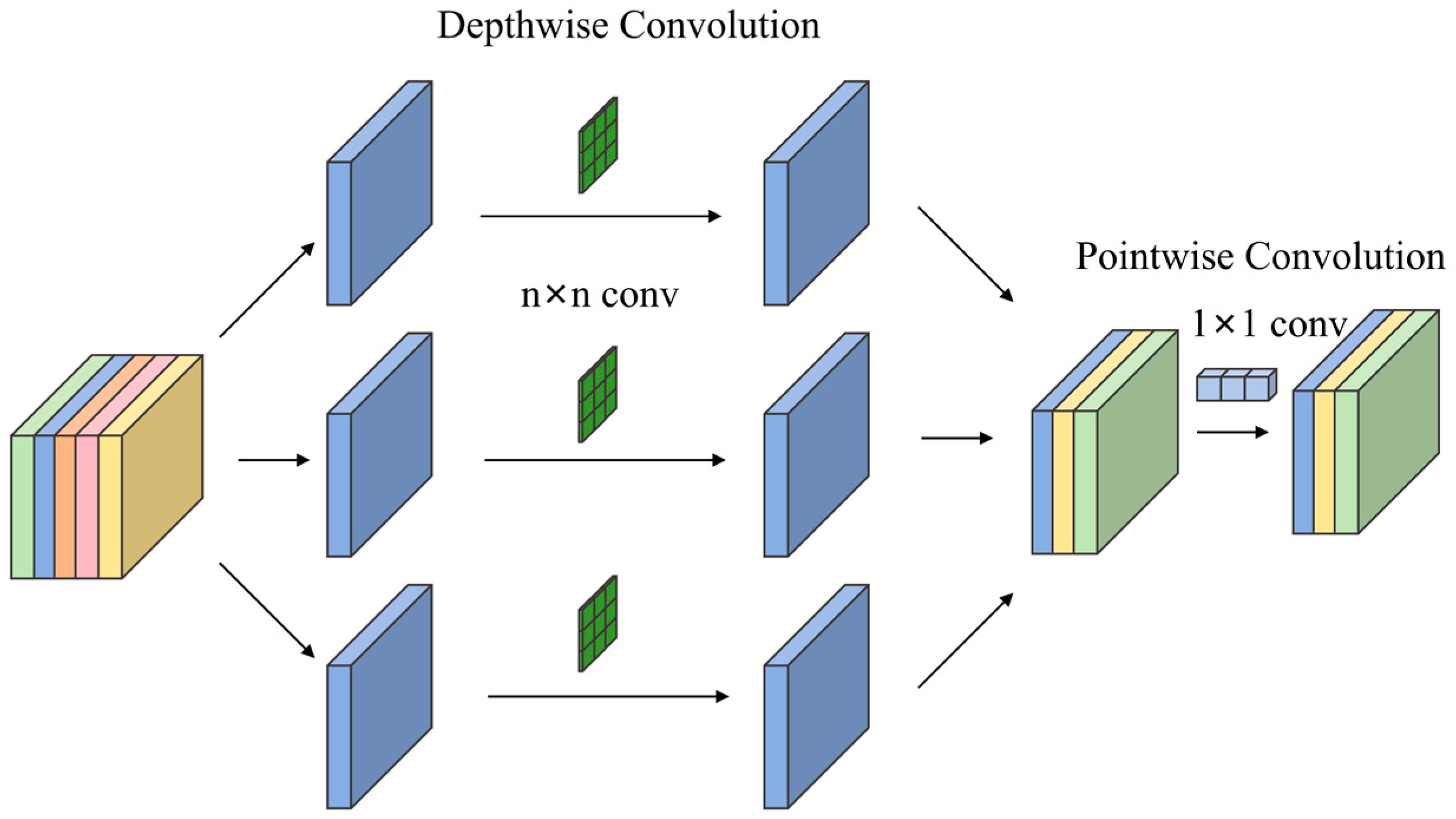
- A high-resolution detection branch (P2) was constructed, enabling the effective fusion of shallow-layer feature maps with deep-layer feature maps within the neck network. This significantly enhances the network’s perception capability for small targets. Concurrently, Depthwise Separable Convolution (DSConv) was employed for downsampling operations, effectively reducing model parameter complexity.
- (2)
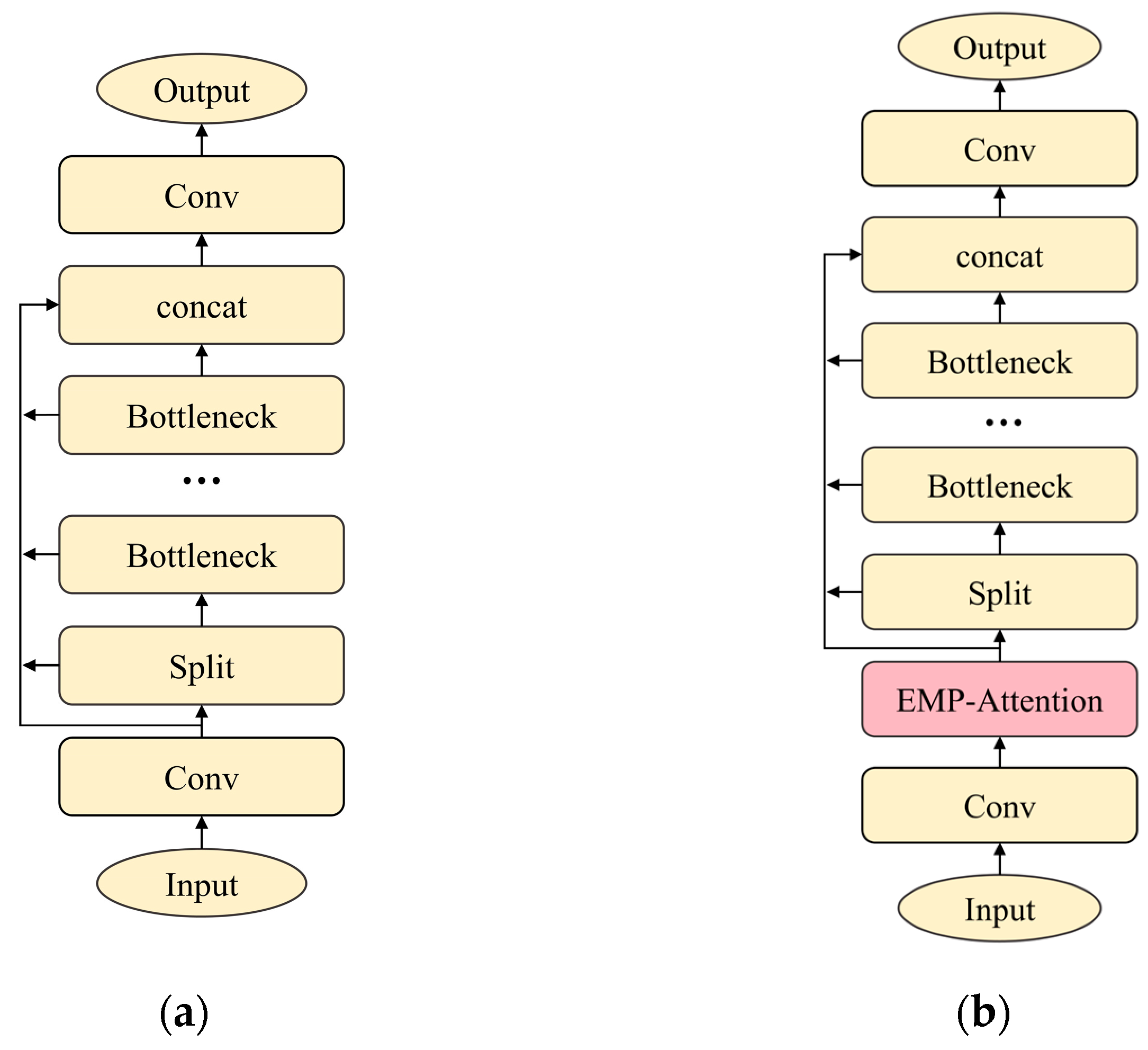
- The Edge-enhanced Multi-scale Parallel Attention mechanism (EMP-Attention) was proposed. It achieves effective feature enhancement through the multi-level collaboration of a Multi-scale Spatial Attention module, a Channel Attention module, and an Edge Feature Enhancement module.
- (3)
- The Wise-IoU (W-IoU) loss function, which integrates a dynamic non-monotonic focusing mechanism, replaces C-IoU as the updated bounding box regression loss, resulting in enhanced model detection performance.
- (4)
- Comparative experiments were conducted on the PKU-Market-PCB and DeepPCB datasets. The experimental results show that, compared to other models, YOLO-HDEW achieves higher detection accuracy.
2. Methods
2.1. YOLO-HDEW Model
2.1.1. Detection Probe Improvements
- (1)
- Small target detection layer
- (2)
- Depthwise separable convolution
2.1.2. EMP-Attention
2.1.3. Improvement of C2f
2.1.4. W-IoU
3. Results
3.1. Subsection
3.2. Experimental Setup
3.3. Evaluation Indicators
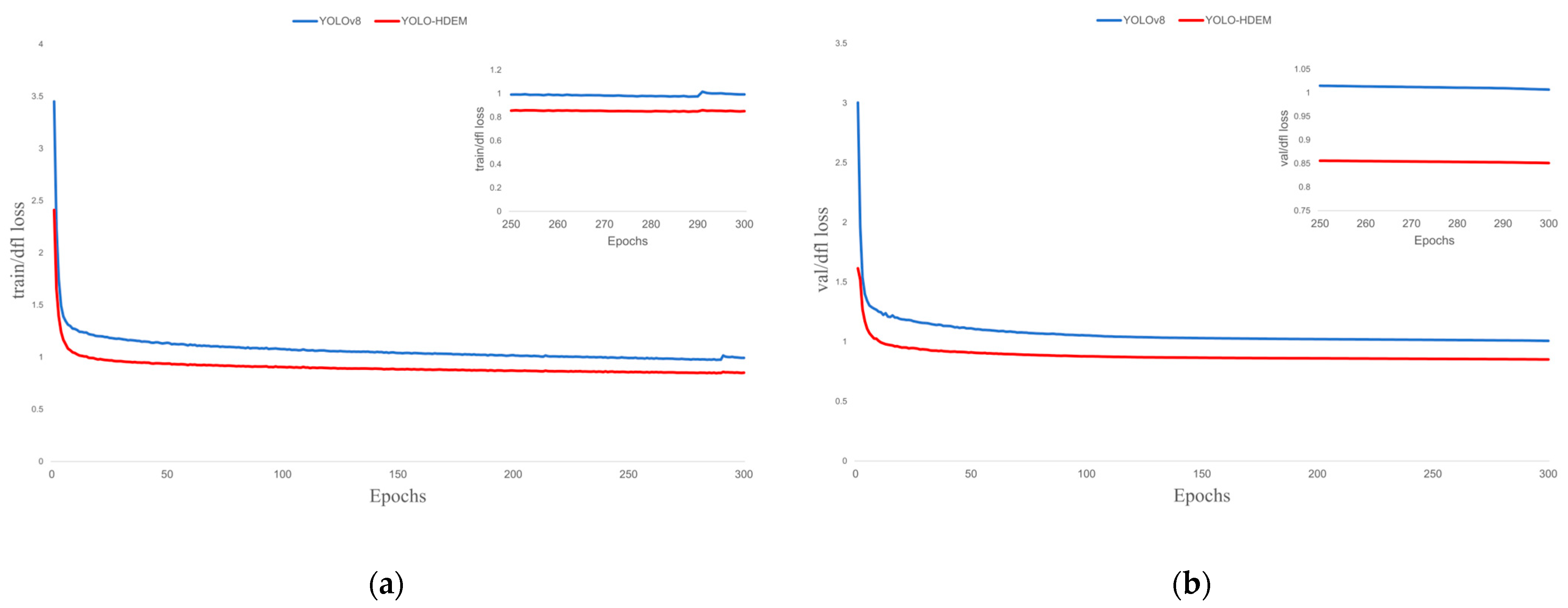
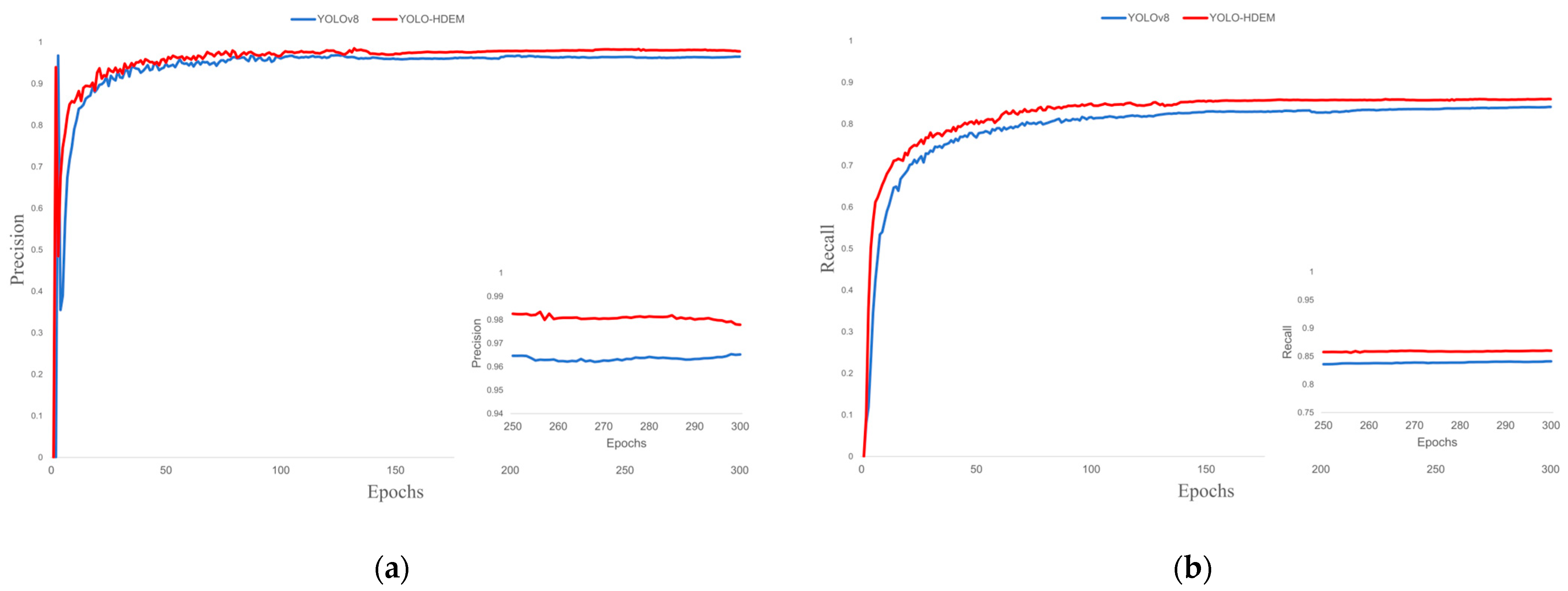
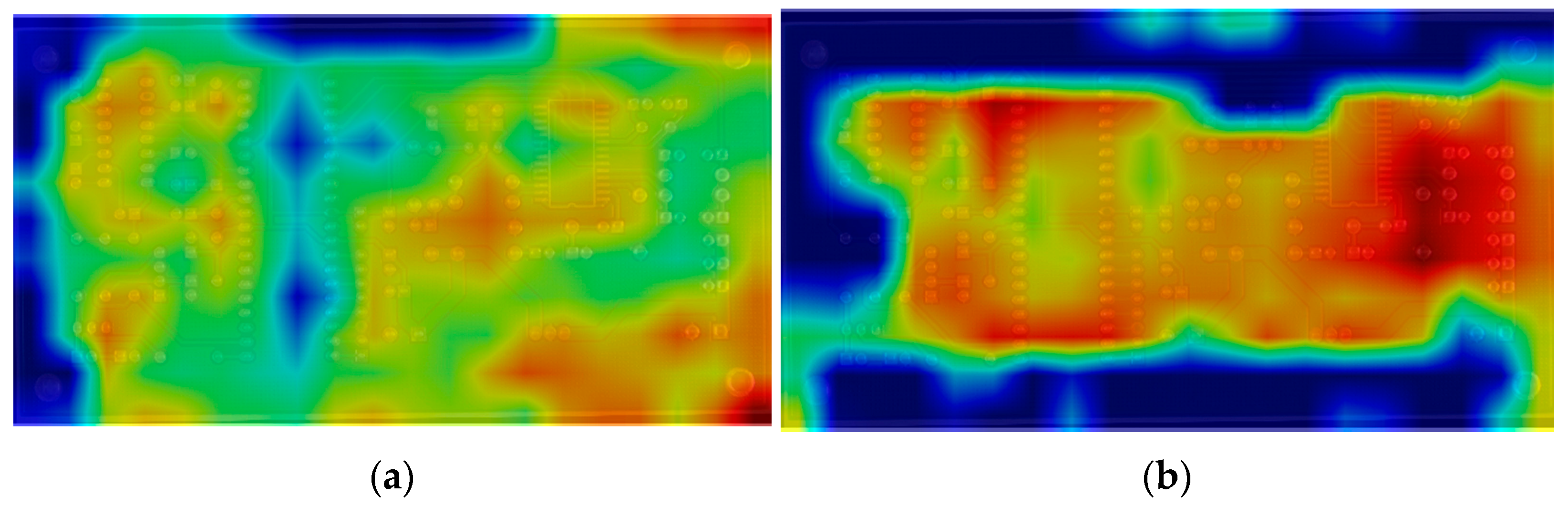
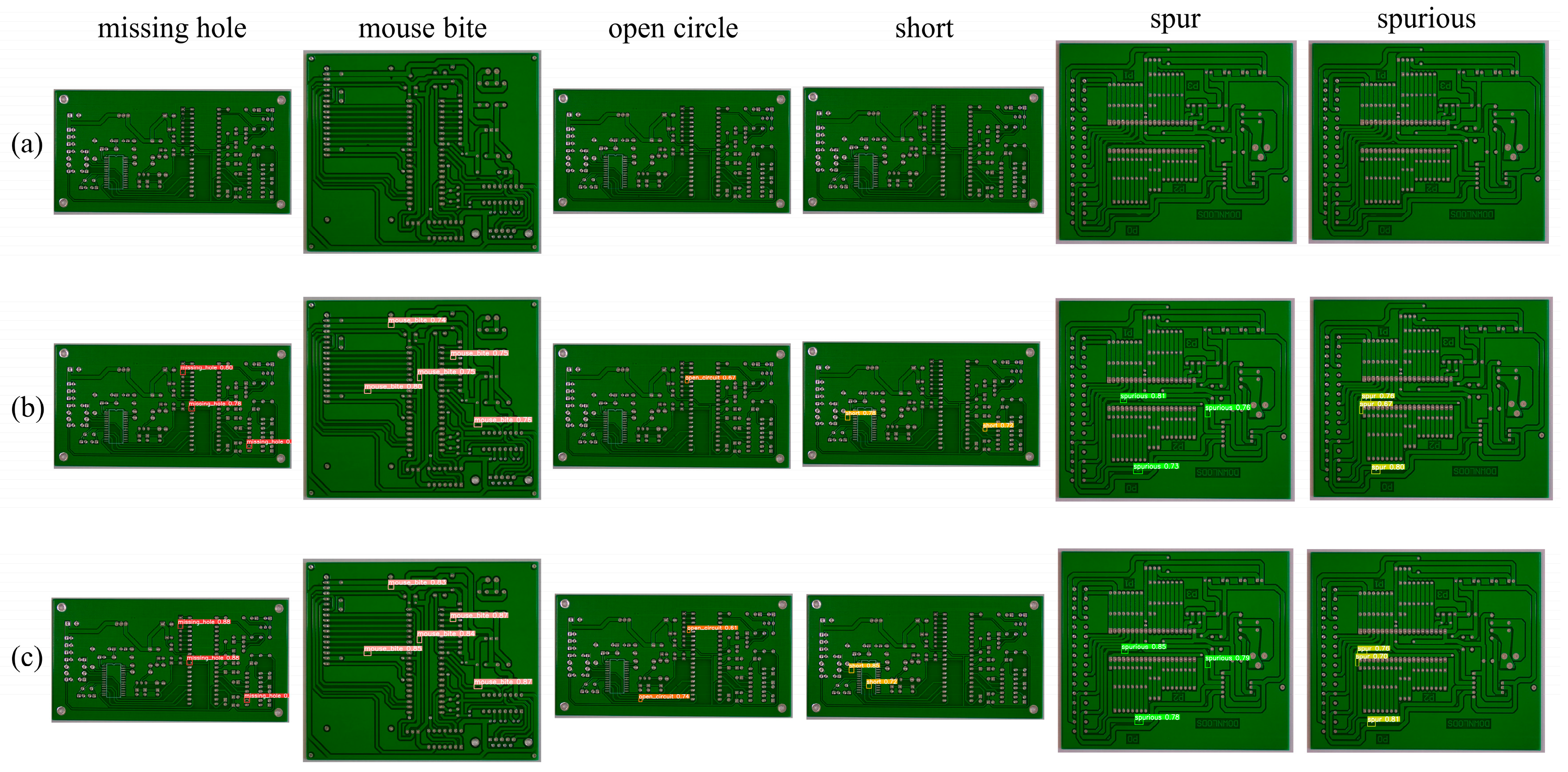
3.4. Analysis of Experimental Results
3.4.1. Ablation Experiments
3.4.2. Comparative Test
- (1)
- Comparative Experiments of Different Attention Mechanisms
- (2)
- Comparison experiments of different loss functions
- (3)
- Comparison experiments of various models
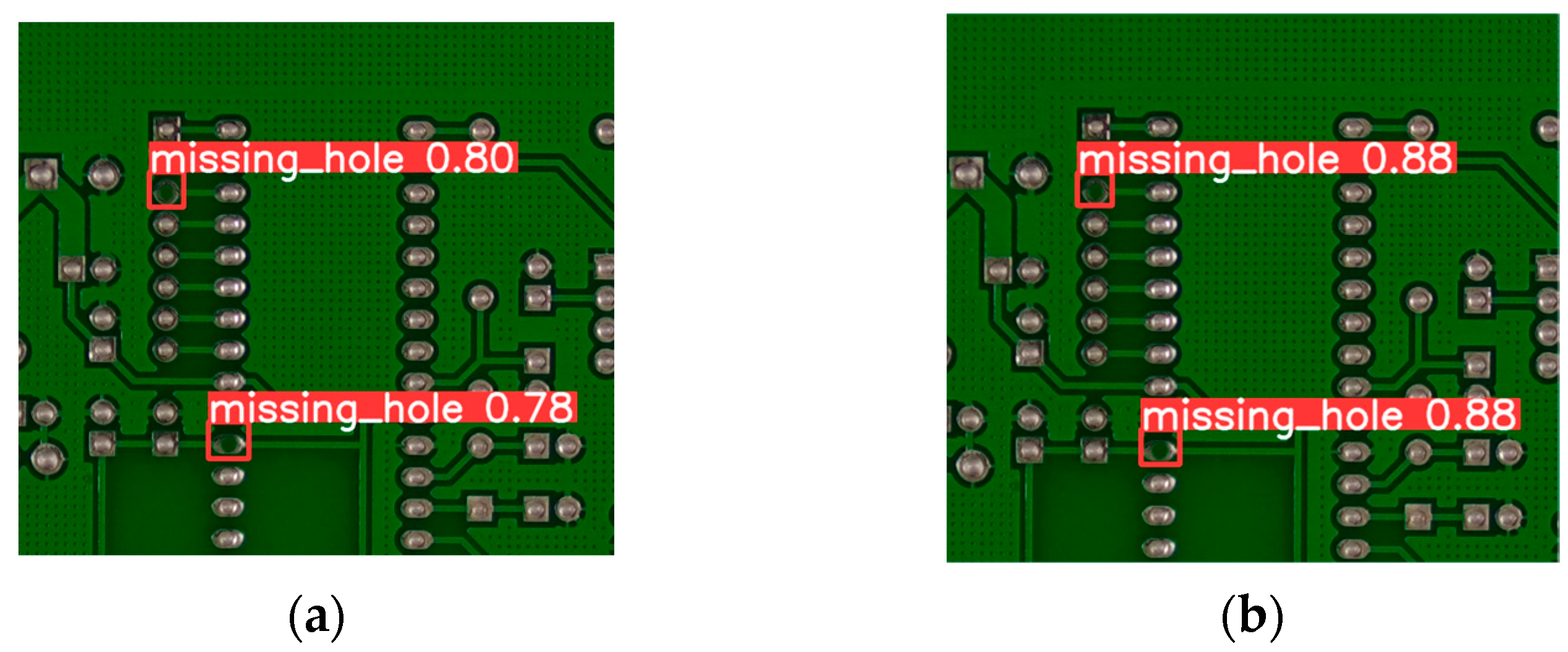
3.4.3. Model Performance Validation
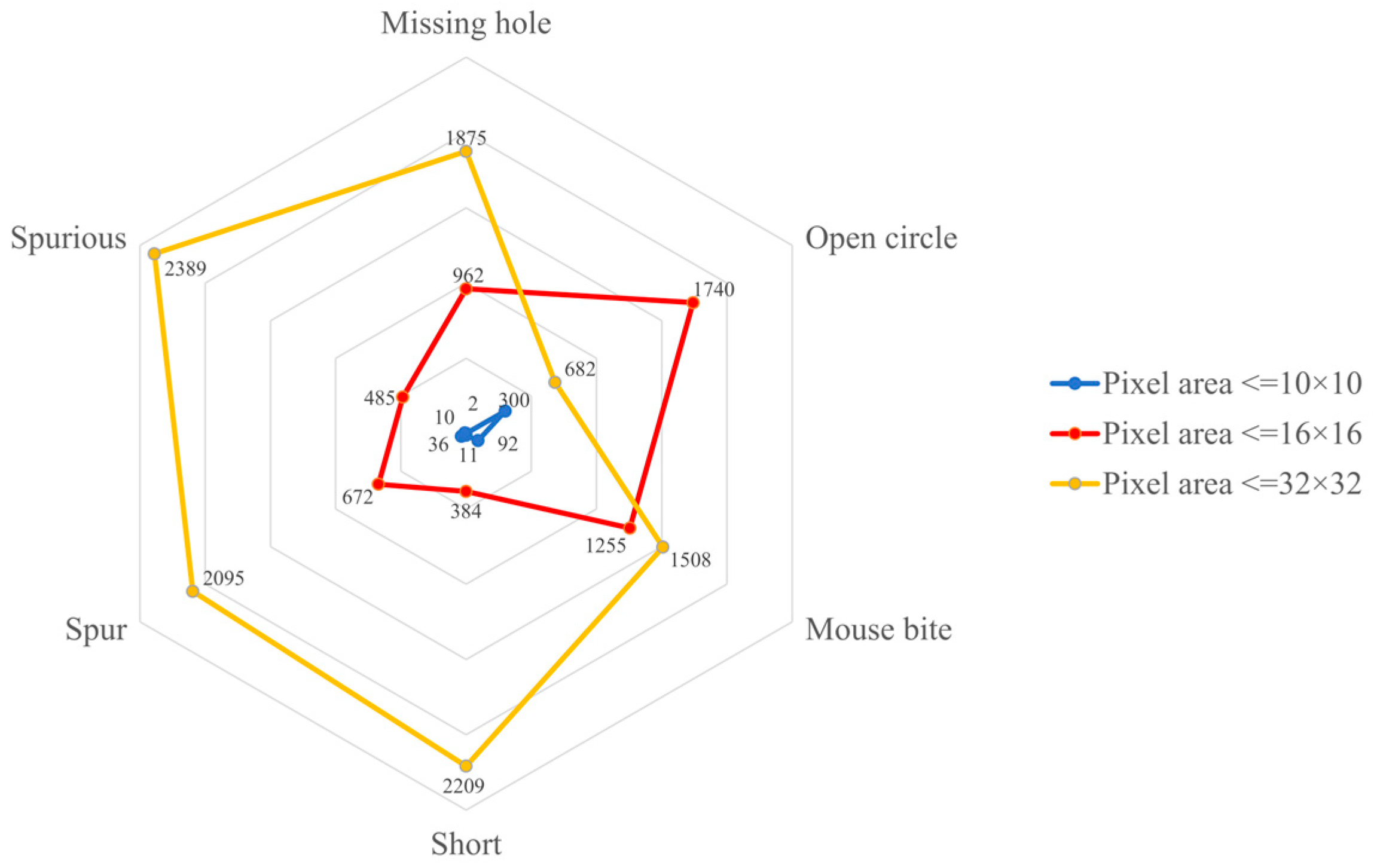
3.4.4. Experimental Results of DeepPCB
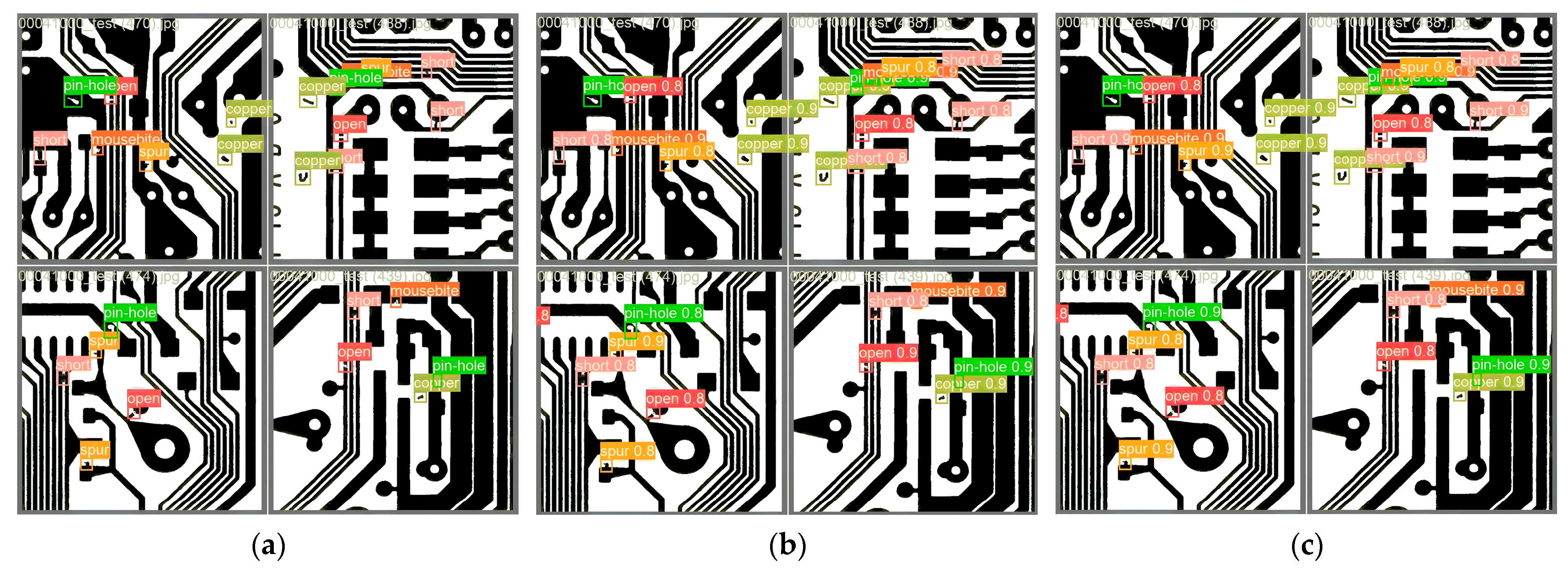
3.4.5. Experimental Results of NEU-DET
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Li, C. State of the Art in Defect Detection Based on Machine Vision. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Technol. 2022, 9, 661–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulbure, A.-A.; Tulbure, A.-A.; Dulf, E.-H. A Review on Modern Defect Detection Models Using DCNNs–Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. J. Adv. Res 2022, 35, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Yuan, M.; Zhang, J.; Ding, G.; Qin, S. Review of vision-based defect detection research and its perspectives for printed circuit board. J. Manuf. Syst. 2023, 70, 557–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Chen, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, Z.; Wei, H. An Efficient Lightweight Convolutional Neural Network for Industrial Surface Defect Detection. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 10651–10677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, L.; Li, C. CS-ResNet: Cost-Sensitive Residual Convolutional Neural Network for PCB Cosmetic Defect Detection. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 185, 115673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Chang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xu, H.; Chen, H.; Luo, Z. A survey of defect detection applications based on generative adversarial networks. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 113493–113512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adibhatla, V.A.; Shieh, J.S.; Abbod, M.F.; Chih, H.C.; Hsu, C.C.; Cheng, J. Detecting Defects in PCB Using Deep Learning via Convolution Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 13th International Microsystems, Packaging, Assembly and Circuits Technology Conference (IMPACT), Taipei, Taiwan, 24–26 October 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kaya, G.U. Development of hybrid optical sensor based on deep learning to detect and classify the micro-size defects in printed circuit board. Measurement 2023, 206, 112247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Q. Printed circuit board quality detection method integrating lightweight network and dual attention mechanism. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 87617–87629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Li, Q.; Zhou, Y.; He, X. PCB Defects Target Detection Combining Multi-Scale and Attention Mechanism. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 123, 106359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, D.; He, S.; Tang, J. Divide-and-Conquer: Confluent Triple-Flow Network for RGB-T Salient Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2025, 47, 1958–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Chang, J.; Wang, K.J.P.C.S. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 183, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X. Development of a real-time Printed Circuit board (PCB) visual inspection system using You Only Look Once (YOLO) and fuzzy logic algorithms. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2023, 45, 4139–4145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Sun, S.; Hu, J. Apple Detection During Different Growth Stages in Orchards Using the Improved YOLO-V3 Model. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 157, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Wan, F.; Lei, G.; Xu, L.; Xu, C.; Xiong, Y. YOLO-MBBi: PCB surface defect detection method based on enhanced YOLOv5. Electronics 2023, 12, 2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Dang, Z. Fast PCB defect detection method based on FasterNet backbone network and CBAM attention mechanism integrated with feature fusion module in improved YOLOv7. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 95092–95103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Zhou, Y.; Ren, X.; Zhi, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H. YOLO-HMC: An improved method for PCB surface defect detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Sun, G.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z. Automated Detection and Segmentation of Tunnel Defects and Objects Using YOLOv8-CM. Tunn. Underground Space Technol. 2024, 150, 105857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhao, F.; Chen, L. Defect Detection Network in PCB Circuit Devices Based on GAN Enhanced YOLOv11. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.06879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Qi, L.; Qin, H.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8759–8768. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, Z.Y.; Niu, Z. CNN with Depthwise Separable Convolutions and Combined Kernels for Rating Prediction. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 170, 114528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Z.; Yu, R. Wise-IoU: Bounding box regression loss with dynamic focusing mechanism. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.10051. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.-H.; Zhang, F.; Li, J.; Xie, Y. Attention Mechanisms in Computer Vision: A Survey. Comput. Vis. Media 2022, 8, 331–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Yang, M.; Zhang, L.; Wei, Y.; Liu, J. Delving Deep into Spatial Pooling for Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 121, 108159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, Z. IEAM: Integrating Edge Enhancement and Attention Mechanism with Multi-Path Complementary Features for Salient Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wei, P.; Zhang, M.; Liu, H. HRIPCB: A challenging dataset for PCB defects detection and classification. J. Eng. 2020, 2020, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezatofighi, H.; Tsoi, N.; Gwak, J.; Sadeghian, A.; Reid, I.; Savarese, S. Generalized Intersection Over Union: A Metric and a Loss for Bounding Box Regression. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 658–666. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.-F.; Ren, W.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, Z.; Wang, L.; Tan, T. Focal and Efficient IOU Loss for Accurate Bounding Box Regression. Neurocomputing 2021, 506, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevorgyan, Z. SIoU Loss: More Powerful Learning for Bounding Box Regression. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.12740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Dai, L.; Li, G.; Liu, H. TDD-net: A tiny defect detection network for printed circuit boards. CAAI Trans. Intell. Technol. 2019, 4, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



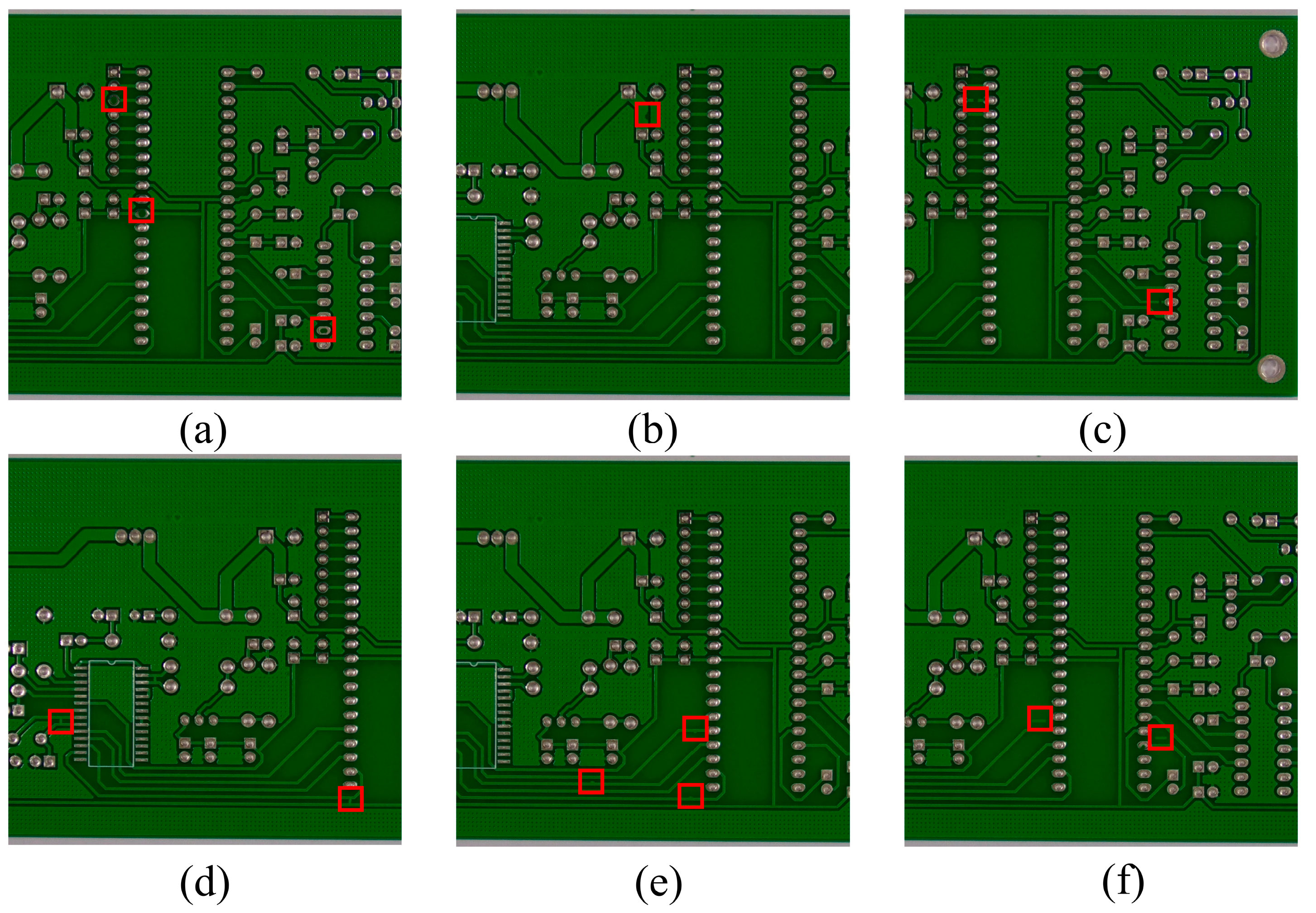
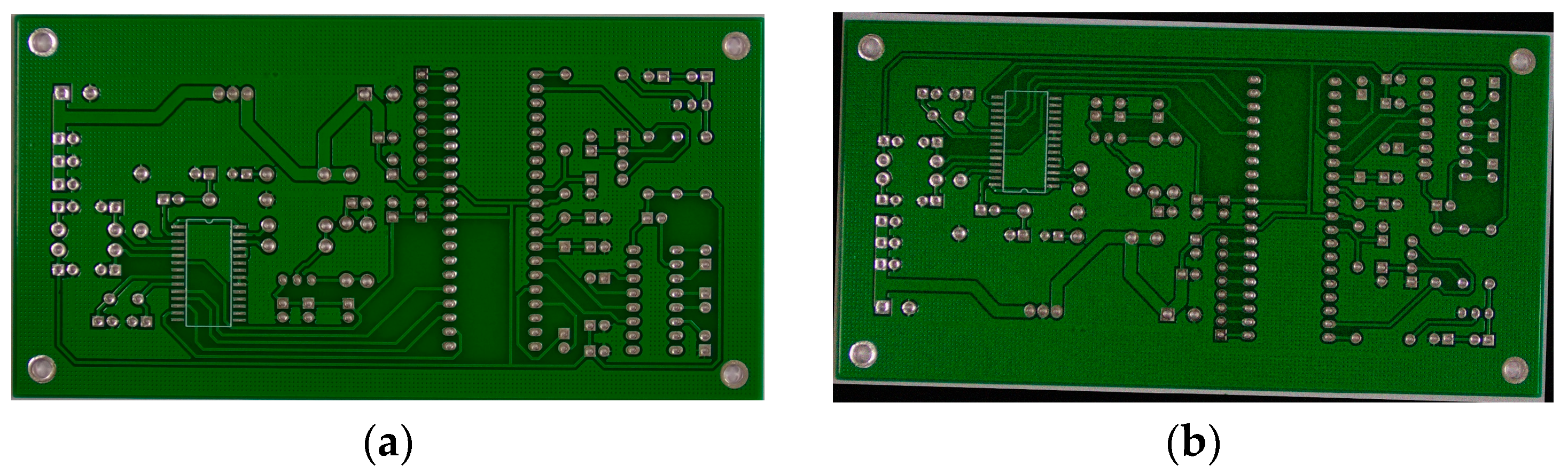
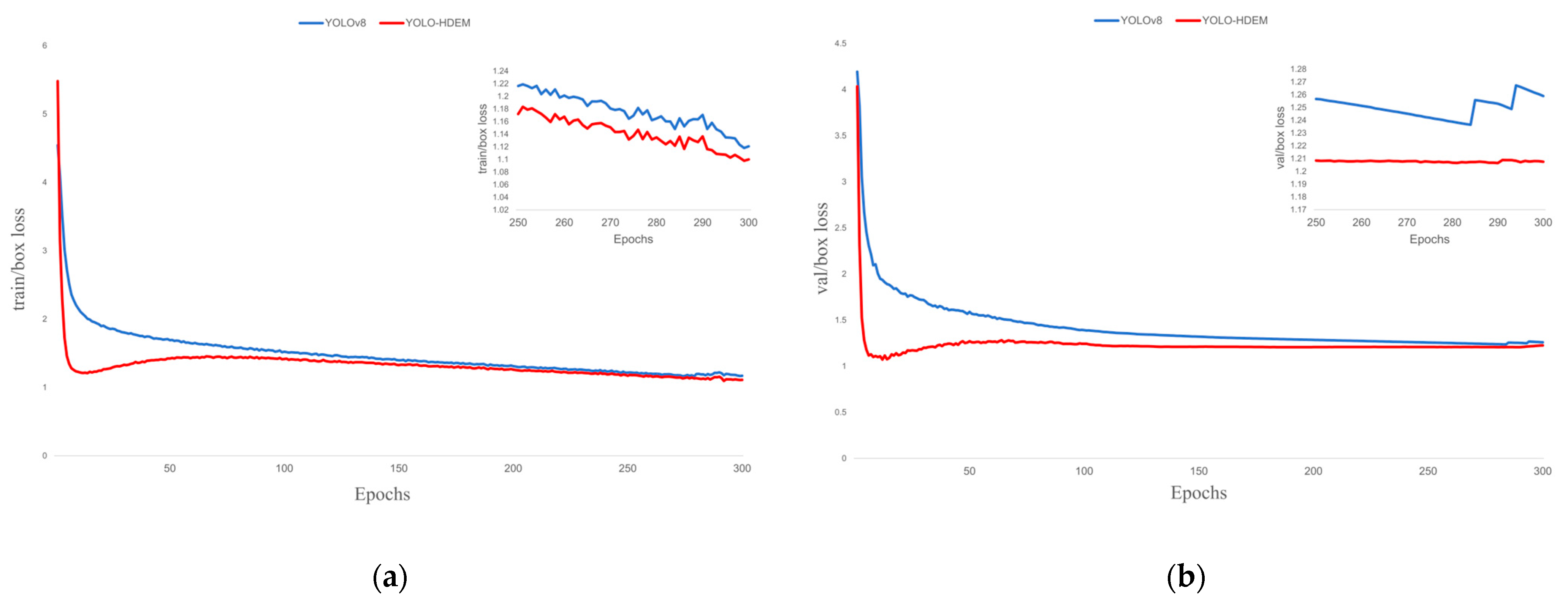
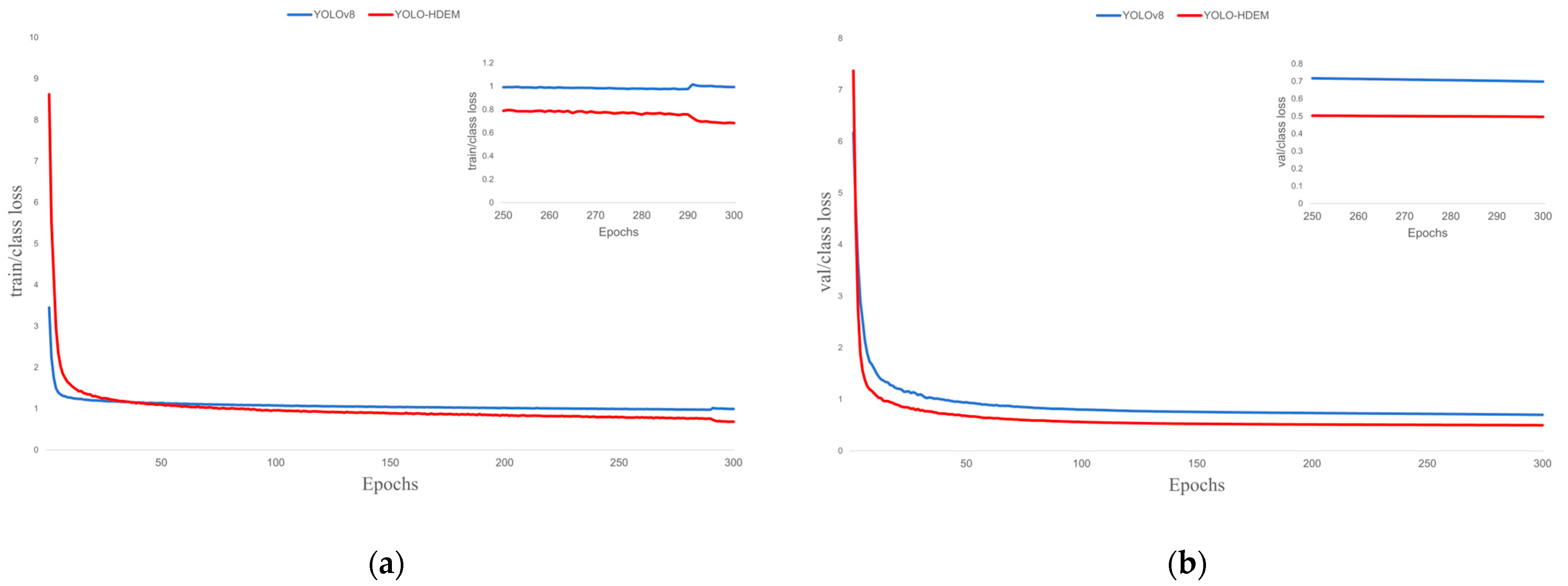



| Parameters | Setup |
|---|---|
| Epochs | 300 |
| Imgsize | 640 |
| Batch Size | 16 |
| Optimizer | SGD |
| Learning Rate | 0.01 |
| Weight-Decay | 0.0005 |
| +P2 | +DSConv | +EMP | +W-IoU | P | R | mAP @0.5 | mAP @0.5:0.95 | Params (M) | Volume (Mb) | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.966 | 0.893 | 0.891 | 0.598 | 3.106 | 6.3 | 79.4 | ||||
| √ | 0.969 | 0.901 | 0.894 | 0.605 | 3.674 | 7.3 | 76.8 | |||
| √ | 0.965 | 0.901 | 0.893 | 0.599 | 2.553 | 5.2 | 84.3 | |||
| √ | 0.972 | 0.925 | 0.907 | 0.619 | 3.311 | 6.6 | 76.7 | |||
| √ | 0.974 | 0.917 | 0.906 | 0.617 | 3.213 | 6.4 | 78.8 | |||
| √ | √ | 0.968 | 0.901 | 0.894 | 0.605 | 3.243 | 6.5 | 78.4 | ||
| √ | √ | √ | 0.976 | 0.912 | 0.898 | 0.615 | 3.408 | 6.9 | 77.1 | |
| √ | √ | √ | √ | 0.981 | 0.916 | 0.903 | 0.617 | 3.461 | 7.1 | 76.9 |
| Models | P | R | mAP@0.5 | mAP@0.5:0.95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8n | 0.966 | 0.921 | 0.891 | 0.598 |
| YOLOv8n + SE | 0.967 | 0.917 | 0.898 | 0.611 |
| YOLOv8n + CA | 0.974 | 0.922 | 0.897 | 0.617 |
| YOLOv8n + CBAM | 0.970 | 0.924 | 0.883 | 0.58 |
| YOLOv8n + EMP | 0.972 | 0.925 | 0.907 | 0.619 |
| Models | P | R | mAP@0.5 | mAP@0.5:0.95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-IoU | 0.963 | 0.892 | 0.894 | 0.616 |
| G-IoU | 0.966 | 0.897 | 0.893 | 0.615 |
| E-IoU | 0.969 | 0.896 | 0.894 | 0.611 |
| S-IoU | 0.972 | 0.896 | 0.895 | 0.613 |
| W-IoU | 0.974 | 0.917 | 0.906 | 0.617 |
| Models | P | R | mAP @0.5 | mAP @0.5:0.95 | Params (M) | Volume (Mb) | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster R-CNN | 0.923 | 0.844 | 0.855 | 0.561 | 43.319 | 92.1 | 12.0 |
| TDD-Net | 0.958 | 0.897 | 0.901 | 0.597 | 4.056 | 8.9 | 59.3 |
| YOLOX-tiny | 0.908 | 0.609 | 0.716 | 0.553 | 3.057 | 6.2 | 82.7 |
| YOLOv3 | 0.852 | 0.782 | 0.754 | 0.557 | 13.021 | 28.3 | 59.9 |
| YOLOv5 | 0.932 | 0.864 | 0.910 | 0.552 | 7.156 | 14.7 | 89.3 |
| YOLOv7 | 0.961 | 0.910 | 0.892 | 0.601 | 6.626 | 13.6 | 65.7 |
| YOLOv8 | 0.966 | 0.893 | 0.891 | 0.598 | 3.106 | 6.3 | 79.4 |
| YOLOv11 | 0.968 | 0.905 | 0.898 | 0.615 | 3.591 | 7.4 | 74.6 |
| Ours | 0.981 | 0.916 | 0.903 | 0.617 | 3.461 | 7.1 | 76.9 |
| Models | P | R | mAP@0.5 | mAP@0.5:0.95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster R-CNN | 0.921 | 0.825 | 0.829 | 0.533 |
| TDD-Net | 0.962 | 0.937 | 0.913 | 0.601 |
| YOLOX-tiny | 0.923 | 0.719 | 0.806 | 0.577 |
| YOLOv3 | 0.827 | 0.790 | 0.739 | 0.542 |
| YOLOv5 | 0.937 | 0.898 | 0.902 | 0.550 |
| YOLOv7 | 0.968 | 0.963 | 0.937 | 0.611 |
| YOLOv8 | 0.972 | 0.953 | 0.926 | 0.786 |
| YOLOv11 | 0.981 | 0.964 | 0.988 | 0.796 |
| Ours | 0.973 | 0.971 | 0.989 | 0.801 |
| Models | P | R | mAP@0.5 | mAP@0.5:0.95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster R-CNN | 0.673 | 0.696 | 0.714 | 0.404 |
| TDD-Net | 0.662 | 0.619 | 0.701 | 0.417 |
| YOLOX-tiny | 0.647 | 0.611 | 0.708 | 0.437 |
| YOLOv3 | 0.677 | 0.681 | 0.729 | 0.410 |
| YOLOv5 | 0.655 | 0.688 | 0.724 | 0.394 |
| YOLOv7 | 0.664 | 0.653 | 0.720 | 0.418 |
| YOLOv8 | 0.660 | 0.753 | 0.814 | 0.463 |
| YOLOv11 | 0.674 | 0.716 | 0.796 | 0.459 |
| Ours | 0.683 | 0.745 | 0.835 | 0.490 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, C.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, Y.; Qi, Q.; Wang, Z.; Hu, K. YOLO-HDEW: An Efficient PCB Defect Detection Model. Electronics 2025, 14, 3383. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14173383
Song C, Zhou Y, Ma Y, Qi Q, Wang Z, Hu K. YOLO-HDEW: An Efficient PCB Defect Detection Model. Electronics. 2025; 14(17):3383. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14173383
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Chuanwang, Yuanteng Zhou, Yinghao Ma, Qingshuo Qi, Zhaoyu Wang, and Keyong Hu. 2025. "YOLO-HDEW: An Efficient PCB Defect Detection Model" Electronics 14, no. 17: 3383. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14173383
APA StyleSong, C., Zhou, Y., Ma, Y., Qi, Q., Wang, Z., & Hu, K. (2025). YOLO-HDEW: An Efficient PCB Defect Detection Model. Electronics, 14(17), 3383. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14173383






