Torque Ripple Reduction in BLDC Motors Using Phase Current Integration and Enhanced Zero Vector DTC
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Related Work
1.2. Research Objectives and Contributions
2. Direct Torque Control Strategy Based on Phase Current Integration
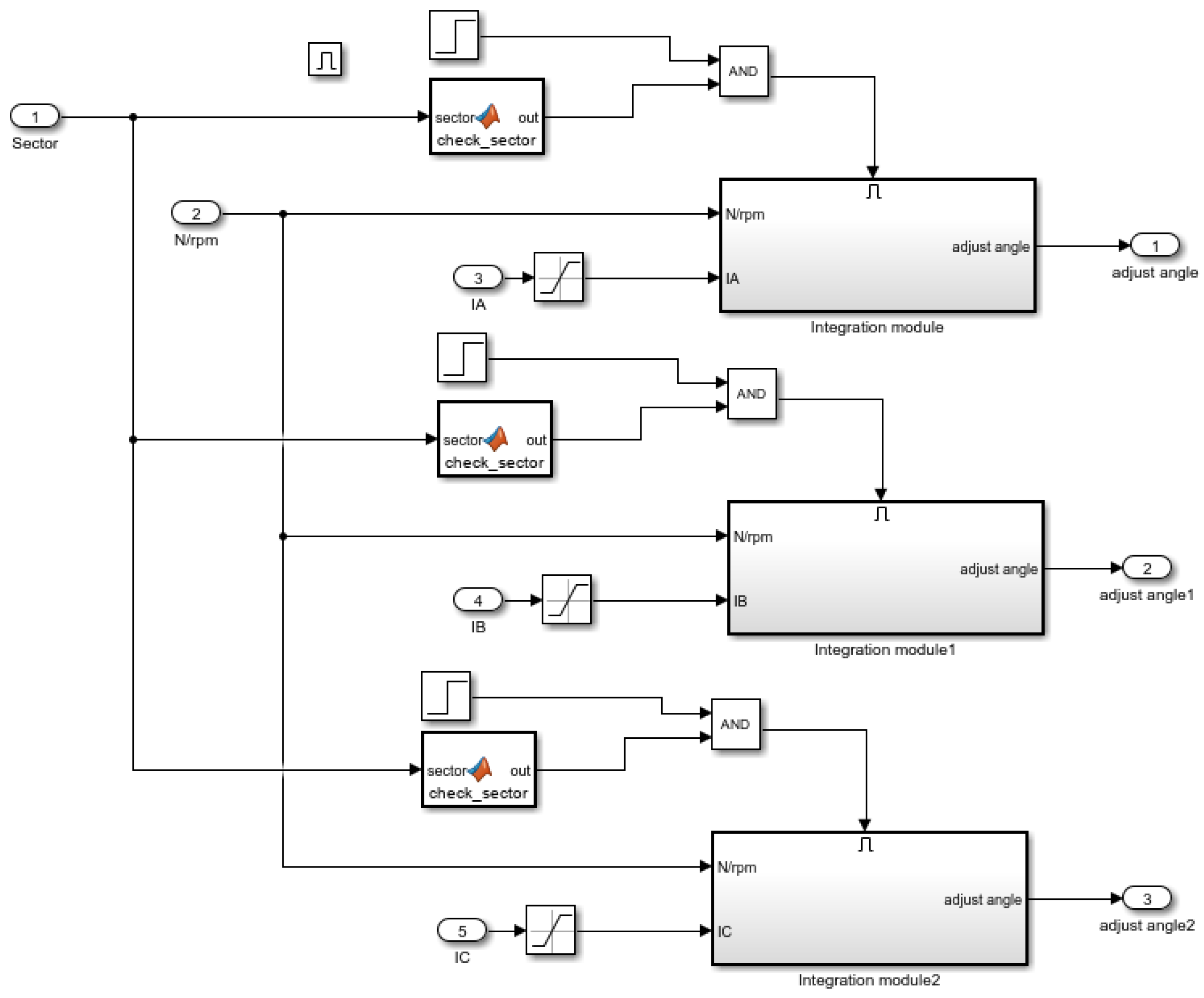
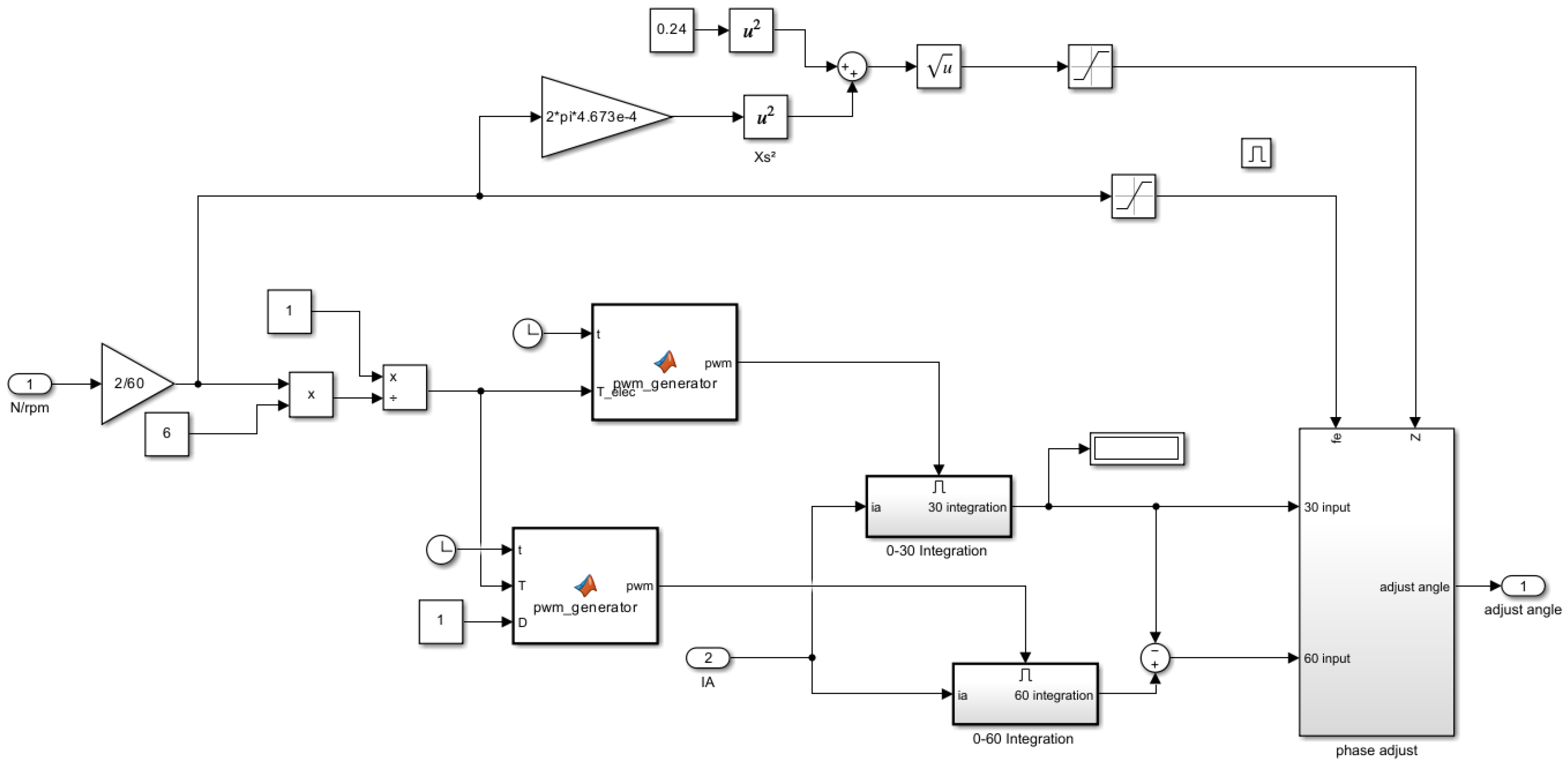
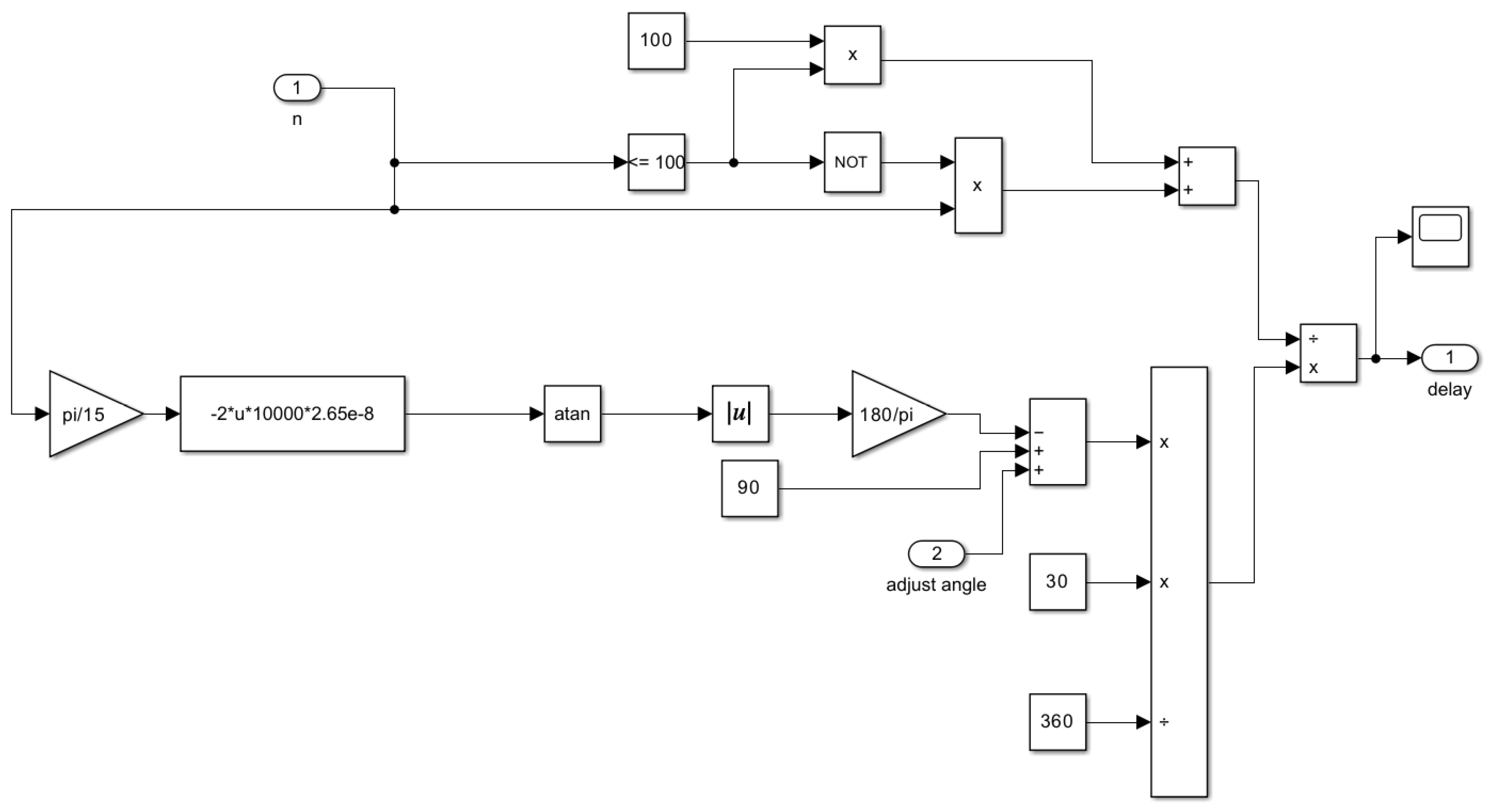
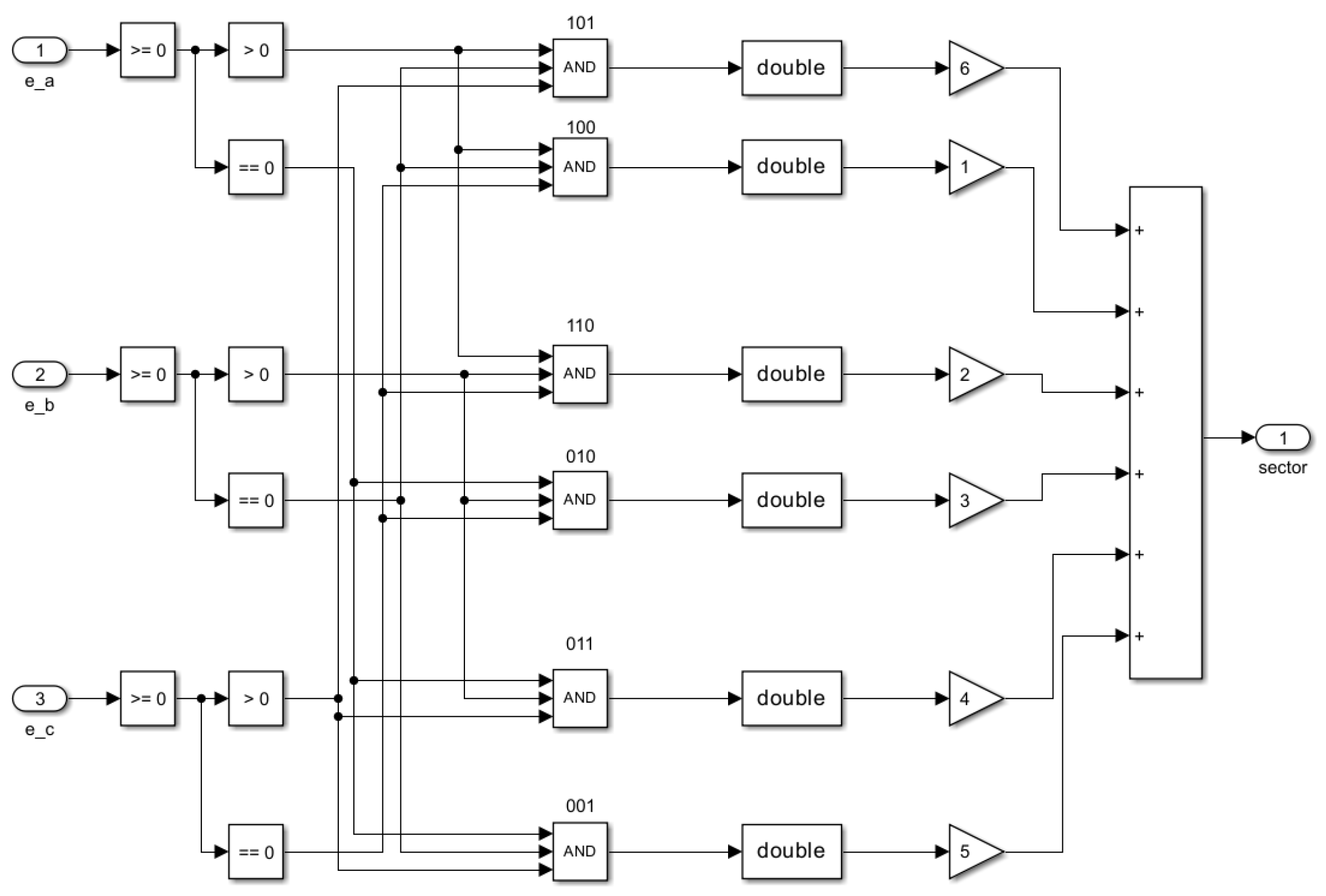
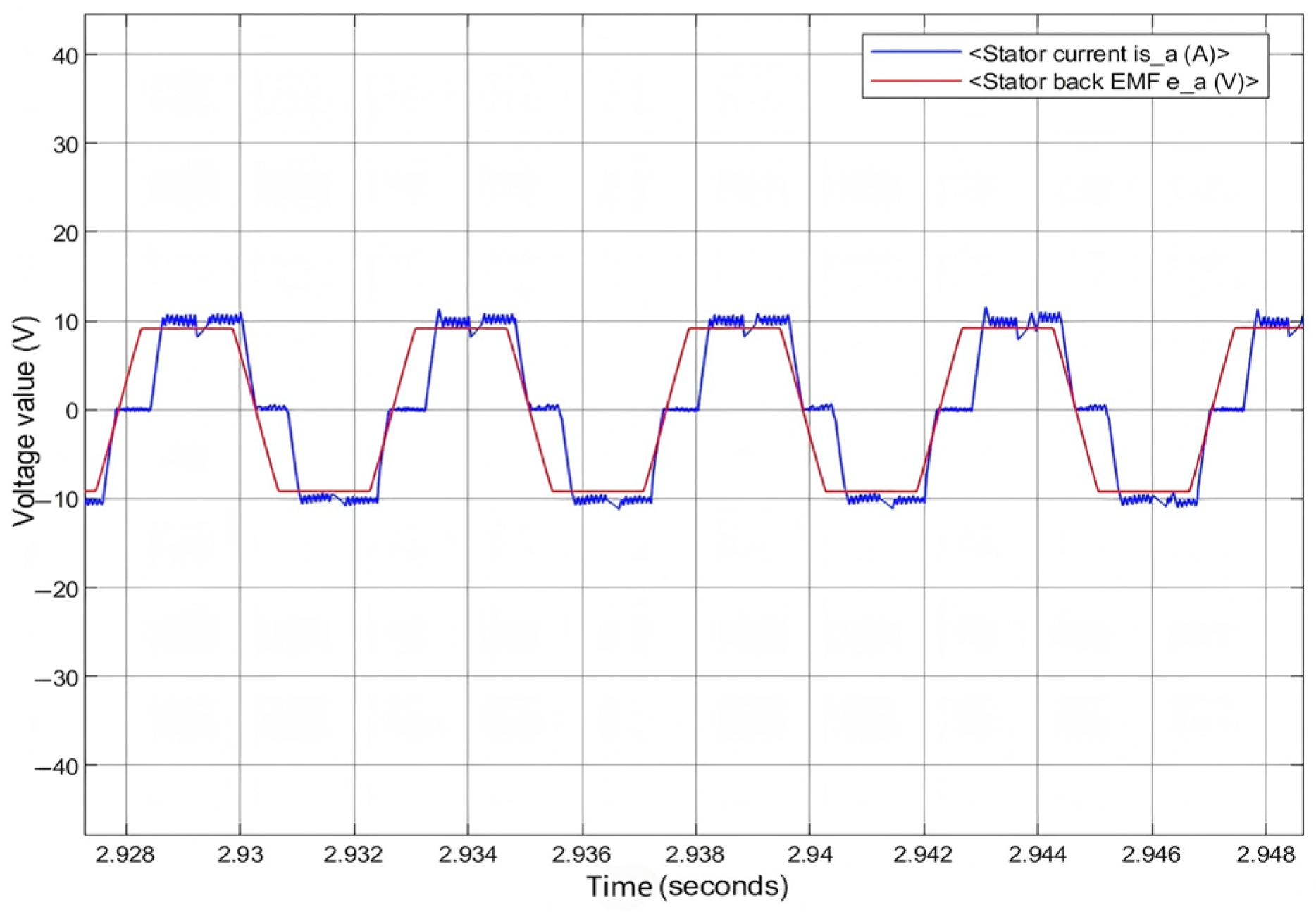
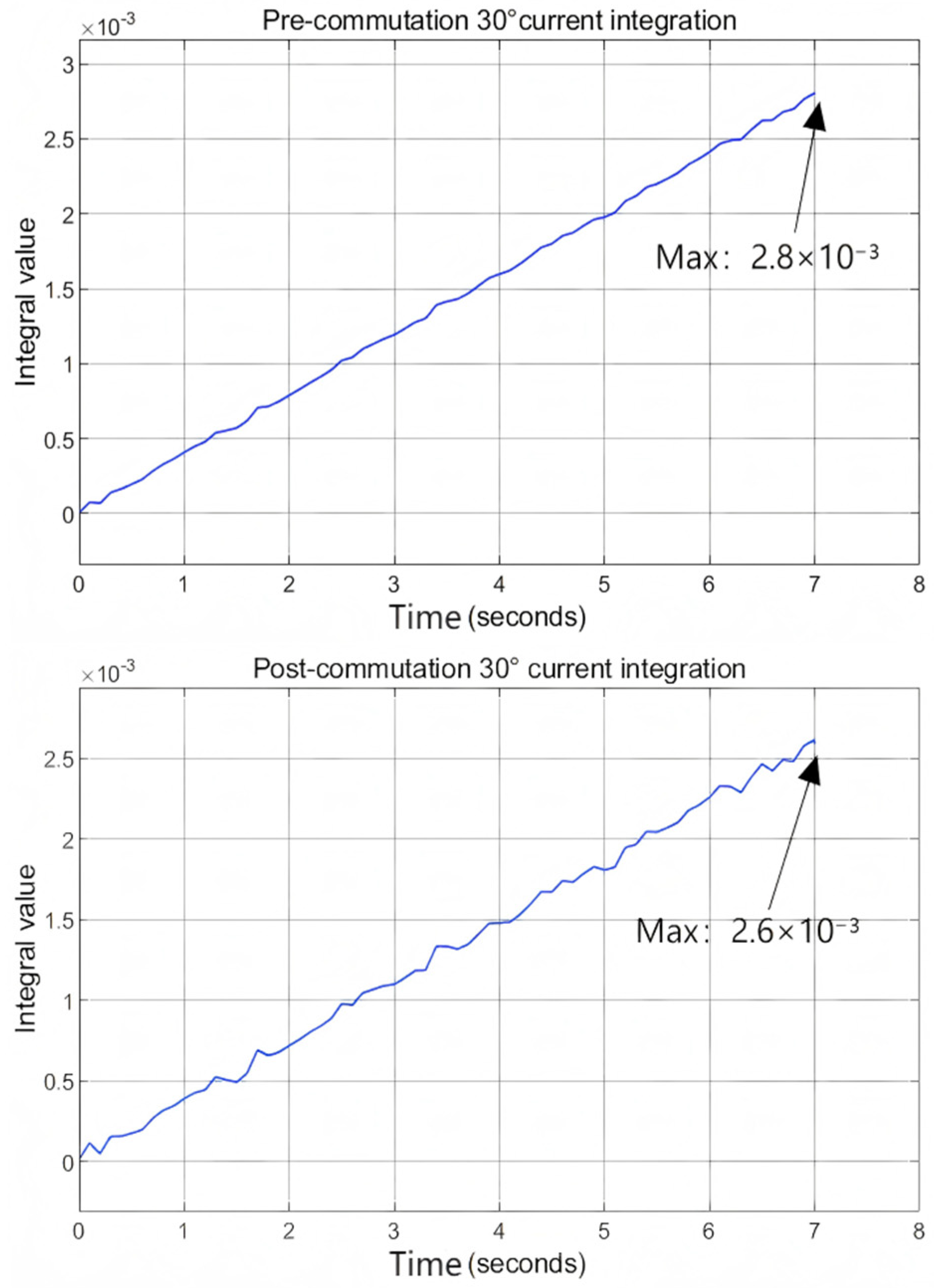
2.1. Analysis of Commutation Correction Based on Phase Current Integration
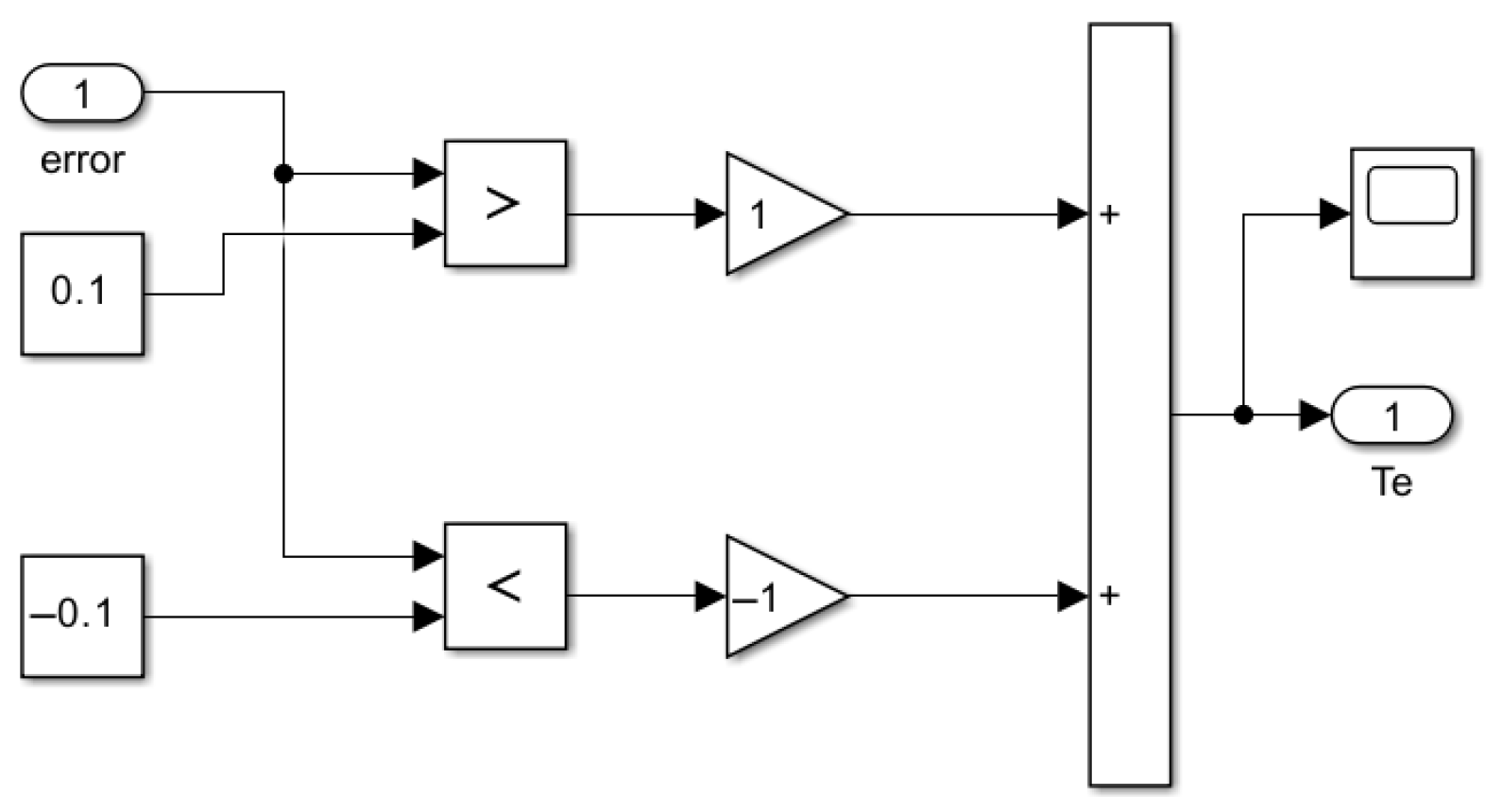
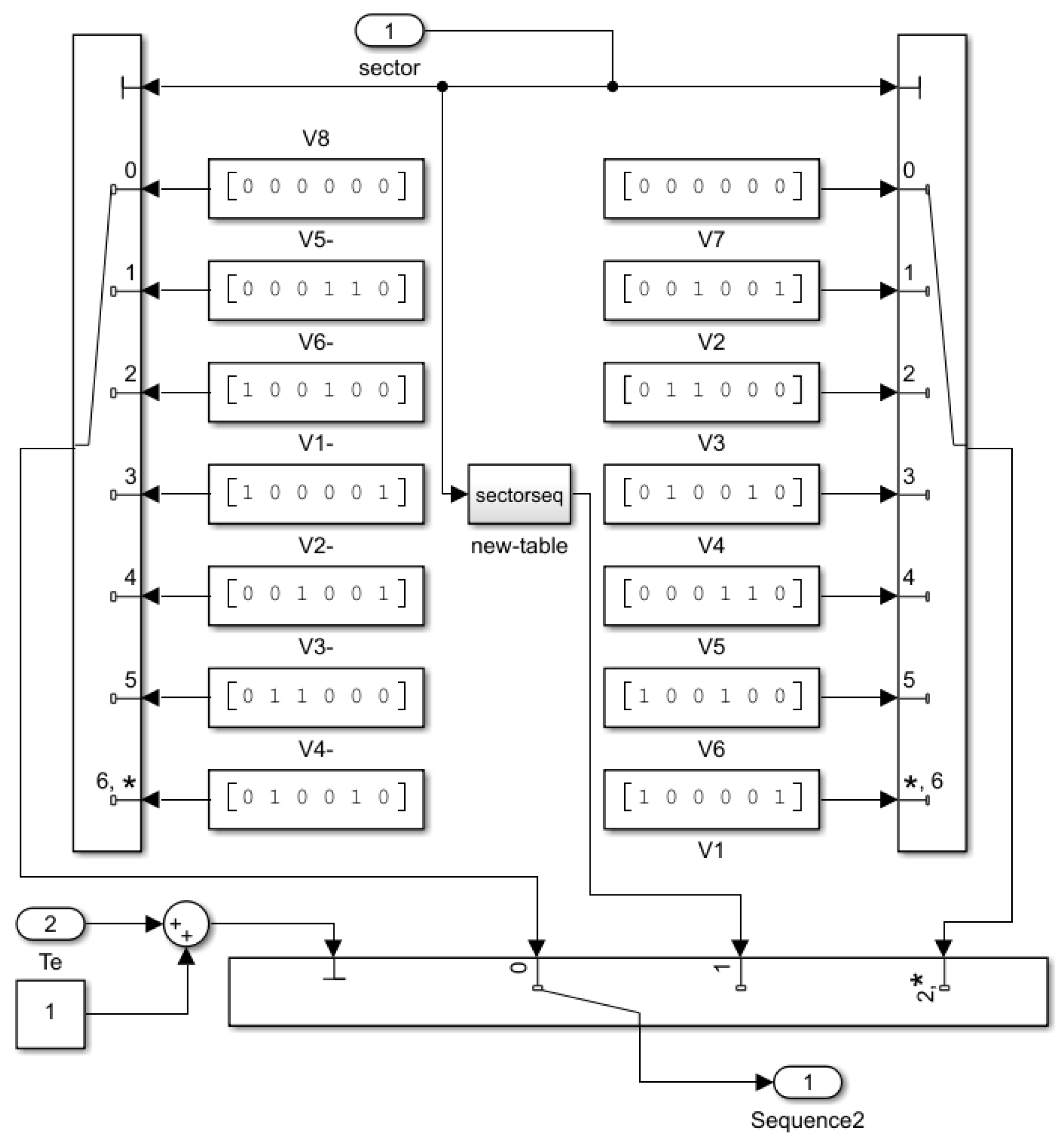
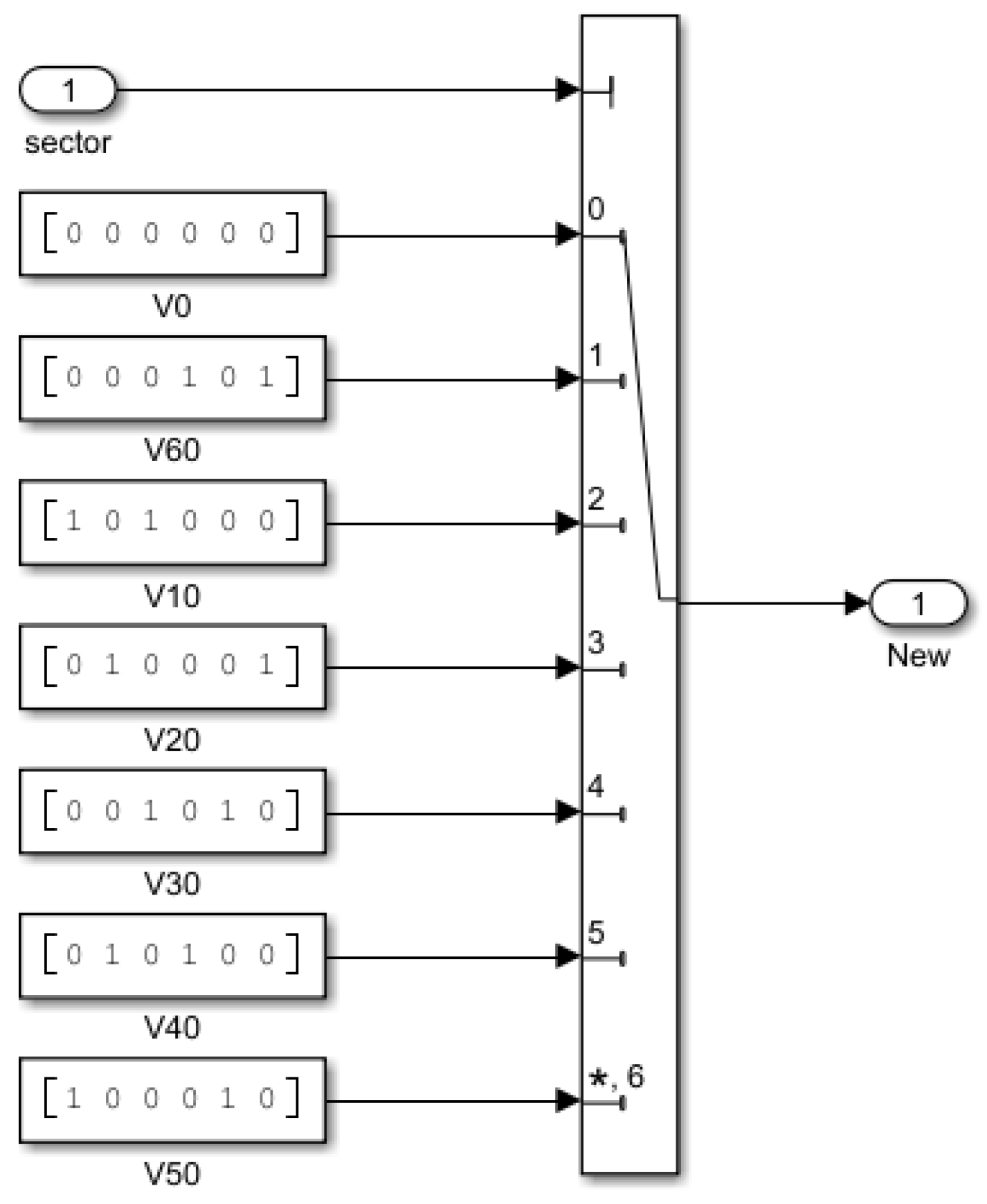
2.2. Optimization of Direct Torque Control Based on New Zero Vector
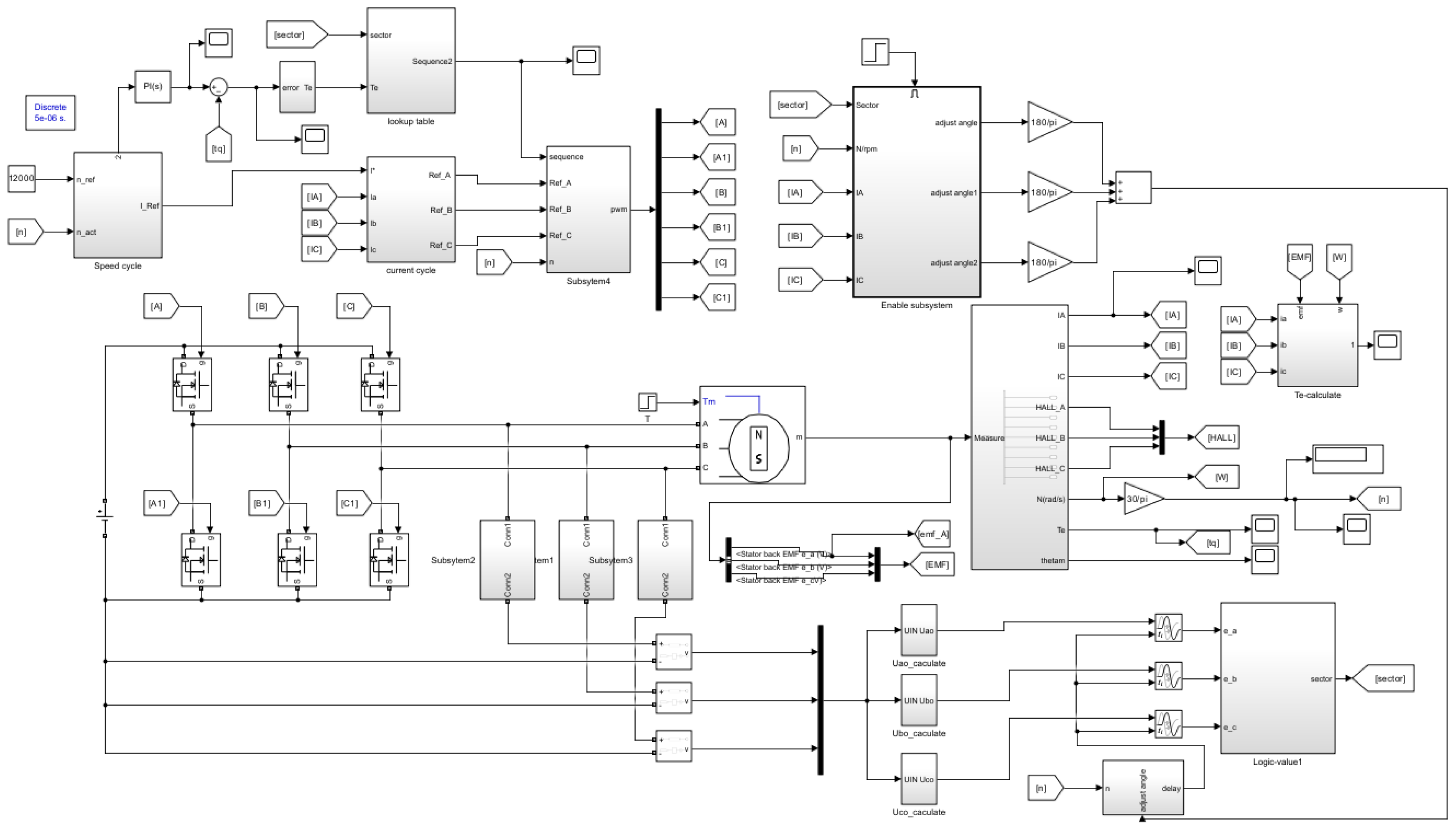
3. Simulation Verification Model Construction
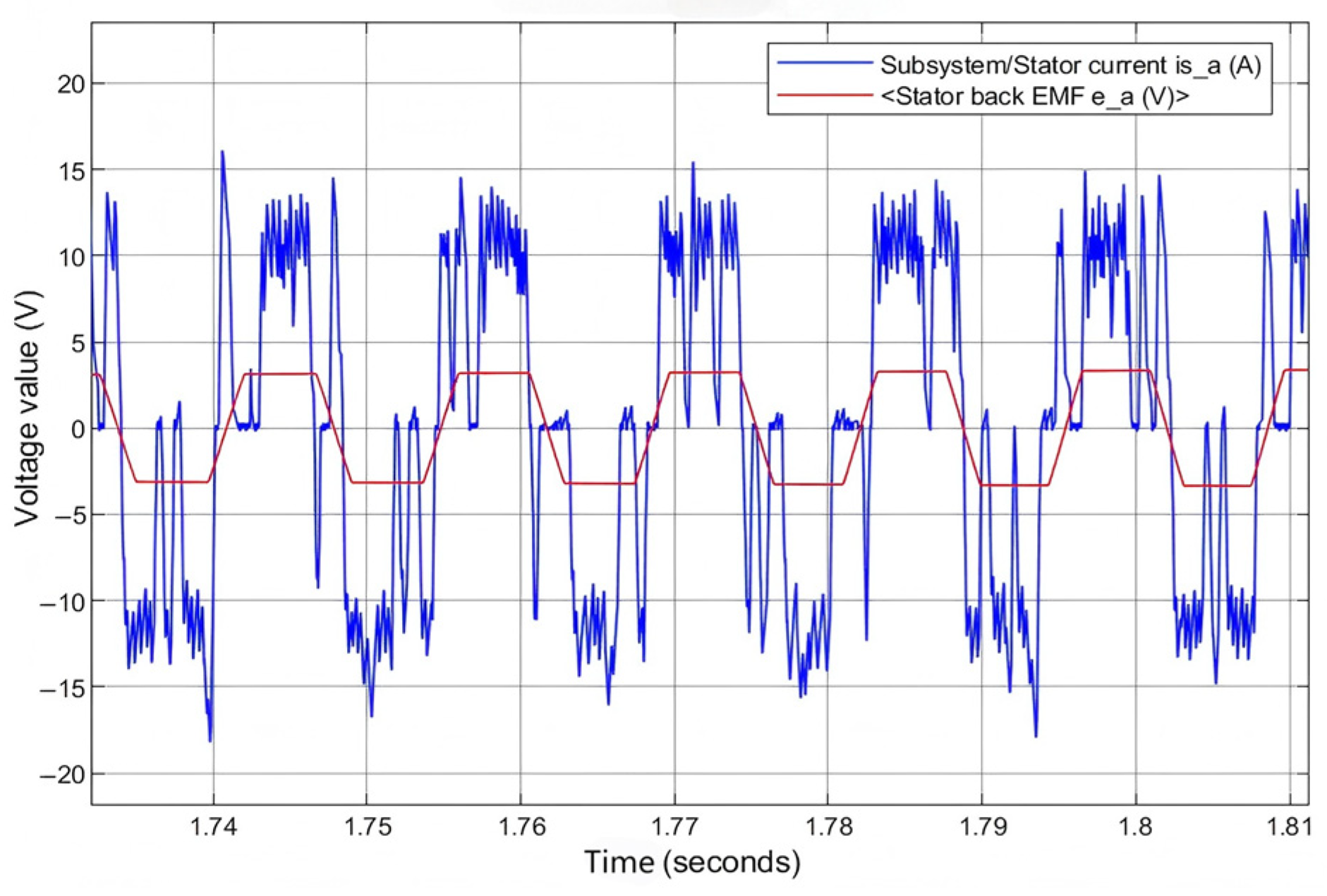
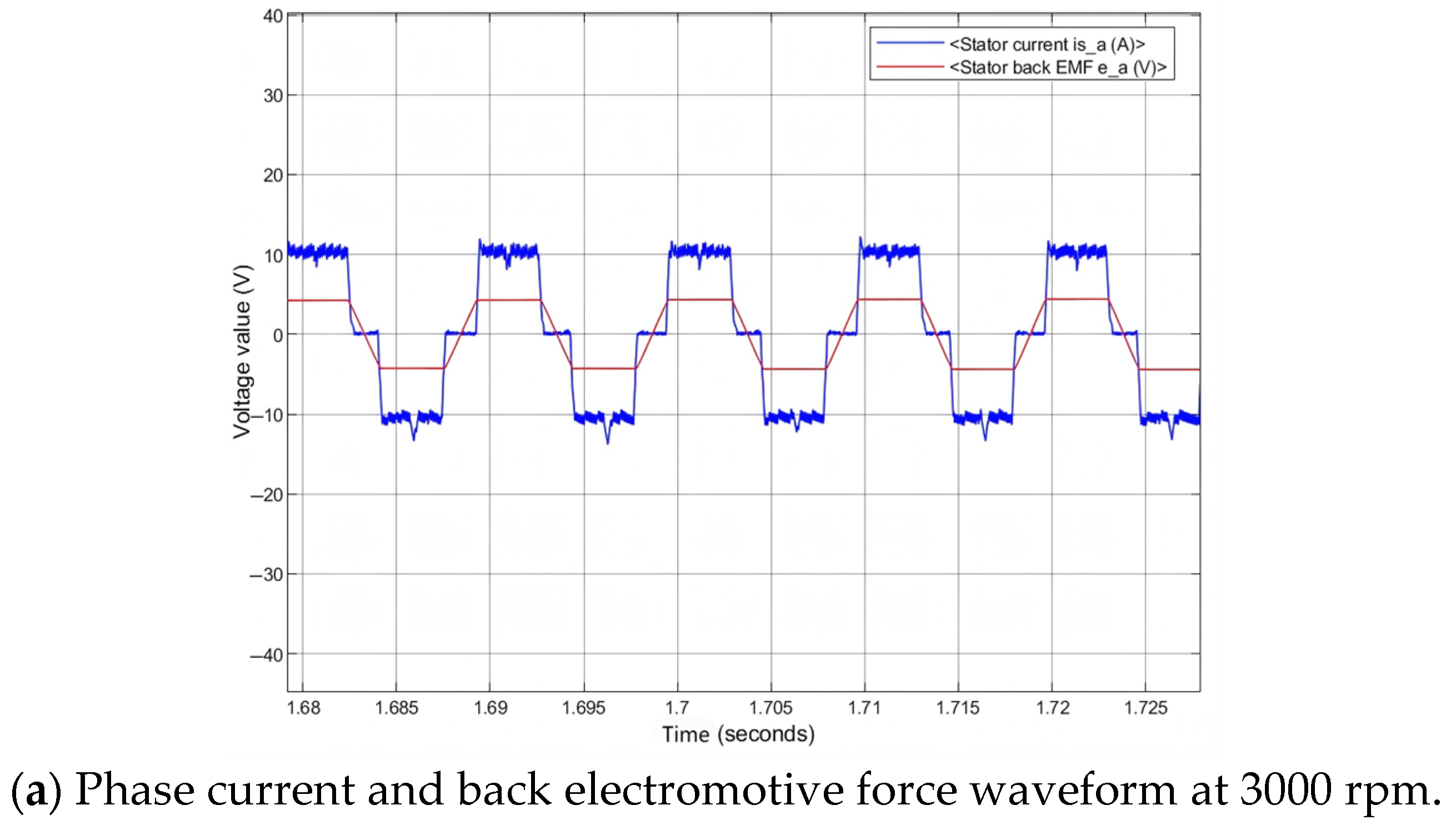
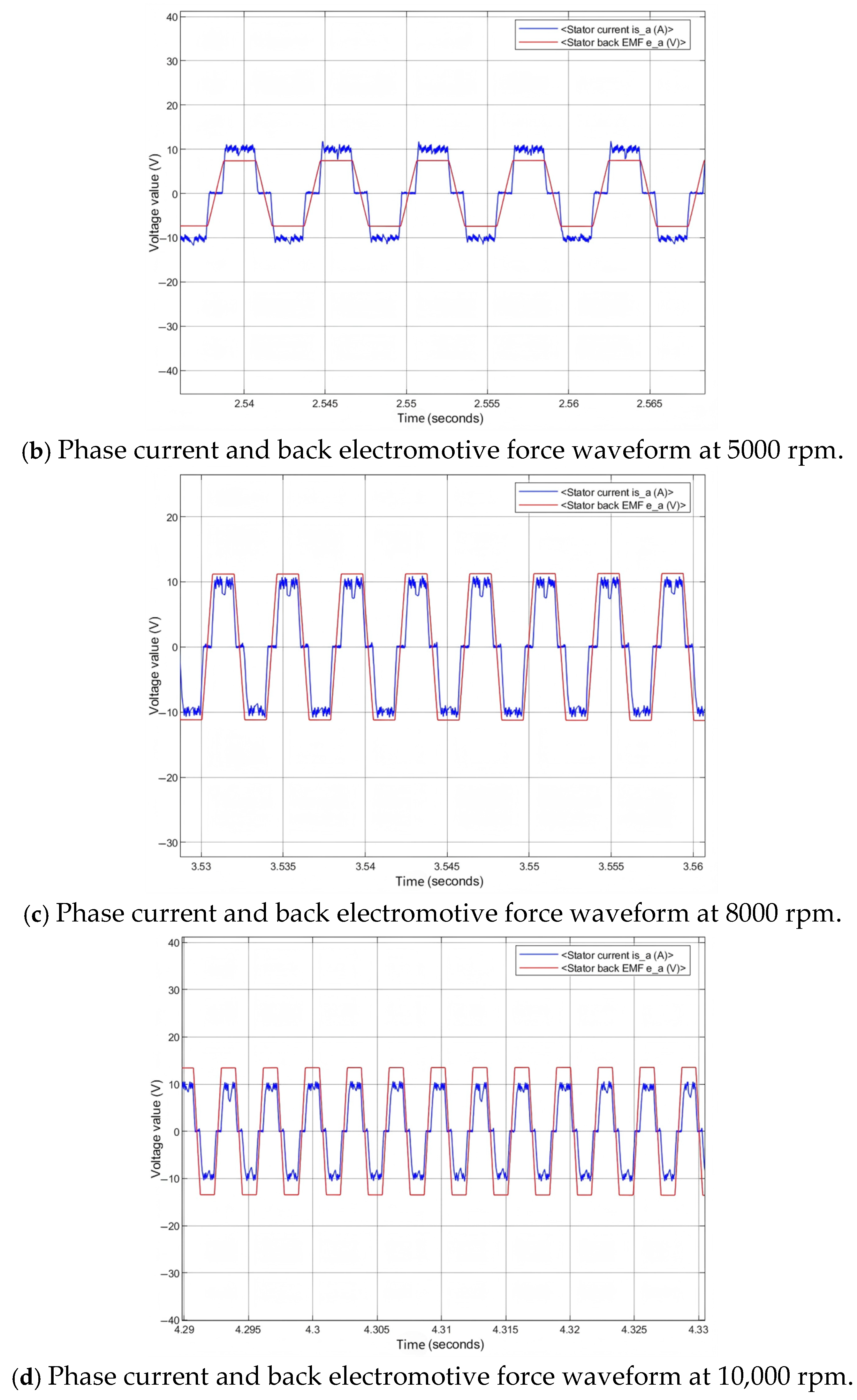
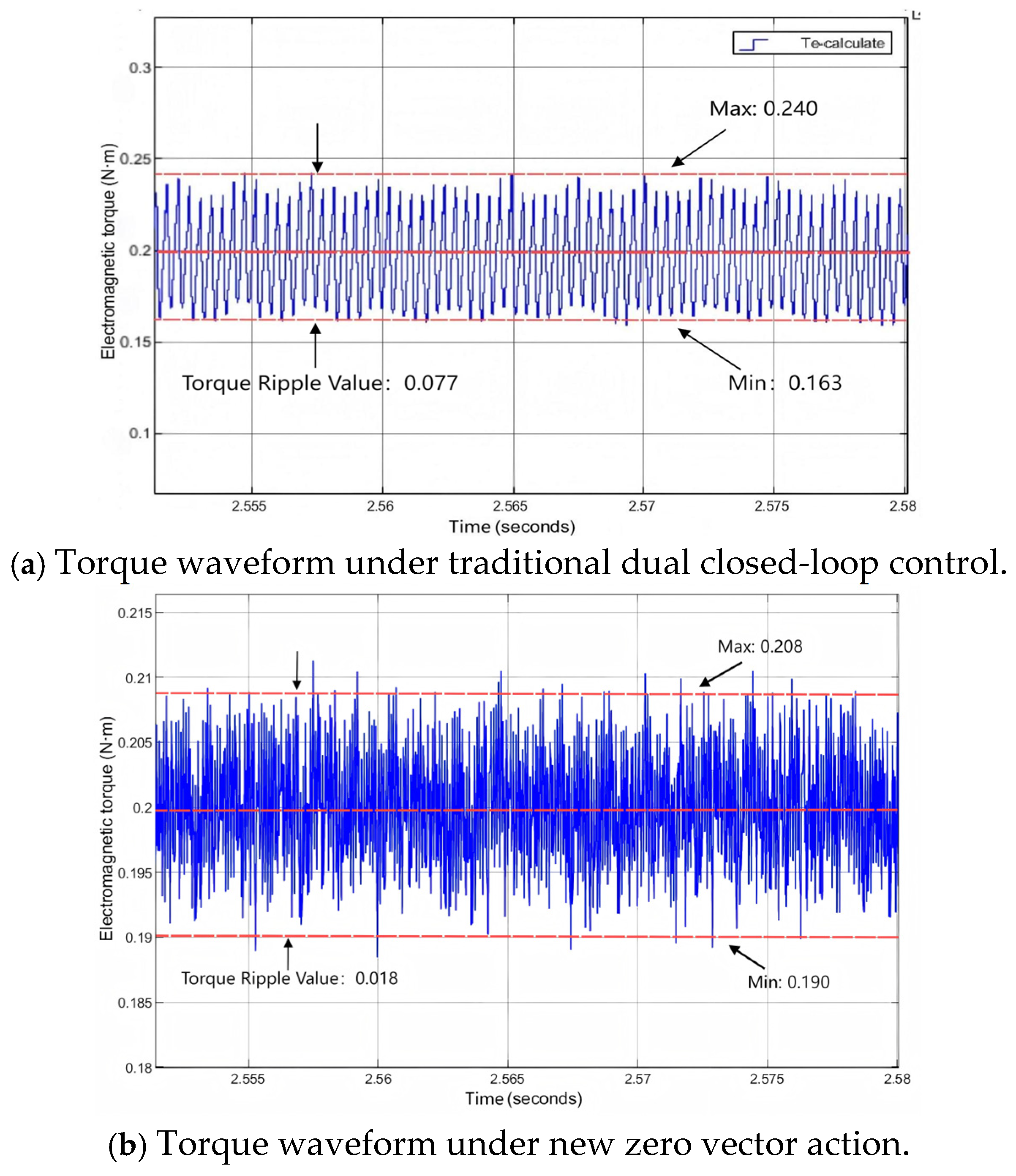
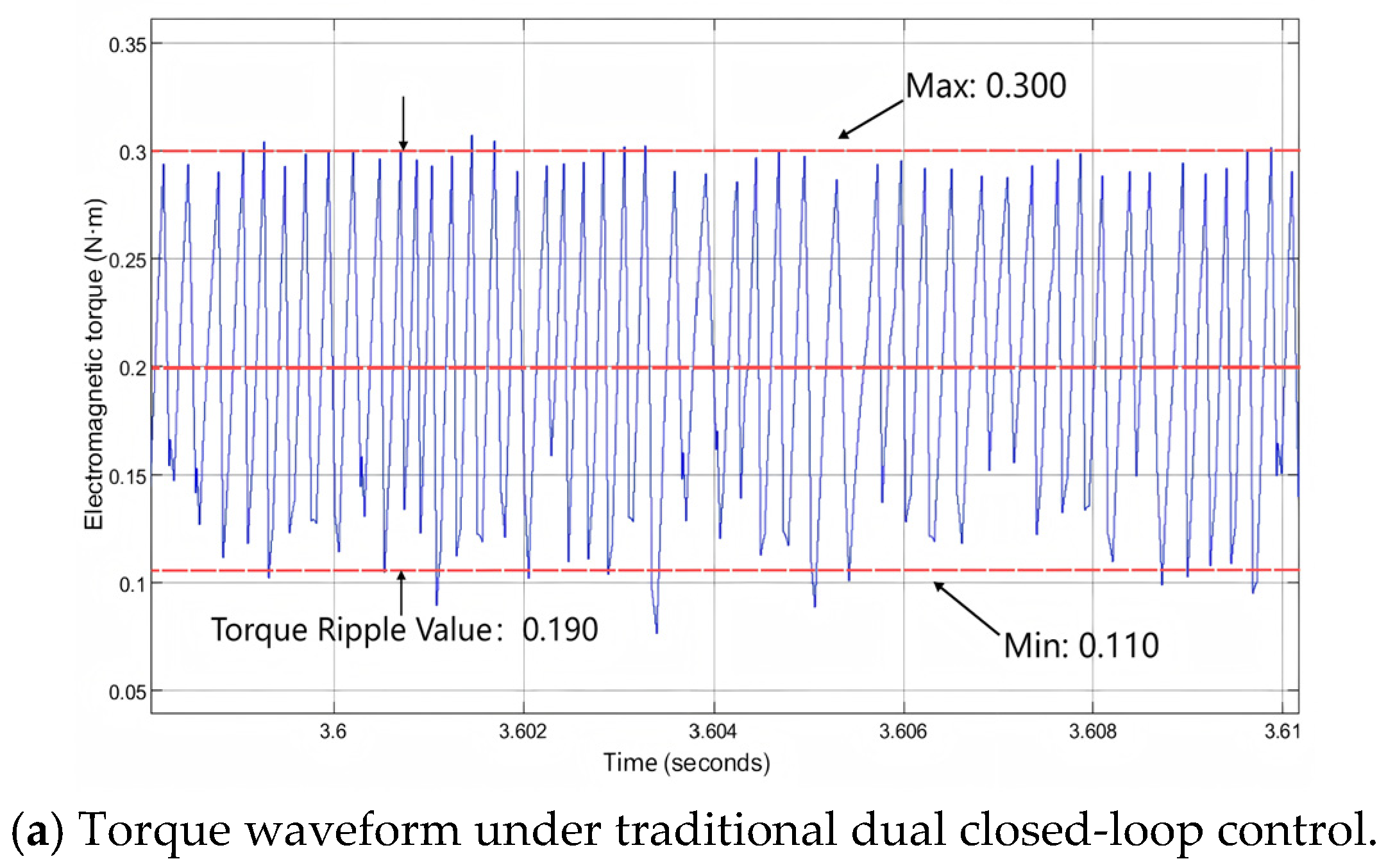
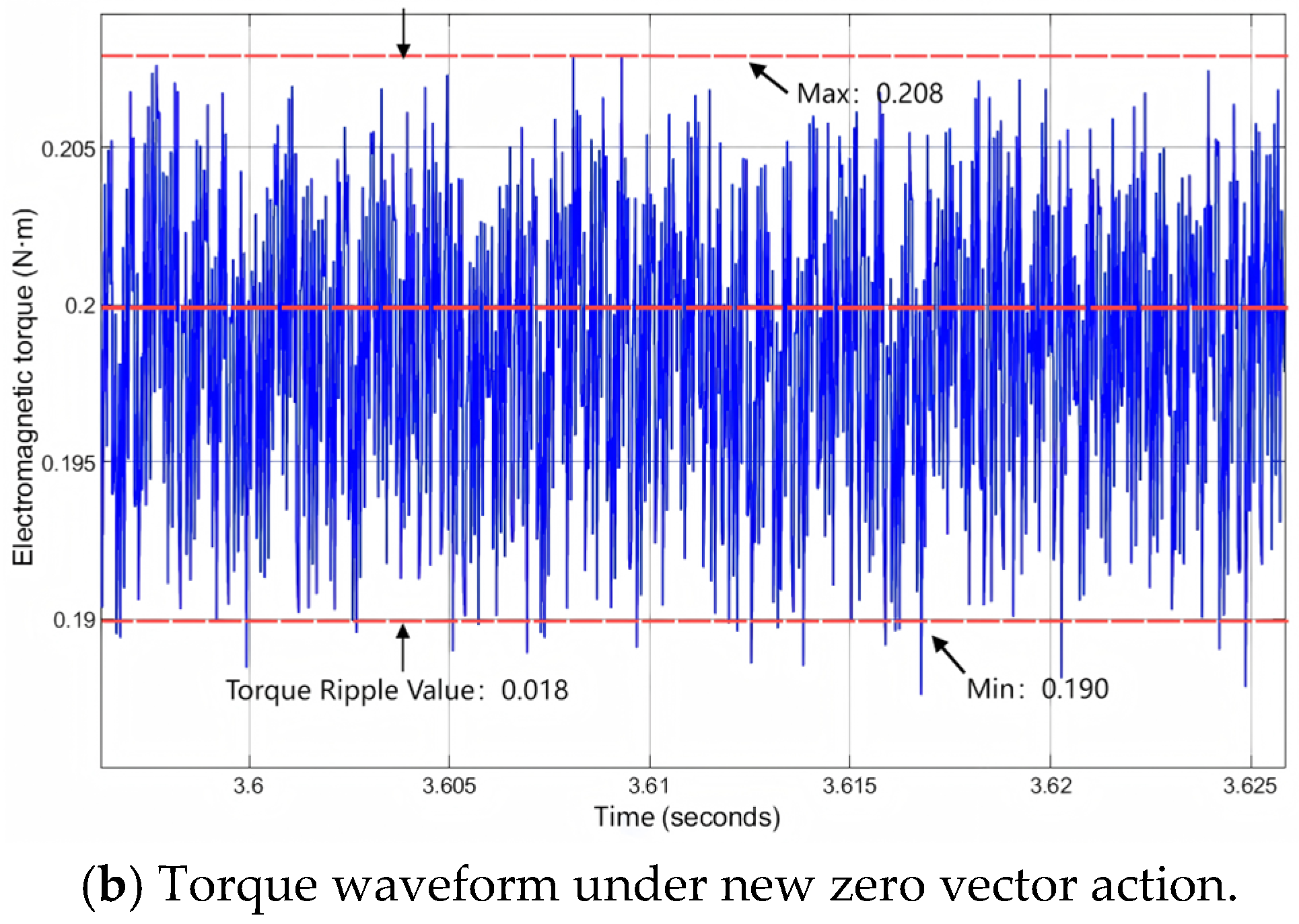
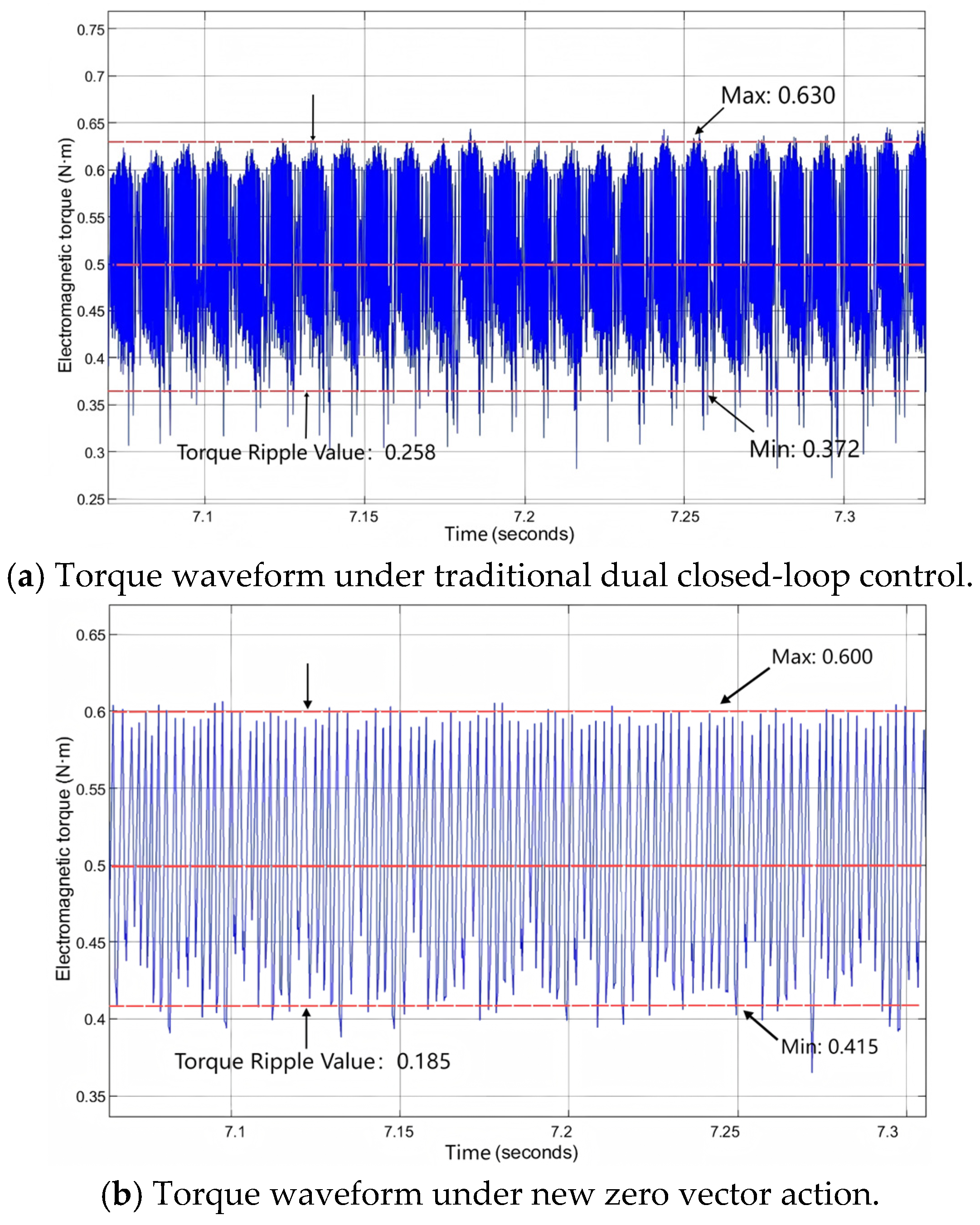
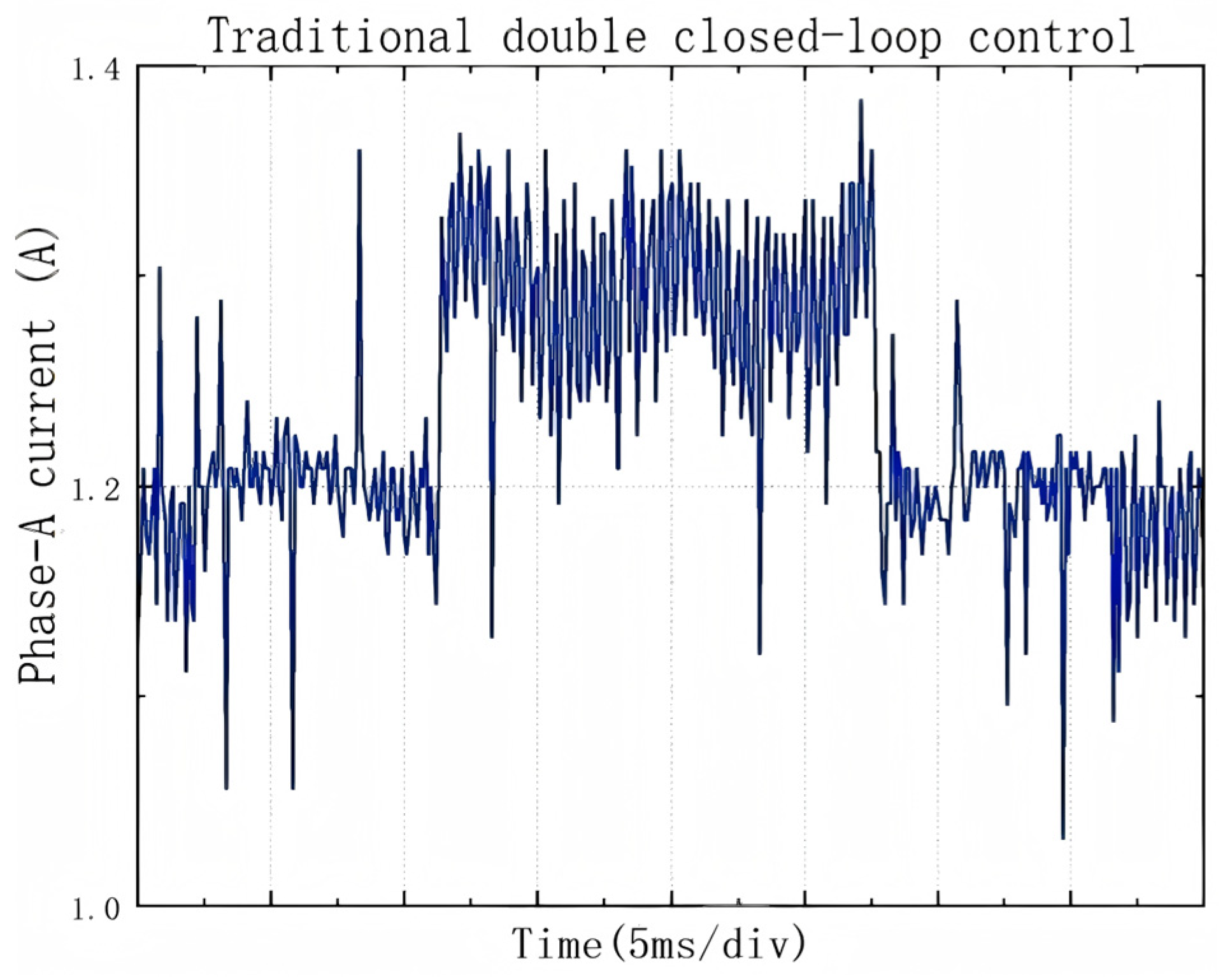
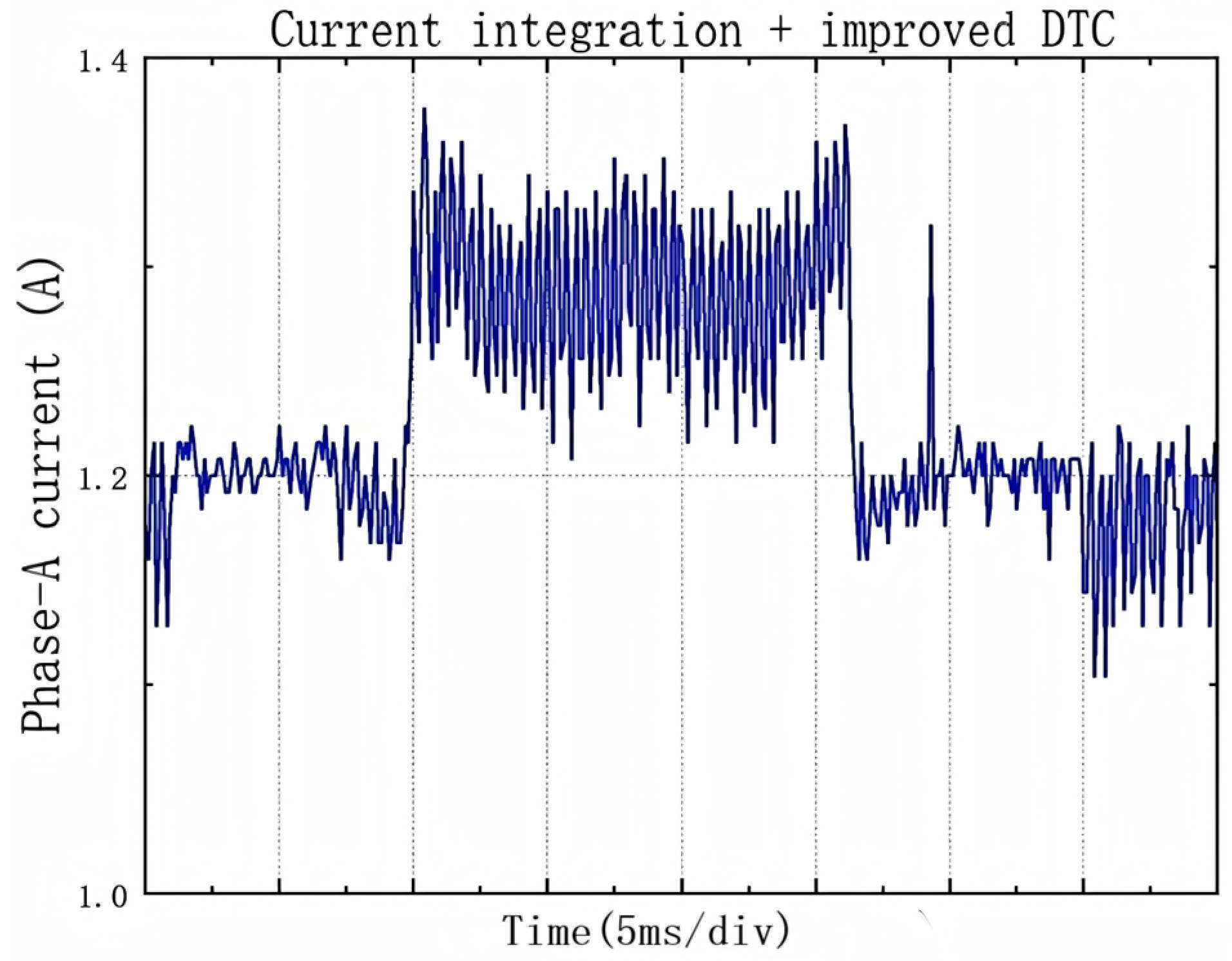
4. Analysis of Simulation Results and Experimental Verification
4.1. Simulation Research
4.2. Experimental Verification
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.; Wu, H.; Jin, H.; Li, H. High-Dynamic and Low-Cost Sensorless Control Method of High-Speed Brushless DC Motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 19, 5576–5584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çetintaş, O.G.; Akgül, K.; Ergene, L.T. Position Sensorless Speed Control of BLDC Motor with Using Back-EMF Method. In Proceedings of the 2023 14th International Conference on Electrical and Electronics Engineering (ELECO), Bursa, Turkiye, 30 November–2 December 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Shuang, B.; Bin, H. Adaptive threshold correction strategy for sensorless high-speed brushless DC drives considering zero-crossing-point deviation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 5246–5257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, G. Sensorless optimal commutation steady speed control method for a nonideal back-EMF BLDC motor drive system including buck converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 6147–6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla-García, E.A.; Cervantes-Culebro, H.; Rodriguez-Angeles, A.; Cruz-Villar, C.A. Selection/control concurrent optimization of BLDC motors for industrial robots. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0289717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akrami, M.; Jamshidpour, E.; Nahid-Mobarakeh, B.; Pierfederici, S.; Frick, V. Sensorless control methods for BLDC motor drives: A review. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2024, 11, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Lin, H.; Zhao, J. Line voltage difference integral method of commutation error adjustment for sensorless brushless DC motor. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), San Antonio, TX, USA, 4–8 March 2018; pp. 843–847. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, X.; Zeng, F.; Tang, J. Fast commutation instant shift correction method for sensorless coreless BLDC motor based on terminal voltage information. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 9460–9472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Wang, X.; Xu, L.; Xia, L.; Huangfu, Y. A New Phase-Delay-Free Commutation Method for BLDC Motors Based on Terminal Voltage. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 4971–4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Liu, G.; Zhang, H.; Feng, R. Auto-Correction Commutation Method Based on Phase Voltage Threshold for Position Sensorless Brushless DC Motor. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2024, 39, 1468–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Li, J.; Cao, Y. Optimal Commutation Error Compensation Strategy for High-Speed Sensorless Brushless DC Motors. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2025, 13, 3411–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, X.; Peng, C.; Zhou, Y. High performance nonsalient sensorless BLDC motor control strategy from standstill to high speed. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 4365–4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Hong, B.; Gong, L. A commutation error compensation strategy for high speed brushless DC drive based on adaline filter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 3728–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Sun, J.; Chen, S. Commutation delay error compensation method for high-speed magnetically levitated BLDC motor based on terminal voltage symmetry. Micro Mot. 2017, 50, 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Deng, L.; Jin, H.; Li, H.; Zheng, S.; Zhou, X. Phase Synchronization-Based Commutation Error Correction Method for Position Sensorless Brushless DC Motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024, 20, 3964–3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Wang, X.; Tan, B.; Xu, L.; Yuan, C.; Huangfu, Y. Fast Commutation Error Compensation for BLDC Motors Based on Virtual Neutral Voltage. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 1259–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.-C.; Fan, C.-J.; Chen, G.-H. Current integral method for fine commutation tuning of sensorless brushless DC motor. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 9249–9266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Deng, L.; Li, H.; Zheng, S.; Jin, H.; Chen, B. Commutation Point Optimization Method for Sensorless BLdc Motor Control Using Vector Phase Difference of Back EMF and Current. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2024, 29, 423–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Song, X.; Zhou, X.; Huang, Z.; Zheng, S. A Sensorless Commutation Error Correction Method for High-Speed BLDC Motors Based on Phase Current Integration. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 16, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Ramesh, R.R.; Tahim, E.S.; Zhang, J.; Ebrahimi, S.; Jatskevich, J. Torque Ripple Reduction in Brushless DC Motors with 180° Commutation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2025, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ouanjli, N.; Derouich, A.; El Ghzizal, A.; Motahhir, S.; Chebabhi, A.; El Mourabit, Y.; Taoussi, M. Modern improvement techniques of direct torque control for induction motor drives—A review. Prot. Control Mod. Power Syst. 2019, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Liu, J.; Jin, X.; Li, M.; Zhang, Q. Direct Torque Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor for Reducing Torque Ripple. In Proceedings of the IECON 2023—49th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Singapore, 16–19 October 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abosh, A.H.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Ren, Y. Reduction of Torque and Flux Ripples in Space Vector Modulation-Based Direct Torque Control of Asymmetric Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 2976–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.S.; Satheesh, G.; Peddakotla, S. Design of optimal PI controller for torque ripple minimization of SVPWM-DTC of BLDC motor. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. 2023, 14, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, A.; Gu, C.; Wang, X.; Buticchi, G.; Bozhko, S.; Gerada, C. Torque-Performance Improvement for Direct Torque-Controlled PMSM Drives Based on Duty-Ratio Regulation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaee, A.; Zarchi, H.A.; Markadeh, G.A.; Hesar, H.M. MTPA strategy for direct torque control of brushless DC motor drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 68, 6692–6700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Kim, J.-W.; Park, B.-G.; Lee, D.-H. A Novel Predictive Direct Torque Control Using an Optimized PWM Approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2021, 57, 2537–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


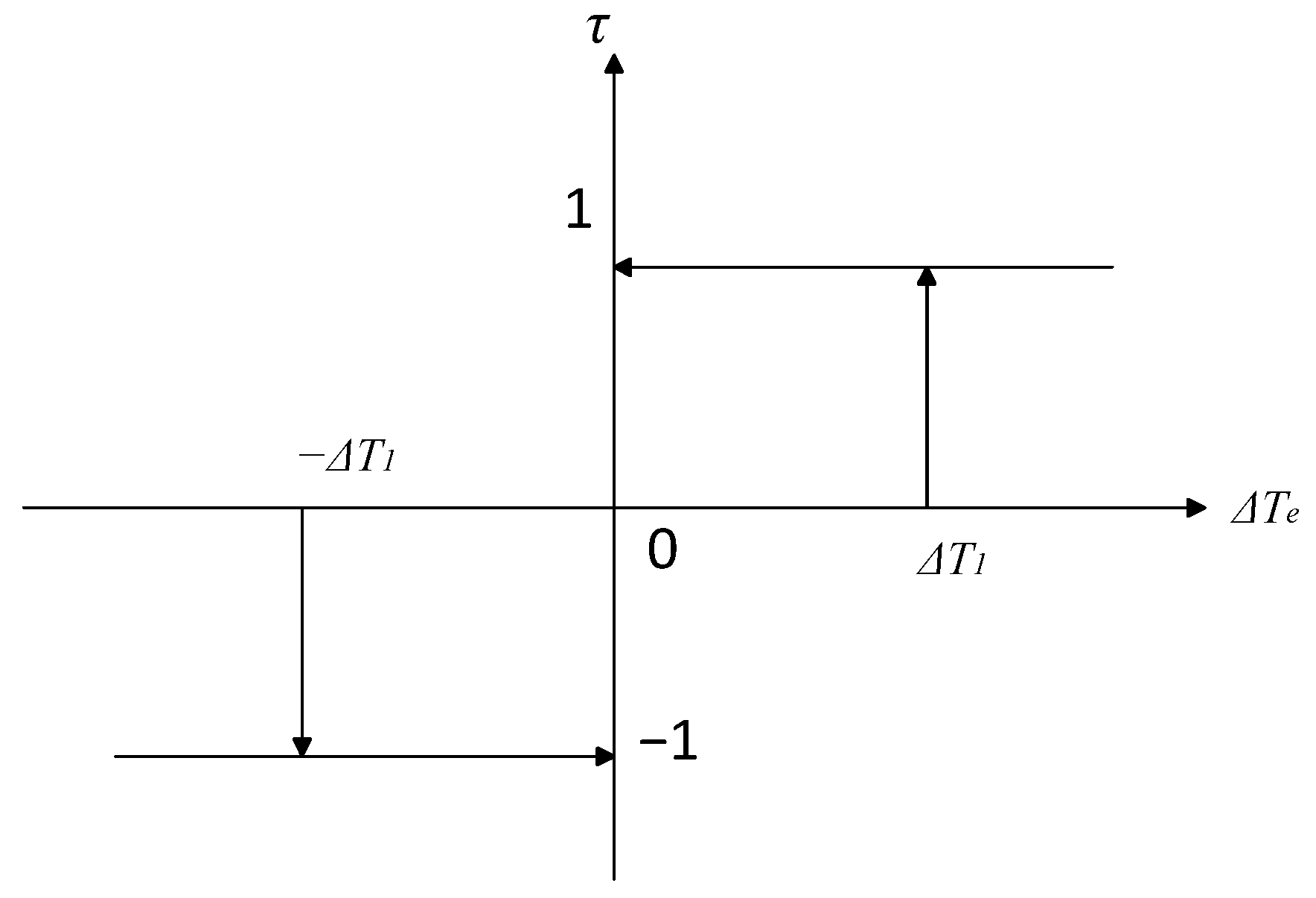
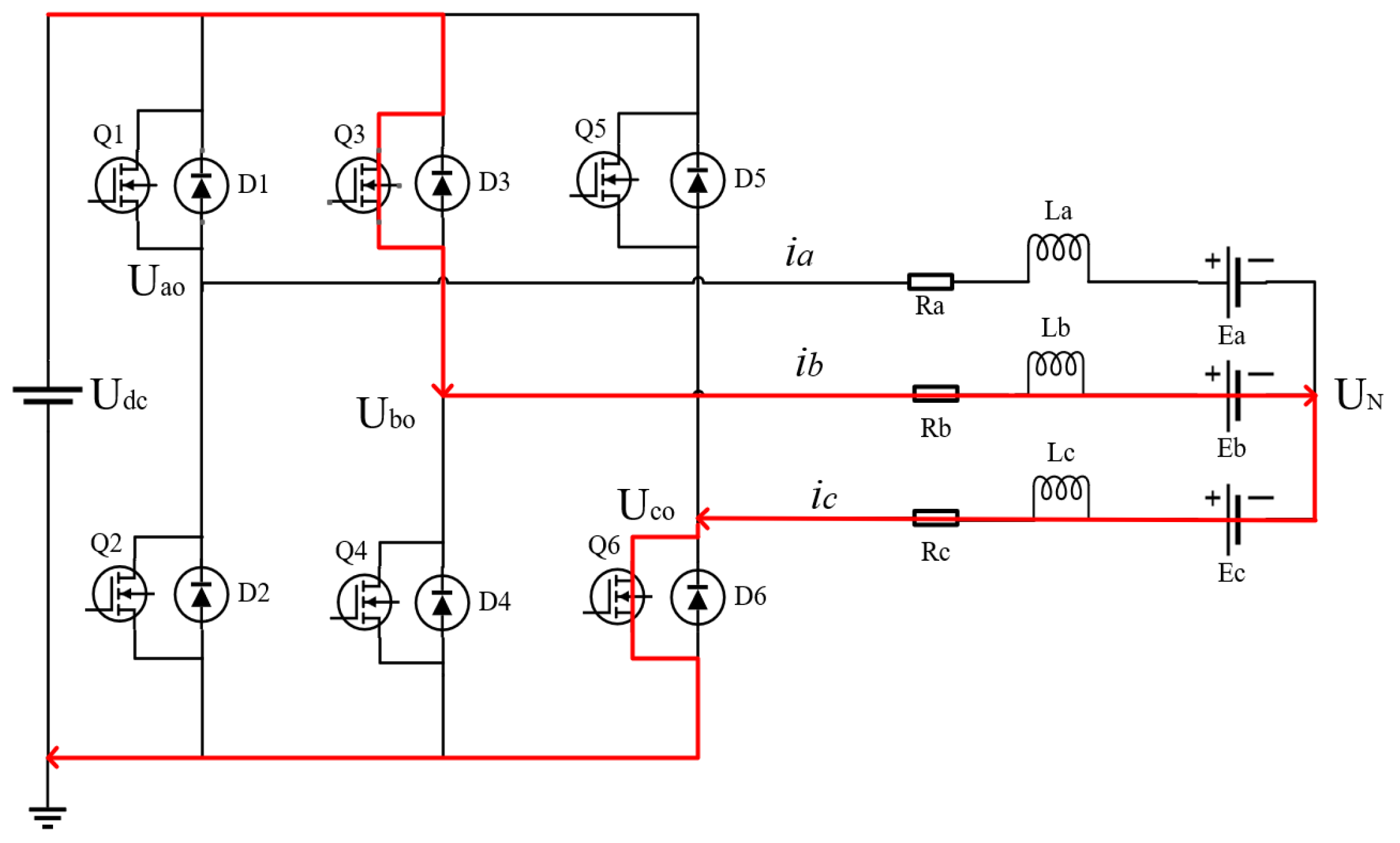


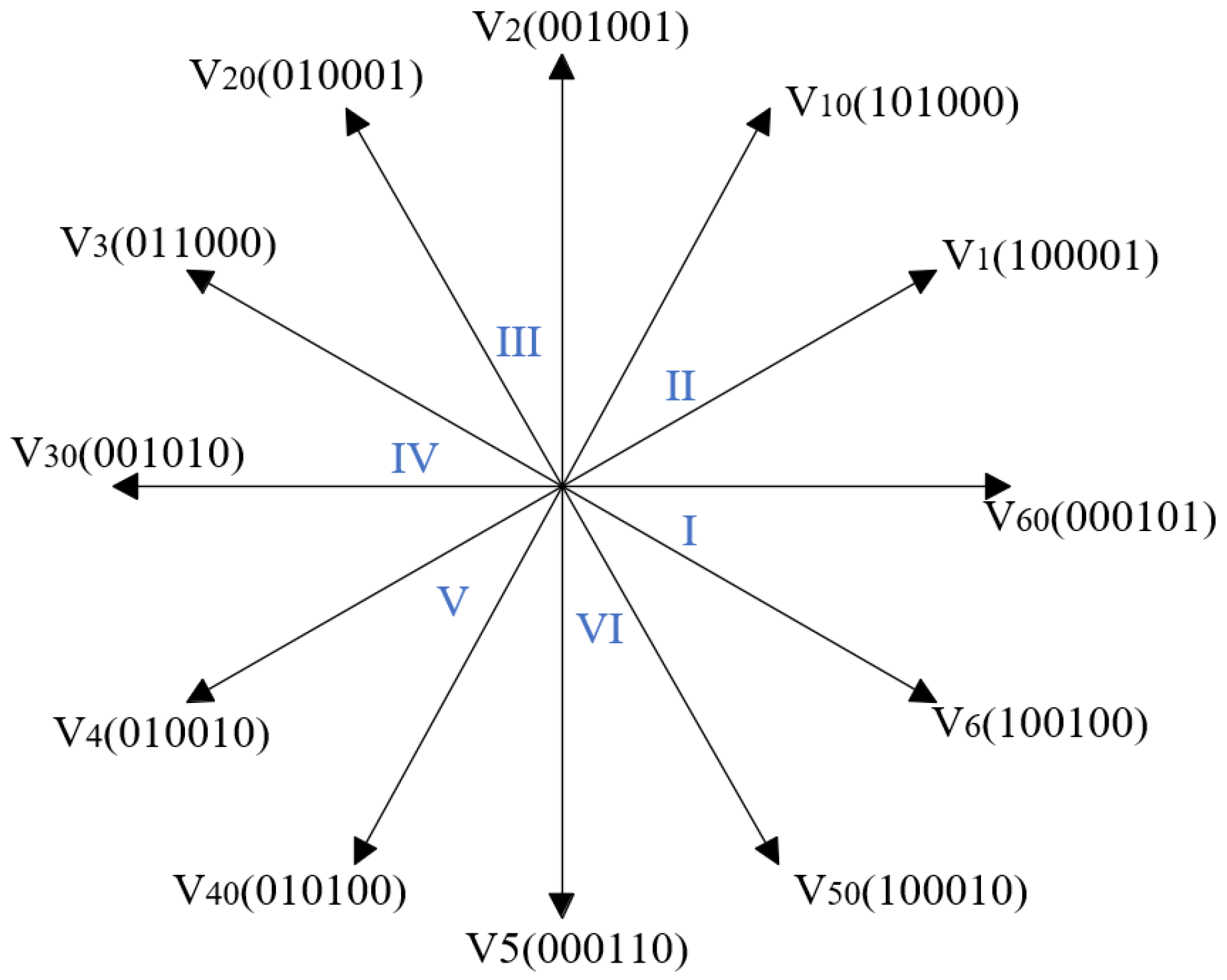




| Sector | τ | Voltage Vector (Counterclockwise) | Voltage Vector (Clockwise) |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | 1 | ||
| 0 | |||
| −1 | |||
| II | 1 | ||
| 0 | |||
| −1 | |||
| III | 1 | ||
| 0 | |||
| −1 | |||
| IV | 1 | ||
| 0 | |||
| −1 | |||
| V | 1 | ||
| 0 | |||
| −1 | |||
| VI | 1 | ||
| 0 | |||
| −1 |
| Sector | τ | Voltage Vector (Counterclockwise) | Voltage Vector (Clockwise) |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | 1 | ||
| 0 | |||
| −1 | |||
| II | 1 | ||
| 0 | |||
| −1 | |||
| III | 1 | ||
| 0 | |||
| −1 | |||
| IV | 1 | ||
| 0 | |||
| −1 | |||
| V | 1 | ||
| 0 | |||
| −1 | |||
| VI | 1 | ||
| 0 | |||
| −1 |
| Parameters | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Stator phase resistance | ||
| Stator phase inductance | ||
| Moment of inertia | ||
| Back electromotive force constant | ||
| Rated torque | ||
| Number of pole pairs | ||
| Rated speed | ||
| DC voltage |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sa, X.; Wu, H.; Zhao, G.; Zhao, Z. Torque Ripple Reduction in BLDC Motors Using Phase Current Integration and Enhanced Zero Vector DTC. Electronics 2025, 14, 2999. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14152999
Sa X, Wu H, Zhao G, Zhao Z. Torque Ripple Reduction in BLDC Motors Using Phase Current Integration and Enhanced Zero Vector DTC. Electronics. 2025; 14(15):2999. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14152999
Chicago/Turabian StyleSa, Xingwei, Han Wu, Guoqing Zhao, and Zhenjun Zhao. 2025. "Torque Ripple Reduction in BLDC Motors Using Phase Current Integration and Enhanced Zero Vector DTC" Electronics 14, no. 15: 2999. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14152999
APA StyleSa, X., Wu, H., Zhao, G., & Zhao, Z. (2025). Torque Ripple Reduction in BLDC Motors Using Phase Current Integration and Enhanced Zero Vector DTC. Electronics, 14(15), 2999. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14152999





