A Steganographic Message Transmission Method Based on Style Transfer and Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose a dual-layer protection method. The message is encoded using object-based images and then hidden inside a customizable cover image.
- Inspired by conditional models, we are the first to use DDPM by regarding the image restoration problem as global image inpainting, to recover the original secret image from the stego image.
2. Related Work
2.1. Steganography Techniques
2.2. Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models
2.3. Image-to-Image Translation
2.3.1. Style Transfer
2.3.2. Image Inpainting
2.4. Object Detectors
3. Background
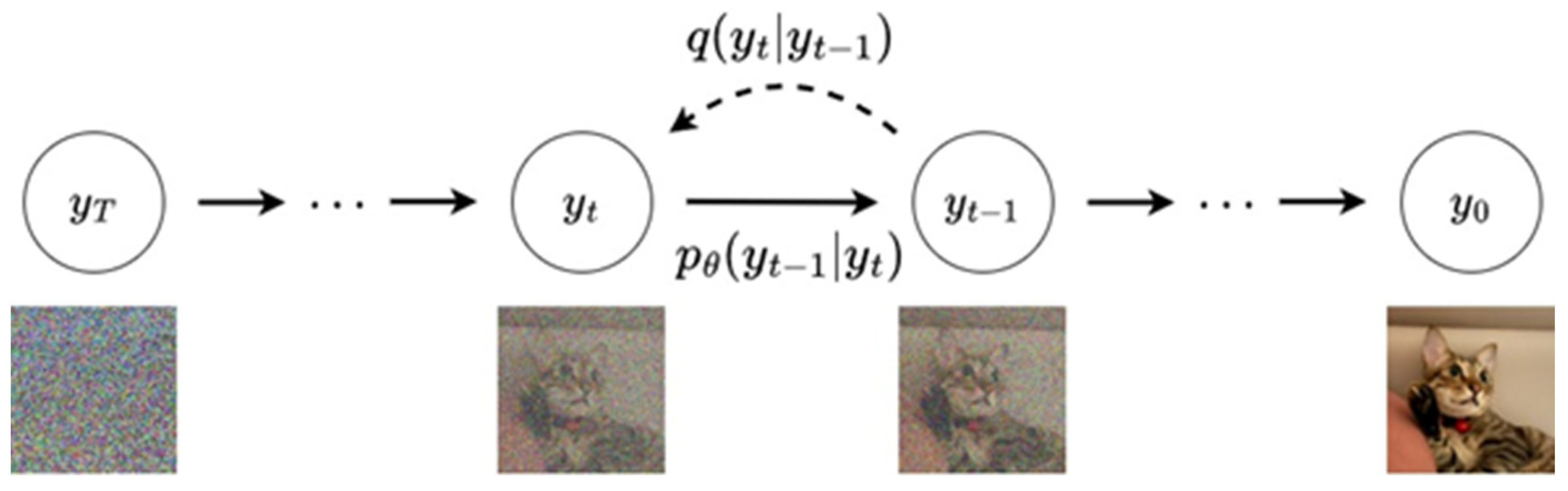
3.1. Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model
3.2. Conditional Diffusion Probabilistic Models
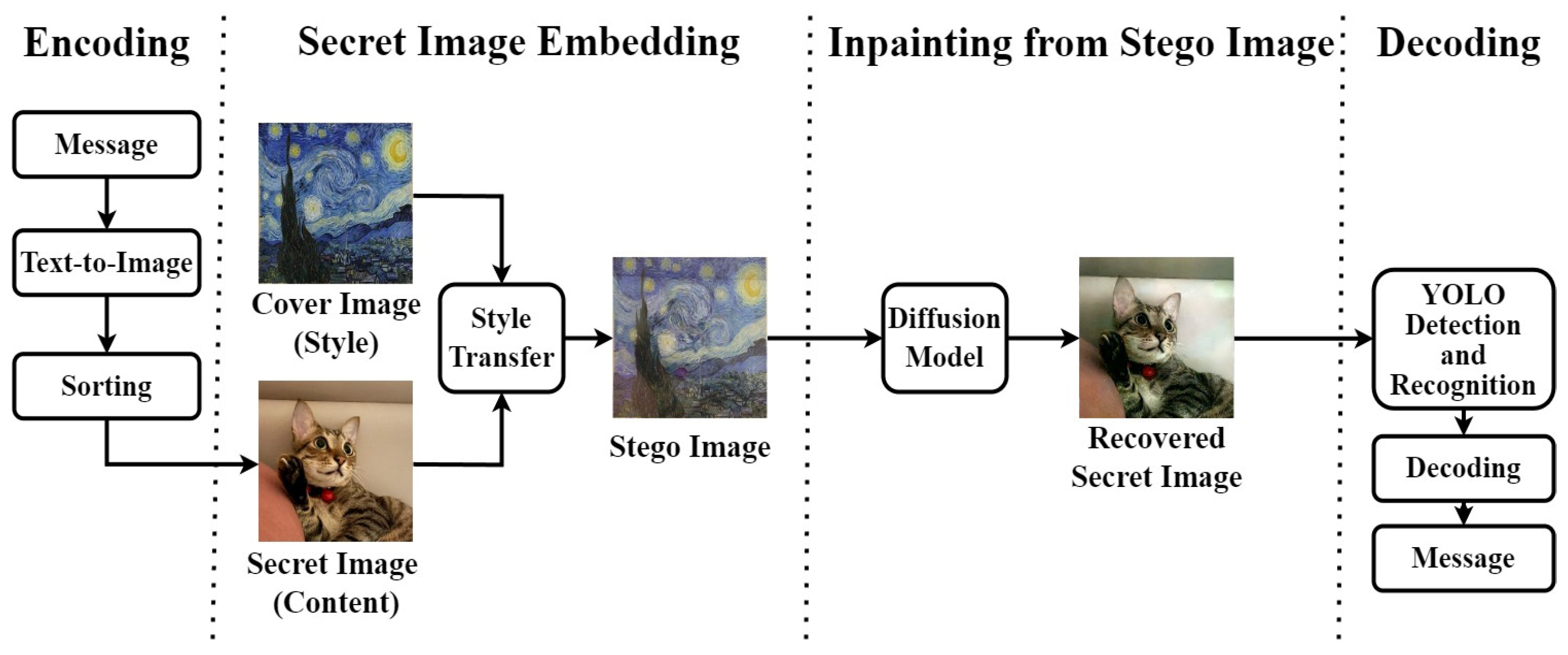
4. Methodology
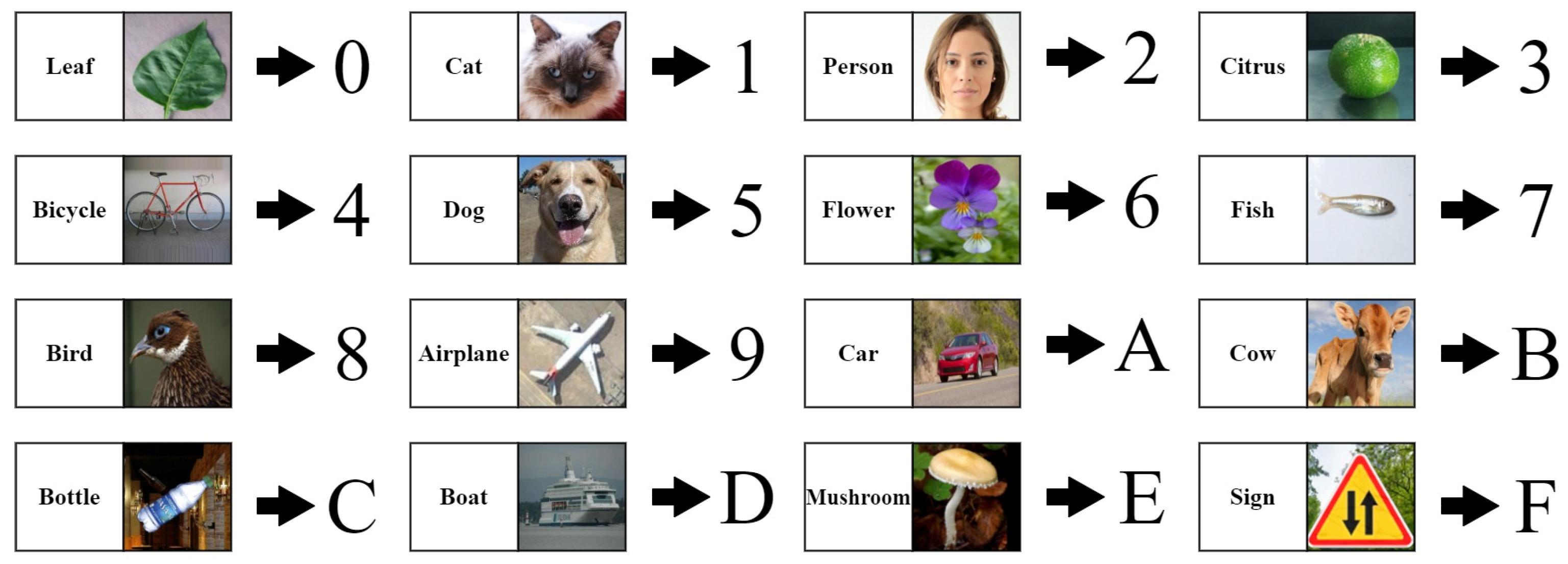
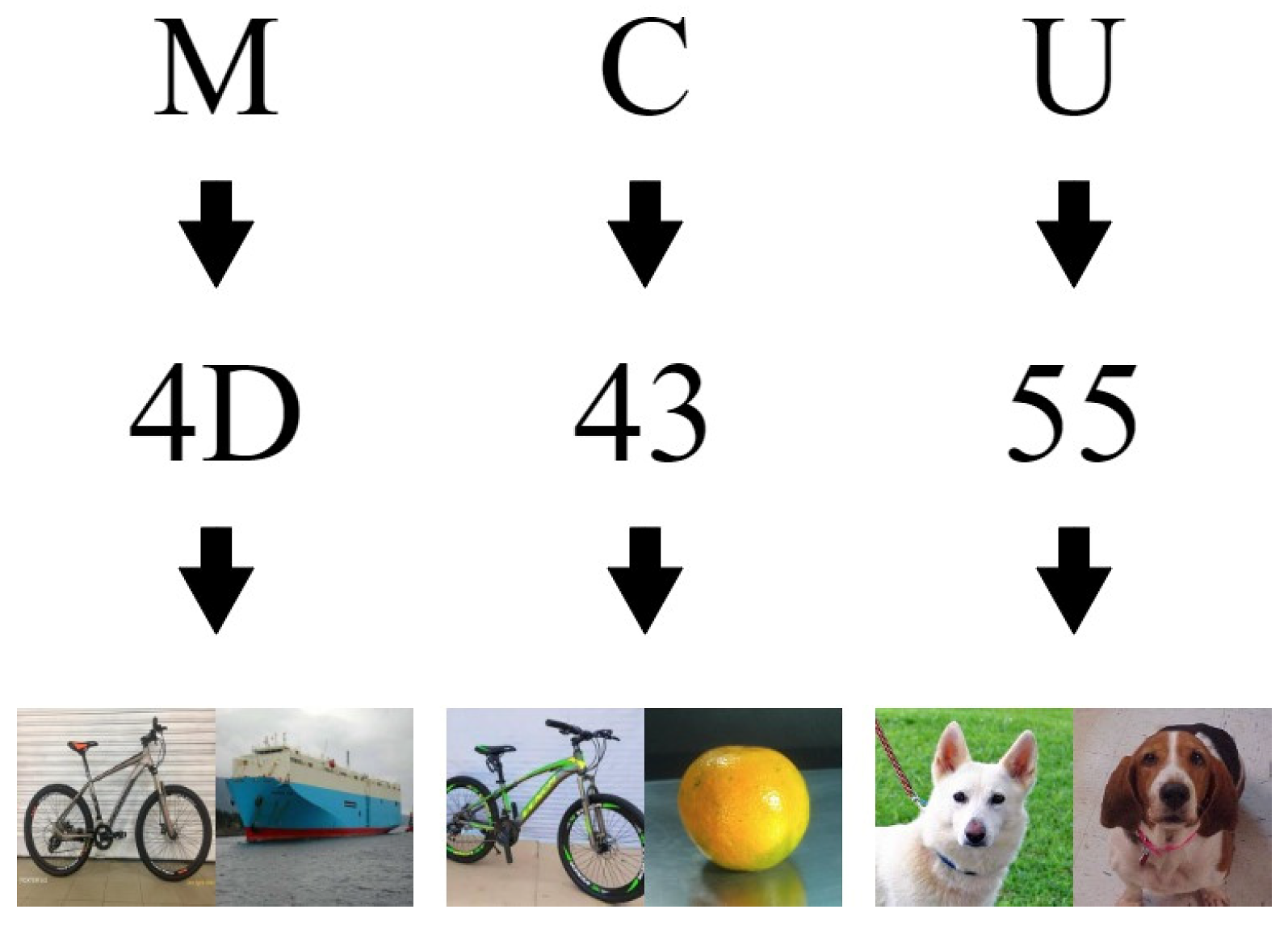
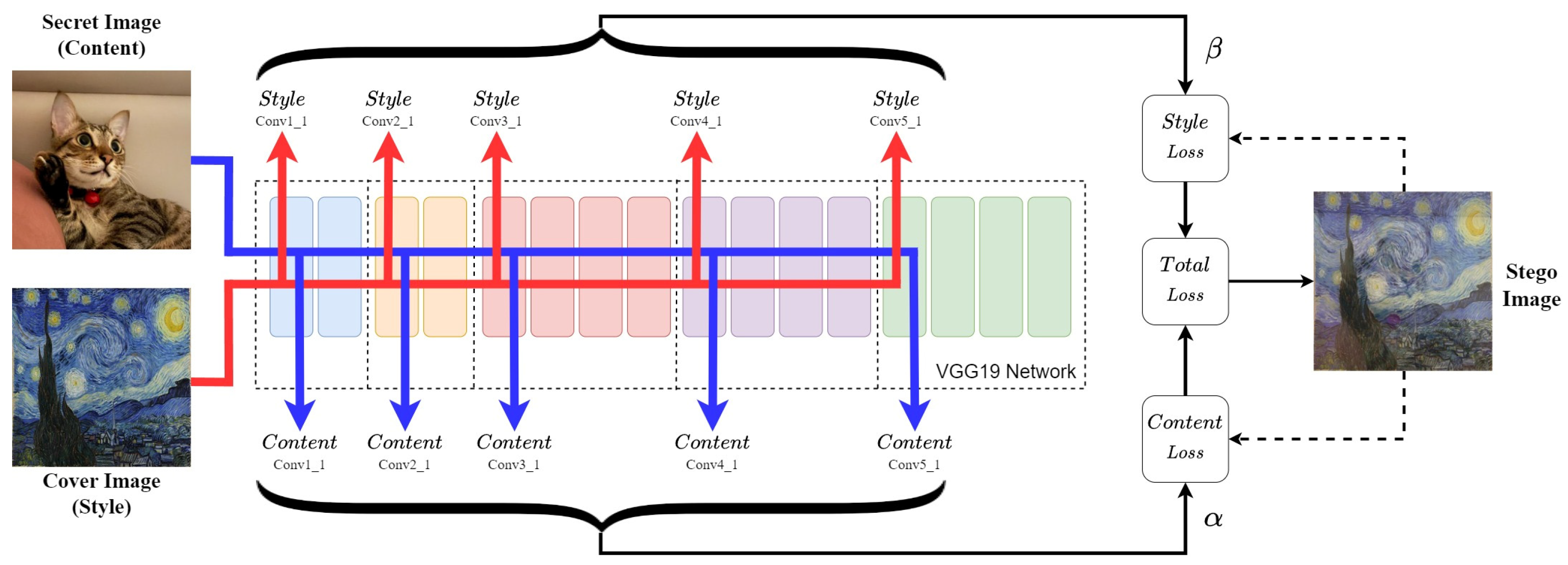
4.1. Encoding
4.2. Stego Image Generation
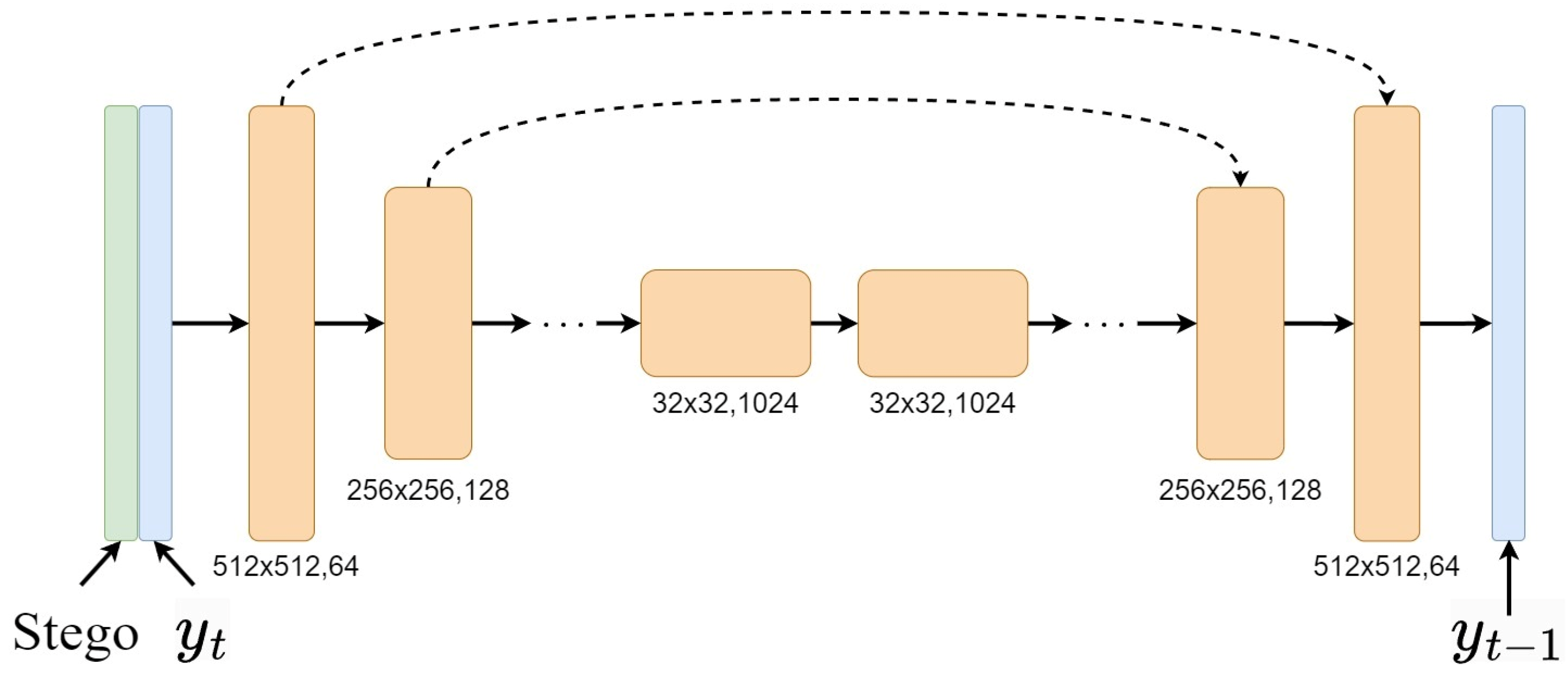
4.3. Secret Image Inpainting
4.4. Decoding
5. Experimental Results and Analysis
5.1. Experimental Set-Up
5.1.1. Image Quality Evaluation Metrics
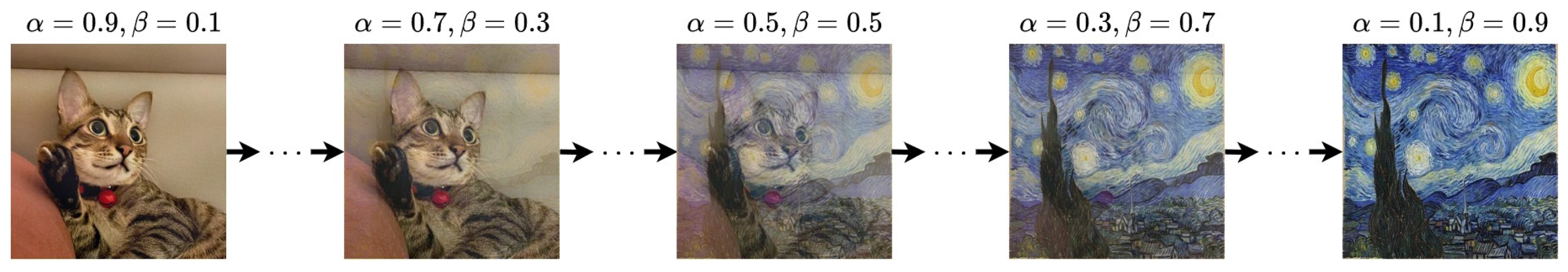
5.1.2. Style Transfer Hyperparameters
5.1.3. DDPM Hyperparameters
5.1.4. YOLO Hyperparameters
5.1.5. Training Dataset
5.2. Experimental Results
5.2.1. Encoding Results
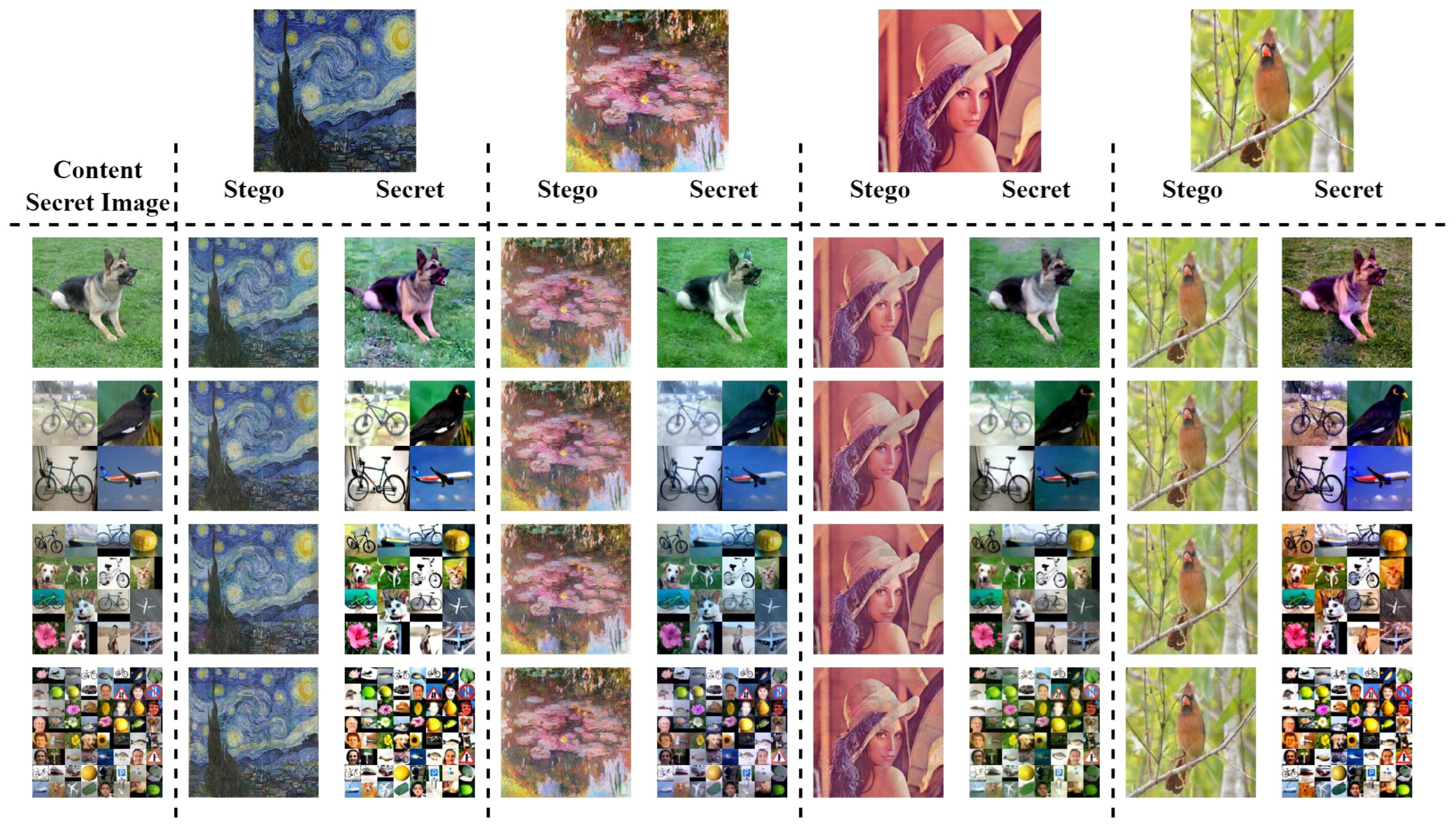
5.2.2. Results for Steganography and Inpainting
5.2.3. Object Detection and Message Decoding
5.3. Computational Efficiency
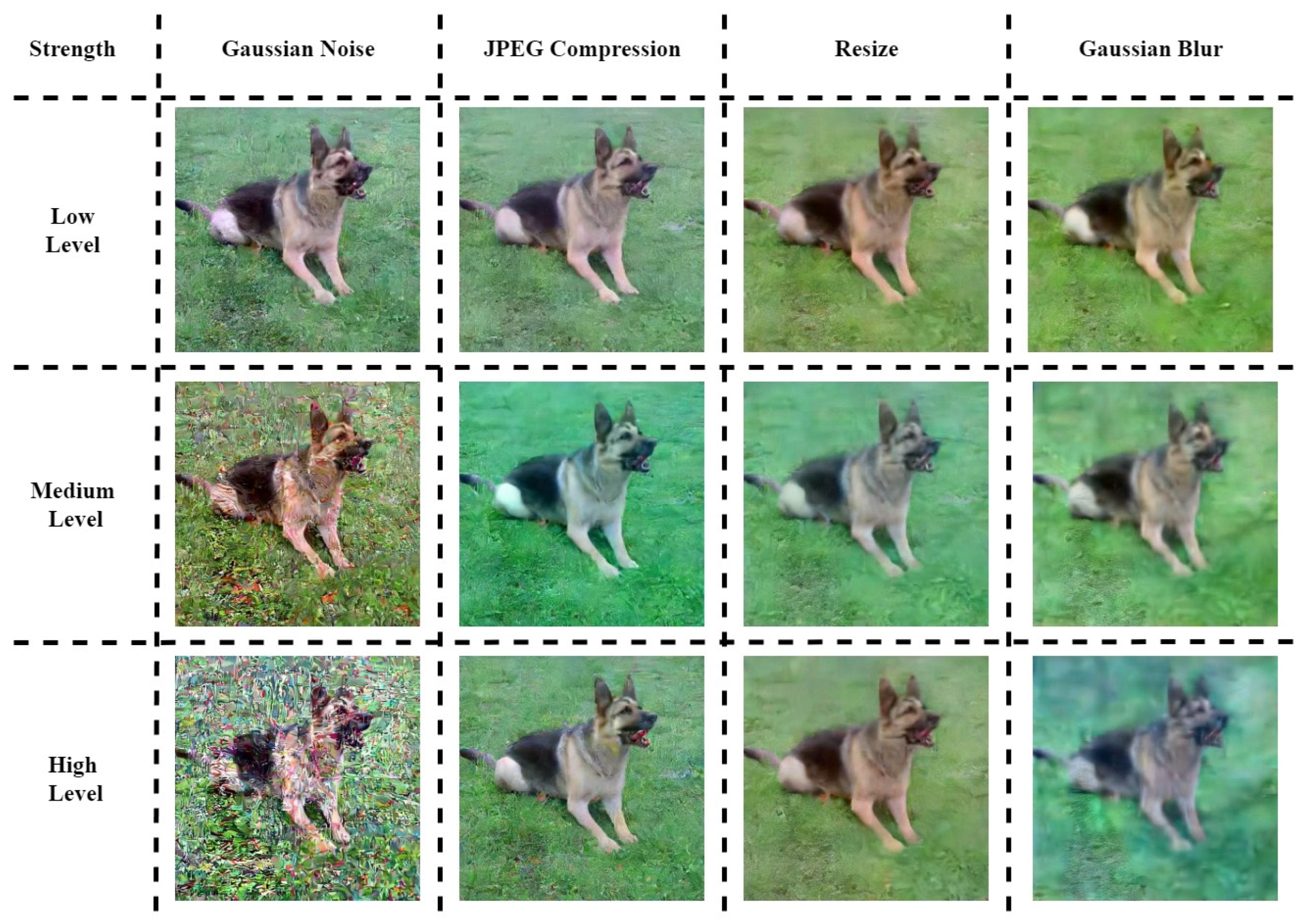
5.4. Robustness Evaluation
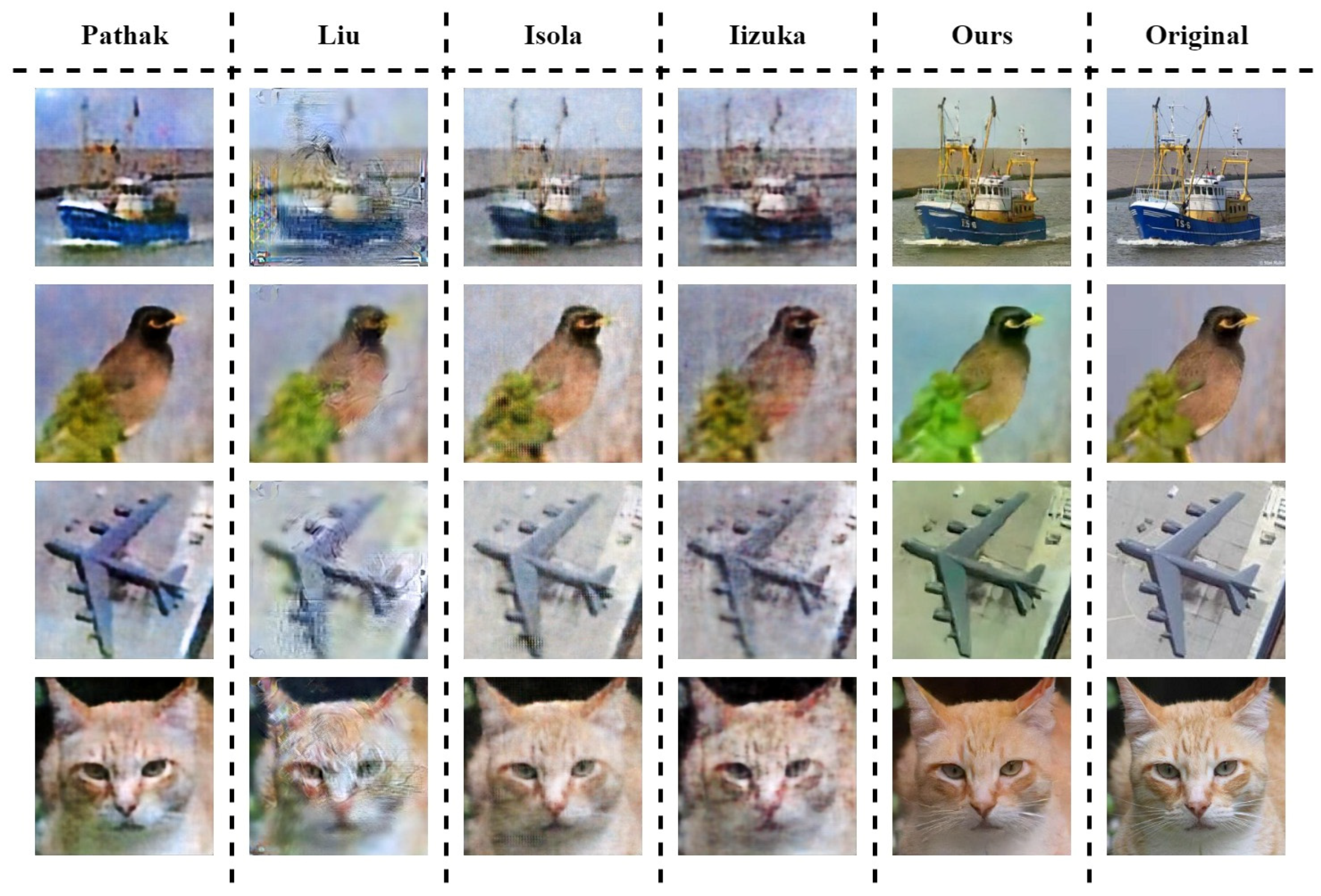
5.5. Qualitative Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Subramanian, N.; Fawad; Nasralla, M.M.; Esmail, M.A.; Mostafa, H.; Jia, M. Image steganography: A review of the recent advances. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 23409–23423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatys, L.A.; Ecker, A.S.; Bethge, M. Image style transfer using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Saharia, C.; Chan, W.; Saxena, S.; Li, L.; Whang, J.; Salimans, T.; Ho, J.; Fleet, D.J.; Norouzi, M. Palette: Image-to-image diffusion models. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH Conference, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–11 August 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, J.; Jain, A.; Abbeel, P. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 6840–6851. [Google Scholar]
- Bender, W.; Gruhl, D.; Morimoto, N.; Lu, A. Techniques for data hiding. IBM Syst. J. 1996, 35, 313–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, E.T.; Delp, E.J. A review of fragile image watermarks. In Proceedings of the ACM Multimedia Security Workshop, Orlando, FL, USA, 2–3 October 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Pooja, K. Steganography—A data hiding technique. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2010, 9, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-P.; Hsieh, C.-H. Delivering messages over user-friendly code images grabbed by mobile devices with error correction. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo Workshops, Turin, Italy, 29 June–3 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rahim, R.; Nadeem, S. End-to-end trained CNN encoder-decoder networks for image steganography. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Baluja, S. Hiding images in plain sight: Deep steganography. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 2066–2076. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.; Gao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Huang, X. Image steganography based on style transfer. In Proceedings of the 2024 3rd International Conference on Image Processing and Media Computing (ICIPMC), Xi’an, China, 12–14 January 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; He, L.; Li, M.; Liu, W.; Li, G. The research and analysis of robust image steganography for arbitrary style transfer. In Proceedings of the 2024 5th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Engineering (ICAICE), Beijing, China, 22–24 March 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Volkhonskiy, D.; Nazarov, I.; Burnaev, E. Steganographic generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 16–18 November 2019; Volume 11433. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Z.; Wang, F.; Cheng, X. The secure steganography for hiding images via GAN. EURASIP J. Image Video Process. 2020, 2020, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Sohl-Dickstein, J.; Kingma, D.P.; Kumar, A.; Ermon, S.; Poole, B. Score-based generative modeling through stochastic differential equations. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2011.13456. [Google Scholar]
- Dhariwal, P.; Nichol, A. Diffusion models beat GANs on image synthesis. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 8780–8794. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Meng, C.; Ermon, S. Denoising diffusion implicit models. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.02502. [Google Scholar]
- Rombach, R.; Blattmann, A.; Lorenz, D.; Esser, P.; Ommer, B. High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, J.; Alahi, A.; Fei-Fei, L. Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ubhi, J.S.; Aggarwal, A.K. Neural style transfer for image within images and conditional GANs for destylization. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2022, 85, 103483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.-Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, J. Dualast: Dual style-learning networks for artistic style transfer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bertalmio, M.; Sapiro, G.; Caselles, V.; Ballester, C. Image inpainting. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH Conference, New Orleans, LA, USA, 23–28 July 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Pathak, D.; Krahenbuhl, P.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Efros, A.A. Context encoders: Feature learning by inpainting. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Reda, F.A.; Shih, K.J.; Wang, T.C.; Tao, A.; Catanzaro, B. Image inpainting for irregular holes using partial convolutions. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Iizuka, S.; Simo-Serra, E.; Ishikawa, H. Globally and locally consistent image completion. ACM Trans. Graph. 2017, 36, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharia, C.; Ramesh, A.; Ge, S.; Gharbi, M.; Norouzi, M.; Fleet, D.J.; Salimans, T. Image super-resolution via iterative refinement. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 4713–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugmayr, A.; Danelljan, M.; Timofte, R. Repaint: Inpainting using denoising diffusion probabilistic models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast R-CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 11–18 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single shot multibox detector. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLO9000: Better, faster, stronger. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLOv3: An incremental improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.-Y.; Liao, H.-Y.M. YOLOv4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.-Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–24 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Roboflow Universe. Available online: https://universe.roboflow.com/ (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Zhang, R.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A.; Shechtman, E.; Wang, O. The unreasonable effectiveness of deep features as a perceptual metric. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Heusel, M.; Ramsauer, H.; Unterthiner, T.; Nessler, B.; Hochreiter, S. GANs trained by a two time-scale update rule converge to a local Nash equilibrium. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the Inception architecture for computer vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
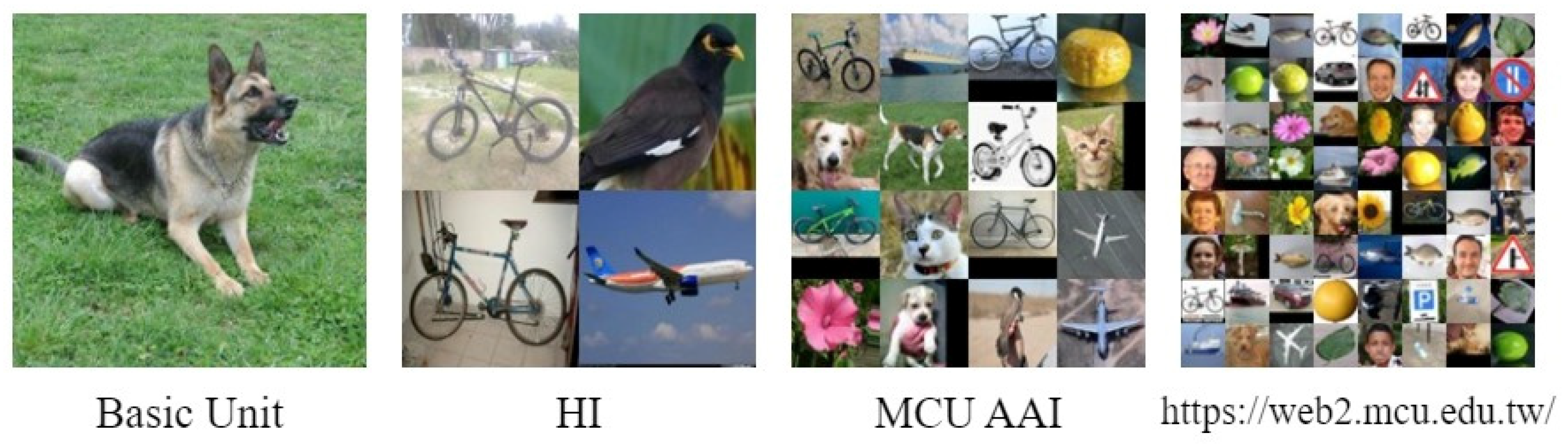


| Hyperparameters | PSNR (dB) | SSIM | LPIPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| , | 13.8846 | 0.1764 | 0.7364 |
| , | 14.6891 | 0.2866 | 0.6994 |
| , | 15.7198 | 0.4219 | 0.6365 |
| , | 17.0660 | 0.5717 | 0.5192 |
| , | 18.7488 | 0.7115 | 0.3385 |
| , | 20.8038 | 0.8249 | 0.2171 |
| , | 25.2631 | 0.9035 | 0.1247 |
| , | 30.1567 | 0.9352 | 0.0596 |
| , | 33.0311 | 0.9893 | 0.0203 |
| Different Levels | Starry Night | Water Lilies | Lenna | Bird | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Unit | Message Accuracy | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Total Accuracy | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | |
| HI | Message Accuracy | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Total Accuracy | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | |
| MCU AAI | Message Accuracy | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Total Accuracy | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | |
| https://web2.mcu.edu.tw/ | Message Accuracy | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Total Accuracy | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | |
| Strength | JPEG Compression (%) | Resize | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Level | 10 | 90 | 0.9 | 3/1.0 |
| Medium Level | 20 | 80 | 0.8 | 5/1.5 |
| High Level | 30 | 70 | 0.7 | 7/2.0 |
| Different Levels | Basic Unit | HI | MCU AAI | https://web2.mcu.edu.tw/ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gaussian Noise | Low Level | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Medium Level | 100% | 100% | 75% | 84.37% | |
| High Level | 0% | 0% | 31.25% | 48.44% | |
| JPEG Compression | Low Level | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Medium Level | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | |
| High Level | 100% | 100% | 100% | 98.44% | |
| Resize | Low Level | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Medium Level | 100% | 100% | 100% | 98.43% | |
| High Level | 100% | 100% | 100% | 96.88% | |
| Gaussian Blur | Low Level | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Medium Level | 100% | 75% | 81.25% | 79.69% | |
| High Level | 0% | 50% | 50% | 42.19% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Y.-H.; Huang, C.-P.; Huang, P.-S. A Steganographic Message Transmission Method Based on Style Transfer and Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model. Electronics 2025, 14, 3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14163258
Lin Y-H, Huang C-P, Huang P-S. A Steganographic Message Transmission Method Based on Style Transfer and Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model. Electronics. 2025; 14(16):3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14163258
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Yen-Hui, Chin-Pan Huang, and Ping-Sheng Huang. 2025. "A Steganographic Message Transmission Method Based on Style Transfer and Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model" Electronics 14, no. 16: 3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14163258
APA StyleLin, Y.-H., Huang, C.-P., & Huang, P.-S. (2025). A Steganographic Message Transmission Method Based on Style Transfer and Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model. Electronics, 14(16), 3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14163258







