A Configurable Parallel Architecture for Singular Value Decomposition of Correlation Matrices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The SVD Algorithm
2.1. SVD of Correlation Matrices
2.2. SVD Using Jacobi’s Algorithm
2.3. CORDIC Algorith
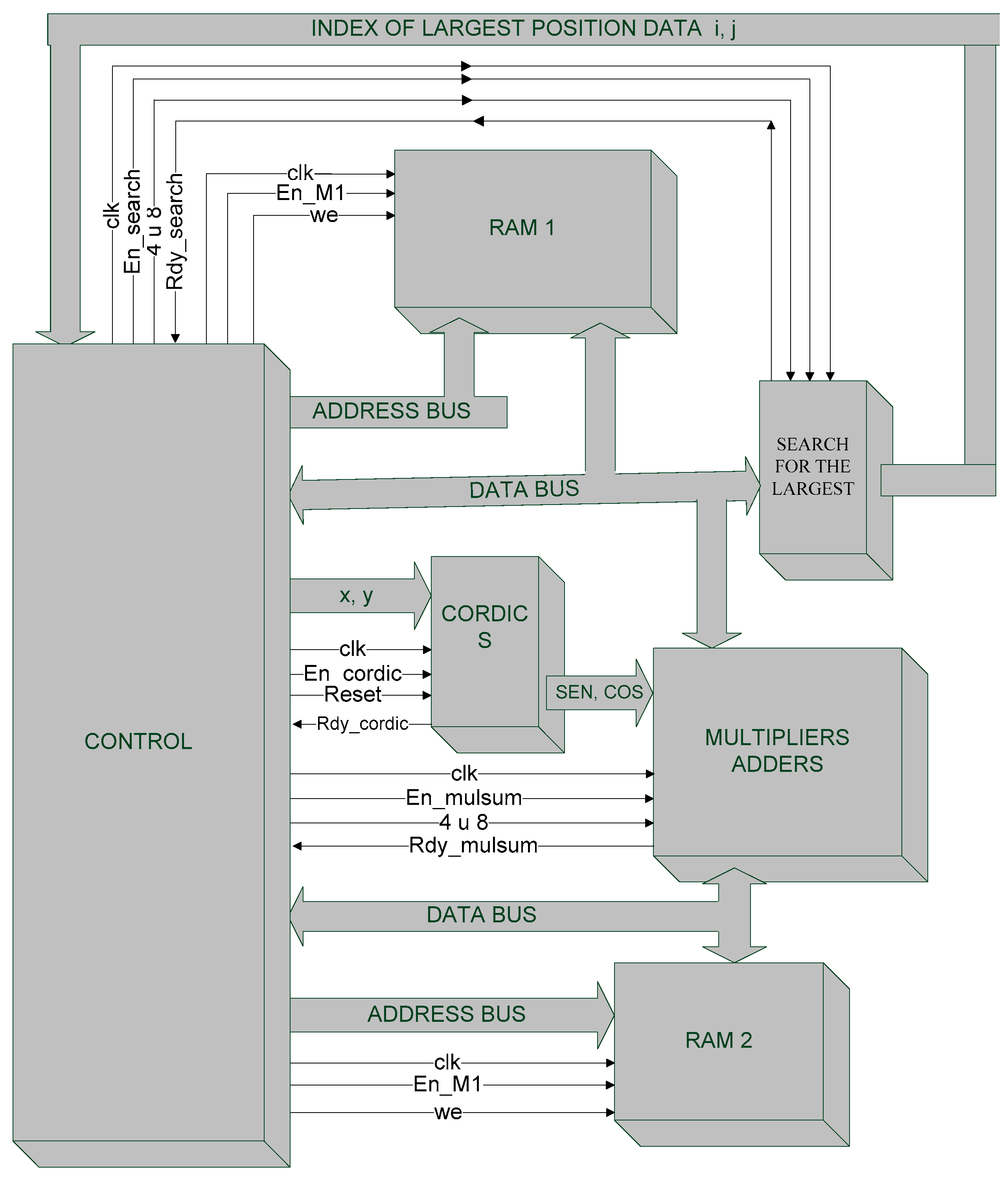
3. Architecture for SVD
| Algorithm 1: Jacobi Meets CORDIC |
| If enable = 1 and rising edge of clock: |
| If reset = 1: |
| Initialize variables and states |
| Else: |
| Repeat up to 50 times: |
| 1. Find the pair (i, j) with the largest off-diagonal contribution (using search_mem) |
| 2. Compute the sine and cosine of the corresponding rotation angle (using tg_sen) |
| 3. Apply the rotation: |
| - Update rows i and j in the original matrix (memo1) |
| - Update columns i and j (memo2) |
| - Merge the updated columns back into the original matrix |
| End repeat |
| Final outputs: |
| - eig_val ← most recently computed value |
| - eig_vec ← most recently computed vector |
4. Implementation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, H.; Kang, C.C.; Xi, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Ding, Y. FPGA-Optimized Hardware Accelerator for Fast Fourier Transform and Singular Value Decomposition in AI. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Computing Innovation, Intelligence, Technologies and Education (CIITE), Sepang, Malaysia, 5–7 September 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y. A distributed and secure algorithm for computing dominant SVD based on projection splitting. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.03461. [Google Scholar]
- Laganà, F.; Bibbò, L.; Calcagno, S.; De Carlo, D.; Pullano, S.A.; Pratticò, D.; Angiulli, G. Smart electronic device-based monitoring of SAR and temperature variations in indoor human tissue interaction. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Hasan, R.A.; Hamza, E.K. An Improved Intrusion Detection System Using Machine Learning with Singular Value Decomposition and Principal Component Analysis. Int. J. Intell. Eng. Syst. 2023, 16, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokane, O.; Teman, A.; Jha, A.; SL, G.P.; Raut, G.; Lokhande, M.; Chand, S.V.J.; Dewangan, T.; Vishvakarma, S.K. CORDIC Is All You Need. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.11685. [Google Scholar]
- Forsythe, G.E.; Henrici, P. The cyclic Jacobi method for computing the principal values of a complex matrix. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 1960, 94, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volder, J.E. The CORDIC trigonometric computing technique. IRE Trans. Electron. Comput. 2009, EC-8, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, T.D.; Maciejewski, A.A.; Siegel, H.J. A parallel algorithm for singular value decomposition as applied to failure tolerant manipulators. In Proceedings of the 13th International Parallel Processing Symposium and 10th Symposium on Parallel and Distributed Processing, IPPS/SPDP 1999, San Juan, PR, USA, 12–16 April 1999; pp. 343–349. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.; Kaye, M.E.; Luke, D.M.; Doraiswami, R. An FPGA-based singular value decomposition processor. In Proceedings of the 2006 Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 7–10 May 2006; pp. 1047–1050. [Google Scholar]
- Szecówka, P.M.; Malinowski, P. CORDIC and SVD implementation in digital hardware. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference Mixed Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems-MIXDES 2010, Wroclaw, Poland, 24–26 June 2010; pp. 237–242. [Google Scholar]
- Senning, C.; Studer, C.; Luethi, P.; Fichtner, W. Hardware-efficient steering matrix computation architecture for MIMO communication systems. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Seattle, WA, USA, 18–21 May 2008; pp. 304–307. [Google Scholar]
- Studer, C.; Blosch, P.; Friedli, P.; Burg, A. Matrix decomposition architecture for MIMO systems: Design and implementation trade-offs. In Proceedings of the 2007 Conference Record of the Forty-First Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 4–7 November 2007; pp. 1986–1990. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Qi, Q.; Cheng, H.; Sun, L.; Zhao, Y.; Chai, J. A vital signs fast detection and extraction method of UWB impulse radar based on SVD. Sensors 2022, 22, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandrini, M.; Biagetti, G.; Crippa, P.; Falaschetti, L.; Manoni, L.; Turchetti, C. Singular value decomposition in embedded systems based on arm cortex-m architecture. Electronics 2020, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Guo, L.-X.; Wang, P.; Lu, H. Compact 8 × 8 mimo antenna design for 5 g terminals. Electronics 2022, 11, 3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versaci, M.; Angiulli, G.; La Foresta, F.; Laganà, F.; Palumbo, A. Intuitionistic fuzzy divergence for evaluating the mechanical stress state of steel plates subject to bi-axial loads. Integr. Comput. Aided Eng. 2024, 31, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Cheng, Z.; Guo, B. Anomaly detection in satellite telemetry data using a sparse feature-based method. Sensors 2022, 22, 6358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azimi, M.; Eslamlou, A.D.; Pekcan, G. Data-driven structural health monitoring and damage detection through deep learning: State-of-the-art review. Sensors 2020, 20, 2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EBrusa; Cibrario, L.; Delprete, C.; Di Maggio, L.G. Explainable AI for machine fault diagnosis: Understanding features’ contribution in machine learning models for industrial condition monitoring. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Gangsar, P.; Porwal, R.; Atulkar, A. Artificial intelligence application in fault diagnostics of rotating industrial machines: A state-of-the-art review. J. Intell. Manuf. 2023, 34, 931–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torun, M.U.; Yilmaz, O.; Akansu, A.N. FPGA, GPU, and CPU implementations of Jacobi algorithm for eigenanalysis. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2016, 96, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Węgrzyn, M.; Voytusik, S.; Gavkalova, N. FPGA-based Low Latency Square Root CORDIC Algorithm. J. Telecommun. Inf. Technol. 2025, 99, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changela, A.; Kumar, Y.; Woźniak, M.; Shafi, J.; Ijaz, M.F. Radix-4 CORDIC algorithm based low-latency and hardware efficient VLSI architecture for N th root and N th power computations. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andraka, R. A survey of CORDIC algorithms for FPGA based computers. In Proceedings of the 1998 ACM/SIGDA Sixth International Symposium on Field Programmable Gate Arrays, Monterey, CA, USA, 22–25 February 1998; pp. 191–200. [Google Scholar]
- Salehi, F.; Farshidi, E.; Kaabi, H. Novel design for a low-latency CORDIC algorithm for sine-cosine computation and its Implementation on FPGA. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2020, 77, 103197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.; Liu, T.; Hou, B.; Gao, Y.; Yao, Y.; Sun, H. A low-latency rdp-cordic algorithm for real-time signal processing of edge computing devices in smart grid cyber-physical systems. Sensors 2022, 22, 7489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, K.N.H.; Prabha, I.S.; Matcha, V.G.R. CORDIC KSVD based Online Dictionary Learning for Speech Enhancement on ASIC/FPGA Platforms. Recent Adv. Comput. Sci. Commun. 2023, 16, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timofte, R.; Agustsson, E.; Van Gool, L.; Yang, M.-H.; Zhang, L. Ntire 2017 challenge on single image super-resolution: Methods and results. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 114–125. [Google Scholar]
- Pullano, S.A.; Oliva, G.; Titirsha, T.; Shuvo, M.M.H.; Islam, S.K.; Laganà, F.; La Gatta, A.; Fiorillo, A.S. Design of an Electronic Interface for Single-Photon Avalanche Diodes. Sensors 2024, 24, 5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versaci, M.; Laganà, F.; Morabito, F.C.; Palumbo, A.; Angiulli, G. Adaptation of an Eddy Current Model for Characterizing Subsurface Defects in CFRP Plates Using FEM Analysis Based on Energy Functional. Mathematics 2024, 12, 2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitzke, J.P.; Zangl, H. A review on electrical impedance tomography spectroscopy. Sensors 2020, 20, 5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peri, E.; Xu, L.; Ciccarelli, C.; Vandenbussche, N.L.; Xu, H.; Long, X.; Overeem, S.; van Dijk, J.P.; Mischi, M. Singular value decomposition for removal of cardiac interference from trunk electromyogram. Sensors 2021, 21, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, A.S.; Asha, V.; Jayaram, M.N. GNP/FE electrode for real time EMG signal acquisition. Discov. Electron. 2025, 2, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golub, G.H.; Van Loan, C.F. Matrix Computations; JHU Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Saad, Y. Iterative Methods for Sparse Linear Systems; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lane, D.M.; Sahafi, A. ADNA: Automating Application-Specific Integrated Circuit Development of Neural Network Accelerators. Electronics 2025, 14, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE 802.11n; IEEE Standard for Information Technology—Local and Metropolitan Area Networks—Specific Requirements—Part 11: Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications Amendment 5: Enhancements for Higher Throughput. IEEE Standards Association: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009.
- Pratticò, D.; Laganà, F.; Oliva, G.; Fiorillo, A.S.; Pullano, S.A.; Calcagno, S.; De Carlo, D.; La Foresta, F. Integration of LSTM and U-Net models for monitoring electrical absorption with a system of sensors and electronic circuits. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2025, 74, 2533311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliffe, I.T.; Cadima, J. Principal component analysis: A review and recent developments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 374, 20150202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, Y.; Bell, R.; Volinsky, C. Matrix factorization techniques for recommender systems. Computer 2009, 42, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, H.; Williams, L.J. Principal component analysis. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2010, 2, 433–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.; Heath, R.W. High SNR capacity of millimeter wave MIMO systems with one-bit quantization. In Proceedings of the 2014 Information Theory and Applications Workshop (ITA), San Diego, CA, USA, 9–14 February 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, J.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Zhao, C. Machine learning based low-complexity channel state information estimation. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2023, 2023, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.K.; Khokhar, A.; Ahmed, S. Lightweight Deep Learning-Based Channel Estimation for RIS-Aided Extremely Large-Scale MIMO Systems on Resource-Limited Edge Devices. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2507.09627. [Google Scholar]
- Deerwester, S.; Dumais, S.T.; Furnas, G.W.; Landauer, T.K.; Harshman, R. Indexing by latent semantic analysis. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. 1990, 41, 391–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, P.C.; Nagy, J.G.; O’leary, D.P. Deblurring Images: Matrices, Spectra, and Filtering; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]

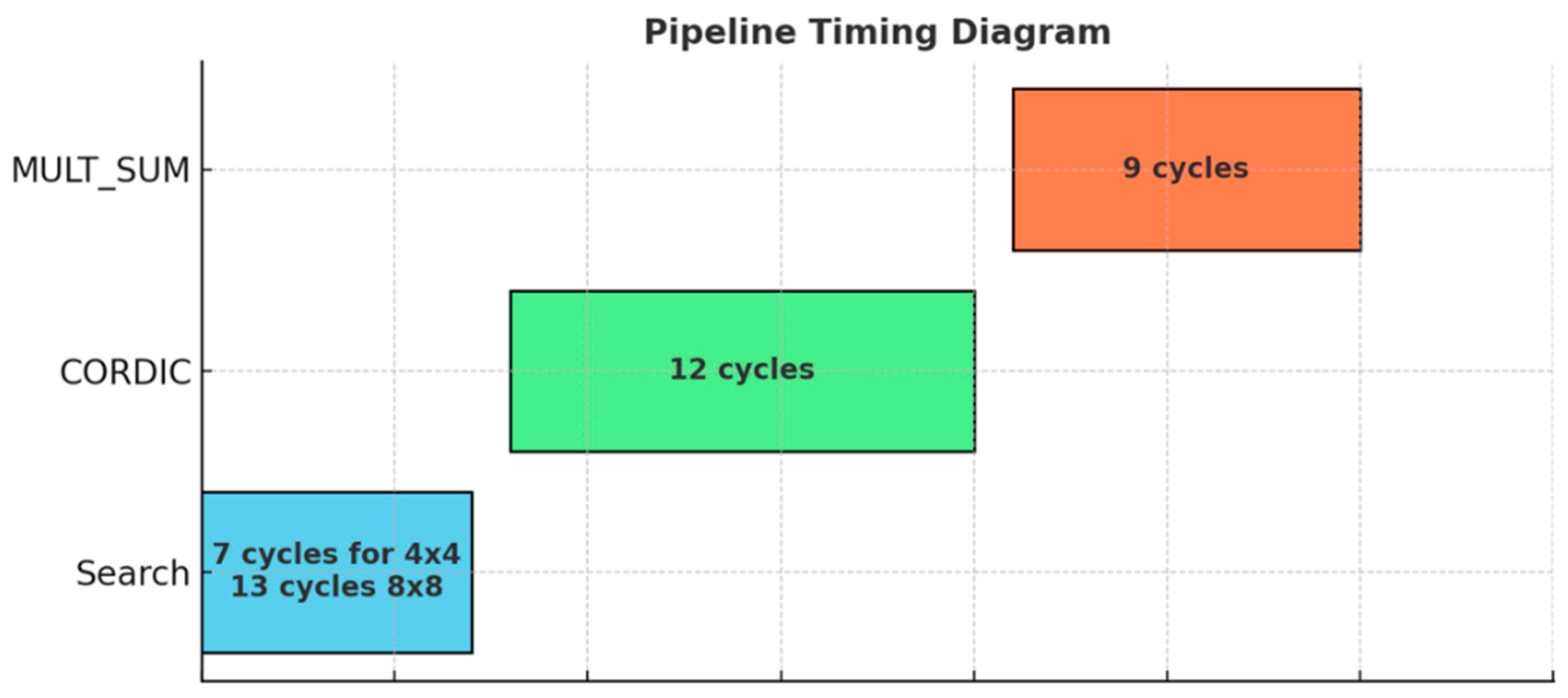
| Number of Slice Registers: | 3416 out of 12,480 27% |
| Number of Slice LUTS | 9729 out of 12,480 77% |
| Number of DSP48Es | 16 out of 24 66% |
| Multipliers | Multiplier = 16 18 × 18 bit |
| On-Chip | Power (W) |
|---|---|
| Clocks | 0.075 |
| Logic | 0.012 |
| Signals | 0.044 |
| DSPs | 0.002 |
| IOs | 0.001 |
| Leakage | 0.322 |
| Total | 0.456 |
| Work | Frequency (MHz) | Slices/LUTs/Registers | Latency/Time | Bits | Data Type | Matrix Size | Latency Per Matrix Size/MHz | Scalability/Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [4] 1CPP | Not specified | Not specified | 14 ms | Not specified | Real | 6 × 7 | Not specified | Parallel SIMD, lacks hardware details |
| [4] 2CPP | Not specified | Not specified | 18 ms | Not specified | Real | 6 × 7 | Not specified | Similar to above |
| [5] ESVD_12bits | 7.4 | 8531 | Not specified | 12 | Real | 4 × 4 | Not specified | Fixed architecture, no scalability |
| [6] 25bitsFixedP | 148 | 2609 Slices | Not specified | 25 | Real | 2 × 2 | Not specified | High frequency, small matrix size |
| [6] 25bitsFloating | 35 | 4648 Slices | Not specified | 25 | Real | 2 × 2 | Not specified | Lower frequency, fixed architecture |
| [11] VLSI | 149 | Not specified | 3.3 µs | 16 | Complex | 4 × 4 | Not specified | ASIC-based, high-speed design |
| [12] MDU-II | 272 | Not specified | 15.8 µs | 32 | Complex | 4 × 4 | Not specified | ASIC, good frequency but higher latency |
| [12] MDU-I | 133 | Not specified | 11.6 µs | 32 | Complex | 4 × 4 | Not specified | ASIC, moderate performance |
| Timofte et al. (2017) [28] | ~100 | Not specified | Not specified | Not specified | Real/CORDIC | Variable | Not specified | Systolic array, moderate time efficiency |
| Ma et al. (2006) [9] | 133 | Not specified | 11.6 µs | 32 | Complex | 4 × 4 | Not specified | Uses Xilinx CORDIC IP, fixed-size architecture |
| Szecówka & Malinowski [10] | 148 | 2609 Slices | 3.3 µs | 16 | Complex | 4 × 4 | Not specified | Fixed architecture, no scalability |
| This Work 1 (4 × 4) | 130.41 | 9729 LUTs/3416 Registers | 5.29 µs | 18 | Real | 4 × 4 | 0.189 | High scalability (configurable for 4 × 4/8 × 8 matrices) |
| This Work 2 (8 × 8) | 130.41 | 9729 LUTs/3416 Registers | 24.25 µs | 18 | Real | 8 × 8 | 0.0412 | High scalability (configurable for 4 × 4/8 × 8 matrices) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
López-López, L.E.; Luviano-Cruz, D.; Cota-Ruiz, J.; Díaz-Roman, J.; Sifuentes, E.; Silva-Aceves, J.M.; Enríquez-Aguilera, F.J. A Configurable Parallel Architecture for Singular Value Decomposition of Correlation Matrices. Electronics 2025, 14, 3321. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14163321
López-López LE, Luviano-Cruz D, Cota-Ruiz J, Díaz-Roman J, Sifuentes E, Silva-Aceves JM, Enríquez-Aguilera FJ. A Configurable Parallel Architecture for Singular Value Decomposition of Correlation Matrices. Electronics. 2025; 14(16):3321. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14163321
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez-López, Luis E., David Luviano-Cruz, Juan Cota-Ruiz, Jose Díaz-Roman, Ernesto Sifuentes, Jesús M. Silva-Aceves, and Francisco J. Enríquez-Aguilera. 2025. "A Configurable Parallel Architecture for Singular Value Decomposition of Correlation Matrices" Electronics 14, no. 16: 3321. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14163321
APA StyleLópez-López, L. E., Luviano-Cruz, D., Cota-Ruiz, J., Díaz-Roman, J., Sifuentes, E., Silva-Aceves, J. M., & Enríquez-Aguilera, F. J. (2025). A Configurable Parallel Architecture for Singular Value Decomposition of Correlation Matrices. Electronics, 14(16), 3321. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14163321









